Binary+ Network Protocols
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This Text goes over Week 2 for IT Infrastructure and Networking- Components of a Computer
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
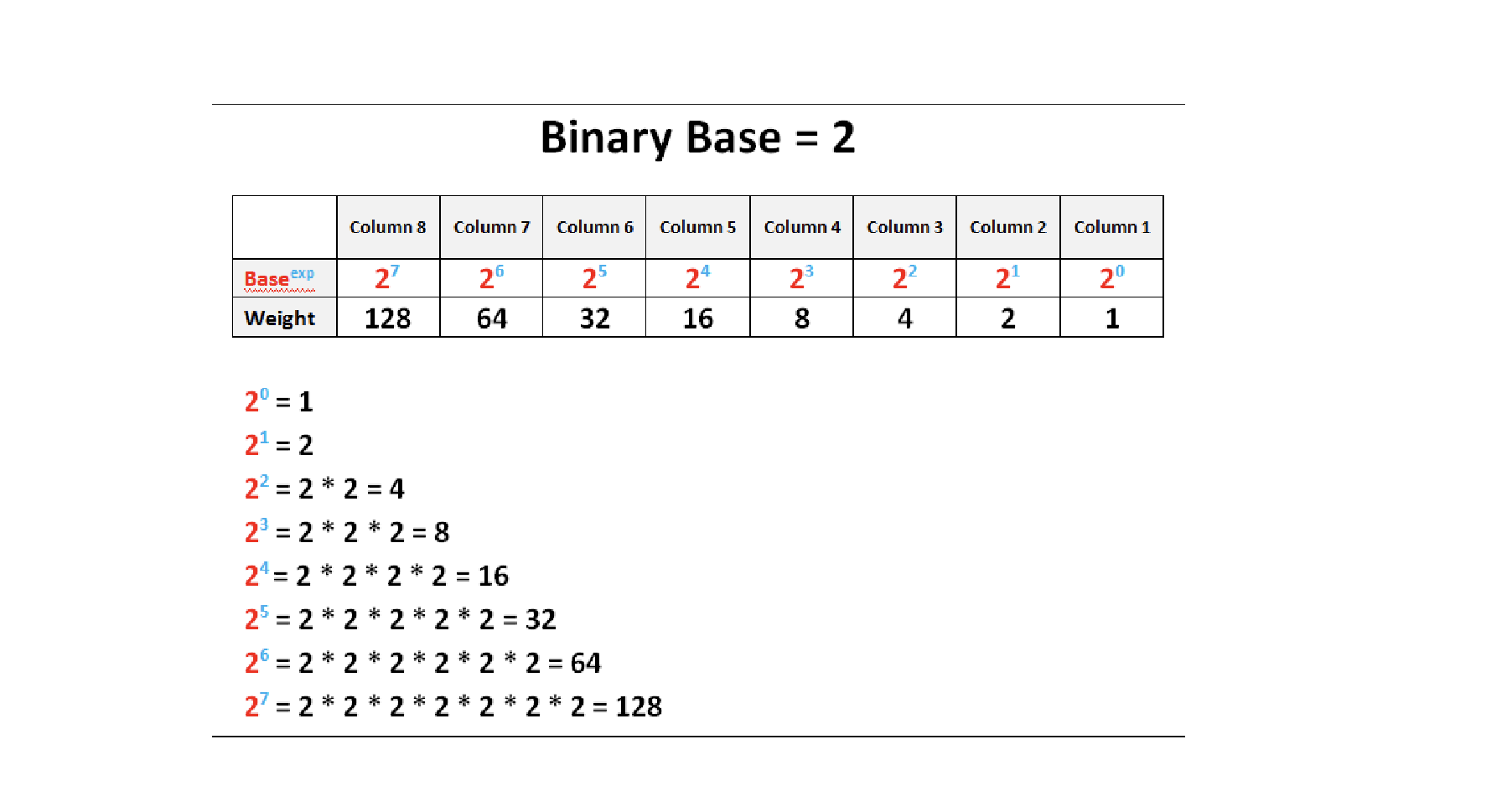
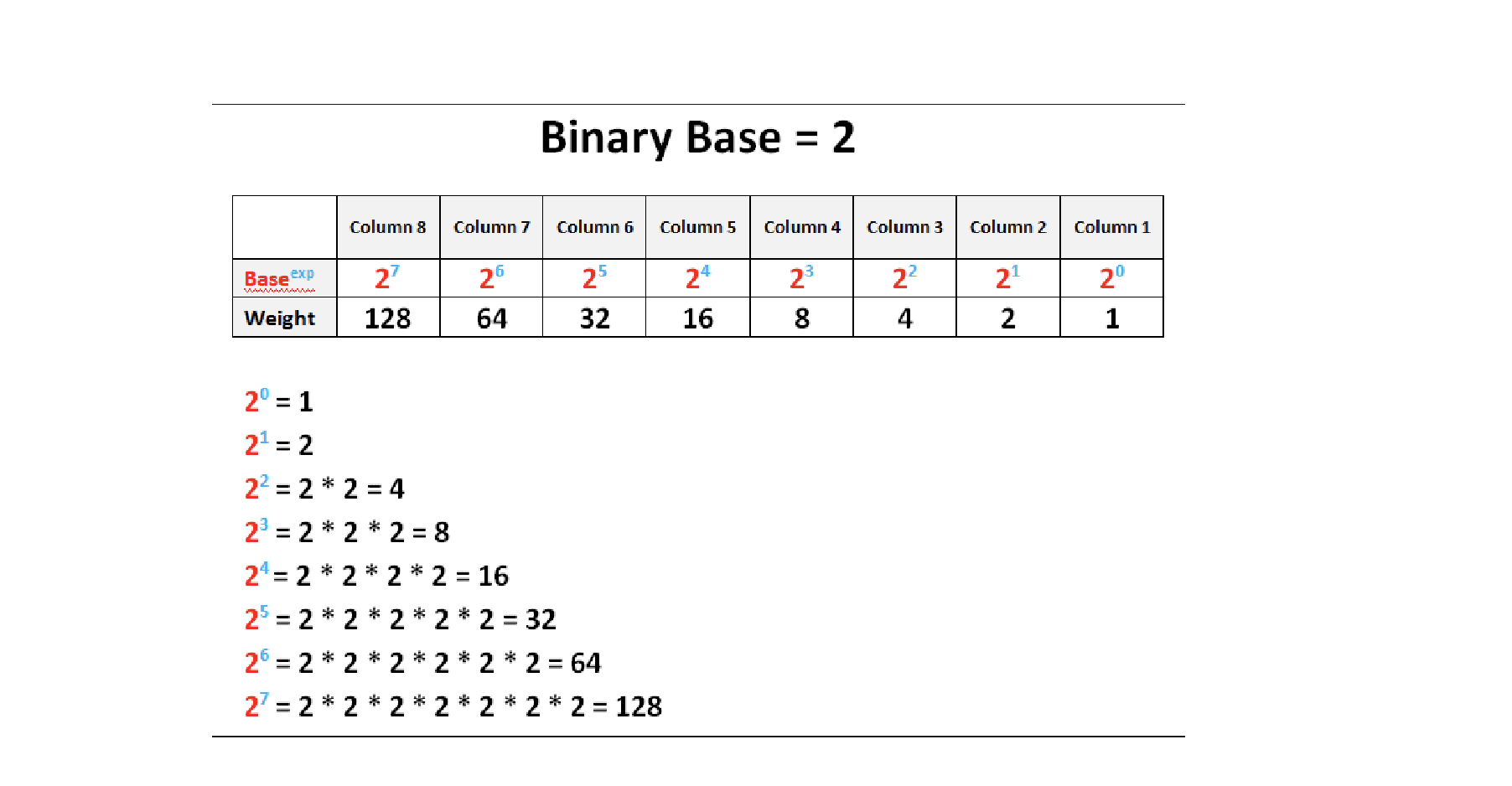
Bit
A binary digit, the smallest unit of data in computing.
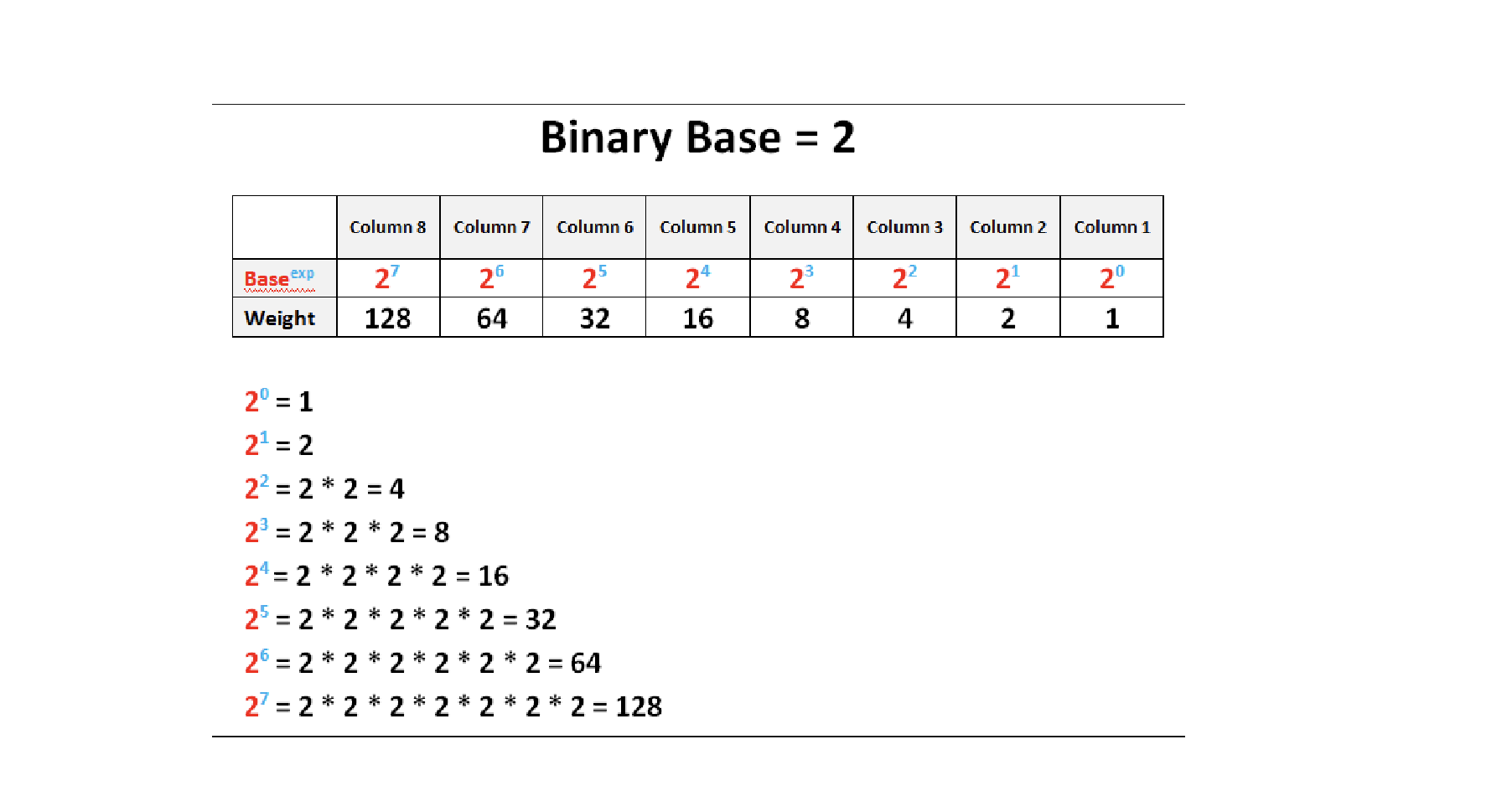
Binary System
The communication method used by computers, represented in a base-2 numeral system consisting of ones and zeros.
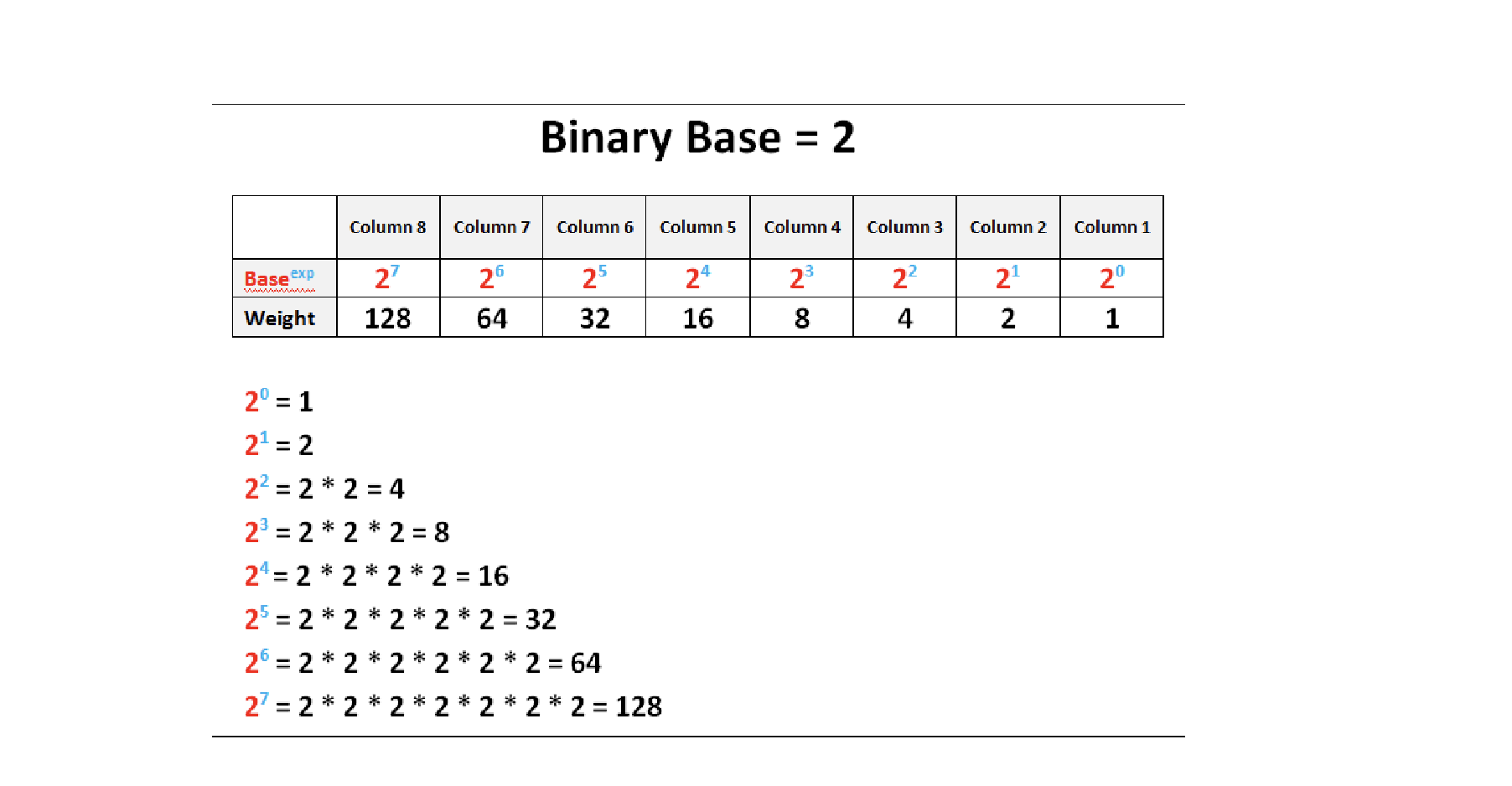
Byte
A group of 8 bits, capable of storing one character with 256 possible values.
Character Encoding
The process of assigning binary values to characters for computer understanding.
