25: Liver, Pancreas, and Spleen
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What major structure leaves a major impression in the caudate lobe of the liver?
caudal vena cava
List all of the lobes of the liver from left to right.
left lateral (LL)
left medial (LM)
quadrate (Q)
right medial (RM)
right lateral (RL)
caudate (above right medial and lateral lobes)
There are two parts of the caudate lobe. List them and their approximate position.
papillary process (PP): more medial, ventral cranial surface
caudate process (CP): more lateral, right ventral surface
The gall bladder is located between what two lobes of the liver?
quadrate
right medial
The hilum of the liver is called what?
porta hepatis
The falciform ligament is located between what two lobes o the liver?
left medial
quadrate
What surface of the liver touches the diaphragm?
parietal
List the structures of the biliary system, in order from which bile would pass.
gall bladder
cystic duct
hepatic ducts
bile duct
major duodenal papilla
What is the gallbladder, and how does it perform its function?
a sac that stores bile
contracts to push big into the duodenum (to digest lipids/fats
The hepatic ducts serve what function?
transport bile from liver itself to the bile duct
What is the function of the cystic duct?
carry bile from the gall badder to the bile duct
What is the function of the bile duct? Where does it connect, and what structure does it connect with?
collects all bile from cystic and hepatic ducts and transports to the lumen of the descending duodenum via the major duodenal papilla
What is the function of the ligaments of the liver?
hold the liver in position
What are the two ligaments of the liver?
right triangular ligament
left triangular ligament
coronary ligament
The right triangular ligament courses where?
right crus of the diaphragm to the right lateral lobe of the liver
The left triangular ligament courses where?
from the left crus of the diaphragm to the left lateral lobe of the liver
The coronary ligament courses where?
between the diaphragm and liver around the caudal vena cava and hepatic veins (attaches parietal surface of the liver to the diaphragm)
The right lobe of the pancreas runs by what structure?
parallel to the duodenum
