Bis 2C- Animals (Moore)
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
Diagnostic Features of Bilaterians
1. bilateral symmetry along the anterior-posterior axis of the body
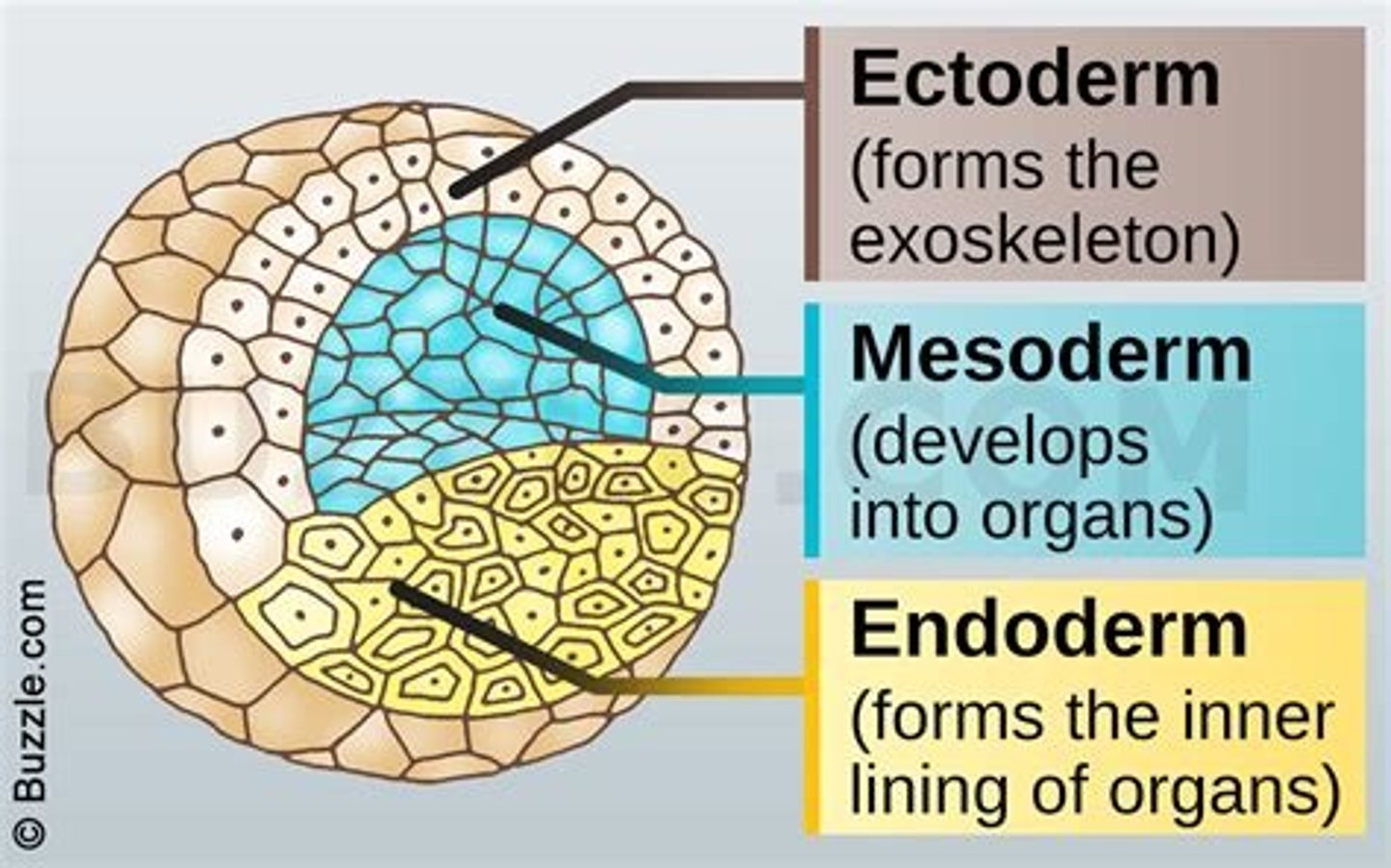
2. three germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm)
3. central nervous system (CNS)
Germ layers
Three layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm.
Central nervous system (CNS)
A complex network of neurons that coordinates sensory information and motor functions.
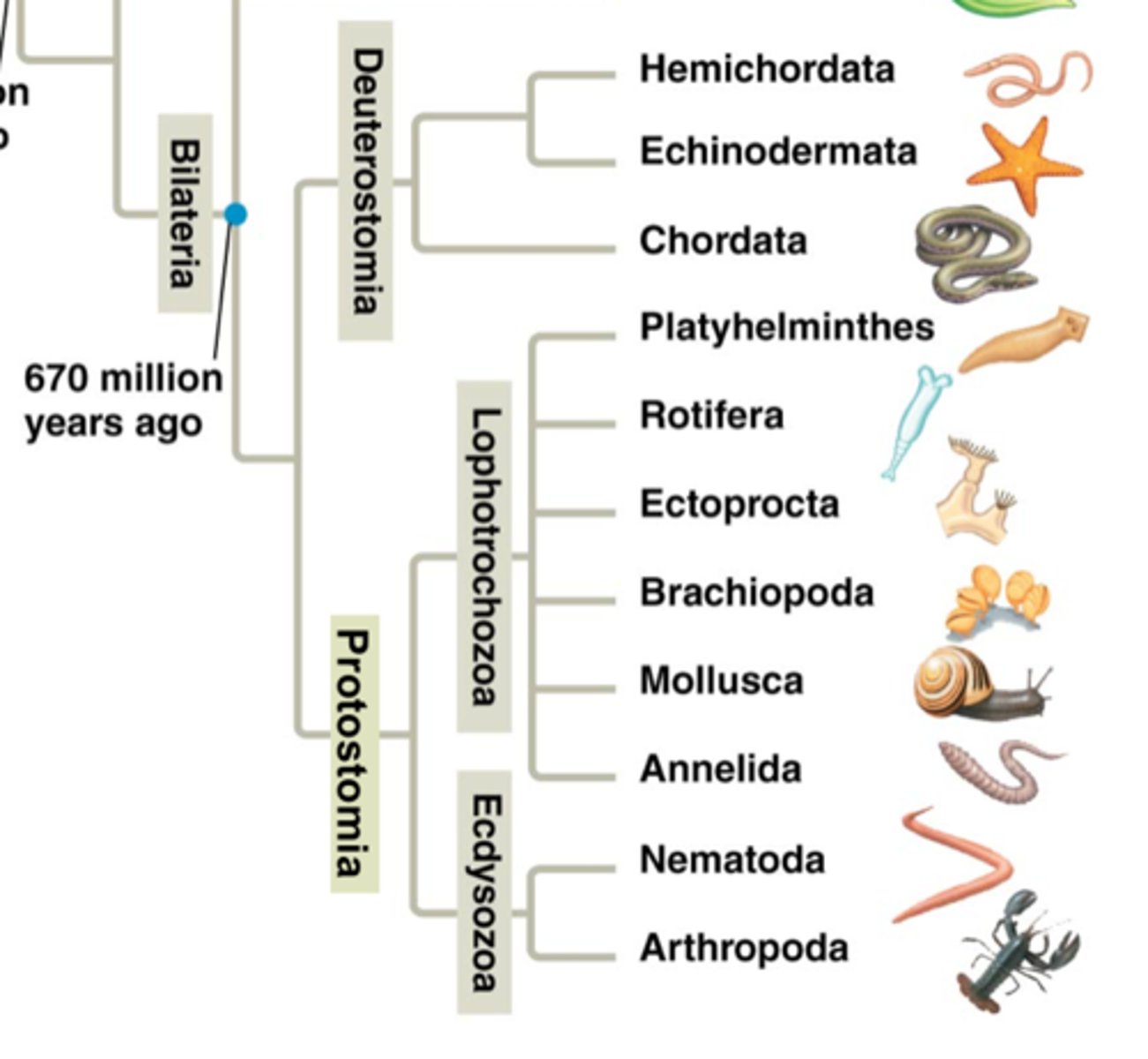
Protostomes
Bilaterians where the blastopore develops into the mouth.
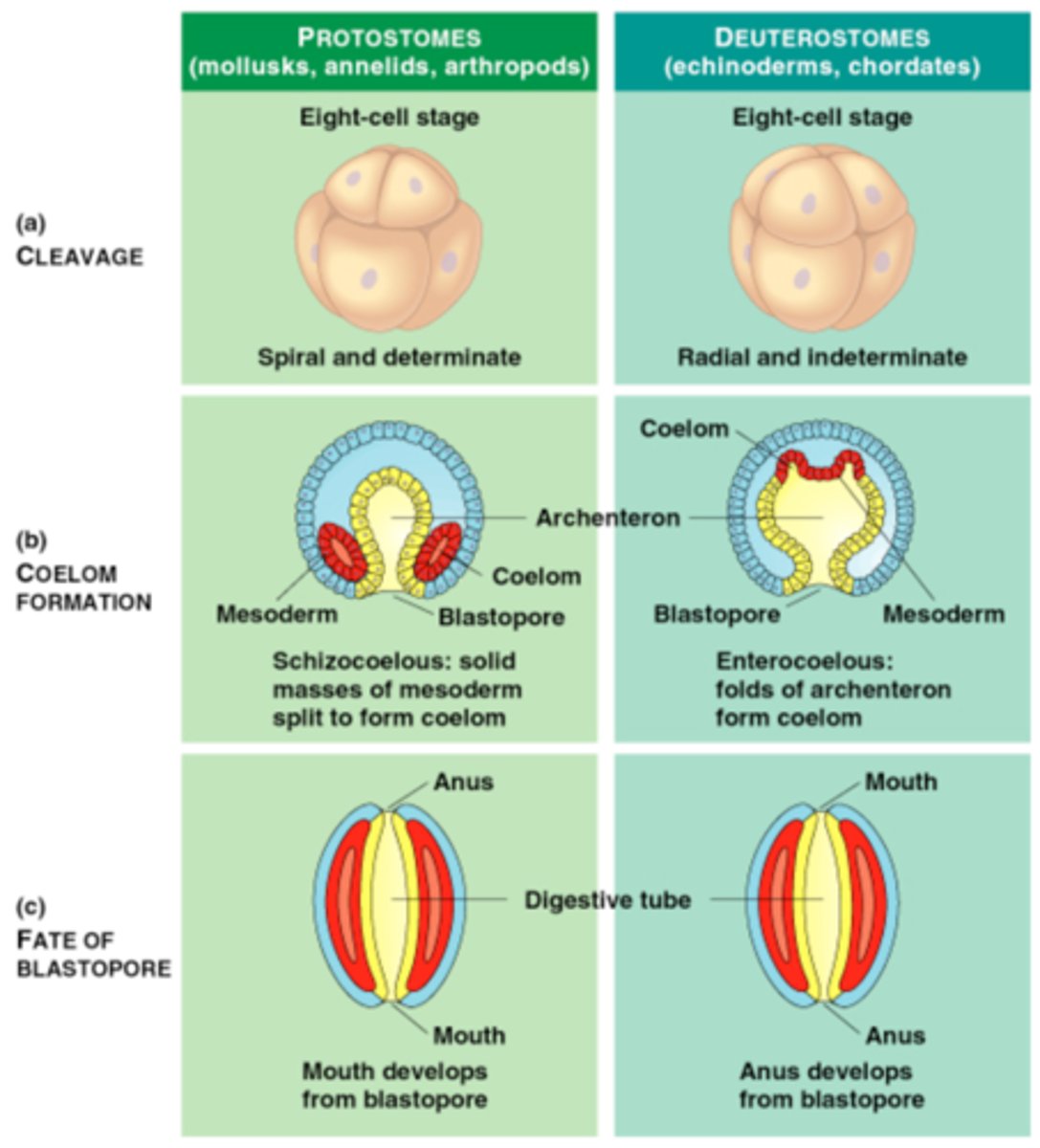
Deuterostomes
Bilaterians where the blastopore develops into the anus.
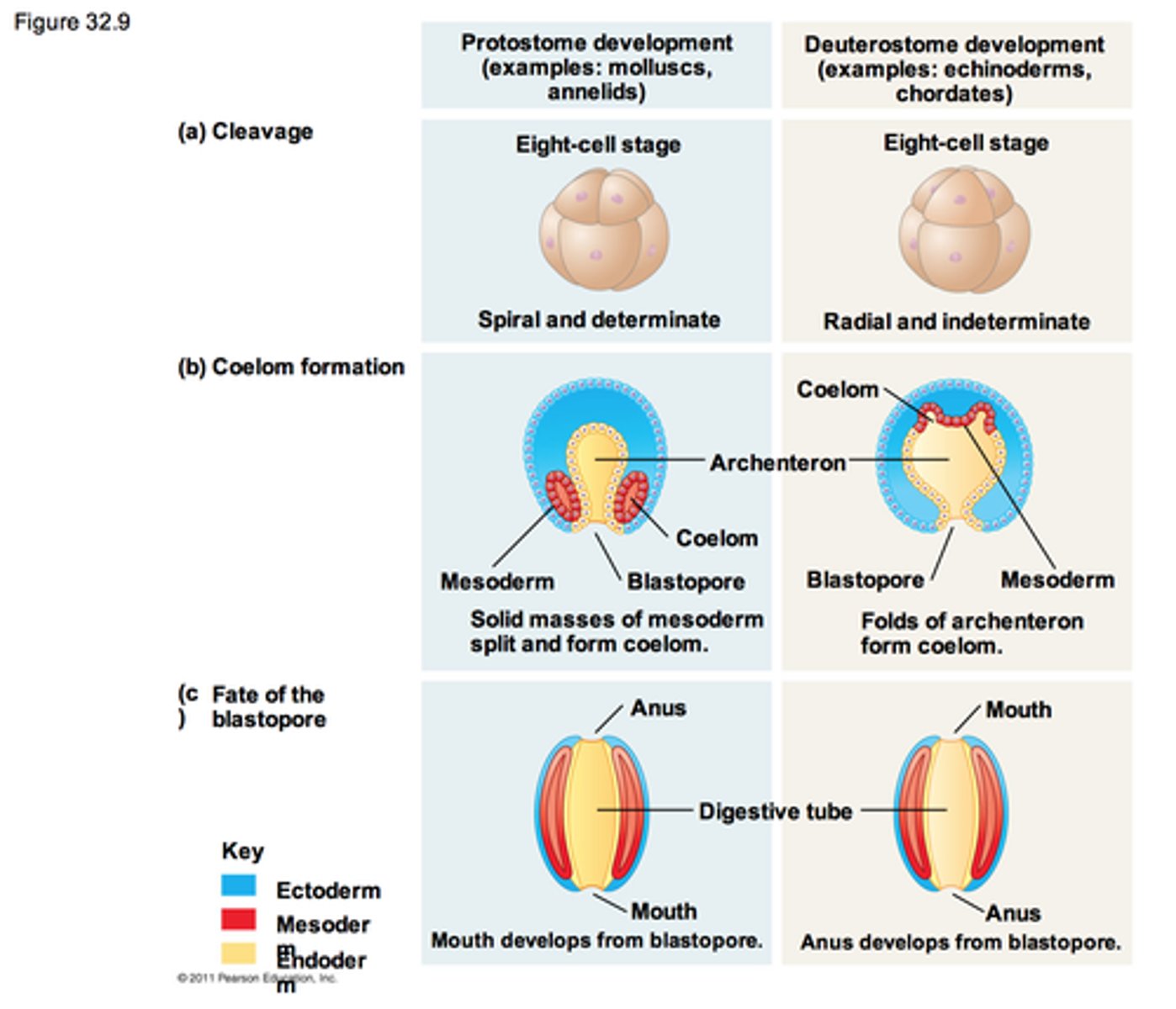
Lophotrochozoans
A group of protostomes characterized by a lophophore or trochophore larval stage.
Diagnostic feature of Ecdysozoans
1. external chitinous exoskeleton
2. ecdysis (exoskeletal molting)

