CMS II: Ortho - Hand and Wrist
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
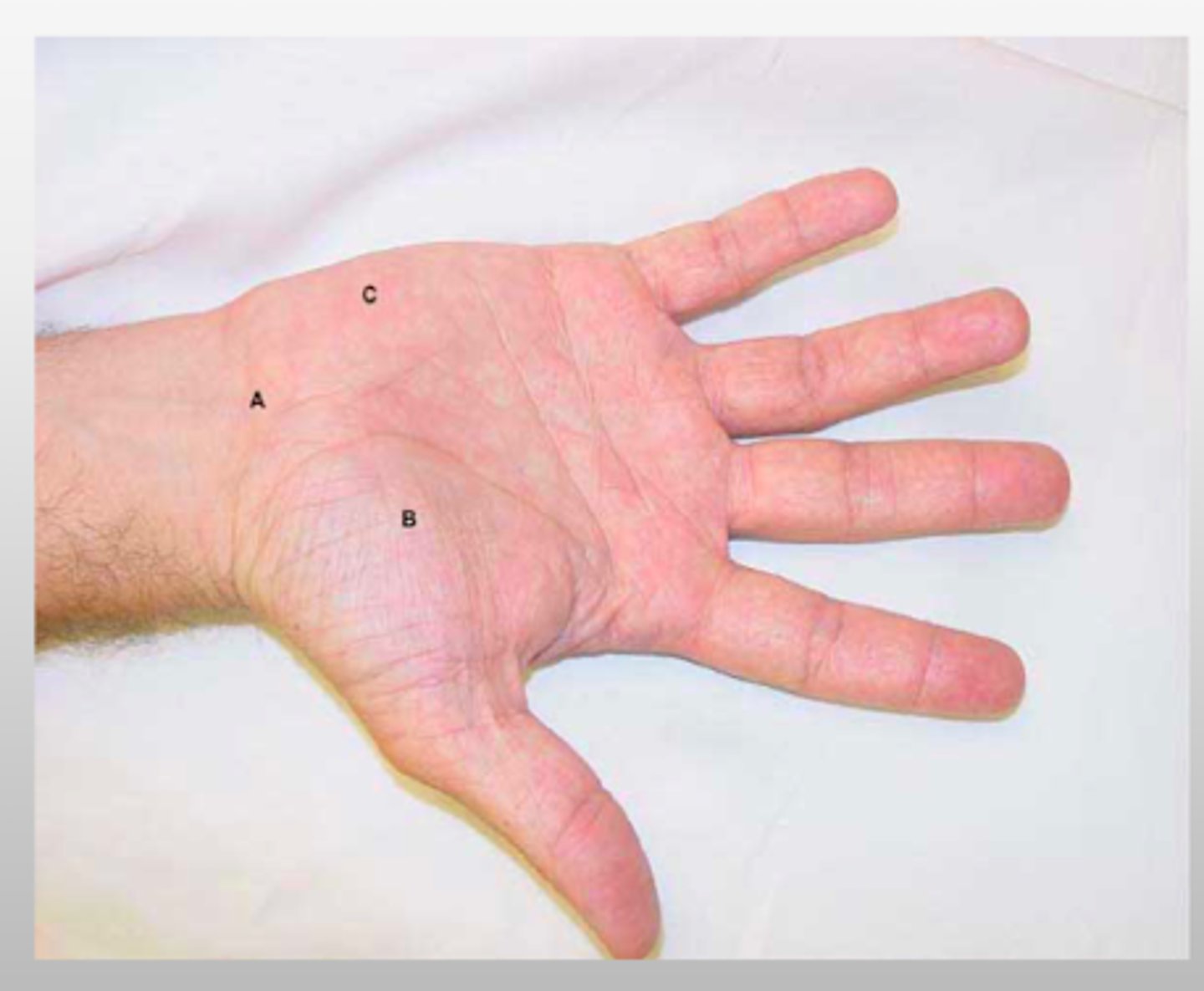
REVIEW: Hand Surface anatomy
A → distal wrist crease
B → thenar eminence
C → hypothenar eminence
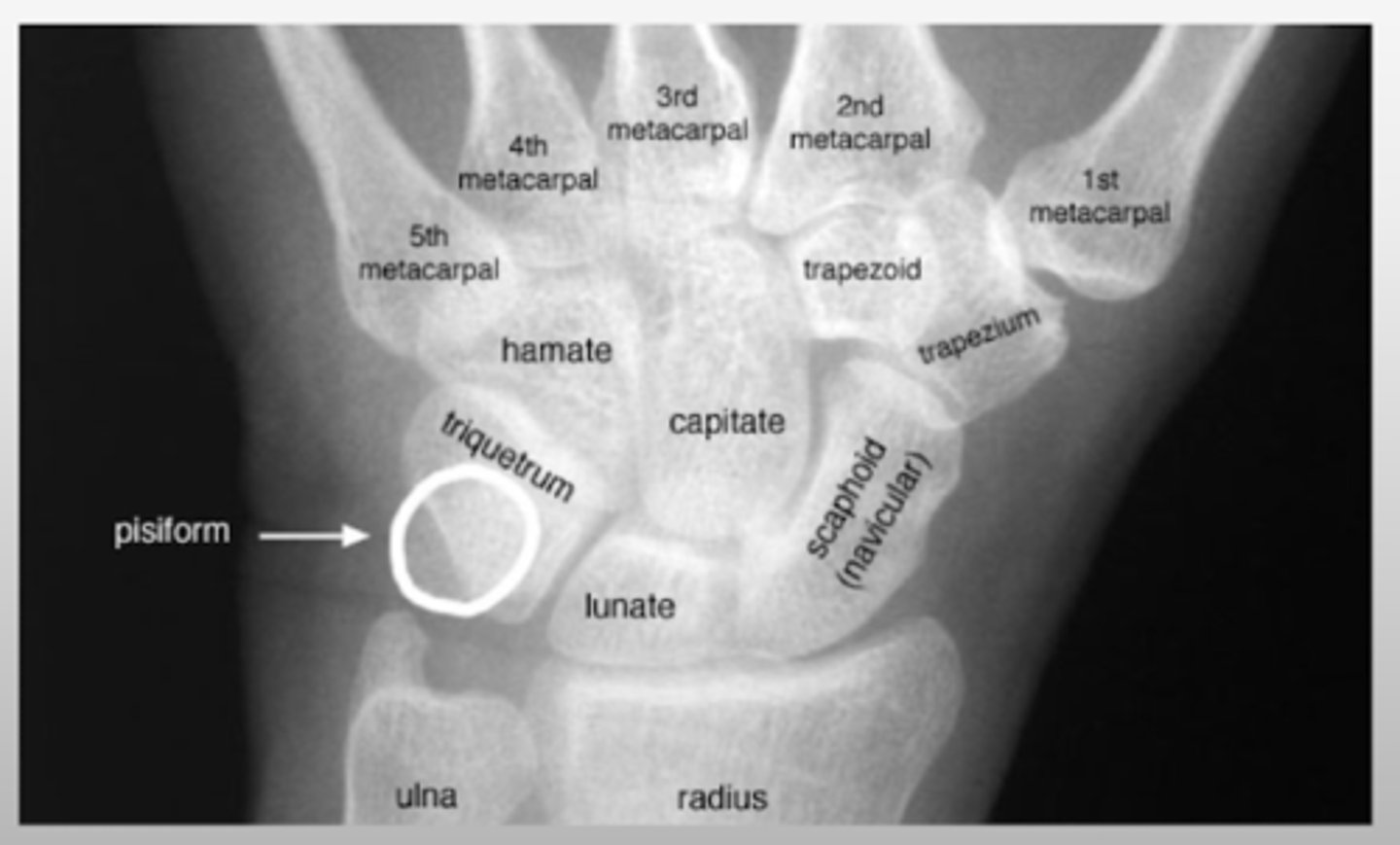
What are the EIGHT carpal bones?
So Long To Pinky Here Comes The Thumb
Scaphoid
Lunate
Triquetral
Pisiform
Hamate
Capitate
Trapezoid
Trapezium
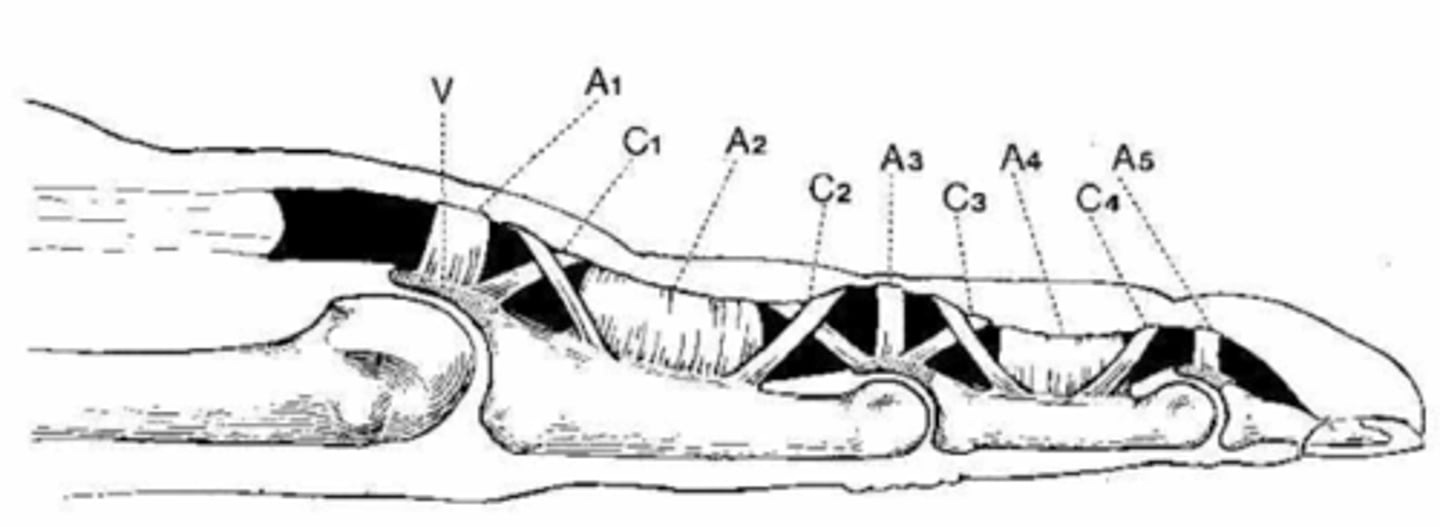
T/F. Flexor tendons travel through a series of tunnels and pulleys as they travel down the finger.
TRUE - prevent bowstringing and keep the tendon opposed to the bone
What are the THREE types of flexor tendon pulley systems?
Annular
Cruciate
Oblique
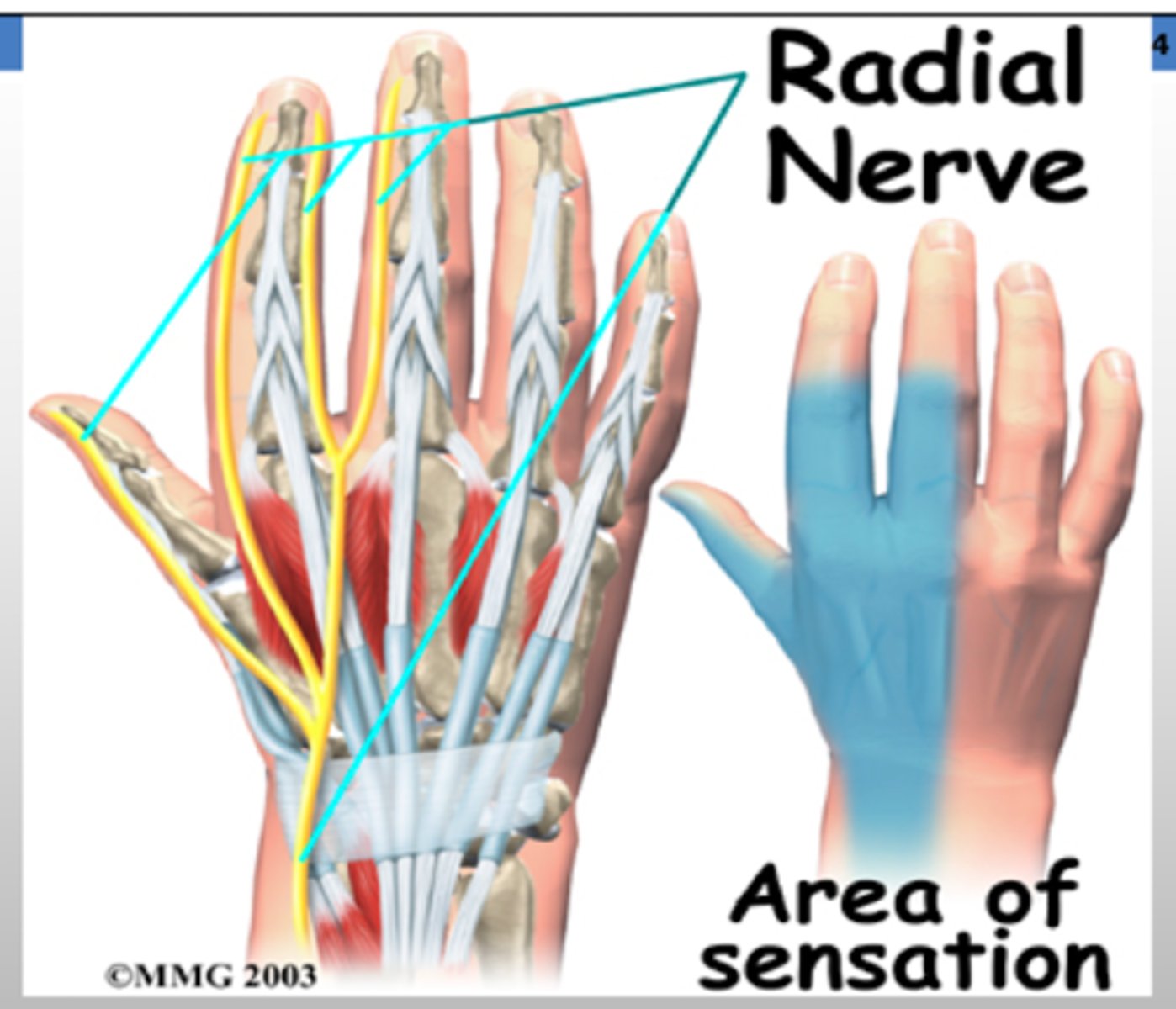
REVIEW: Radial nerve dermatomal distribution.