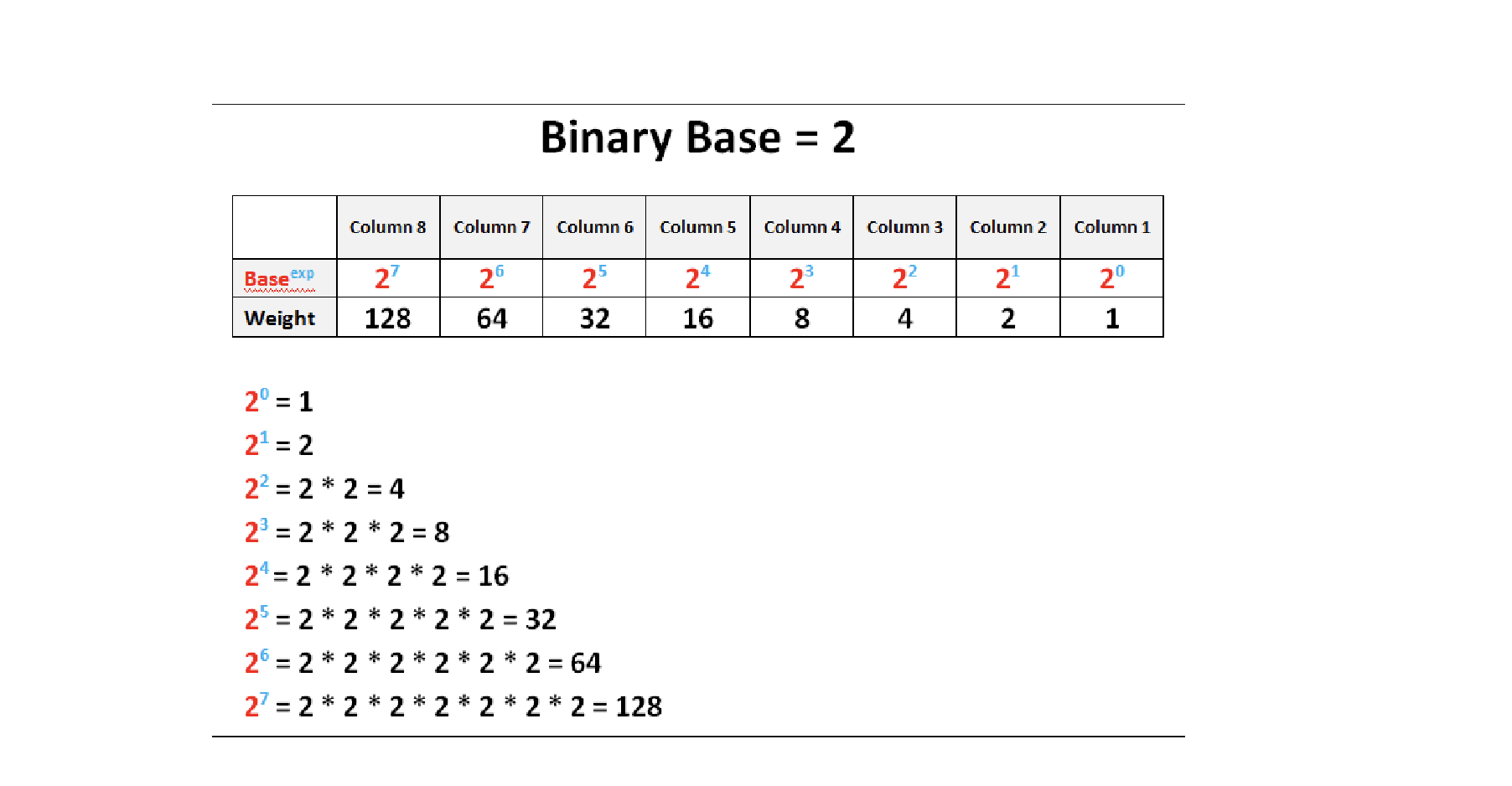
Decimal System
A numerical system based on the number 10, using powers of ten.
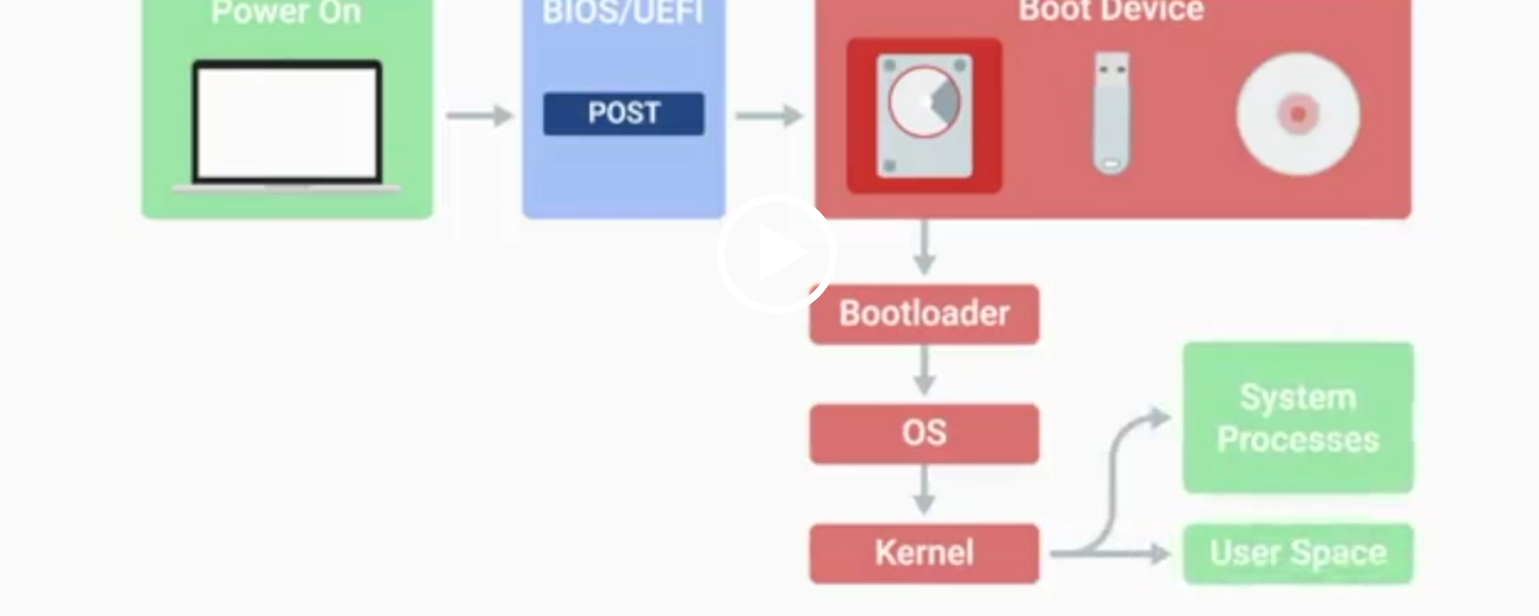
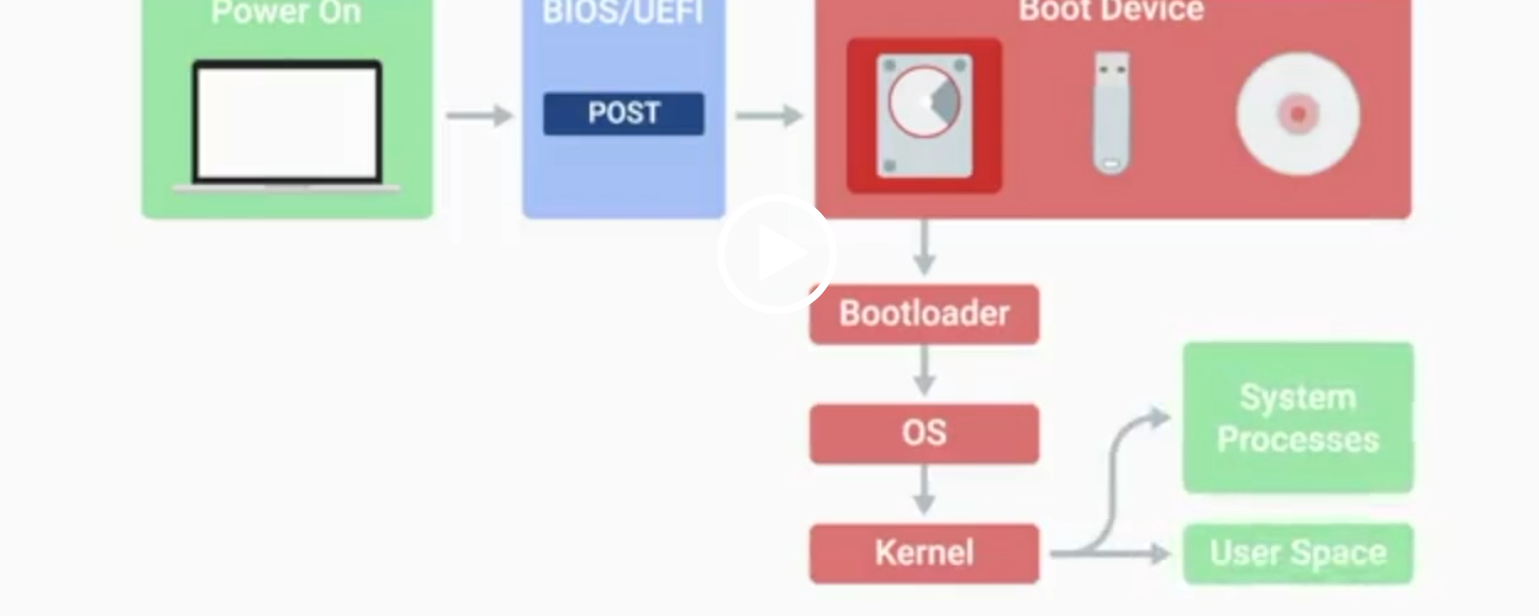
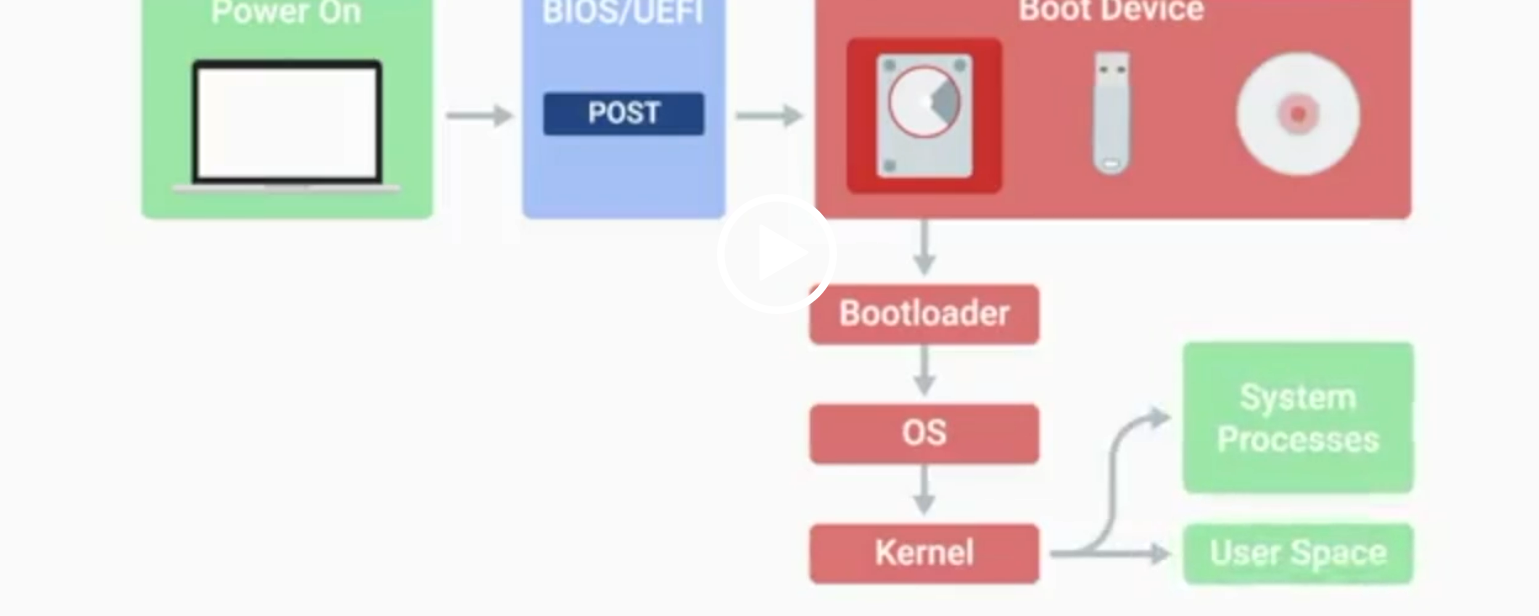
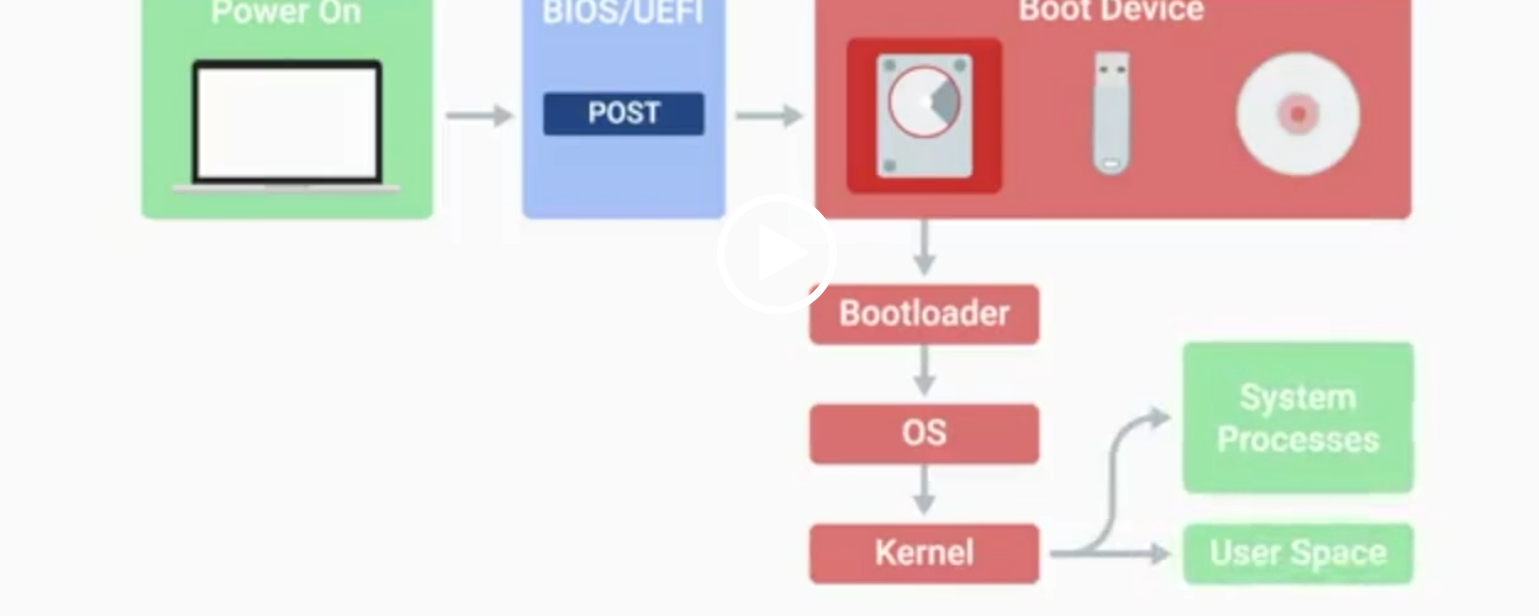
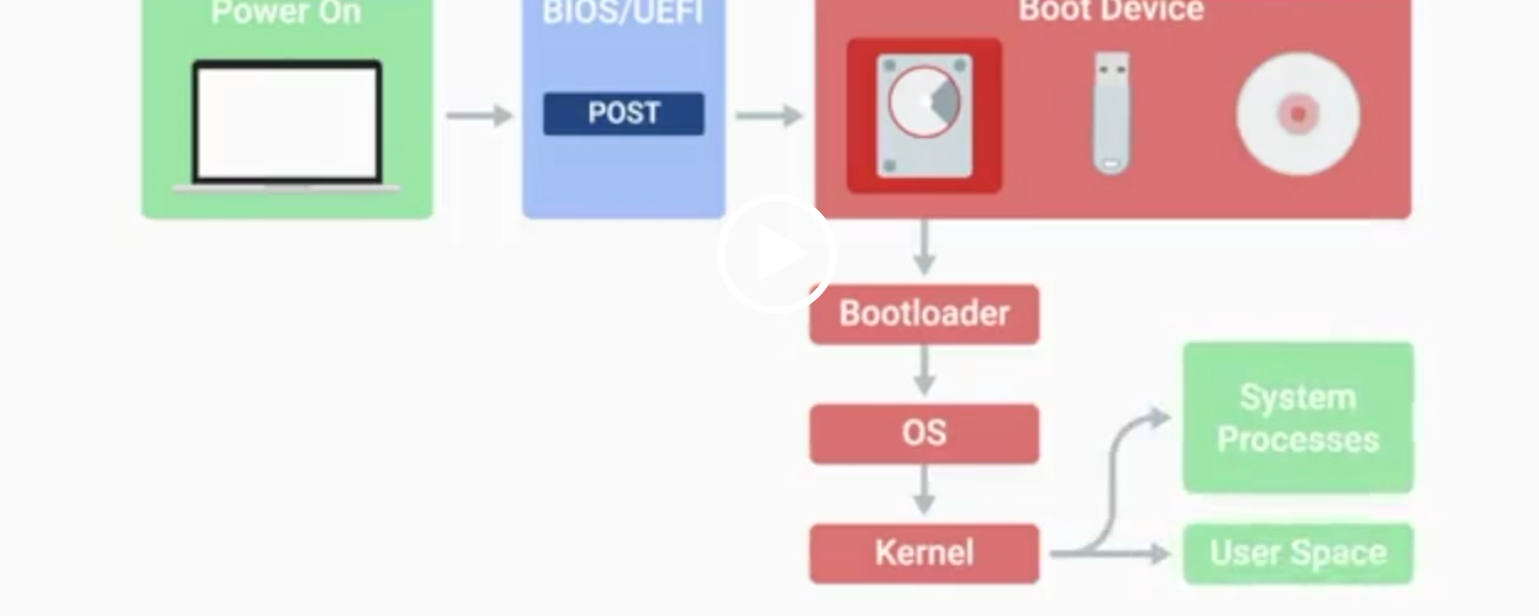
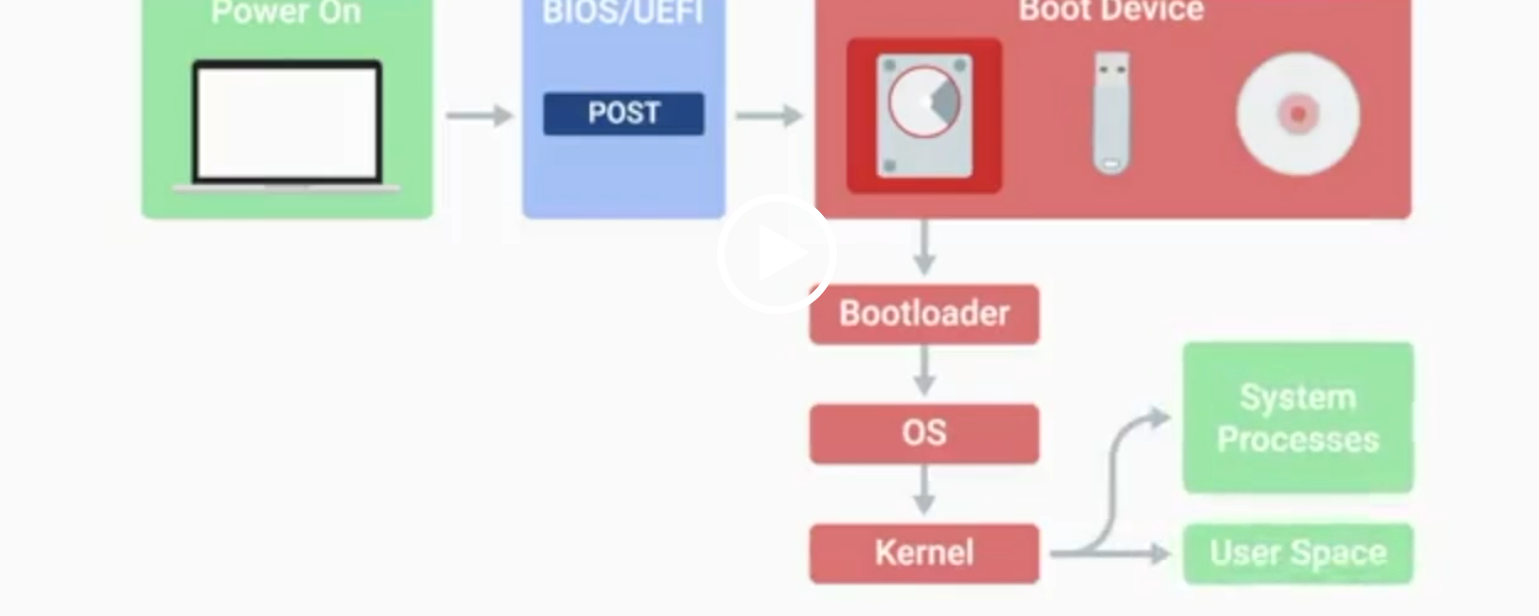
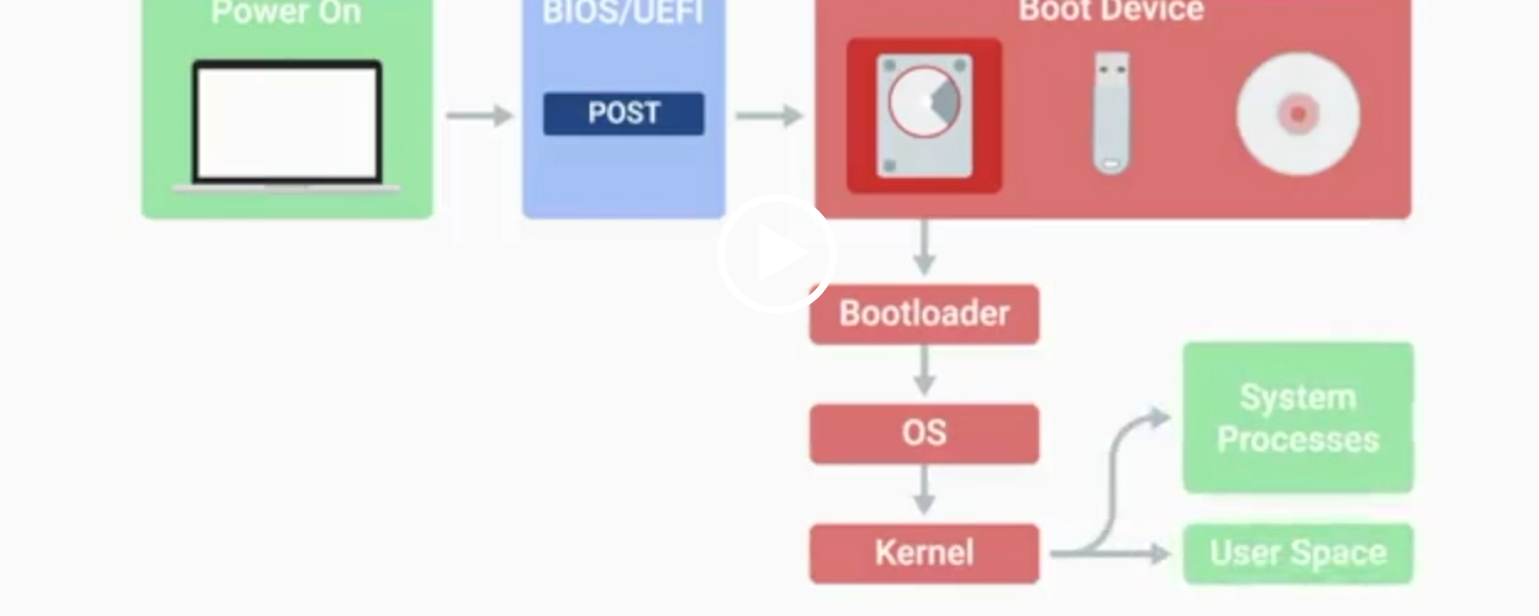
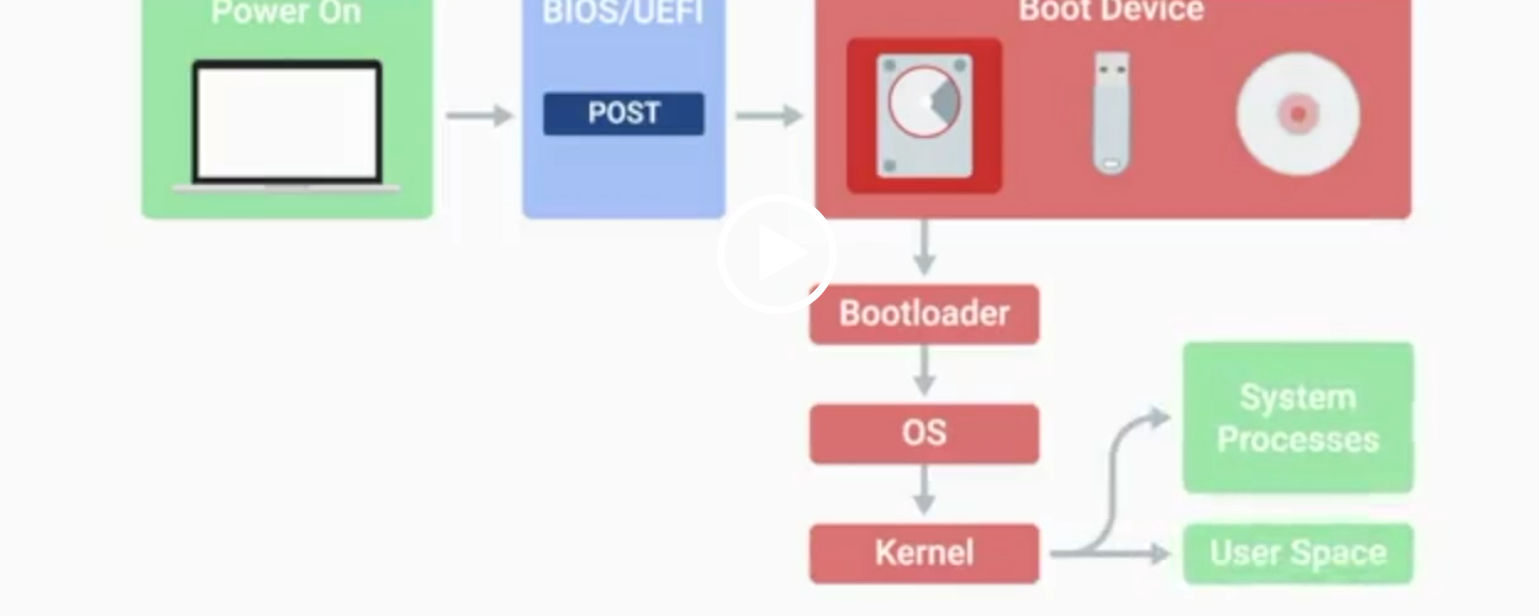