Ecdysis
The process of exoskeletal molting in Ecdysozoans.
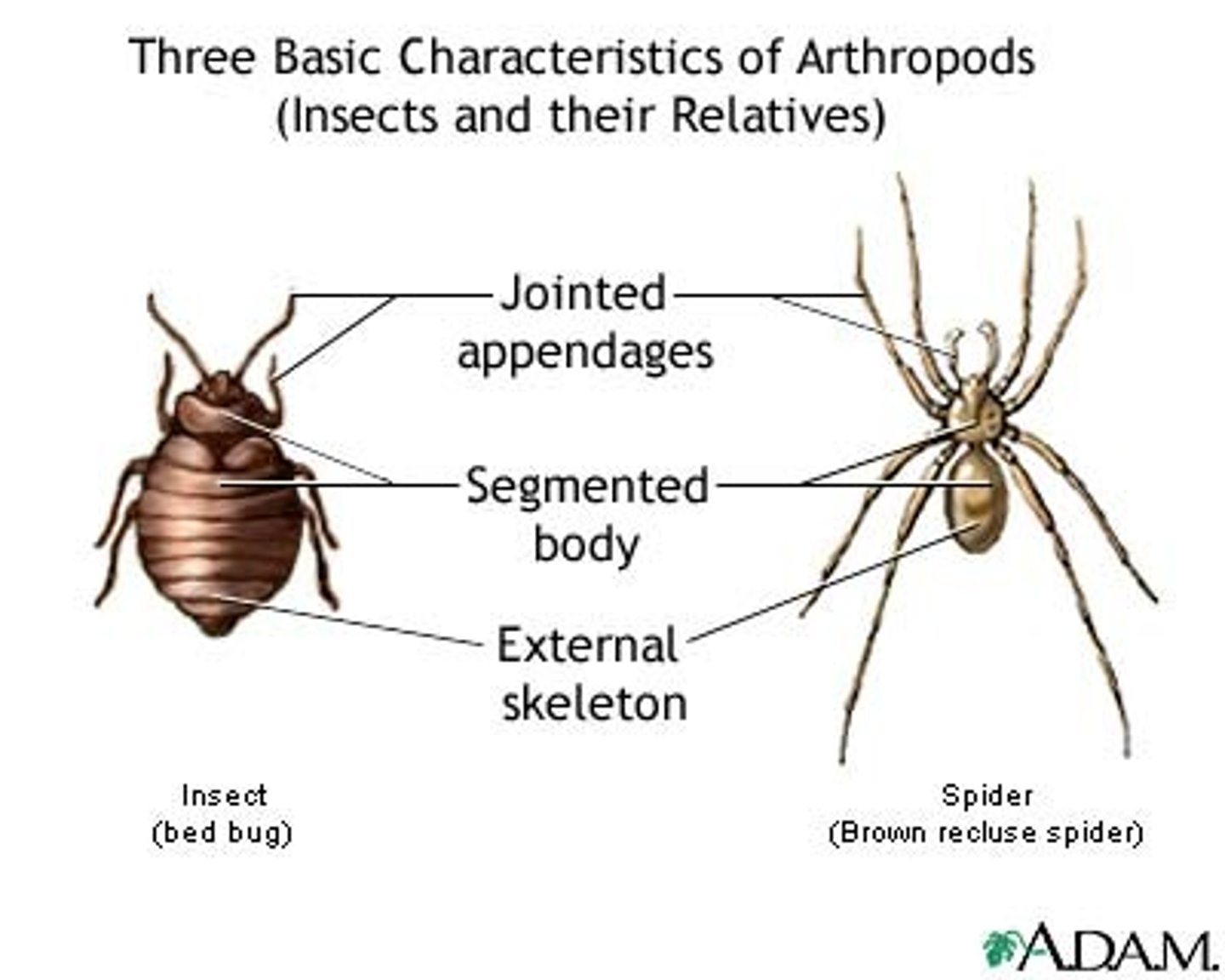
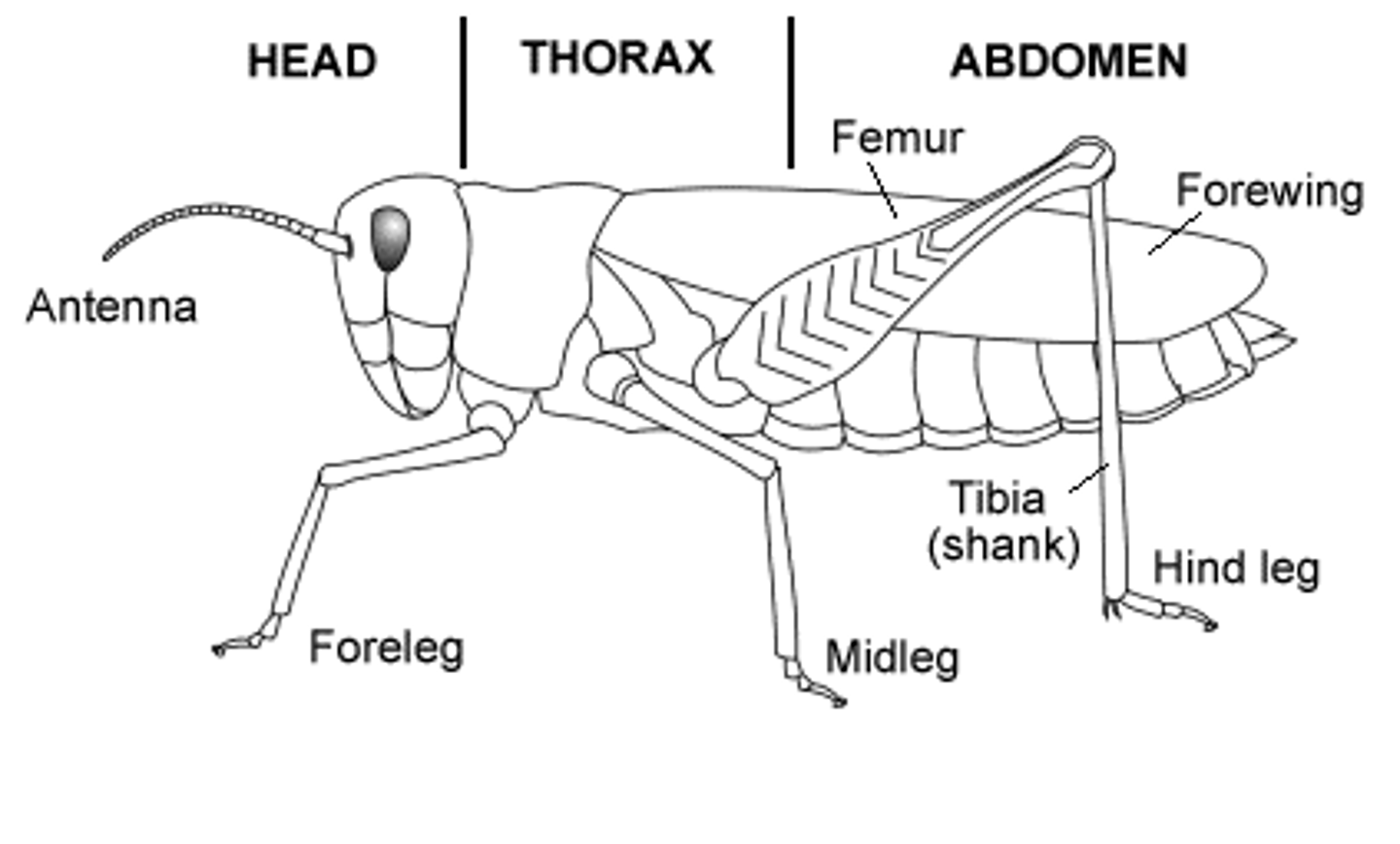
Diagnostic features of Arthropods
1. jointed appendages
2. compound eyes comprised of light-sensing strictures called ommatidia
3. tagmosis (fusion of body segments into regions that perform specialized functions)
Jointed appendages
Limbs that are segmented and can bend at the joints.
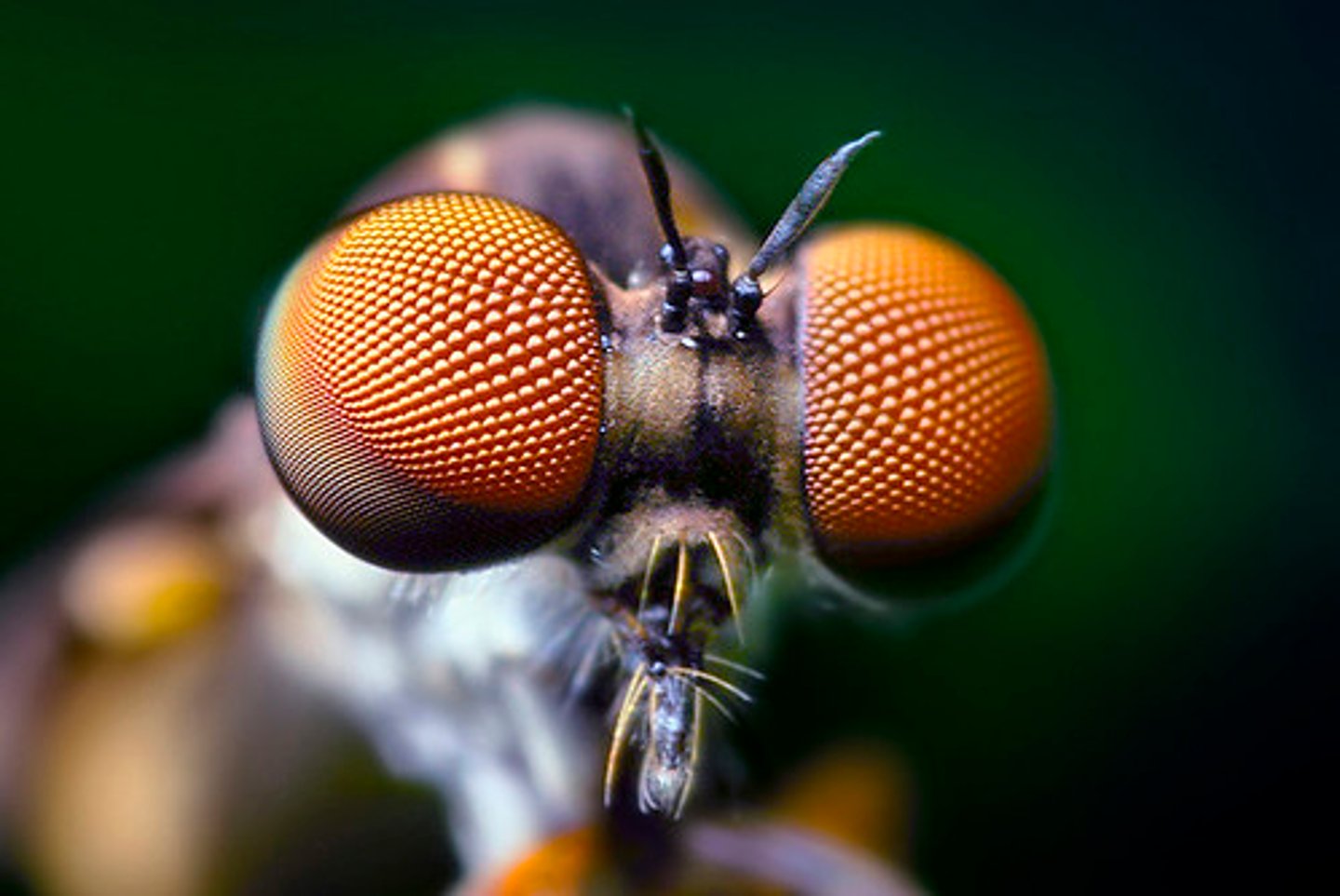
Compound eyes
Eyes made up of multiple light-sensing structures called ommatidia.

Tagmosis
The fusion of body segments into regions that perform specialized functions.
true or false: arthropods originated ~540 mya in an aquatic environment
true
true or false: between ~480-420 mya, several groups of arthropods independently colonized lands, where these terrestrial colonization events are associated with the independent evolution of various respiratory innovations
true.
What are the 4 types of arthropods?
1. Chelicerates
2. Myriapods
3.Malacostracans
4. Hexapods
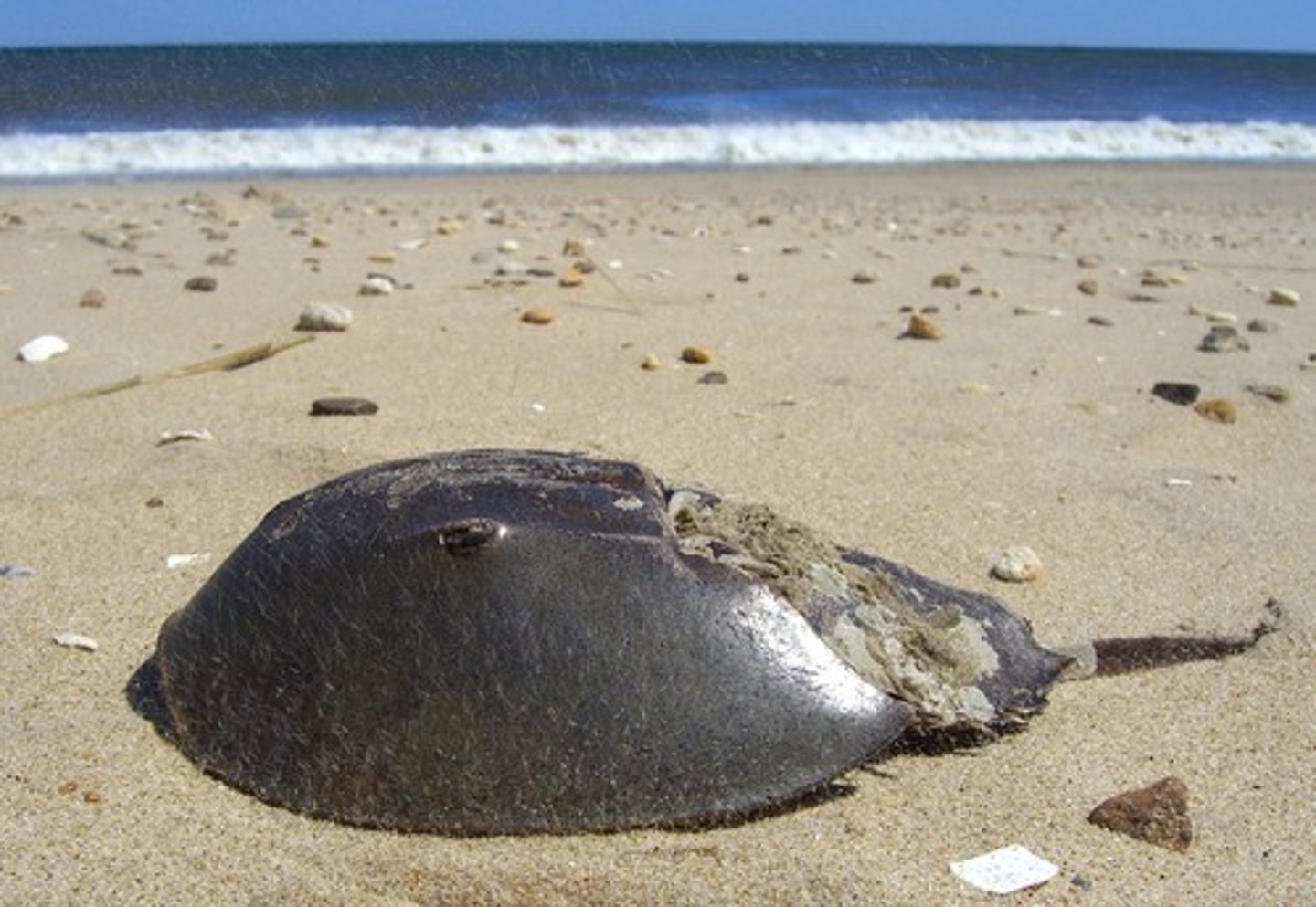
Chelicerates (tagma, paired, jointed appendages, etc.)
-2 tagma
-4 pair of legs
-chelicerae (feeding appendages)
-pedipalps (feeding/ sensory appendages)
-horseshoe crabs, ticks/mites, scorpions, spiders
-TERRESTIAL chelicerates possess a book-lung respiratory system