DORSAL HAND - 1st-3rd digit
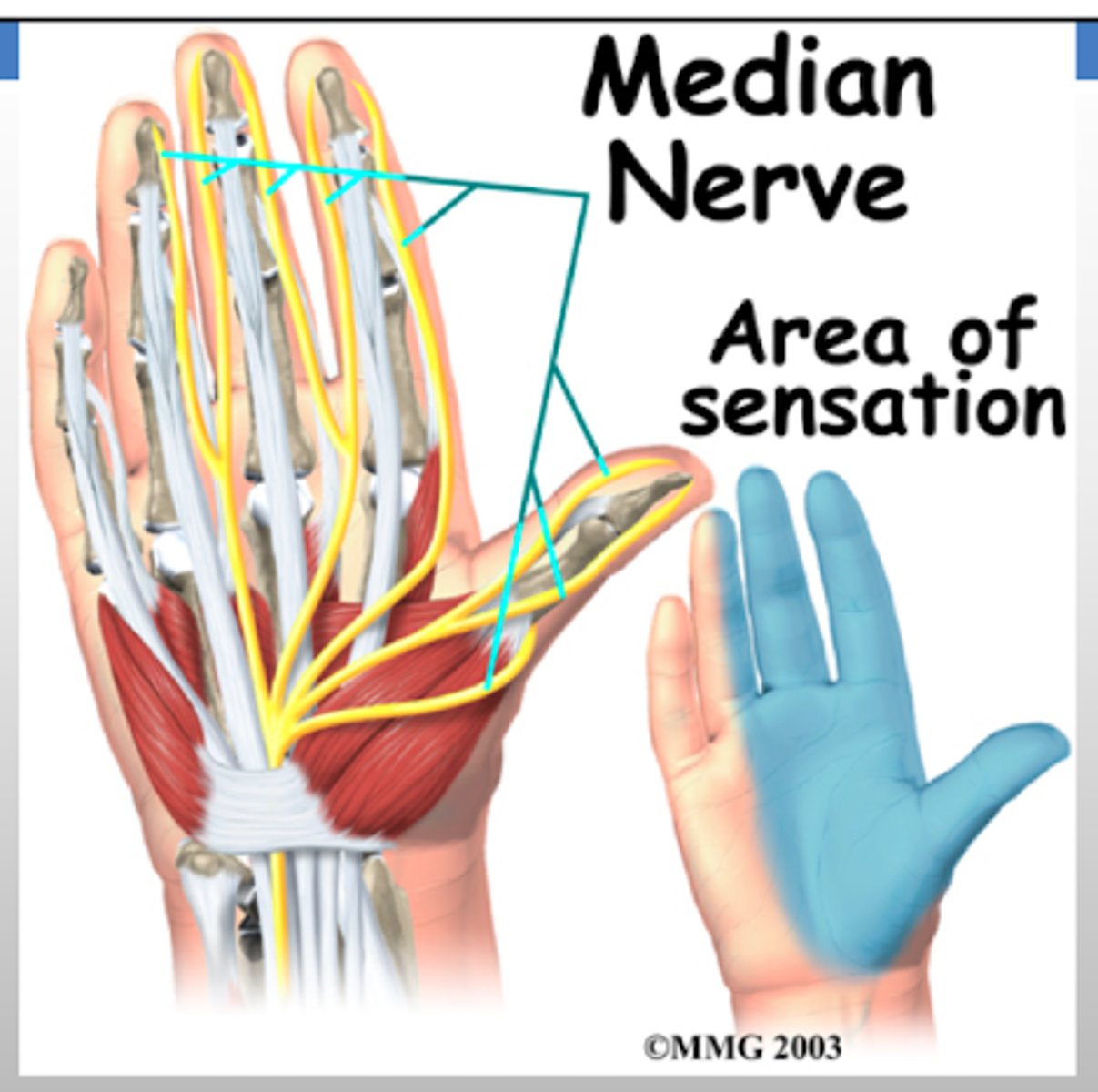
REVIEW: Median nerve dermatomal distribution.
PALMAR HAND - 1st -3rd digit PLUS 1/2 of the 4th digit
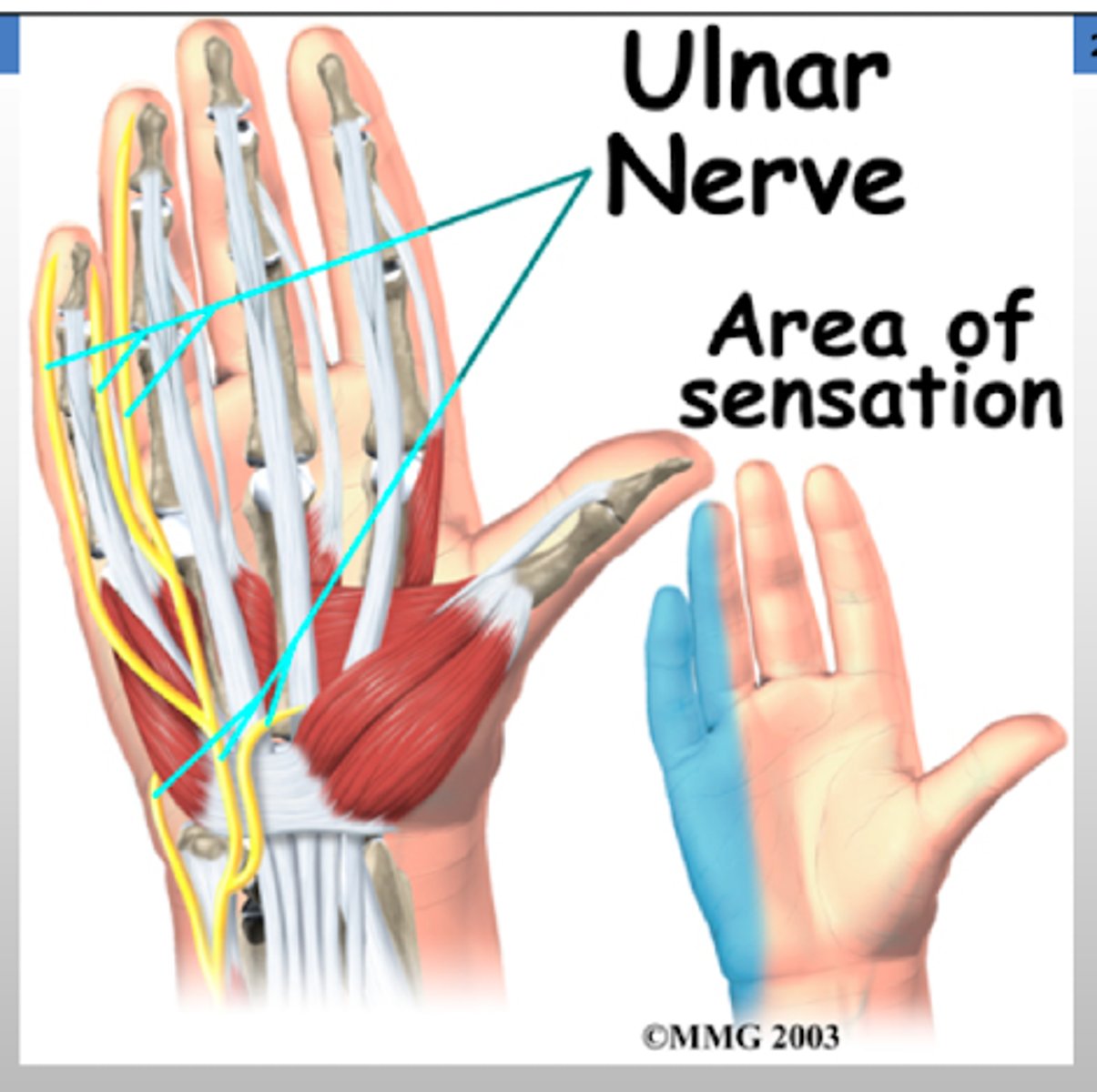
REVIEW: Ulnar nerve dermatomal distribution.
PALMAR HAND - 1/2 of the 4th + 5th digit
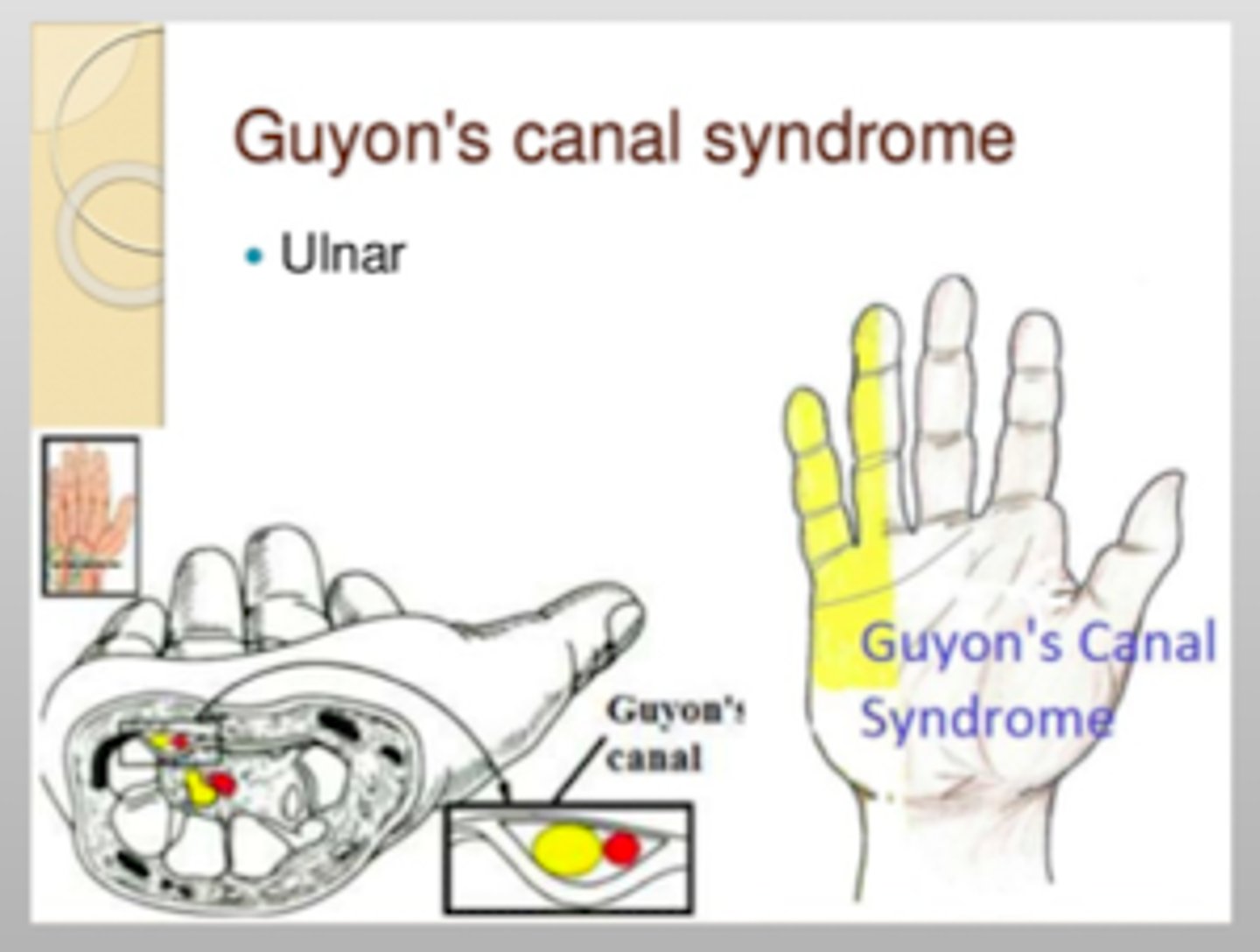
What is the Guyon Tunnel? What are its FOUR components?
anatomical fibro-osseous canal located on the medial side of the hand
Includes:
- Ulnar artery
- Ulnar nerve
- Hamate
- Pisiform

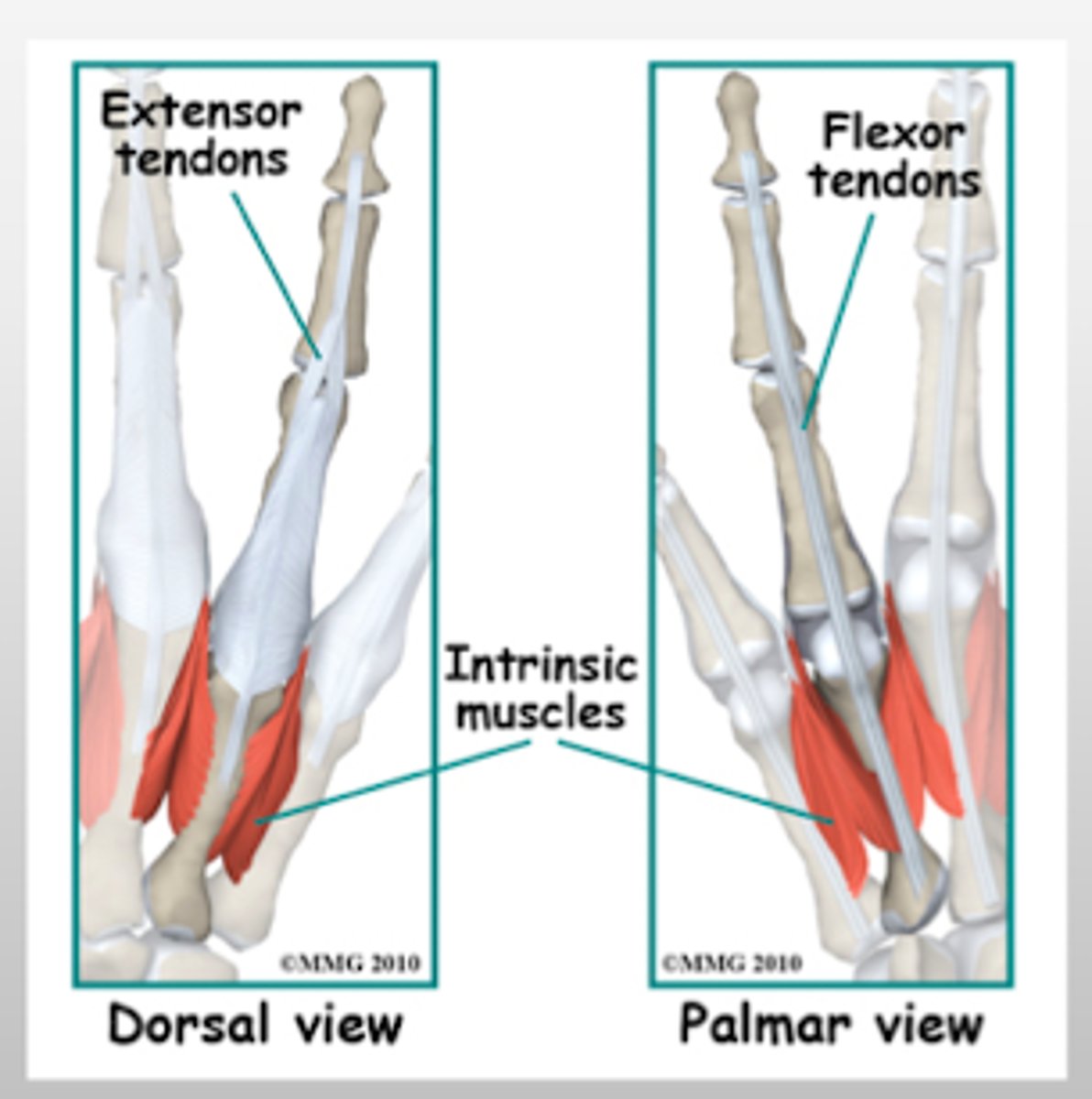
_____ muscles are on the DORSAL surface, while _____ muscles are on the PALMAR surface of the hand.
flexor; extensor
Injury associated with the EXTENSOR tendon will result in what type of contracture?
flexed - unable to extend!
