module 8 | other aspects of aqueous equilibria
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
common ion effect
shift in position of equilibrium upon adding a substance that provides more of an ion that’s already there
le chatelier’s principle; if there’s extra stuff on the right, it’ll shift left, and vice versa
buffer
solution that resists change in pH w/addition of either an acid or base
must contain significant amounts of weak acid/base with conjugate base/acid
acid neutralizes any OH- ions, base neutralizes any H3O+ ions
three ways to make a buffer
mixing weak acid/base w/conjugate salt (ex. CH3COOH&NaCH3COO, NH3&NH4Cl)
mixing two salts that make a conjugate acid-base pair (NaH2PO4 and NA2HPO4)
reacting SOME of a weak base w/a strong acid or SOME of a weak acid w/a strong base - calculations
effectiveness of buffer depends on
pka/pkb of buffering system
pH of environment
henderson-hasselbalch equation
used when rule of 100 applies - initial acid/salt concentrations at least 100x greater than ka
pH = pK + log ([conjugate b/a]/[b/a'])
calculating pH changes in a buffer system
stoichiometry calculation (how addition changes relative amounts—moles—of acid and conj. base) - added acid reacts w/A- to make more HA, added base reacts w/HA to make more A-
equilibrium calculation (calculate pH based on new amounts of acid/conj base)
buffer capacity
the max amount of acid/base that a buffer can neutralize before the pH changes a lot
limited capacity of H3O/OH that can be soaked up
eventually, all HA reacts w/added OH- and all A- reacts w/added H3O+
max buffer capacity
when [HA] and [A-] are large and equal to each other
buffer range
most effective buffer range → pka ± 1
choose an acid w/pka close to desired pH
equivalence point
moles of acid = moles of base
moles of H3O+ = moles of OH-
stoichiometrically equivalent
inflection point
depends on pH of salt solution
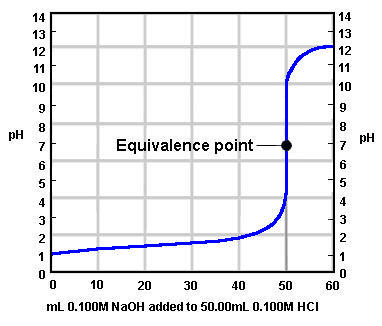
strong acid and strong base titration
equivalence point = 7
ex. HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O
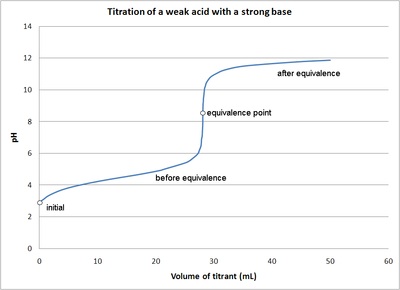
weak acid and strong base titration
equivalence point > 7
ex. CH3COOH + NaOH → CH3COONa + H2O
half-equivalence point
during titration of weak acid/base w/strong acid/base, HALF of WEAK substance has been converted to conjugate
pH = pKa for weak acid titration
volume at half equivalence point * 2 = volume at equivalence point
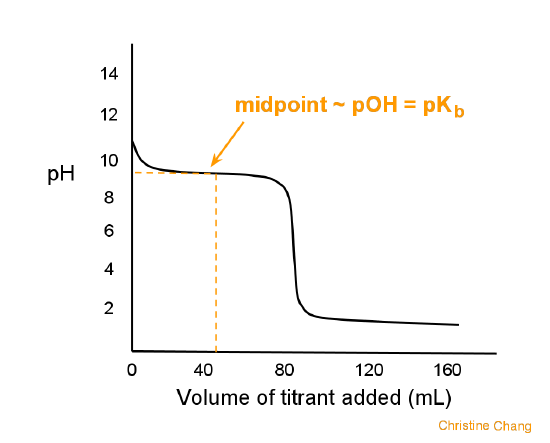
strong acid and weak base titration
pH @ equivalence point < 7
ex. HCl + NH3 → NH4 + Cl-
weak acid and weak base titration
pH of equivalence point depends on Ka of weak acid and Kb of weak base in products
ex. if Ka = Kb, neutralization products have neutral pH
ksp
solubility product constant
larger Ksp = more soluble