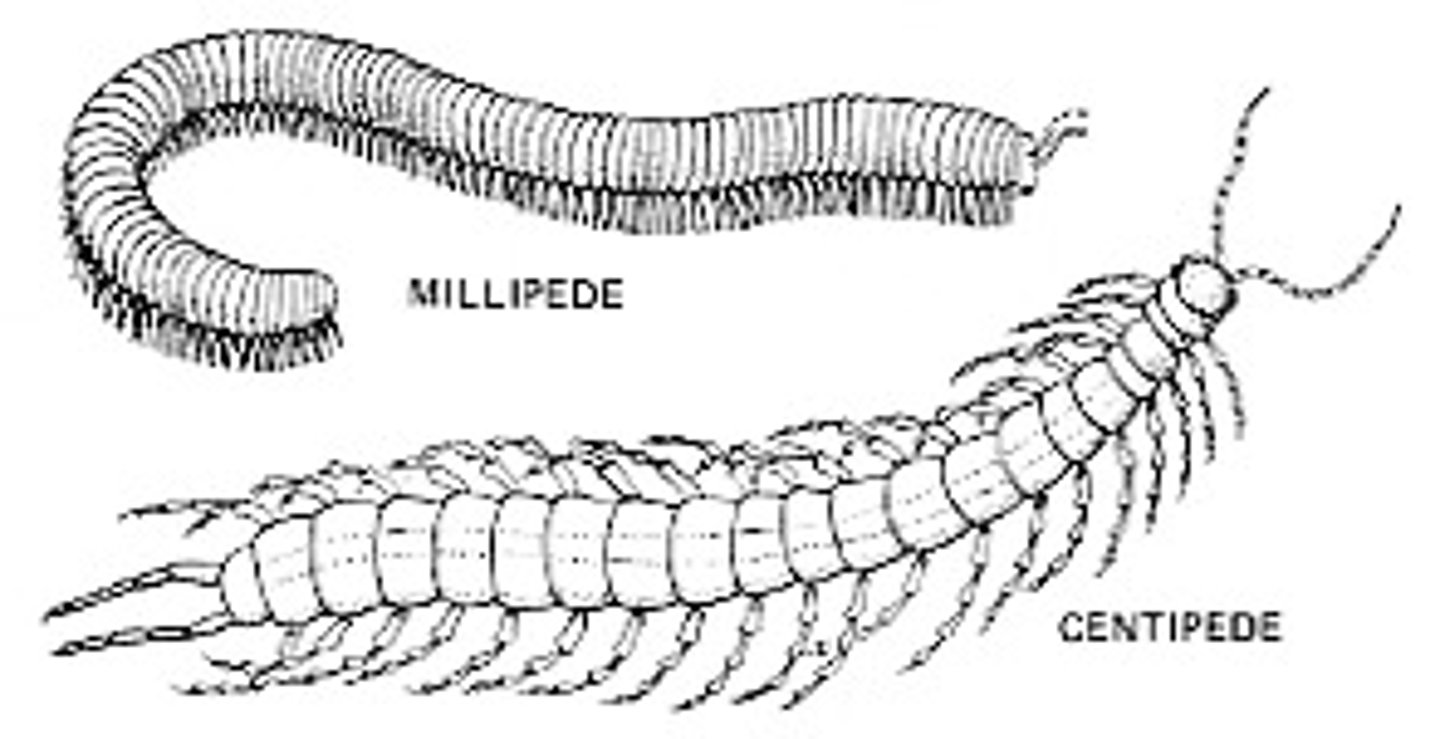
Myriapods (tagma, paired, jointed appendages, etc.)
-1 tagma
-many segments with one pair of legs (centipede) or two pairs of legs per segment (millipede)
-possess a respiratory system with spiracles (openings) and trachea (tubules)
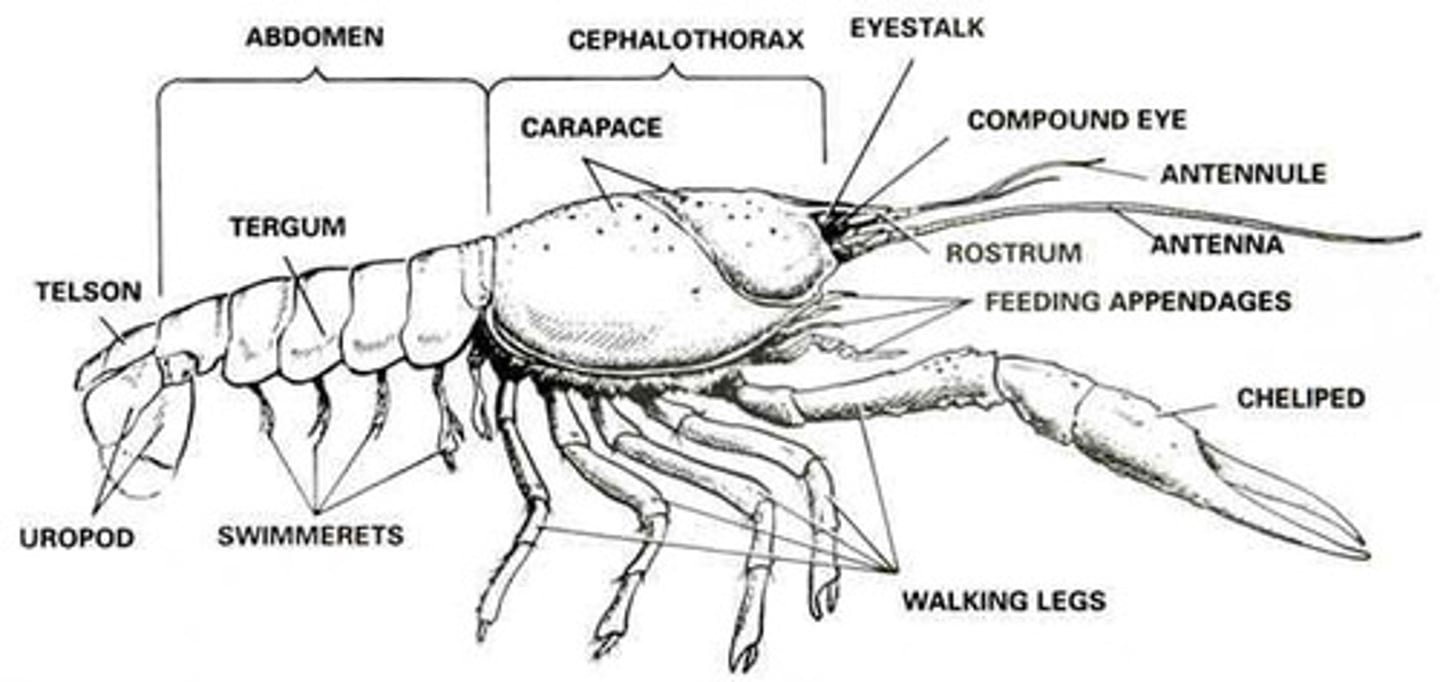
Malacostracans (tagma, paired, jointed appendages, etc.)
-3 tagma (head, thorax, abdomen, with head and thorax fused into a carapace)
-two pairs of antennae
-includes: crabs, shrimp, lobsters, and crayfish
-terrestrial malacostracans possess a gill respiratory system
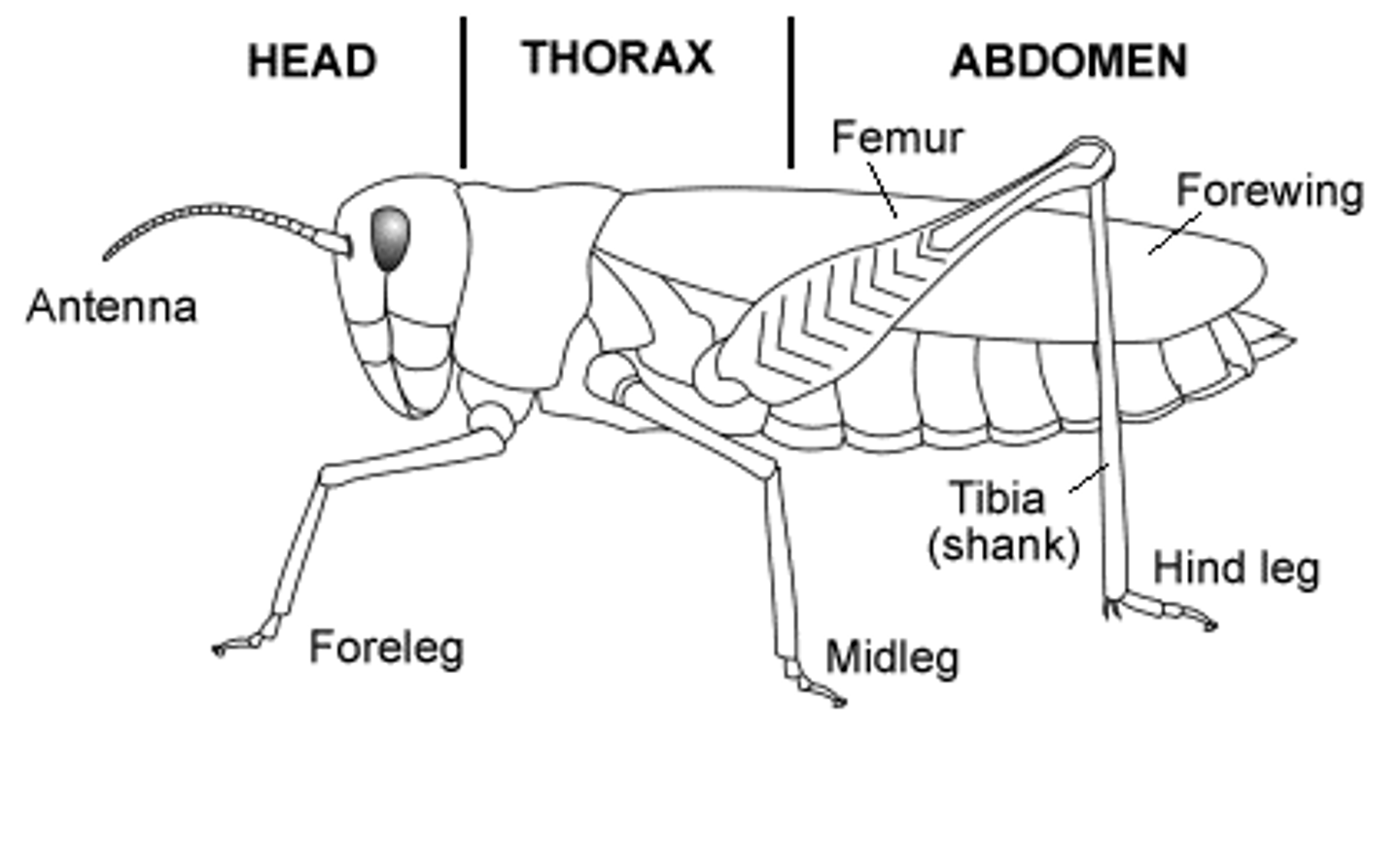
Hexapods (tagma, paired, jointed appendages, etc.)
-3 tagma
-3 pairs of legs
-one pair of antennae
-includes: "apterygota" and insects.
-possess a respiratory system with spiracles (openings) and tracheae (tubules)
true or false: "crustacea" are paraphyletic with respect to hexapods
true
true or false: hexapods include a paraphyletic grade insecta (insects) and a monophyletic group, apterygota
false. hexapods include a paraphyletic grade ("Apterygota") and a monophyletic group, insecta (insects)
Apterygota
A paraphyletic grade of small, flightless hexapods lacking wings that have an internal (retracted) mouthparts.

What habitats are Apterygota restricted to and why?
-restricted to moist habitats (soil, leaf litter) because they have poor developed respiratory systems
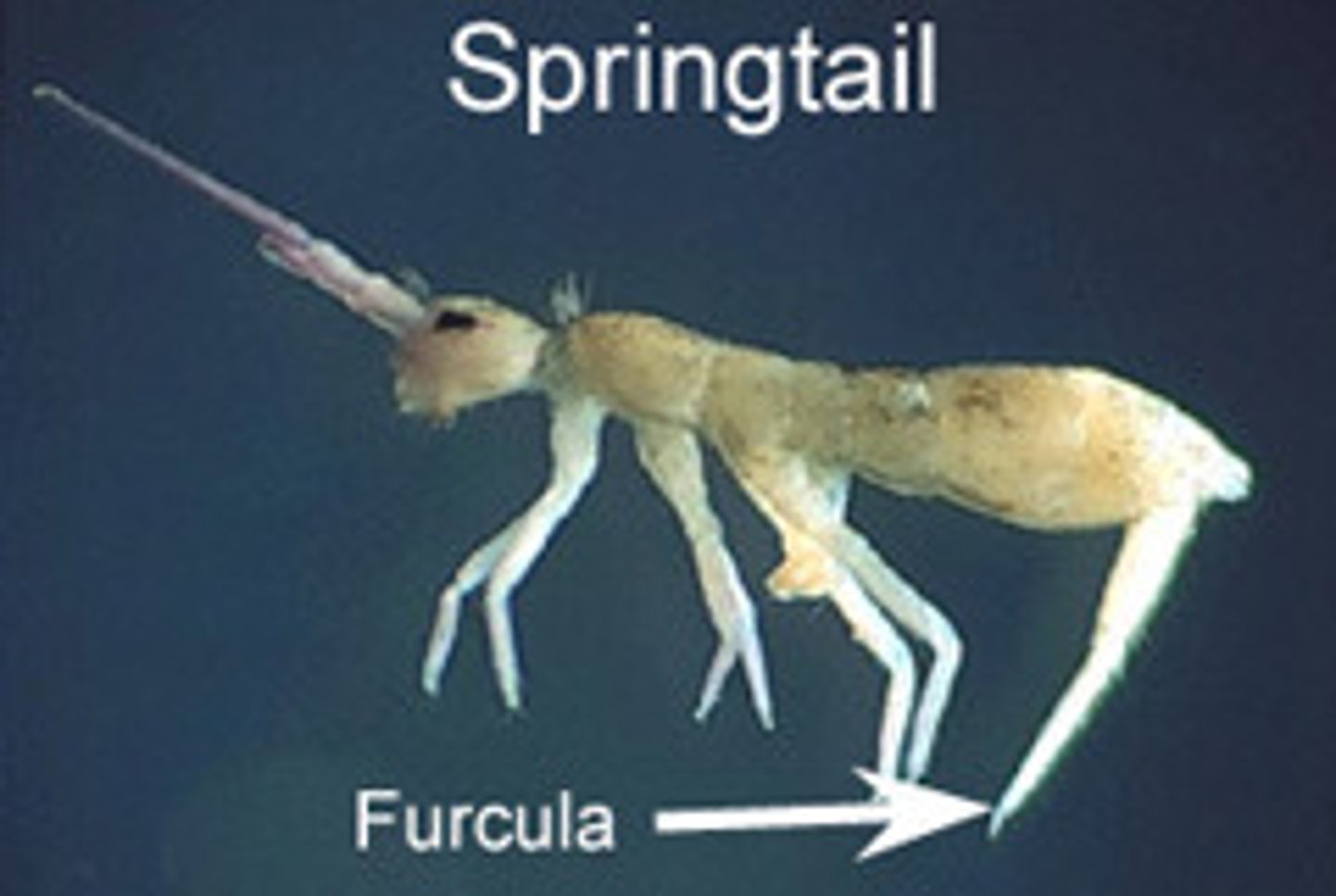
Entognatha
A group within Apterygota that includes springtails, bristletails, and coneheads

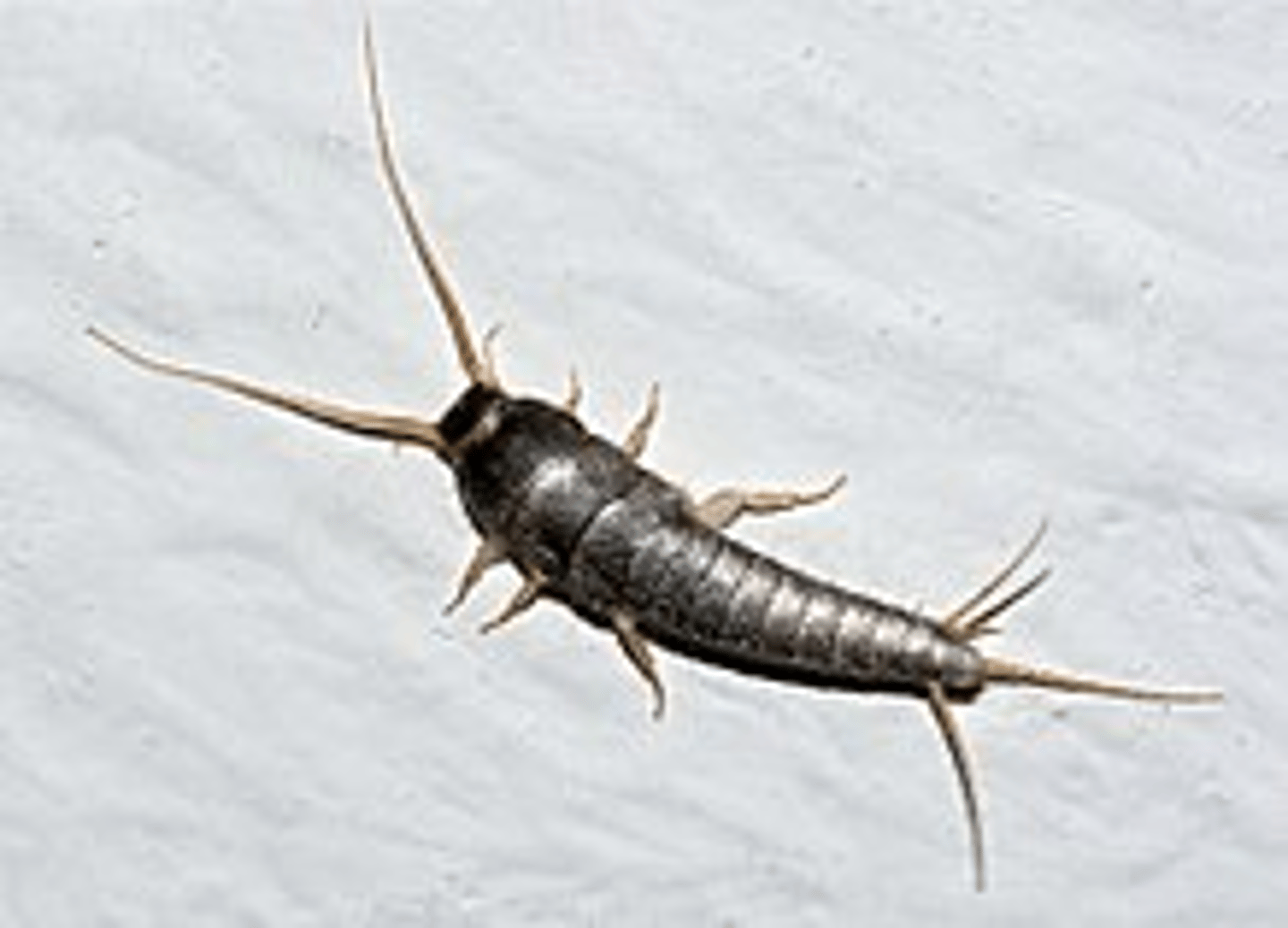
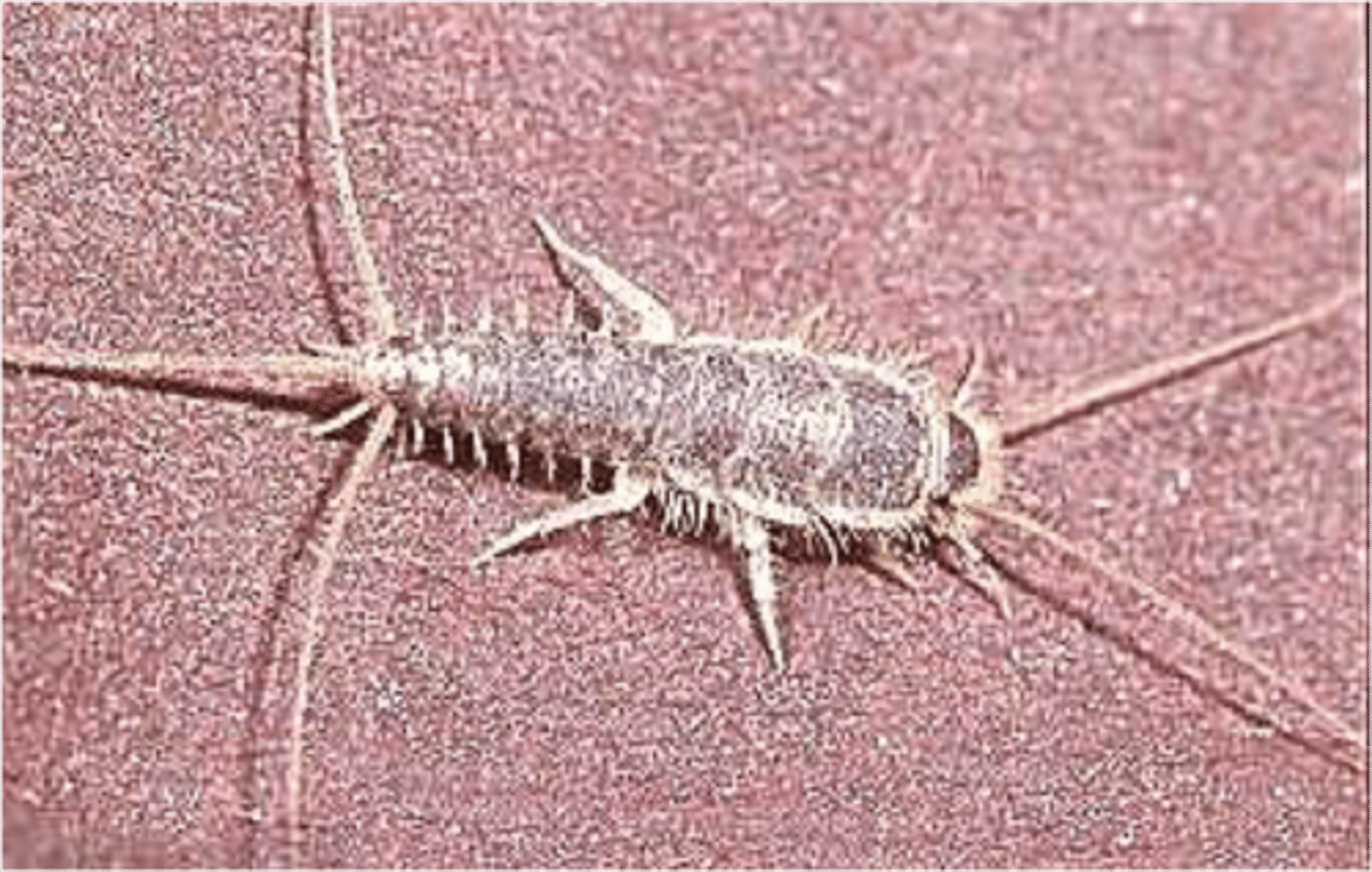
Zygentoma
A group within Apterygota that represents a "bridge" between "non-insect hexapods" and insects)
-includes silverfish and firebrats.

