APES Midterm
1/150
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
151 Terms
The middle, partially melted zone of the interior of the earth is called the
a. crust
b. tectonic plate
c. core
d. mantle
e. magma
D
Which of the following is a local area's short-term temperature, precipitation, and humidity?
a. climate
b. weather
c. biomes
d. ecosystems
e. currents
b
Where does the largest input of solar energy occur?
a. North pole
b. South Pole
c. 30* North
d. 30* South
e. equator
E
Prevailing winds are the result of what?
a. temperature
b. direction the sun strikes the earth
c. rotation of the earth on its axis
d. ocean currents
e. sun storms
C
The rain shadow effect refers to
a. more light on the windward side of mountain ranges
b. more moisture on the leeward side of mountain ranges
c. moister conditions on the windward side of mountain ranges
d. drier conditions on the windward side of mountain ranges
e. less light available on the leeward side of mountain ranges
C
In certain sea area winds, ocean currents, and other factors cause water to come uo from the depths to the surface bringing nutrient from the ocean bottom. This process is called a(n)
a. downdraft
b. updraft
c. El nino
d. la nina
e. upwelling
E
Large sections of the earth's crust, called _______, move slowly on the mantle below them
a. asthenosphere
b. mantle
c. tectonic plates
d. core
e. oceanic rides
C
When and oceanic plate collides with a continental plate usually slides up and over the denser oceanic plate, pushing it down the mantle, a process called
a. production
b. subduction
c. induction
d. convection
e trenching
B
Tectonic plates move in opposite but parallel directions along a fault at a
a. divergent plate boundary
b. convergent plate boundary
c. subduction zone
d. mantle fault
e. transform fault
E
The place where an earthquake begins is called its
a. start
b. focus
c. magnitude
d. epicenter
e. fault
B
Large waves generated in the ocean by an earthquake, landslide, or volcanic activity are called
a. pipe waves
b. quake waves
c. seismic waves
d. rollers
e. tsunamis
E
The correct sequence of the layers of the atmosphere from intermost to outermost
a. mesosphere-stratsophere-thermosphere-troposphere
b. troposphere-stratosphere-mesosphere-thermosphere
c. stratsophere-thermosphere-troposphere-mesosphere
d. thermosphere-stratsophere-mesosphere-troposphere
B
Stratospheric ozone is responsible for all of the following except
a. screening out ultraviolet radiation
b. allowing the evolution of life on land
c. preventing ozone formation in the troposphere
d. helping protect humans from sunburn and cataracts
e. lower atmospheric water vapor
E
Most deserts are located near the 30 north and 30 south latitudes because humidity is lower at 30*. The best explanation for this is
a. warm air rises at 90 latitude, cools and sinks at 30
b. cool air rises at 30* latitude warms and sinks at equator
c. warm air rises at the equator, cools, and sinks at 30* latitude
d. trade winds transfer moisture away from 30* latitude
e. rain shadow effects are most pronounced at 30* latitude
C
Which latitude gets 24 hours of no light on December 21?
