History of Architecture: A compilation from HOA 1 to 4
1/429
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
430 Terms
Gothic Architecture
A style that reacted against the classic, hence it was called "barbaric"; a style that departed from the classic lines; characterized by:
• elaborate and ornate decor
• high, pointed ends
Tracery
An ornamental stonework on the upper part of a Gothic window
Plate Tracery
A type of tracery; uses thick areas of stone to separate glazed areas; the stone dominates the window rather than the glass
Bar Tracery
A type of tracery; composed of thin stone elements rather than thick ones; glass dominates the window rather than stone
Gargoyle
Functional waterspouts during the Gothic Era and are said to scare off evil spirits
L'architecture Ogivale
The french term for the Gothic architectural style from the word "ogive" referring to a pointed arch
Ogival System
The vaulting framework of intersecting pointed arch ribs
Chevet
An apse having a surrounding ambulatory of which are chapels; the east or apsidal end of a Gothic church, including the choir, ambulatory and radiating chapels.
Apse
A recess, usually semicircular, in the wall of a building, commonly found at the east end of a church.
Lady Chapel
A chapel dedicated to the Virgin Mary
Fleche
A slender spire rising from the ridge of a roof, esp. one above the crossing of a Gothic church
Albi Cathedral
A French Cathedral; Formally known as Cathedral Basilica of Saint Cecilia, it is a fortress church with a large vaulted hall (18 m.), the widest in France
Amiens Cathedral
A French Cathedral; Has slightly projecting transepts and sweeping chevet of 7 chapels
Beauvais Cathedral
A French Cathedral; The most daring achievement of Gothic architecture, having the highest nave in Europe (48.5 m.); It has 3 tiers of flying buttresses
Bourges Cathedral
A French Cathedral; Is remarkable for the absence of transepts and its shortness in proportion to the width.
Le Mans Cathedral
A French Cathedral; Has a notable chevet with 13 chapels of unusual projection.
La Sainte Chapelle
A French Cathedral; conceived by Louis IX as a kind of gigantic reliquary for the most precious religious relics in all Christendom (including the "true cross" of Christ, the "Crown of Thorns" and other relics connected to the actual passion of Christ); The windows fill more than 3 quarters of the height of the walls producing a luminous filigree effect
Filigree
Delicate ornamental tracery
Chartres Cathedral
A French Cathedral; A Latin Rite Catholic cathedral; Has the most complete collection of medieval stained glass in the world, renowned for their vivid blue color; with reputation to be the Stone Age Bible, it was considered as the Middle Ages expression
Strasbourg Cathedral
A French Cathedral; Used to be the world's tallest building in the 1600s with a spire reaching up to 466 ft. (142 m.); today it is the 6th tallest church in the world
Notre Dame Cathedral
A French Cathedral; Is 850 years old and is one of the oldest French Gothic Cathedrals; Begun by Bishop Maurice de Sully and restored by one of France's most famous architects, Eugene Viollet-le-Duc
Reims Cathedral
A French Cathedral; The coronation church of the French kings and one of the finest Gothic structures ever built; adorned with sculptures from the 13th and 14th cent., including the "Smiling Angel of Reims"
Soissons Cathedral
A French Cathedral; Has a single tower that dates from the mid-13th century and is an imitation of those of Notre Dame de Paris.
Rouen Cathedral
A French Cathedral; Has the highest spire in France (151 m.); Used to be the world's tallest building in the late 1800s; Its spire was built in the late Gothic Period (Flamboyant Style)
Flamboyant Style
A Late Gothic style of architecture superseding the Rayonnant style and named for the flame-like appearance of its pointed bar tracery mainly used in describing French buildings
Le Mont Saint Michel
A French fortified town; used to be a fortified stronghold of the Roman-Bretons in the 6th and 7th century; Best known for the medieval Benedictine Abbey and steepled church; Known as "Wonder of the West"
Carcassone
A French fortified town was restored in 1853 by Eugene Viollet-le-Duc (one of France's most famous architects)
Chateau Gallard
A French castle; uses early principles of concentric fortification; one of the earliest European castles to use machicolations
Machicolation
Part of a castle; A projecting gallery or parapet supported on corbels having openings through which missiles could be dropped; Also called "murder holes"
Chateau de Pierrefonds
A French castle; was a defensive military architecture from the middle ages by Louis I de Valois; Classified as a monument historique by the French Ministry of Culture
Chateau d' Amboise
A French castle; was once home to the French royal court; built of French late Gothic Flamboyant style; also known as Chapel of Saint Hubert and is the burial place of Leonardo da Vinci
Renaissance Architecture
Means "rebirth of classical"; The reintroduction of Classical Architecture all over Europe dating from the 15th to 18th century; characterized by:
• formality achieved through symmetry
• Trabeated and Arcuated systems
• use of pediments, horizontal cornices and columnar arcades
Baroque
An architectural style under the Renaissance era, known for its curved lines shown in elements such as twisted columns and pediments; elaborate an extensive ornamentation in decorative art and architecture that flourished in Europe in the 17th century
Rococo
Extreme Baroque style; An architectural style under the Renaissance era, known for its symmetrical plans, walls constructed with ashlar masonry, doors with semi-circular heads and Greek entablatures, Roman mouldings, classic order columns, fresco paintings and sgraffito
Sgraffito
Color plaster; a ceramic or mural decoration made by scratching off a surface layer to reveal the color underneath
Italy (Florence)
The birthplace of Renaissance architecture
Filippo Brunelleschi
The most famous architect in Italy; designed the Dome of Florence Cathedral and the Palazzo Pitti
Alberti
The author of the first architecture book after the invention of printing; designed the Church of Santa Andrea, Mantua (the prototype of later renaissance)
De re Aedificatoria
Alberti's publication on Architecture; It was the first printed work on architecture of the Renaissance.
