Chapter 17 - Fungal Diversity
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Are fungi more closely related to humans/animals or plants?
animals/humans
What is mycology?
the study of fungi
What is mycelium?
filamentous network of compromised of individual strands of hyphae (fungal growth is at the tips of hyphae)
What is fungal cell wall made of?
Chitin, also found in exoskeleton of arthropods like insects and crustaceans
How do fungi consume nutrients?
Fungi are heterotrophs that derive food from organic sources (don’t create their own)
digestion occurs outside the fungus body; cells secrete digestive enzymes
Absorption: products of digestion are taken up by cells
rapid expansion of hyphae leads to large surface area for food absorption
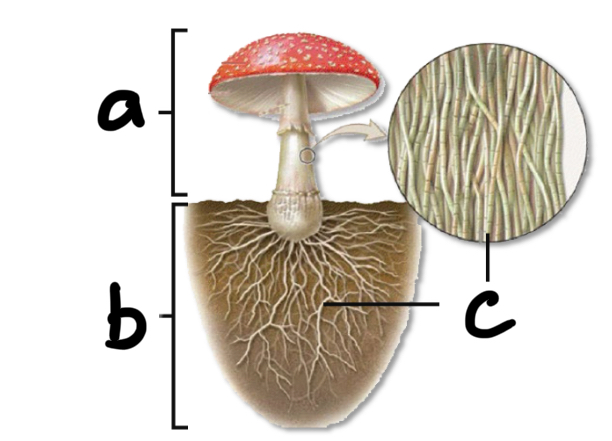
Label a, b, and c
a - fruiting body
b - mycelium
c- hyphae
What is the role of decomposers?
break down organic matter to release nutrients (this includes structural compounds like lignin in wood)
Why is decomposition an important ecological function of fungi?
recycles nutrients and stores carbon
What types of substances are some fungi capable of decomposing?
potentially toxic substances, petroleum, oil spills, plastic, cancer causing chemicals (breaking down microplastics, under a lot of study to see how it can affect the use of harmful substances)
What are mycorrizhae?
a mutualistic symbiotic relationship between fungi and plant roots “fungus root”
What important function do mycorrhizae have?
90% of plants have symbiotic relationship with mycorrhizal fungi
hyphae of some mycorrhizal fungi enter into root cells of plants
hyphae of species of mycorrhizal fungi surrounded roots
the fungi absorb water and minerals from the soil, and trade those to the plant for sugars produced by photosynthesis
(most of the plants that we eat, fungi have a relationship with it) (fungi helps tree absorb water, tree provides fungi with dextrose)
What are the stages of sexual reproduction in fungi? What are haploid, what are diploid?
1) Hyphae from each haploid mycelium meet and cytoplasms fuse
Heterokaryotic stage: cells contains 2 distinct haploid nuclei
2) Parental nuclei fuse creating diploid zygote
3) Zygotes undergo meiosis producing haploid spores for dispersal and colonization
What is meant by heterokaryotic stage?
a stage in which the cells of the mycelium contain two or more genetically different nuclei, often derived from different parents
How does asexual reproduction in fungi work? What is the ploidy of these stages?
1) haploid spores arise from haploid mycelia
(many fungi can choose either sexual or asexual reproduction) (“imperfect” fungi can only use asexual reproduction)
Fungal mycelia and spores are both
Haploid (n)
What type of fungus contributes to a decline in amphibian populations?
Chytrids (they have flagellated spores and are common in soil and aquatic habitat)
What specifically (which protein, where is the protein located) do chytrids infect?
Infects keratin, which is a protein in epidermis
What is the most threatened vertebrate group?
Amphibians
What specifically (which protein, where is the protein located) do athlete’s foot and ringworm infect?
affect keratinized areas of humans (e.g. skin epidermis)
What type of fungi contribute to production of both antibiotics and blue cheese?
Zygomycetes/mold: rapidly growing fungi that reproduce asexually by producing spores
What type of fungi contribute to fermentation involved in beer, wine, and bread production?
Yeast (single-celled fungi)
reproduce asexually, often by budding
What are the valuable underground fungi (that pigs and dogs are trained to find) generally called?
Truffles and Morels
Why must you be sure about proper mushroom identification before consuming them?
psychedelic mushrooms, poisonous mushrooms
What does lichen consist of?
mutualistic relationship between fungi (ascomycetes) and a photosynthesizer (green algae or cyanobacteria)
What does it mean that lichens are a pioneer species? How do they help create new plant habitat?
lichens are “pioneer species” the first to come into an area that has recently been disturbed by events including lava, glaciers, and other natural disasters
secrete acid that breaks down rock to soil → plant habitat
very sensitive to air pollution because they obtain minerals from air
What two unique adaptations to enhance spore diverse via insects did we cover in class?
Bioluminescent: lucifeyrase enzyme (same as fireflies) attracts insects to aid in spreading spores
Cordyceps fungus: genus of parasitic sac fungi, mycelium invades and replaces host tissue, insect is compelled to move to an area that is favorable for fungal growth and spore dispersal
What is the largest known single organism on earth? What state is it located in?
Honey fungus (Armillaria ostoyae) covers over 3 square miles in eastern Oregon
How do fungi negatively affect the agricultural economy (generally)?
Approximately 30,000 species of fungi cause about 80% of known plant diseases
What two psychedelic compounds are derived from fungi? What promising therapeutic applications do they have? Know that research shows this is connected to facility
Psilocybin: active compound in “magic mushrooms”
LSD: lysergic acid derived from ergot fungus
show radical change in the way that brain cells talk to each other, for PTSD, anxiety, depression
research shows this is connected to facilitating neuroplasticity