Yamaki - clostridioides difficile
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Clostridioides difficile
gram-positiv bacillus (rod), strict anaerobe
spore-forming
some are toxin producing (A & B)
in 1970s discovered as a cause of pseudomembranous colitis and antibiotic-associated colitis
fecal-oral route transmission
C. difficile epidemiology
accounts for 20-30% of cases of antibiotic-associated diarrhea
stool carriage of C. difficile reaches 16-35%
occurs in community ~7/100,000 people
~500,000 infections/yr
mortality 29,000/yr
CDI rates and mortality increase with ________
increased patient age
CDI new epidemic
in US ↑incidence continues to increase as well as severity:
↑ toxic megacolon
↑ colectomy
↑ refractory to therapy, relapse
now considered by CDC as a major public health threat
Orange County has one of the highest C. diff rates in California
possible reasons for increased CDI incidence and severity
changes in underlying host susceptibility
changes in antimicrobial prescribing
new strain with increased virulence/resistance
changes in infection control practices
BI/NAP1/027 strain
distinctions from typical C. diff strains:
hyper-production of Toxin A/B
3rd, binary toxin
hypersporulation
Fluoroquinolone resistance
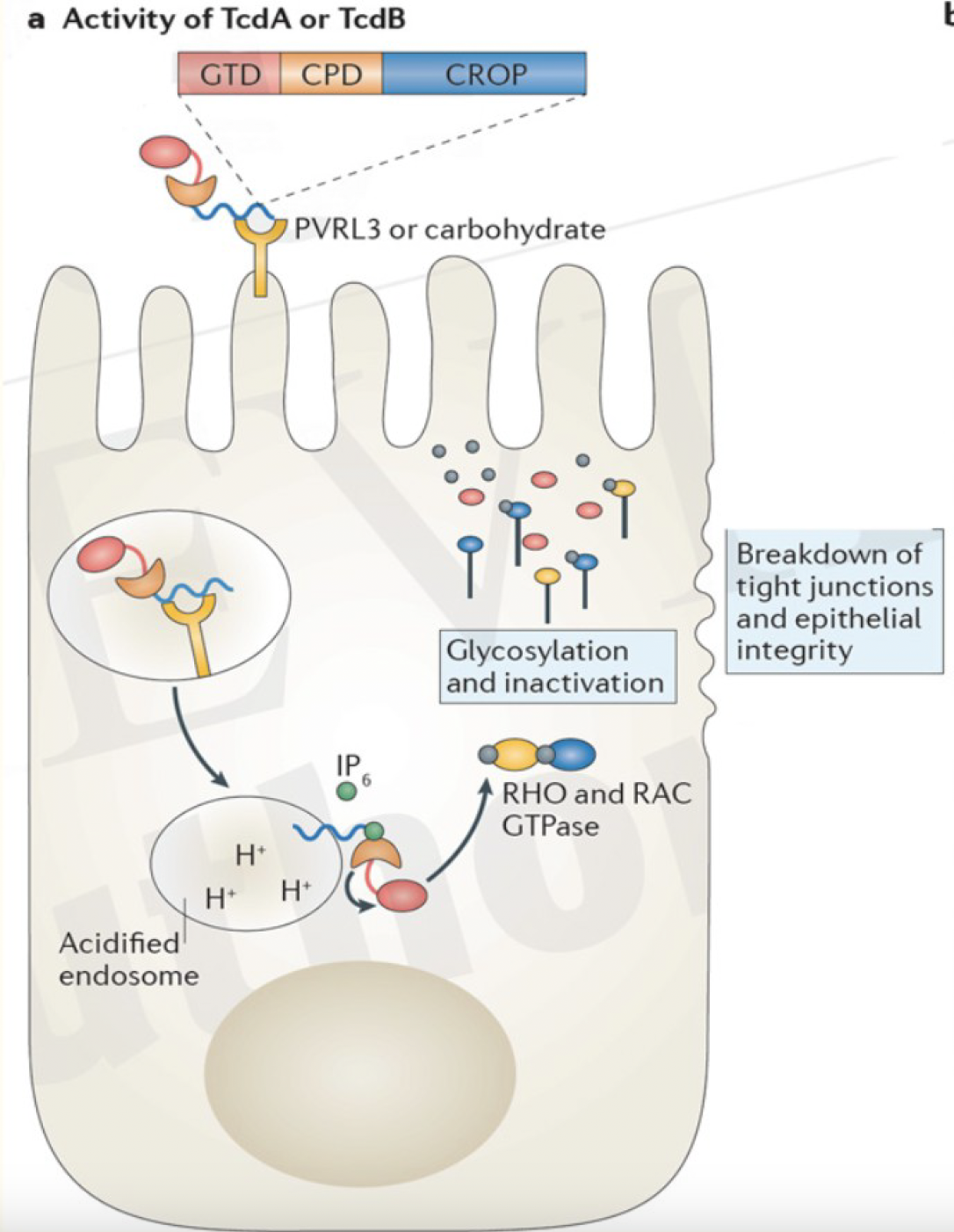
disease pathogenesis
C. difficile ingested —>
C. diff spores germinate in the intestine —>