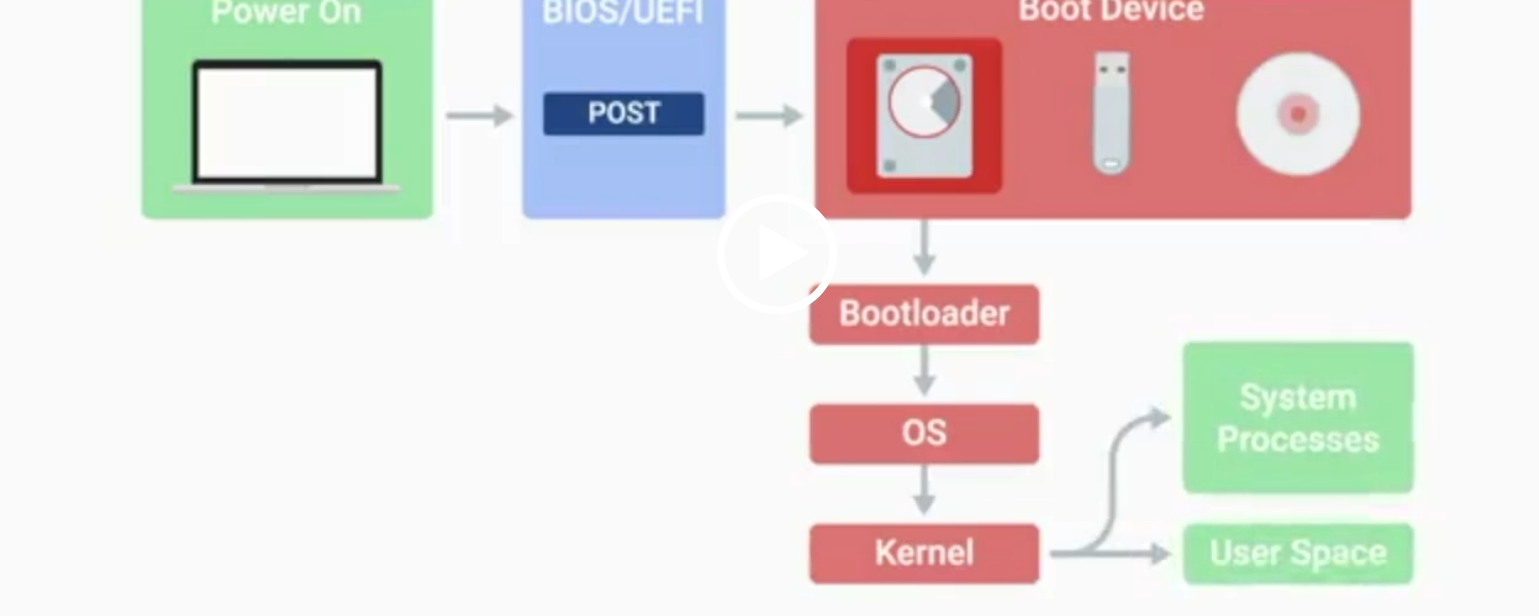
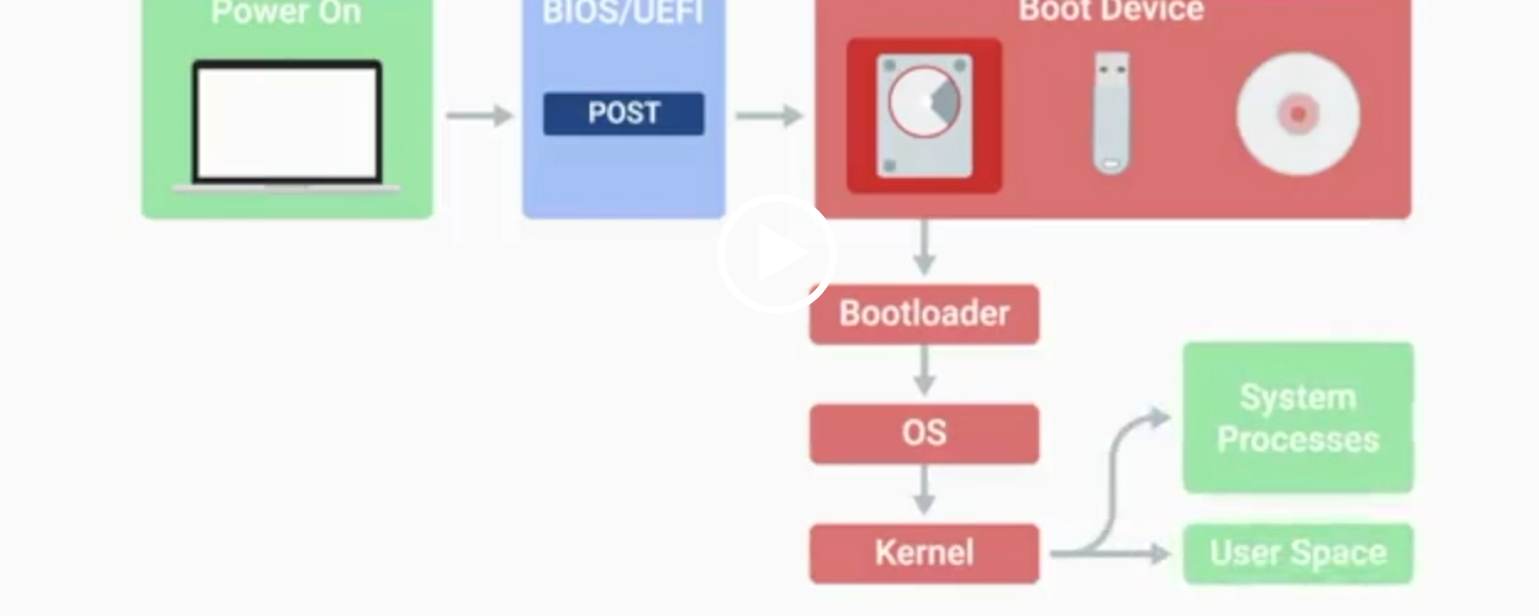
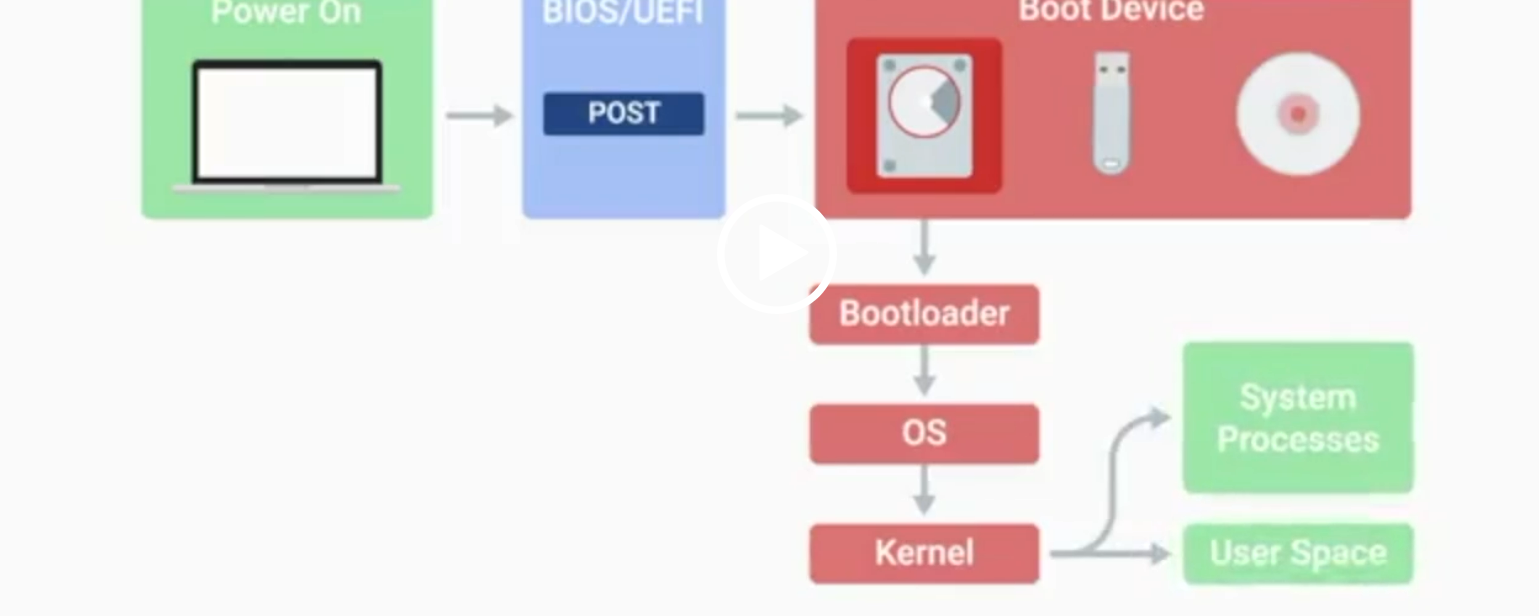
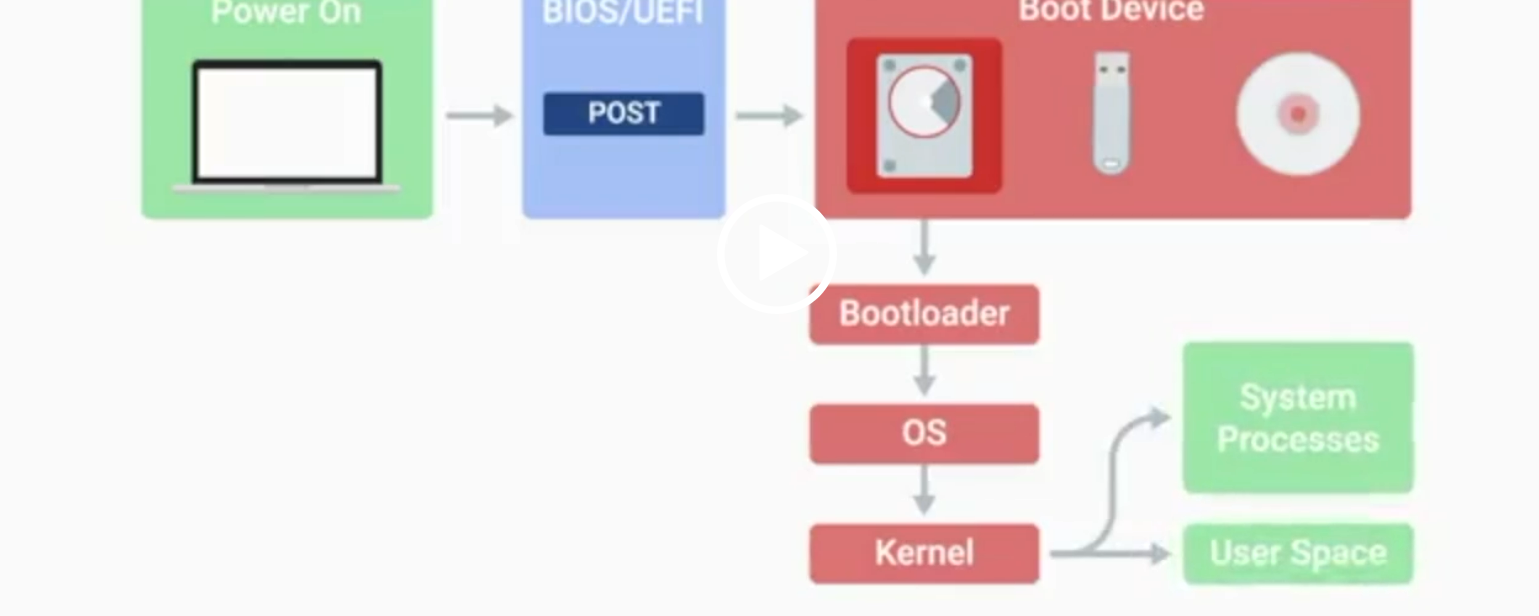
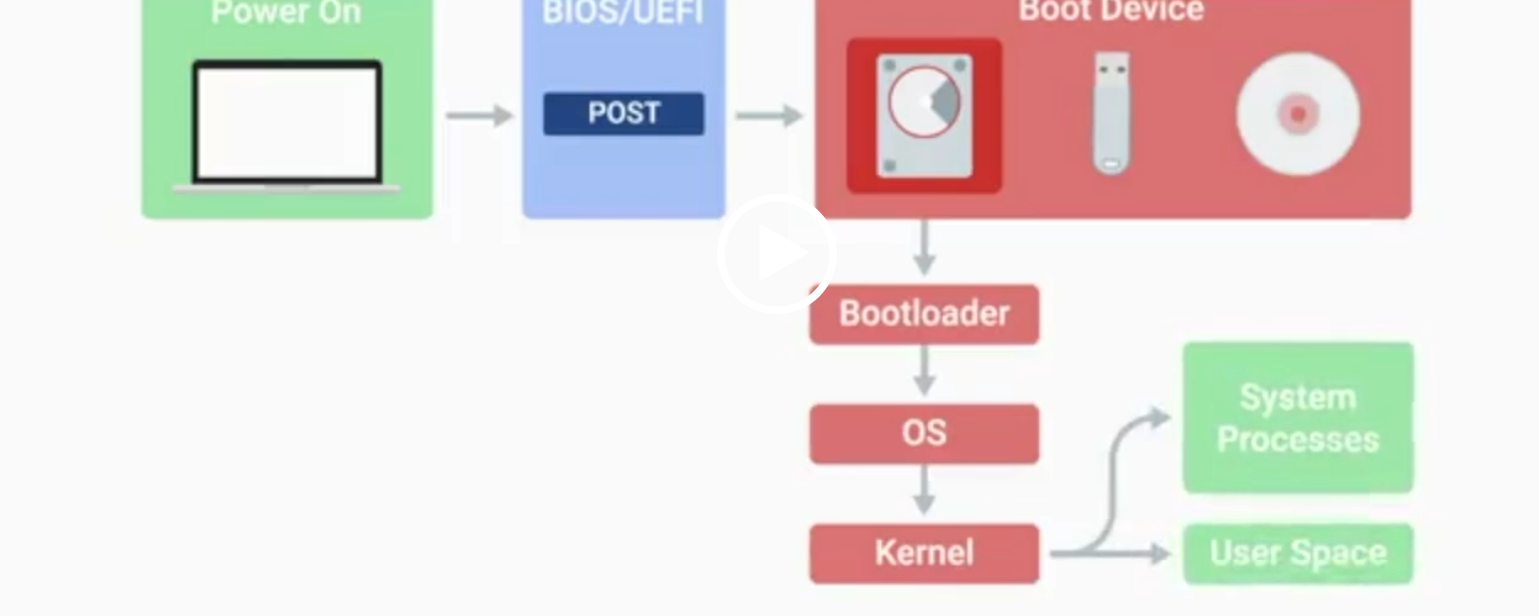
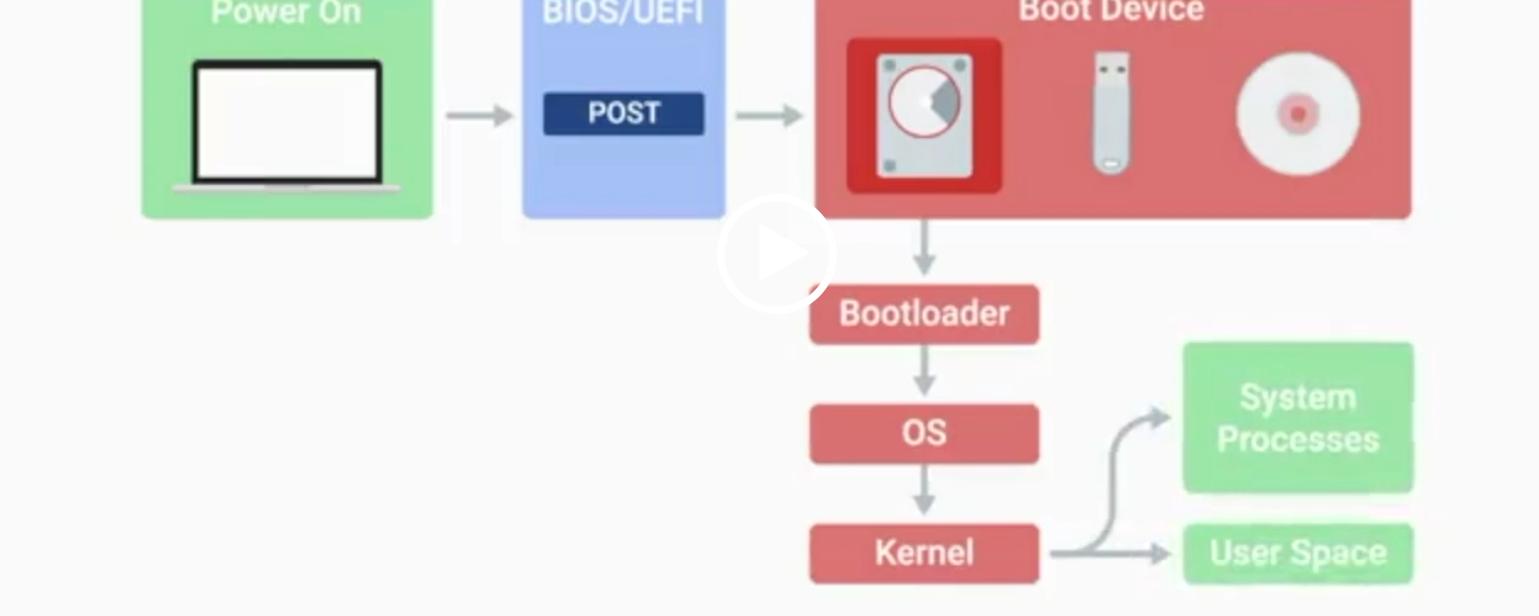
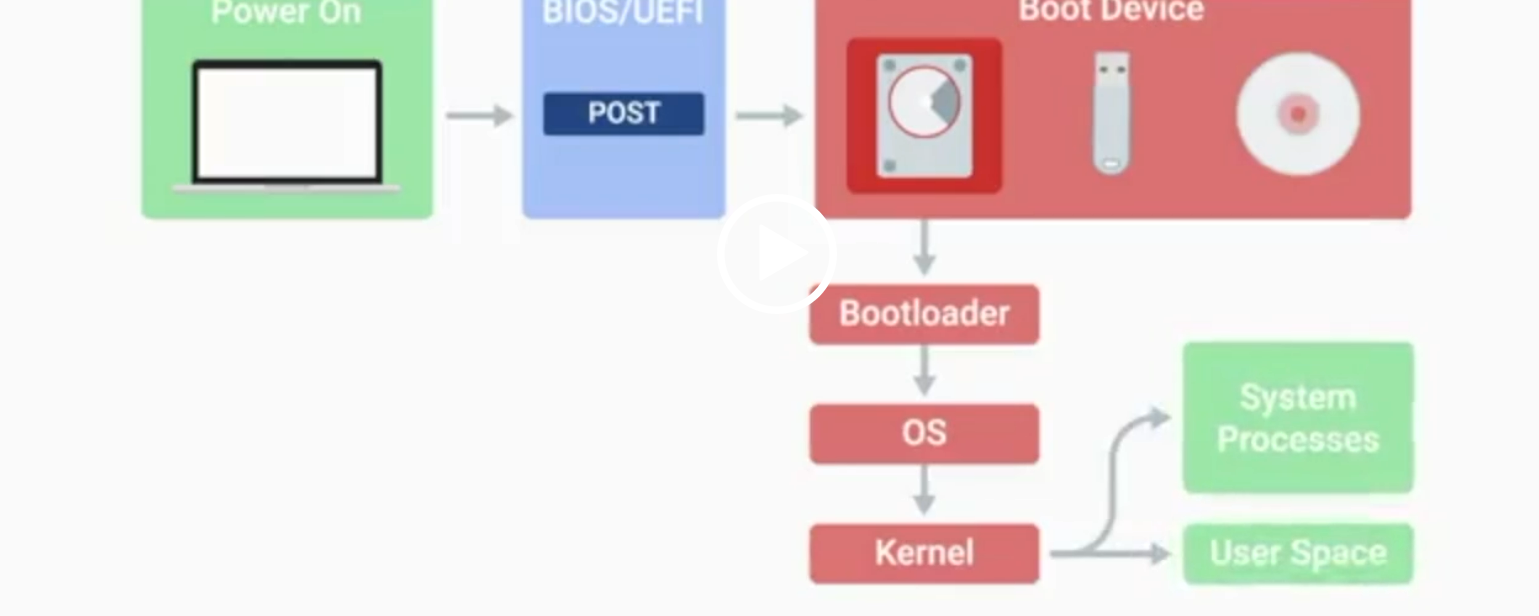
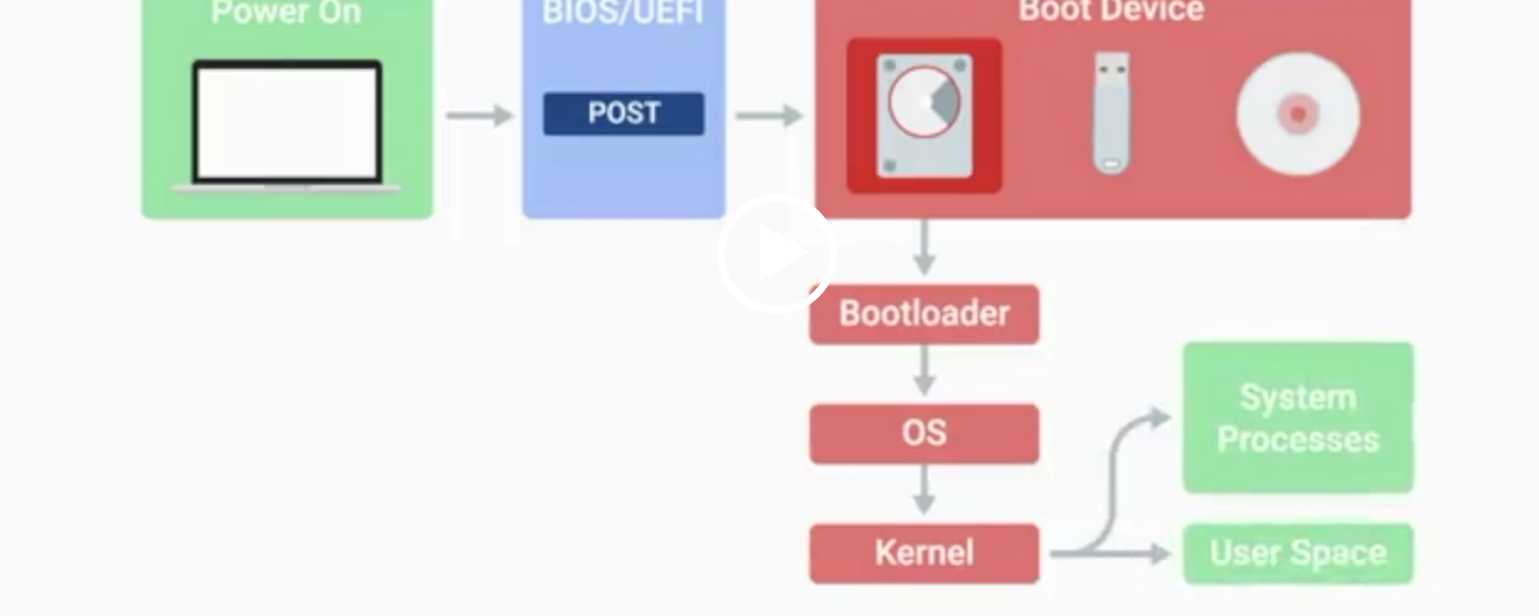
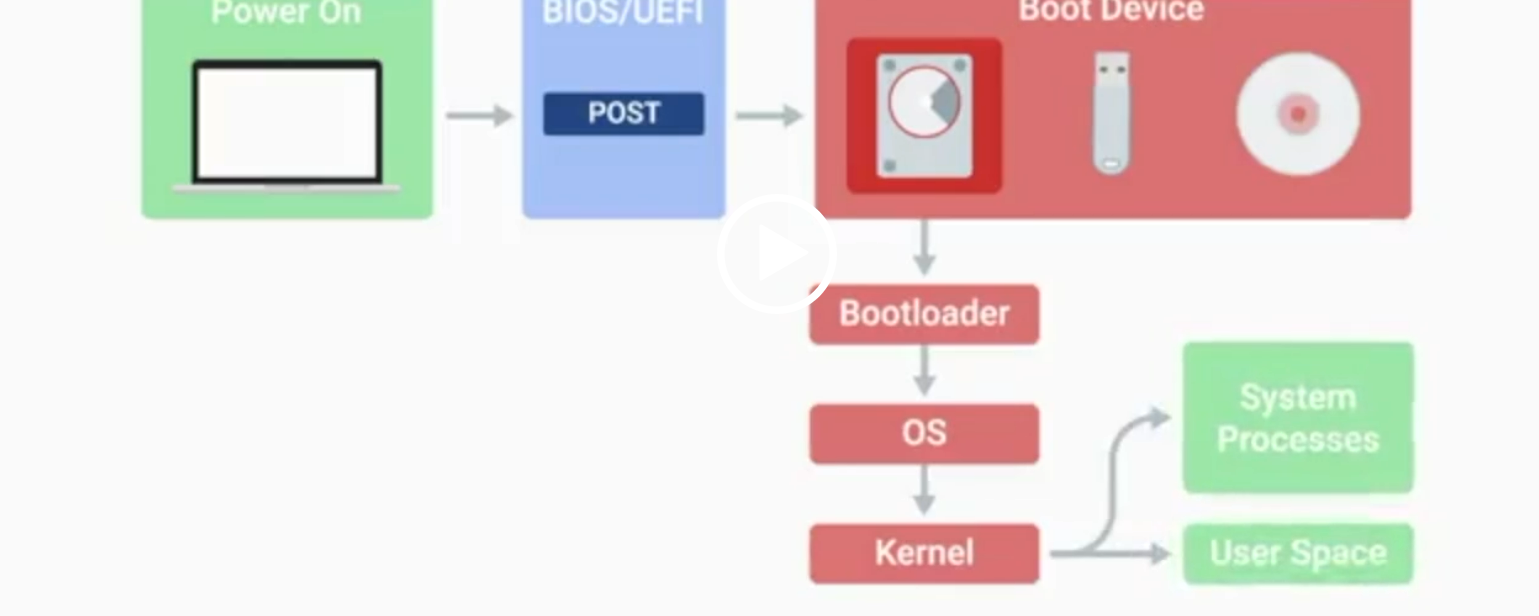
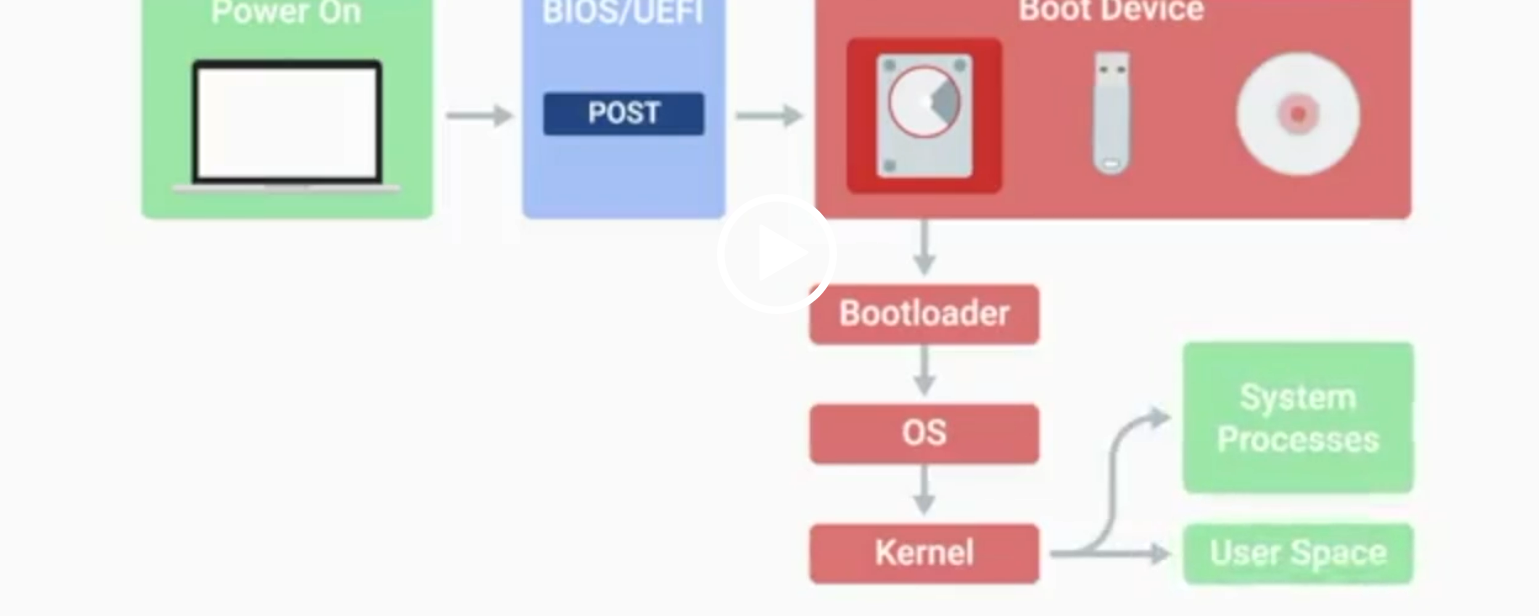
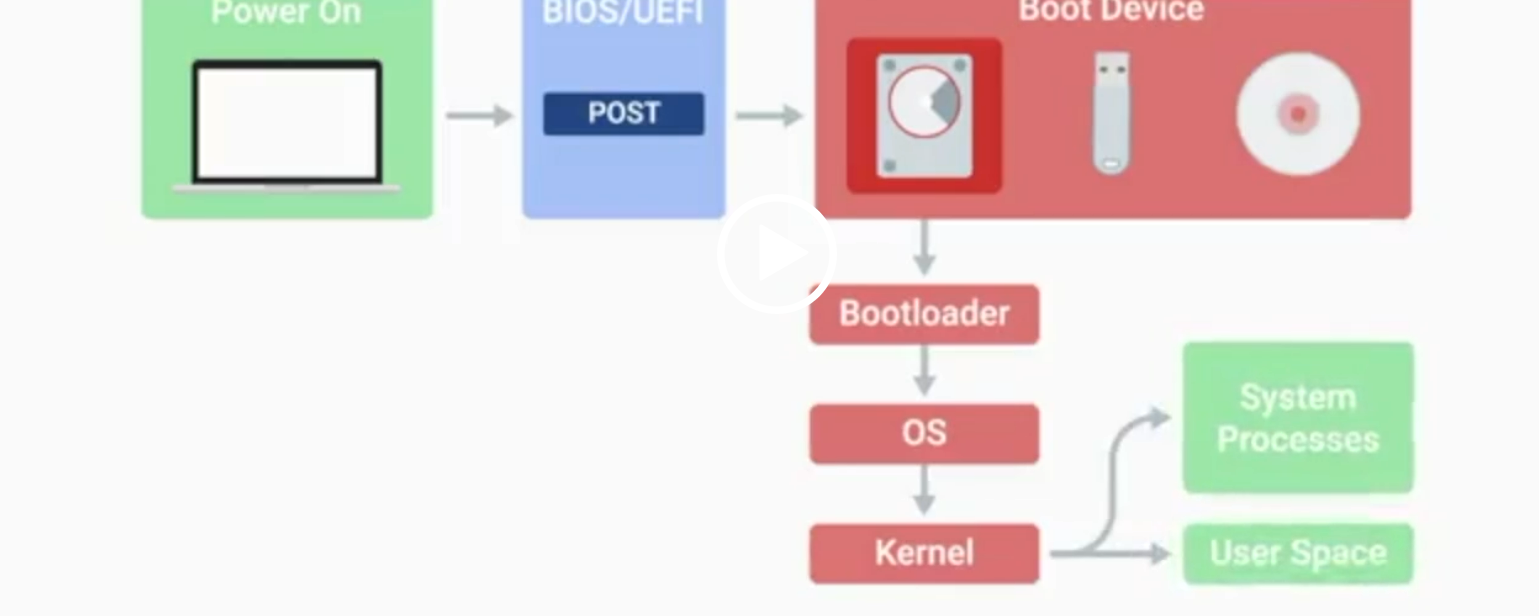
