Lecture 7- transport across membranes
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
the K+ ion channel is:
voltage-gated
he Na+/Ca++ exchanger (NCX) works by what to
control Ca++ levels
antiport
removes calcium from the what by using energy stored by the Na+ gradient (one Ca++ “out” for 3 Na+ in) secondary active
transport (coupled)
cytosol
the Na+/Ca++ exchanger (NCX) works by antiport to
control Ca++ levels: has a low affinity for Ca++ but what
capacity (ie, fast at high concentrations
high
Ca++ is an important messenger within the cell and can be released to send what
signals
Calcium levels are low in the cytosol because it is pumped out into the what and the membrane is highly impermeable to the ion
extracellular space
Calcium channels can be transiently opened by
action potential or what itself
calcium
Calcium binds to what, which
can initiate downstream signals (like heart beats)
calcium-binding proteins
ouabain and digoxin bind to the Na+/K+ pump (not shown) and
inhibit it, resulting in what intracellular sodium.
this reduces the NCX function and yields what intracellular calcium, making heartbeats stronger and more frequent
higher
what transporters are highly regulated
active
Ca2+ATPase hydrolyses # ATP for each Ca2+ ion transported
1
Ca2+ ATPase can export Ca++ (on plasma membrane) or pump it into the ER (or sarcoplasmic reticulum) for what when needed
storage
with respect to the Na+/K+ ATPase pump, which of the following is TRUE?
ions move more slowly through a pump than a channel because because only a few ions move per ATP hydrolysis instead of continuously
with respect to the Na+/K+ ATPase pump, which of the following is FALSE?
it must have a higher binding affinity for K+ outside of the cell and a lower binding affinity for K+ inside the cell
the difference in charge across the membrane is the what
membrane potential
membrane potential is largely due to Na+ K+ ATPase and some flow of K+ back via what channels
leak
# mV is a standard membrane potential for a
(resting) mammalian neuron, but varies according
to cell type/organism
-70
the myelin sheath acts as a what
insulator
the disease Multiple sclerosis (MS) is caused by what of the myelin sheath
disruption
an action potential is the what change in charge across the membrane
rapid
action potential occurs in what cells, ie, nerves, muscle, beta pancreatic cells, endocrine cells, some plant cells
excitable
takes place via the rapid what of voltage gated ion channels (then what
opening, closing
action potential stimulus does what to the membrane
depolarizes
Na+ channel opens, Na+ influx →
#mV (close to equilibrium)
40
Change in potential opens K+ gates
→ #mV (repolarization)
-80
action potential: Na+ stimulus K+ slowly leaks out
what mV
-70
action potential: Na+ depolarization (past threshold)
what mV
-50
action potential: Na+ voltage gated channels open, Na+ goes in
what mV
40
action potential: K+ voltage gated channels open (Na+ channels close) (K+ out)
what mV
30
action potential: K+ channels close (although leak channels are open)
what mV
-80
changes in membrane potential regulate the which channel
K+
the voltage required to open/close the channel is what type dependent
cell/protein
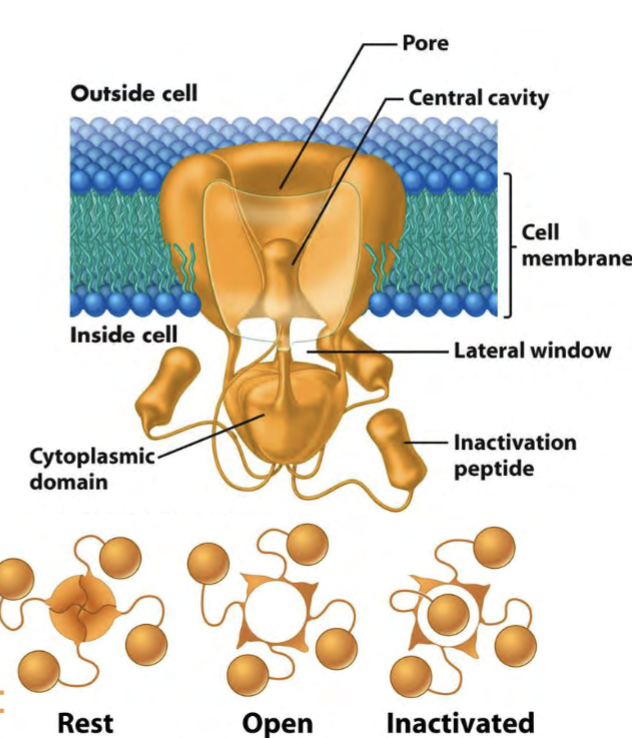
depolarization of membrane
Rest
spontaneous
Open/Inactivated
K+ Leak channels are or are not voltage gated
are not
nerves “do what” to muscles at the neuromuscular junction
talk
how nerves send signals in your body
synaptic transmission