The left lobe of the pancreas runs by what structure?
deep, along greater curvature of stomach
The pancreas has endocrine and exocrine functions. What are they?
exocrine: produces pancreatic juice (has enzymes that enter the duodenum)
endocrine: produces hormones that enter directly into the bloodstream
The body of the pancreas runs by what structure?
pylorus of the stomach
The right lobe of the pancreas is located within which mesentery?
mesoduodenum
The left lobe of the pancreas is located within what mesentery?
deep leaf of the greater omentum
The pancreatic duct empties at what structure?
major duodenal papilla
What is the size difference between the pancreatic and accessory pancreatic ducts in dogs? Are they both present?
pancreatic duct is smaller than the accessory
sometimes absent in dogs
The accessory pancreatic duct empties into what structure?
minor duodenal papilla
Describe the pancreatic drainage in a dog.
accessory pancreatic duct is larger, pancreatic duct is smaller and sometimes absent
Describe the pancreatic drainage in a cat.
the pancreatic duct is always present
accessory pancreatic duct is only present 20% of the time
What is the largest lymphatic organ in the body?
spleen
Within what mesentery is the spleen located?
superficial leaf of the greater omentum
What is the gastrosplenic ligament?
a peritoneal fold that connects the greater curvature of the stomach to the hilus of the spleen
Which organ is known for its elongated hilus? What does this hilus contain?
spleen
many ANS nerves and vessels
Describe the shape of the ventral end of the spleen, and what region it is located in.
wider, more mobile
left flank/ umbilicus, depending on the dog
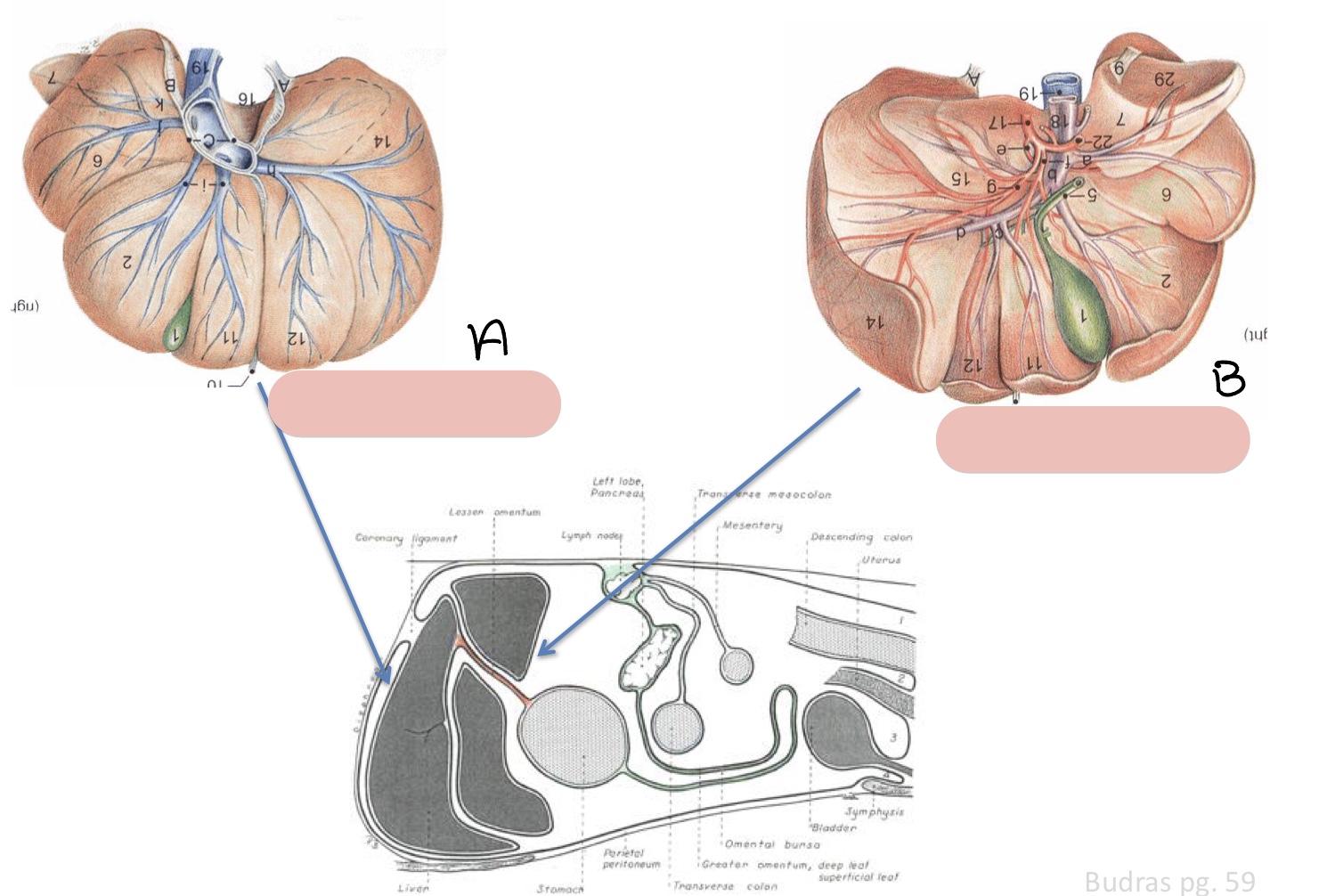
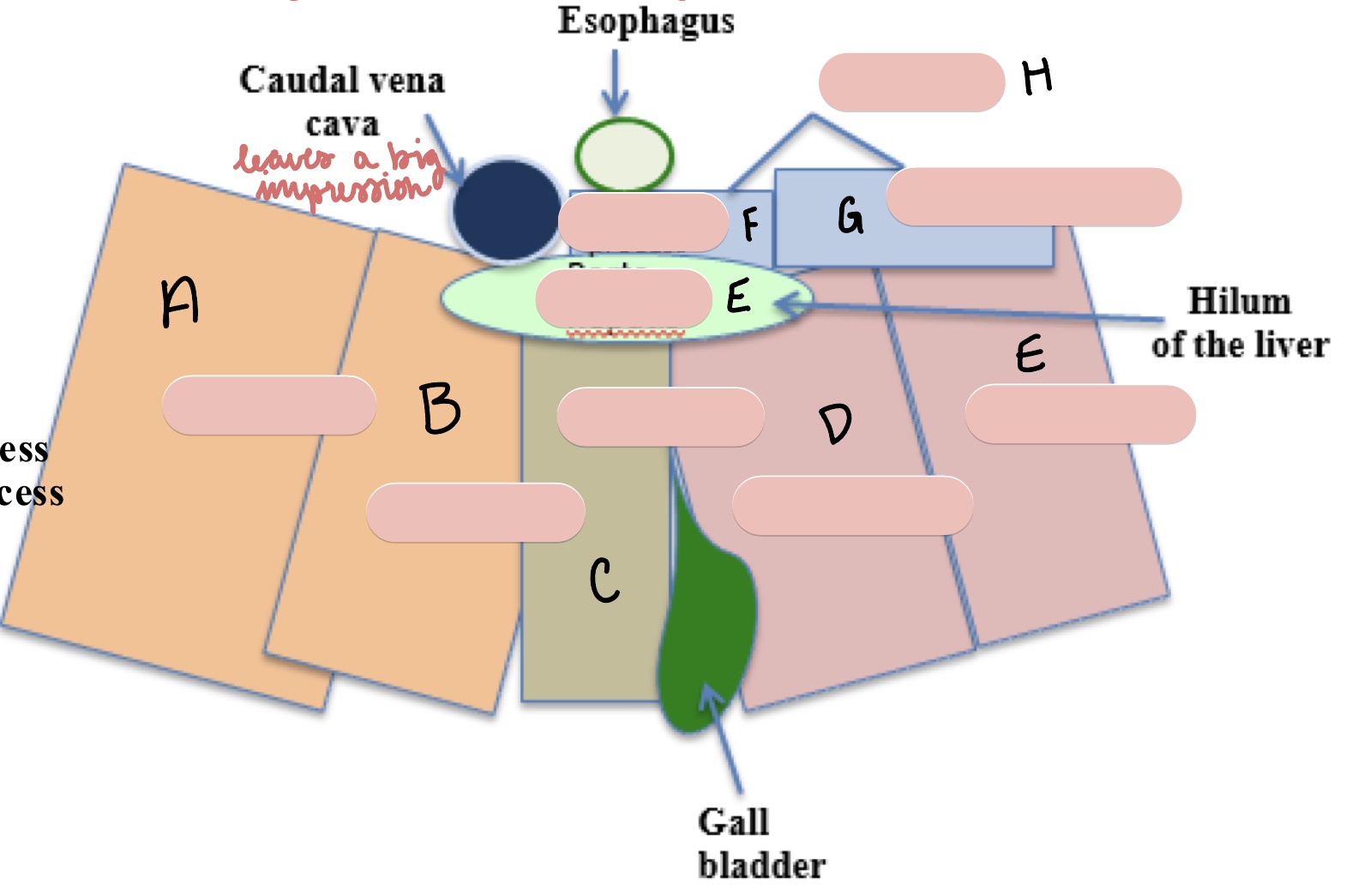
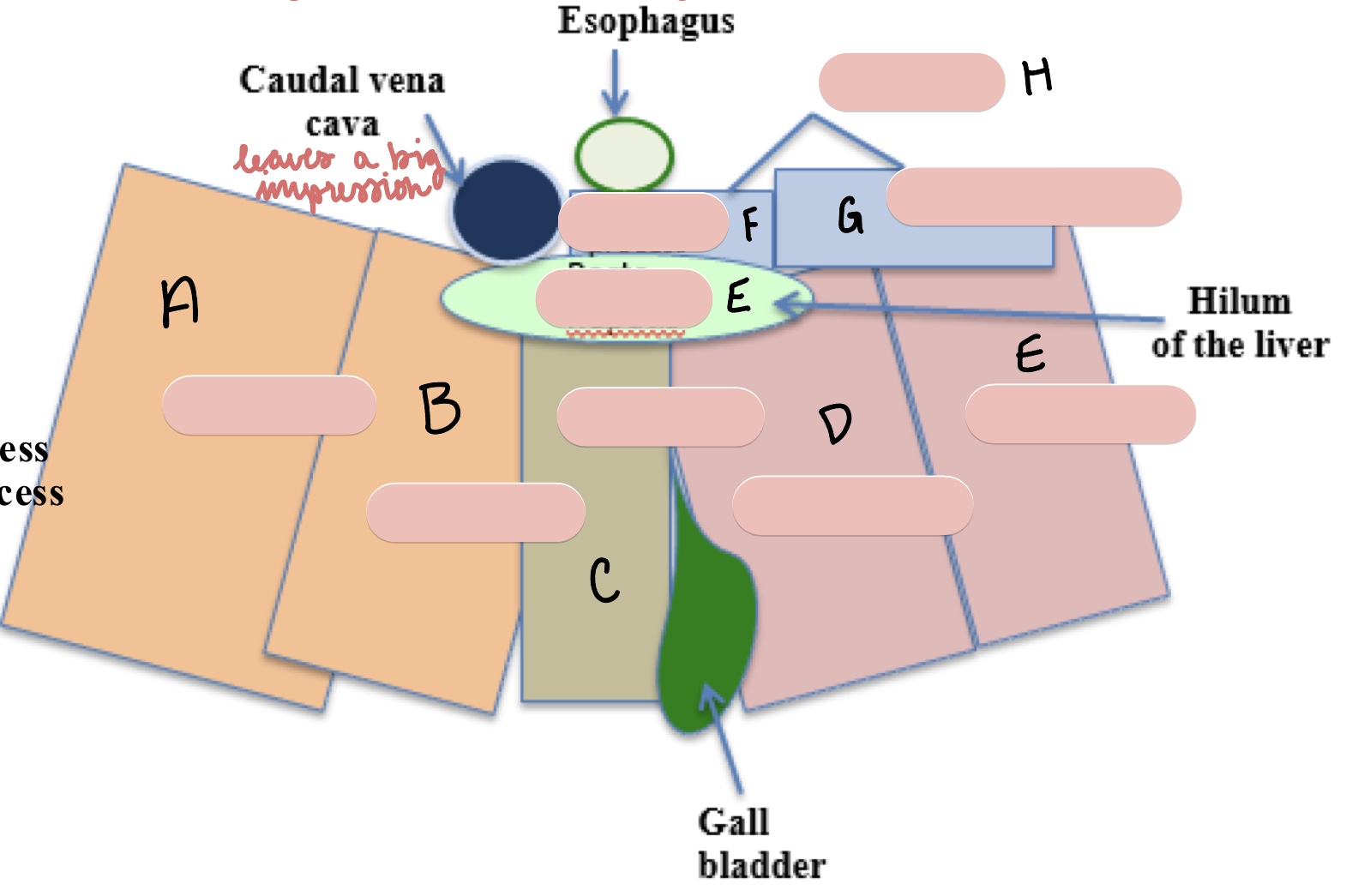
Name the surfaces of the liver represented by a and b.
parietal surface
visceral surface
Name the structure(s) indicated by a, b, and c.
left lateral lobe
left medial lobe
quadrate lobe
Name the structure(s) indicated by d, e, and f.
right medial lobe
right lateral lobe
porta hepatis
Name the structure(s) indicated by g, h, and i.
papillary process
caudate process
caudate lobe
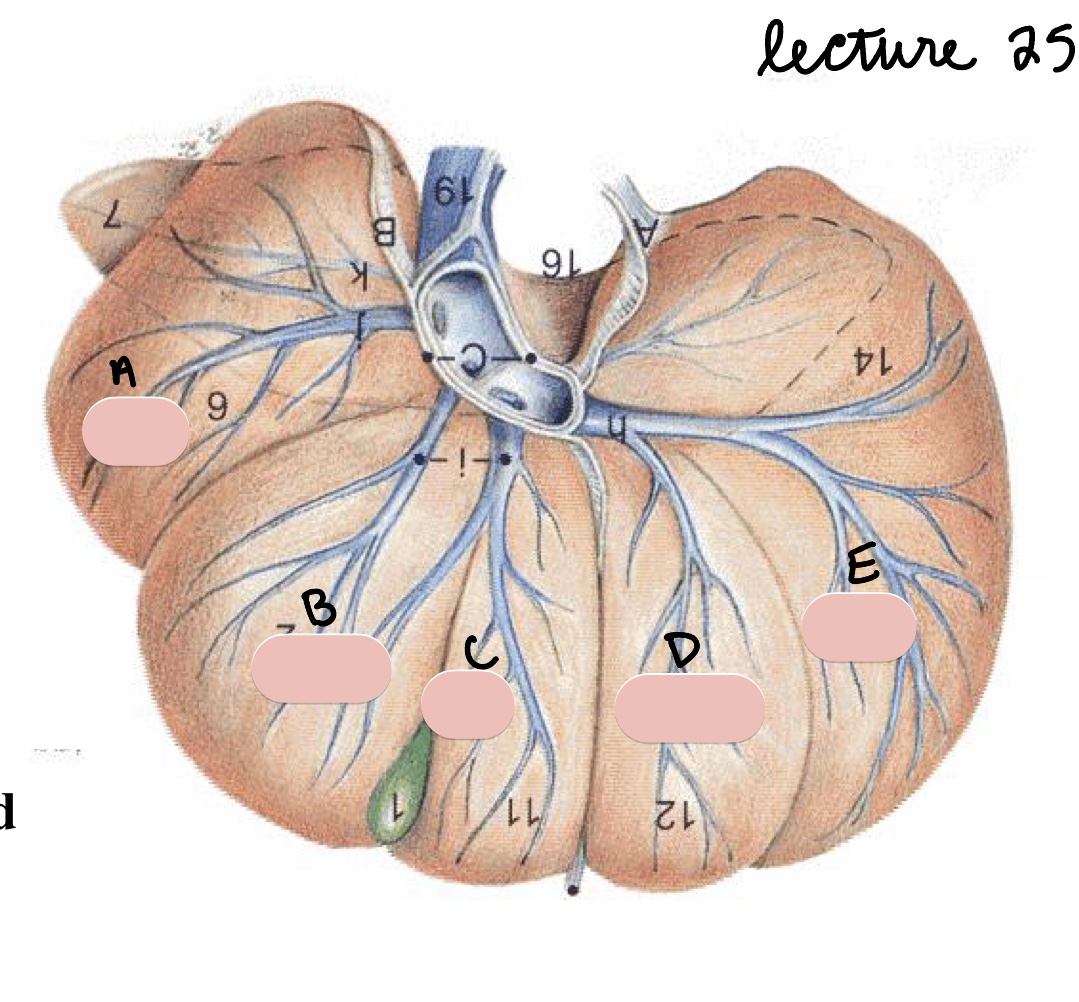
Name the structure(s) indicated by a, b, and c.