in the large intestine, C. difficile-associated disease can arise if the normal flora has been disrupted by antibiotic therapy —>
toxin A & B production leads to colon damage ± pseudomembrane
why do taking antibiotics lead to CDI
primary bile acids (cholic acid, taurocholic acid) trigger C diff spore germination
primary bile acid made by liver —> intestine
normal flora in GI convert primary to secondary bile acids
secondary bile acids suppress C diff growth and toxic production
promote healthy GI normal flora
intracellular modifications by TcdA and TcdB
risk factors
advanced age (≥ 65 yrs)
prior hospitlizaiton
resides in skilled nursing facility
prior C. difficile infection
immunosuppression
medications:
antibiotics — clindamycin, fluoroquinolones, 3rd gen cephalosporins, long duration of therapy
PPIs
prolonged corticosteroid use
chemotherapy
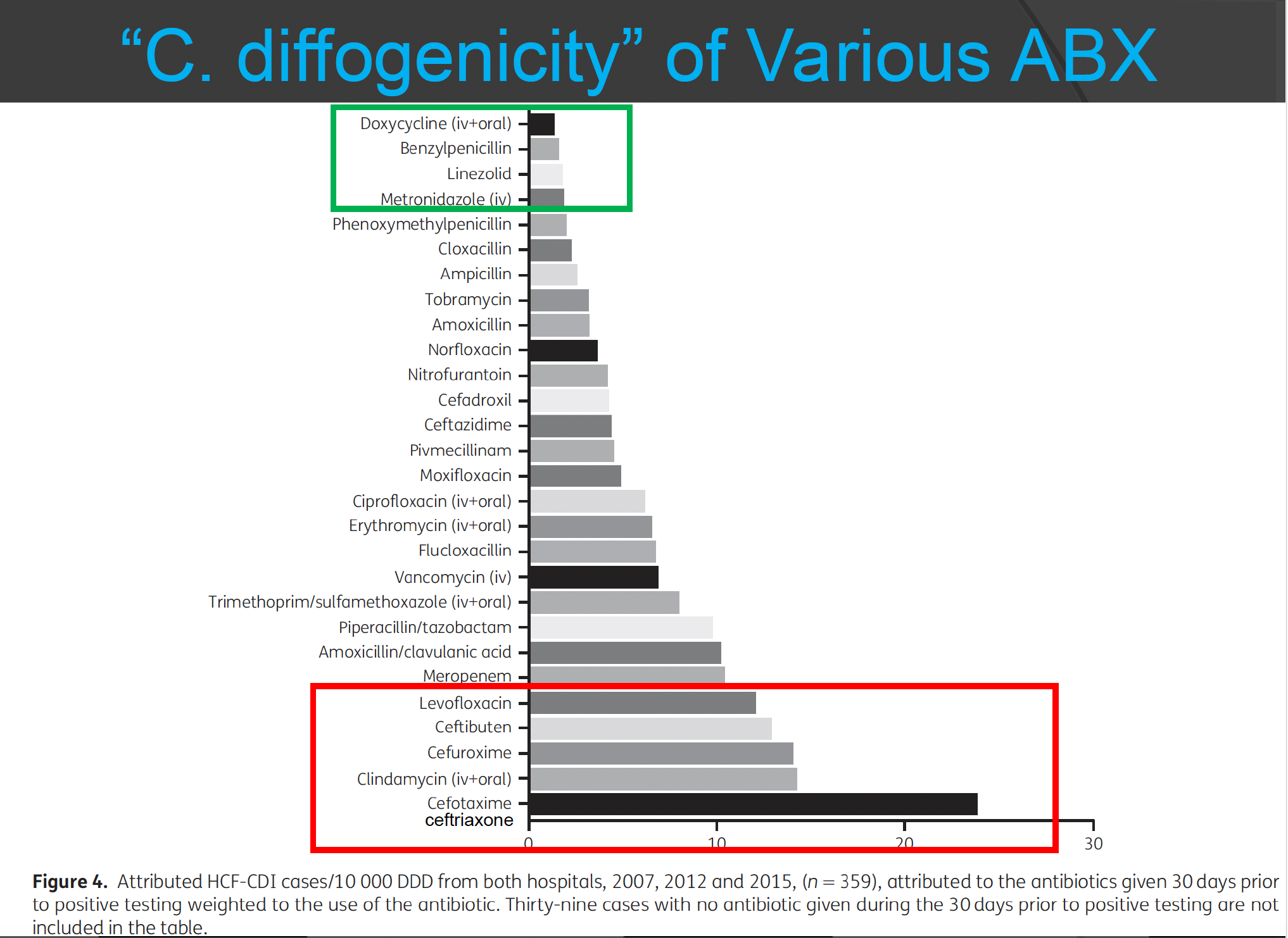
“C. diffogenicity”of various ABX
red = more likely to cause CDI
green = less likely to cause CDI
disease presentation — general signs/symptoms
diarrhea ≥3 times a day
cramps/abdominal pain
fever
leukocytosis
inflammation on colonic biopsy
toxic megacolon
dehydration/electrolyte imbalance
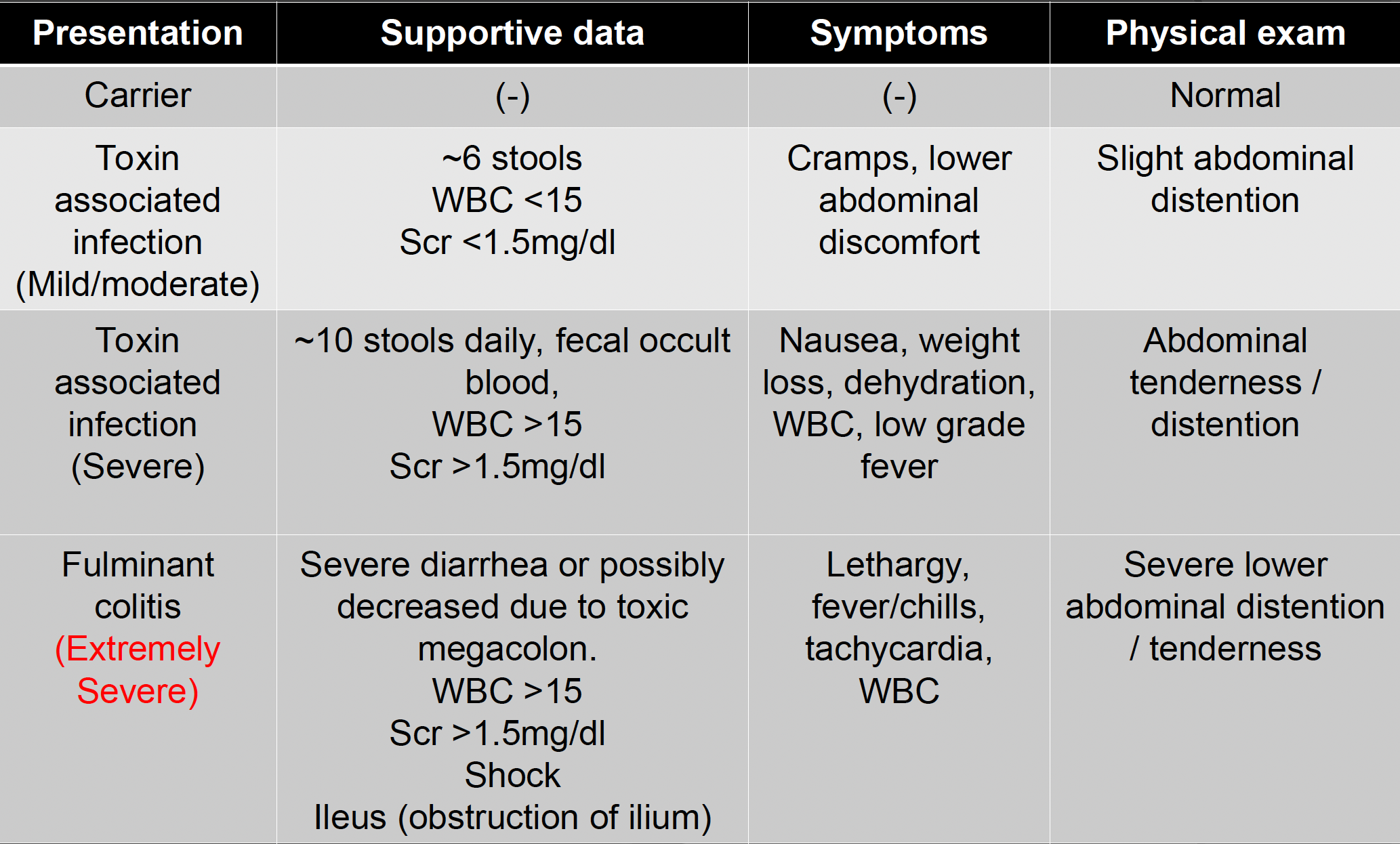
disease presentation — mild/moderate, severe, extremely severe
*KNOW EXTREMELY SEVERE
complications
dehydration
electrolyte imbalances
