Labour Markets
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
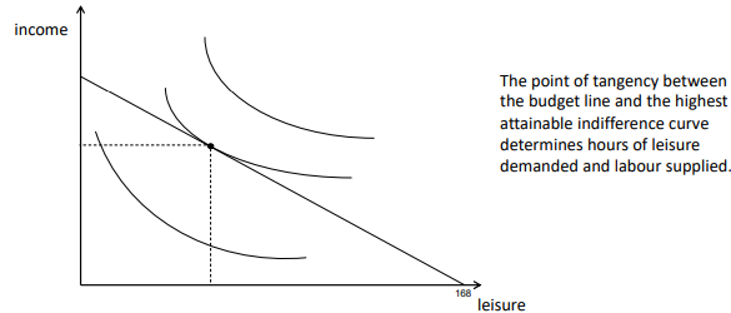
Working out Labour Supply
imagine that we have two options with how we spend our time
Spend Time Earning Money (Working)
Spend Time Enjoying Leisure
Factor Market - Wage Determination
a decline in the wage leads to a change in leisure demand, and also a change in labour supply
the change can be divided into an income effect and a substitution effect
the substitution effect of a wage change on labour supply is always positive, the income effect of a wage change on labour supply may be positive or negative
Labour Demand
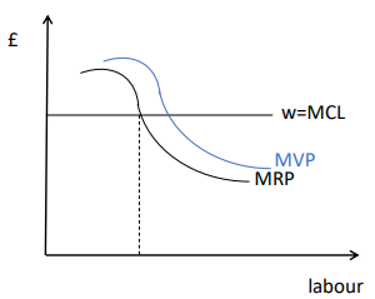
In a perfectly competitive labour market, the wage is the marginal cost of labour, and each firm treats it as given
The perfectly competitive, profit maximising firm will employ workers up to the point where w=MVPL
In a perfectly competitive labour market, the wage is the marginal cost of labour, and is given
What do you get when you multiply the Marginal Product of Labour (MPL) by Output Price, and what is it?
the marginal value product of labour (MVPL)
the labour demand curve of a perfectly competitive profit maximising firm
What does a Workers Attractiveness to an Employer depend on?
how many units of good they produce
the price of the good
the wage rate
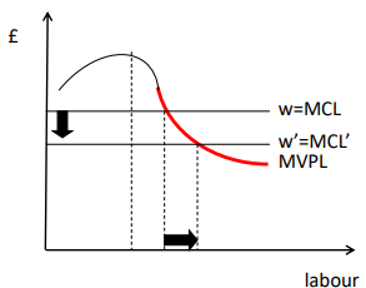
Monopoly Power
the MPL should be multiplied by the MR (not price) to give the labour demand curve (the marginal revenue product of labour)
The MRP is left of the MVP
Since a monopoly produces less output than a competitive firm, it will also employ fewer workers
The firm is still in perfect competition in the labour market so the wage and MCL are still given
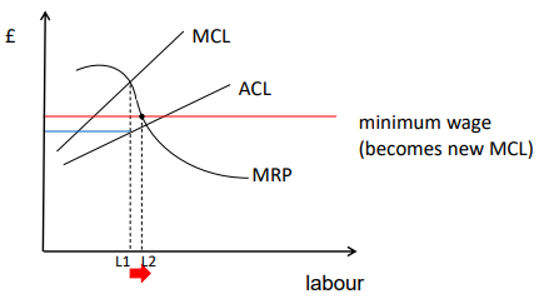
Monopsony Power
If the firm has monopsony power in the labour market, the MCL will be upward sloping
Profit maximisation occurs where MCL=MRP, but wage is determined by the average cost of labour (= labour supply)
Firms gain monopsony power when workers are not constantly searching for alternative employment
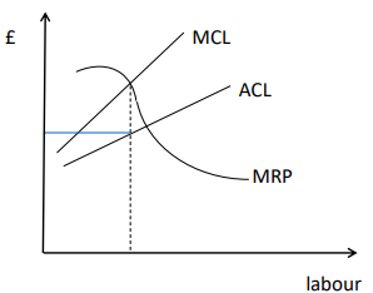
Minimum Wages
Can generate an excess supply of labour – that is, unemployment
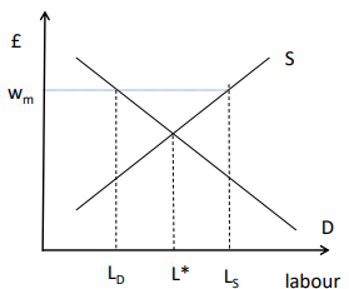
Minimum Wages in a Monopsony
Can raise employment
Once it’s imposed, the MCL becomes it (up to the point where ACL passes above it)
Explaining Differences in Earnings
Reflect differences in the corresponding marginal value product of labour
But even if people appear equally talented and hard-working, we may observe differences in their incomes
The Human Capital Theory
a theory of pay determination that says a worker’s wage will be proportional to his or her stock of human capital
What is Human Capital?
an amalgam of factors such as education, training, experience, intelligence, energy, work habits, trustworthiness and initiative that affect the value of a worker’s marginal product
Trades Unions
a group of workers who bargain collectively with employers for better wages and working conditions

When may 2 workers with the same amount of Human Capital ear different Wages?
when one of them belongs to a labour union - getting them a better wage
Compensating Wage Differential
a difference in the wage rate – negative or positive – that reflects the attractiveness of a job’s working conditions
Discrimination by Employers
refers to wage differentials reflecting an arbitrary preference by an employer for one group of workers over another
Customer Discrimination
the willingness of consumers to pay more for a product produced by members of a favoured group, even if the quality of the product is unaffected
Winner-Takes-All Markets
the top performer or a small number of top performers capture a disproportionately large share of the rewards—such as profits, market share, or attention—while everyone else gets little to nothing
Gini Coefficient
a measure of equality of distribution of income or wealth by percentages of households or individuals from poorest to richest
provides a basis for comparing distributions on a objective numerical basis