right lateral lobe
right medial lobe
quadrate lobe
Name the structure(s) indicated by d and e.
left medial lobe
left lateral lobe
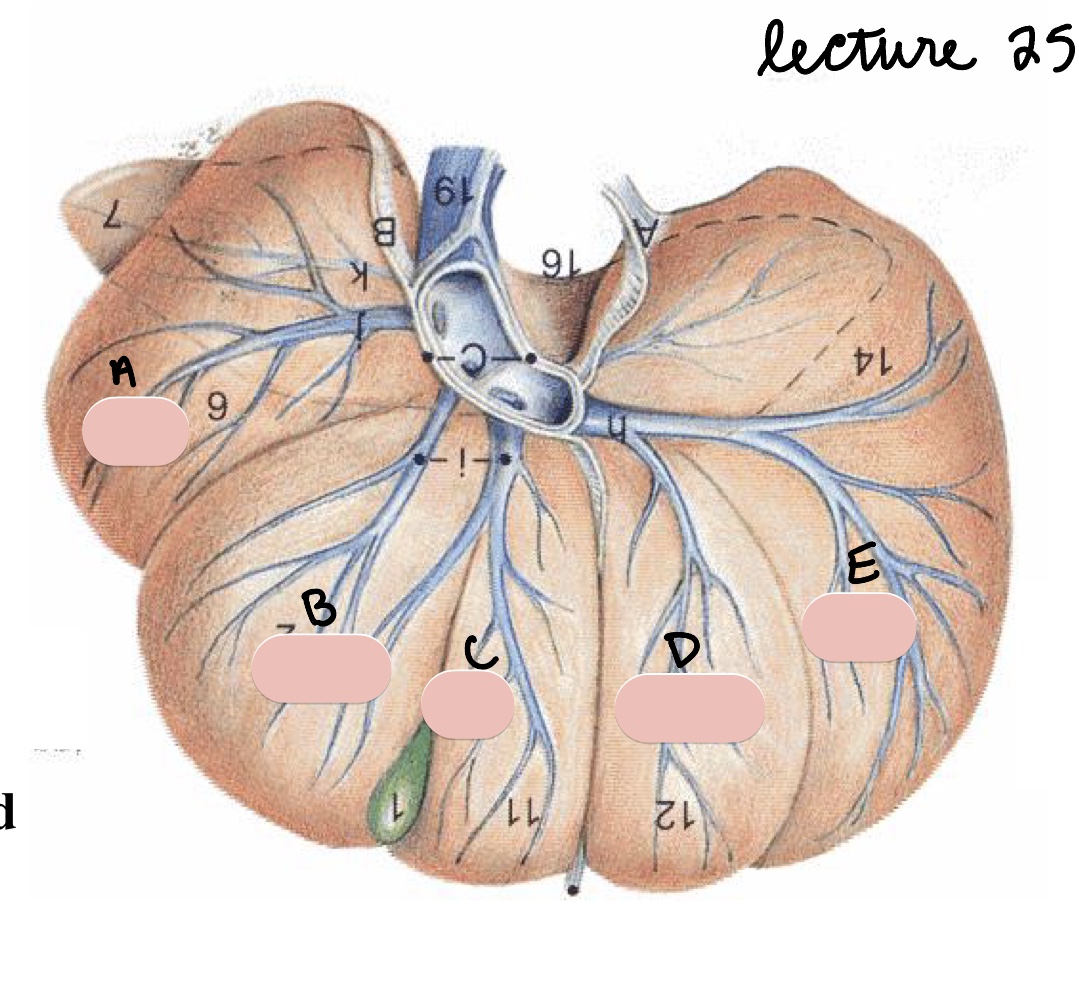
Name the structure(s) indicated by a, b, and c.
left lateral lobe
left medial lobe
quadrate lobe
Name the structure(s) indicated by d and e.
right medial lobe
right lateral lobe
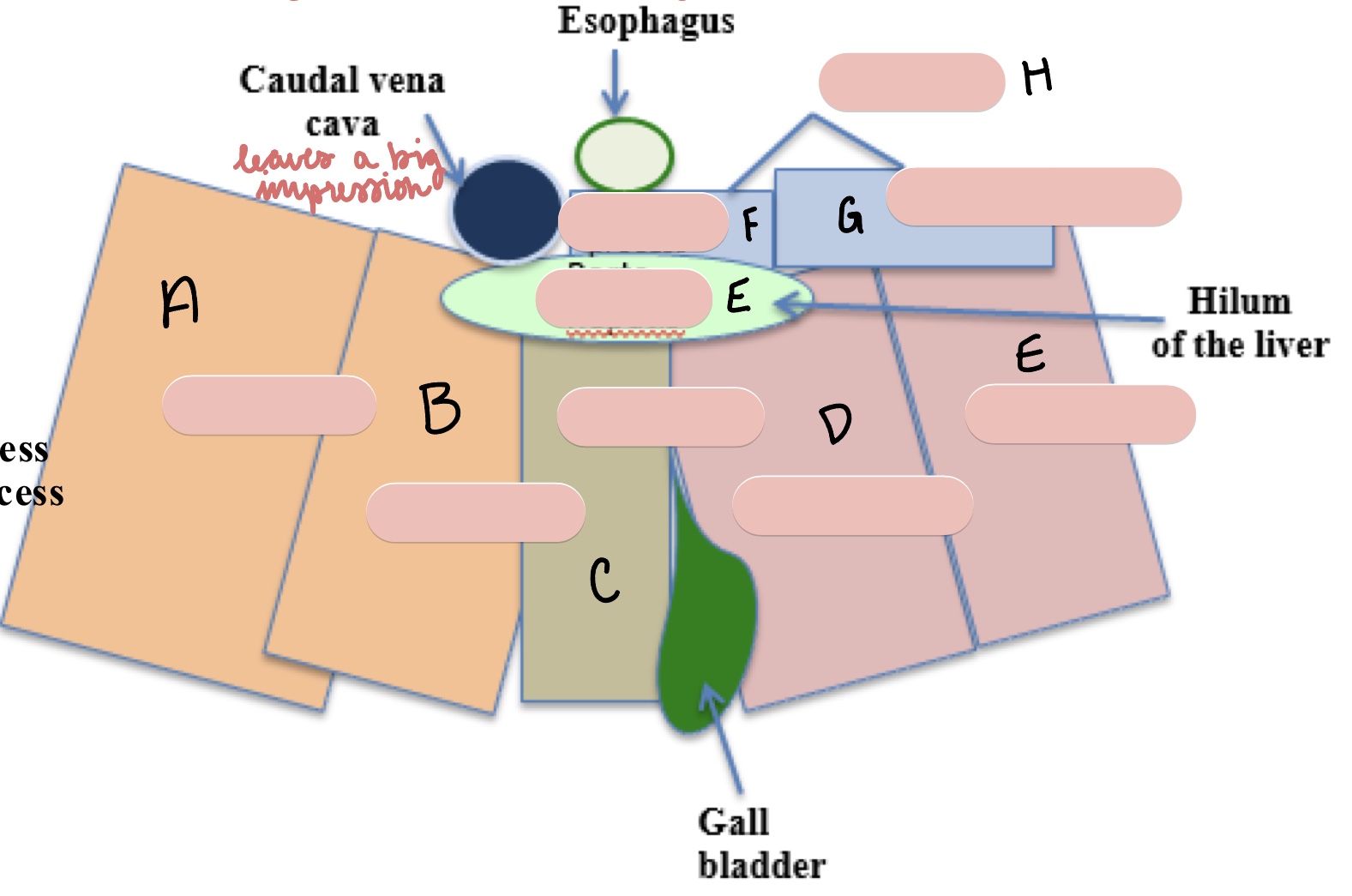
Name the structure(s) indicated by f, g, and h.