hypoalbuminemia
AKI
toxic megacolon or pseudomembraneous colitis
sepsis
death
diagnosis
PCR detection — highly sensitive, may detect colonization
appropriate sample testing is necessary
diagnosis should NOT be made on lab test alone, but needs to consist of the entire clinical picture including additional patient objective data (WBC, PE, symptoms, etc)

treatment
fidaxomicin (Dificid) PO
vancomycin (Vancocin) PO
metronidazole (Flagyl) PO/IV
primary treatment 1st line
Fidaxomicin (Dificid) PO
used for mild/moderate/severe infections and recurrent infection (fidaxomicin is superior for recurrent infections)
very narrow spectrum macrocyclic lactone (macrolide), non-systemic
200 mg PO q12h x 10d
Vancomycin (Vancocin) PO (NOT IV)
used for mild/moderate/severe/fulminant infections and recurrent infection
125 mg PO q6h x 10d, can give higher dose (250 mg), in severe give 500 mg
poor absorption no need for monitoring levels
OR 500 mg in approximately 100 mL normal saline per rectum every 6 hrs as a retention enema
alternative treatment (2nd line)
metronidazole (Flagyl) PO/IV
mild/moderate CDI metronidazole 500 mg PO q8h 10-14 day (if cannot take vanco or fidaxomicin) NO longer 1st line
severe complicated infection fulminant colitis give 500 mg IV q8h with vancomycin 500 mg PO q6h, or 500mg enema q6h
guidelines — mild/moderate and severe