Insecta
A monophyletic group of hexapods comprising over one million described species.
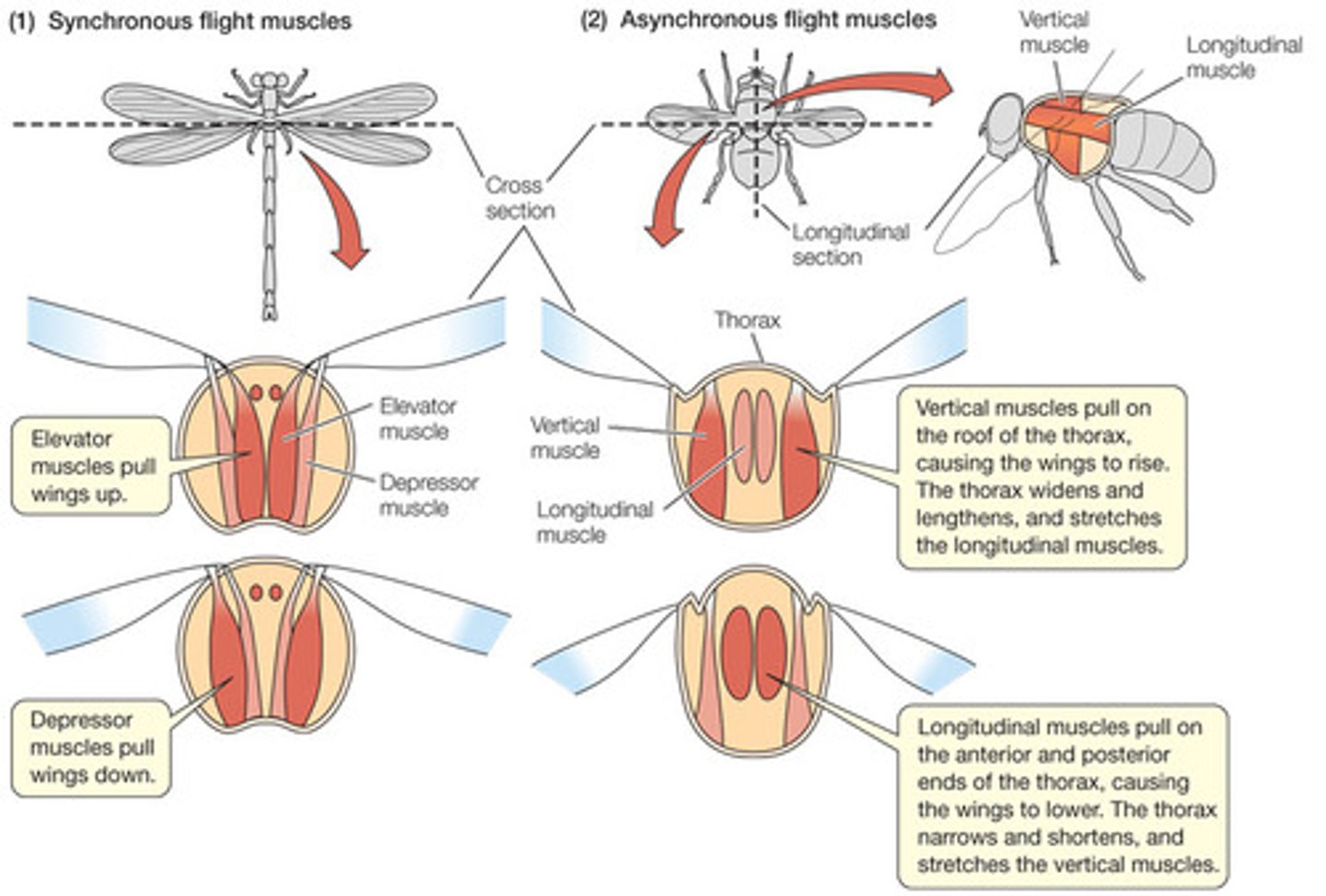
Flight in insects
Evolved once in the MRCA of Pterygota but has been lost independently many times.
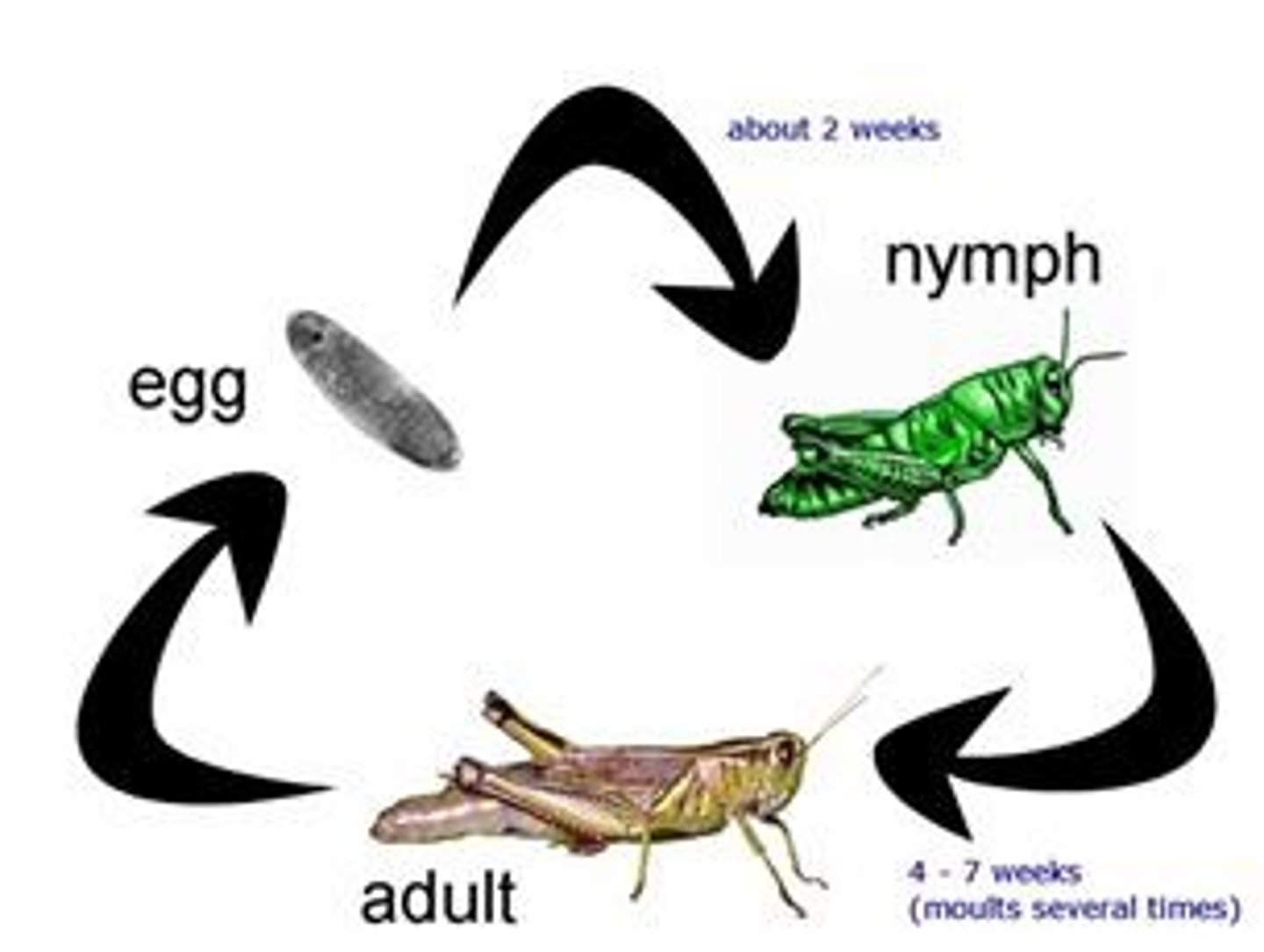
Incomplete metamorphosis
Development with gradual changes via a series of molts through stages until reaching the adult stage.
-every stage eats the same thing
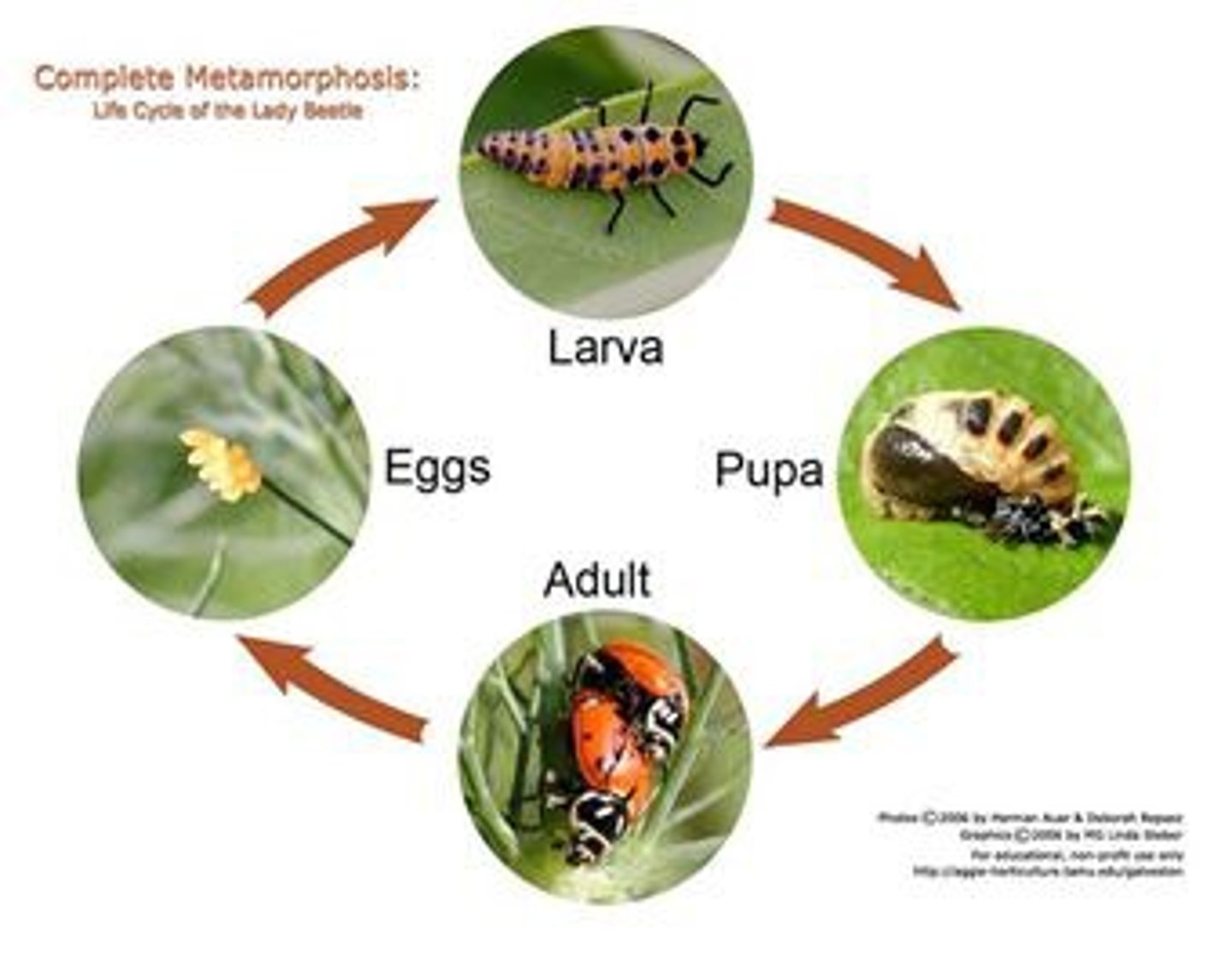
Complete metamorphosis
Development involving punctuated changes over four stages: embryo, larva, pupa, adult.
-larva and adults use different food stages
-occurs in Hymenoptera, Coleoptera, Diptera, and Lepidoptera
What are the 7 main insect groups?
1. Palaeoptera
2. Orthoptera
3. Hemiptera
4. Hymneoptera
5. Coleoptera
6. Diptera
7. Lepidoptera
Palaeoptera
-(palaiós = old, pterón = wing)
-Insects with 2 pairs of non-folding wings and aquatic nymph stages.
-includes mayflies, dragonflies, damselflies

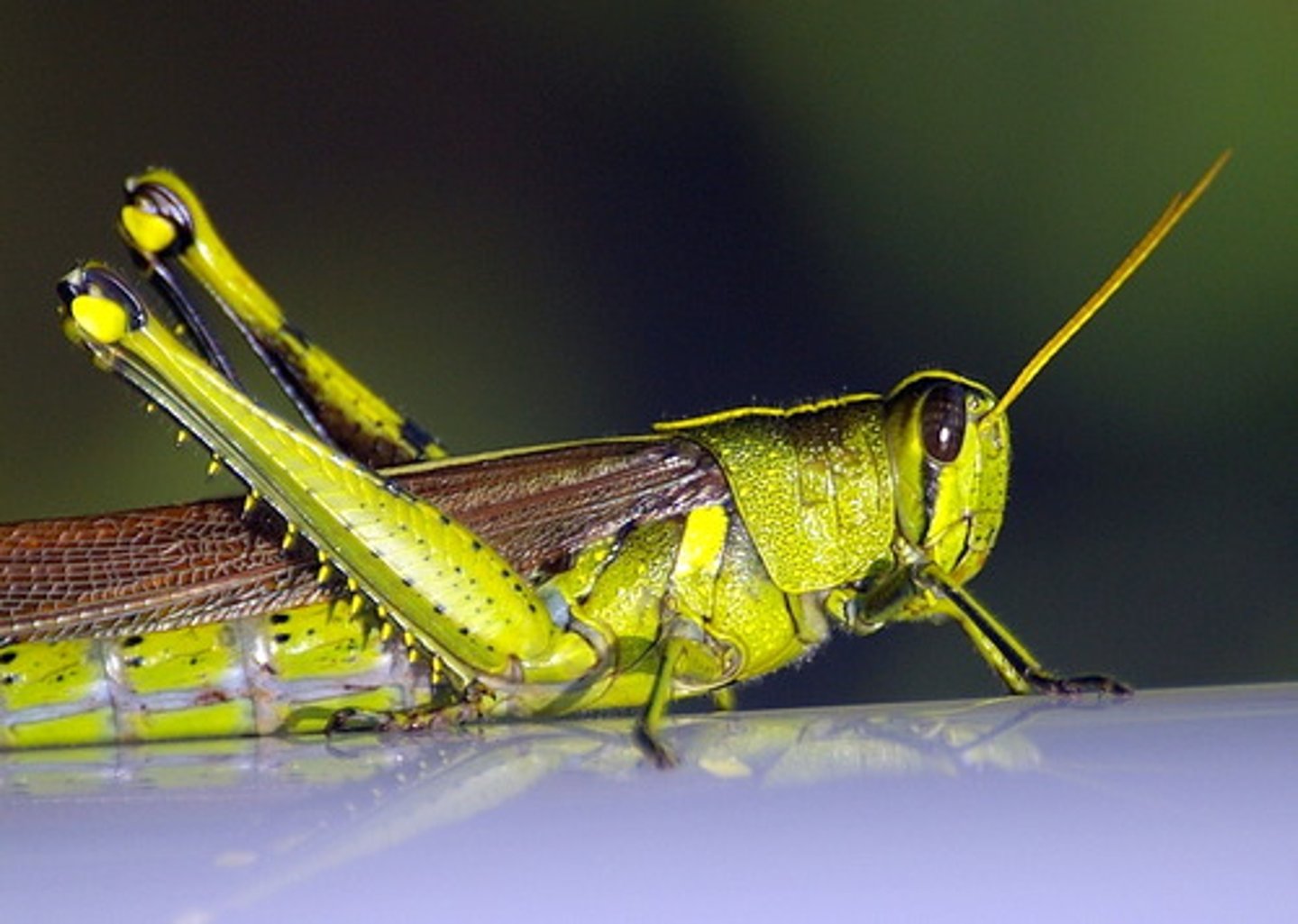
Orthoptera
-(orthós = straight, pterón = wing)
-Insect group with chewing mouthparts
-grasshoppers, locusts, crickets, roaches, termites.

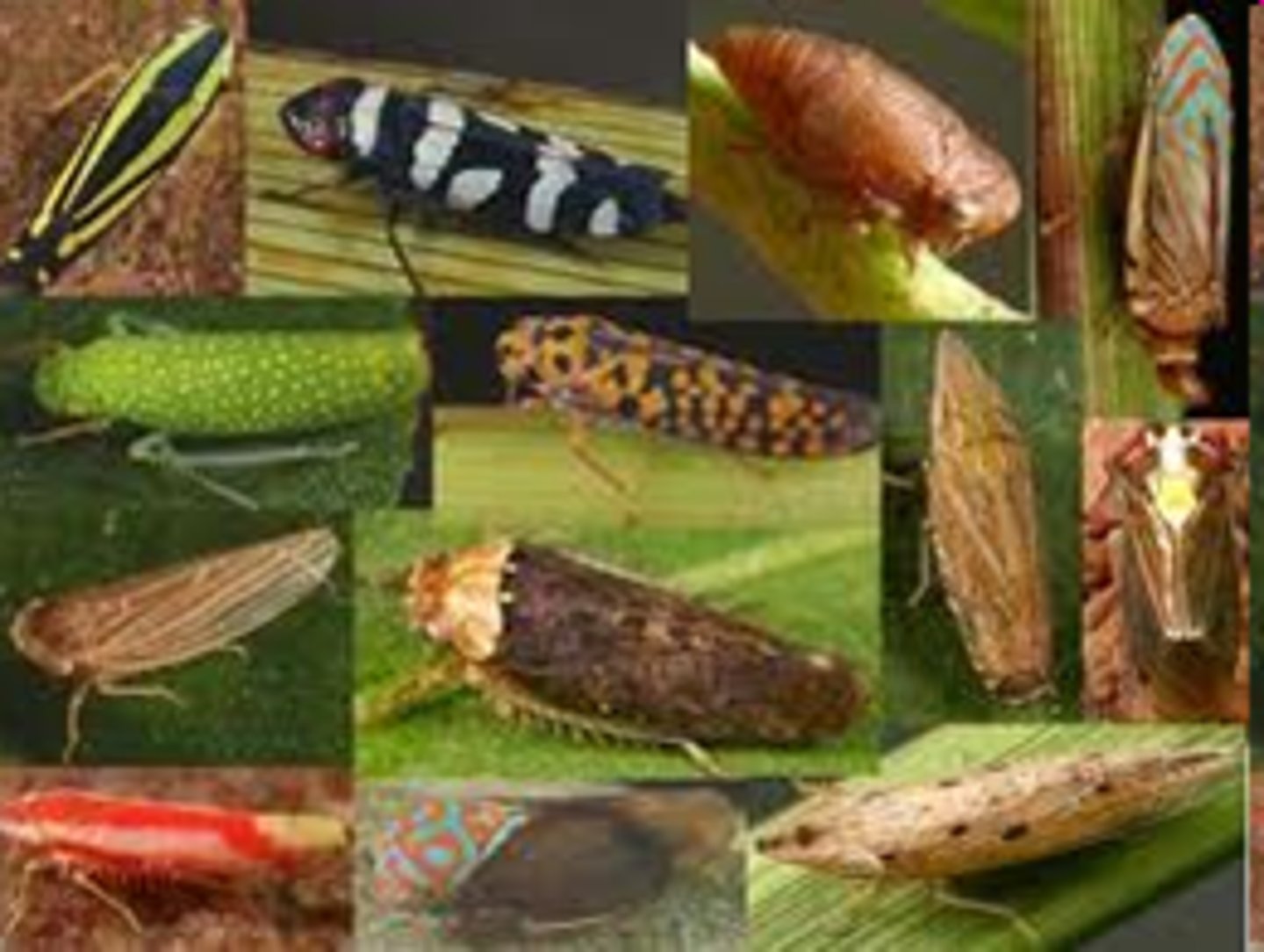
Hemiptera
-(hemi = half, pterón = wing)
-Insect group known as true bugs with piercing/sucking mouthparts
-cicadas, aphids, bed bugs, kissing bug, lice.