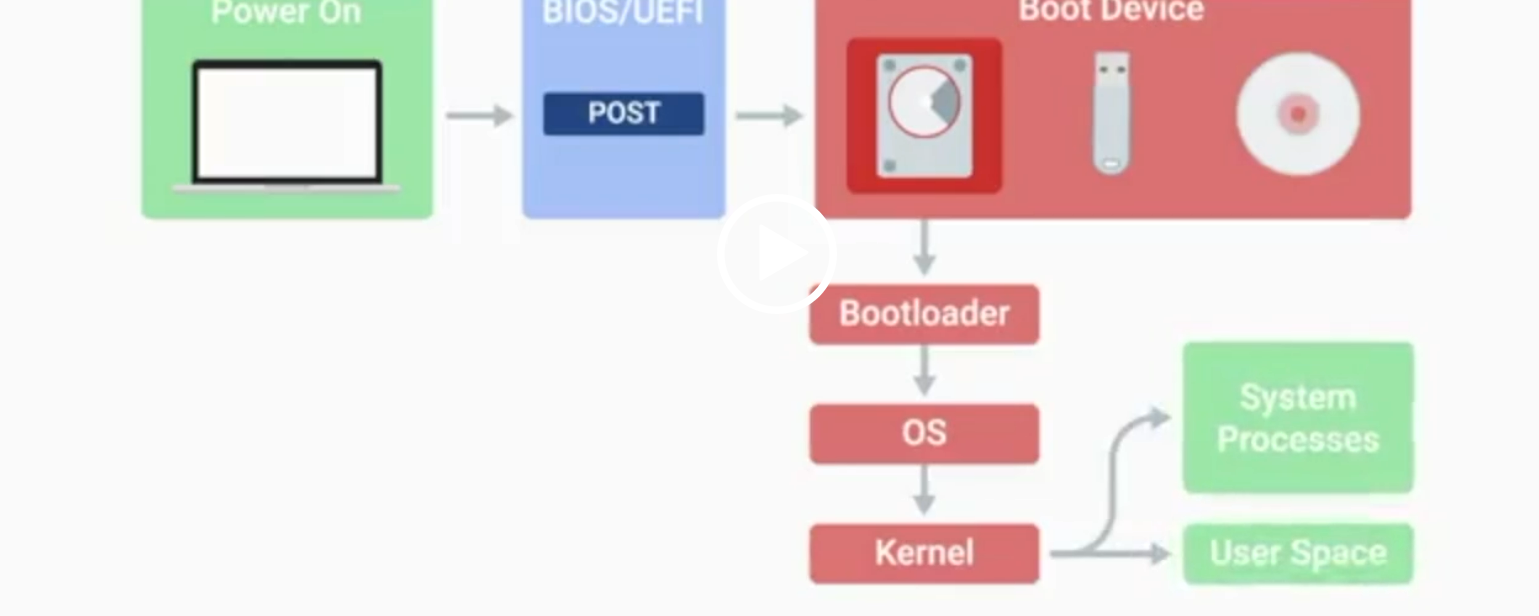
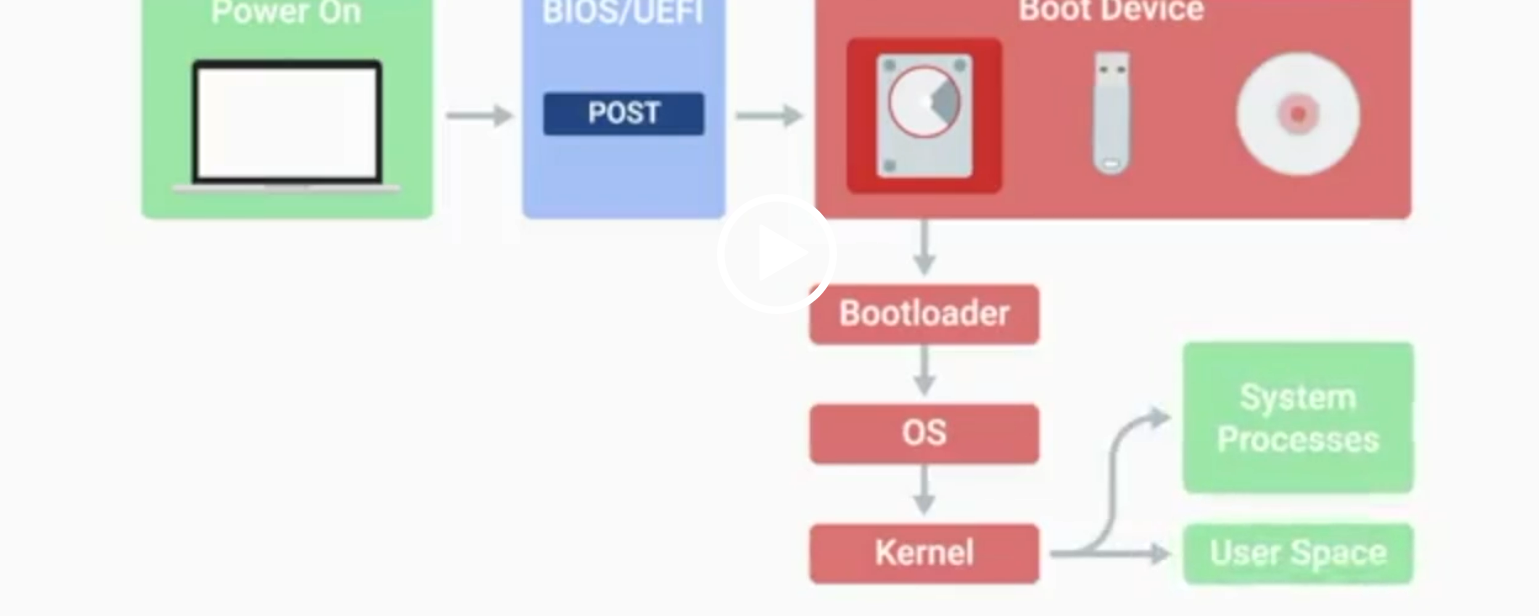
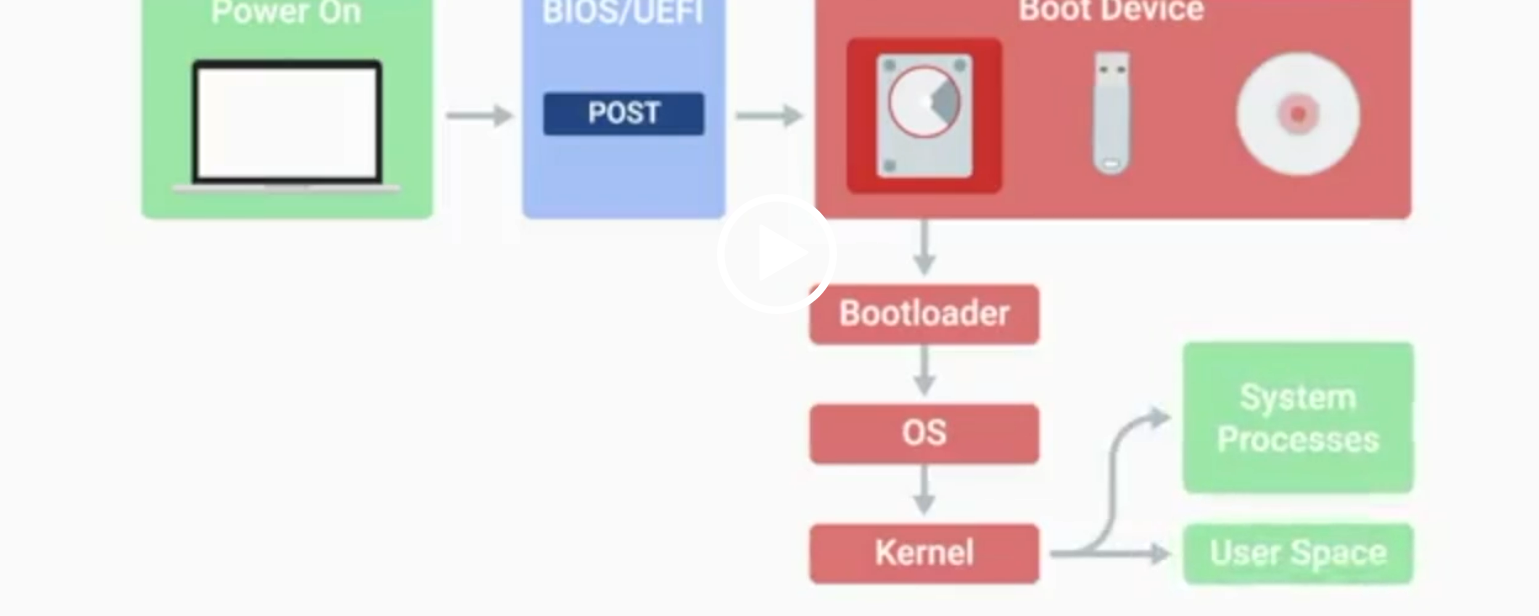
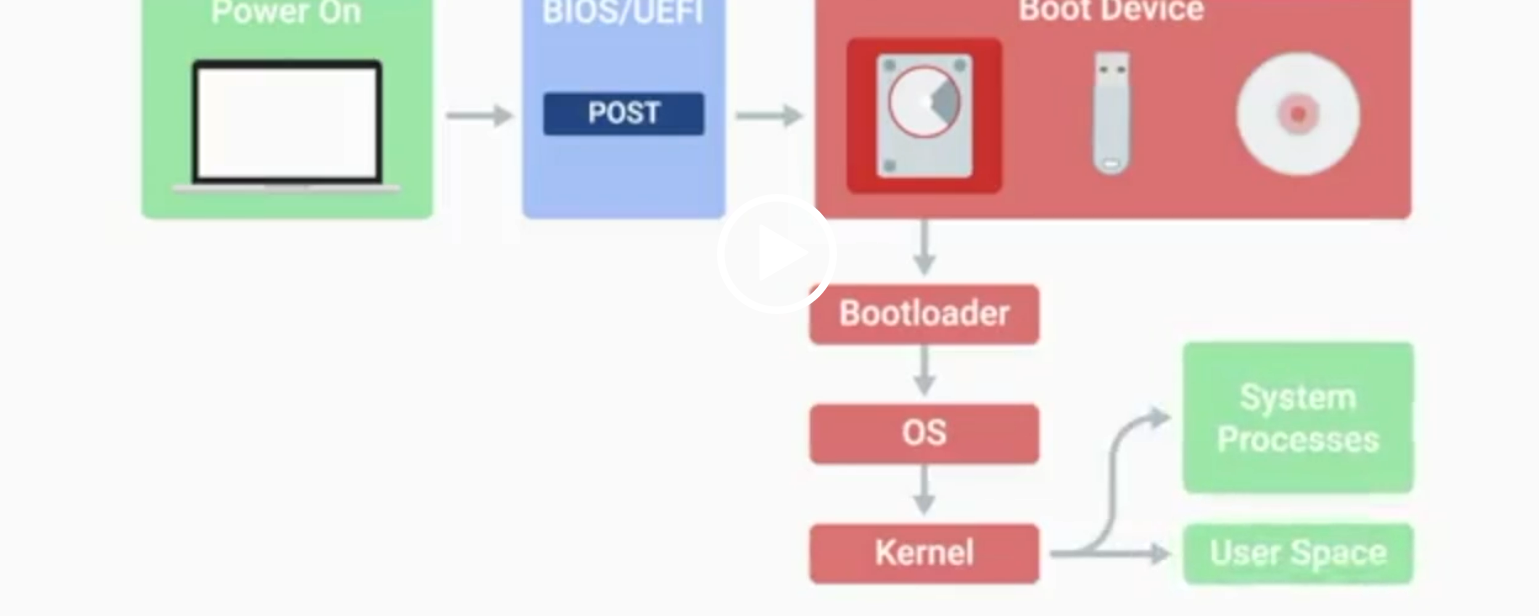
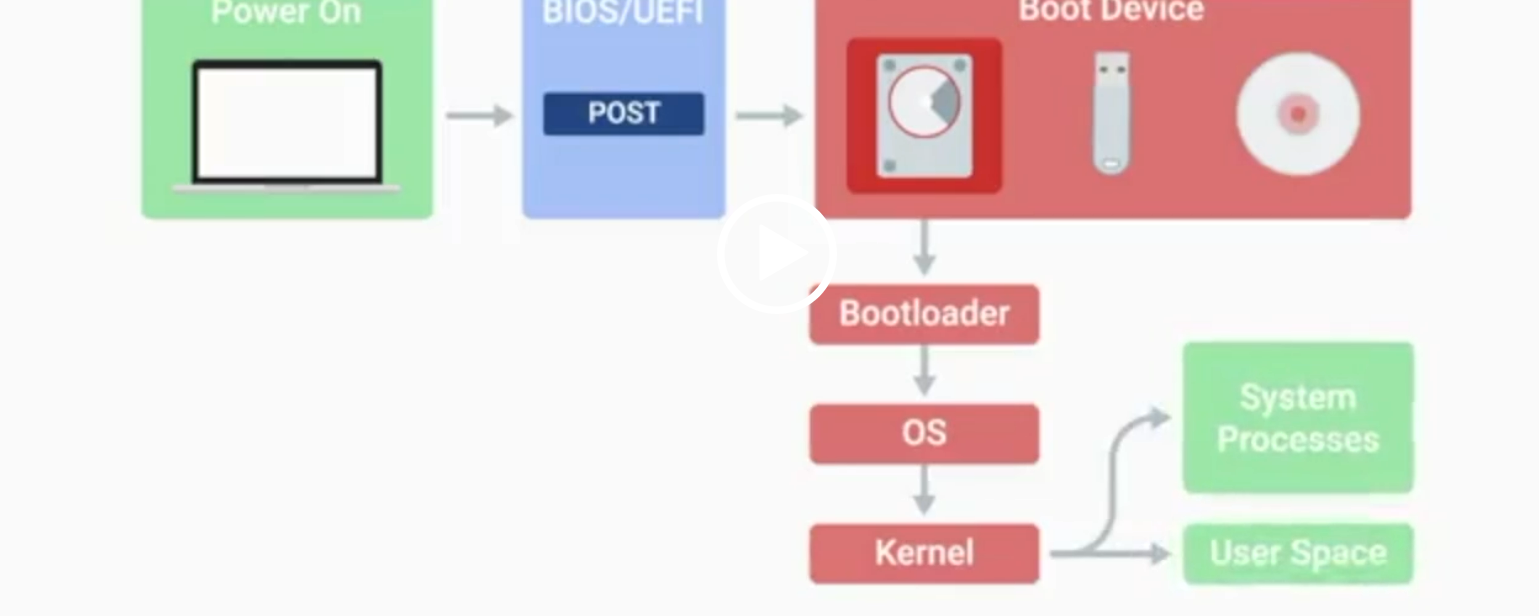
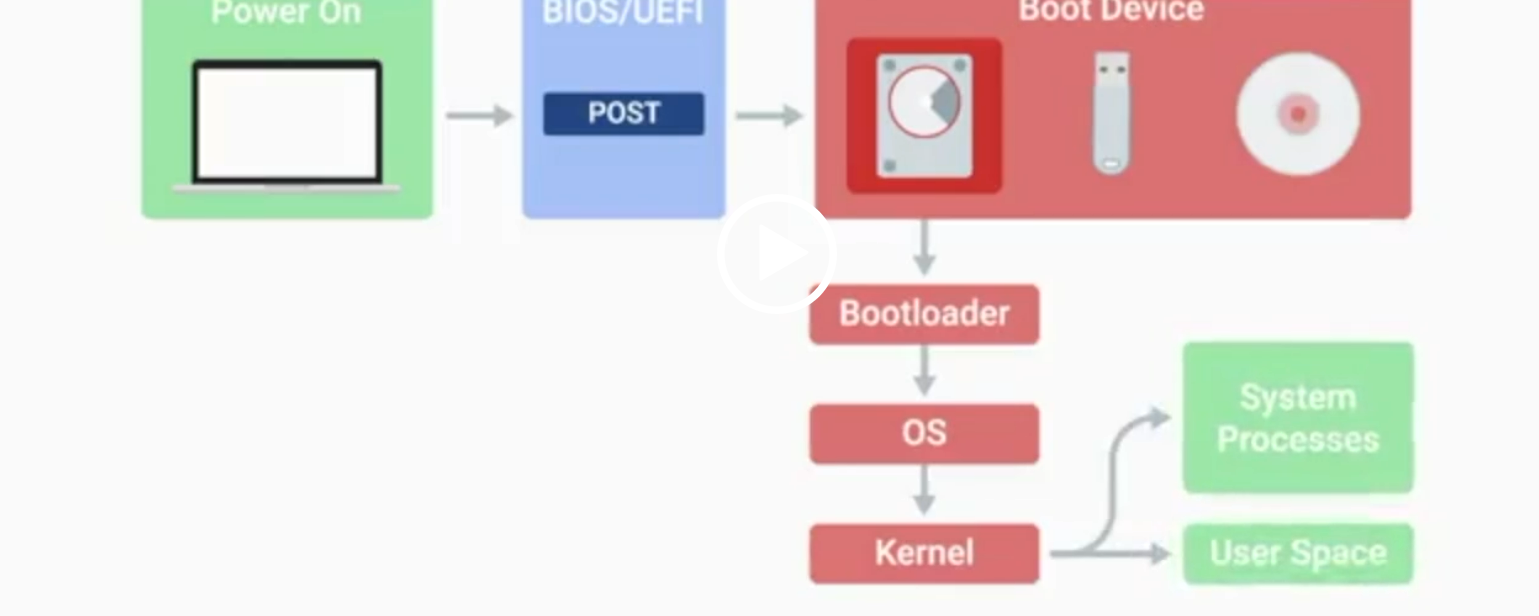
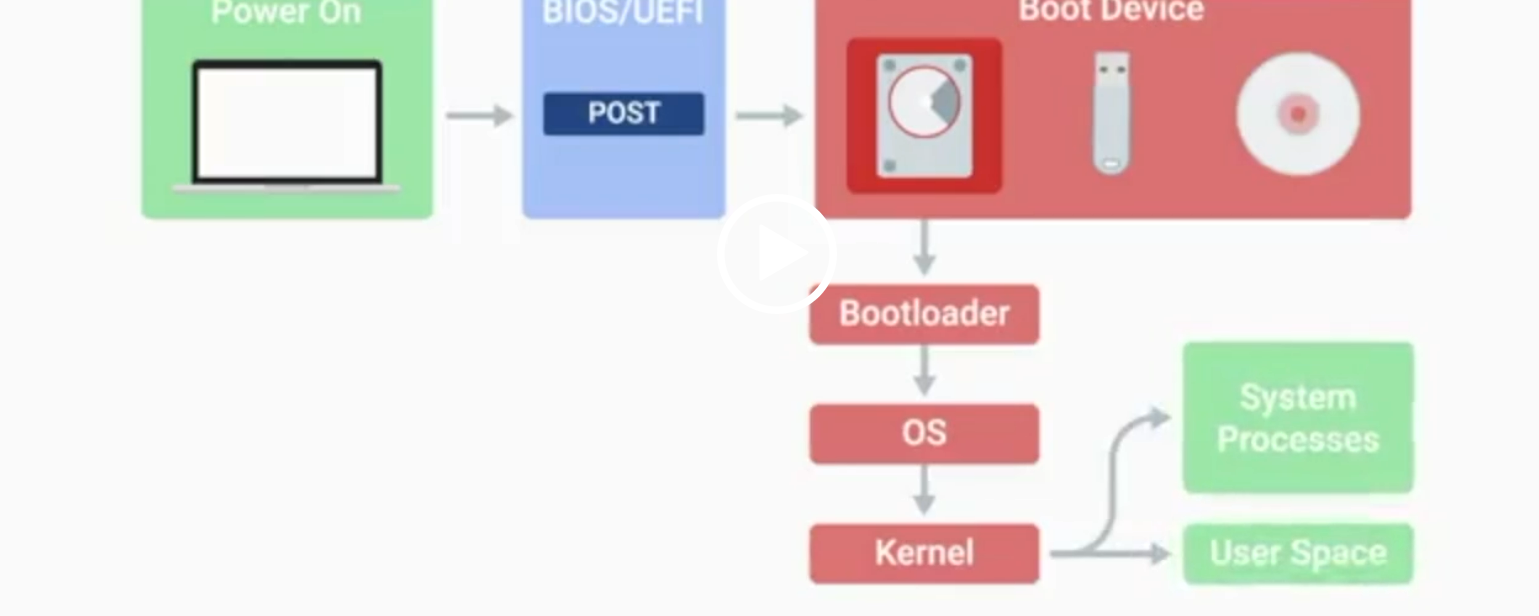
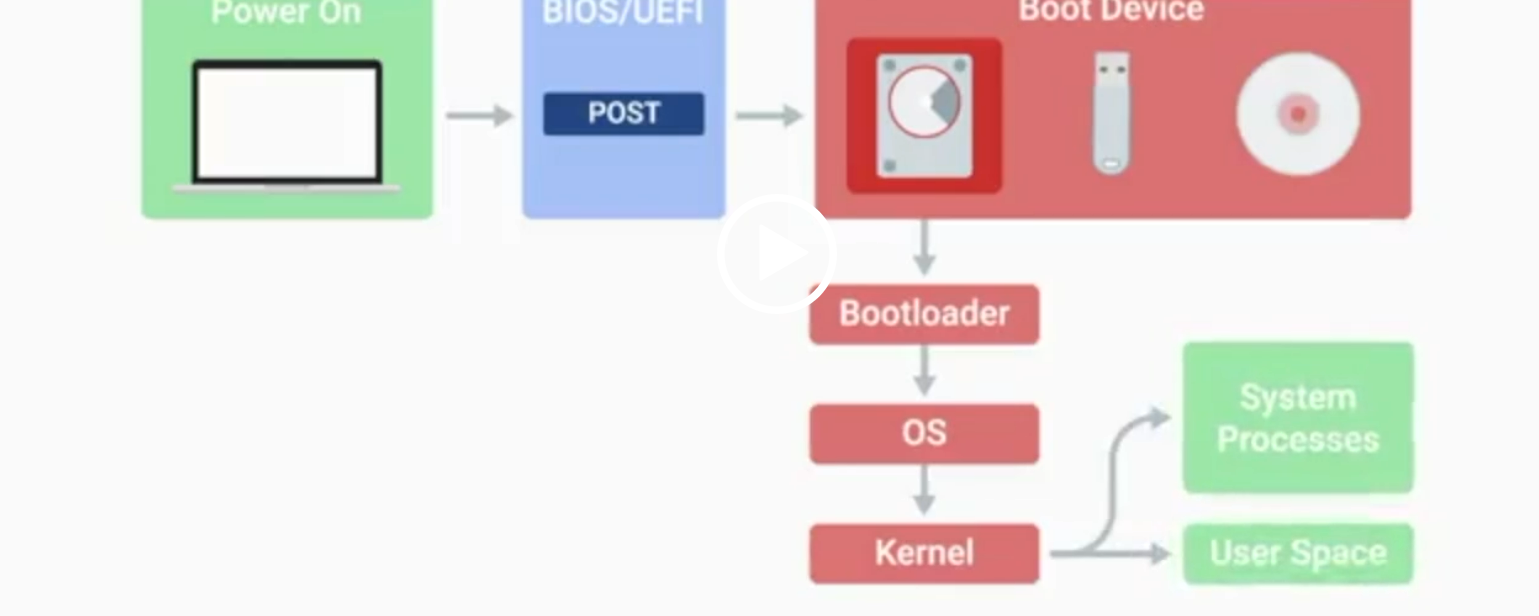
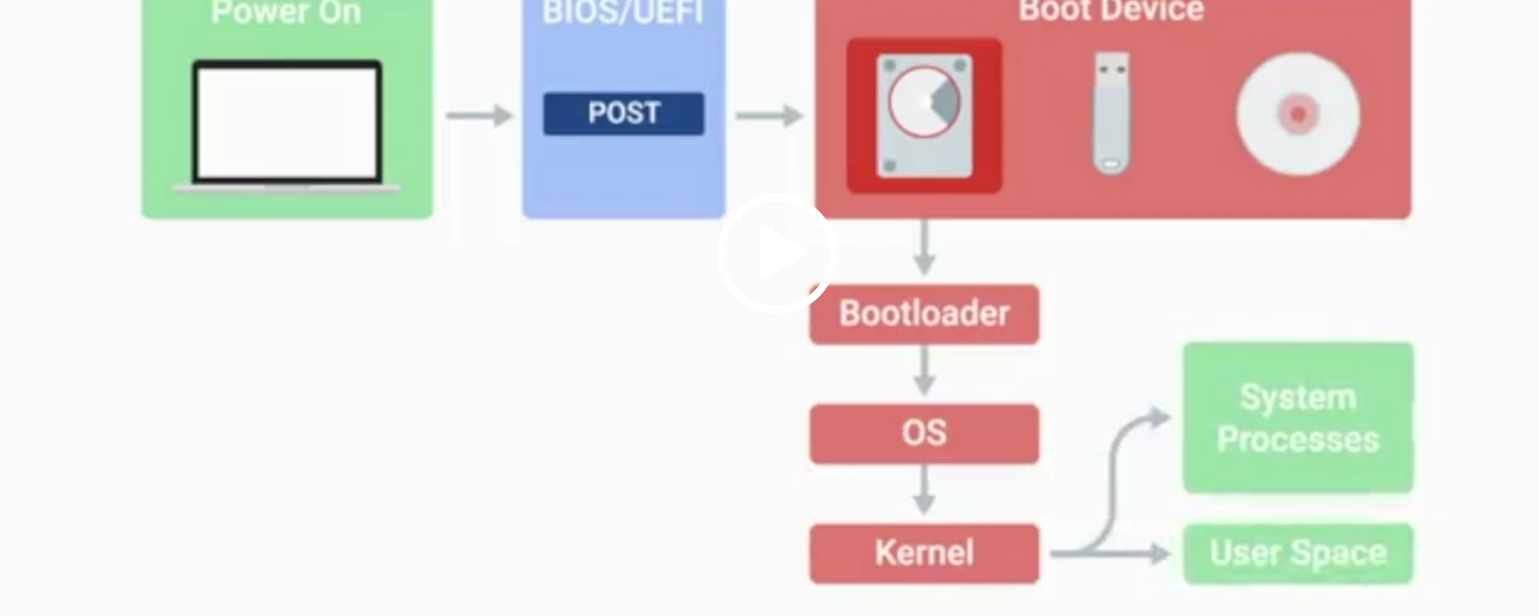
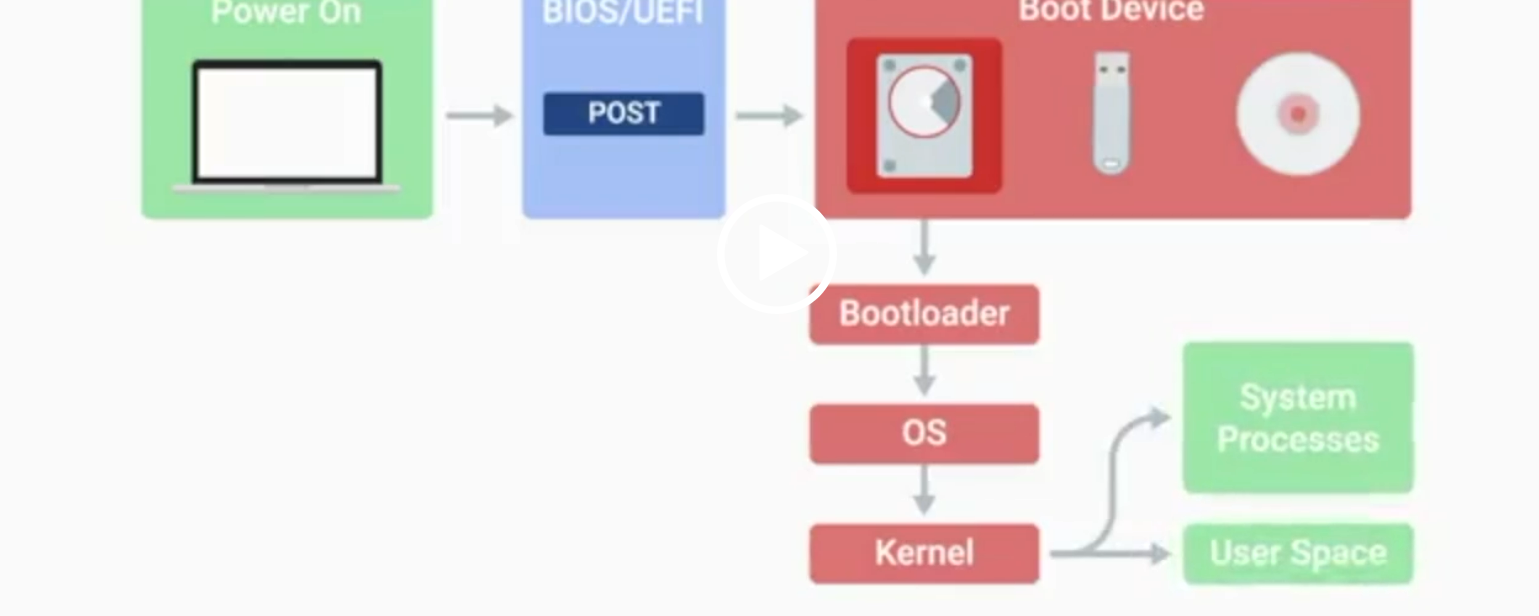
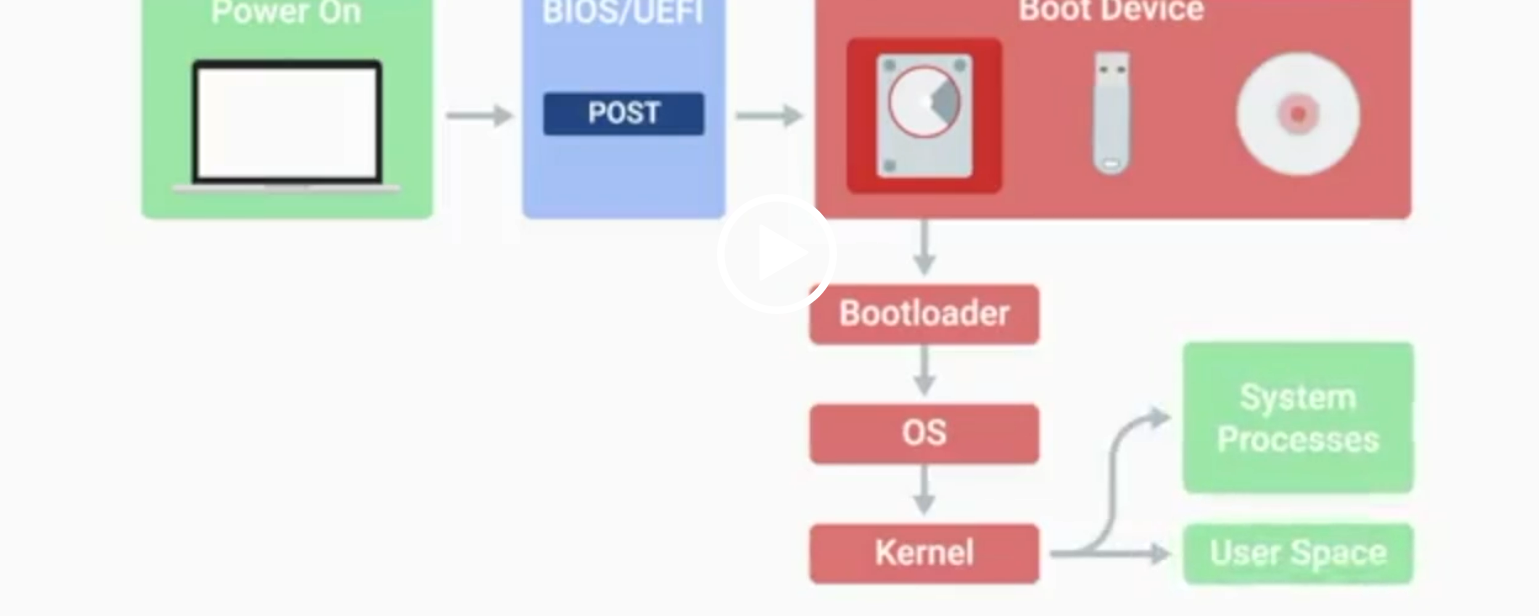
