DNA Damage & Repair II
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Radiation-Induced Damage
- continuously exposed to various sources of radiation.
•Ionising radiation:
-energy can knock electron out of atomic shell
-Generates free radicals - break covalent bonds
•Ultraviolet Light (UV)
-Electromagnetic radiation
-Wavelength shorter than visible light
UV light
increases energy in thymine pyrimidine
UV light produces bulges in DNA
Replication cant proceed
- •UV causes formation of thymine dimers
Nucleotide Excision Repair (NER)
•Cuts out a section of DNA around the mutation and replaces it
•Detects distortion in DNA double helix caused by pyrimidine dimer
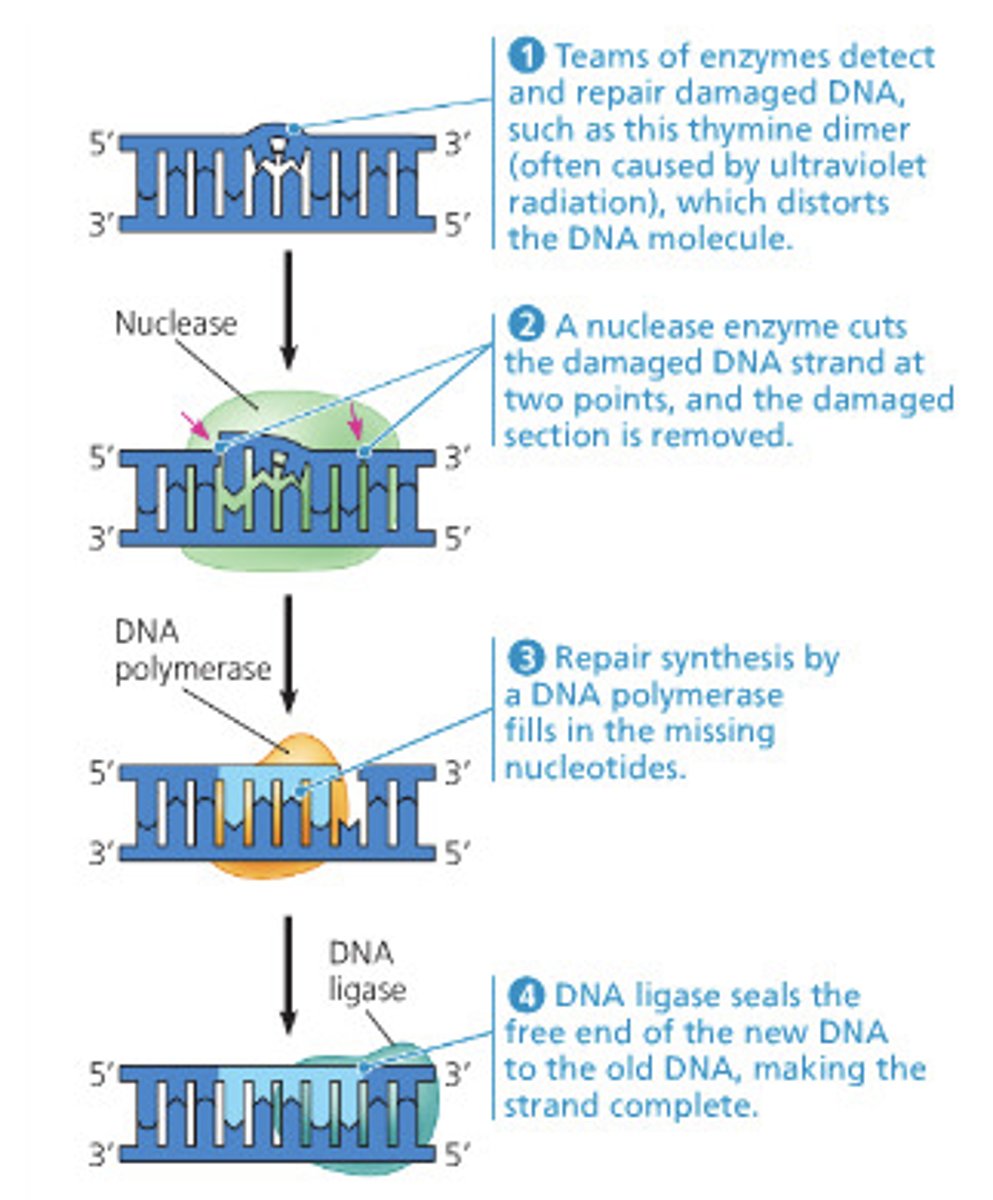
how does NER work
•Makes two cuts around the damaged DNA:
•8 nucleotides to the 5'
•4 nucleotides to the 3'
•Excinuclease activity removes 12 nucleotides
•DNA pol I uses other strand as template to fill the gap
•DNA ligase seals the phosphate-sugar backbone
Trans-lesion DNA Synthesis
- last resort
•Normal pols are derailed by DNA lesions
•Specialised polymerases are brought in at lesion sites
TLS polymerases:
•Error-prone
•little/no proof-reading capacity
•
→Induce mutations
Better than cell death!
