[BIO 120.12] Final Exam - Exercises 5 to 8
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
Sucrose
Example of an oligosaccharide
Glucose
Example of a monosaccharide
Starch, Glycogen
Examples of polysaccharides
Triple Sugar Iron Agar
Rich medium designed to differentiate bacteria based on glucose, sucrose, and lactose fermentation
Glucose, Sucrose, Lactose
What sugars are being tested in TSI agar?
Phenol red
pH indicator used in TSI agar
TRUE
T/F: Phenol red is a pH indicator in TSI agar
FALSE
T/F: Phenol red is an indicator of H2S production
Sulfur reduction
Aside from sugar fermentation, TSI agar is also used to test for?
Iron
What is used as H2S indicator in TSI agar?
Ferrous sulfate, Sodium thiosulfate
In TSI Agar, what are the sources of oxidized sulfur?
Ferments glucose and lactose/sucrose
TSI: Yellow slant and butt
Gas production from fermentation of any of the sugars
TSI: Fissures in the medium (lifting the agar off the bottom of the tube)
Ferments glucose but not lactose and/or sucrose
TSI: Red slant and yellow butt
H2S production; Ferments glucose and lactose/sucrose
TSI: Black butt, yellow slant
H2S production; Ferments glucose
TSI: Black butt, red slant
No fermentation; Peptone and amino acids as C and N sources under aerobic and anaerobic conditions
TSI: Red slant and butt
No fermentation; Peptone and amino acids as C and N sources under aerobic conditions only
TSI: Red Slant
Ability to use citrate as sole carbon source and perform citrate fermentation
What does the citrate utilization test for?
Enterobacteriaceae
Citrate utilization is best used for differentiating members of?
Simmons Citrate Agar
What agar is used for Citrate Utilization?
Citrate
Sole C source in SCA?
Ammonium phosphate
Sole N source in SCA?
Bromothymol blue
pH indicator in SCA?
Citrate permease
Citrate Utilization: Bacteria with ___ can transport citrate into the cell
Green at pH 6.9, Blue at pH 7.6
What are the results of SCA with bromothymol blue as pH indicator?
Citrate is hydrolyzed into oxaloacetate and acetate using citrate lyase
What happens to citrate after it has been transported into the cell?
Oxaloacetate is converted to pyruvate, Pyruvate can be converted to a variety of products depending on pH
In Citrate Utilization, after oxaloacetate and acetate has been produced from hydrolysis of citrate, what happens to these two?
Citrate is utilized; Ammonium phosphate is converted to ammonia and ammonium hydroxide (alkalinize the agar)
Citrate Utilization: Blue (even a small amount)
Citrate is utilized; Incomplete incubation
Citrate Utilization: No color change, with growth
Citrate is not utilized
Citrate Utilization: No color change, no growth
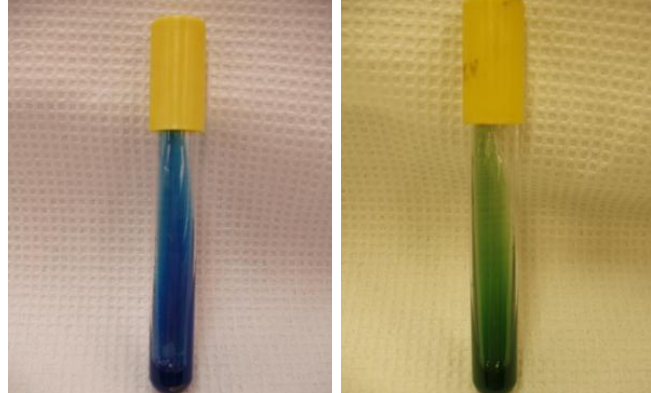
Enterobacter, E. coli
Give the most probable species that give the following results (L-R)
Starch Hydrolysis
Amylase Test is a test for?
0.1% glucose, 1% sucrose, 1% lactose
What are the %s of the sugars added in TSI?
a-D-glucose subunits bonded by 1,4-a-glycosidic (acetal) linkages
What is starch made up of in terms of subunits and linkages?
Amylose (linear), Amylopectin (branched)
What are the 2 forms of starch?
Amylopectin
What is the predominant form of starch?
α-amylase and Oligo-1,6,-glucosidase
2 extracellular enzymes that can hydrolyze starch
TRUE
T/F: α-amylase and Oligo-1,6,-glucosidase are extracellular enzymes
FALSE
T/F: α-amylase and Oligo-1,6,-glucosidase are intracellular enzymes
Break glycosidic linkages between sugar subunits
What is the mechanism of α-amylase and Oligo-1,6,-glucosidase in hydrolyzing starch?
Iodine
Detects the presence or absence of starch in the vicinity around the bacterial growth
Iodine
Substance that is later added in Starch Agar plate that reacts with starch
Blue or dark brown
What color is produced by Iodine in Starch Agar Hydrolysis?
Clear zone surrounding growth
What is the indication of starch hydrolysis in an SA plate?
