8.Reproduction in plants & Humans
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
What is asexual reproduction?
A process resulting in genetically identical offspring from one parent
Does asexual reproduction involve gametes or fertilisation?
No
How many parents are required for asexual reproduction?
One
What are offspring produced by asexual reproduction called?
Clones
Why are offspring in asexual reproduction genetically identical?
There is no fusion of gametes or mixing of genetic information
What type of asexual reproduction do bacteria use?
Binary fission
What happens during binary fission?
A bacterium divides into two genetically identical cells
Name two plant structures used in asexual reproduction
Bulbs and tubers
What are bulbs and tubers?
Underground food storage organs that can grow into new plants
How do runners reproduce plants asexually?
They grow side shoots with plantlets that develop roots and form new plants
Give an example of a plant that reproduces using runners
Strawberry plant
State one advantage of asexual reproduction in wild species
Rapid population growth
State one disadvantage of asexual reproduction in wild species
Low genetic variation
Why are asexual populations vulnerable to disease?
A disease can affect all individuals due to identical genetics
Why is evolution slow in asexual reproduction?
There is no genetic recombination
Give one advantage of asexual reproduction in crop plants
Uniform characteristics or high yield
Give one disadvantage of asexual reproduction in crop plants
Vulnerability to disease outbreaks
What is sexual reproduction?
Fusion of nuclei of two gametes to form a zygote producing genetically different offspring
Define fertilisation
Fusion of gamete nuclei
What is a gamete?
A sex cell
Name the male and female gametes in humans
Sperm and egg
Name the male and female gametes in plants
Pollen nucleus and ovum
What does haploid mean?
Containing half the normal number of chromosomes
How many chromosomes are in a human gamete?
23
What does diploid mean?
Containing the full number of chromosomes
How many chromosomes are in a human zygote?
46
Why does sexual reproduction produce variation?
Gametes come from two different parents
Give one advantage of sexual reproduction
Increased genetic variation
Give one disadvantage of sexual reproduction
Offspring may be less successful
What is the role of flowers?
To enable fertilisation by bringing gametes together
Where are male gametes found in plants?
In pollen grains
Where are female gametes found in plants?
In ovules
Define pollination
Transfer of pollen from anther to stigma
Name two types of pollination
Insect and wind pollination
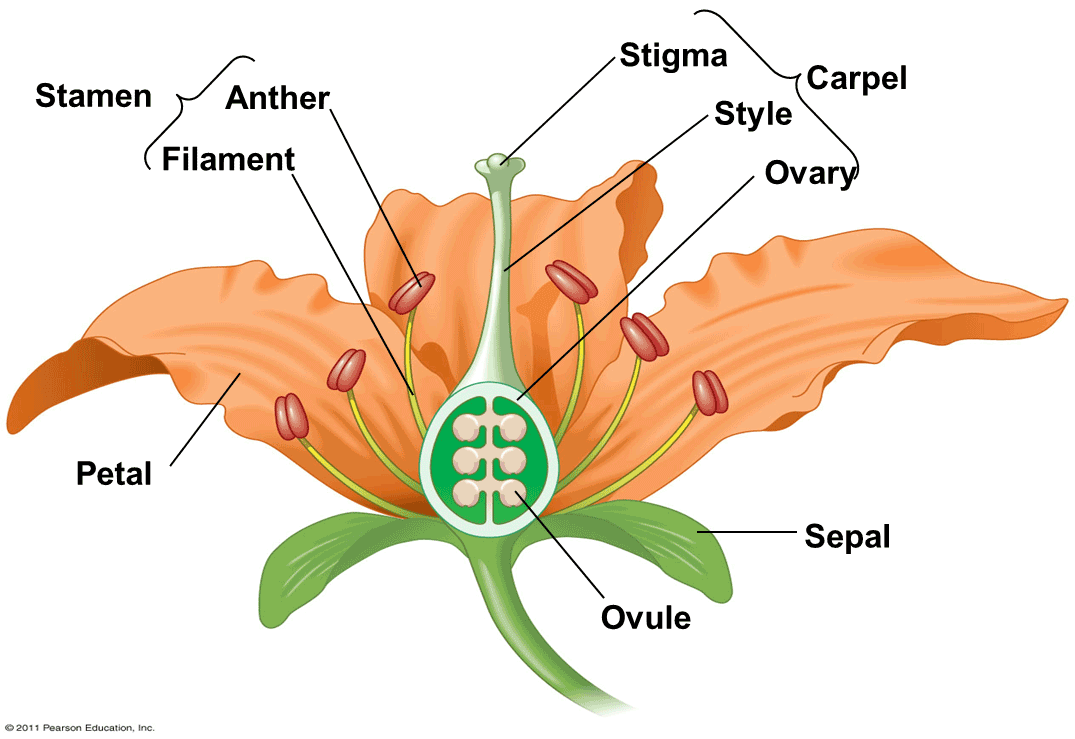
List three parts of an insect-pollinated flower
Petals anther stigma
What is the function of sepals?