Bramante
The first Roman architect of Renaissance time; designed the Pazzo Della Cancellaria and started the Vatican Palace in Rome
Raphael
The cousin and pupil of Roman architect Bramante; designed the Vatican Loggia; The architect who changed the plan of the Vatican from the Greek cross plan to the Latin cross plan
Vignola
The architect who designed the Palazzo Farnese, Villa of Pope Julius in Rome, the Caprarola (the most magnificent of Roman palaces), and the Gesu Church (prototype of Jesuit Church in baroque style)
Medici Family
The wealthiest family in Italy and ruled Florence during the Renaissance
Longhena
The architect of the Sta. Maria Della Salute, Venice (the structure in the middle of a canal)
St. Peter's Basilica
Largest Christian church in the world; Located in the Vatican City in Italy. The dome was created by Michelangelo
Panthenon
A large, domed temple built in ancient Rome to honor many gods and goddesses; has the largest dome in Italy
French Renaissance
An architectural style influenced by the Italian Renaissance; Notable for its sober and restrained composition of design
Mansard Roof
A roof characterized by steeply sloped facets surrounding a flat or nearly flat center section; Also known as "Gambrel Roof"
Chateau de Blois
A French residential palace known for its monumental spiral staircase, covered with fine bas-relief sculptures and looking out onto the château's central court
Palais de Louvre
A former royal palace designed by Pierre Lescot located on the Right Bank of the Seine in Paris, now a museum containing a large collection of historical artifacts
Arc de Triomphe
A monument commemorating Napoleon's victories; built in 1836 and reminded people of Napoleon's legacy
Versailles Palace
This palace was the center of political power built for Louis XIV in the Île-de-France region of France; designed by Le Vau