B. subtilis
Bacteria used as a control for starch hydrolysis (+ starch hydrolysis)
S. aureus
Bacteria used as a control in SCA (+ for citrate utilization)
K
Symbol for alkaline in TSI
A
Symbol for acid in TSI
A/A with gas production
What is the expected result for E. coli in TSI?
FALSE
T/F: Gelatin is a carbohydrate derived from collagen
TRUE
T/F: Gelatin is a protein derived from collagen
Collagen
A component of vertebrate connective tissue from which gelatin is derived
Gelatinase
An extracellular enzyme and can hydrolyze gelatin
Gelatin → Polypeptides → Amino Acids
Explain how gelatinase works in hydrolyzing gelatin
Gelatin
Solidifying agent and substrate for enzymatic activity
Liquefied medium
What is an indication of a gelatinase positive bacteria?
S. aureus
Example of a gelatinase positive bacteria
S. epidermidis
Example of a gelatinase negative bacteria
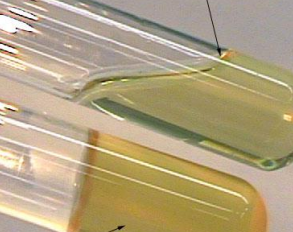
Gelatinase Positive, Gelatinase Negative
Gelatin Liquefaction: Interpret the results (top - bottom)
Lipid
Water insoluble organic biomolecules that serve as good source of metabolic fuels when broken down to fatty acids
Lipase
Bacterial extracellular enzyme that hydrolyzes lipid
Tween 80
Non-ionic emulsifier that is added to cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and foods as a source of lipid
Source of lipid
What is the function of Tween 80?
Polysorbate 80
Tween 80 is also known as?
Ca2+ and Na2+
These are the ions in ST (Sierra’s Medium with Tween 80) plate that react with fatty acids released due to lipolysis
Precipitates composed of crystals and calcium soap
The reaction between Ca2+ and Na2+ and fatty acids result to?
White or opaque zone of precipitation around line of streak
What is the expected result for lipase test for a bacteria that has lipolytic activity
Urease Test
What test is done to determine hydrolysis of urea?
Urease
Hydrolyzes urea into ammonia (usable form of nitrogen) and carbon dioxide
Hydrolyzes urea into ammonia (usable form of nitrogen) and carbon dioxide
What does urease do?
Proteus
Example of a bacteria with urease as a virulence factor?
Christensen’s medium
Differentiates rapid urease-positive bacteria from slow urease-positive and urease-negative bacteria
FALSE
T/F: Christensen’s medium differentiates rapid urease-positive bacteria from urease-negative bacteria
TRUE
T/F: Christensen’s media differentiates rapid urease-positive bacteria from slow urease-positive and urease-negative bacteria
Decarboxylation of certain amino acids
Urea is a product of?
Urine
Urea is the primary nitrogenous waste in ___.
Phenol red
pH indicator in Christensen’s medium
Yellow or orange (below pH 8.4), Red or pink (above pH 8.4)
What are the 2 expected results for Christensen’s medium with phenol red as a pH indicator?
Rapid urea hydrolysis; Strong urease production
Urease Test: Pink
No urea hydrolysis; No urease production
Urease Test: Orange or Yellow
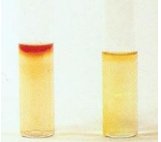
Rapid urea hydrolysis; Strong urease production; No urea hydrolysis; No urease production
Interpret (L-R)

Indole production from tryptophan
What does the indole test test for?
Tryptone broth
Source of tryptophan in indole production test?
Tryptophanase
Hydrolyzes tryptophan to pyruvate, ammonia, and indole
Pyruvate, Indole, Ammonia
Tryptophanase can hydrolyze tryptophan to __
Tryptophan hydrolysis
What is detected by the addition of Kovac’s reagent in the indole test?
Kovac’s Reagent
Added to detect tryptophan hydrolysis
Para-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde (DMABA)
Component of Kovac’s reagent that reacts with indole and produces a quinoidal compound that turns the reagent layer red
Quinoidal compound
What compound is produced by DMABA that turns the reagent layer red?
Alcohol layer
In what layer of the Kovac’s reagent is the red color expected?
Tryptophanase production + Tryptophan hydrolysis; No tryptophanase production + No tryptophan hydrolysis
Interpret the results of the Indole production tests shown (L-R)
37 deg C for 24 h
Isolation temp and time for urea hydrolysis
37 deg C for 36-48 h
Isolation temp and time for indole production
37 deg C for 48 h
Incubation temp and time for H2S production
2 drops
How many drops of Kovac’s reagent is used in testing for indole production?
15 minutes
How many minutes are the incubated NG tubes placed in an ice bath to see if liquefaction occurs?
Lead Acetate Agar
Agar that is used to test for H2S production
Sodium thiosulfate
Component in LAA that serves as source of thiosulfate
Peptone (cysteine)
Component in LAA that serves as an organic sulfur-containing compound