Protect the unopened flower
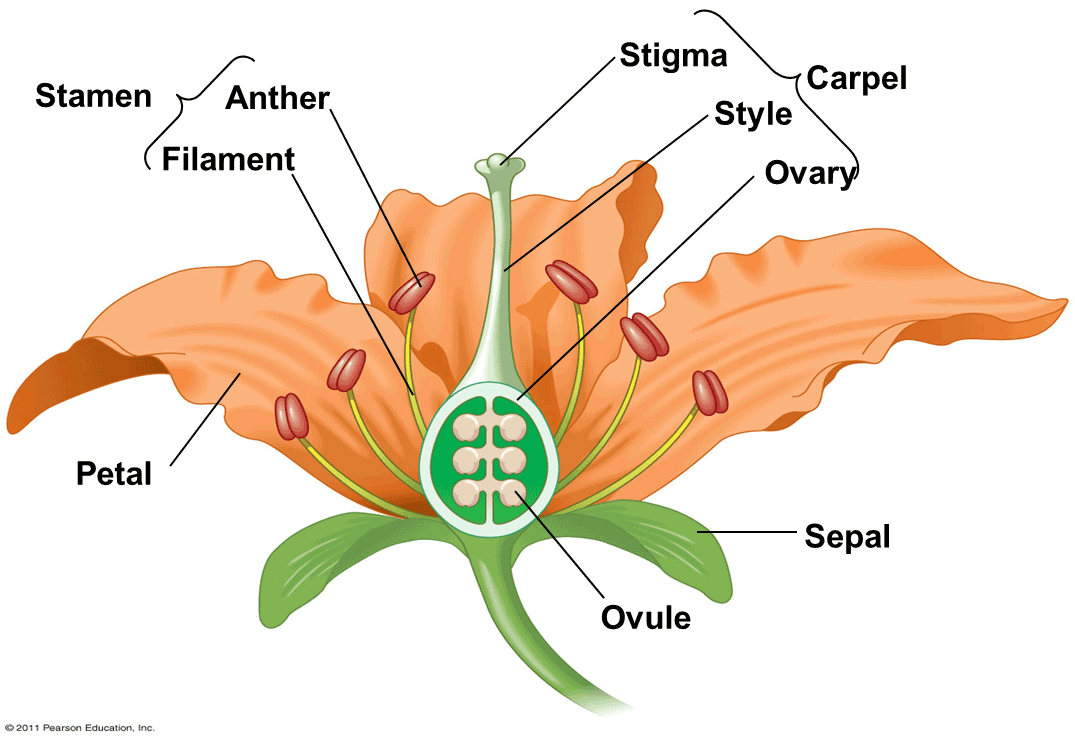
What is the function of petals?