Petit Trianon
A small chateau on the palace grounds of Versailles in which Marie Antoinette would retreat to
Les Invalides
Church that was built as part of a military hospital; the tomb of Napoleon Bonaparte
Panthéon
A secular mausoleum originally built as a church dedicated to St. Geneviece
La Madeleine
A Catholic church designed in its present form as a temple to the glory of Napoleon's army
Plateresque Style
Spanish Renaissance style; From Spanish "platero" for "silversmith". Late Gothic and early Renaissance architecture that was decorated with very elaborated motifs; also "Isabelline Architecture"
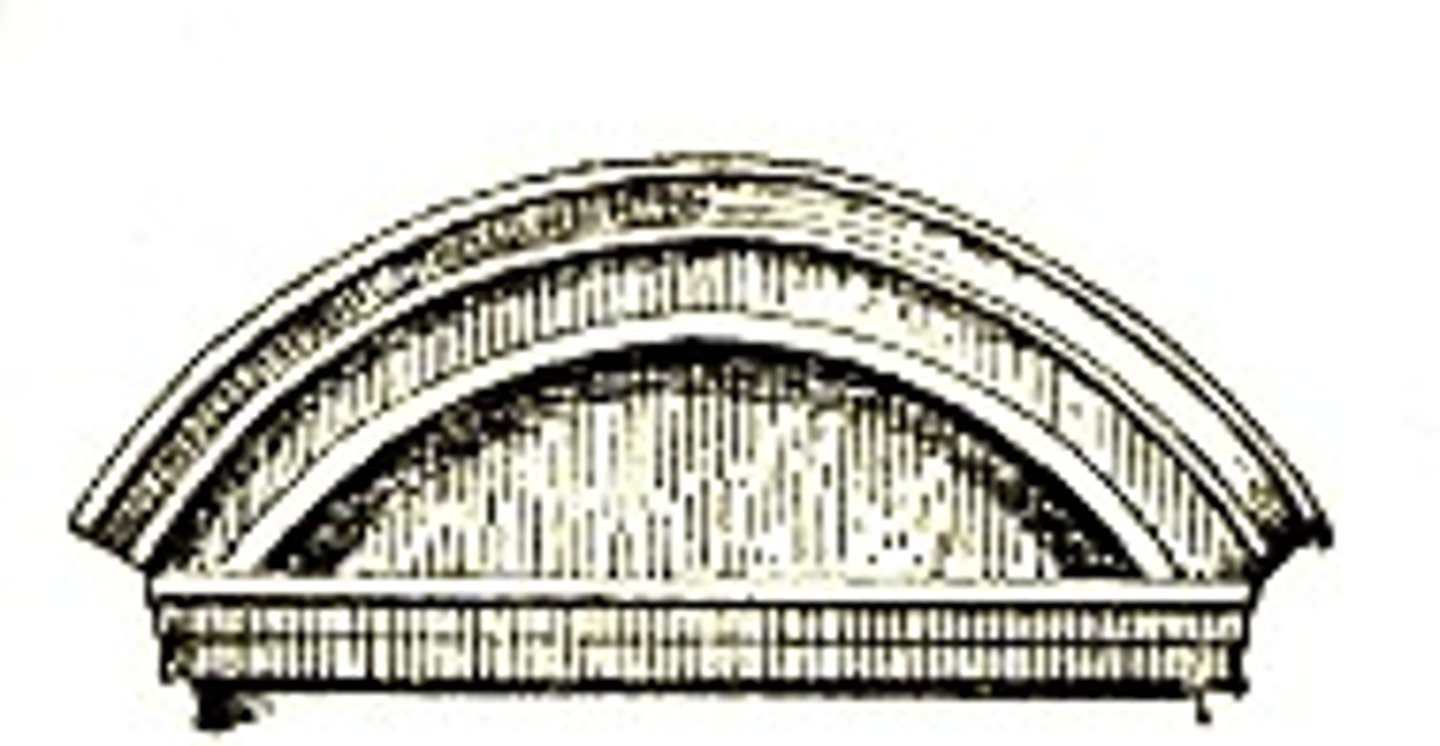
Segmental or Segmented
A type of baroque pediment
Scrolled
A type of baroque pediment
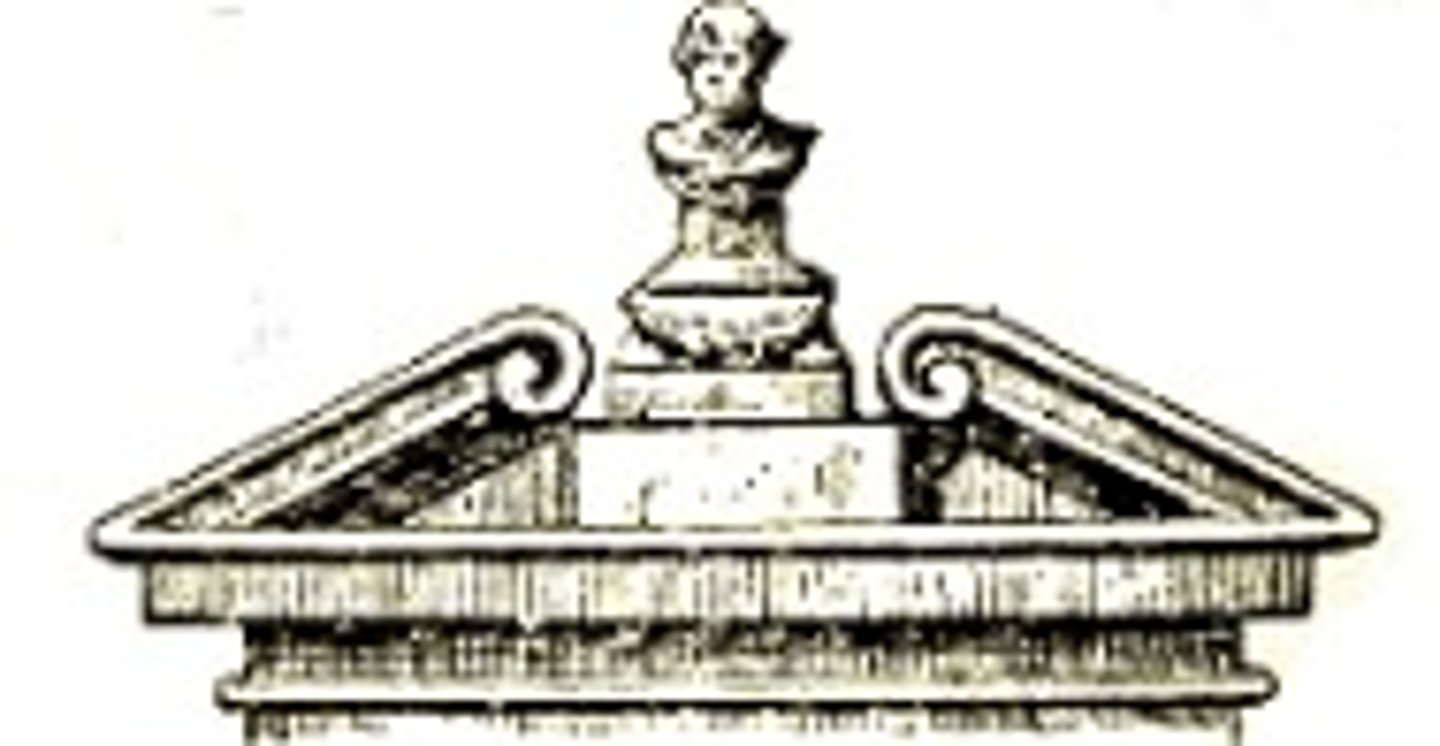

Swan Neck
A type of baroque pediment
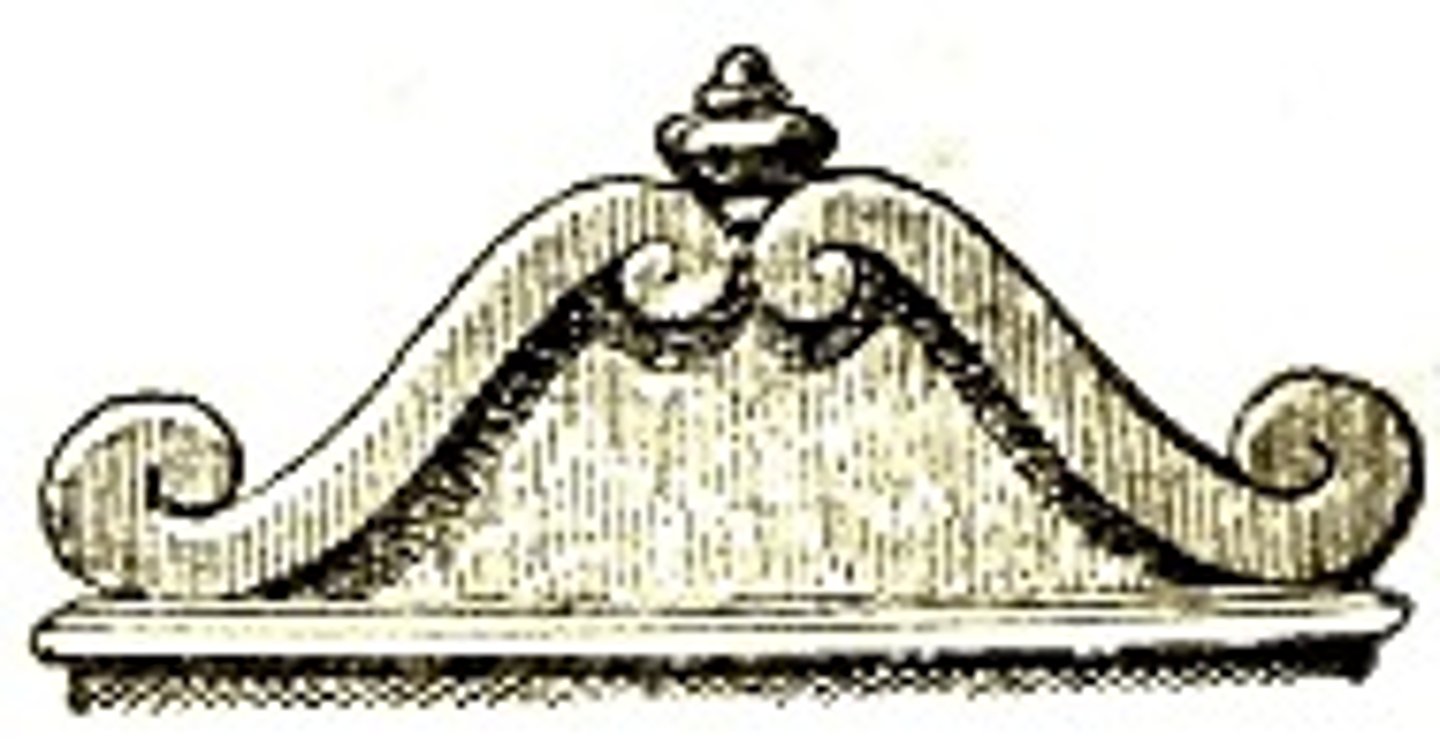
Open
A type of baroque pediment
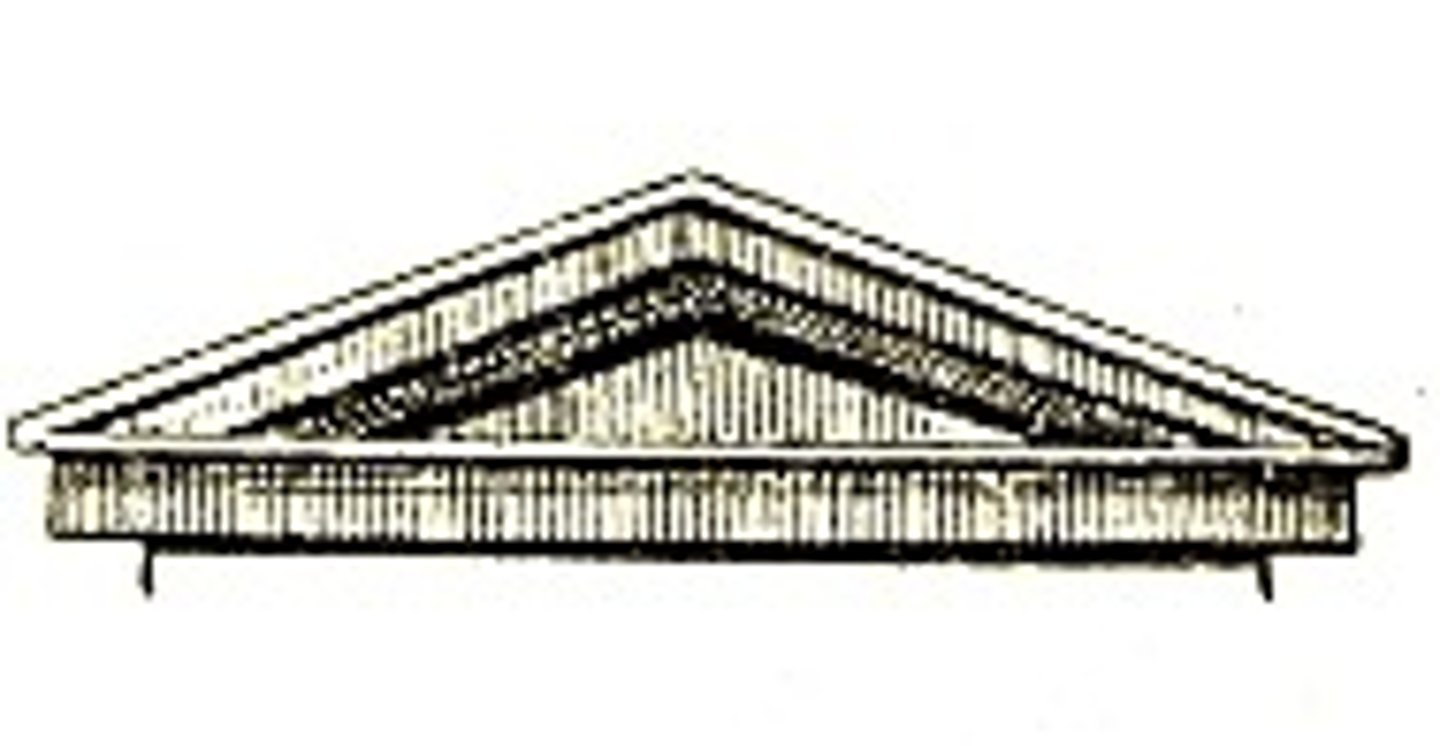

Broken
A type of baroque pediment

Churrigueresque
The Spanish variation of the Baroque, this style was arguably the most exuberant of all national variations of the Baroque; it was named after a family of architects - Jose Churriguera and his brothers Alberto and Joaquin
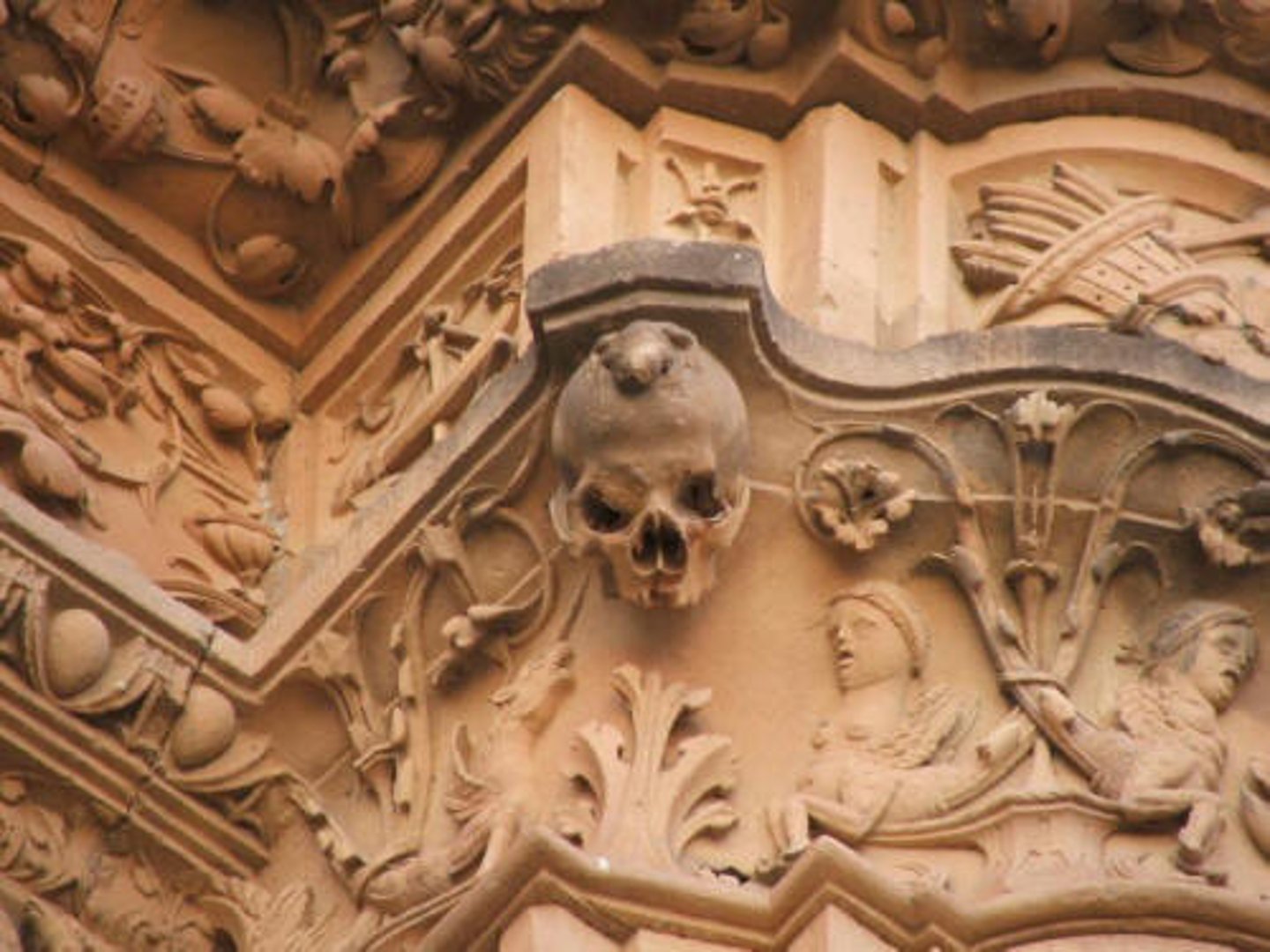
University of Salamanca
The oldest Spanish University and one of the four greatest Universities in the world; known for its "frog on skull" ornament

Casa de las Conchas
"House of Shells"; Currently houses a public library in Spain; Its facade is decorated with more than 300 shells
Elizabethan Architecture
English Renaissance architecture during the reign of Queen Elizabeth I; Remnants of Gothic Architecture
Anglo-Saxon Architecture
A period in the history of architecture in England; Secular buildings in Britain during this era were generally simple, constructed mainly using timber with thatch for roofing.