papillary process
caudate process
caudate lobe
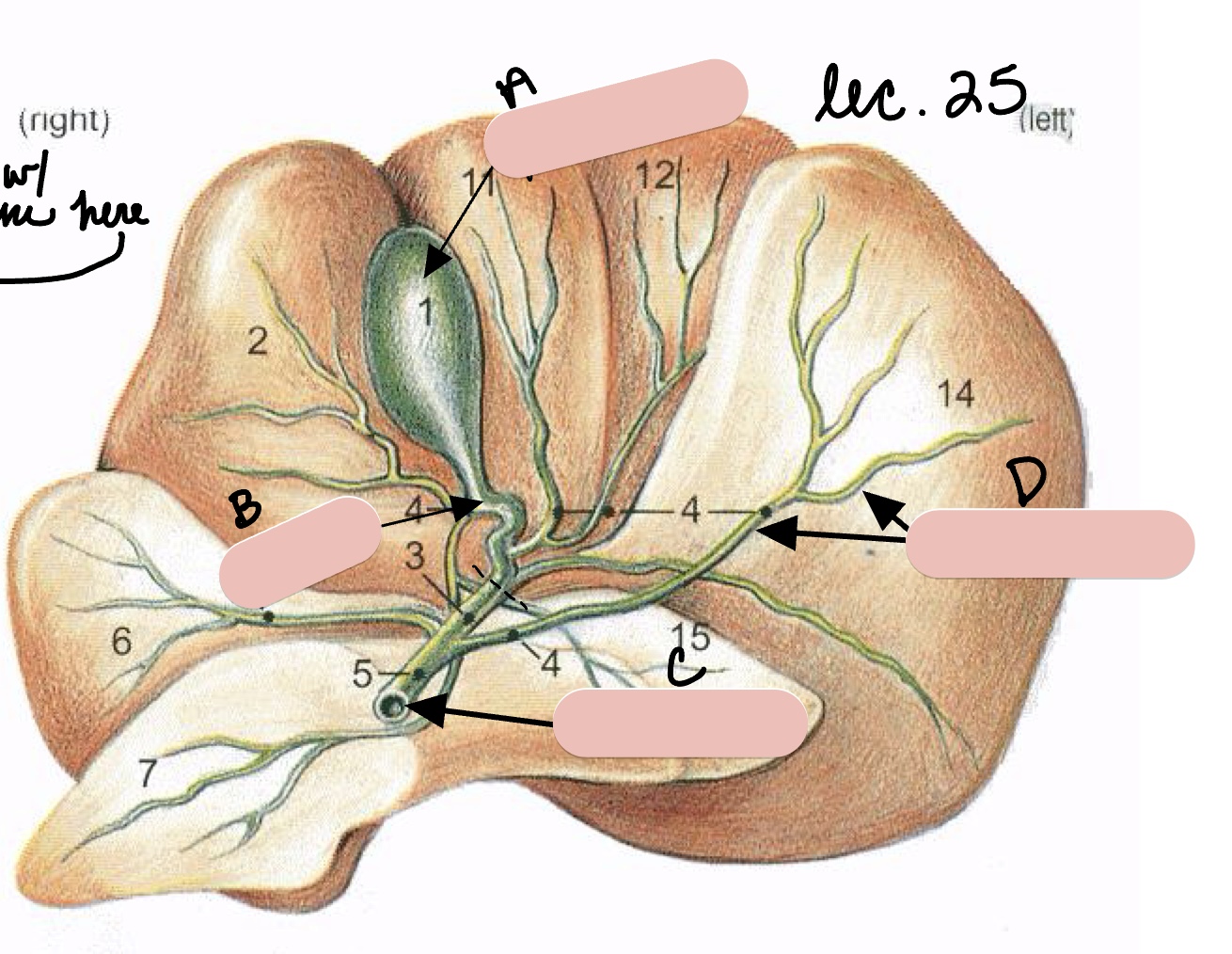
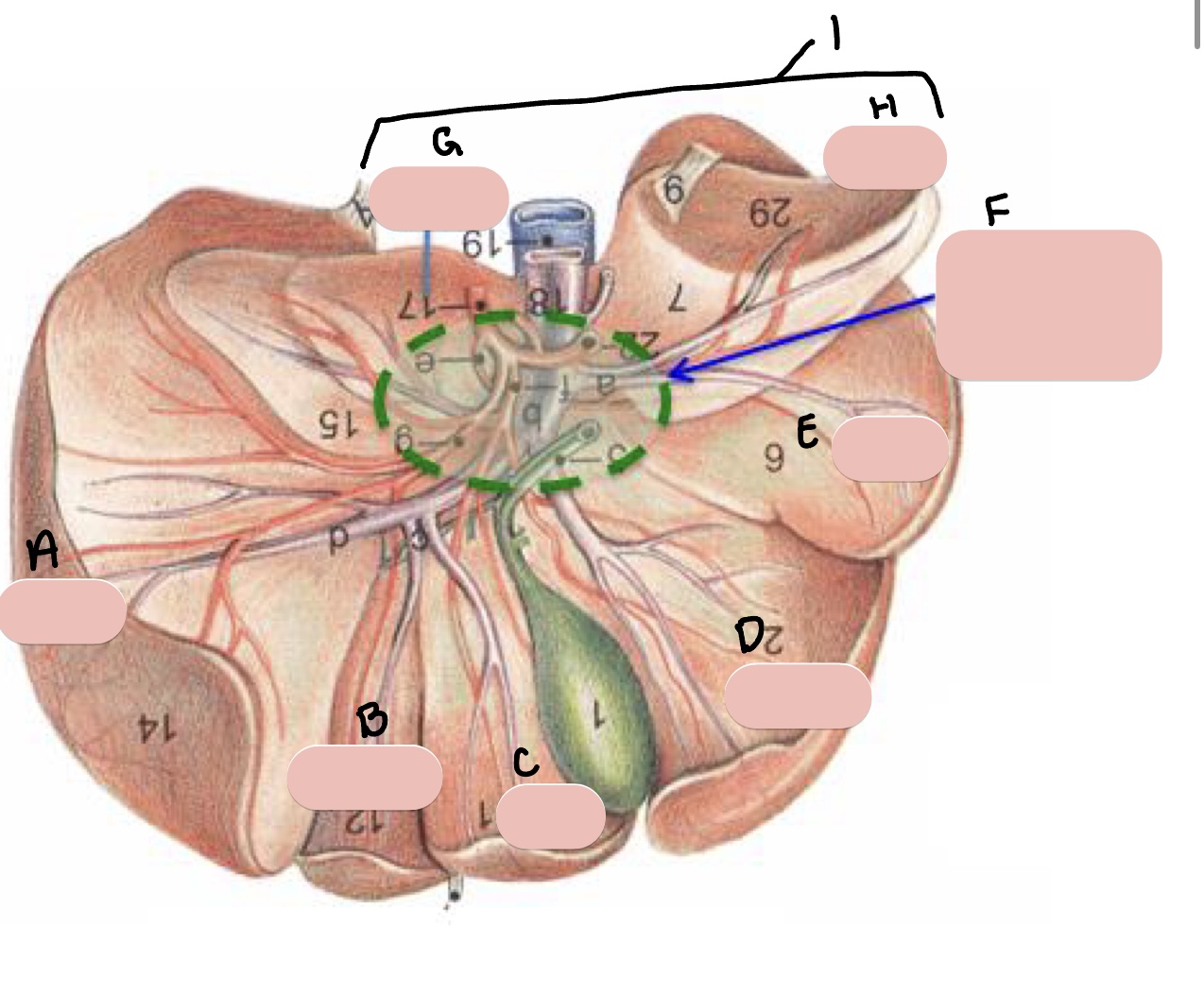
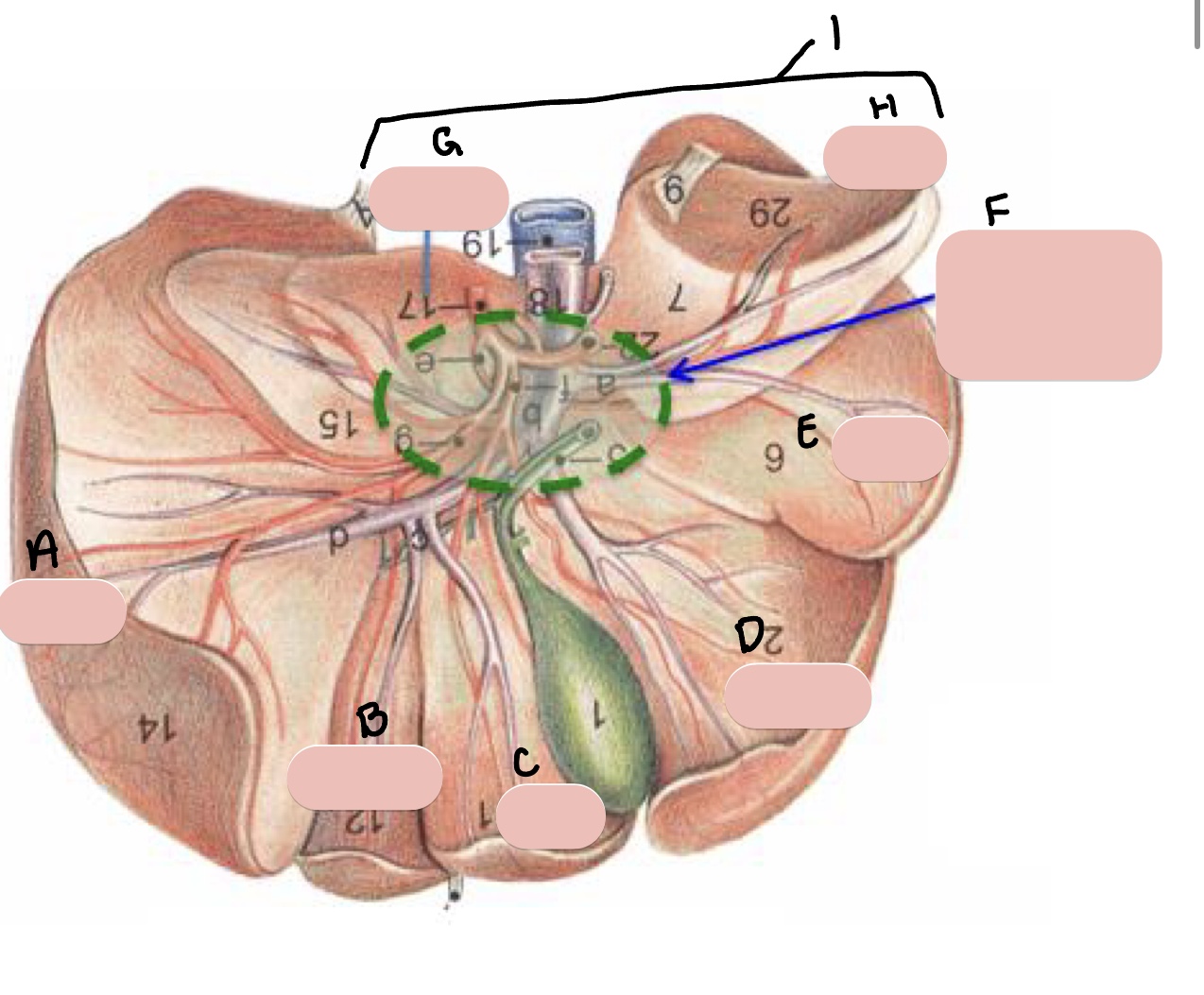
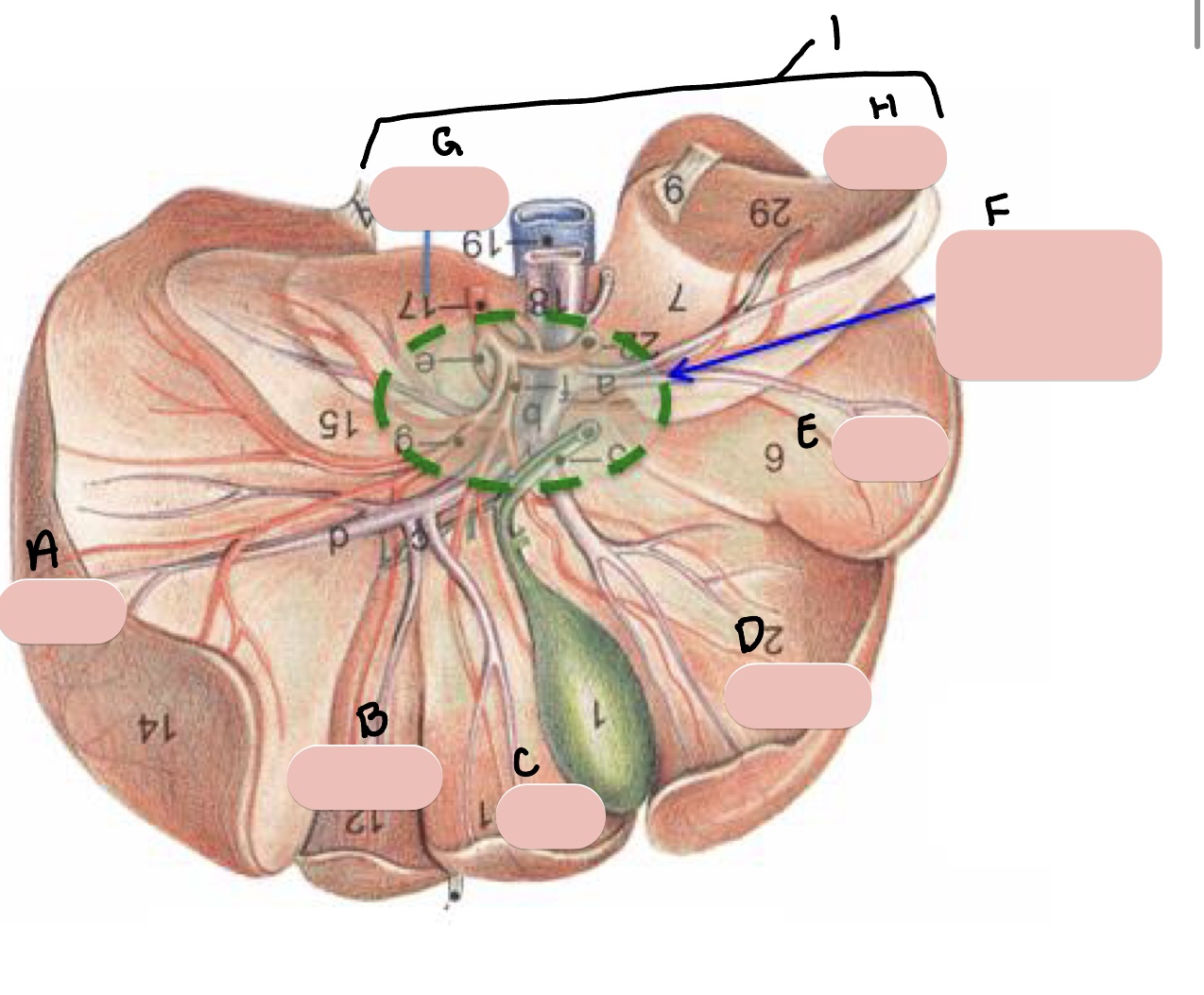