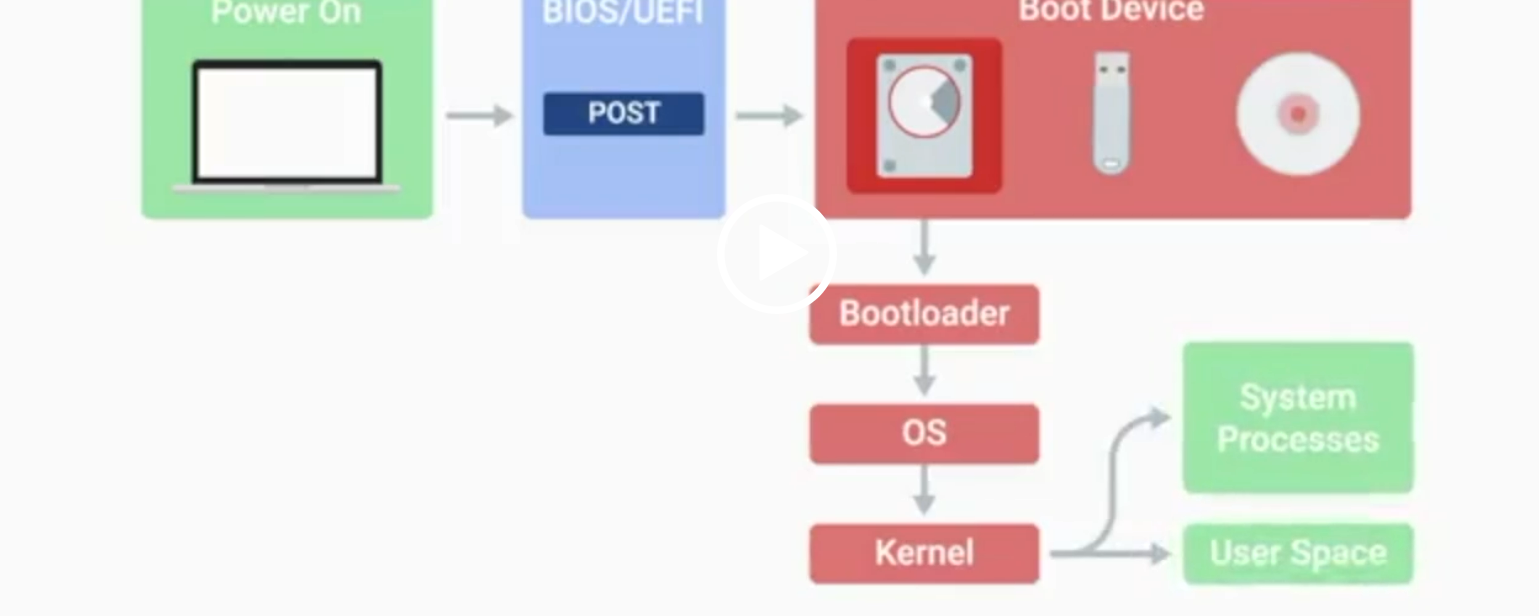
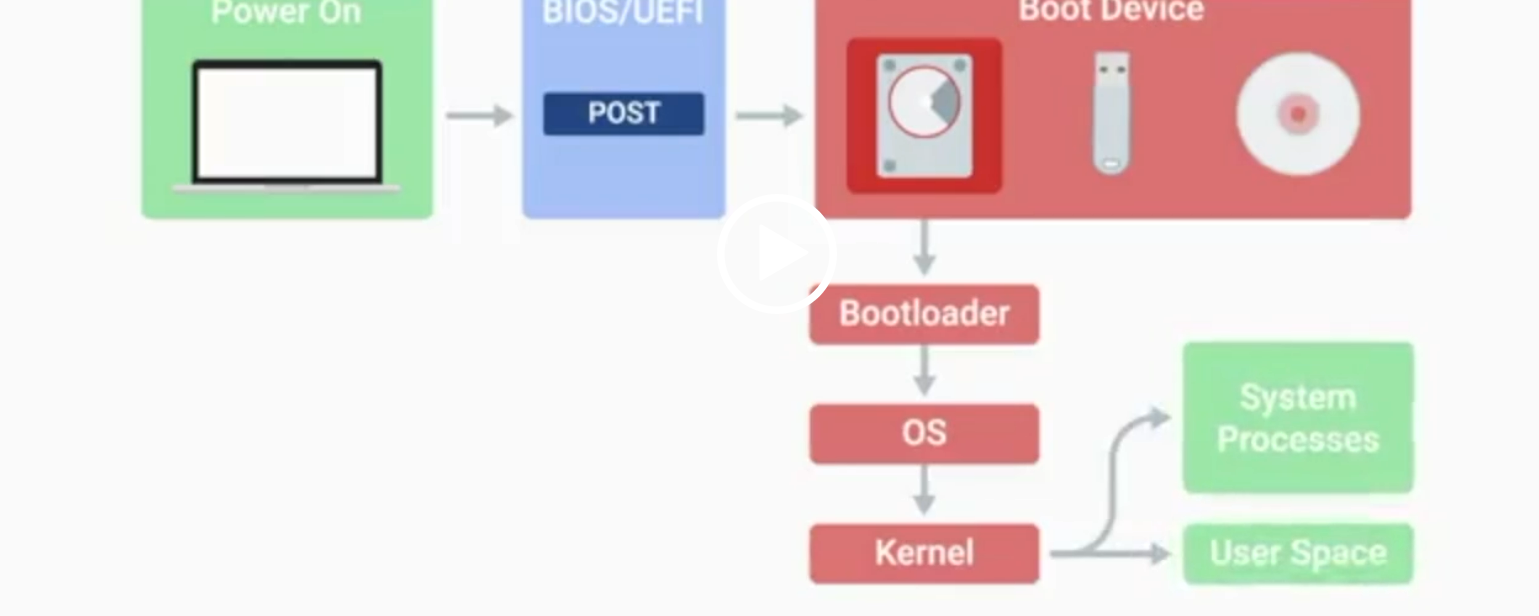
User Space
The environment where users can see and interact with the computer.
Hardware
The physical components of a computer or device.
Software
The internal systems that allow users to operate hardware, consisting of rules and instructions.
System Software
A platform that enables other software and programs to operate.
Application Software
Software designed specifically for end users, such as text editors.