a. arctic circle
b. tropic of cancer
c. equator
d. tropic of capricorn
e. antarctic circle
A
Which of the following annual population growth rates is paired with the correct doubling time
a. 1%... 700 years
b. 2%... 35 years
c. 3.5%... 12 years
d. 5%.... 350 months
e. 7%... 70 months
B
The primary cause of Earth's seasons is the ________
a. constant tilt of he Earth's rotational axis with respect to the plane of its orbit around the sun
b. changing distance of the Earth from the Sun at different times of the year
c. periodic wobbling of Earth on its axis of rotation
d. changing relative positions of Earth, its moon, and the Sun
e. periodic changes in solar energy output
A
This layer of the atmosphere has the highest density of any atmospheric layer and contains most of the water vapor in the atmosphere
a. troposphere
b. stratosphere
c. mesosphere
d. thermosphere
A
Which of the following shoes the approximate concentration of CO2, N2, and O2 in dry air
a. 78%, <1%, 21%
b. 43%, <1%, 56%
c. 36%, 8%, 56%
d. 10%, 70%, 20%
e. <1%, 78%, 21%
E
The root cause of food insecurity is
a. war
b. political upheaval
c. poverty
d. corruption
e. climate change
C
Both the underfed/underweight and the overfed/overweight face similar health problems, potentially including all of the following except
a. lower life expectancy
b. overabundance of energy
c. greater susceptibility to disease
d. lower productivity
e. lower quality of life
B
Which of the following soil horizons is considered topsoil
a. O
b. A
c. B
d. C
e. E
B
This type of irrigation's often used by small-scale farming operations, and it requires extensive labor to set up individual irrigation lines
a. Drip irrigation
b. Flood irrigation
c. Furrow irrigation
d. Spray irrigation
A
What is the largest cause of soil erosion
a. Moving water
b. Still water
c. Wind
d. Sink holes
E. Mountain avalanches
A
When the productive potential of soil, especially on arid or semiarid land, falls by 10% or more because of prolonged drought and human activities, it is called
a. salinization
b. desertification
c. soil erosion
d. overgrazing
e. water logging
B
Repeated irrigation in dry climates leads to soil degradation of the upper layers, a process called
a. salinization
b. desertification
c. soil erosion
d. overgrazing
e. water logging
A
One of the most important characteristics of a pesticide is how long it will stay deathly in the environment, a characteristic called
a. lethal dose
b. history
c. usefulness
d. impact
e. persistance
E
Farmers need to make many decisions about how they grow their crops. One of these decisions is whether to use synthetic fertilizer or organic fertilizer, such as manure. An advantage of using synthetic fertilizer instead of organic fertilizer is that _______________
a. Synthetic fertilizer can provide more targeted macronutrients to the crops
b. Synthetic fertilizer remains in the soil longer than organic fertilizer does, reducing the volume needed and, therefore, the cost to the farmer
c. Synthetic fertilizer adds to soil texture and increases the soils water-holding capacity
d. Organic fertilizer runs off more readily into waterways, leading to nutrients overload.
A
All of the following are alternatives to using pesticides, except
a. rotation crops planted in a field each year
b. Provide homes for pest enemies
c. Use sex attractants to lure pests into their traps
d. Bring in natural enemies
e. freeze the pets
D\
The best way to maintain soil fertility is through.
a. applying animal manure
b. applying commercial inorganic feed
c. applying organic fertilizer
d. soil conservation
e. using low till planting
C
Farmers use various methods of irrigation on crops. Which of the following statements correctly pairs an irrigation method with an advantage or disadvantage
a. Drip irrigation is readily used in large scale farming because of the low cost associated with this method
b. Flood irrigation is often used in agricultural fields, however, it increases surface erosion and salinization of the soil
c. Furrow irrigation is a method in which farmers plant two different types of crops in alternating strips which increases productivity.
d. Spray irrigation loses the least amount of water to evaporation
B
Which of the following best describes the advantages and disadvantages of drip irrigation
a. This method is suitable for a range of topographies and is easy to operate, but it requires a high initial investment in machinery
b. this method most efficiently delivers water directly to plants roots compared with other methods, and wastes less water, but it may be too costly for farmers in developing countries to use.
c. This method delivers water to the field by pipes and water flows directly over the soil but there is a large amount of runoff.
d. This method applies water directly to trenches dug in the soil and is cost effective but water is often lost to evaporation.
B
some individuals in a population have genetic traits that enhance their ability to survive and produce offspring, a process called
a. natural selection
b. adaptability
c. genetic drift
d. mutation
e. scientific theory
a. natural selection
For natural selection to occur, an adaptive trait
a. must be to a physical trait
b. must be to a physiological trait
c. must be to a psychological trait
d. must be to a heritable trait
e.. must not be to a heritable trait
d
biological evolution by natural selection is when genes _______, individuals ________, and populations _______.