Name the structure(s) indicated by a, b, c, and d.
gall bladder
cystic duct
bile duct
hepatic ducts
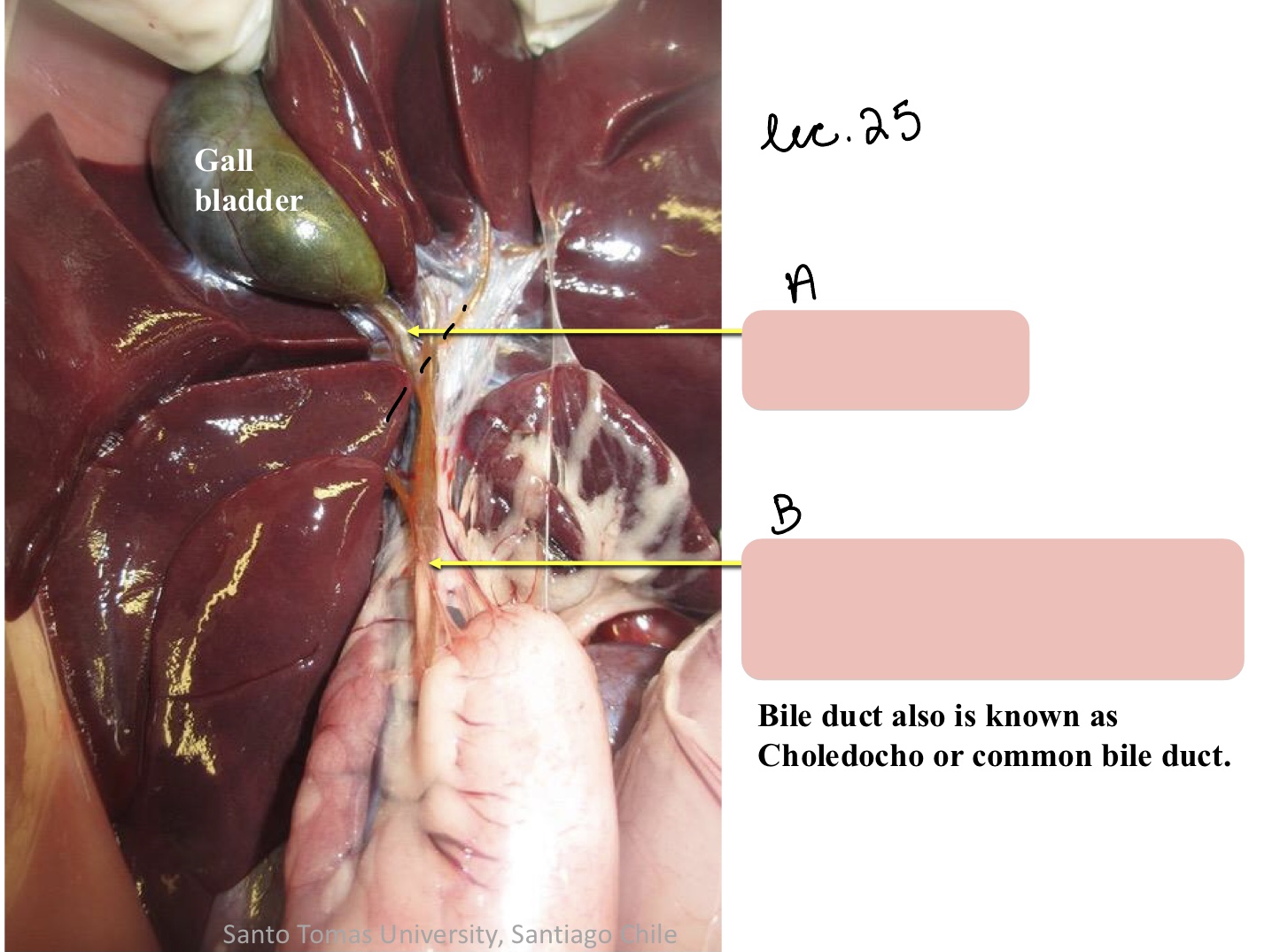
Name the structure(s) indicated by a and b.