Norman Architecture
A period in the history of architecture in England; known as the "English Romanesque" or "Twelfth Century Style"; general appearance is bold and massive, and presents many similarities with the architecture in Normandy
Early English Style
A period in the history of architecture in England; Also known as the "Lancet"; shaking itself free from the massive Norman style; characterized by dog-tooth ornaments, foliaged capitals, and tall and narrow lancet openings.
Decorated Style
A period in the history of architecture in England; Also known as the "Geometric and Curvilinear"; Characterized by enlarged clerestories, numerous vaulting ribs; an example of this style is the Westminster Abbey
Jacobean Architecture
English architecture and decorative style of the early 17th century adapting the Elizabethan style to continental renaissance influences
Inigo Jones
A notable English architect of the Banqueting House in Whitehall, and the Queen's House; "English Palladio" known for his use of Palladian Motif; Disciple of Italian Renaissance
Sir Christopher Wren
An English architect in the 17th and 18th century; architect of Saint Paul's Cathedral; Designed many buildings (51 new churches) in London for the large rebuilding effort that followed the city's "Great Fire" of 1666; Disciple of French Renaissance
Quoins
Masonry blocks at the corner of a wall; Exist in some cases to provide actual strength for a wall made with inferior stone or rubble
Italian Renaissance
Also known as "Florentine Renaissance"; characterized by:
• massive blocks of rusticated masonry in lower stories of palaces
• general absence of pilasters as decorative features
• sparing use of carved details
• massive cornices that crown the structures
Astylar
It means having no columns and pilasters, unsupported architecture
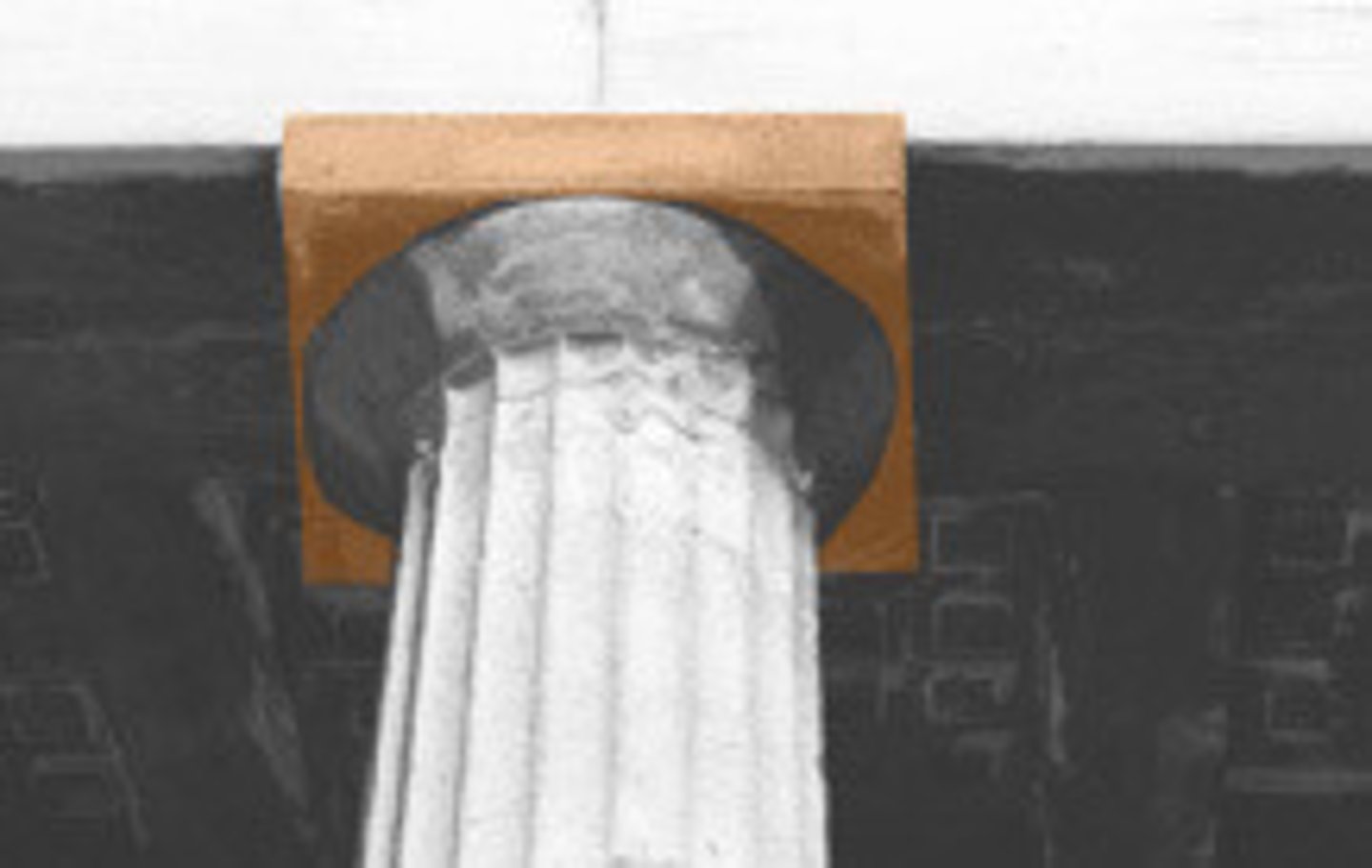
Abacus
At the top of a capital, a thick rectangular slab of stone that serves as the flat, broad surface on which the architrave rests.

Aisle
A passage or corridor parallel to the nave of a church or an ancient basilica and separated from it by columns or piers.