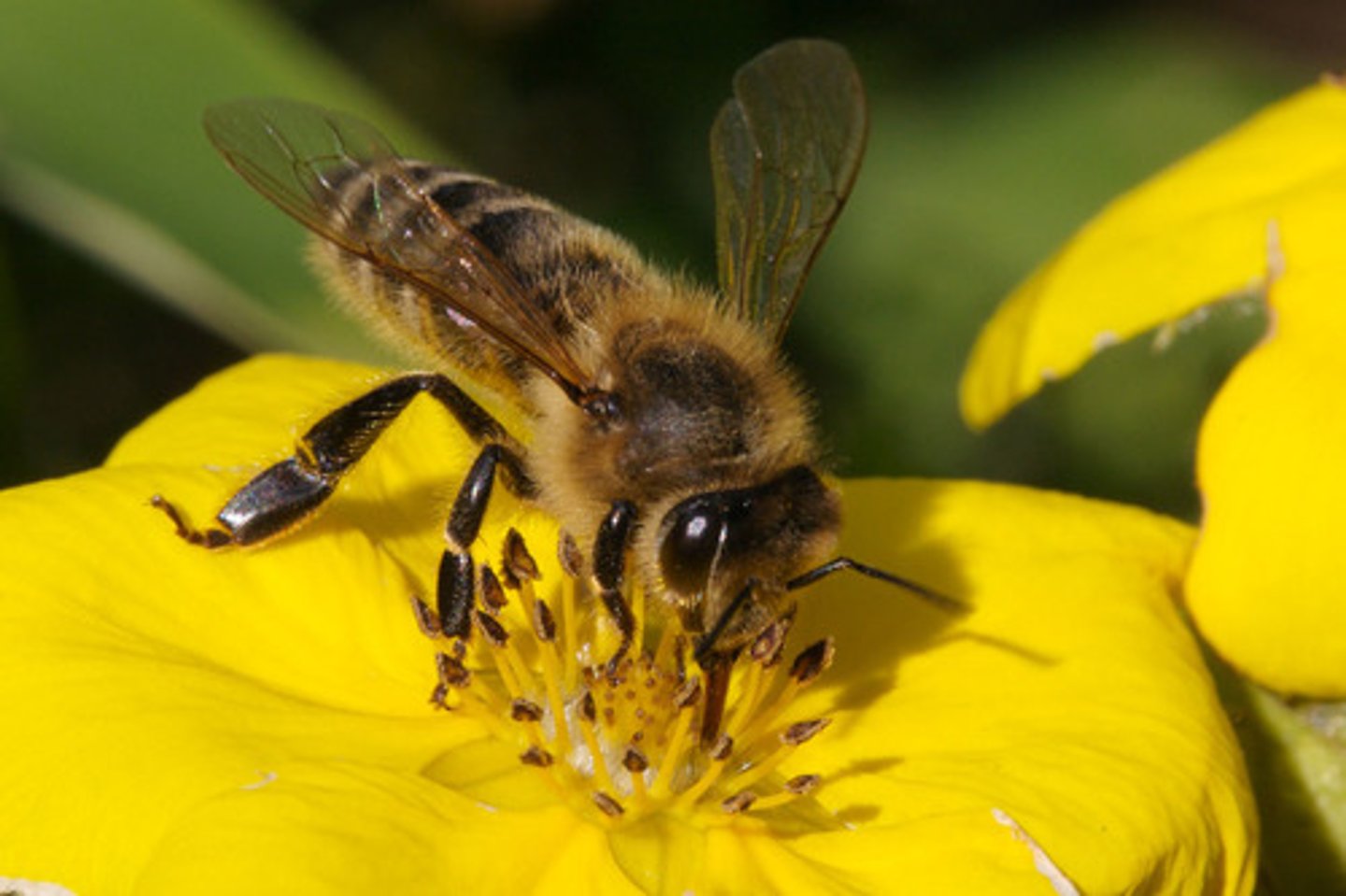
Hymenoptera
-Insect group with 2 pairs of wings (fore and hind) connected by zipper-like hamuli
-ants, bees, wasps.

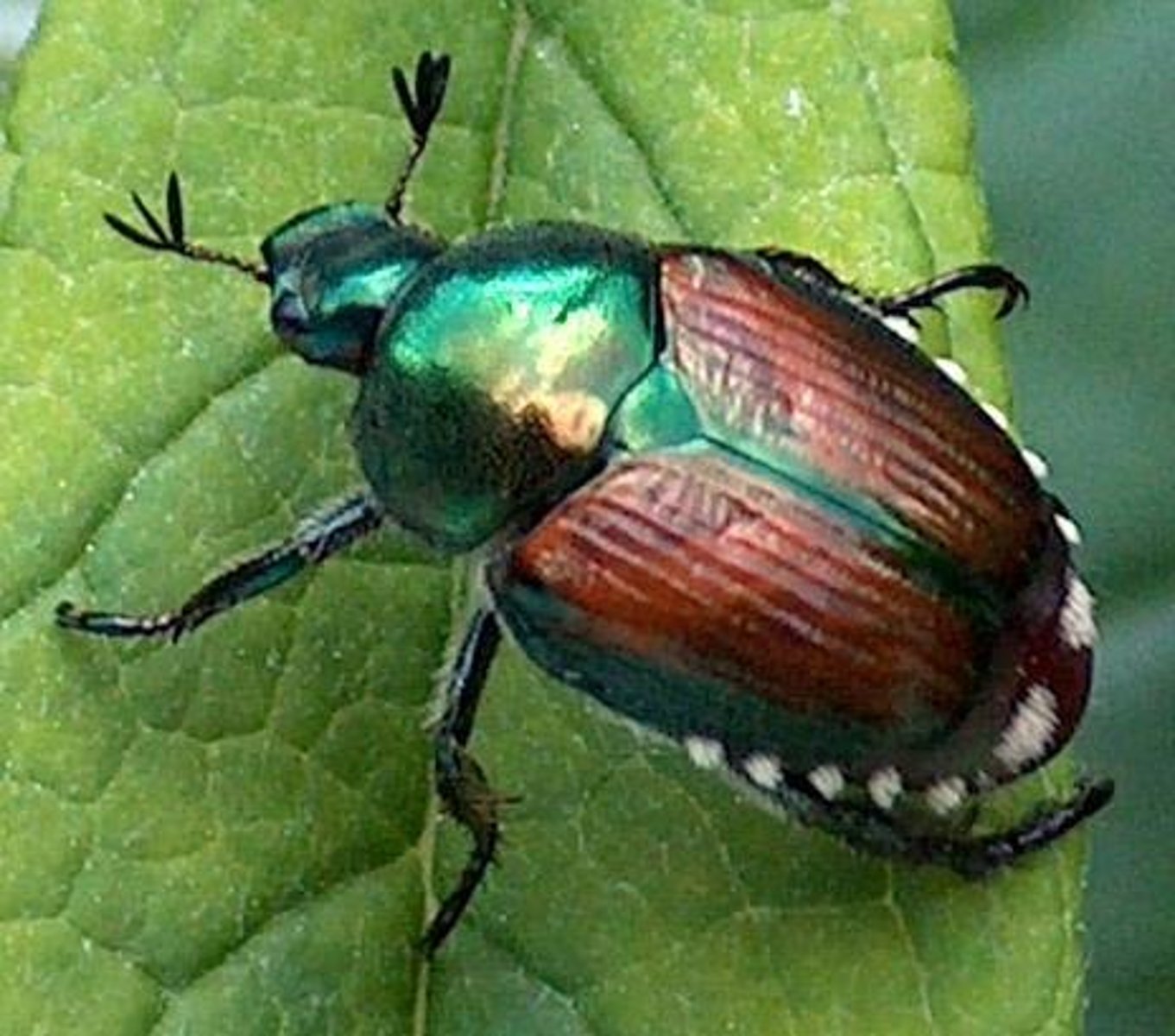
Coleoptera
-(koleos = sheath, pterón = wing)
-Insect group of beetles with 2 pairs of wings, forewings modified into hardened wing cases (elytra)
-scarab beetle, ladybug, weevils.

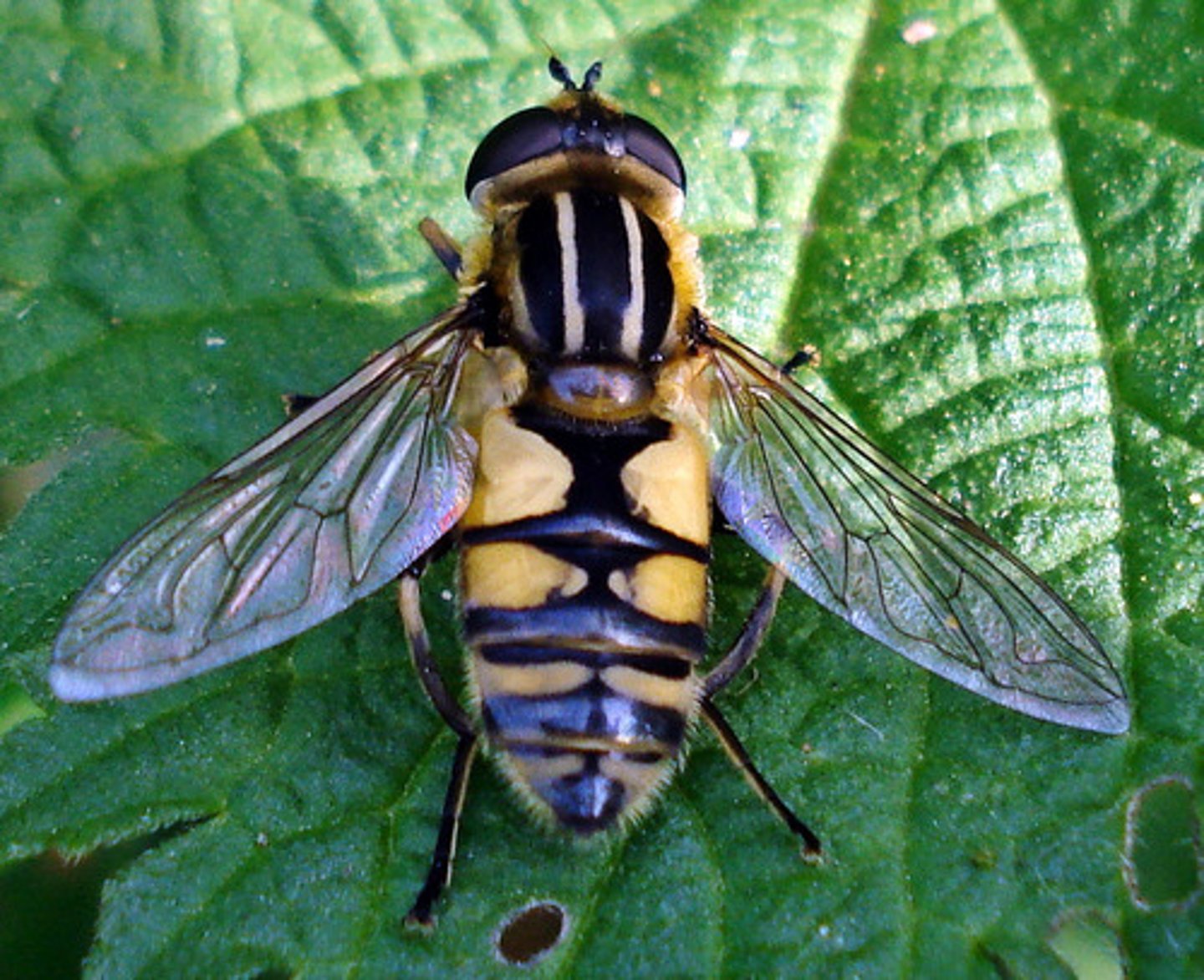
Diptera
-(di = two, ptera = wings)
-Insect group of flies with 2 pairs of wings, hindwings modified into mechanosensory organs (halters)
-house flies, crane flies, mosquitoes.

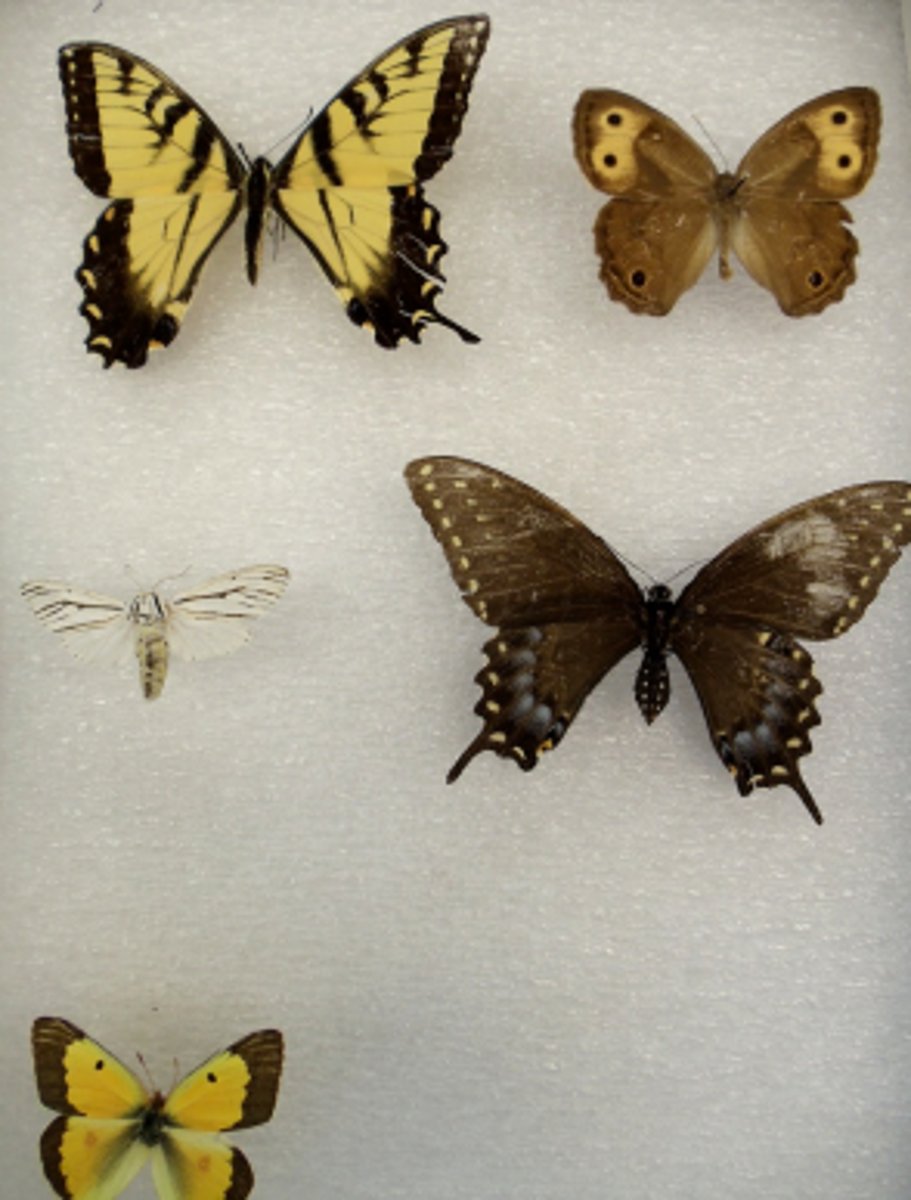
Lepidoptera
-lepídos = scale, ptera = wings)
-Insect group with 2 pairs of wings covered in tiny scales and tubular mouthparts (proboscis) for siphoning nectar
-moths and butterflies.