What does examples all had in common?
Use of the opposite (undamaged) strand as a template
dsDNA Breaks
•Can be repaired, but imperfectly
-No intact template for repair
-Particularly dangerous
dsDNA Breaks causes
-Ionising radiation
-Mishaps at replication fork
-Strong oxidising agents
-Some cellular metabolites
dsDNA Break Repair 2 classes
•Non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ)
•Homologous Recombination
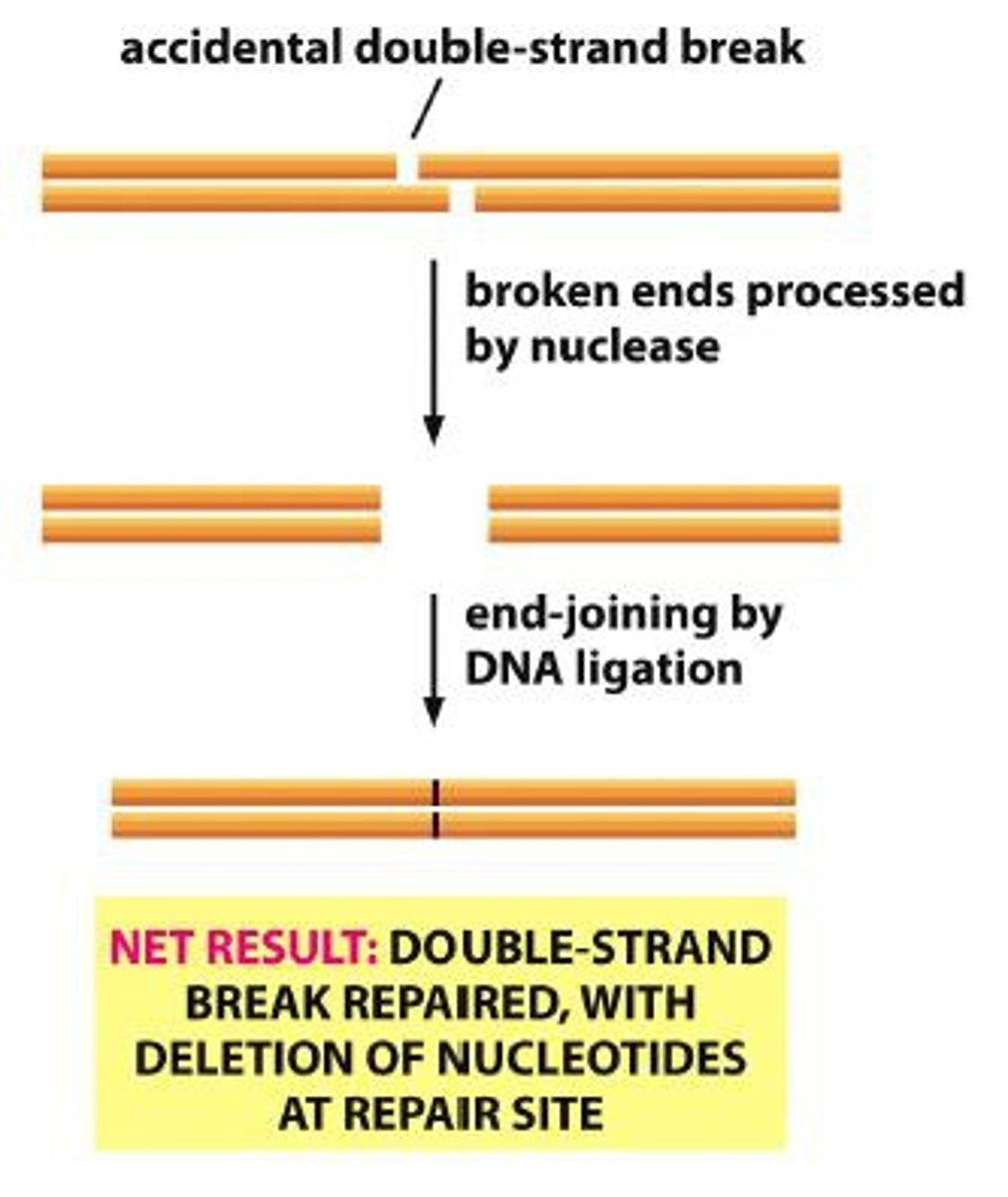
Non-homologous end-joining
•Simple joining of the two broken ends
•All phases of the cell cycle
•No template used
•Error prone
•Loss of nucleotides possible
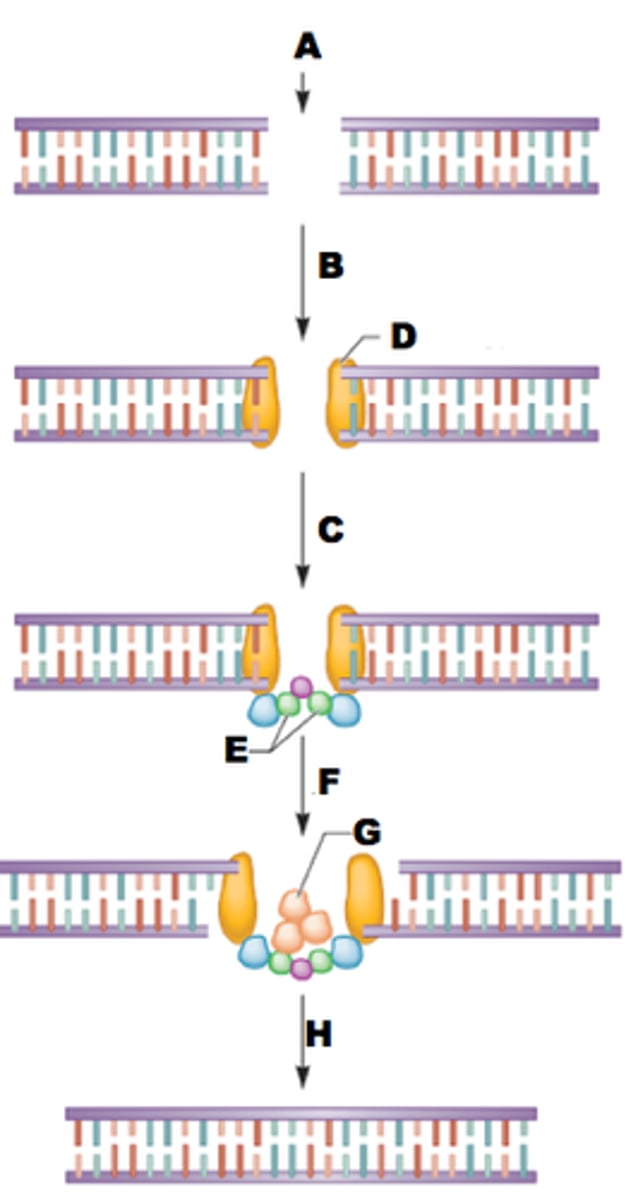