GUI
Graphical User Interface, which uses icons and visuals for user interaction.
CLI
Command Line Interface, which allows users to interact with the computer through text commands.
Time Slice
A short interval of time allocated to a process for CPU execution.
CPU
The central processing unit that performs computations and stores data in RAM.
RAM
Random Access Memory, used for temporary data storage while a computer is running.
Motherboard
The main circuit board that connects all components of a computer.
Peripherals
External devices that perform input and output functions, such as keyboards and mice.
CMOS Chip
A chip that stores BIOS settings and configuration data.
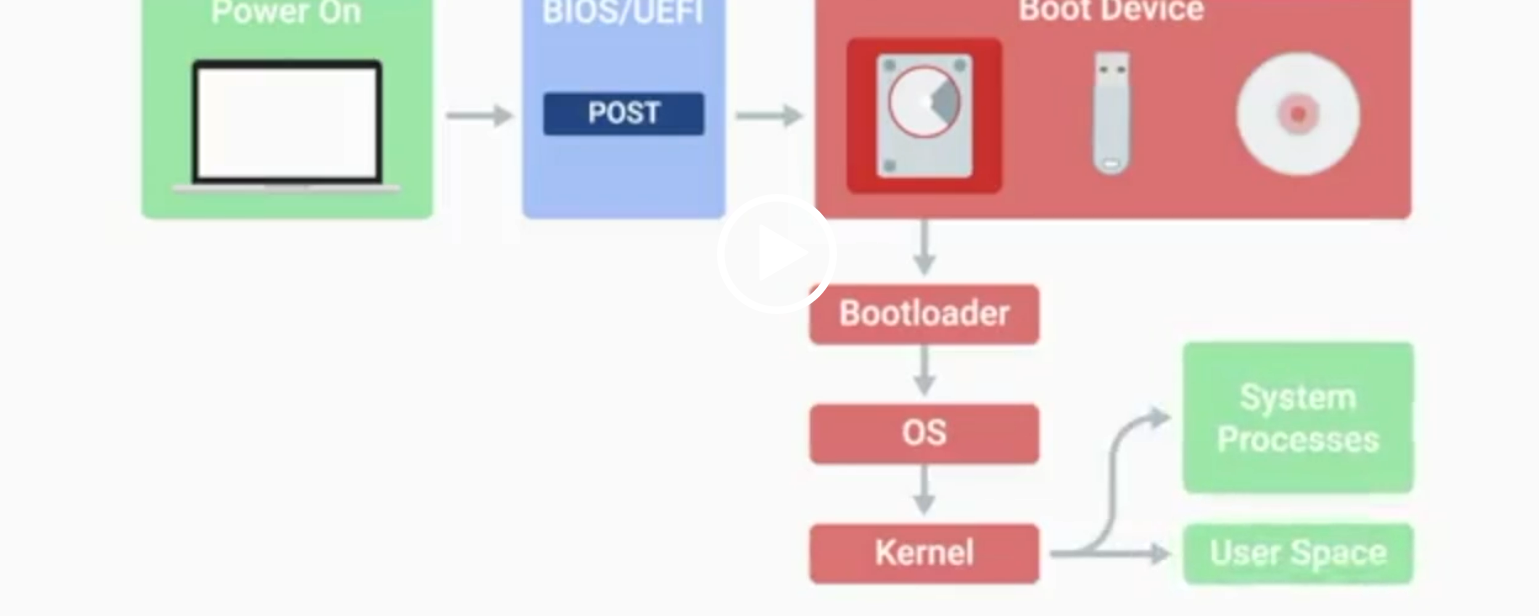
BIOS
Basic Input/Output System, the first software to run when a computer starts.
Rooting Process
The procedure of identifying and configuring all computer hardware.