a. evolve; mutate; are selected
b. are selected; mutate; evolve
c. mutate; evolve; are selected
d. evolve; are selected; mutate
e. mutate; are selected; evolve
e
the number of different species an ecosystem system contains is its
a. speciation
b. species evenness
c. species niche
d. species richness
e. habitats
d
A species' way of life or role in a community contains is its
a. role
b. habitat
c. ecological niche
d. geographical location
e. ecological job
c
A species with a broad niche is considered a(n)
a. endemic species
b. endangered species
c. specialist species
d. native species
e. generalist species
e
a species in an ecosystem that plays a central role in health of that ecosystem, and whose removal may cause the collapse of the ecosystem is called a(n)
a. foundation species
b. indicator species
c. native species
d. keystone species
e. specialist species
d
A species in and ecosystem that shapes the communities by creating and enhancing habitats in ways that benefit other species is called
a, foundation species
b. indicator species
c. native species
d. keystone species
e. specialist species
a
pollen-eating and fruit-eating bats, especially on tropical islands, are
a. alien species
b. indicator species
c. generalists
d. keystone species
e. invasive species
c
Because birds live in every climate and biome, and because they are easy to track and count, they serve as excellent
a. keystone species
b. scapegoats
c. indicator species
d. aesthetic indicators
e. habitat determinators
c
the biggest problem with invasive species is that in the new location is that in the new they often
a. are always bigger than native species
b. have no population controls such as predators
c. are always stronger than native species
d. have higher reproductive rates than native species
e. evolve more quickly than native species
b
which of the following is not a characteristic of a successful invader species
a. high reproductive rate with short generation time
b. long lived
c. high genetic variability
d. high dispersal rate
e. specialist
e
Phytoplankton are most abundant in the upper few hundred feet of most bodies of water because
a. they can readily hide from predators there
b. sunlights does not penetrate to great depths
c. as primary producers, they must be accessible to many organisms
d. they are benthic organisms
e. they feed on zooplankton, which are found in the top layer of water
b
for which of the following reasons do small isolated islands have a greater rate of species extinction than larger, less isolated islands
a. small isolated islands are more likely to receive migrating species
b. small isolated islands provide opportunities for a greater diversity or species
c. because of their size, small isolated islands accumulate more species by chance
d. small isolated islands have a lower availability or recourses
d
involves the gradual establishment of biotic communities in lifeless area where there is no soil in terrestrial environment or bottom sediment in an aquatic ecosystem
primary succession
Any heritable trait that enables an organism to survive through natural selection and reproduce better under prevailing environmental conditions is called
adaption
If a species of frog becomes threatened by a change in environmental conditions, the species would be considered a(n)
indicator
a series of communities with different species developing in places containing soil or bottom sediment is known as
secondary succession
the number and abundance of a species present in an ecosystem refers to
species richness
refers to the range of conditions that an organism can endure before injury or death
range of tolerance
the biotic potential of a population is
a. the current rate of growth in a population
b. determined by subtracting immigration minus emigration
c. the future growth rate of a population
d. the maximum reproductive rate of a population
e. an expression of how many off spring survive to reproduce
d
Which of the following problems is best addressed with contour plowing?
a. Eutrophication
b. Denitrification
c. The pesticide treadmill
d. Soil erosion
e. Soil salinization
D
Which of the following practices is consistent with the production of organic crops according to the United States Department of Agriculture?
a. Using sodium nitrate as a fertilizer on green, leafy vegetables
b. Using strychnine (synthetic poison) to prevent buildup of aphid populations in field crops.
c. Using chemicals known as pheromones (Natural plant hormones) to disrupt insect mating cycles.
d. Using sewage sludge to improve the fertility and structure of soil
e. Using genetically modified plant varieties that kill insects that chew their leaves.
C
Which of the following is the most likely to minimize soil erosion?
a. High yield agriculture
b. Deforestation
c. Herbicide use
d. Annual plowing
e. Cover crops
E
Farmers use various methods of irrigation on crops. Which of the following statements correctly pairs an irrigation method with an advantage or disadvantage?
a. Drip irrigation is readily used in large-scale farming because of the low cost associated with this method.
b. Flood irrigation is often used in agricultural fields, however, it increases surface erosion and salinization of the soil.
c. Furrow irrigation is a method in which farmers plant two different types of crops in alternating strips which increase productivity.
