Chapter 13 A&P Test
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Mr. Dowd A&P1; Initially compiled by tucker50smith on Quizlet. I added pictures
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
A patient with no sensation in the left thumb would most likley have nerve damage of the _________ spinal nerve.
C6
A _________ is a cordlike organ composed of numerous _________.
nerve; axons
Sensory stimuli enter the spinal cord via _________.
afferent axons
A mixed nerve consists of both _________ and _________.
afferent; efferent fibers
The connective tissue that surrounds a nerve fascicle is called the ________.
perineurium
Which of the following nerves originates in the lumbosacral plexus?
Ilioinguinal
Obturator
Sciatic
Phrenic
Axillary
Sciatic
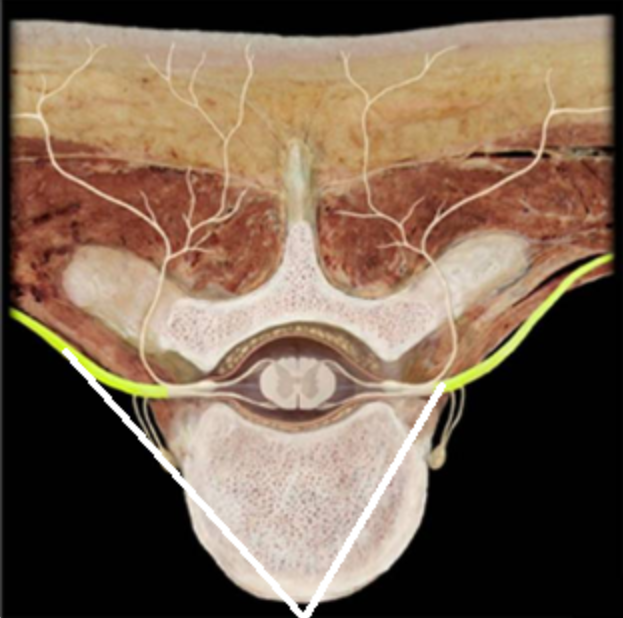
Which structures are highlighted in the picture below (reference leader lines).
Ventral rami
Which of the following is not considered a region of the spinal cord?
Sacral
Pelvic
Lumbar
Thoracic
Cervical
Pelvic
A ganglion is a ________.
cluster of cell bodies in the PNS
Interneurons are located in the ________.
spinal cord
Voluntary motor impulses leave the spinal cord via the _________ of gray matter.
anterior horn
Epidural anesthesia is introduced to the epidural space between the _________ to block pain signals during pregnancy.
dural sheath and vertebral bones
A simple spinal reflex typically involves how many neurons?
3
Which of the following is not a property of reflexes?
Reflexes are responses to sensory inputs.
Reflexes are not voluntary.
Reflexes do not require a stimulus.
Reflex responses are very predictable.
Reflexes are quick responses of the nervous system.
Reflexes do not require a stimulus.
Reflex arcs that only use two neurons are called _________ reflex arcs.
monosynaptic
Which reflex shows the least synaptic delay?
The cross extension reflex
The withdrawal reflex
A polysynaptic reflex
The flexor reflex
The tendon reflex
The tendon reflex
Which one of the following best describes the order of a somatic reflex?
Somatic receptor → efferent nerve fiber→ interneuron → afferent nerve fiber → skeletal muscle
Somatic receptor → efferent nerve fiber → afferent nerve fiber → interneuron → skeletal muscle
Somatic receptor → afferent nerve fiber → interneuron → efferent nerve fiber → smooth muscle
Somatic receptor → afferent nerve fiber → interneuron → efferent nerve fiber → skeletal muscle
Somatic receptor → interneuron → afferent nerve fiber → efferent nerve fiber→ skeletal muscle
Somatic receptor → afferent nerve fiber → interneuron → efferent nerve fiber → skeletal muscle
If a bee sting on the right thigh causes a quick involuntary reaction of the right arm, this would be an example of a(n) _________ reflex.
intersegmental
A reflex in which the sensory input and motor output are on opposite sides of the spinal cord is called _________.
contralateral
In the patellar tendon reflex arc, the patellar ligament is stretched, which stretches the quadriceps femoris muscle of the thigh. This reflex will cause the quadriceps femoris to _________ and the hamstrings to _________.
contract; relax
Which of the following is not a function associated with the spinal cord?
Protect neurons in both the ascending and descending tracts
Coordinate the alternating contraction of several muscle groups associated with locomotion
Mediate a reflex, such as the withdrawal of a hand from pain
Conduct motor information down the cord
Conduct sensory information up to the brain
Protect neurons in both the ascending and descending tracts
Which of the following structures is the richest in lipid content?
Arachnoid mater
Gray matter
Dura mater
Pia mater
White matter
White matter
There are _________ pairs of spinal nerves.
31
The bundle of nerve roots that occupy the vertebral canal from L2 to S5 is called the ________.
cauda equina
Motor commands are carried by _________ from the brain along the spinal cord.
descending tracts
The cervical plexus is the origin of the _________ nerve(s).
phrenic
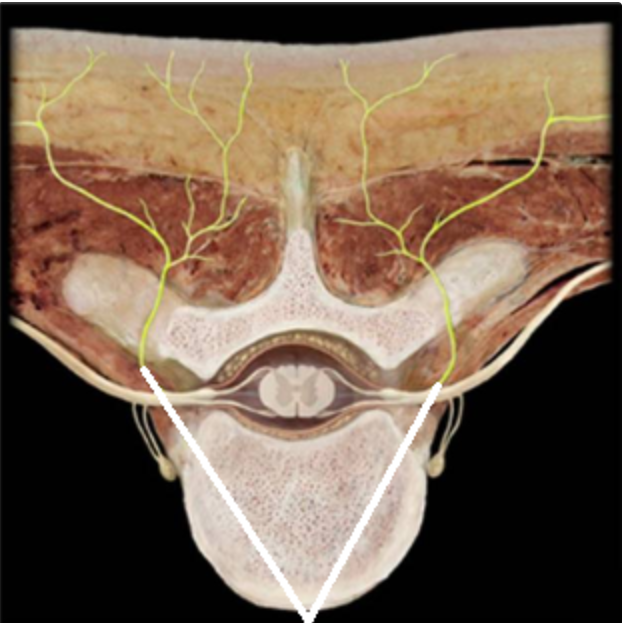
Which structures are highlighted in the picture below (reference leader lines).
Dorsal rami