What TWO extensor muscle tendons are involved in deQuervain's tenosynovitis?
caused by inflammation of the sheath surrounding:
Abductor pollicis longus
Extensor pollicis brevis
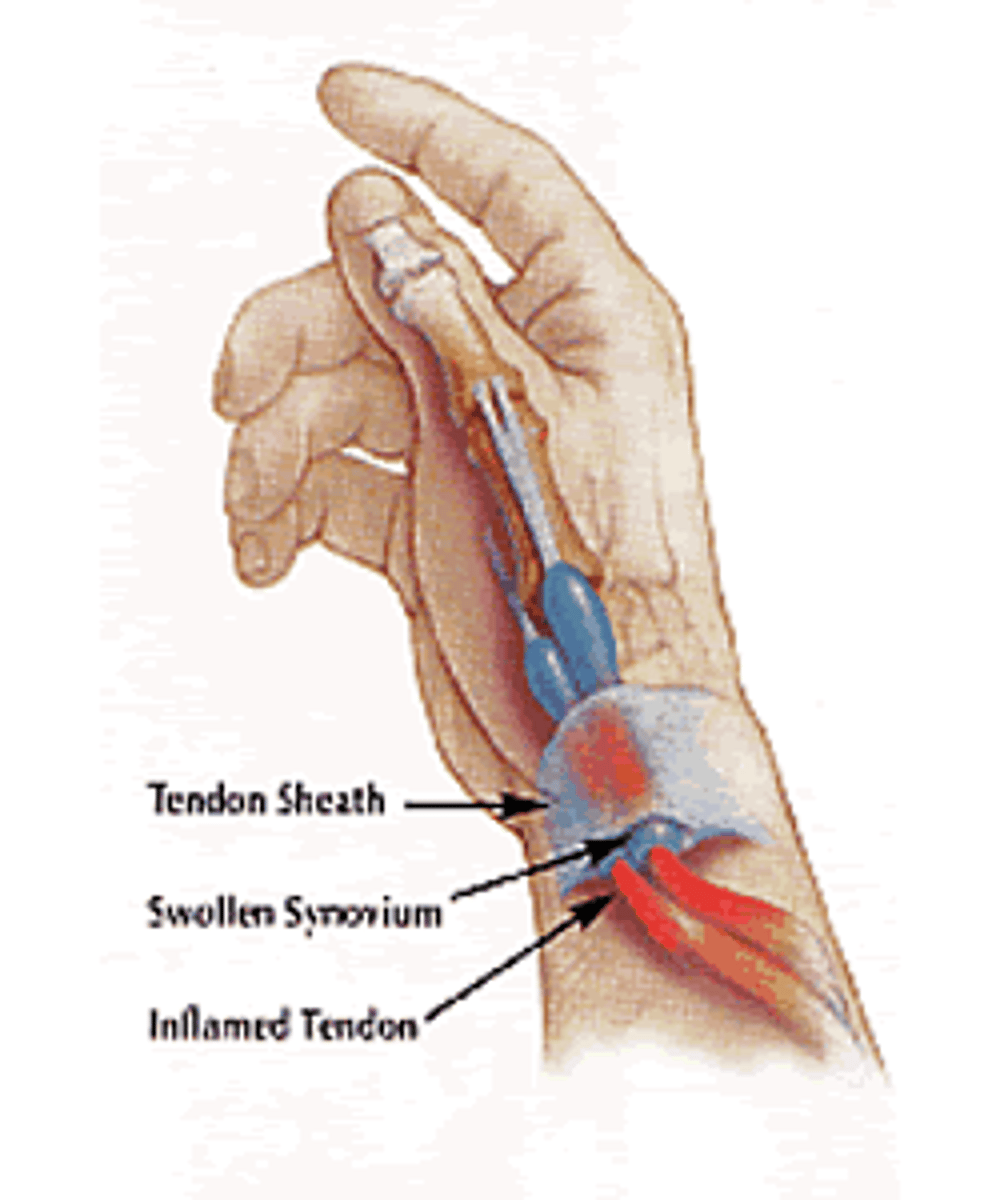
What special test can be used to diagnose deQuervain's tenosynovitis? What is a (+) test?
Finkelstein test
(+) → increased pain along the radial aspect of the wrist along the 1st dorsal compartment
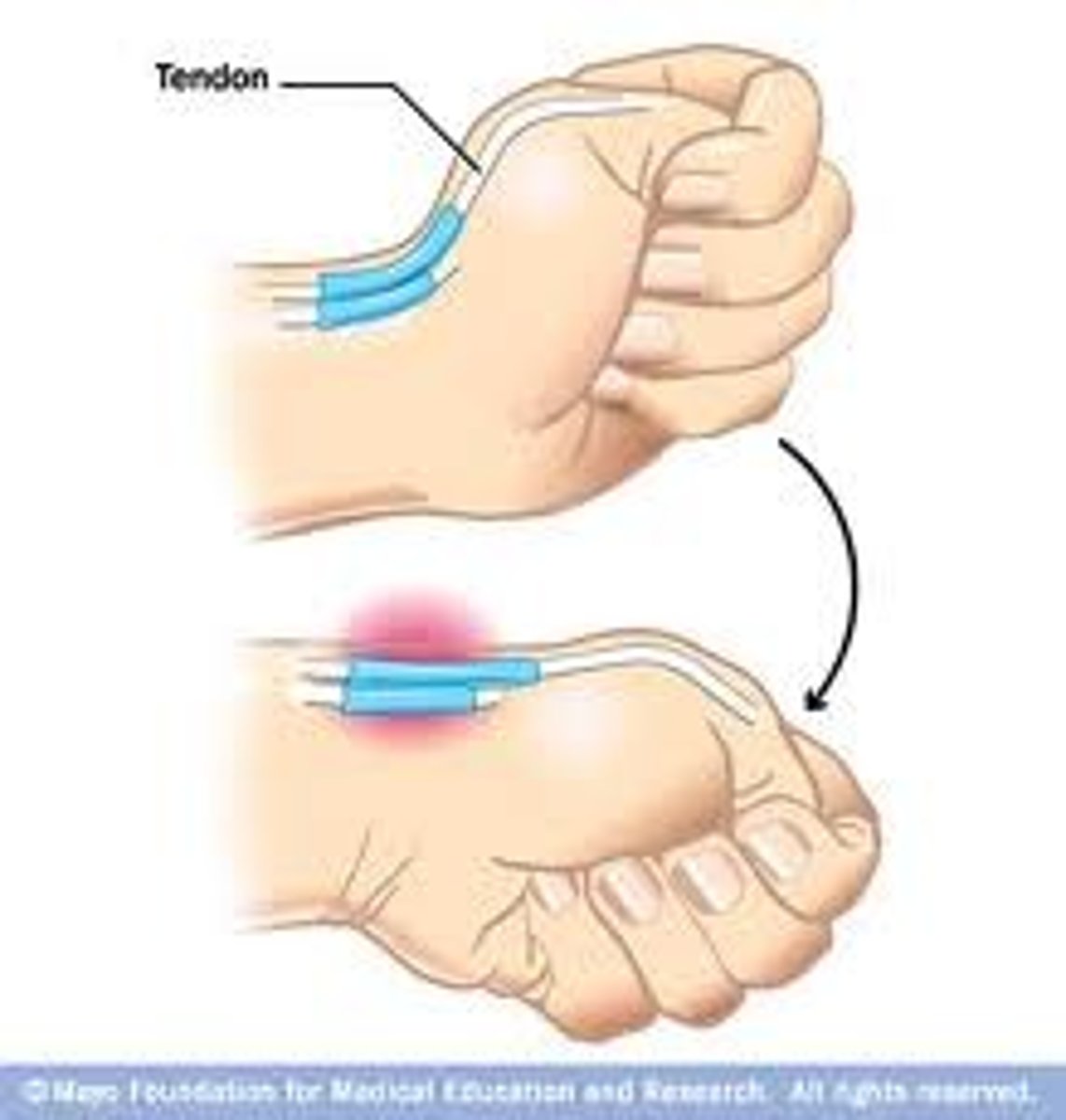
What hand movement can aggravate the symptoms of deQuervain's tenosynovitis?
thumb movement or making a fist
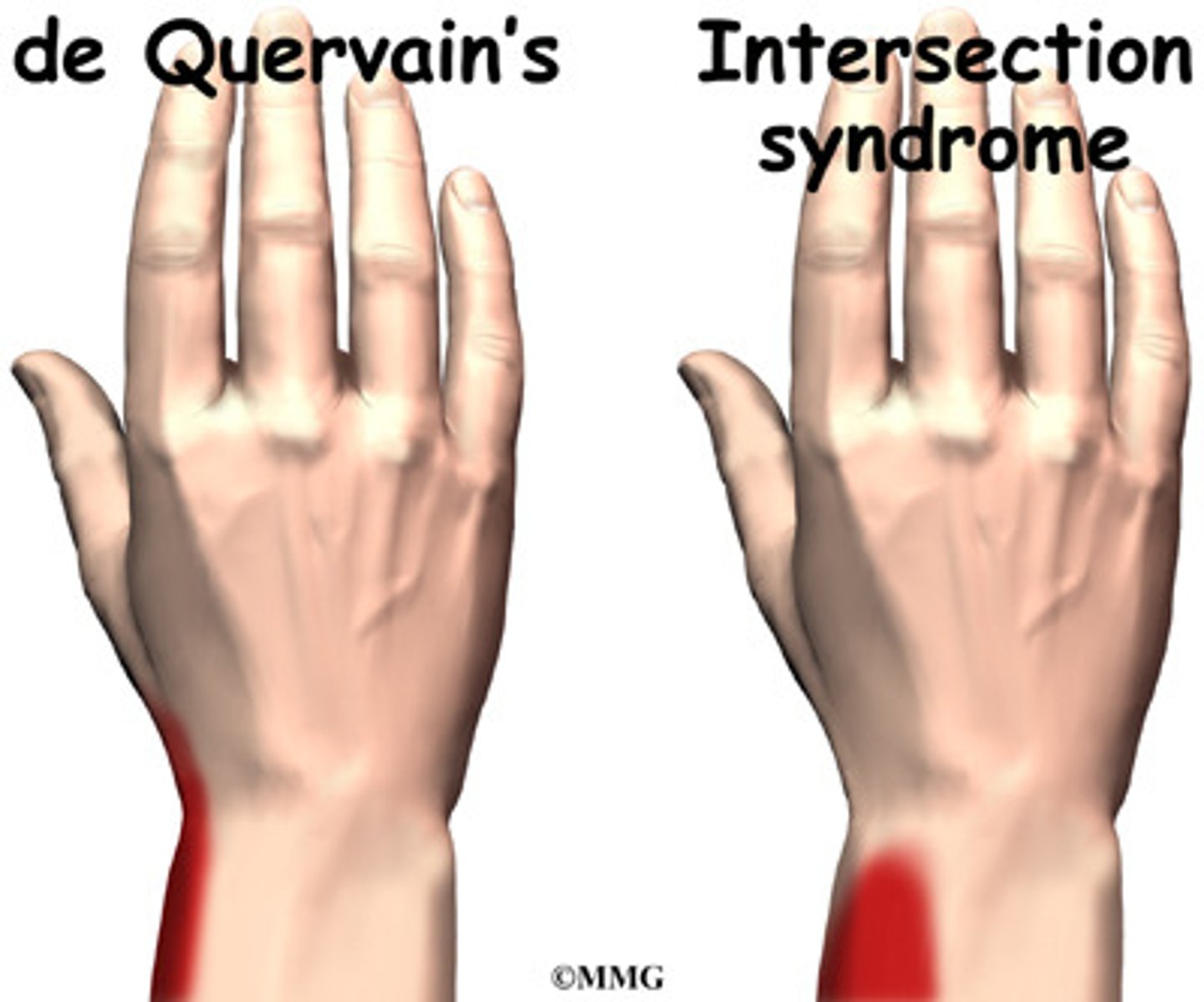
How do we differentiate between intersection syndrome and deQuervain's tenosynovitis?
BOTH result from inflammation of the tendons of the wrist BUT:
Intersection → pain is at the intersection point in the forearm
deQuervain's tenosynovitis → pain is along the edge of the wrist, closer to the hand
What is the treatment for deQuervain's tenosynovitis?
NSAIDs
Rest
Ice
Steroid injection (no more than 2-3)
Thumb spica splint
If refractory → surgery
What condition results from entrapment of the median nerve?
carpal tunnel syndrome
What TWO populations is CTS most commonly seen?
middle-aged women
pregnant women
What S/S are indicative of CTS?
Paresthesias
Weakness
Awaken from sleep due to pain/numbness
Reduced function (ie. unable to drop objects or open jars)
What THREE test if (+) indicate presence of carpal tunnel syndrome?
Tinel's
Phalen's
Durkin's test
What is the most useful diagnostic test for carpal tunnel syndrome?
EMG/NCV
What is the treatment for carpal tunnel syndrome?