NHEJ Human example
•Broken ends bound by heterodimer of Ku70 and Ku80
•Act as a flag to recruit repair enzyme complex
•Mechanism not fully understood
Homologous Recombination
•Error-free repair
•Utilises sister chromatid as template
•No loss of genetic information
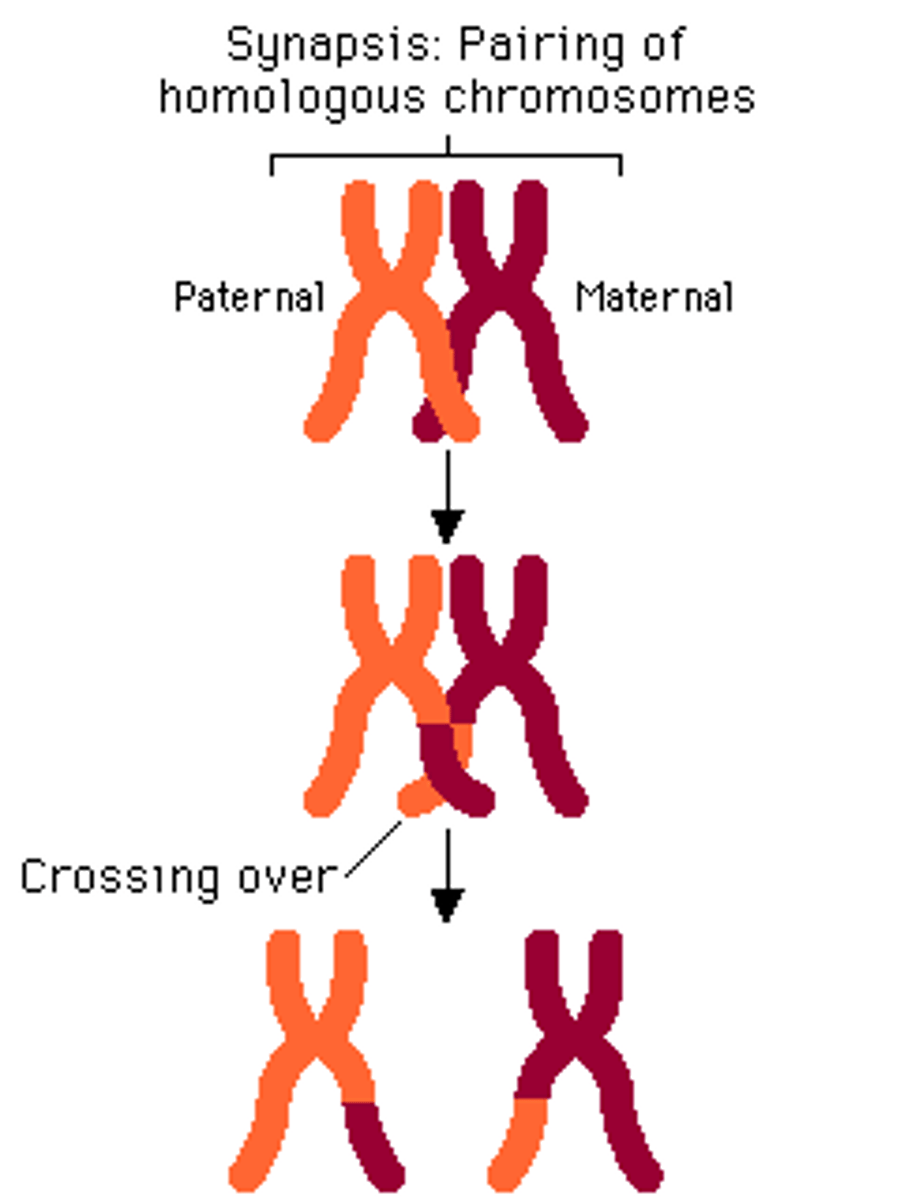
Homologous Recombination Specific time in cell cycle:
•After DNA replication
•Late S and G2 phases
- 2 identical copies of the double helix
Homologous Recombination steps
1. double strand breaks
2. DNA synethesis and migration of branch point
3.
1. Nuclease digests 5' ends of broken strands that leave open 3' end
2. strand invasion then occurs (3' end of damaged DNA gets to template duplex)
3. once stable base-pairing is established, DNA polymerase extends invading strand
4. invading strand released, broken double helix reform
5.. DNA synthesis occurs and DNA ligation
Summary
•DNA repair mechanisms exist in all organisms to maintain the fidelity of the DNA sequence.
•DNA is repaired constantly (during and after replication) and by constitutive and damage-inducible enzyme systems
•Multiple repair mechanisms are necessary to correct errors arising during replication and to repair DNA damage by intrinsic and extrinsic agents.
•Failure of DNA repair leads to mutations and cancer.