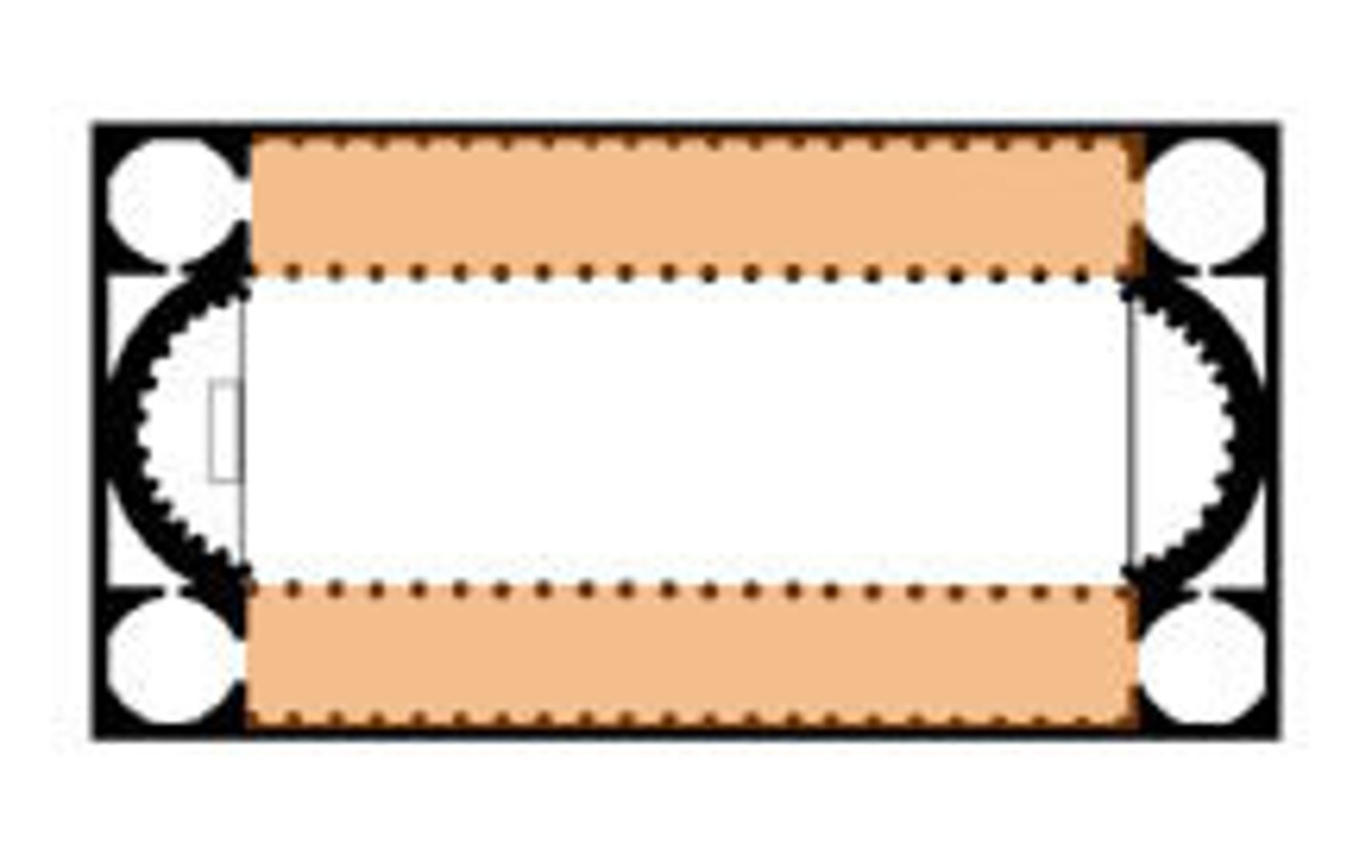
Ambulatory
A semicircular or polygonal passageway around the apse of a church
Anta
In Classical temples, the pilaster like projecting end of a portico wall often framing columns, which are then said to be in antis
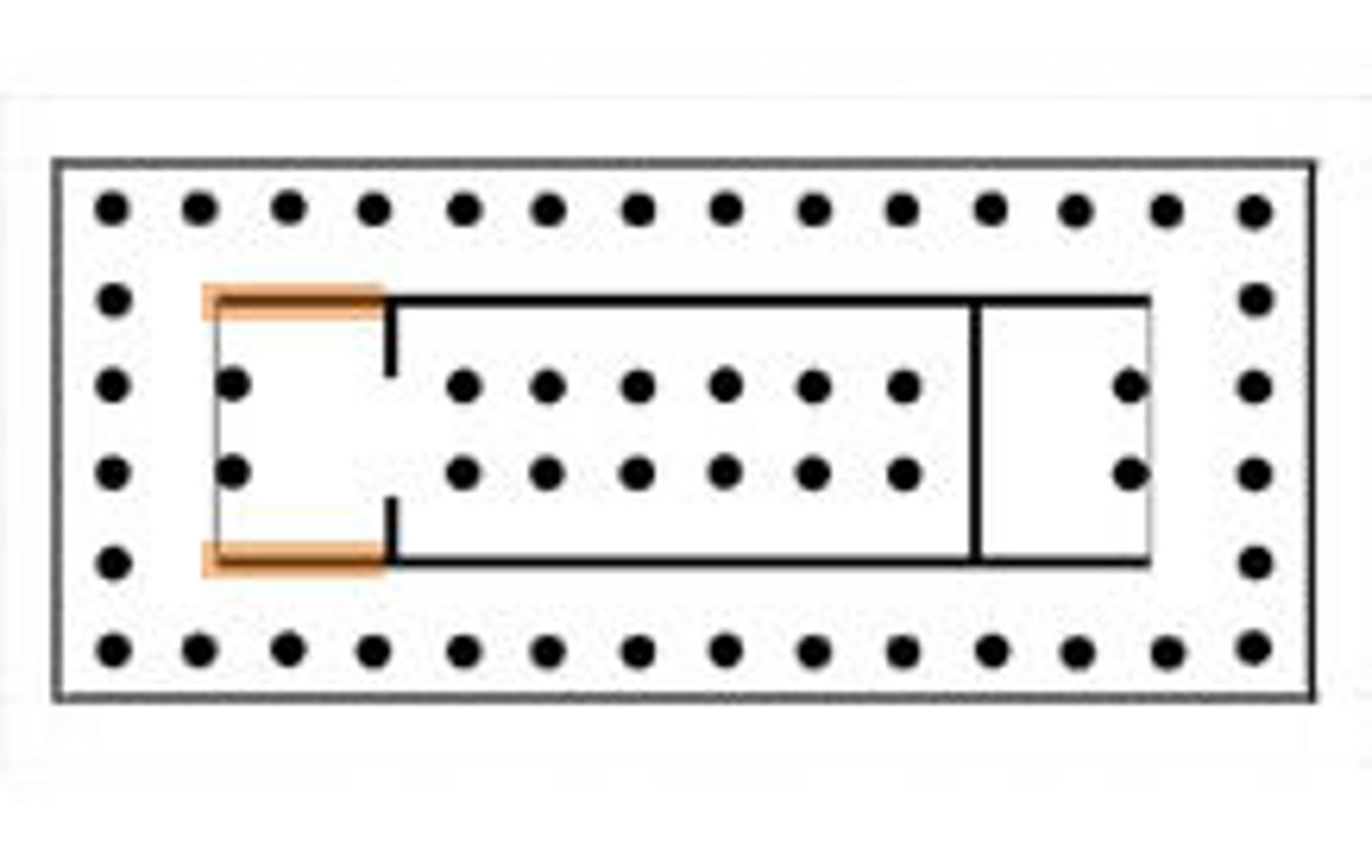
Arcade
A series of arches supported on piers or columns. A "blind" arcade is a row of arches applied to the wall as an ornamental feature.

Arch
A structural devise, curved in shape, to span an opening by means of wedge-shaped bricks or stones (voussoirs) that support each other by exerting mutual pressure and that are buttressed at the sides.