Volar splint
NSAIDs
Steroid injection
Surgical release
What special test can be used to determine patency of blood supply to the hand?
allen test
- used to assess patency for BAG
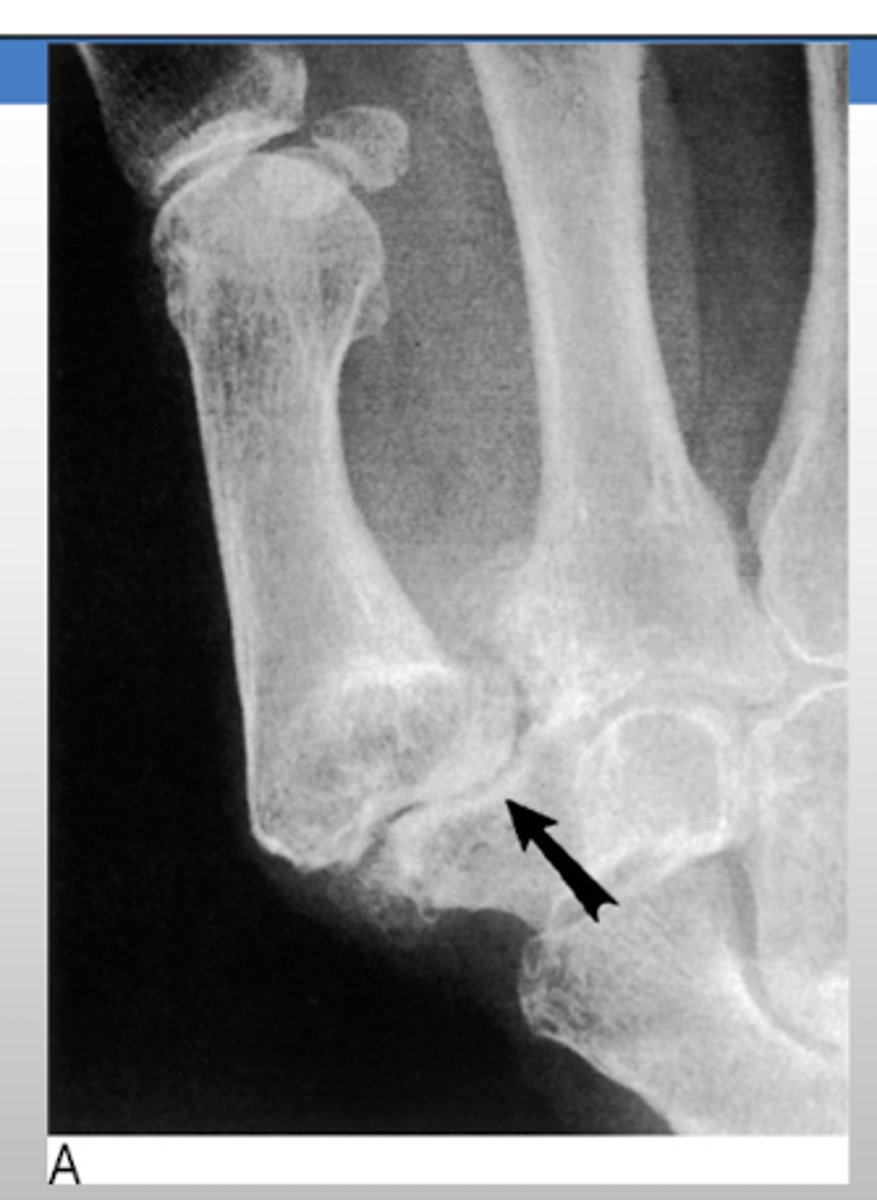
What is the most common carpal bone fracture? In what population is most commonly seen?
scaphoid
- m/c seen in young men
What type of trauma is associated with scaphoid fracture?
trauma with dorsiflexion of wrist
What TWO clinical features will present with a scaphoid fracture?
Pain in the radial side of the wrist
Anatomical snuffbox tenderness
When ordering an XR for a scaphoid fracture, what special view must be obtained?
scaphoid view
- PA view with wrist in an ulnar deviation
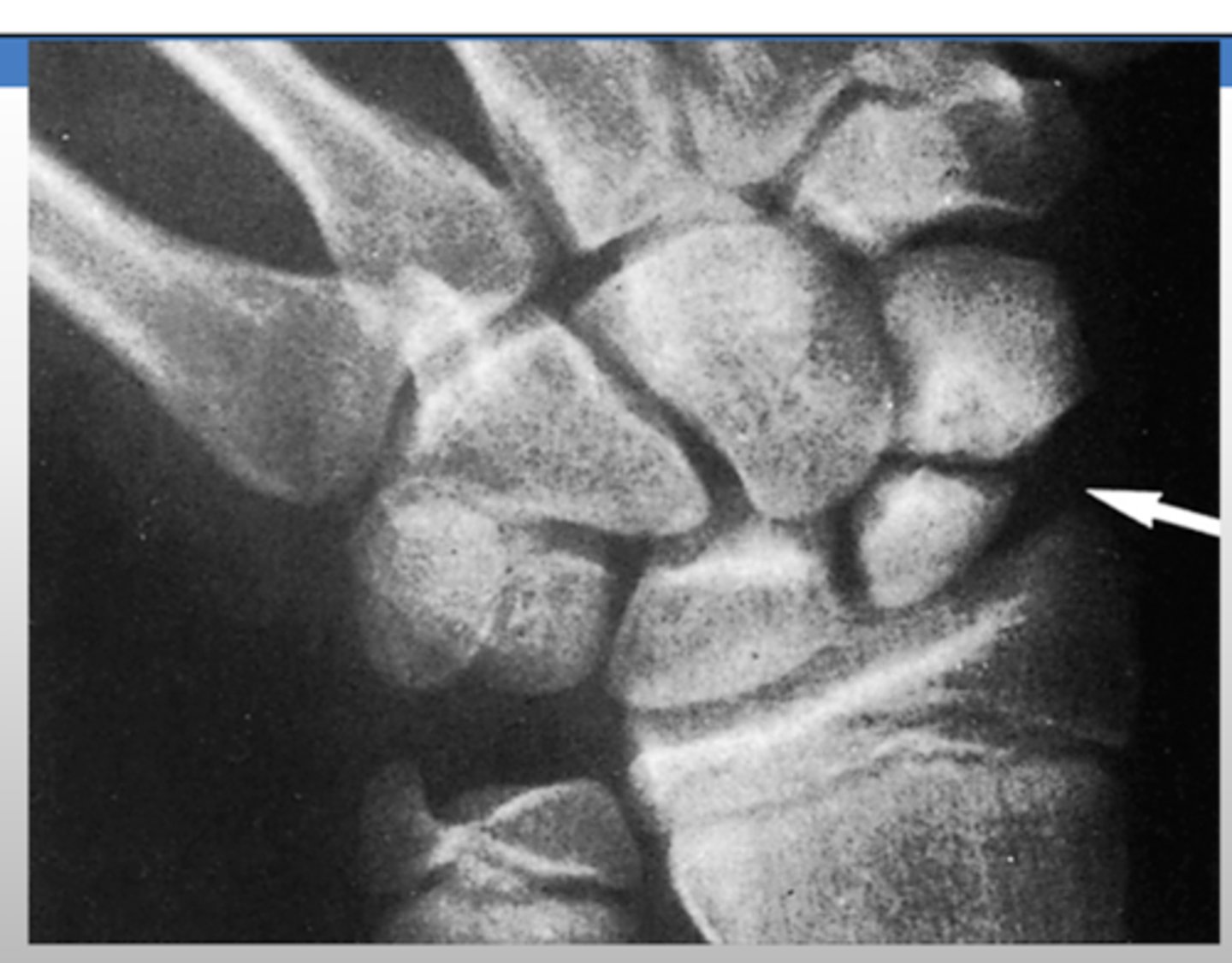
What is the treatment for a scaphoid fracture?
thumb spica splint
What is Kienbock disease?
osteonecrosis of the lunate
- caused interruption of blood supply
- can lead to lunate collapse + end-stage arthritis
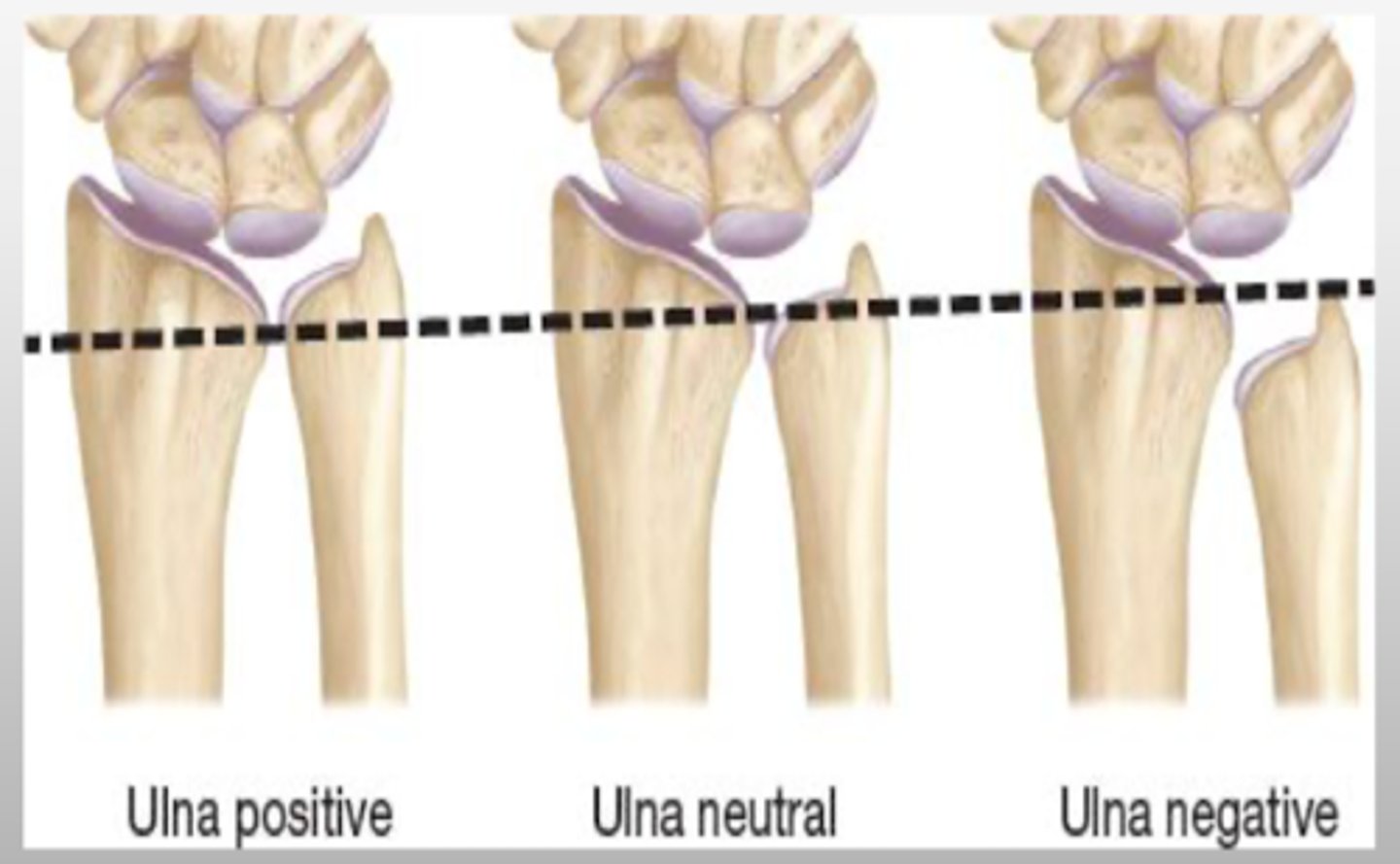
REVIEW: Ulnar Variance.
What type of fracture results from injury to the distal metacarpal neck?
Boxer's fracture
- will typically have a h/o punching an object
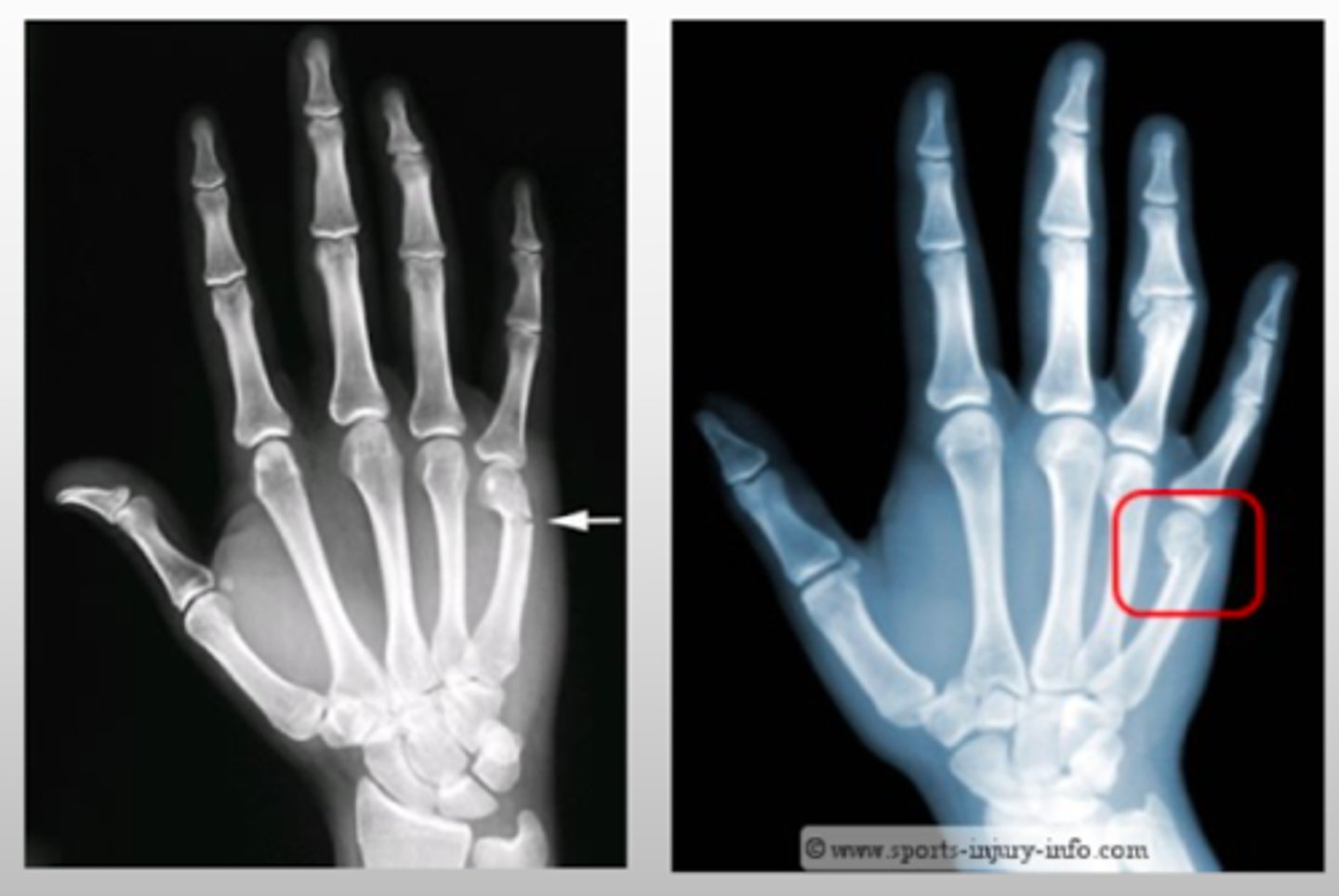
If a patient with a Boxer's fracture has a volar angulation is >25-30 degrees, what treatment is recommended?