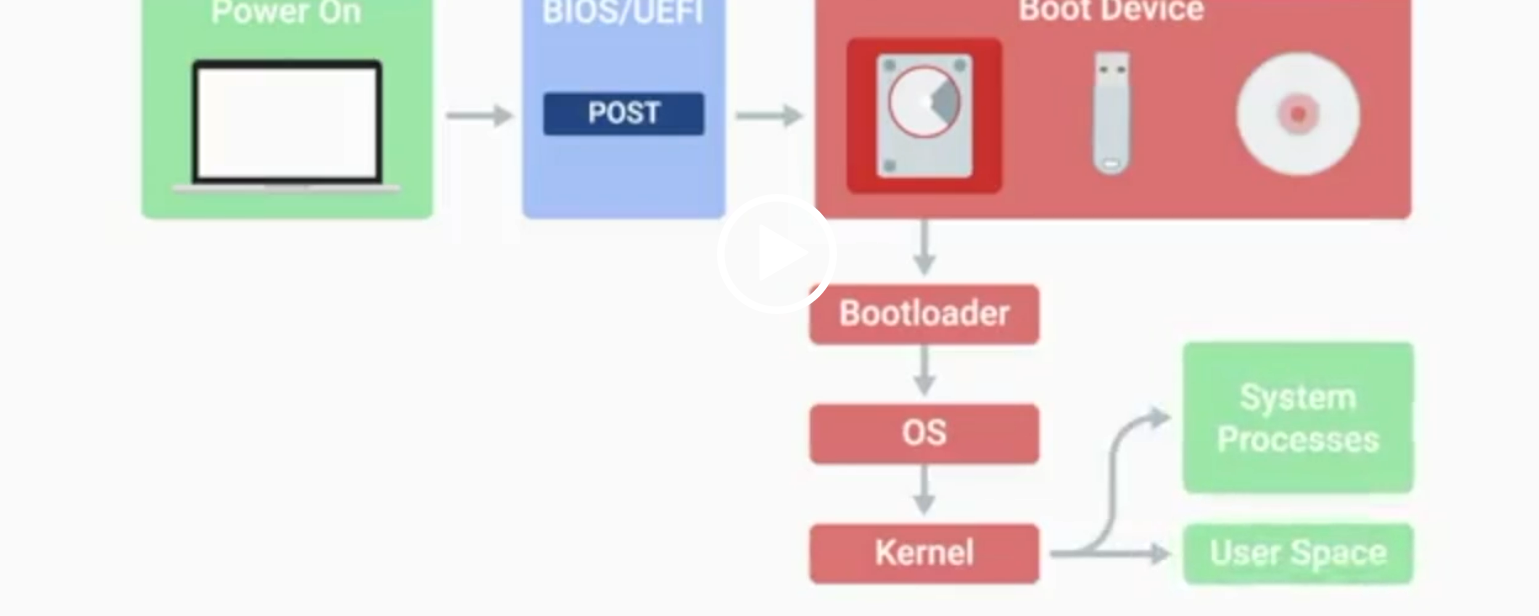
Kernel Space
The core part of the operating system that manages system resources.
ROM
Read-Only Memory, which retains data even when the computer is turned off.
Coding
The process of translating one programming language into another.
Scripting
Writing code in a scripting language for specific tasks.
Programming
Writing instructions in a programming language for computers to execute.
Copyright
Legal protection for original works.
UEFI
Unified Extensible Firmware Interface, a modern replacement for BIOS with better compatibility.
Application Management
The process of managing software applications on a computer.
File System
The method and structure used to store and organize files on a computer.
Virtual Memory
A combination of hard drive space and RAM that allows for more memory usage than physically available.
Logs
Files that record system events, functioning like a diary for the system.
Assembly Language
A low-level programming language that uses human-readable instructions.
Networking
The interconnection of computers and the management of network design and building.
Internet
The global physical connection of computers and networks.
IP Address
A unique identifier assigned to each device on a network.
MAC Address
A hard-coded identifier for network interfaces on devices.
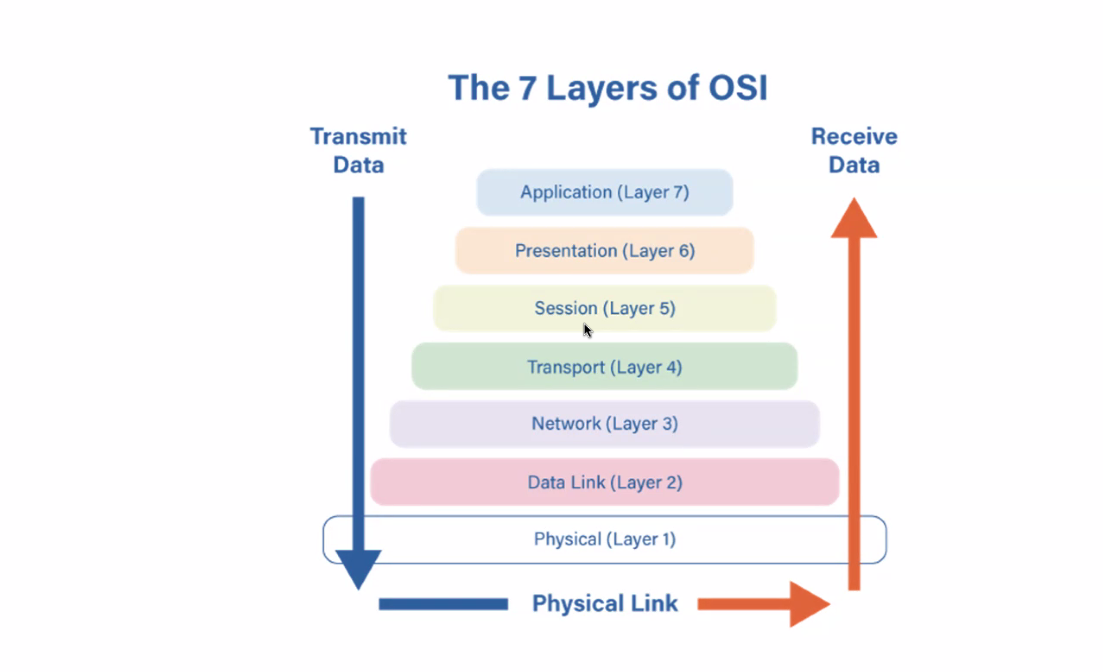
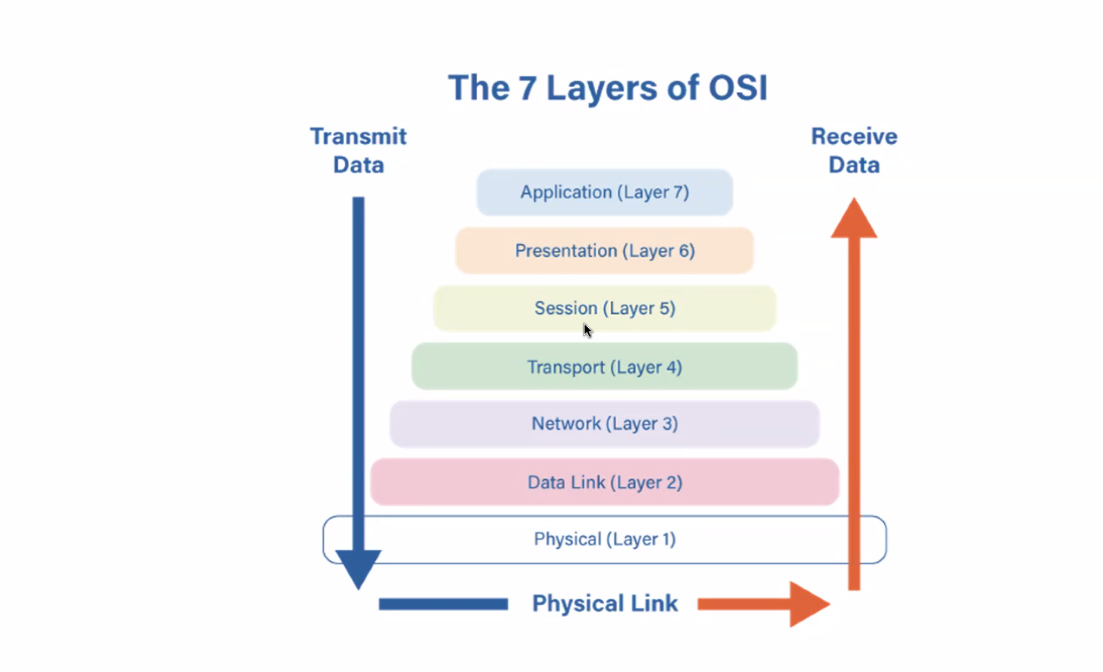
Network Protocols
Rules that govern data transmission and communication between devices.
TCP
Transmission Control Protocol, responsible for delivering information across networks.
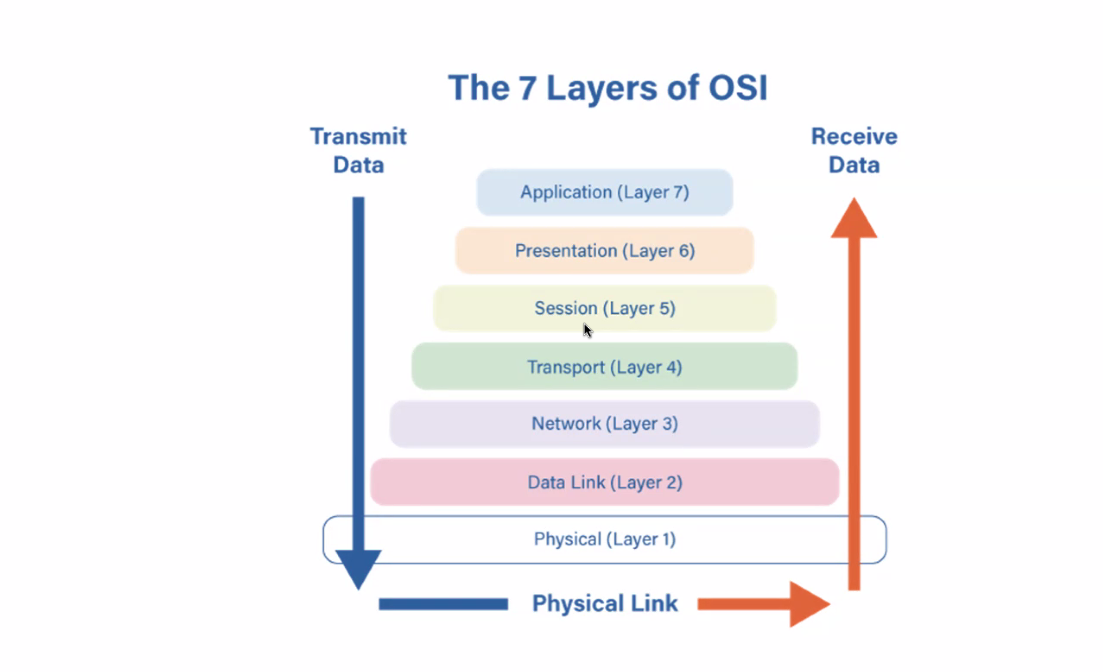
IP
Internet Protocol, which routes packets to the correct destination.
Registers
Small, fast storage locations within a CPU for immediate data and instruction access.
External Data Bus
A communication system that transfers data between components of a computer.
Drivers
Software that allows the operating system to communicate with hardware devices.
POST
Power-On Self-Test, a diagnostic process that checks hardware upon startup.
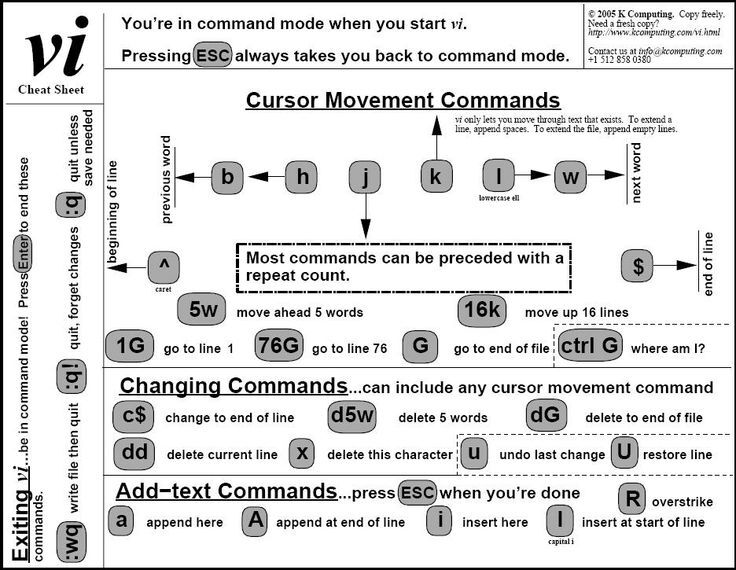
BASH
A command language interpreter for the GNU operating system.
Networking Devices
Equipment used to connect computers and manage data flow, including hubs, switches, and routers.
Coaxial Cable
A type of electrical cable used for transmitting data.
Optical Fiber Cable
A cable that uses light to transmit data, offering high-speed connections.
Twisted Pair Cables
Cables made of pairs of wires twisted together to reduce interference.
HDMI
A standard for transmitting high-definition video and audio, often used in networking contexts.
Distributions
Variants of operating systems, particularly in the context of Linux.
This device allow you to send data from one network to another (think destination)
Router
This device deals with MAC address and allows access through the ports for each device for LAN. It connects multiple devices on a LAN/ home network.
Switch
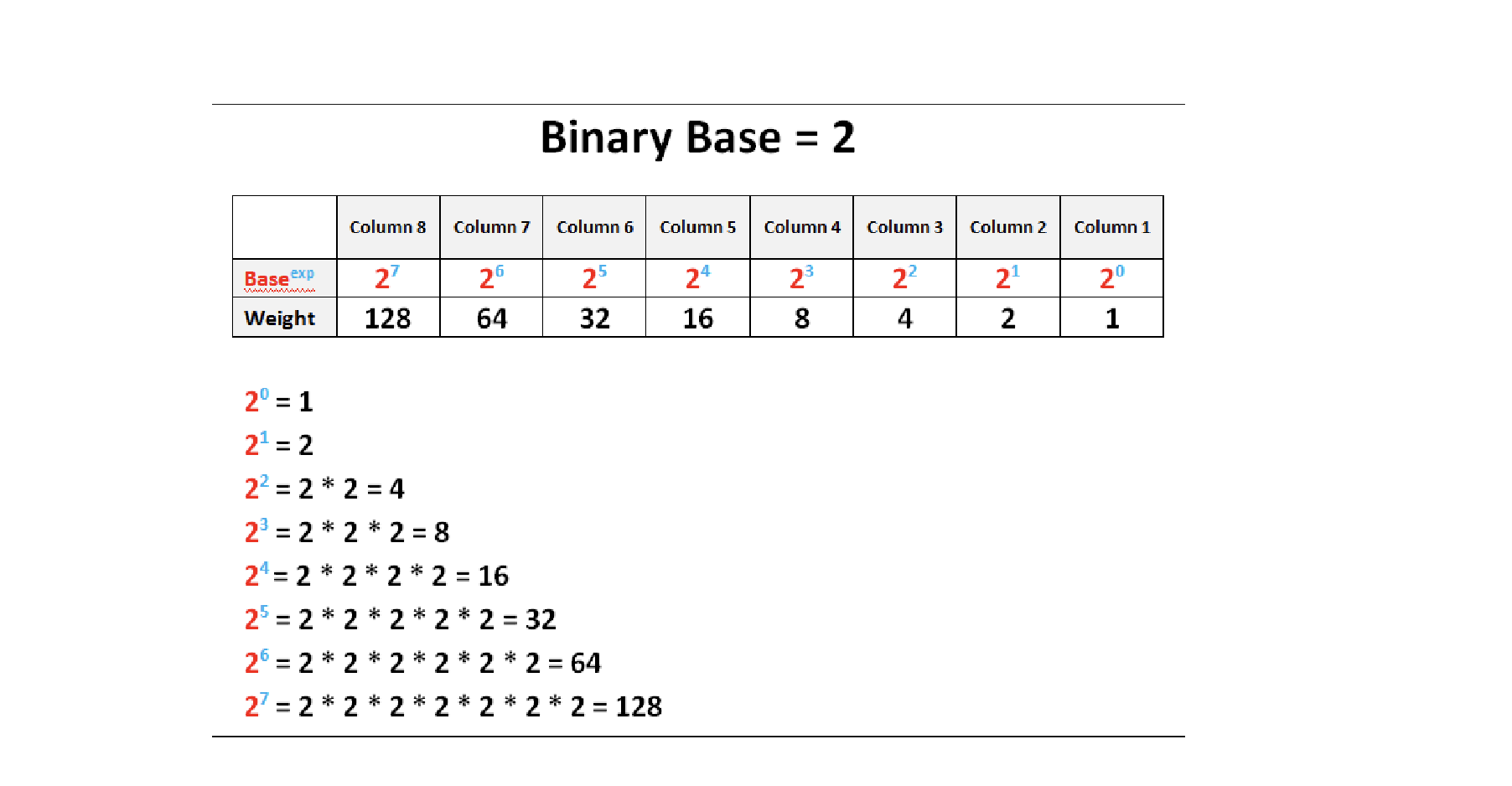
8 bits =
1 Byte
MB
Megabyte
Mb
Megabit
1024 Megabytes =
1 Gigabyte
1 Megabyte =
1024 kilobytes
1 Kilobyte =
1024 bytes