DNA Repair: Xeroderma Pigmentosum (XP)
•Inherited condition
•
•Extreme sensitivity to UV rays from sunlight
•
•Sun exposure causes dry skin and changes in skin pigment
•Greatly increased risk of developing skin cancer
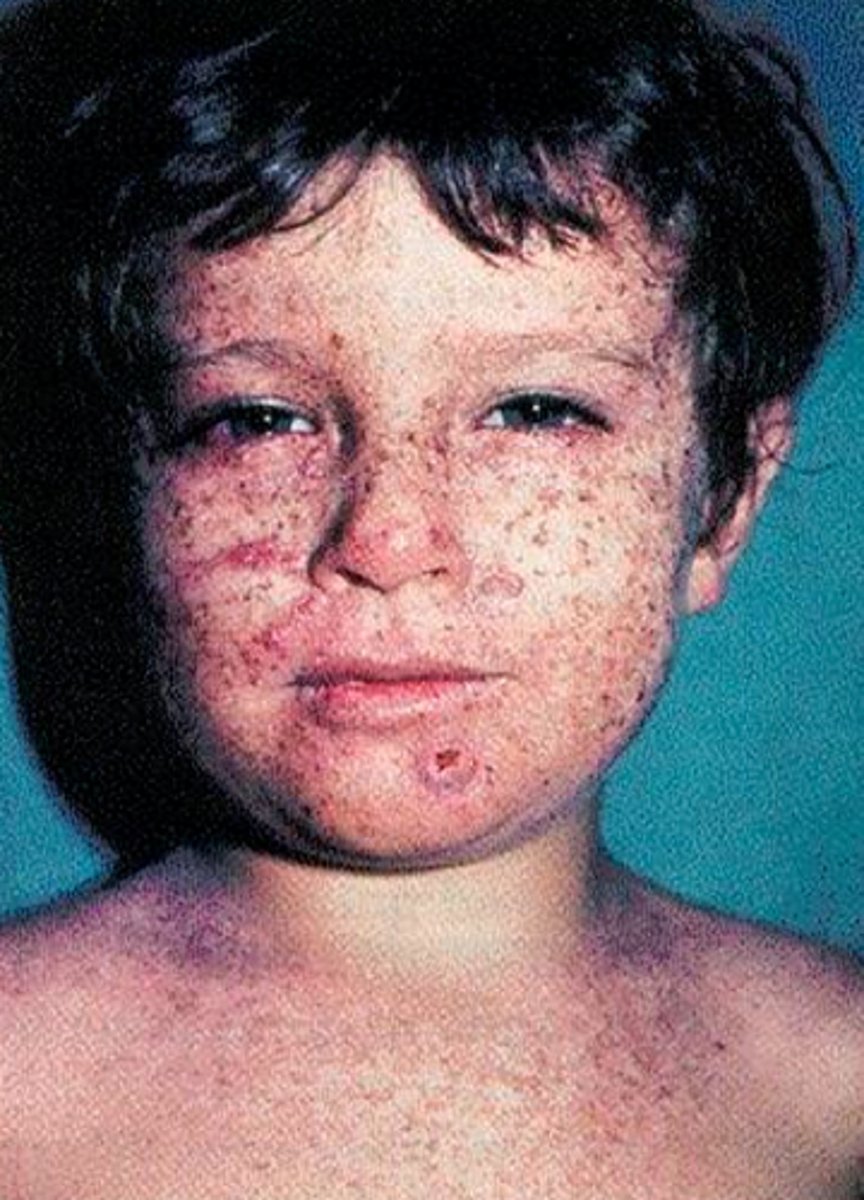
XP
•UV radiation can cause formation of thymine dimers
•Repaired by nucleotide excision repair (NER)
- mutations in XPC or ERCC2 genes
•XPC encodes XPC protein
•DNA damage recognition
•ERCC2 encodes XPD protein
•helicase activity
XPC - damage recognition
XPD - DNA unwinding
•prevent cells from carrying out repair of UV-induced DNA damage.
•Build-up of unrepaired DNA damage.
•UV rays can damage genes that control cell growth and division.
•Unregulated cell growth can lead to development of cancerous lesions.