reduction/splinting
- if >40 → surgery
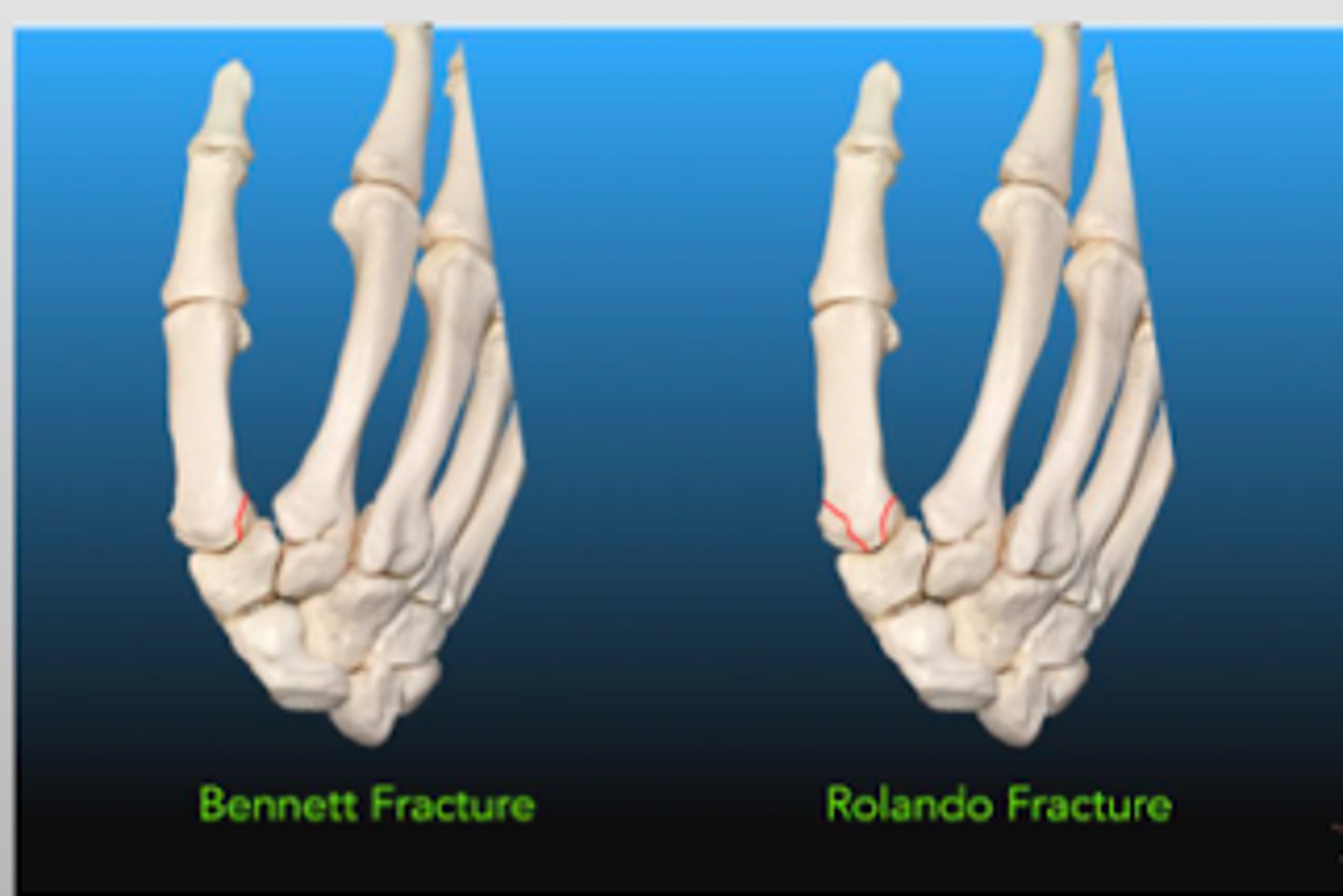
What bone is affected in a Bennett's/Rolando's fracture?
base of the 1st metacarpal
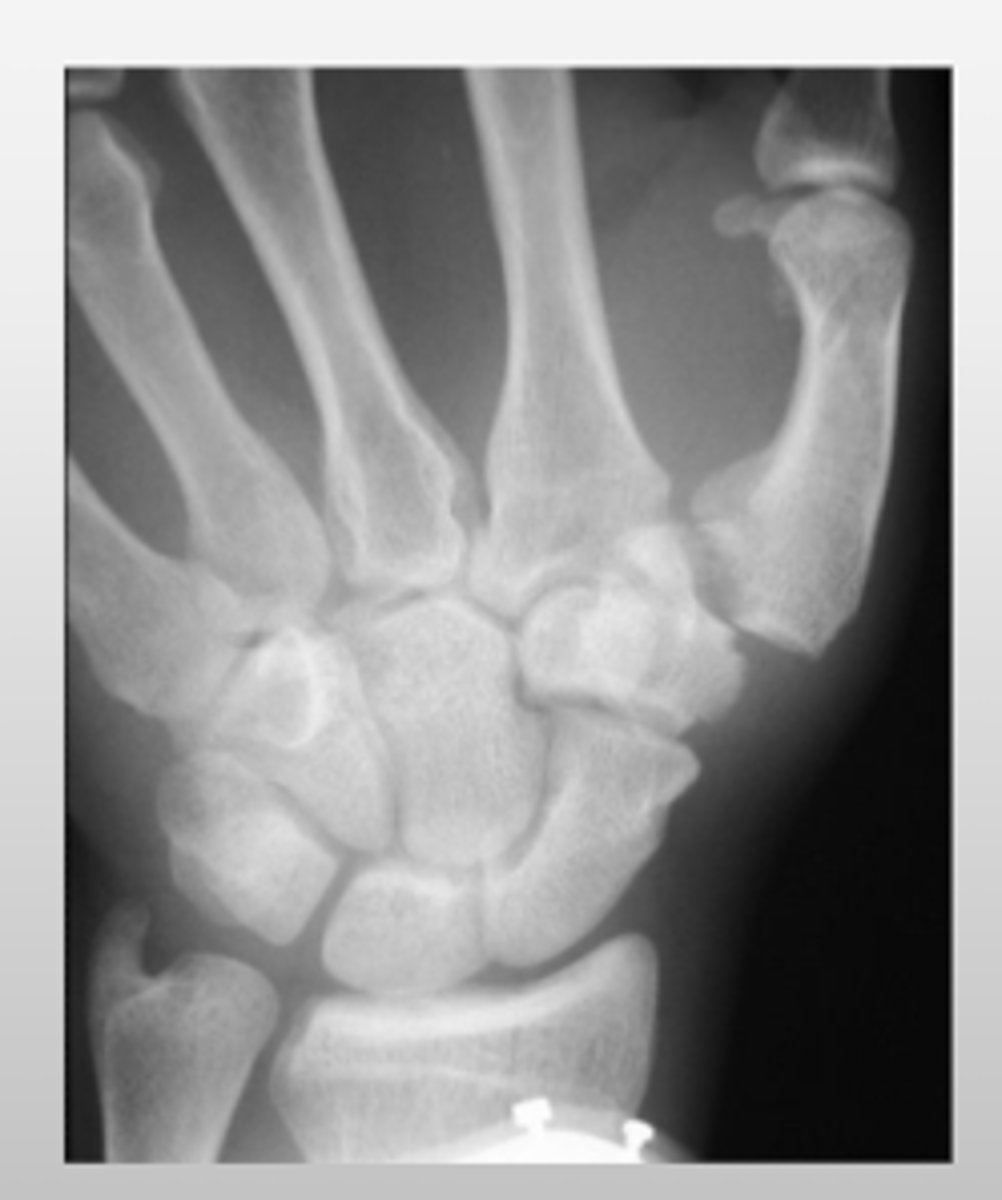
An individual with a Bennett's or Rolando's fracture will have what type of pain?
swelling and pain at the thumb base (CMC)
What is the difference between Bennett's fracture and Rolando's fracture?
Bennett's → oblique Fx
Rolando's → comminuted/displaced Fx
What is the most common distal wrist injury?
colle's fracture
- wrist will have a dorsal angulation
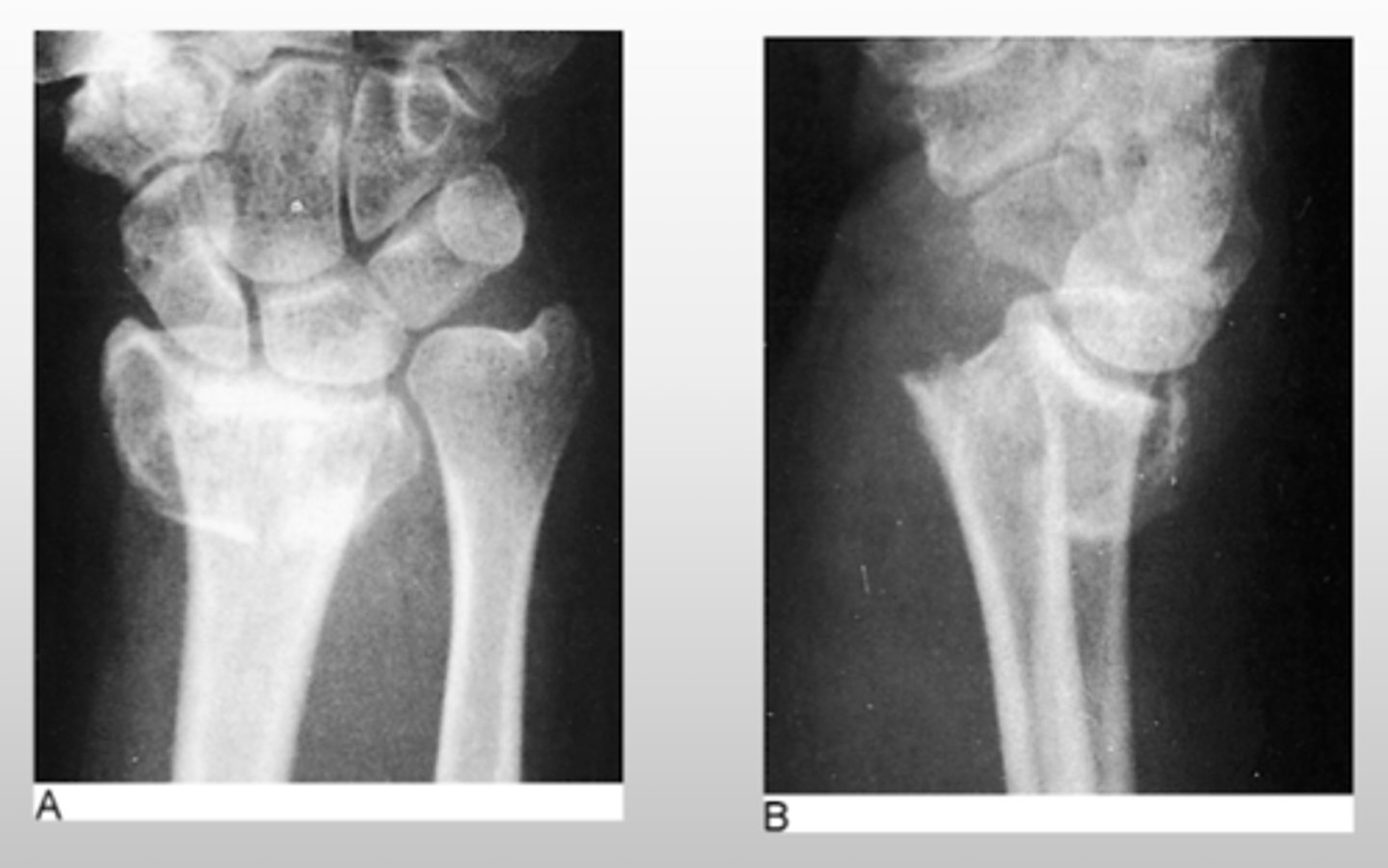
What is the most common complication associated with a colle's fracture?
EPL tendon rupture
**can also lead to malunion or median nerve compression
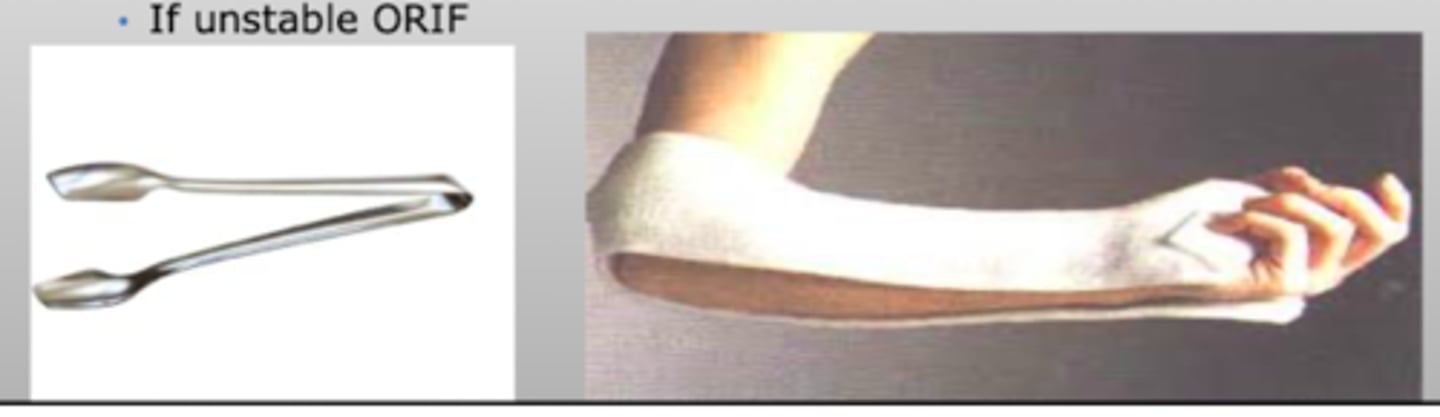
What is the treatment for a Colle's fracture?
Closed reduction
Sugar tong splint
Repeat XR
If unstable → ORIF
What injury will result in a Smith's fracture?