d. Spray irrigation loses the least amount of water to evaporate
B
Which of the following describes a fundamental characteristic of the green revolution in food resources?
a. The addition of calorie, fat, and fiber percentage to the information provided on food package labels.
b. The application of higher levels of organic fertilizers to increase rice production
c. The discovery that chlorophyll adds nutritional value to wheat, rice, and sorghum.
d. The development of new strains of crops with higher yields
e. Deforestation to provide field crops with increased sunlight for photosynthesis
D
This type of irrigation, often used in orchards growing tree crops, distributes water to plants through small parallel channels between crop rows but often leads to increased soil erosion in the field.
a. Drip irrigation
b. Flood irrigation
c. Furrow irrigation
d. Spray irrigation
e. Center pivot overhead irrigation
C
Slash and burn agriculture leads to increase of which gas in the atmosphere?
a. H2O vapor
b. CO2
c. O2
d. N2O
B
Which of the following statements best describes the most unsustainable method of clear-cutting forests to harvest timber?
a. All but the healthiest trees are removed from a forest
b. The highest-value trees are selectively removed from a forest
c. All the shade-intolerant trees in a small section of the forest are cut down
d. All the trees in a forest are cut down and removed in one operation.
D
Overgrazing of grasslands can lead to reduced range quality. Two major effects of overgrazing are?
a. Erosion and desertification
b. Higher productivity and ammonification
c. Higher fire potential and increased productivity
d. Oil compaction and subsidence
e. Eutrophication and increased methane production
A
Which of the following best describes a disadvantage of using genetically engineered crops over crops that are not genetically modified?
a. Genetically engineered plants can decrease the genetic diversity of the crop
b. Genetically engineered plants require greater use of pesticides.
c. Genetically engineered plants require more land to grow on.
d. Genetically engineered plants are more likely to spread disease throughout the crop.
A
Overgrazing of public land by privately owned livestock is an example of the?
a. Right of eminent domain
b. rule of seventy
c. principle of manifest destiny
d. swapping of debt for nature
e. tragedy of the commons
E
Switching from customary large scale agriculture practices to which of the following is most likely to reduce the exposure farmworkers and nearby residents to toxic chemicals?
a. No till cultivation
b. Integrated pest management
c. Contour plowing
d. Crop dusting
e. Use of cover crops
B
what is true of carrying capacity
a. some ecosystems carrying capacity is reduced by human activuty
b. all of the above
c. non of the above
d. species populations often stabilize near the carrying capacity of the ecosystem
e. it is determined both by the avialabilty of resources and of space
b
in 1950, a country had a total fertility rate of 5.9 in 2010 the total fertility rate of the country was 2.3 which of he following is most likely the reason for the change in total fertility rate
a. there were lower infant mortality rates as a result of increased access to heathcare
b. families had limited access to family planning and contraceptives
c. the country shifted to a more agricultural based-economy and the need for child labor decreased.
d. women had increased educational opportunities and had children later in life
d
the most common form of population dispersion found in nature is
clumping
Which of the following accurately describes a benefit of concentrated animal feeding operations (CAFOs)?
a. Concentrated animal feeding operations produce a large amount of manure, which is then often held in large manure lagoons.
b. The animals raised in concentrated animal feeding operations are usually grass-fed and therefore less susceptible to disease.
c. Concentrated animal feeding operations are efficient and relatively low-cost facilities that help keep consumer costs low.
d. When animals are kept in large concentrations in a small area, the water quality of local waterways is protected form excess runoff.
C
The land on an 100 acre farm is equally suited for grazing cattle and growing corn. Of the following ways of distributing land use, which would produce the greatest number of calories of human consumption?