cystic duct
bile duct
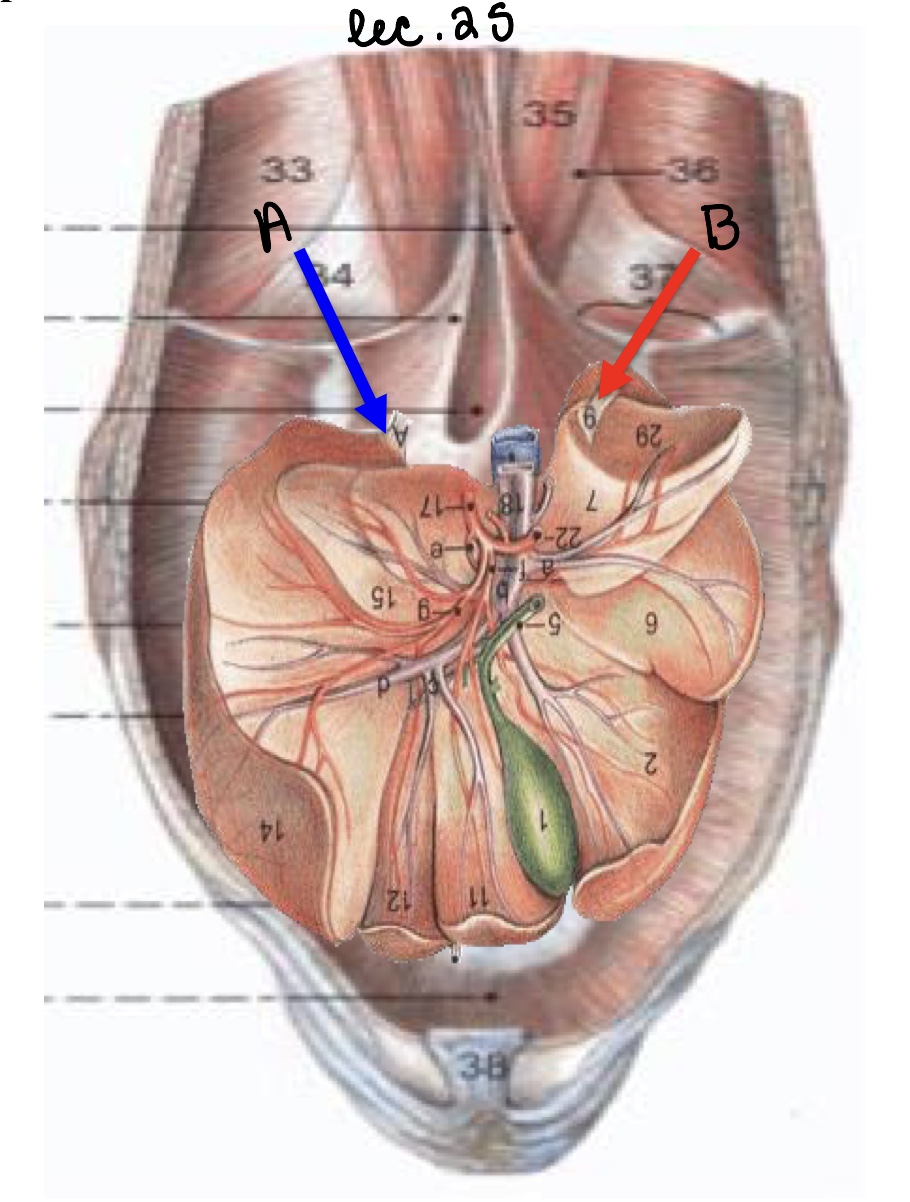
Name the structure(s) indicated by a and b.
left triangular ligament
right triangular ligament
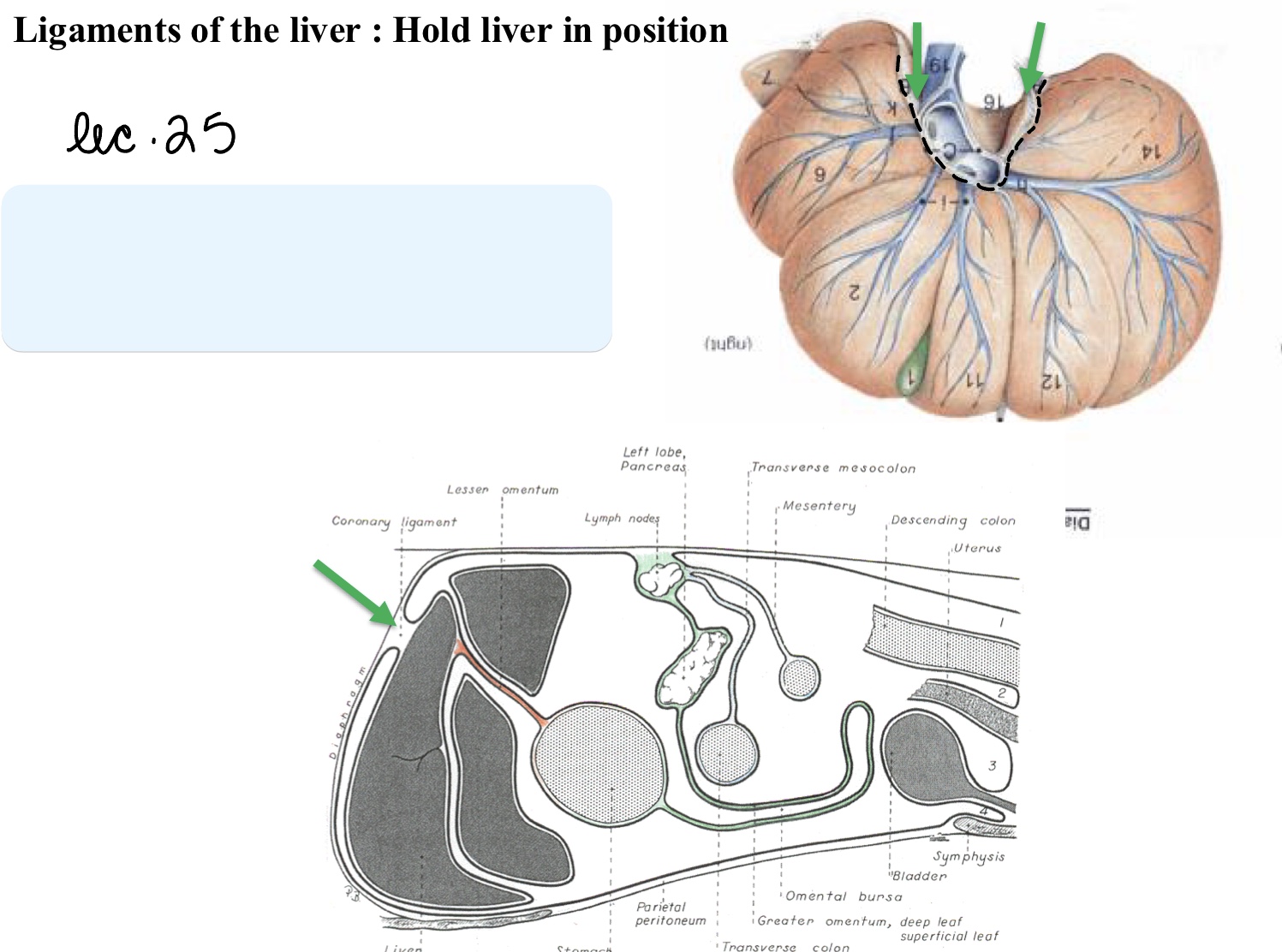
Name the structure(s) indicated by the green arrows.