FOOSH with a FLEXED wrist
- wrist will be displaced anteriorly/towards flexed surface
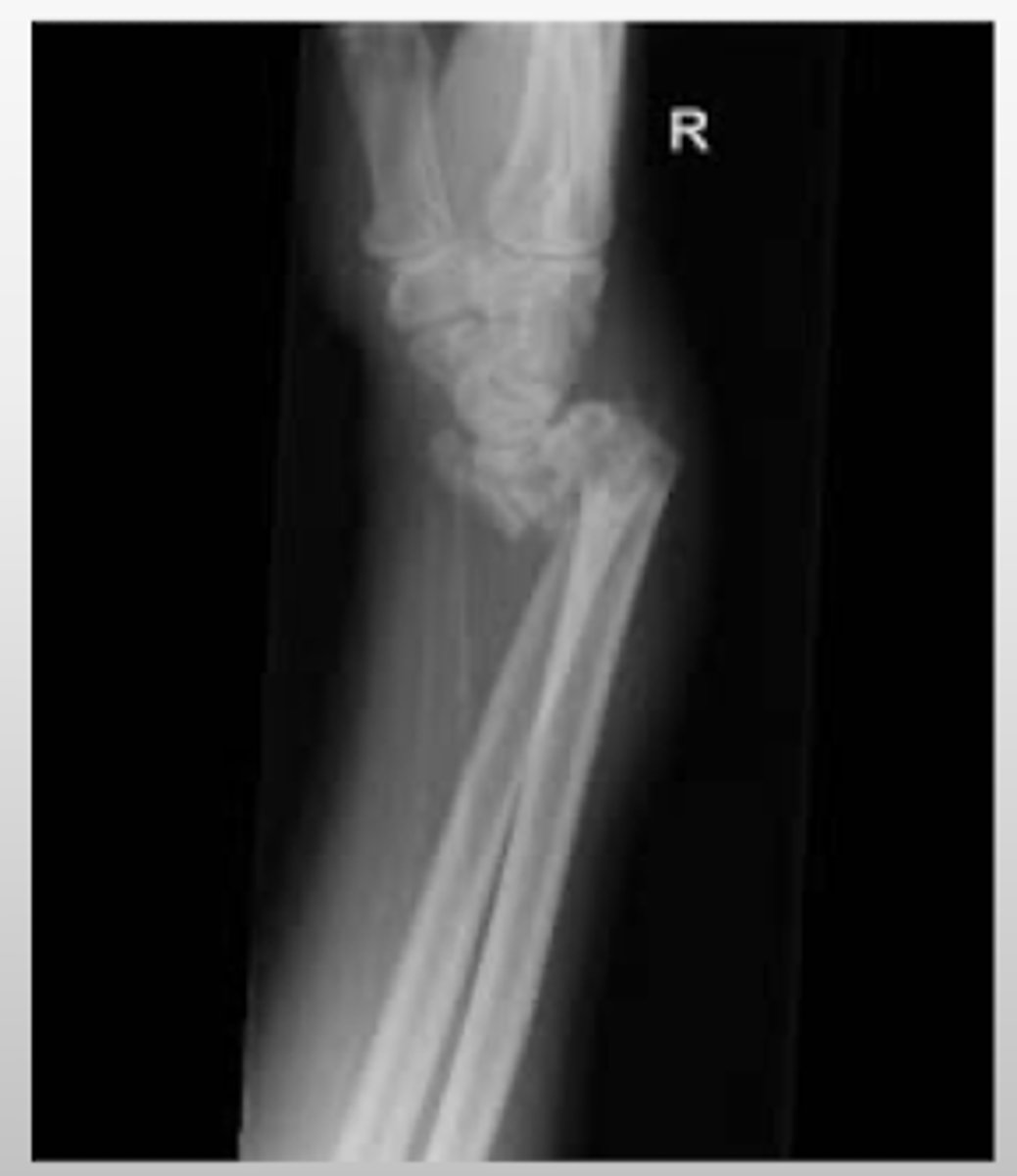
What is a Buckle fracture? What population is it most commonly seen in?
torus fracture
- commonly seen in pediatrics as an incomplete fracture due to softer/pliable bones
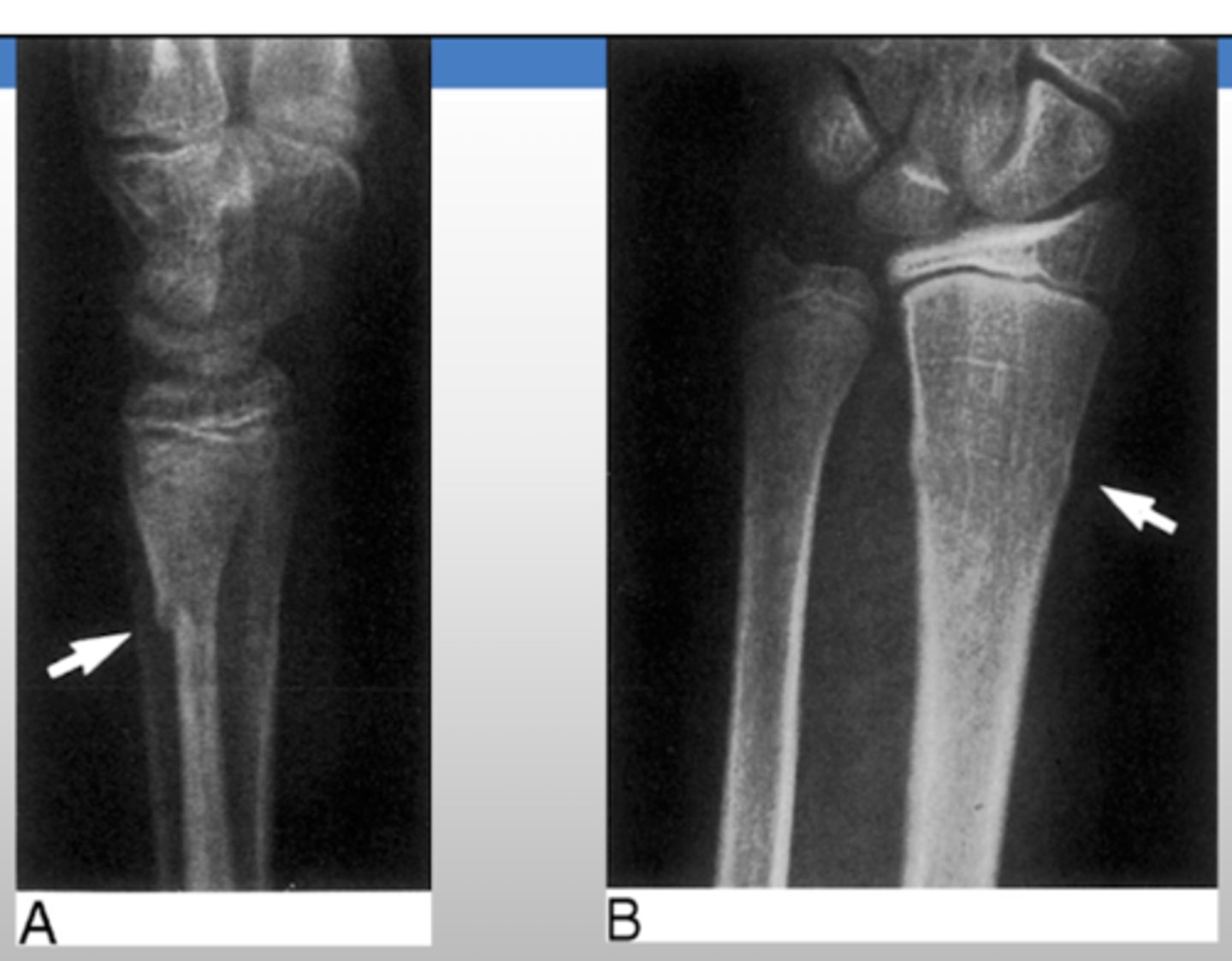
What causes ulnar tunnel syndrome?
space occupying lesions that entraps the ulnar nerve
- includes: tumor, lipoma, ulnar artery aneurysm and muscle anomaly
What special test is (+) can also indicate CTS?
Tinel's
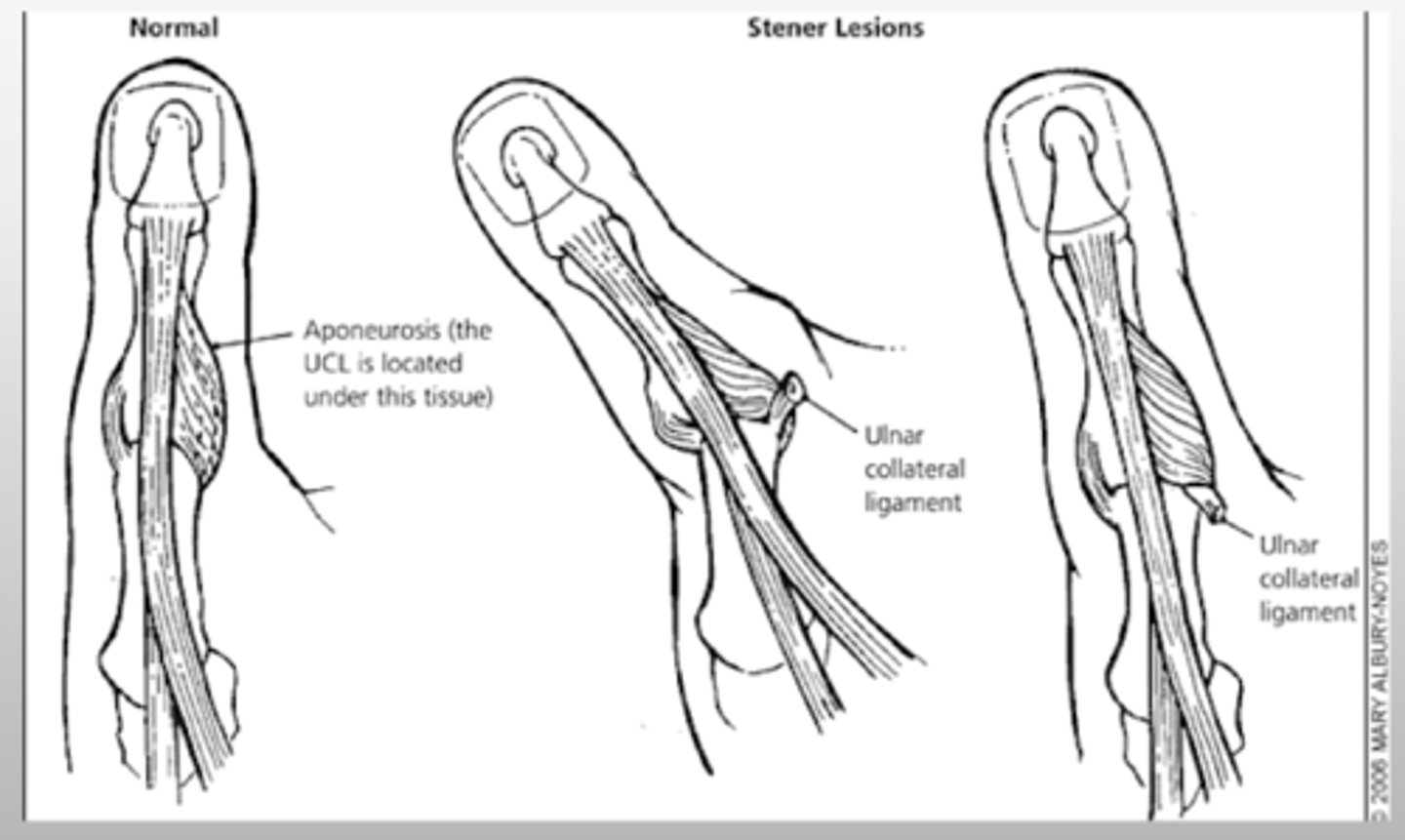
What type of injury occurs in a Gamekeeper's thumb? What causes it?
injury to the ulnar collateral ligament (UCL) of the thumb with or without avulsion
Occurs due to forced abduction or hyperextension of the proximal phalanx of the thumb
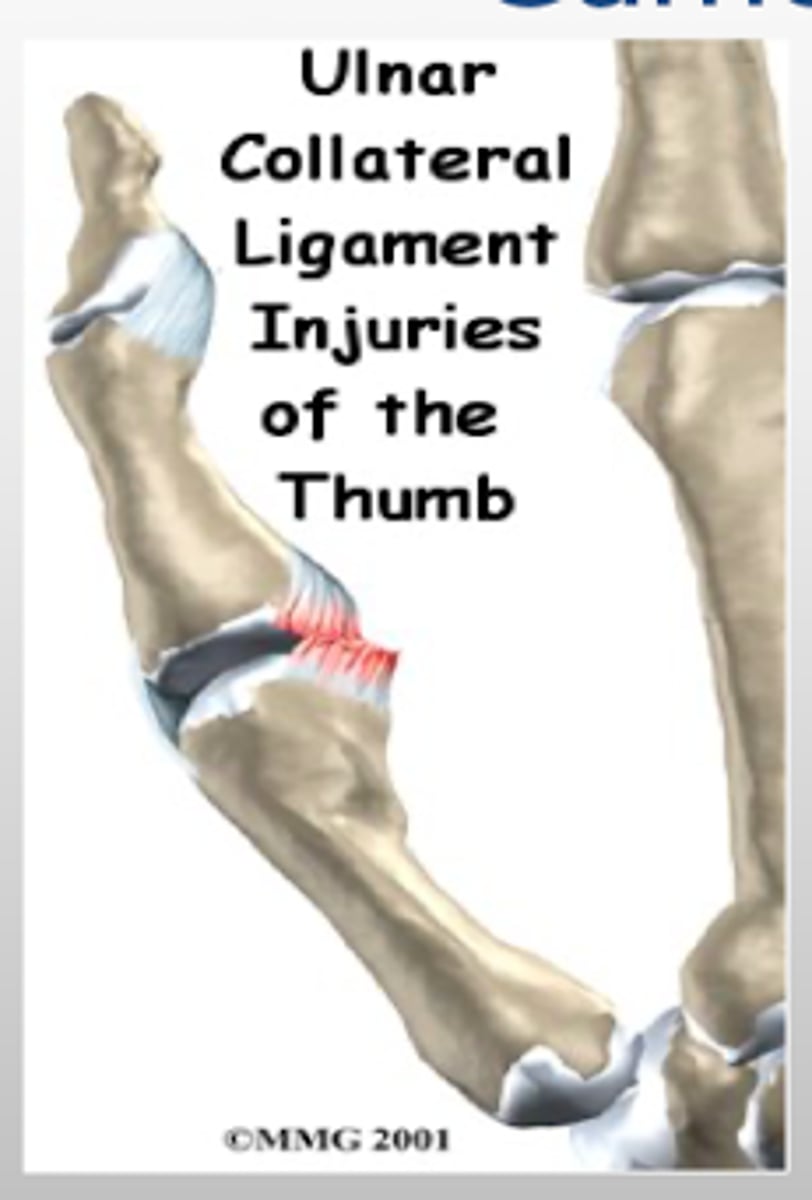
What TWO other terms can be used to describe a Gamekeeper's thumb?