a. Acres of cattle- 100, Acres of corn- 0
b. Acres of cattle- 80, Acres of corn- 20
c. Acres of cattle- 50, Acres of corn- 50
d. Acres of cattle- 20, Acres of corn- 80
e. Acres of cattle- 0, Acres of corn- 100
E
which of the following is an example of a density independent population control
a. weather and climate
b. parasitism
c. competition for resources
d. mutualism
e. infectious disease
a
the k selection reproductive strategy maximizes survival of offspring by producing
a. many off spring with high levels of parental care
b. few offspring with low levels of parental care
d. many offspring without parental care'
b
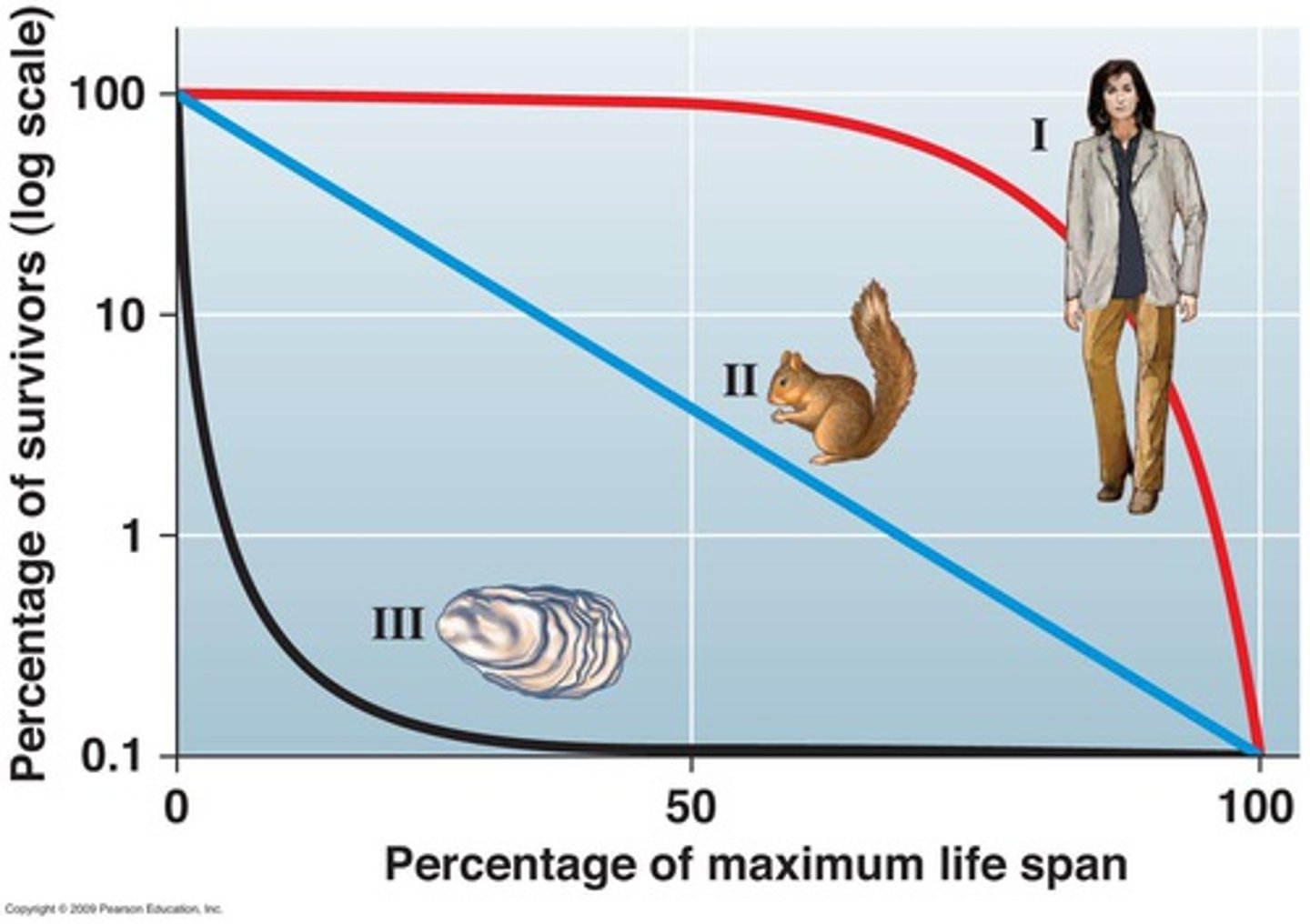
the survivorship curves of many fishes oysters and crabs are
a. convex, starting flat then dropping steeply
b. reflect low death rates during early and middle life and high death at old age
c. are concave dropping sharply at the left and then flattening out
d. reflect steady death rates throughout life
c
which of the following statements about India is TRUE
a. women do not have birth control
b. their is a strong preference to female children
c. their are many cultural norms that favor big families
d. women have a average of 2.1 children
e. government pensions have discouraged need for large families
c
the replacement level fertility rate is ____ for developed countries and ____ for developing countries
a. 2.5, 2.0
b. 1.8, 2.1
c. 1.6, 1.9
d. 2.0, 2.5
e. 2.1, 2.5
e.