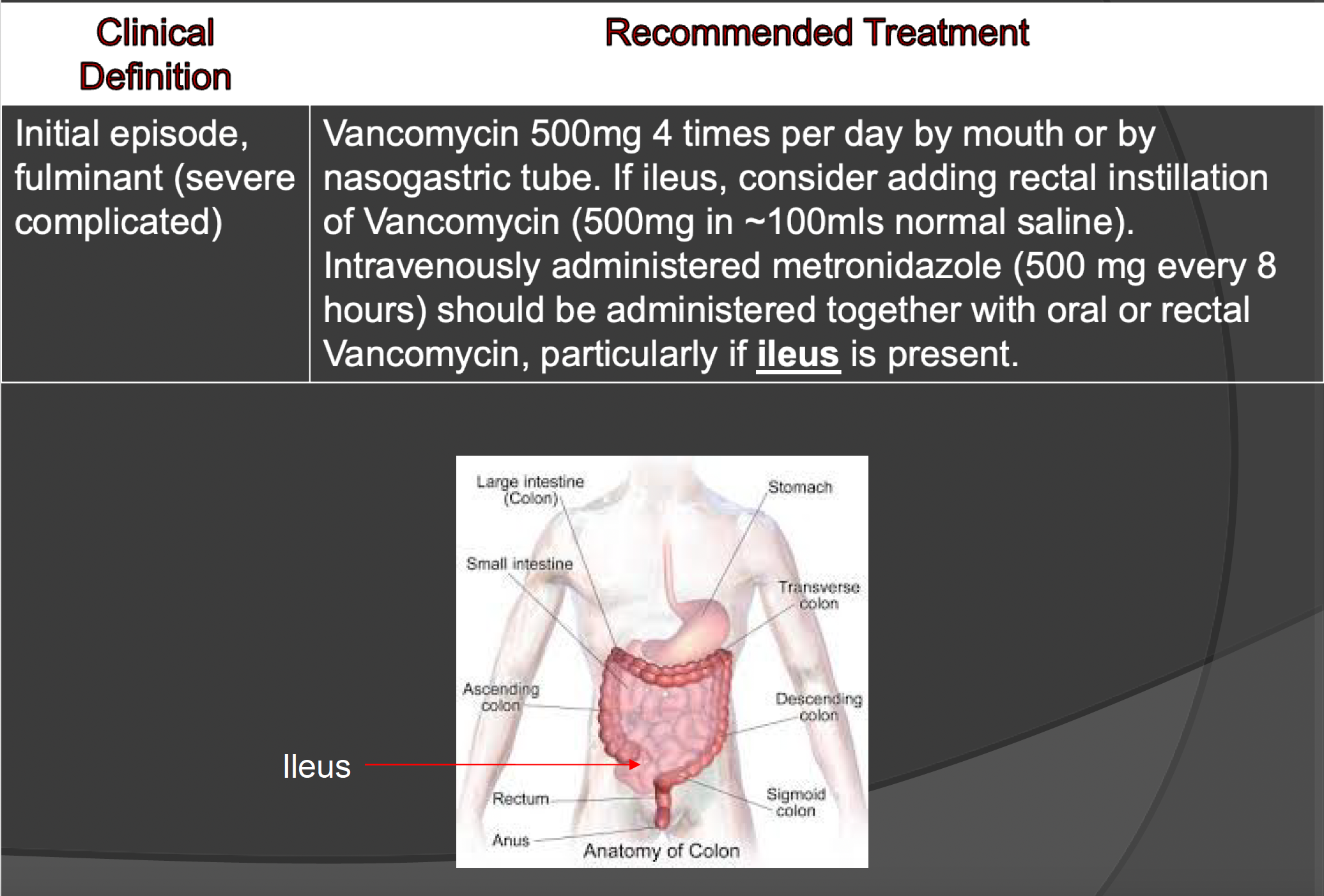
guidelines — fulminant (severe complicated)
recurrent / refractory disease
expect a number of relapses
recurrence — usually within 1 week up to 8 weeks after Rx DC’ed in 20% of atients
recurrent CDI: defied as CDI occurring within 8 weeks after a previous episode resolved with treatment
sustained cured: is defined as no recurrence of symptoms up to 12 weeks after the previous episode
~1/2 of relapse are technically reinfection due to new strains of C. difficile
risk factors for recurrence
≥ 65 yrs of age
receiving one or more systemic antibacterial drugs (during the 12-week period after treatment of CDI)
having one or more episodes of CDI within the 6 months
immunocompromised
clinically severe CDI
infected with hypervirulent strain (ribotypes 027)
recurrent / refractory treatment
vancomycin taper & pulse dosing
125 mg 4 times per day for 10-14 days, 2 times per day for a week, once per day for a week, and then every 2 or 3 days for 2-8 weeks
fidaxomicin (Dificid) — 10 days of 200 mg PO BID is NOT inferior to 10 days vancomycin PO 125 mg QID
recommended treatment for first recurrence

recommended treatment for second recurrence

Bezlotoxumab (Zinplava) IV
DISCONTINUED
monoclonal antibody against toxin B
used as adjunctive therapy to prevent recurrence in patients at risk
NO antibacterial activity —> NOT for treatment alone