Skier's thumb
MCP dislocation
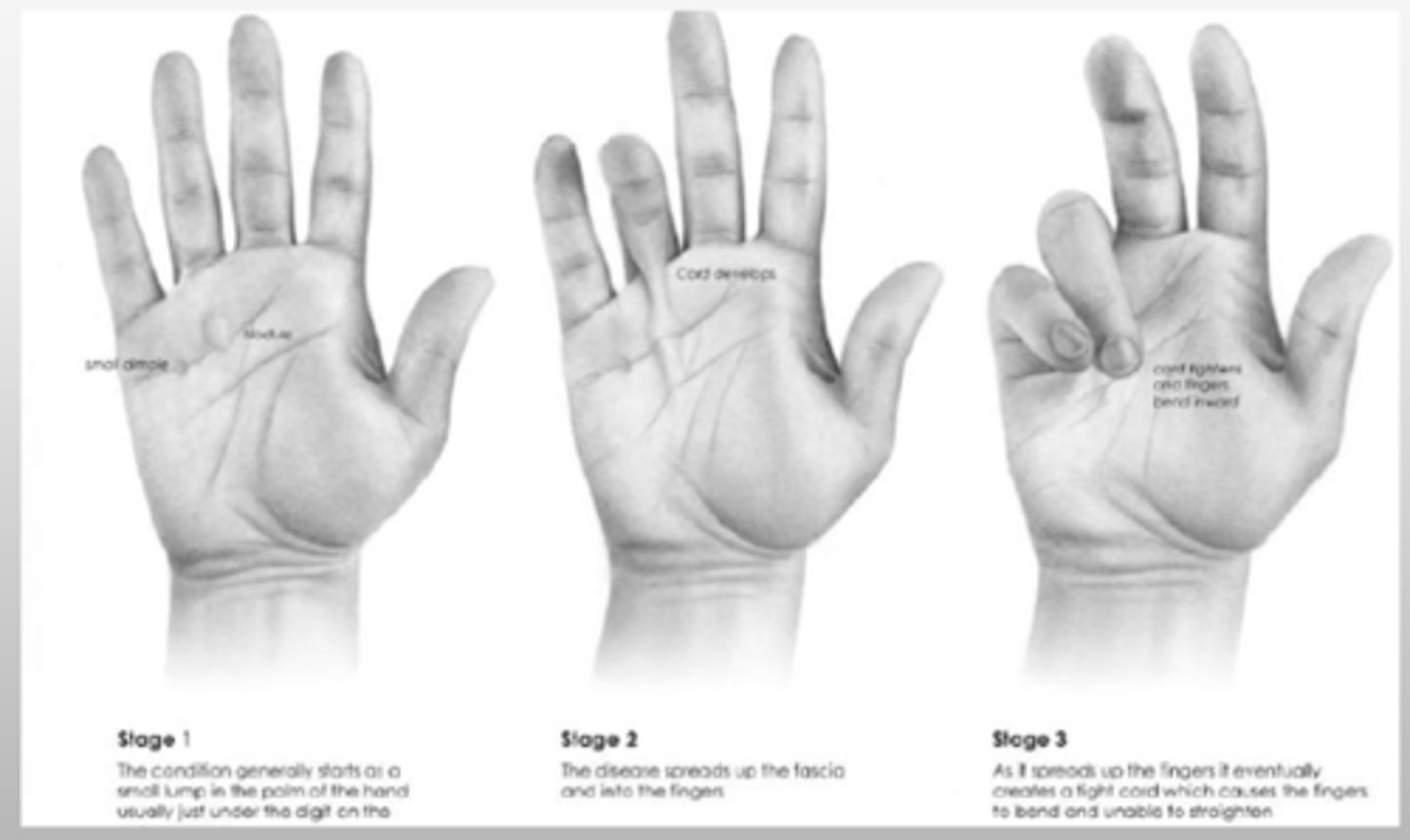
What condition results due to contracture of the palmar fascia due to nodules and cords at MCPs and PIPs?
Dupuytren's contracture
- affects the 4th and 5th digits
Who most commonly suffers a Dupuytren's contracture?
M>F
DM
Alcoholics
Individuals exposed to vibrations
What special test can be used to diagnose a Dupuytren's contracture?
(+) Hueston's table top test
What is the treatment for Dupuytren's contracture?
Intralesional steroid injection
Collagenase injection if >20 at MCP/PIP
PT
If >30 → ortho surgical consult
What causes a trigger finger (locked finger; stenosing tenosynovitis)?
occurs when the annular pulley, through which the flexor tendons glide under, becomes thickened and limits the gliding motion
What population is most commonly affected by a trigger finger?
middle-aged women
What clinical feature is suggestive of a trigger finger?
painful snapping sensation or catch or lock during flexion
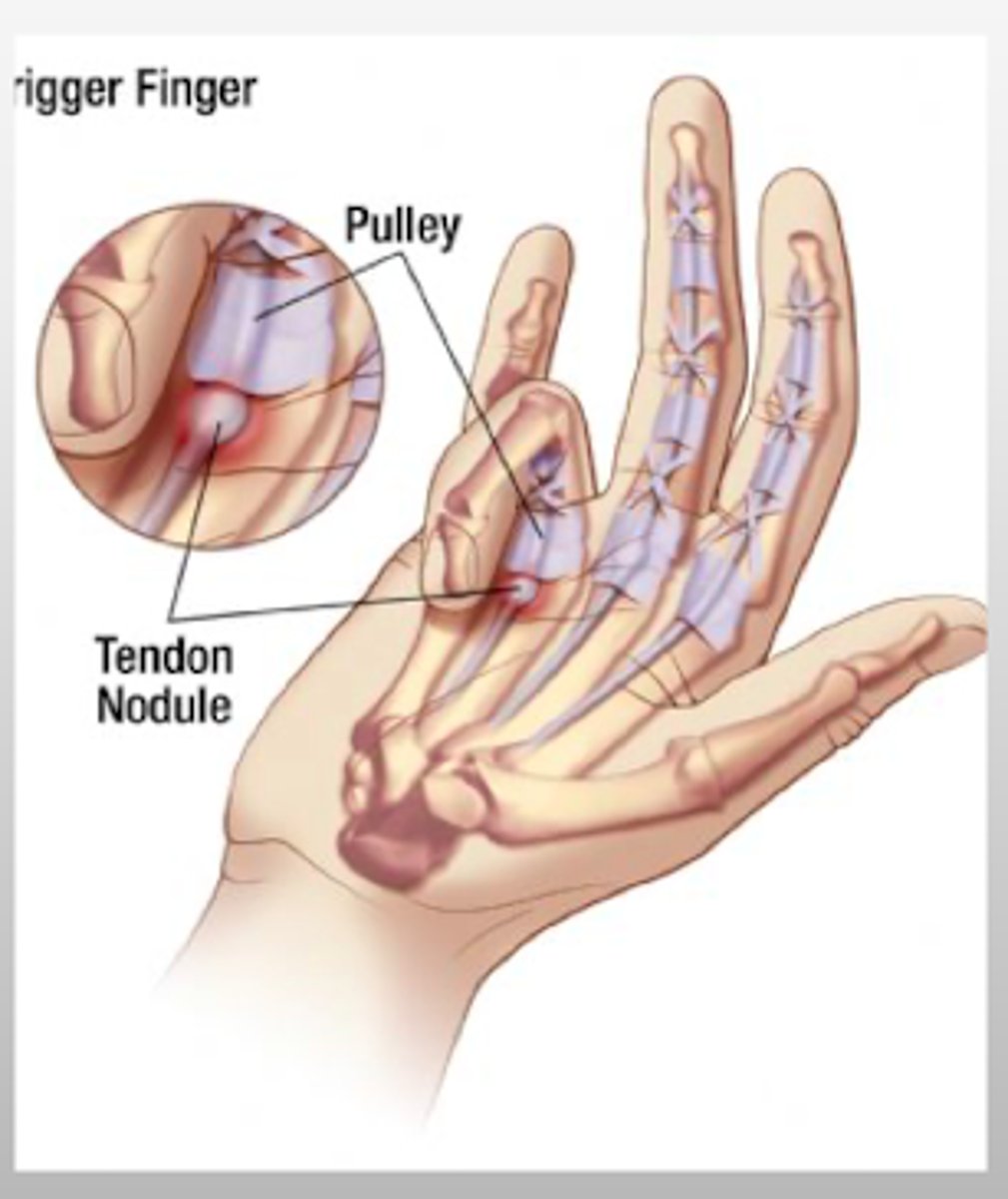
What is the treatment for trigger finger?
NSAIDs
Corticosteroid injection to the tendon sheath
- AVOID TENDON
Surgical release
What is a Boutonniere deformity? What causes it?
occurs when the central portion of the EXTENSOR tendon ruptures
PIP joint will be FLEXED due to lack of extensor pull
DIP joint will HYPEREXTEND

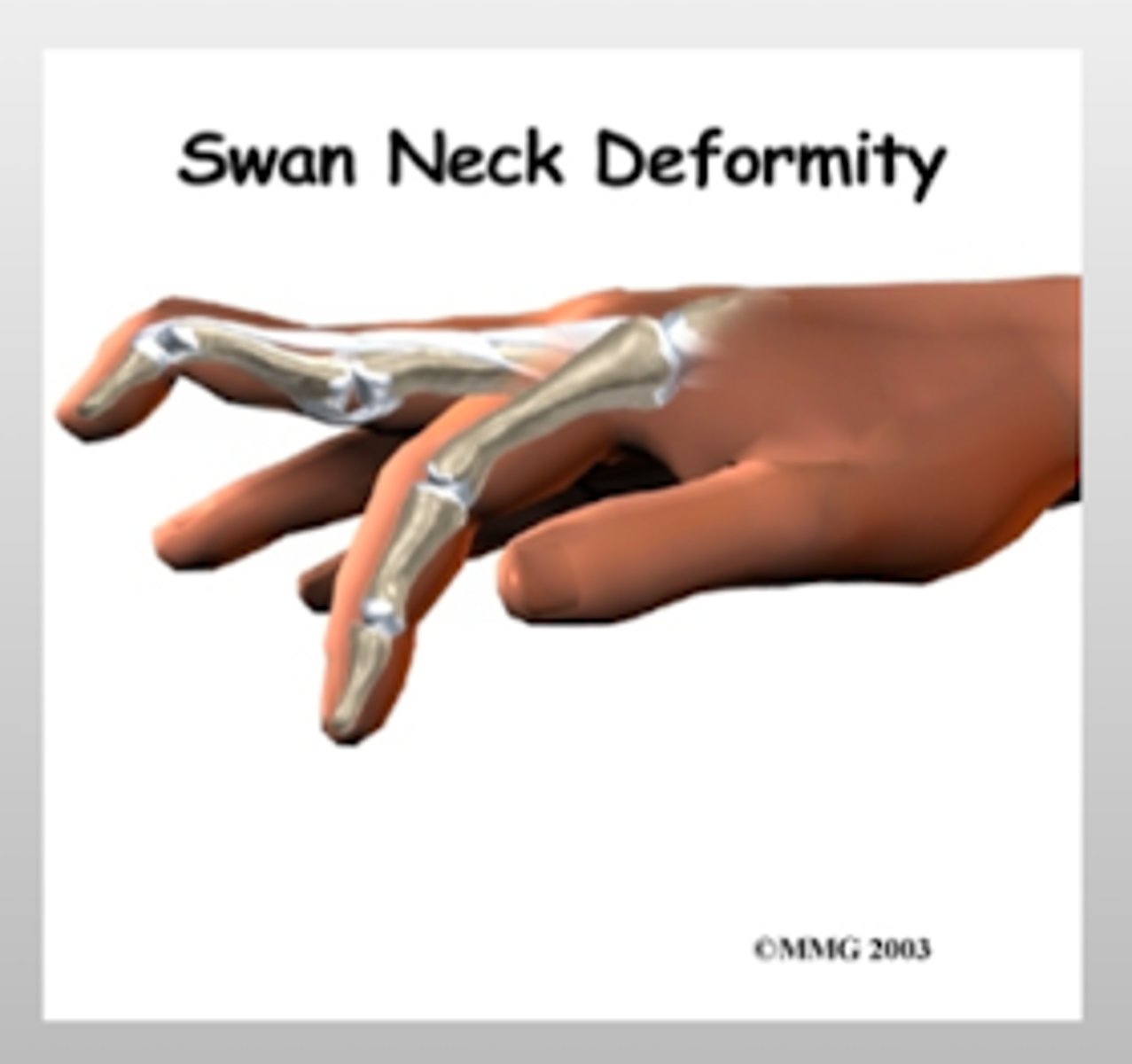
What is a swan neck deformity?