coronary ligament
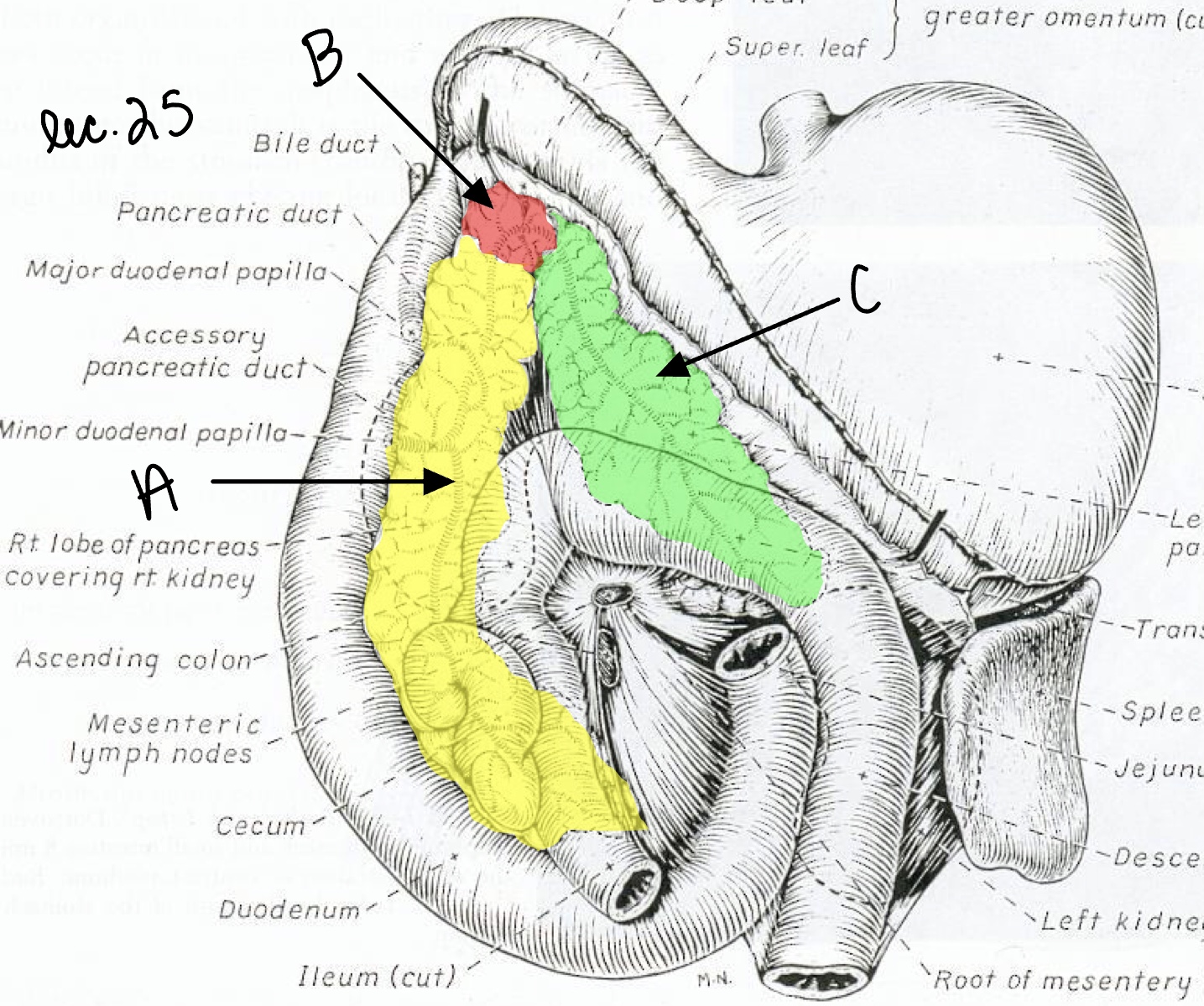
Name the structure(s) indicated by a, b, and c.
right lobe of the pancreas
body of the pancreas
left lobe of the pancreas
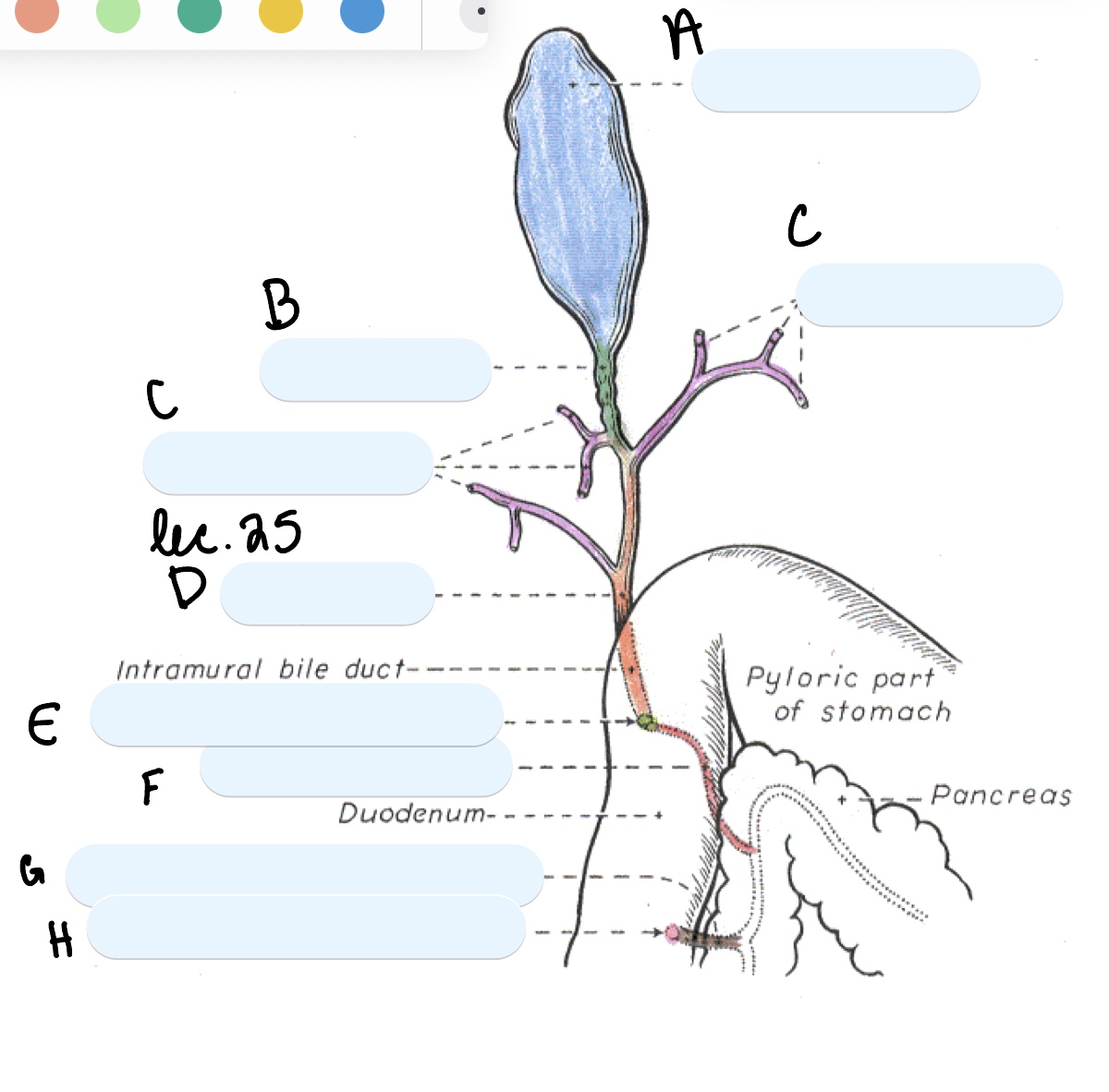
Name the structure(s) indicated by a, b, and c.
gall bladder
cystic duct
hepatic ducts
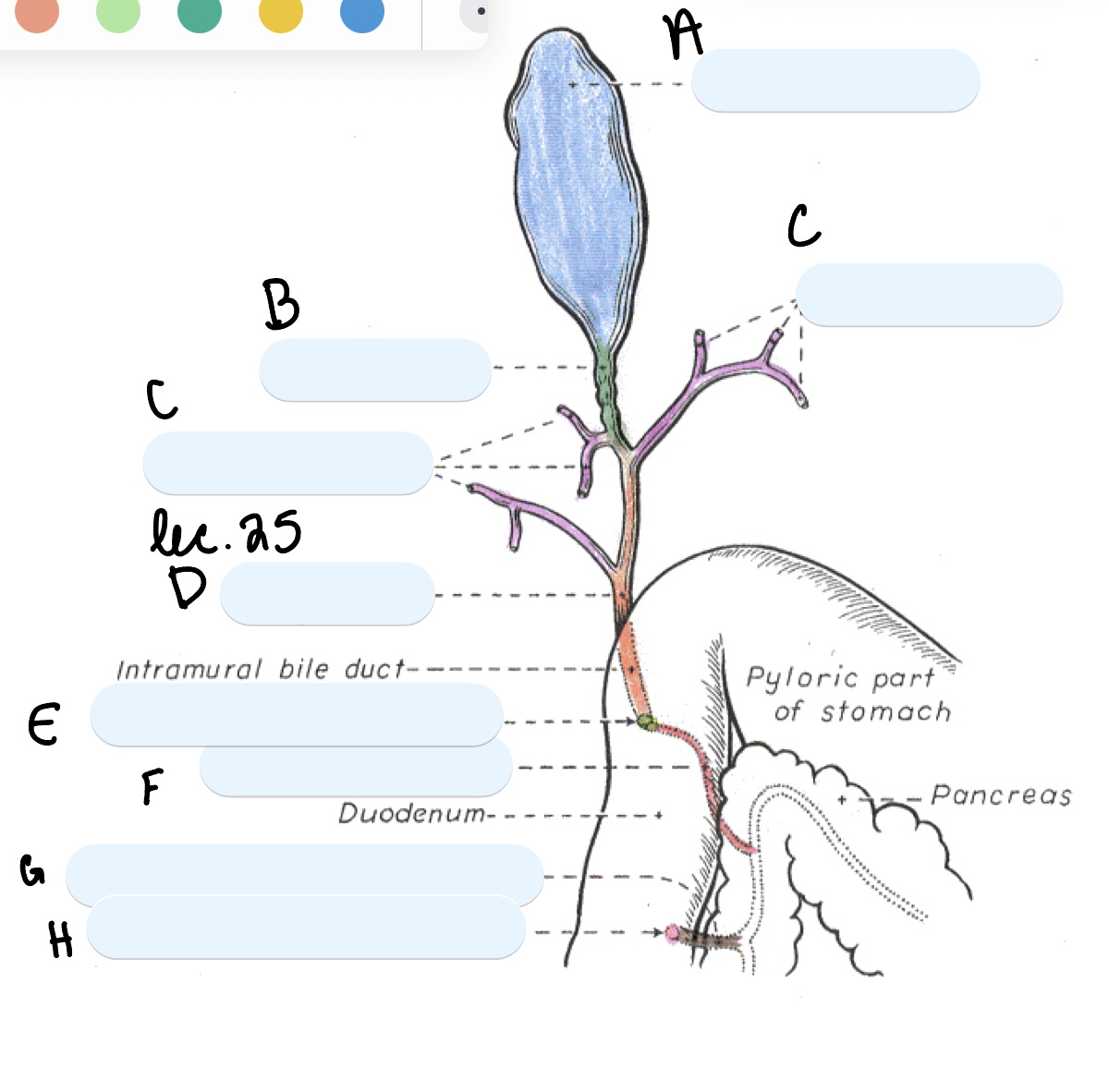
Name the structure(s) indicated by d, e, and f.