What are the 2 deuterostome groups?
1. Echinoderm
2. Chordates
Diagnostic features of Echinoderms
-pentaradial symmetry
-water vascular system
-calcareous endoskeleton with catch collagen under neural control
Water vascular system
system of fluid-filled tubes used by echinoderms in locomotion, feeding, waste/nutrient transport and respiration
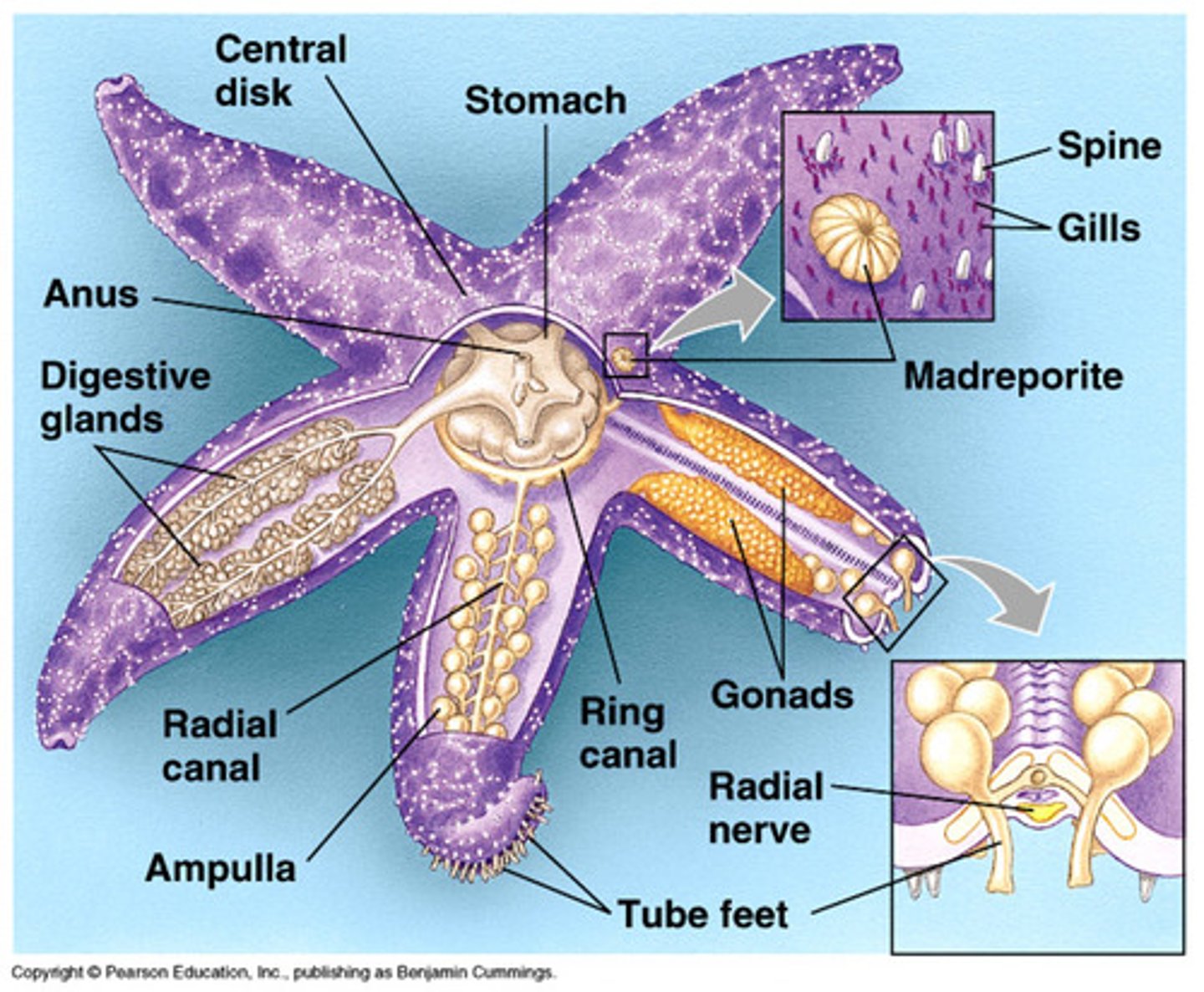
calcareous endoskeleton
Internal skeleton made of calcium carbonate plates

What are the 5 main groups of Echinoderm?
1.Crinoids
2.Asteroids
3.Ophiuroids
4.Echinoids
5.Holothuroids.
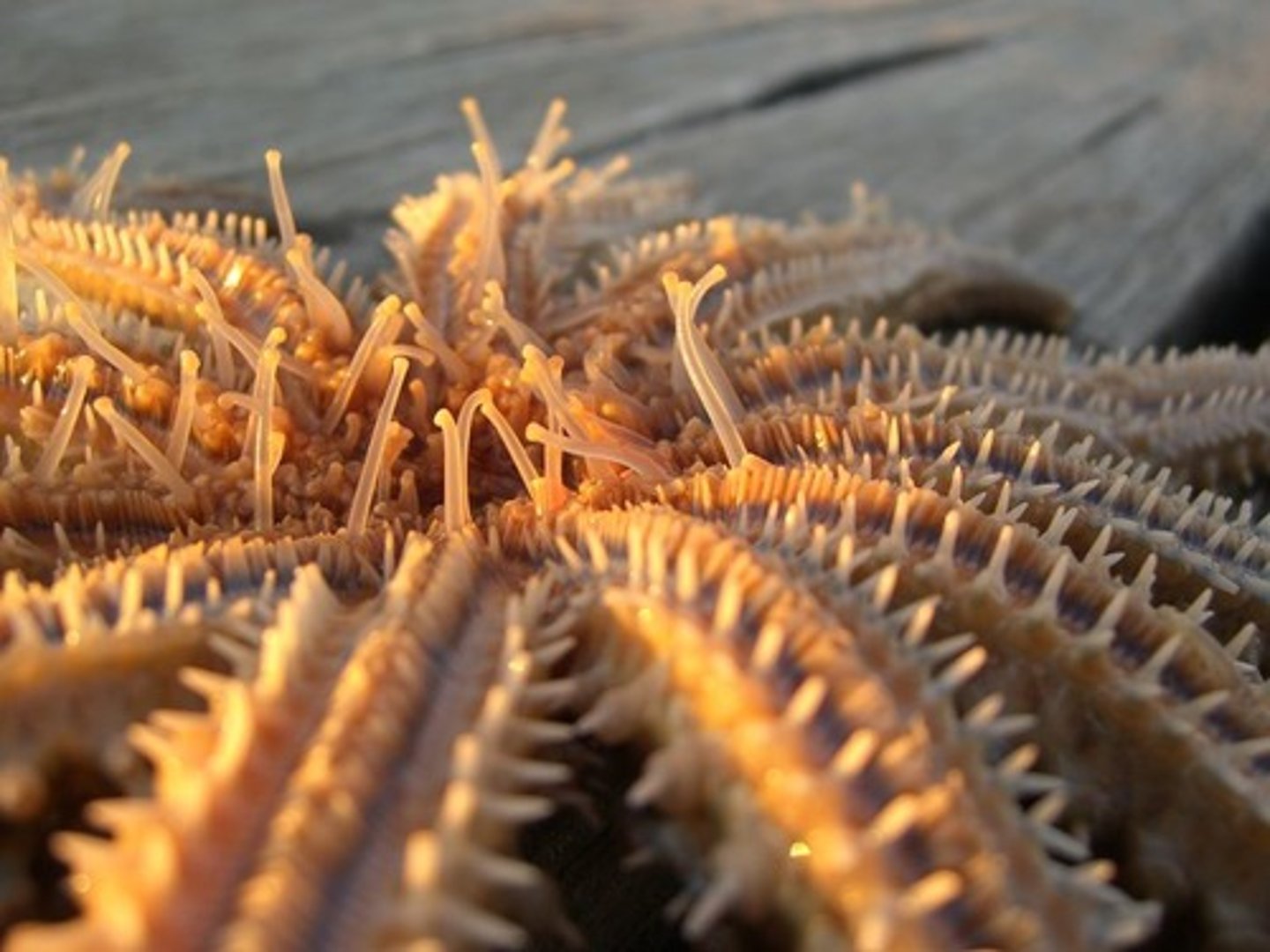
Crinoids
Echinoderm group known as feather stars with a dorsal oral surface.
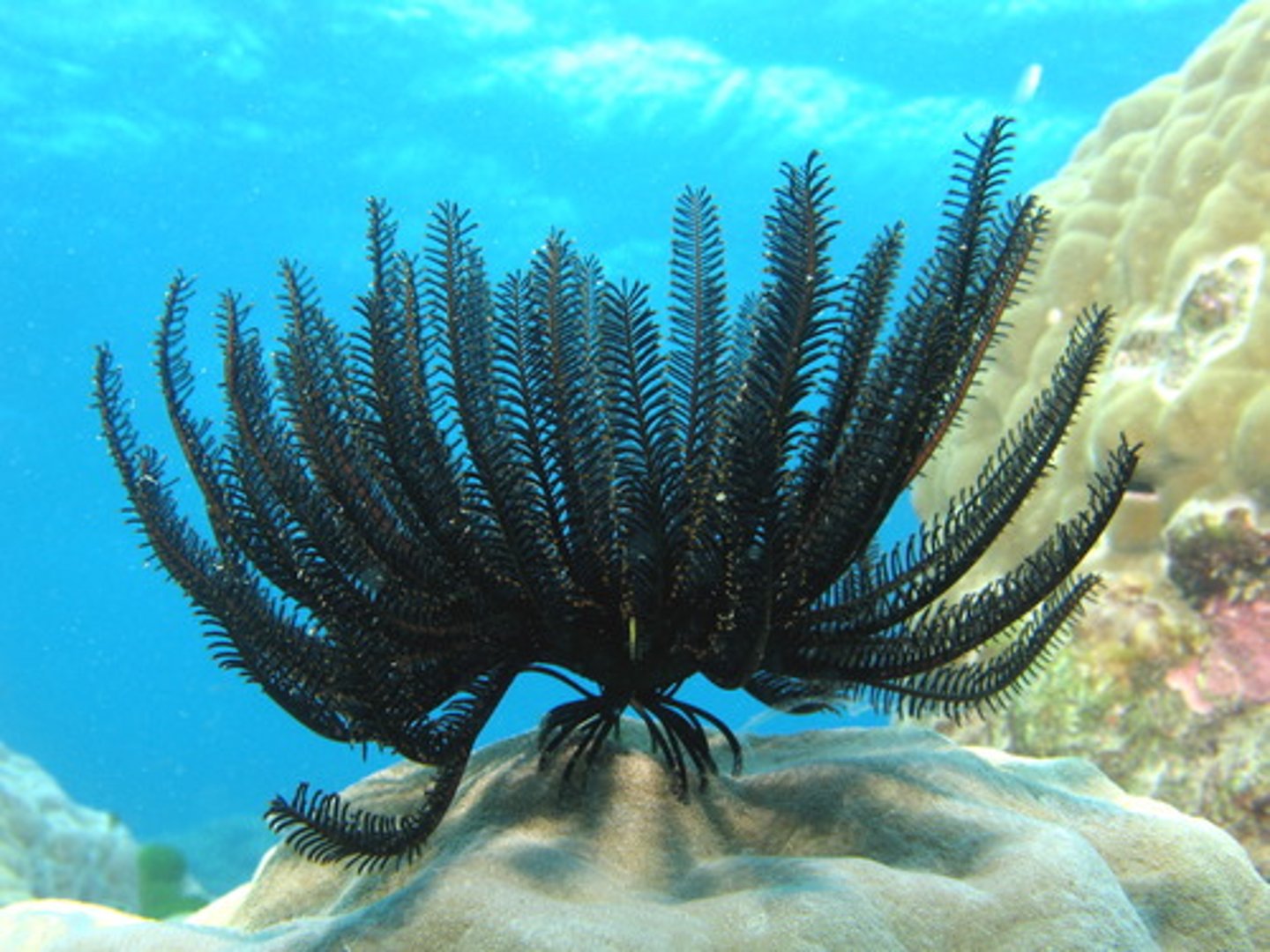

Asteroids
Echinoderm group known as sea stars that feed on bivalves.
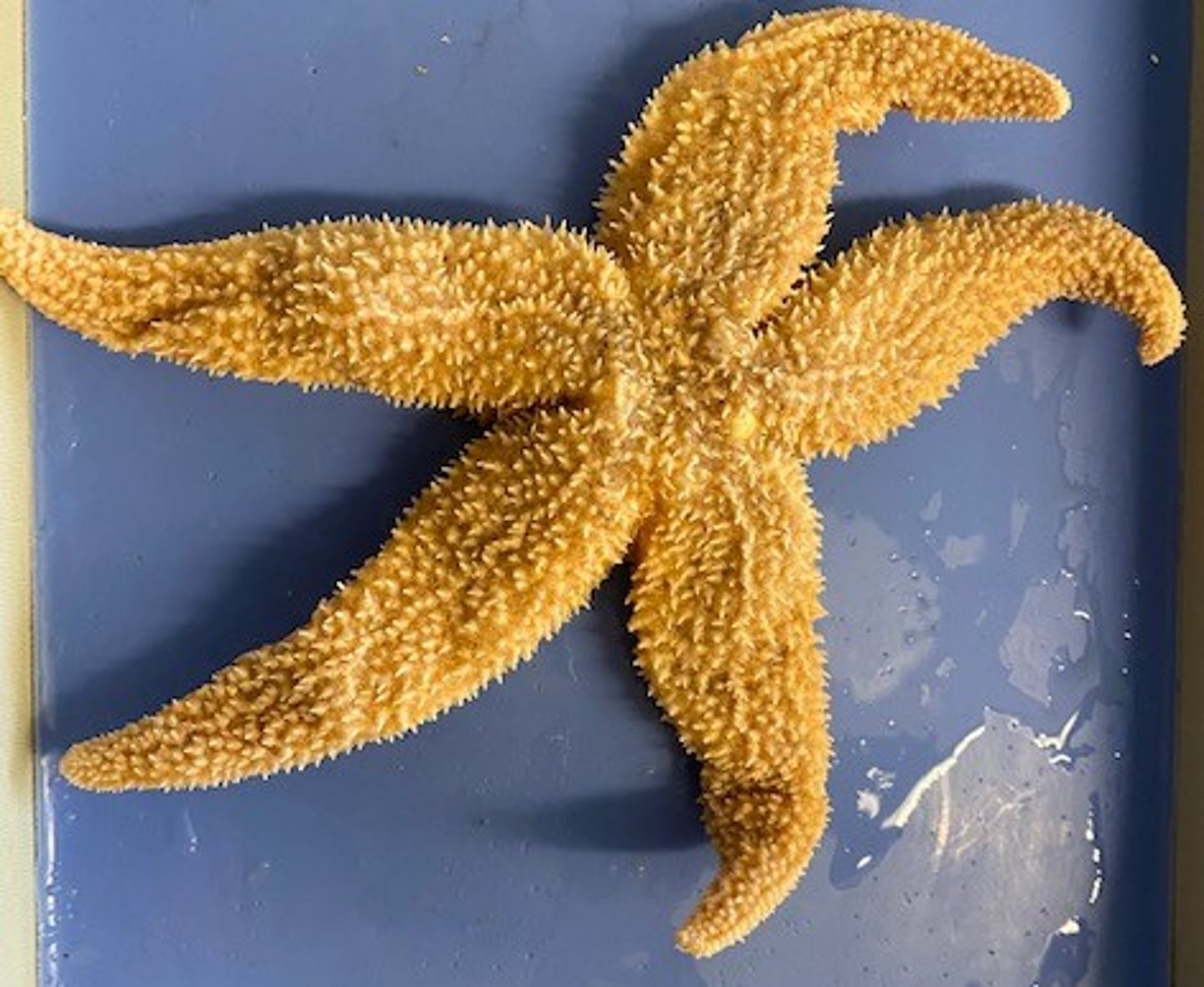

Ophiuroids
Echinoderm group that includes fast-moving predators (brittle stars) and filter feeders (basket stars).
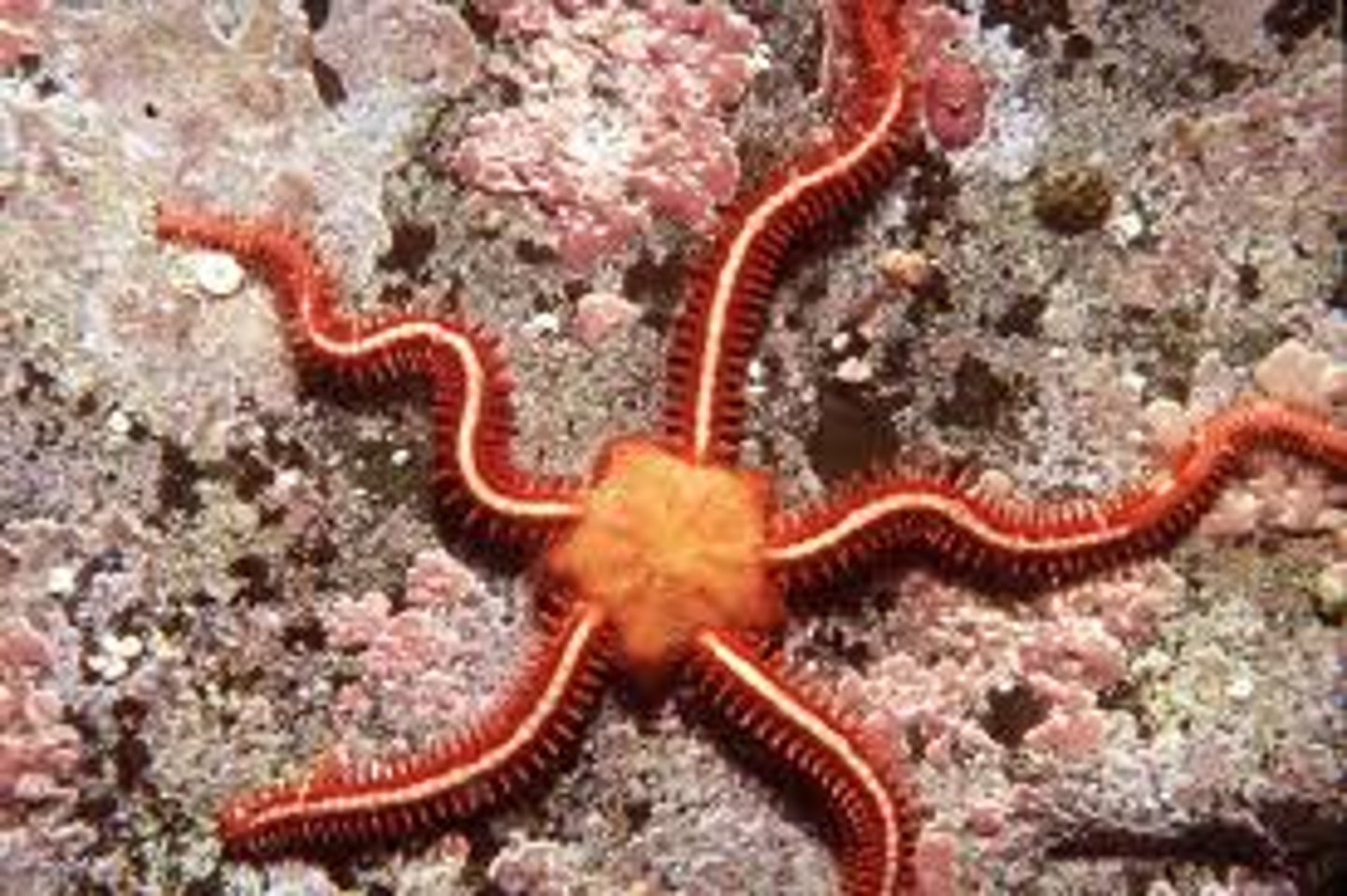

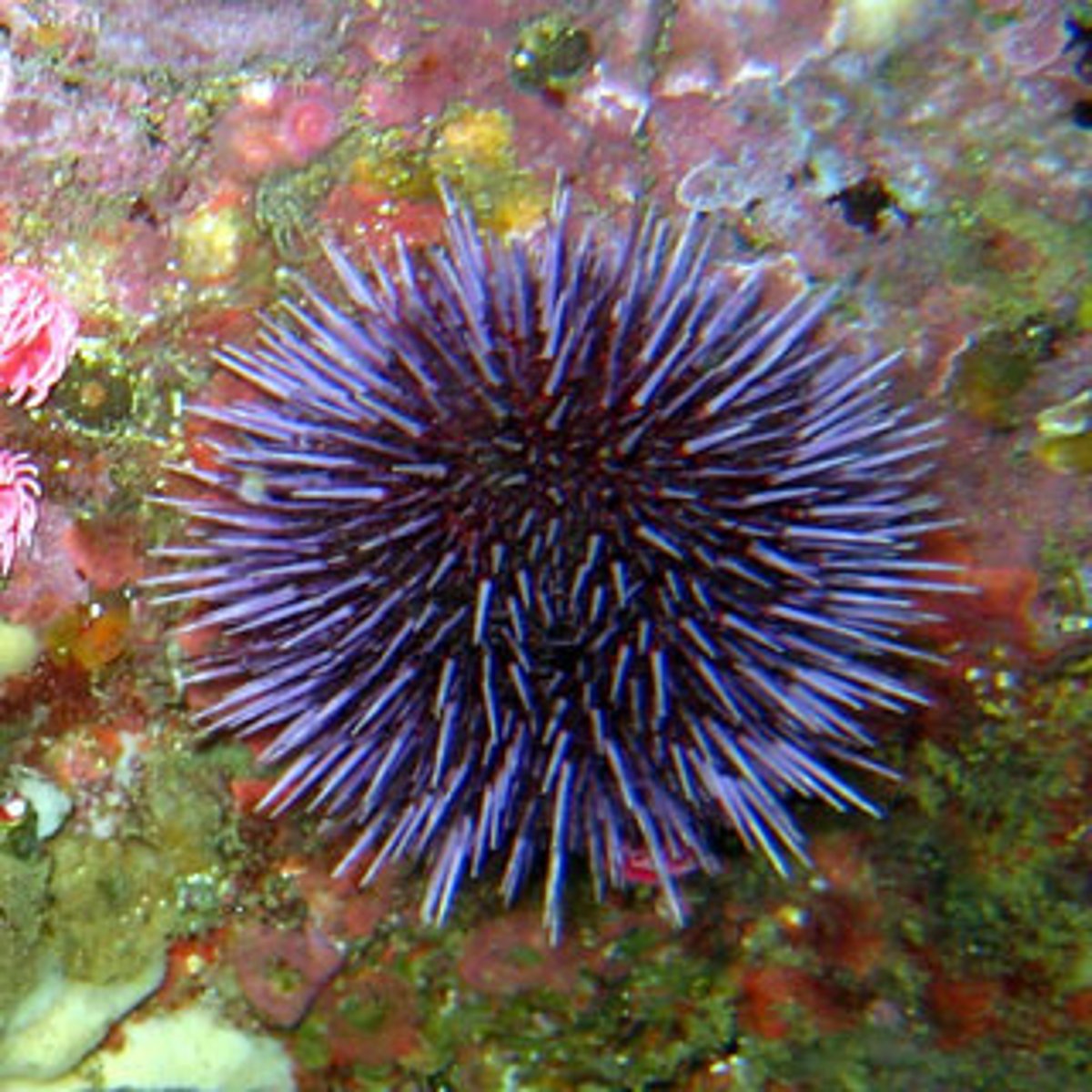
Echinoids
Echinoderm group (sea urchins and sand dollars) that are slow-moving algal grazers.