Attract insects
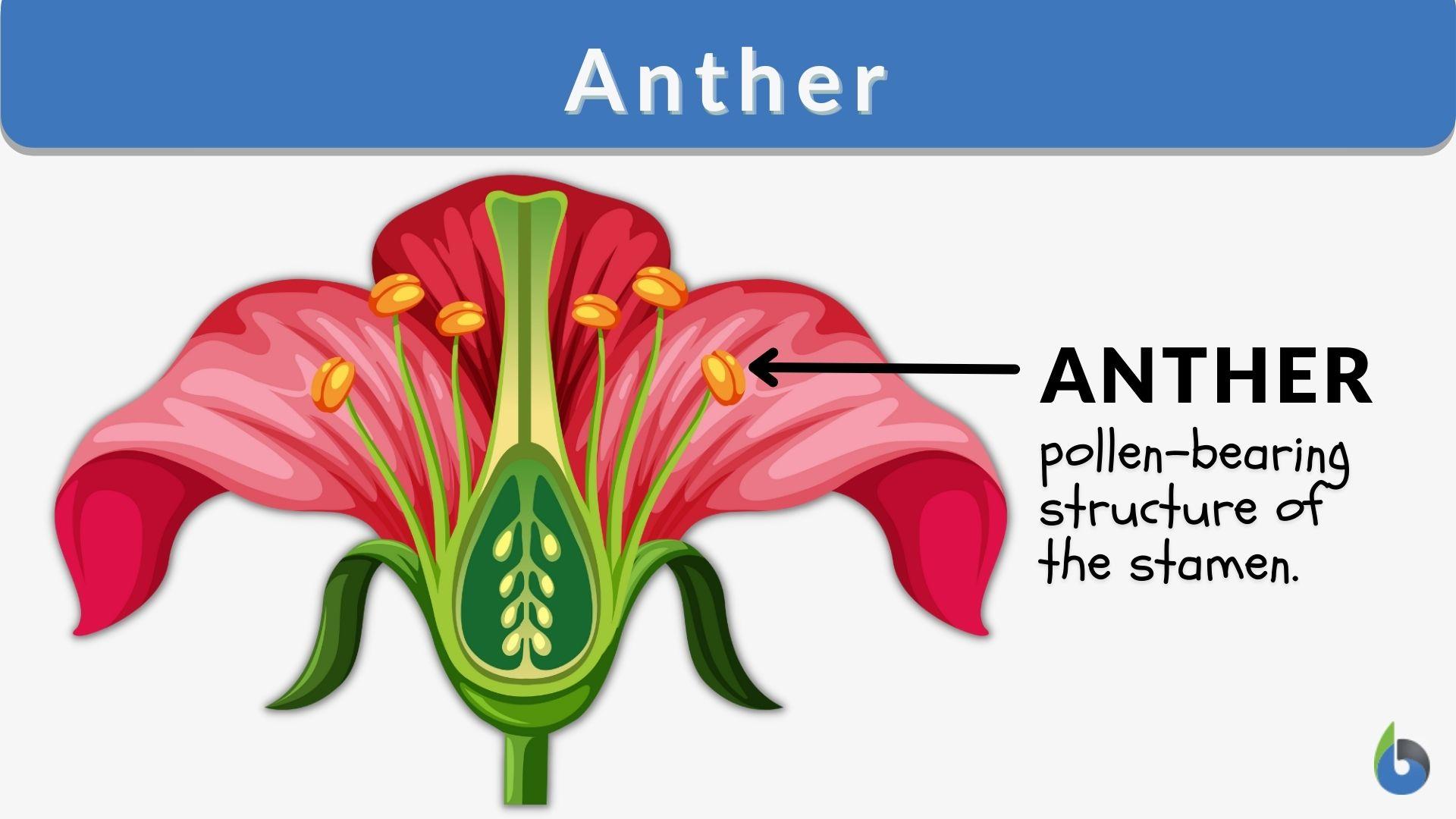
What is the function of the anther?