given as 10mg/kg one-time IV dose while being treated for CD
very expensive (thousands of $)
what should NOT be given as treatment?
along with C. difficile treatment, systemic antibiotic therapy should be DC’ed if possible
de-escalate to less “C. diffogenic” antibiotic
NEVER give anti-motility / anti-diarrheal drugs (e.g., Lomotil - diphenoxylate and atropine - or loperamide)
recurrent / refractory treatment (non-antibiotic treatments)
Vowst (fecal microbiota spores, live-brpk)
FDA-approved PO microbiome therapeutic to prevent C. diff recurrence
does NOT treat C. diff
take 2-4 days AFTER finishing C. diff treatment
Rebyota (fecal microbiota spores, live-jslm)
FDA-approved rectal admin (PR) microbiome therapeutic to prevent C. diff recurrence
does NOT treat C. diff
take 1-3 days AFTER finishing C. diff treatment
stool transplant (FMT)
recommended after 2 recurrences (3 CDIs)
30 grams donor blended w/ 150 mL nS then given by PO, G-tube, enema, and colonoscopy delivery
probiotics — some evidence in prevention
NOT recommended by 2018 guidelines
many hospitals have implemented probiotics for patients on ABX
infection control
wash hands
DO NOT rely on hand sanitizers (EtOH)
patient isolation — follow protocols
antibiotic selection/control
prophylactic metronidazole and vancomycin NOT recommended per guidelines
prophylactic Vanco 125 mg PO q12h if on ABX