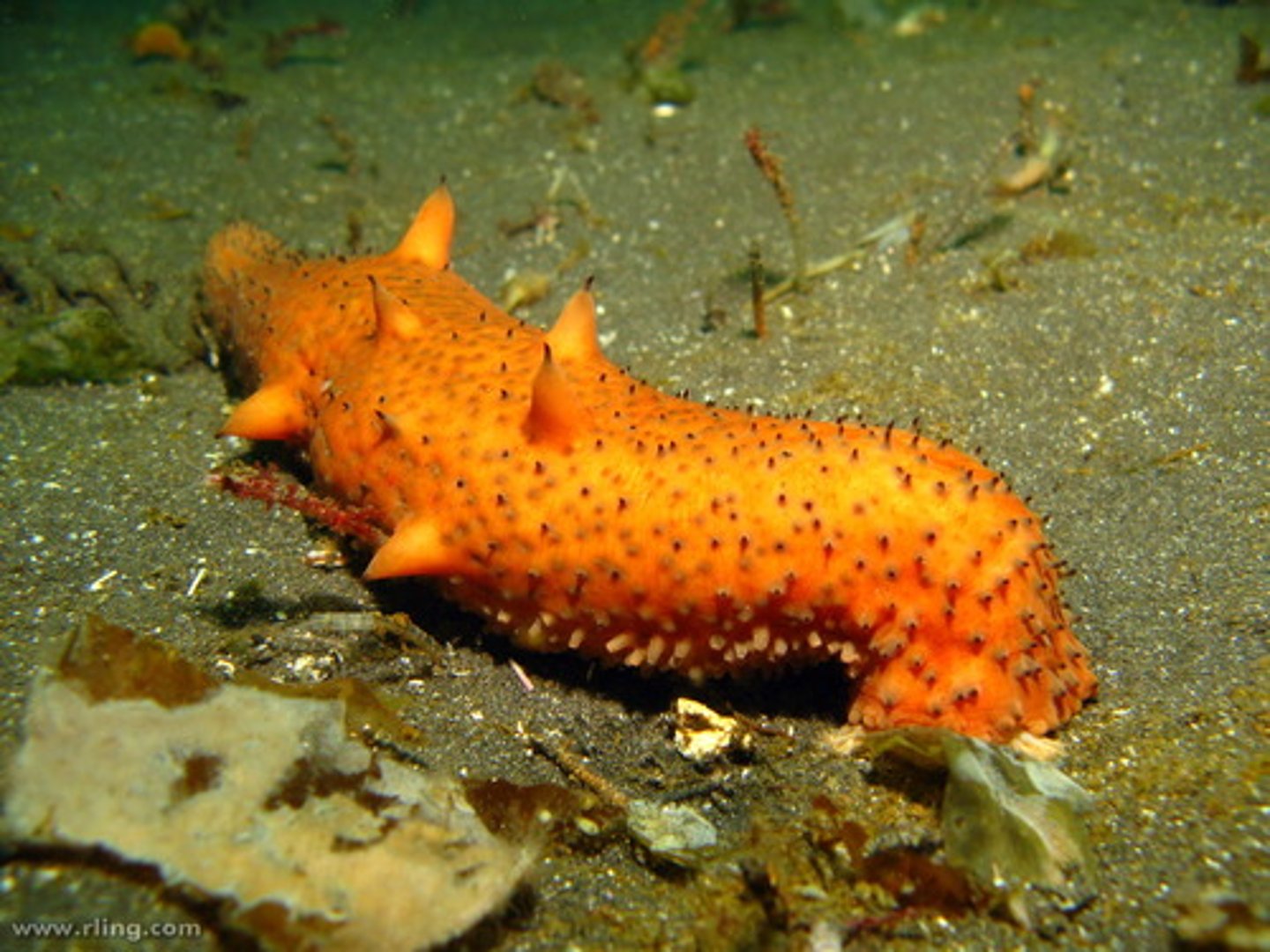
Holothuroids
Echinoderm group known as sea cucumbers, characterized by bizarre forms.

true or false: bilaterial symmetry evolved (secondarily) in the MRCA of Echinoids and Holothuroids
true
Diagnostic features of Chordates
1. Notochord (stiff but flexible rod derived from mesoderm)
2. dorsal hollow nerve cord (DHNC): conveys neural signals along the a-p axis derived from ectoderm via the process of neurulation
3. post-anal tail: used for locomotion
true or false: chordates originated in an aquatic environment and evolved a number of innovations that enabled one group
true
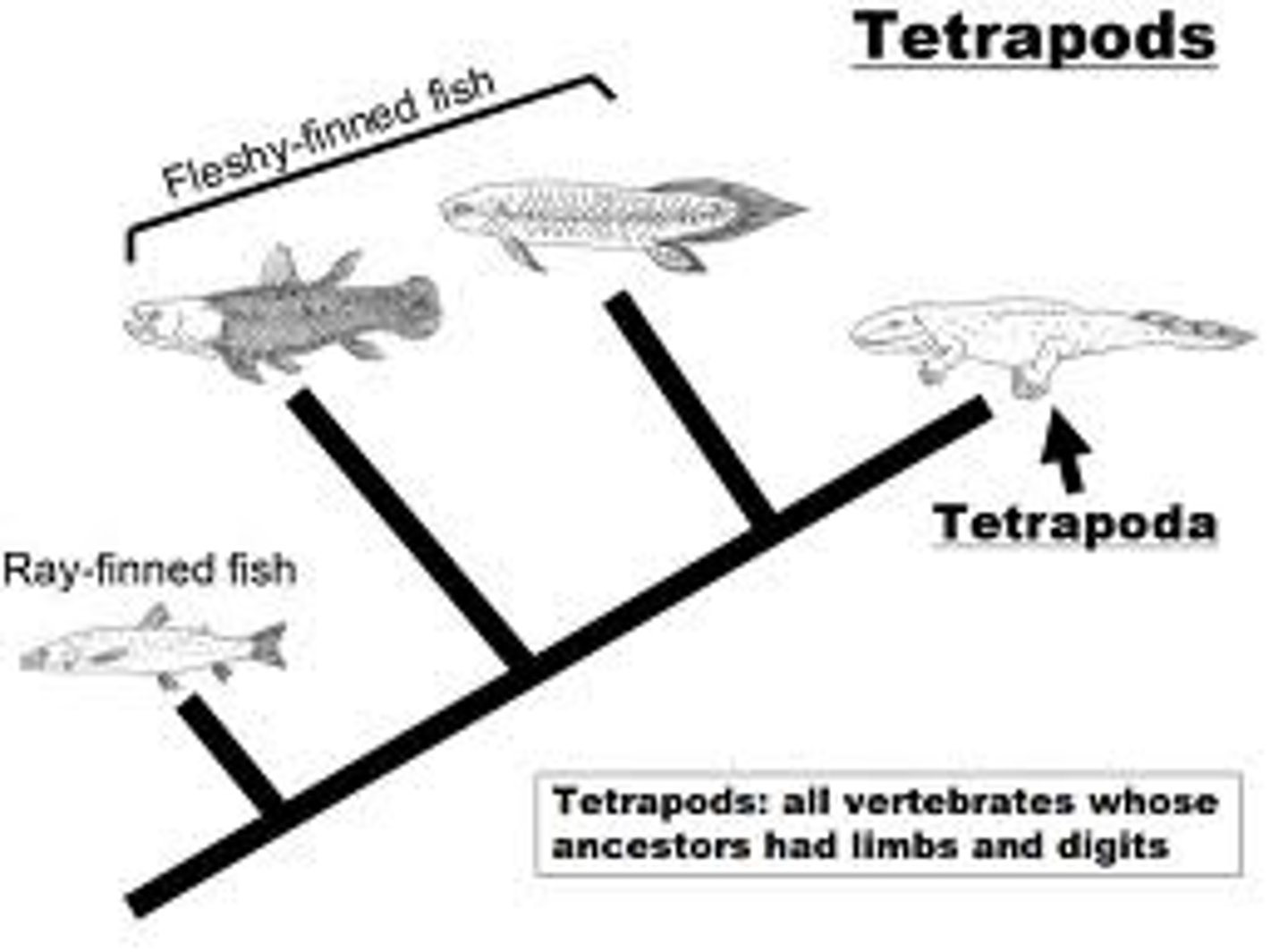
Tetrapods
Group of chordates that colonized land ~360Mya, characterized by four jointed limbs derived from lobed fins.
Diagnostic features of Vertebrates
-Vertebrae surrounding the DHNC
-a cranium (brain case).

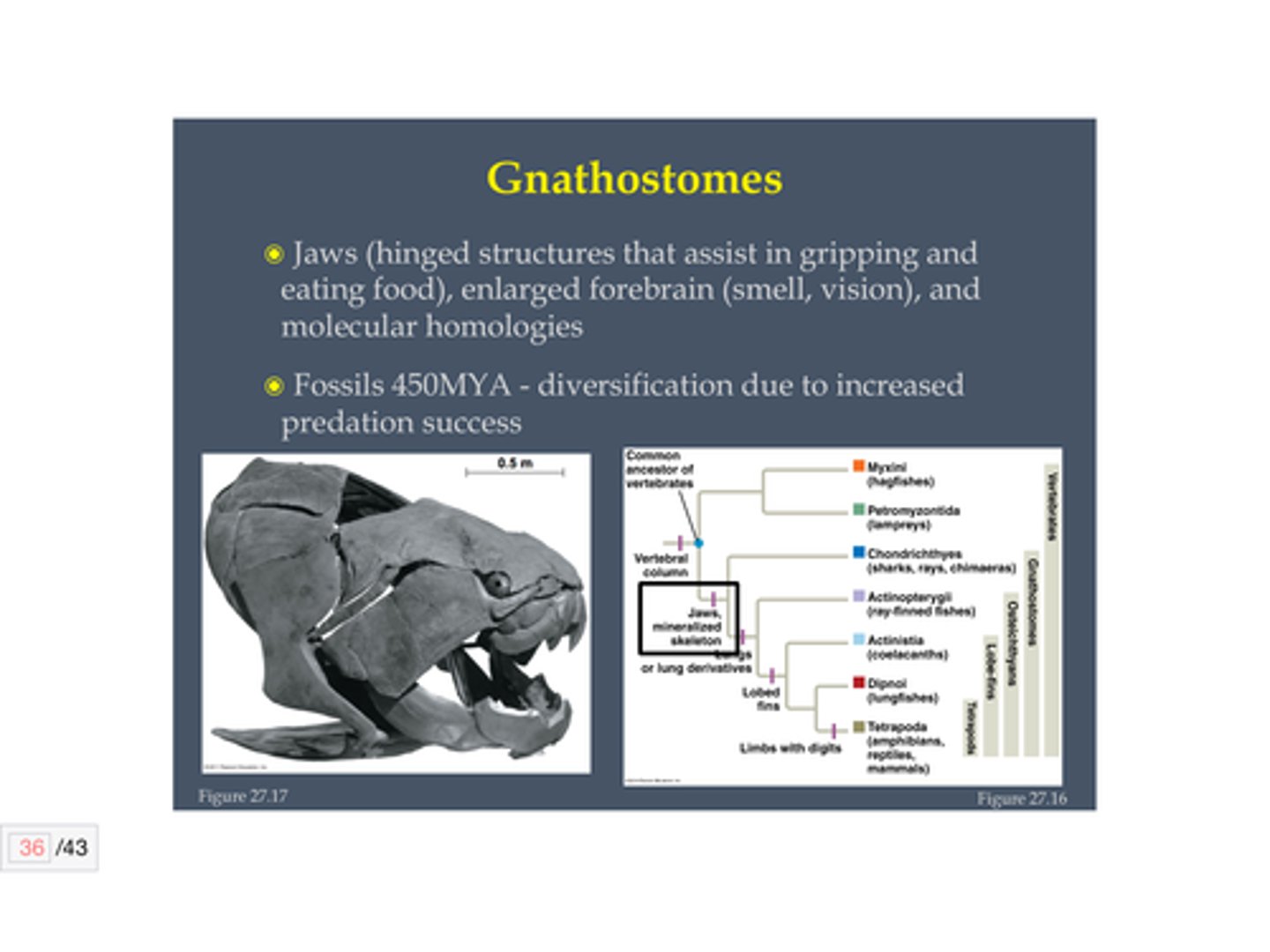
Diagnostic features of Gnathostomes
-Jaws (derived from cartilaginous gill-arch supports)
-teeth
-bone (derived from the mesoderm) providing a rigid endoskeleton.
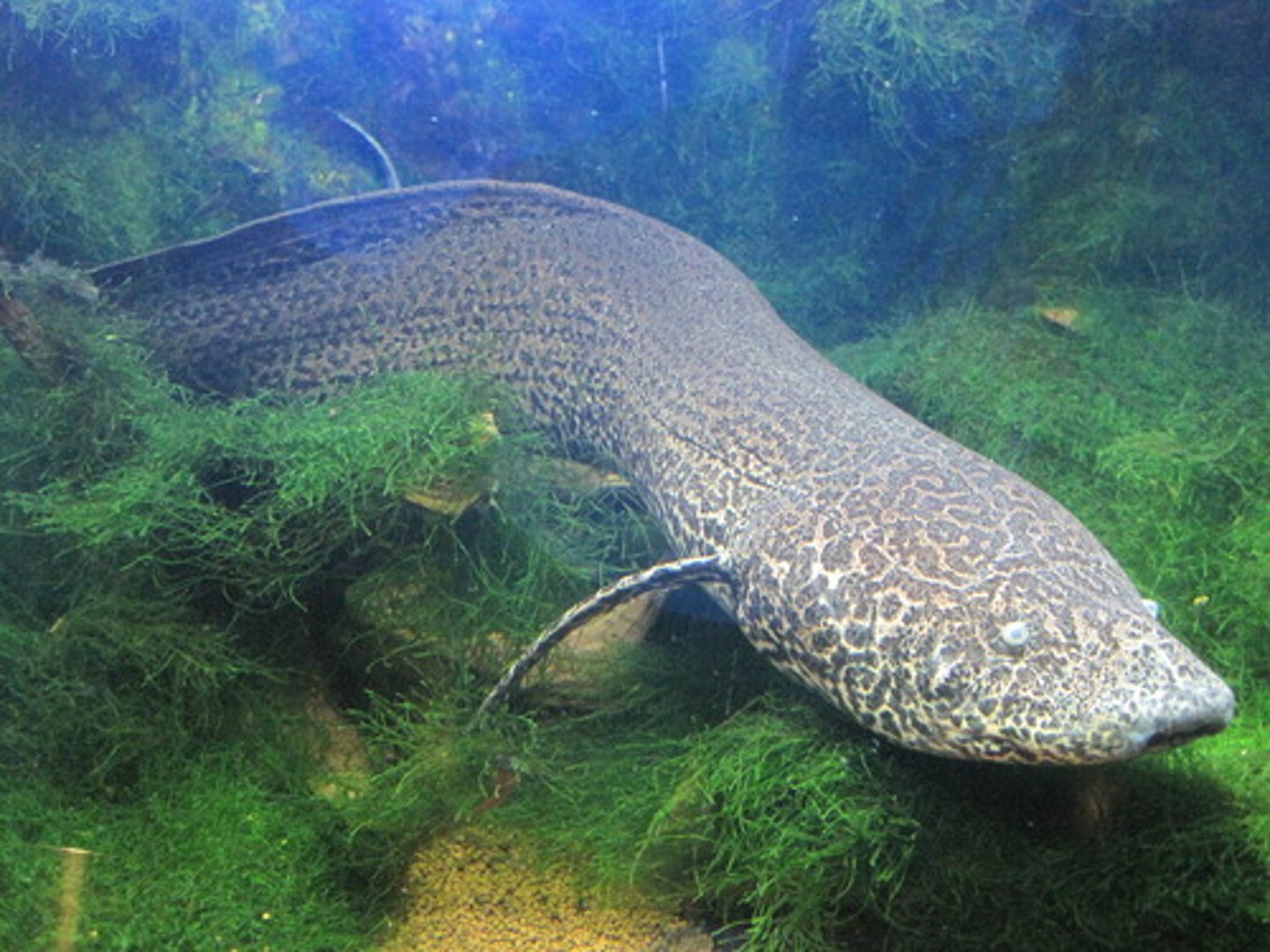
Diagnostic features of Osteichthyes
-Swim bladder: gas-filled sac for buoyancy regulation
-operculum: covering over gill arches for respiration.