Produces pollen
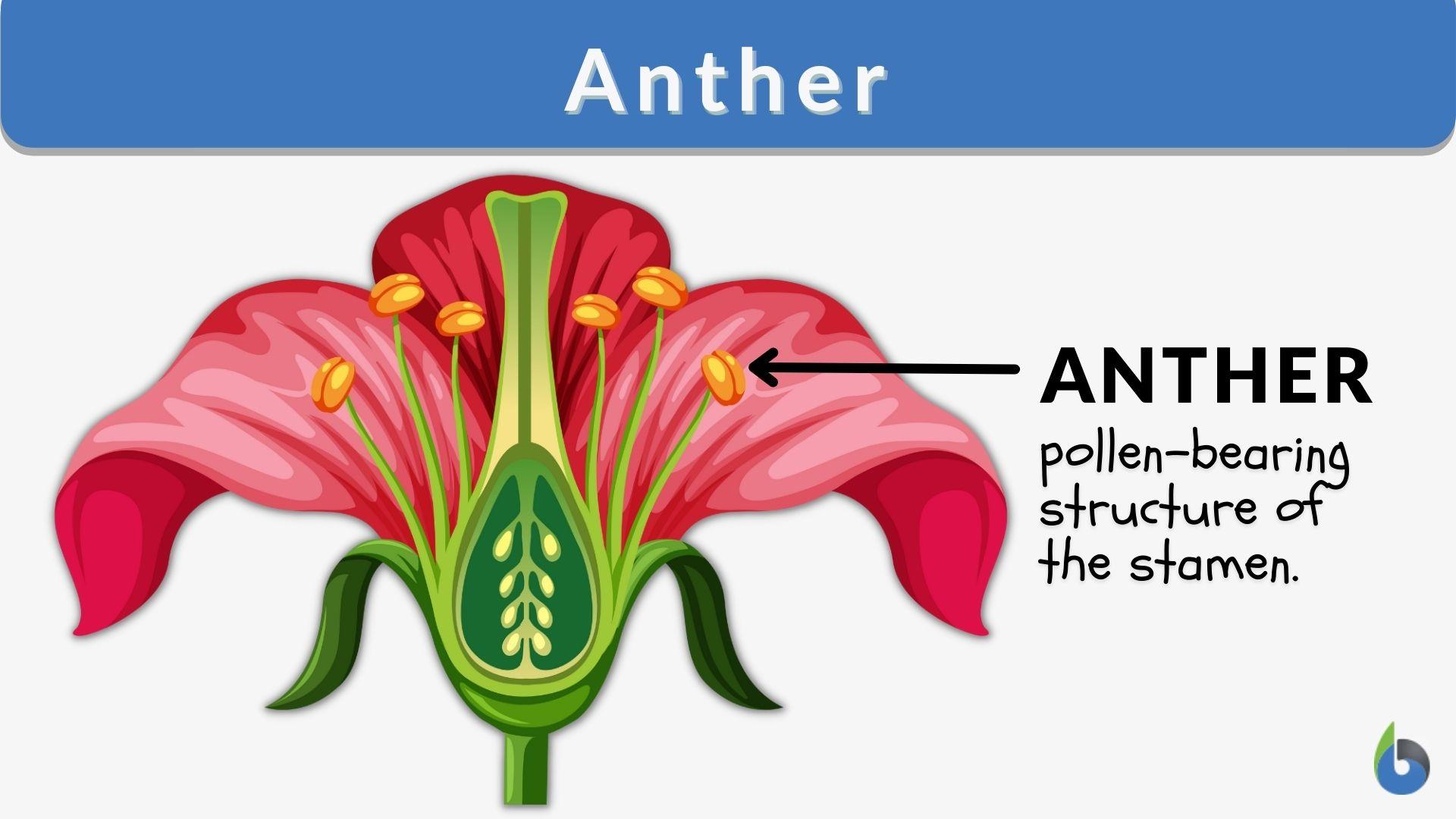
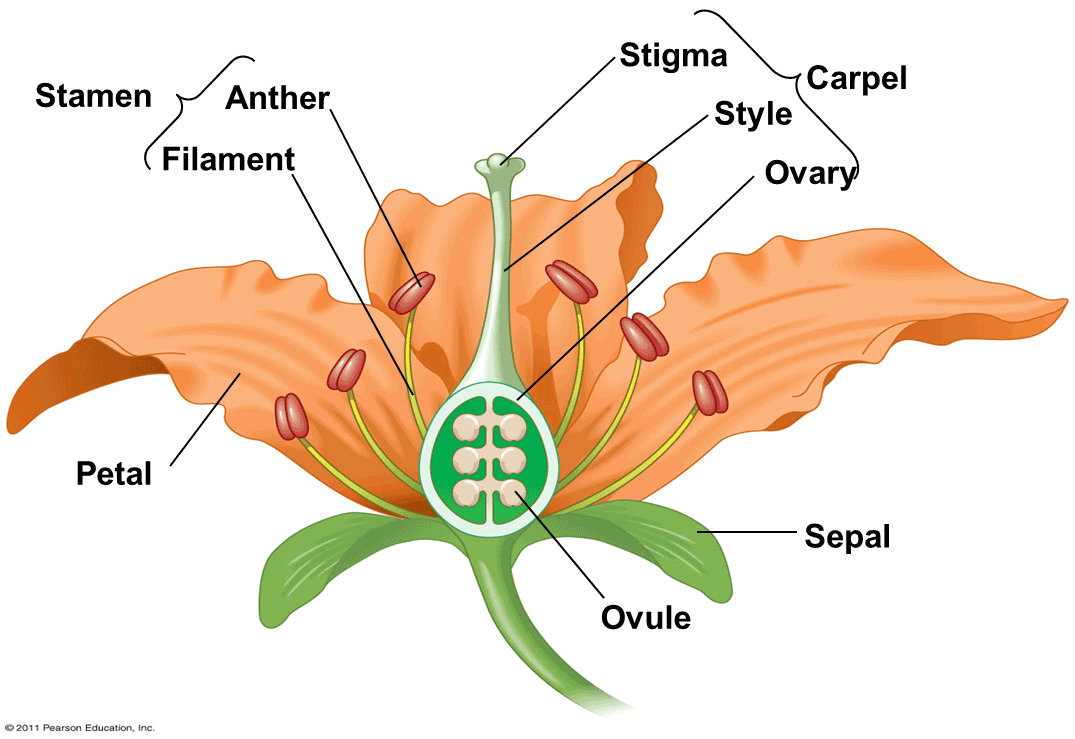
What is the function