4.1- Biothermodynamics Intro to Metabolism and ATP
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Biothermodynamics
the transfer of energy between and within living organisms.
Kinetic Energy
the energy of anything in motion (e.g.
flagella whipping back and forth).
Potential Energy
stored energy, often in chemical bonds
(e.g. glycogen stored in muscles).
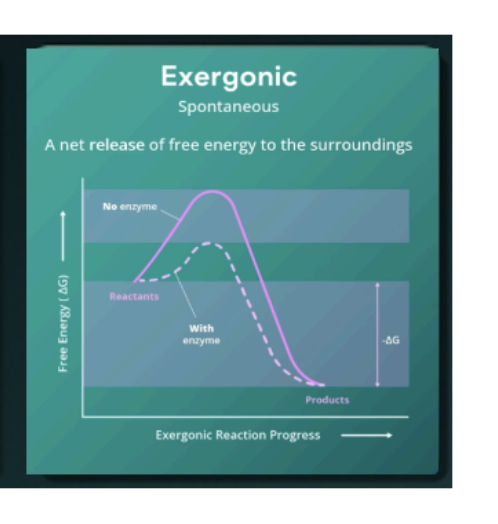
Exergonic
a spontaneous reaction that releases
energy (energy level of products is lower than
reactants).
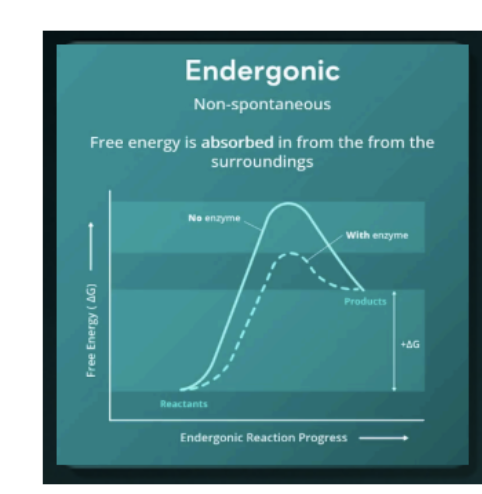
Endergonic
a non-spontaneous that requires energy
(energy level of reactants is lower than products).
Spontaneous reactions can occur…
on their own without the
addition of energy
Gibbs Free Energy formula:.
∆G = ∆H - T∆S; H= enthalpy,
S=entropy, T=temperature.
-∆G = spontaneous (exergonic reaction)
+∆G = nonspontaneous (endergonic reaction)
Endergonic reactions can be driven forward by…
coupling them with exergonic reactions.
Endergonic reactions are often…
coupled to the highly exergonic breakdown of ATP (ATP hydrolysis).
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP):
chemical form of stored energy.
Bonds between the phosphate groups store energy which is released when the bonds are broken.
ATP Hydrolysis:
ATP ➞ ADP + Pi (exergonic/ -∆G).
ATP Synthesis:
ADP + Pi ➞ ATP (endergonic/ +∆G).
ATP harnesses the energy…
of highly exergonic processes (e.g. cellular respiration).
Cell Metabolism:
the sum of all chemical reactions in a
cell (catabolism + anabolism + energy transfer).
Catabolism:
the breakdown of complex molecules
into simpler molecules, releasing energy.
Anabolism:
the synthesis of complex molecules from
simpler molecules, using energy.
3 Laws of Thermodynamics
Energy cannot be created or destroyed – only transferred and transformed.
The entropy of closed systems must increase or remain constant over time.
Livings organisms are not closed systems, so they can become more ordered (decreased entropy) over time by increasing disorder in their surroundings.
Entropy minimizes as a system approaches absolute 0 (0 Kelvin).