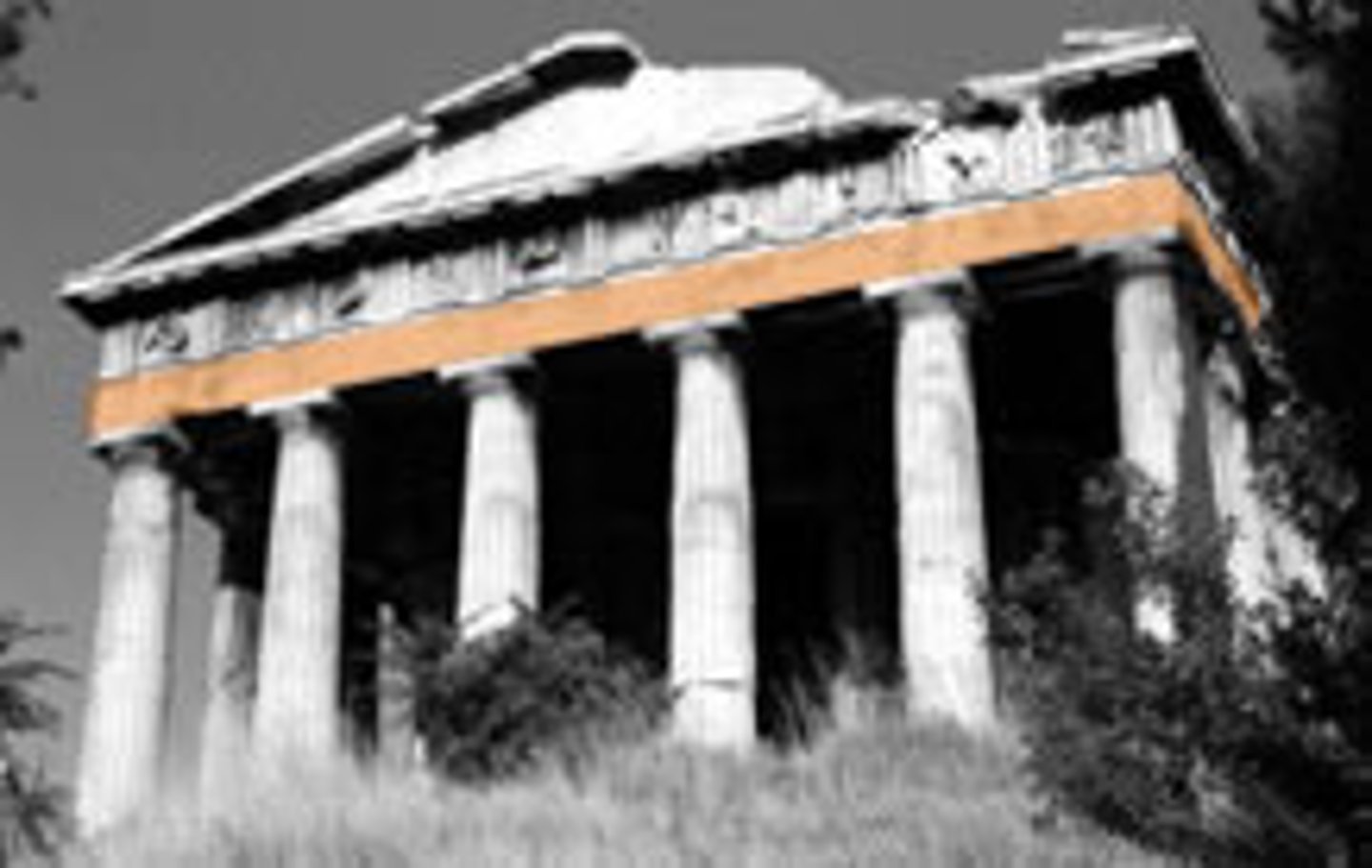
Architrave
A square beam that is the lowest of the three horizontal components of a Classical entablature.

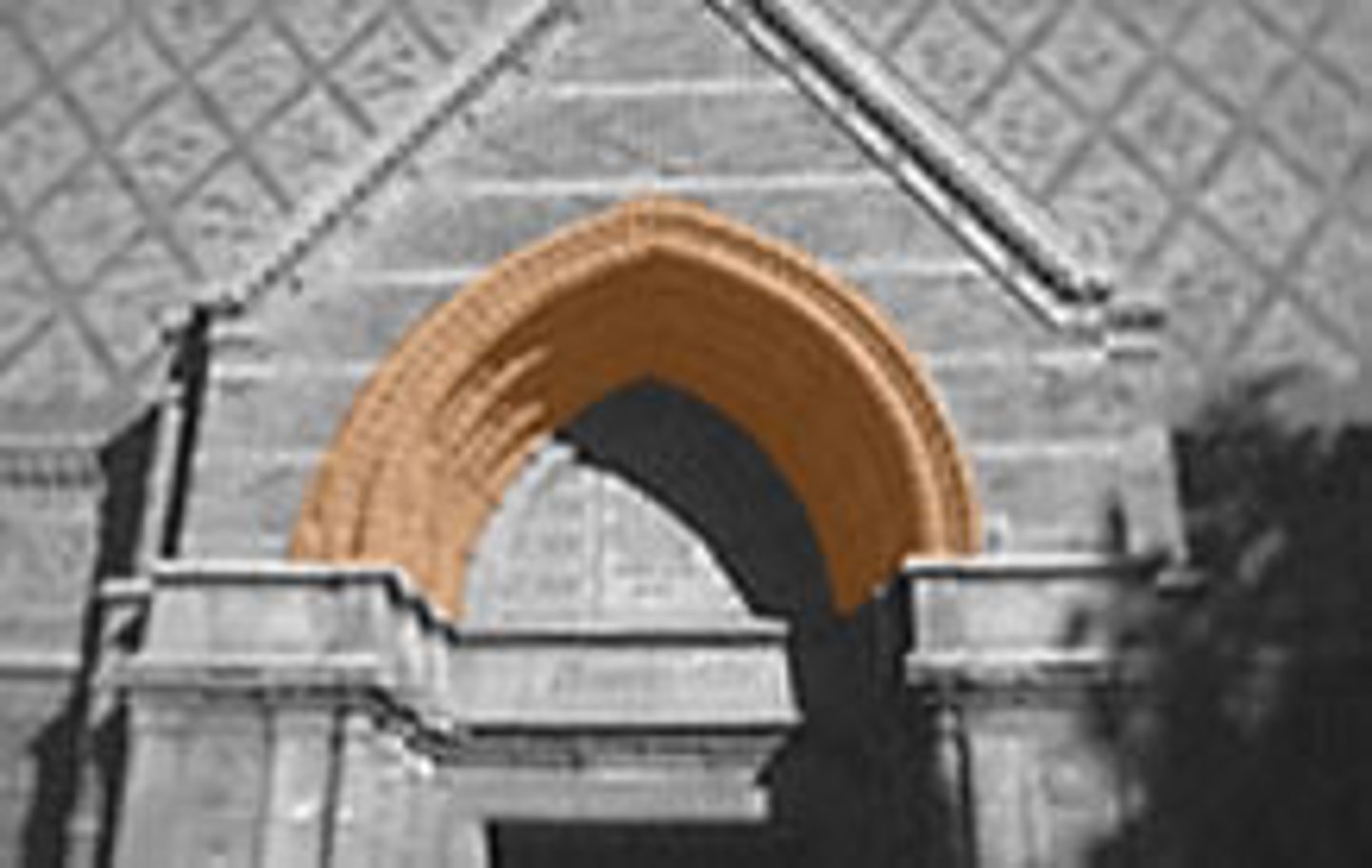
Archivolt
A molded band carried around an arch.

Arcuated
Any form of construction using arches
Ashlar
Building stone that has been squared and finished, and the masonry constructed of such blocks.
Barrel Vault
A half-cylindrical vault, semicircular or pointed in cross section; also called tunnel vault.