of the filament?
Supports the anther
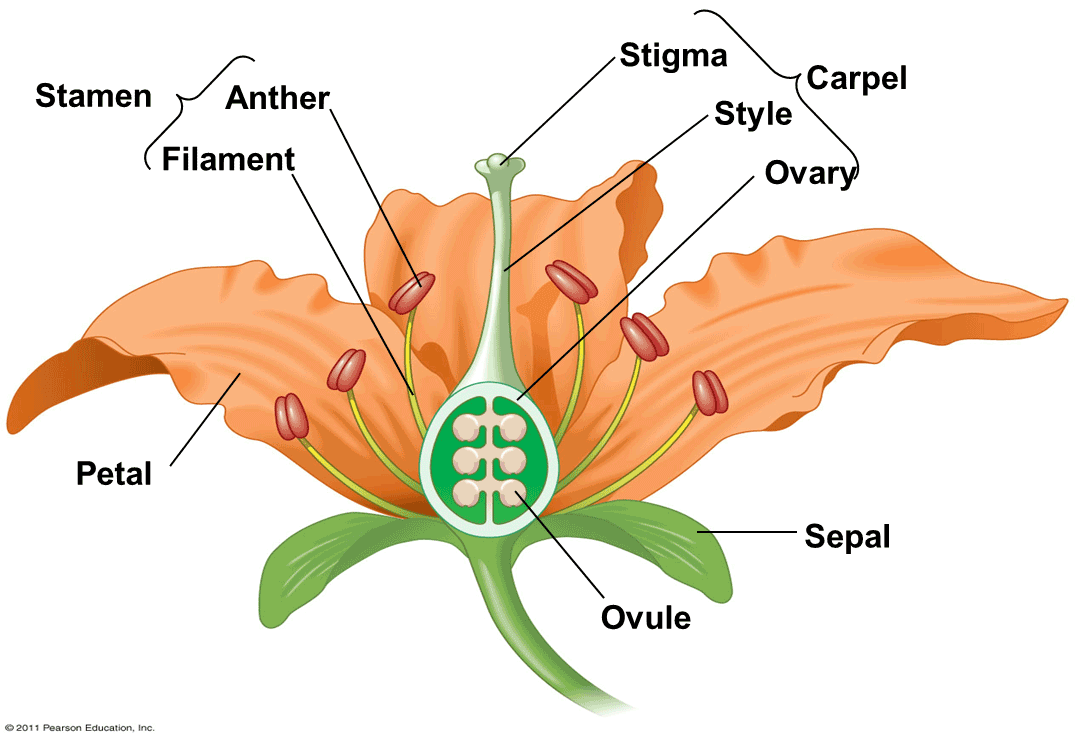
What is the function of the stigma?