bile duct
major duodenal papilla
pancreatic duct
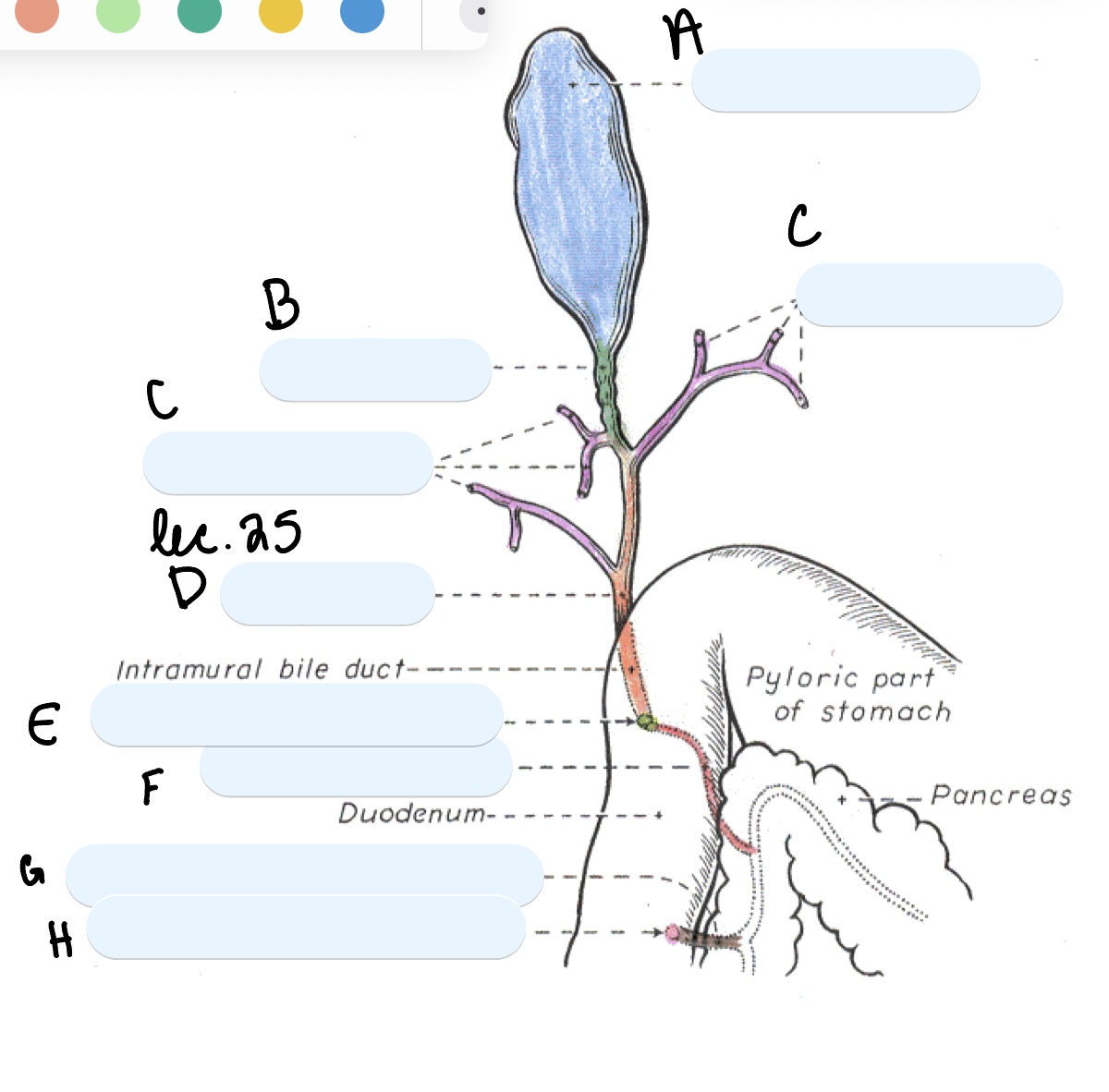
Name the structure(s) indicated by g and h.
accessory pancreatic duct
minor duodenal papilla
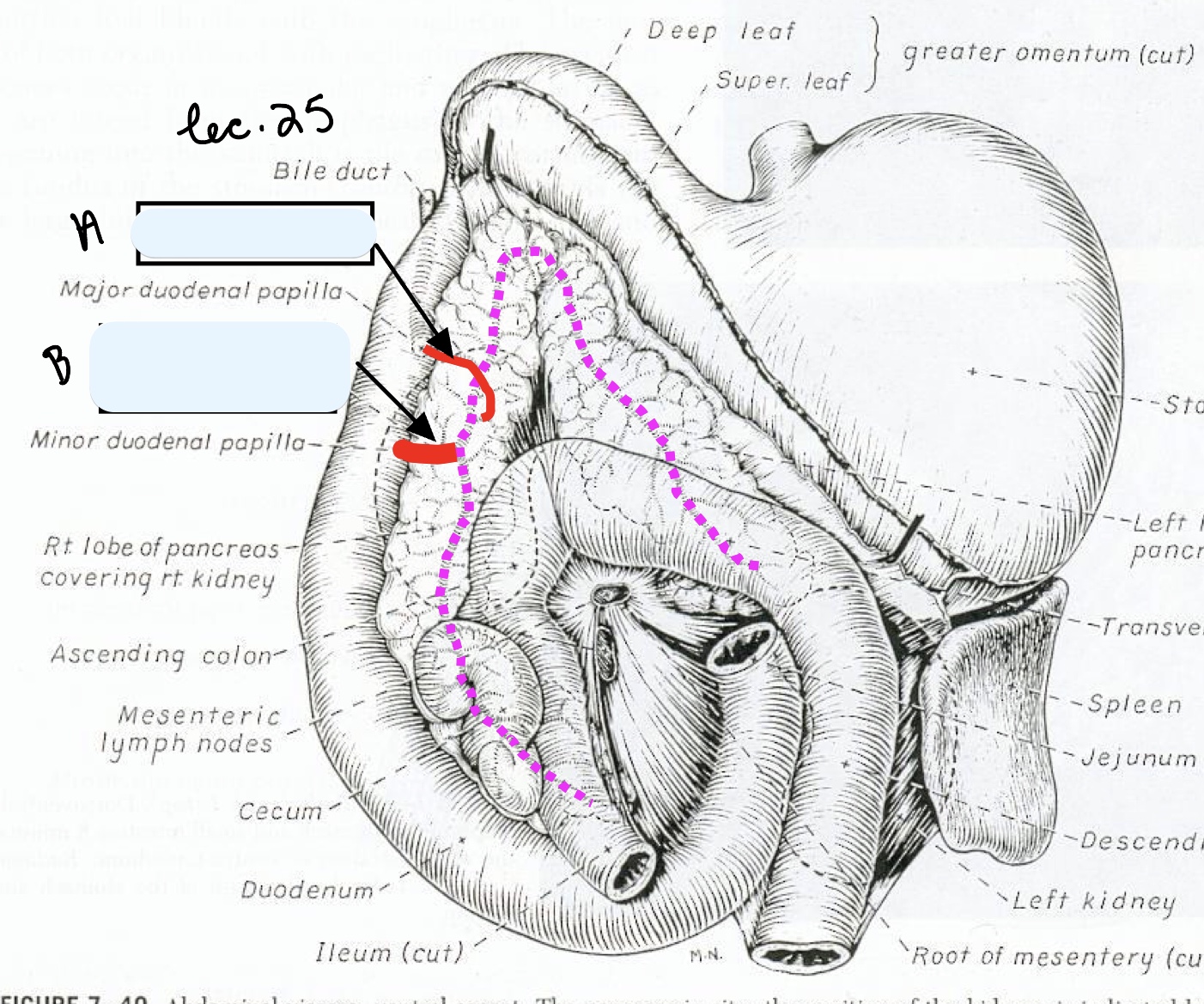
Name the structure(s) indicated by a and b.
pancreatic duct
accessory pancreatic duct