PIP joint will be HYPEREXTENDED
DIP joint will be FLEXED
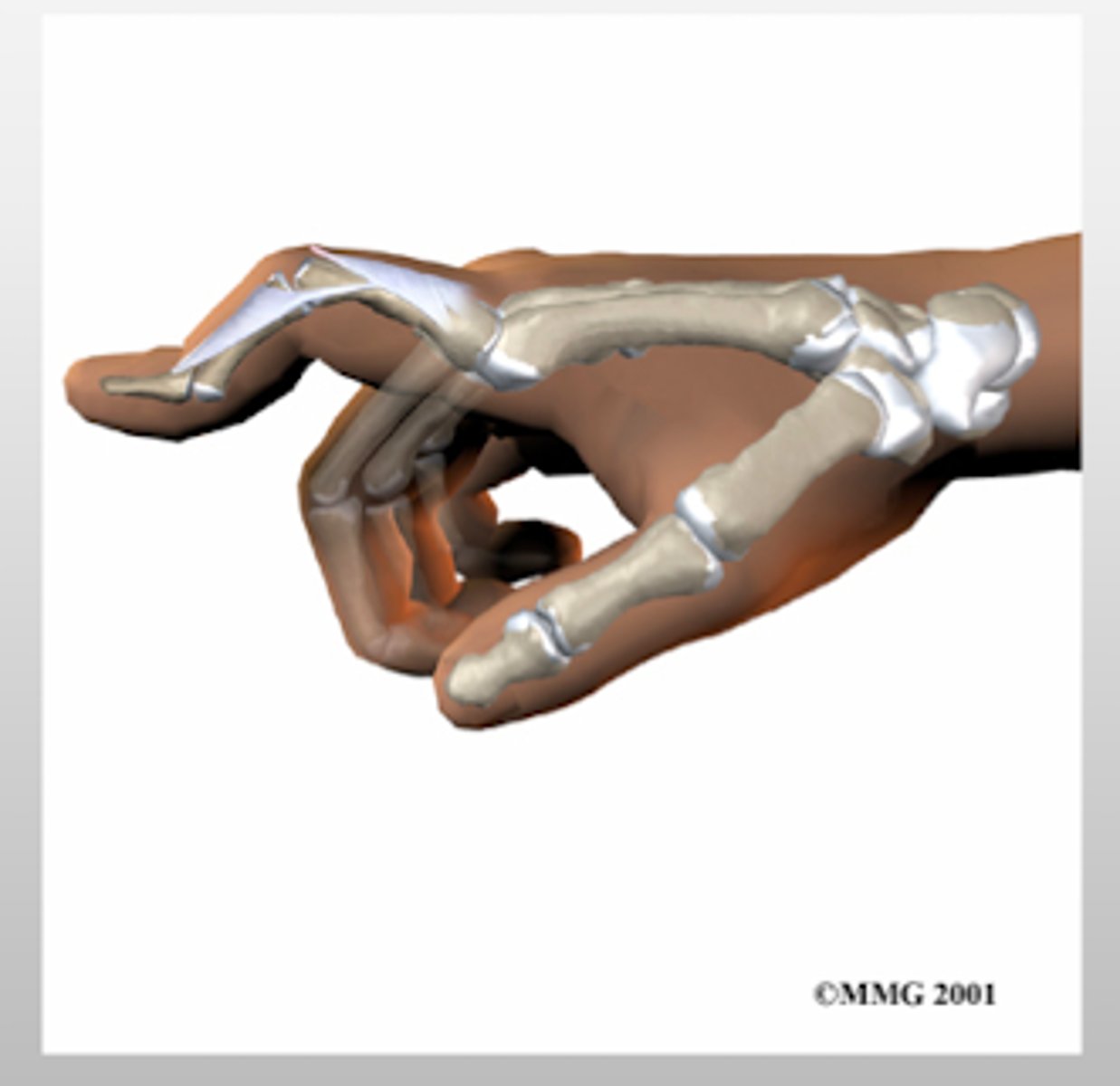
What causes a mallet finger? How will it present?
caused by avulsion of the extensor tendon at the distal insertion
DIP joint will be FLEXED + unable to extend
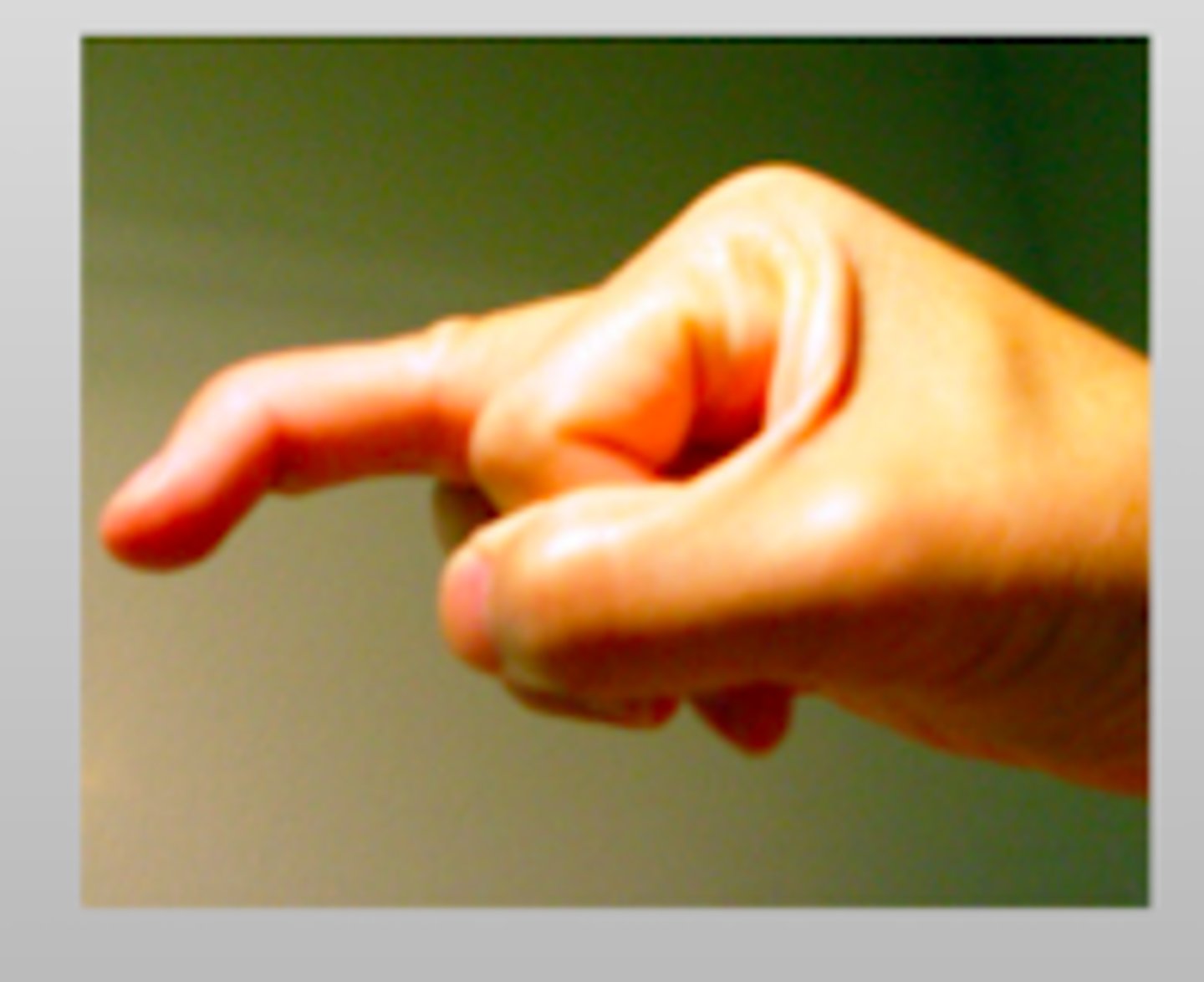

What causes a Jersey finger?
avulsion of the FLEXOR tendon insertion at the DIP base
- most commonly in the ring finger
- unable to flex at the finger tip
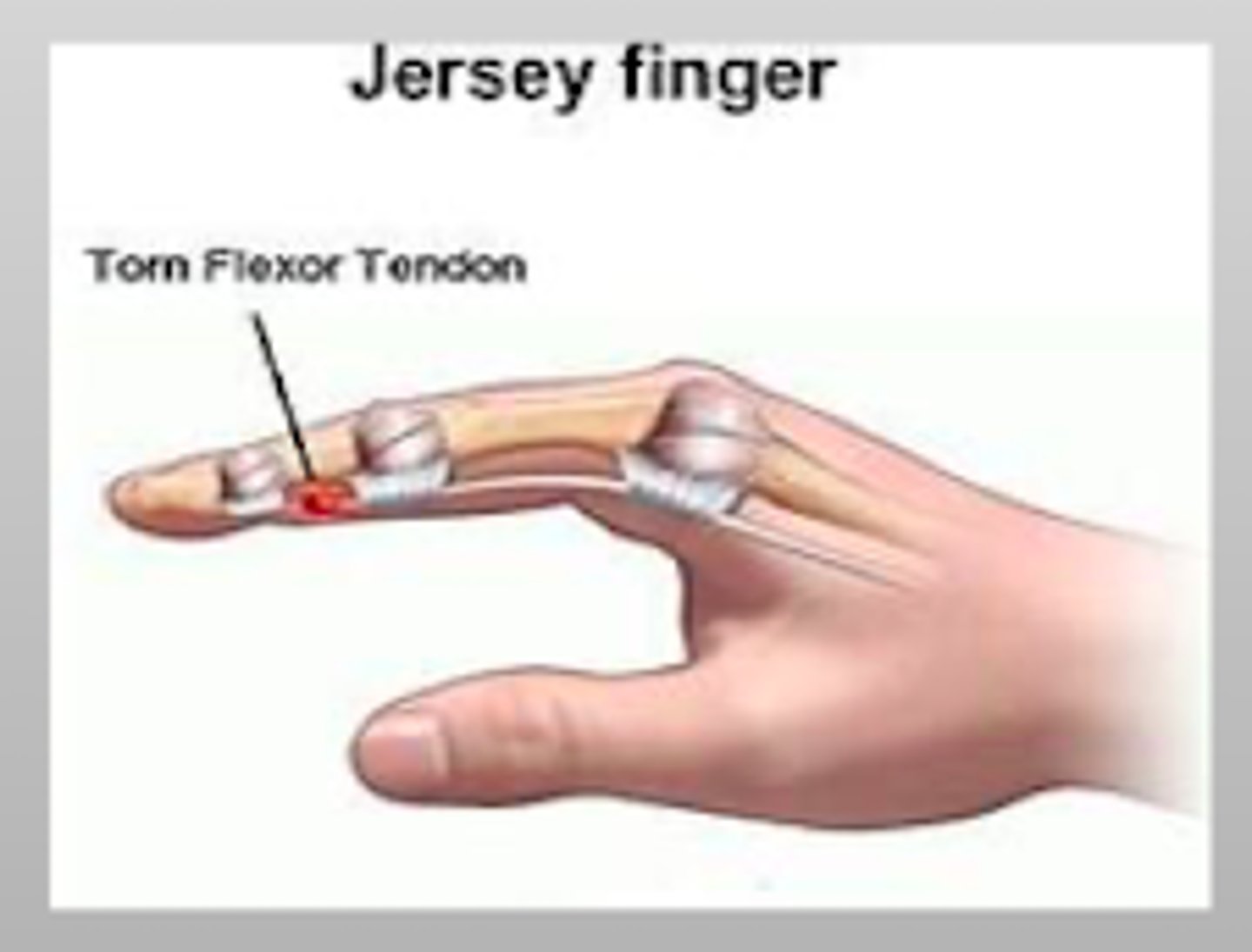
What is the treatment for Jersey finger?
Direct tendon repair or tendon reinsertion
If Fx → ORIF
Metacarpal vs Phalangeal Fx: which one is most common in adults and children?
Adult → metacarpals
Children → phalangeal
T/F. If there is a WOUND near the fracture, it is OPEN until proven otherwise.
TRUE
For a metacarpal or phalangeal Fx, what is the treatment for a non-displaced Fx?
casting or splinting
For a metacarpal or phalangeal Fx, what is the treatment for a displaced Fx?
will need to see hand/ortho specialist
What is the most commonly occurring animal bite in children?
fingers of the dominant hand
What should NOT be forgotten in a patient with an animal/human bite?
tetanus shot
What is most commonly injured in a clenched fist injury?
5th MCP joint
- results in skin lacerations and possible avulsion Fx as the closed fist comes in contact with teeth
Should wounds in a clenched fist injury be sutured closed?
NO - should be cleansed and changed and allowed to heal by secondary intention
What joints are most commonly involved in OA vs RA?
OA → DIP + PIP joints
- will have pain with palpation
RA → MP joints
- no DIP joint involvement and pain will be intermittent
Where do Heberden's nodes occur?
DIP joints (OA)
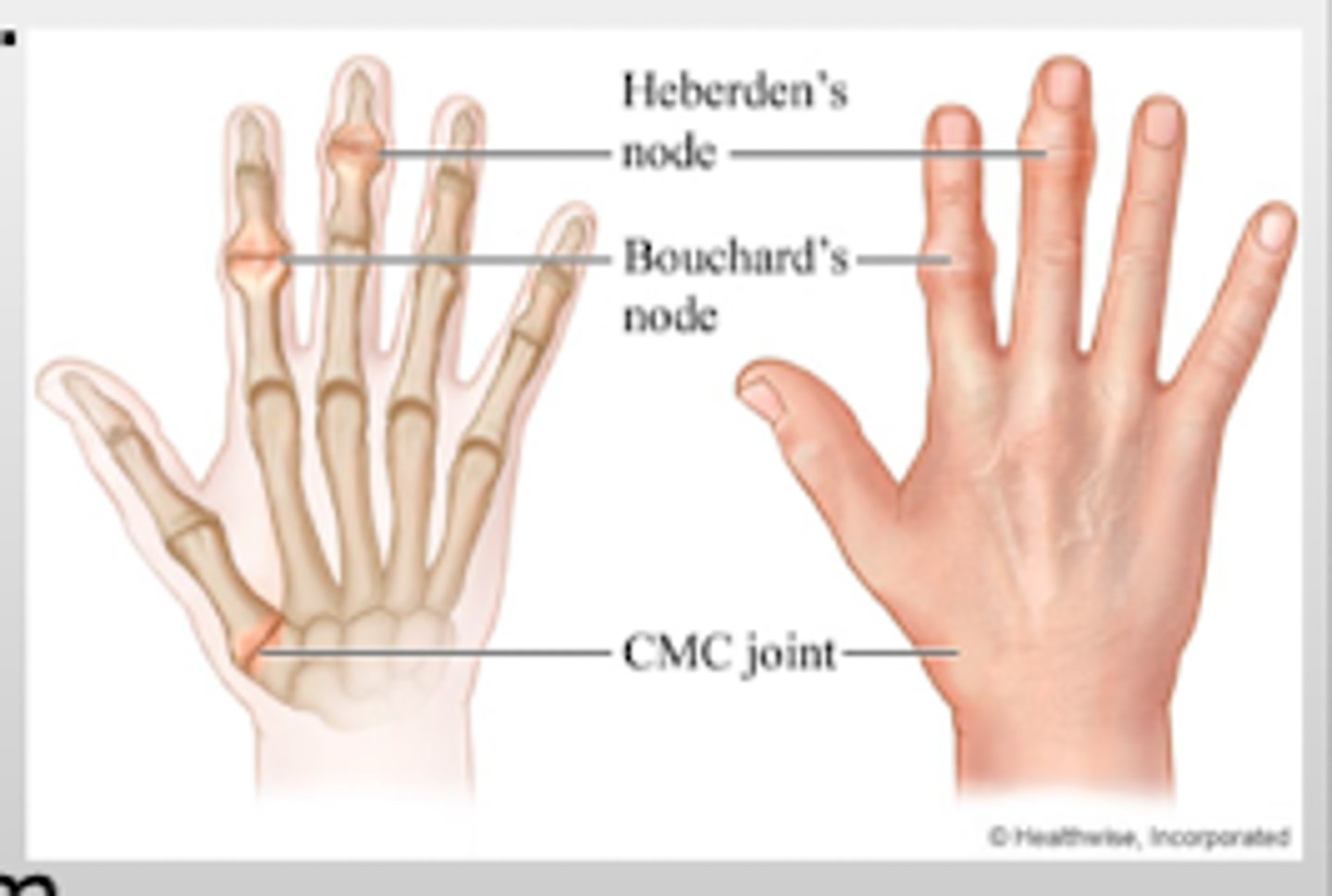
Where do Bouchard's nodes occur?
PIP joints (OA)
Where does OA in the CMC joint most commonly occur?
base of the thumb