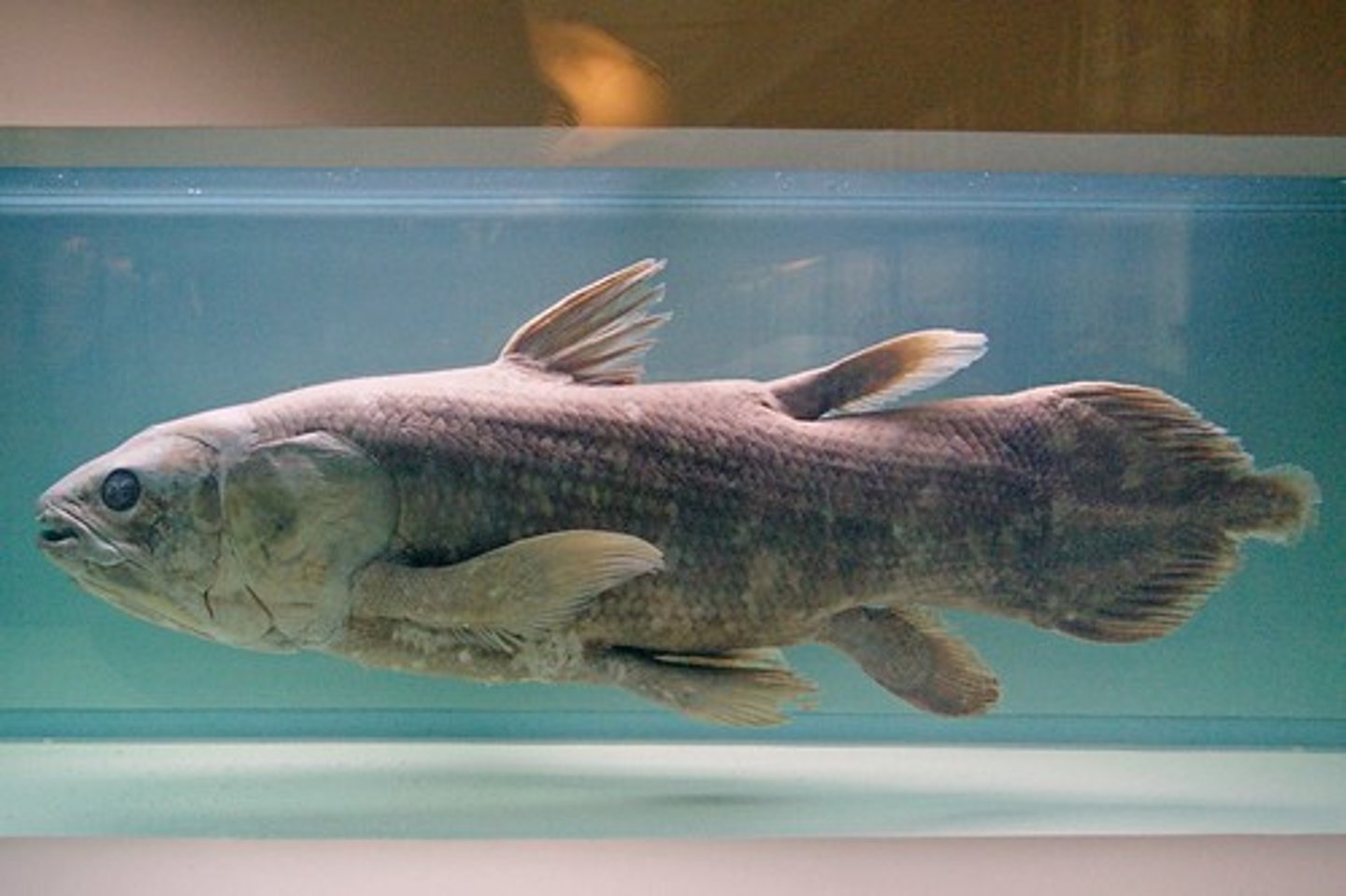
Diagnostic features of Sarcopterygii
Fleshy fins articulate with the body via a single bony element.
Diagnostic features of Rhipidistia
-Lungs (respiratory organs derived evolutionarily from swim bladder) ; initially unpaired with subsequent evolution of paired lungs.

Diagnostic feature of Tetrapods
Four jointed limbs derived evolutionarily from lobed fins.
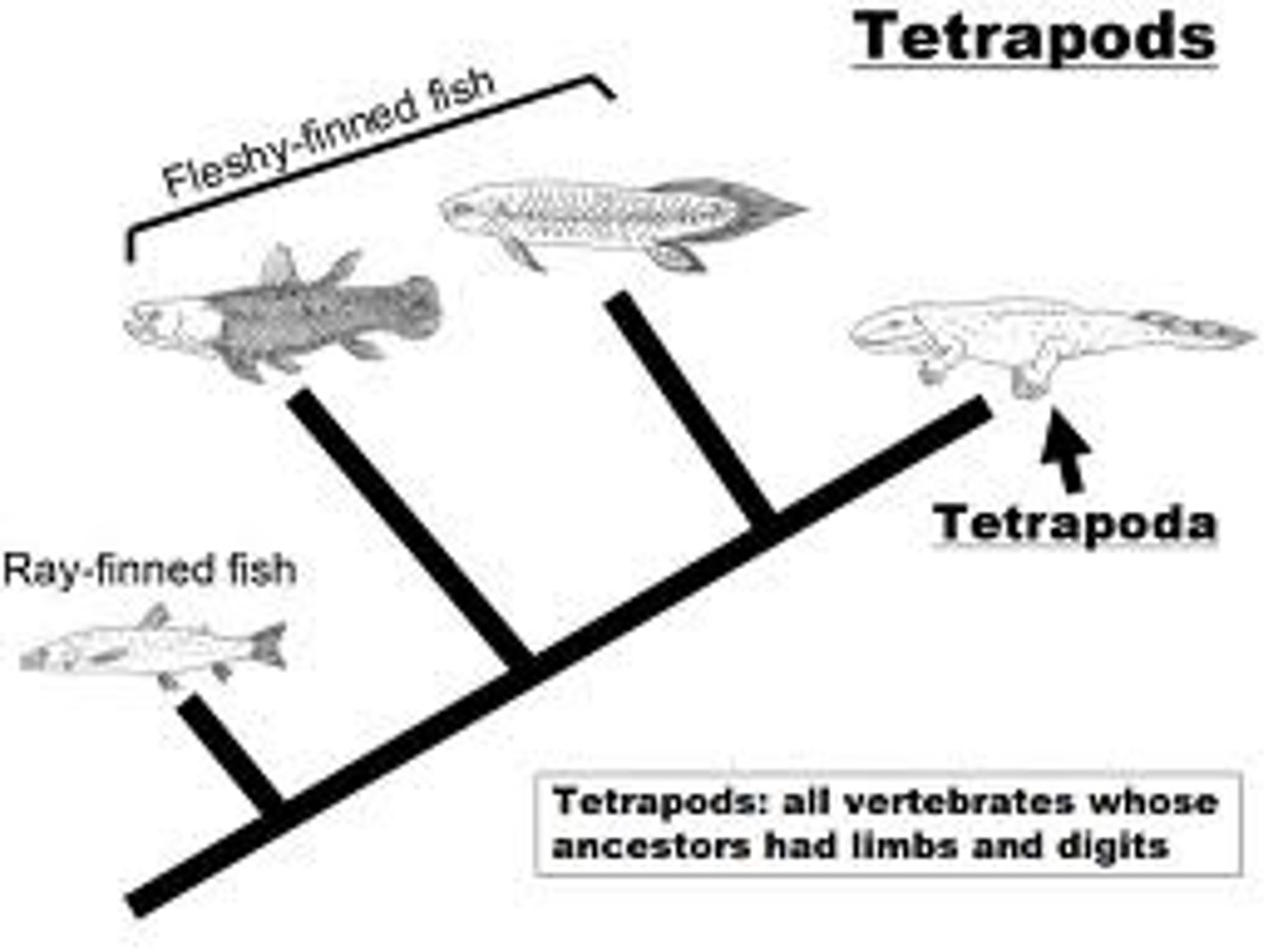
What are the 2 types of tetrapods?
amphibians and amniotes
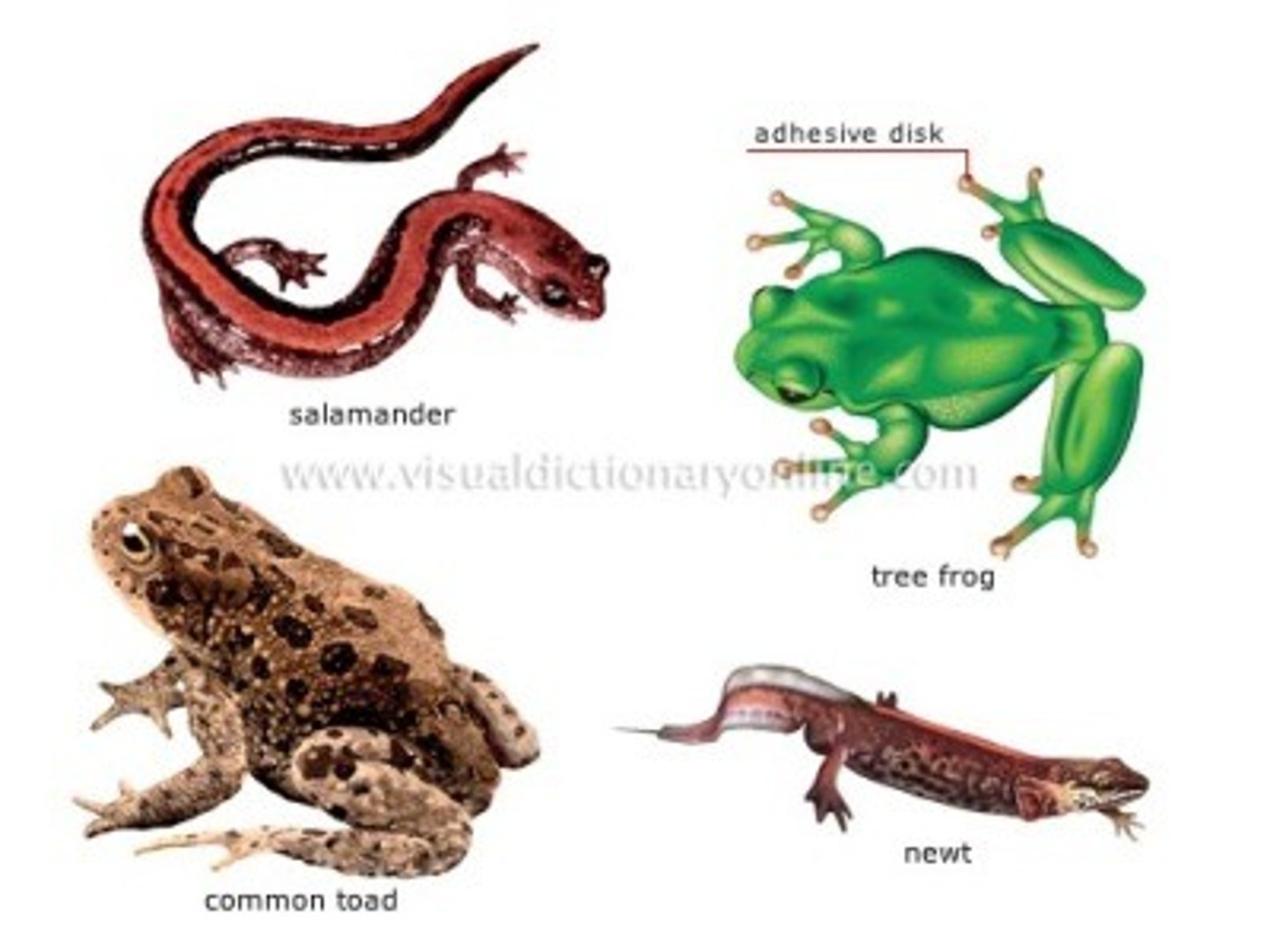
Amphibians
Tetrapods restricted to mesic terrestrial habitats b/c of poorly developed lungs (many species rely on cutaneous respiration) and reproduction (many species are metamorphic with an aquatic larval stage)
-includes frogs/toads, salamanders, and caecilians.
Amniotes
-Tetrapods that evolved features enabling colonization of fully terrestrial habitats
-includes Reptiles and Mammals.
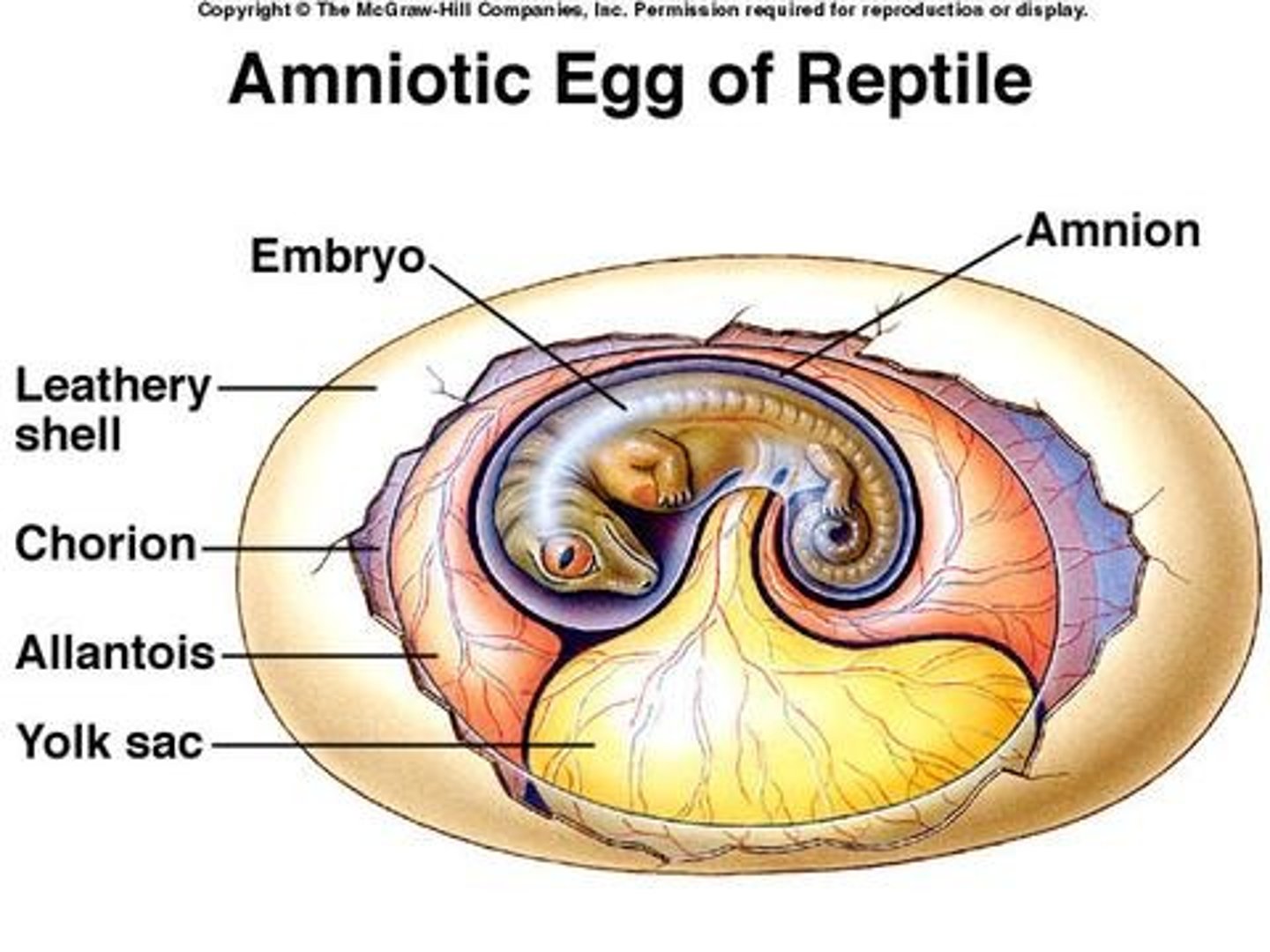
Diagnostic features of Amniotes
Amniotic egg, impermeable skin to reduce water loss.
efficient kidneys
allow nitrogenous metabolic byproducts to be excreted as concentrated urine to minimize water loss
three-chambered heart
a type of heart found in reptiles
two cranial fenestrae
skull openings characteristic of reptiles
Lepidosaurs
ecologically and morphologically diverse group with many secondarily limbless species, includes Tuatara, lizards, snakes and amphisbaenians
Chelonia
primarily aquatic group with a bony shell (comprised of carapace and plastron), includes turtles and tortoises
Crocodilia
marine and freshwater predators confined to tropical and warm-temperate regions, includes crocodiles, alligators and caiman; have 4-chambered hearts
Pterosaurs
now entirely extinct, this was the first group of vertebrates to evolve powered flight, prevalent throughout the Mesozoic (228-66Mya), hollow bones, membranous wings, warm blooded with hair-like filaments known as pycnofibers on the head and torso
Dinosaurs
arose ~240Mya and were the dominant terrestrial vertebrates throughout the Jurassic and Cretaceous (~201-66Mya), with only one group, Birds, surviving the Cretaceous-Paleogene mass-extinction event
mammary glands
secrete nutrient-rich milk to nourish young
endothermy
high metabolic rates and facilitates active lifestyles
hair/fur
provides insulation to minimize heat loss from the body
four-chambered heart
allows for complete separation of de/oxygenated blood
one cranial fenestra
skull opening characteristic of mammals
Monotremes
lay shelled eggs and occur in Australia and New Guinea, includes Platypus and Echidna
Marsupials
have placenta and ventral pouches with teats; juveniles crawl to the pouch where they are nourished until fully developed
Eutheria
have a well-developed placenta and give birth to developed young, includes ~4000 species that are morphologically and ecologically diverse
large brain size
a diagnostic feature of humans
extensive construction and use of tools
a diagnostic feature of humans
Modern humans (Homo sapiens)
arose ~200,000 years ago, and co-existed with several congeneric (hominine) species until only ~40,000 years ago
blastopore develops into anus
a characteristic of deuterostomes
vertebrae
the series of bones forming the backbone in vertebrates
notochord
a flexible rod that provides support in chordates
dorsal hollow nerve cord
a nerve cord found in chordates that runs along the back
post-anal tail
an extension of the body beyond the anus found in chordates