which of the following is TRUE of demographic transition as countries become industrialized
a. birth and death rates rise at the same time
b. death rates drop, followed by birth rates
c. birth rates drop followed by death rates
d. neither birth nor death rates fall
e. birth and death rates fall at the same time
b
infant mortality rate refers to the number of children per 1,000 births that die
a. in their first month
b. before 6 months
c. before birth
d. before their first birthday
e. by their fifth birthday
d
if every woman on earth had no more than an average of 21 children during their reproductive years, the human population would continue to rise for how long
a. 20 years
b. 150 years
c. 5,000 years
d. 50 years
e. 5 years
d
the total fertility rate is
a. the average number of children born to women in their reproductive years
b. the number if children born to a woman during her lifetime
c. the number of children a couple must bear to replace themselves
d. the number of live births per 100 people
a.
a country has a current population of 144 million and a growth rate of 0.93% how long will it take for the population to reach 575 million people
A
which of the following is an example of a density dependent population control
a. habitat destruction
b. fire
c. predation
d. floods
e. plaque
c
During an El Nino event, warm
D
Amount of sunlight is important environmentally because it determines the amount of ___________ done by plants, which influences the ___________ productivity which is the bases of food webs and food chains and the amount of energy available in biomes and ecosystems
photosynthesis, gross
During an El Nino Trade winds crossing the pacific are (stronger/ weaker) than normal
weaker
During an El Nino Peru and Southern US typically get (more/less) rainfall than usual
more
The layer below the crust that is a liquid on which the tectonic plates are above is known as the __________
asthenosphere
The liquid later in the earths interior (not asthenosphere)
outer core
During an El Nino Average global temperatures are usually (warmer/cooler) than usual
warmer
During an El Nino Australia and Indonesia experience (more/less) rainfall than usual.
less
During an El Nino rainfall is pushed (further inland/ further out to sea)
further inland
During an El Nino (more/less) upwelling of cold water in the east. This means (more/less) nutrients available for fish
more, less
The _________ of the earth causes our seasons
tilt
During and El Nino event, which of the following best describes conditions in the eastern part of the tropical pacific Ocean (near Peru and Equador)
a. Sea Surface Temp: Low, Rainfall: Low
b. Sea Surface Temp: Low, Rainfall: high
c. Sea Surface Temp: high, Rainfall: Low
d. Sea Surface Temp: high, Rainfall: high
e. Sea Surface Temp: high, Rainfall: normal
D
El nino and La nina are phenomena associated with changing ocean surface temperatures in the ________ Ocean.
Pacific
Describe one economic impact of El Nino
There will be a decline in fish population, making it harder for fishermen to make money
__________ is the earths main source of energy and is dependent on seasons and latitude or mathematically speaking solar radiation/area
Insolation
Along with the heat from solar radiation, the rotation of the Earth deflects as well . This deflection is known as the _________
Coriolis Effect
Describe one negative ecological impact of El Nino
Moisture from wind will not blow towards Australia and Indonesia resulting in droughts.
which of the following is NOT true of a r-selected species
a. offspring are large in number
b. they have a high rate of population increase
c. offspring are large in individual size
d. they are opportunists
e. they provide little to no parental care
c
which of the following shows the approximate concentration of CO2, N2, and O2 in dry air (respective order)
a. 78%, <1%, 21%
b. 43%, <1%, 56%
c. 36%, 8%, 56%
d. 10%, 70%, 20%
e. <1%, 78%, 21%
E