Bay
A vertical compartment of a building in which several such compartments are repeated; each bay mignt be defined by columns, piers, windows, or vaulting units
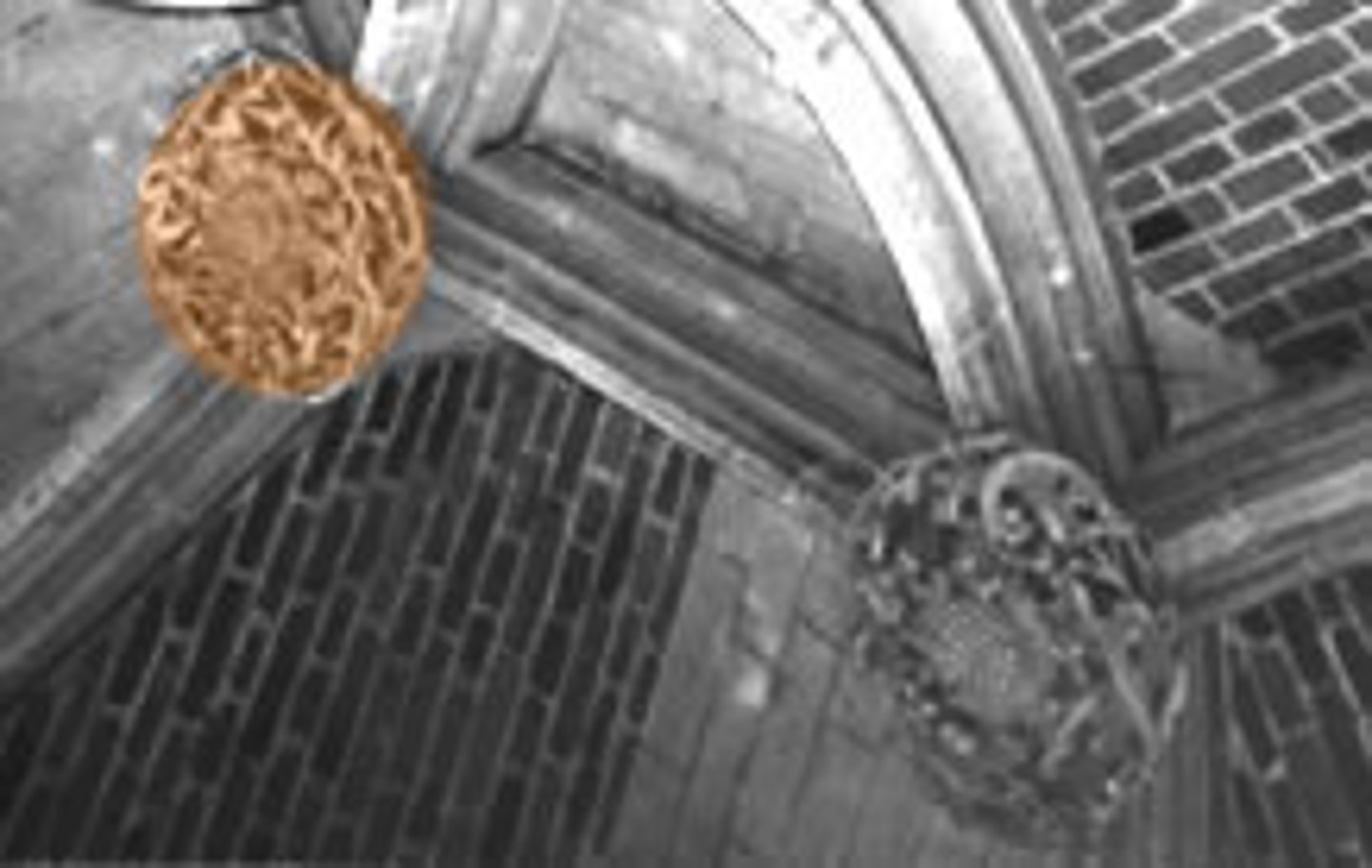
Boss
Sculpted ornament of joints, found primarily in vaults.

Buttress
A projecting mass of masonry serving to provide additional strength for the wall as it resists the lateral thrust exerted by an arch or vault.
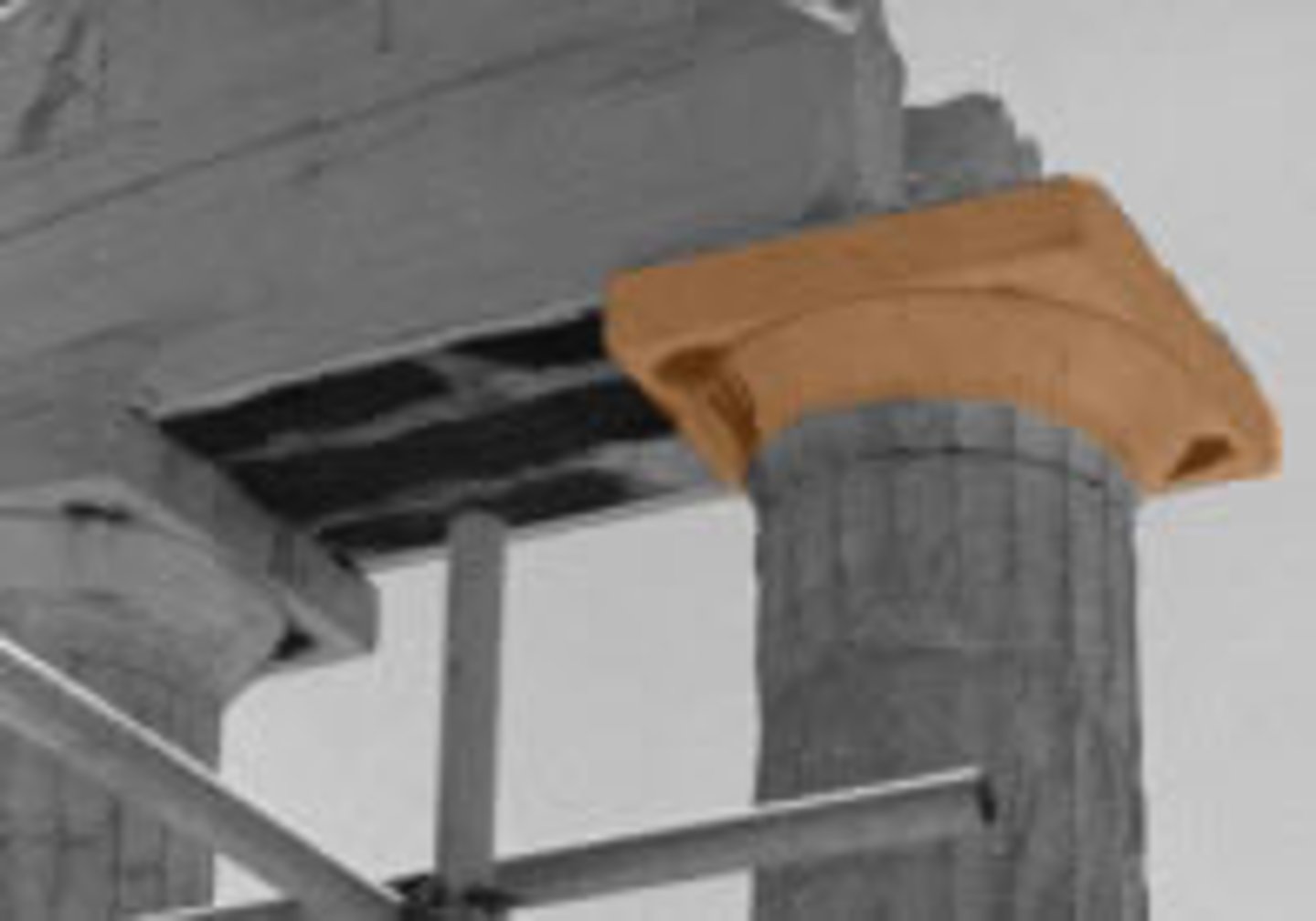
Capital
The uppermost part of a column, usually shaped to articulate the joint with the lintel or arch supported

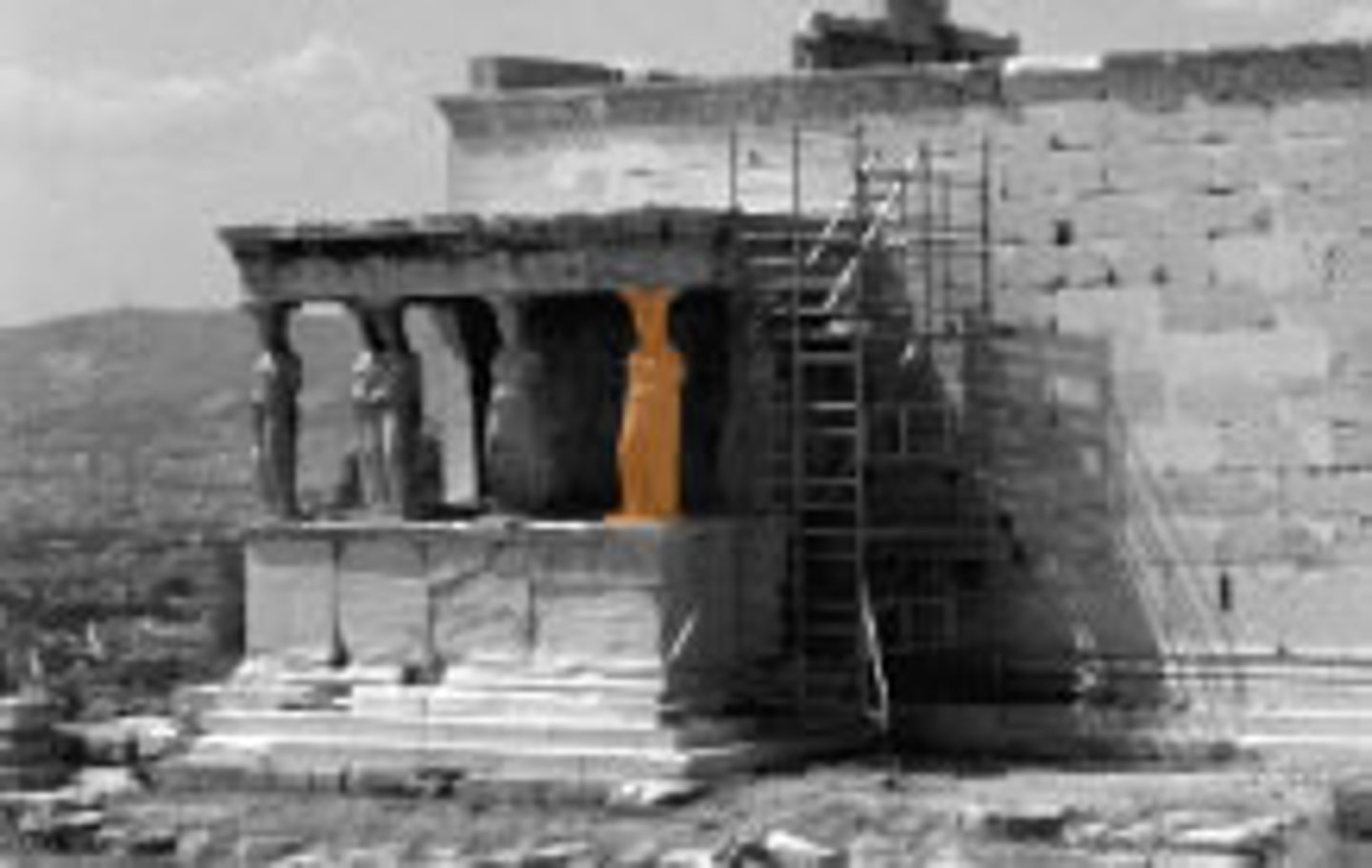
Caryatid
A sculpted female figure used as a support in place of a column or pier.

Cella
The body and main sanctuary of a Classical temple, as distinct from its portico and other external parts; sometimes "Naos"
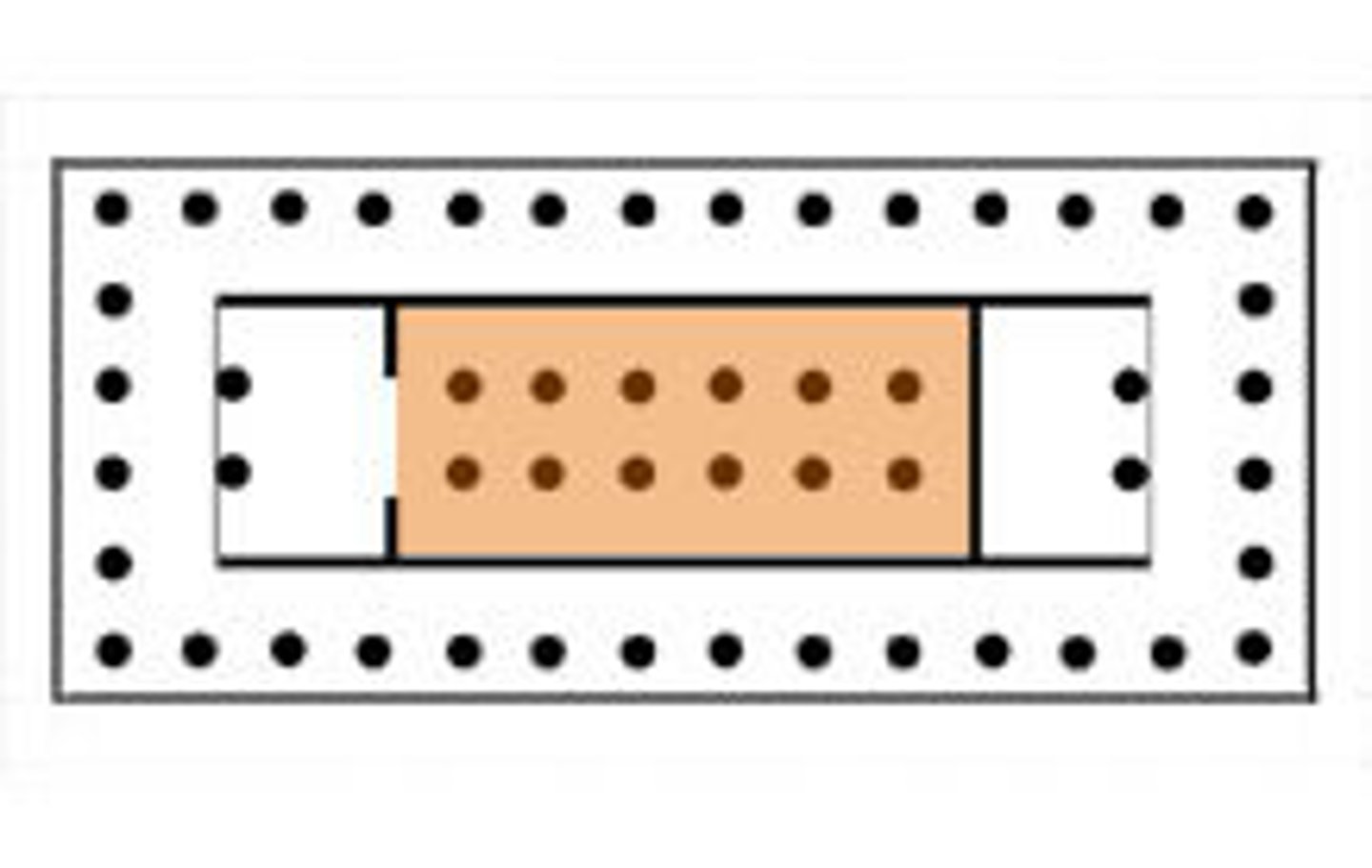
Chancel
The eastern portion of a church set apart for the clergy, and often separated from the main body of the church by a screen, rail, or steps. The term is also used to describe the entire east end of a church beyond the crossing.
Choir
The part of a church, generally located toward or in the apse, reserved for clergy and singers.

Clerestory
A part of a building that rises above adjoining roof-tops and is pierced by window openings to admit light to the interior.

Cloister
An open square court surrounded by a covered ambulatory, often archaded. It is generally attached to a church or monastery and is distinguished from a secular courtyard by its function as a lace of seclusion and repose.
Coffering
Recessed panels, square or polygonal, that ornament a vault, ceiling, or the underside (soffit) of an arch.

Column
A vertical, usually cylindrical, support, commonly consisting of a base, shaft, and capital; in Classical architecture, its parts are governed by proportional rules.
Composite Order
The fifth Classical order; favored in late Roman architecture. On the capital, large conjoined Ionic volutes are combined with the acanthus leaves of the Corinthian order.