Collects pollen
What is the function of the ovary?
Contains ovules
What is the function of ovules?
Contain female gametes
State one adaptation of insect-pollinated flowers
Brightly coloured petals
Why do insect-pollinated flowers produce nectar?
To attract insects
State one adaptation of wind-pollinated flowers
Feathery stigmas
Why do wind-pollinated flowers not produce nectar?
It would waste energy
Describe pollen from insect-pollinated flowers
Large heavy with hooks or spikes
Describe pollen from wind-pollinated flowers
Small light and smooth
What is fertilisation in plants?
Fusion of pollen nucleus with ovum nucleus
What grows from the pollen grain after pollination?
A pollen tube
Where does fertilisation occur in plants?
Inside the ovule
What happens to ovules after fertilisation?
They develop into seeds
What happens to the ovary after fertilisation?
It develops into a fruit
Define germination
The start of growth in a seed
Name three conditions required for germination
Water oxygen warmth
Why is water needed for germination?
To activate enzymes and allow growth
Why is oxygen needed for germination?
For respiration
Why is warmth needed for germination?
To allow enzyme-controlled reactions
Is carbon dioxide needed for germination?
No
Define cross-pollination
Transfer of pollen between different plants of the same species
Why is cross-pollination beneficial?
It increases genetic variation
Define self-pollination
Transfer of pollen to the same flower or same plant
Give one disadvantage of self-pollination
Reduced genetic variation
Name one risk of relying on insect pollinators
Pollinator populations may decline
List the male reproductive organs
Testes sperm duct prostate gland penis
What is the function of the testes?
Produce sperm and testosterone
Why are testes located in the scrotum?
To keep sperm at a lower temperature
What is the function of the prostate gland?
Produces fluid to form semen
What is the function of the sperm duct?
Carries sperm to the urethra
What is the function of the urethra?
Carries urine or semen out of the body
List the female reproductive organs
Ovaries oviduct uterus cervix vagina
Where does fertilisation occur in humans?
In the oviduct
What is the function of the ovary?
Produces ova
What is the function of the uterus?
Site of embryo development
What is the function of the cervix?
Keeps fetus in place during pregnancy
What is the function of the vagina?
Receives penis and sperm
Give one adaptation of sperm cells
Flagellum
Why do sperm contain many mitochondria?
To supply energy for movement
What is the function of enzymes in the sperm head?
Digest a path into the egg
Give one adaptation of egg cells
Large food store
Why does the egg membrane change after fertilisation?
To prevent entry of more sperm
Define implantation
Embedding of the embryo into the uterus lining
How long is human gestation?
About 9 months
What is the placenta?
An organ for exchange between mother and fetus
Name two substances that pass from mother to fetus
Glucose oxygen
Name two substances that pass from fetus to mother
Carbon dioxide urea
How do substances cross the placenta?
By diffusion
Why do maternal and fetal blood not mix?
To prevent immune reactions
What connects the fetus to the placenta?
Umbilical cord
What is amniotic fluid?
Fluid surrounding the fetus for protection
Give one function of the amniotic fluid
Cushions the fetus
What is a hormone?
A chemical messenger carried in the blood
Name the female sex hormone
Oestrogen
Name the male sex hormone
Testosterone
What are secondary sexual characteristics?
Changes at puberty controlled by hormones
Give one female secondary sexual characteristic
Breast development
Give one male secondary sexual characteristic
Deeper voice
What is the menstrual cycle?
Monthly cycle preparing the uterus for pregnancy
How long is the average menstrual cycle?
28 days
What is ovulation?
Release of an egg from an ovary