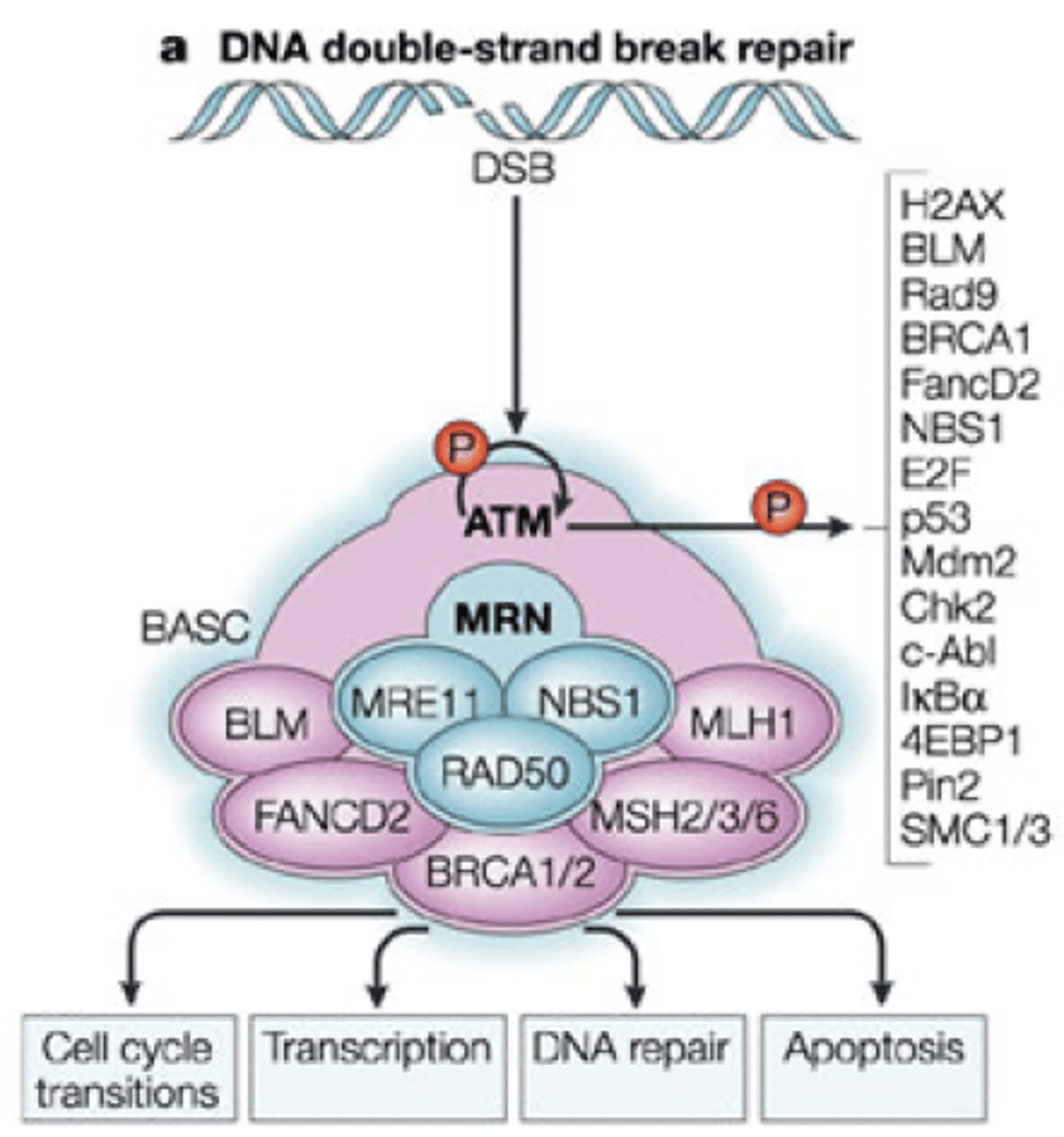
DNA Repair: Familial Breast Cancer
•People with one or more family members affected by breast, ovarian, or a related cancer.
•20% result of mutations in breast and ovarian cancer susceptibility genes - BRCA1 and BRCA2
•BRCA1 and BRCA2 encode proteins involved in homologous recombination
•Part of BASC (BRCA1-Associated Genome Surveillance Complex)
•
•Recognising and repairing DNA damage
•Many mutations found throughout BRCA1 result in a truncated non-functional protein.
•
•185delAG mutant produces 39 amino acid protein lacking all known functional domains
•L1786P
•
•Within BRCT domain of BRCA1
•
•Site of protein-protein interactions
•Likely result in the termination of the alpha helix structure
•Disrupts interactions with DNA repair proteins