The Ultimate AP World History Set
1/1519
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
1520 Terms
Mesopotamia
A region between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers that developed the first urban societies. In the Bronze Age this area included Sumer and the Akkadian, Babylonian and Assyrian empires, In the Iron Age, it was ruled by the Neo-Assyrian and Neo-Babylonian empires.
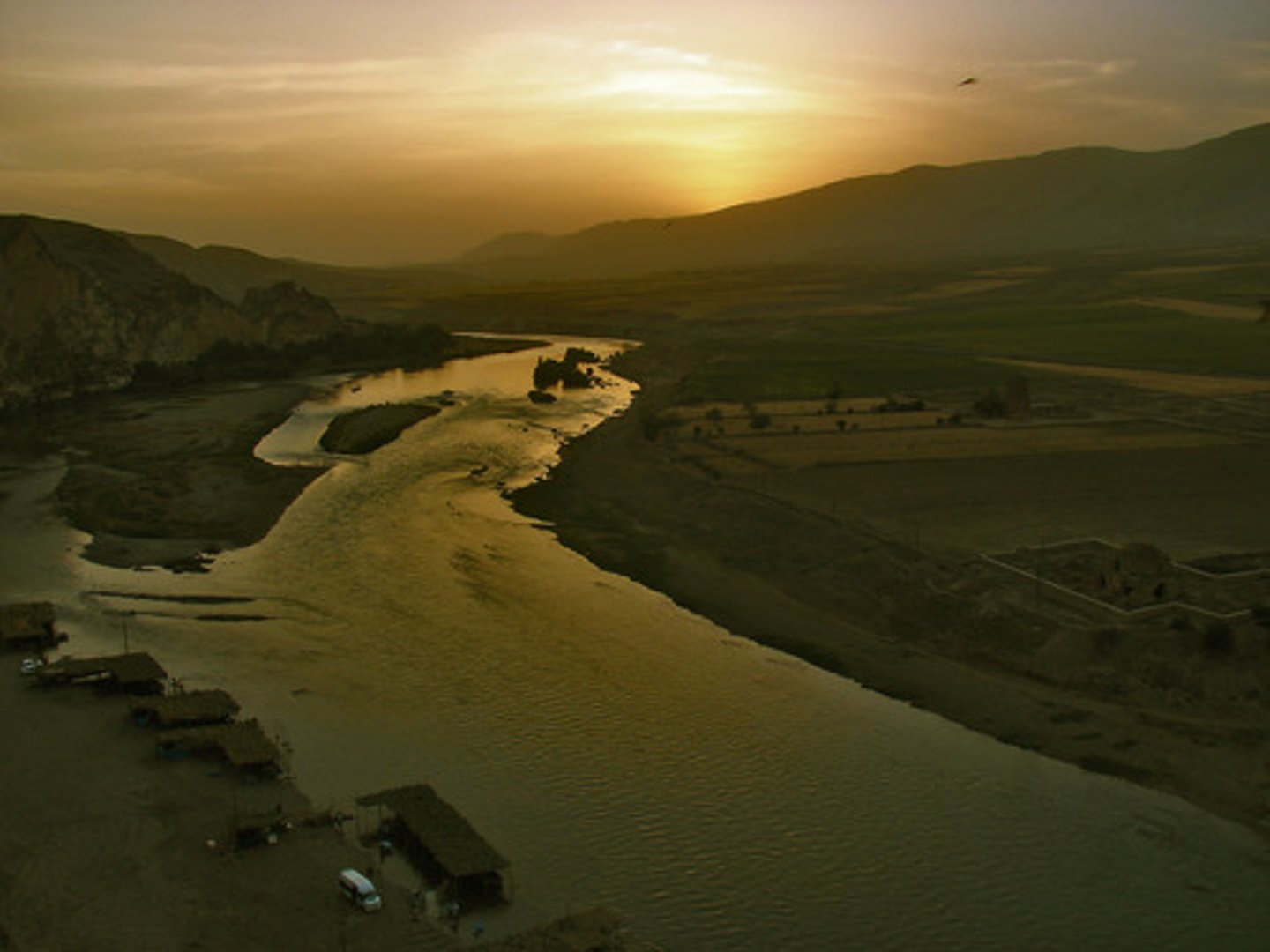

Fertile Crescent
The Tigris and Euphrates Rivers gave life to the first known agricultural villages in this area about 10,000 years ago and the first known cities about 5,000 years ago.

ziggurat
A temple tower of ancient Mesopotamia, constructed of square or rectangular terraces of diminishing size, usually with a shrine made of blue enamel bricks on the top

pictograms
A pictorial symbol or sign representing an object or concept
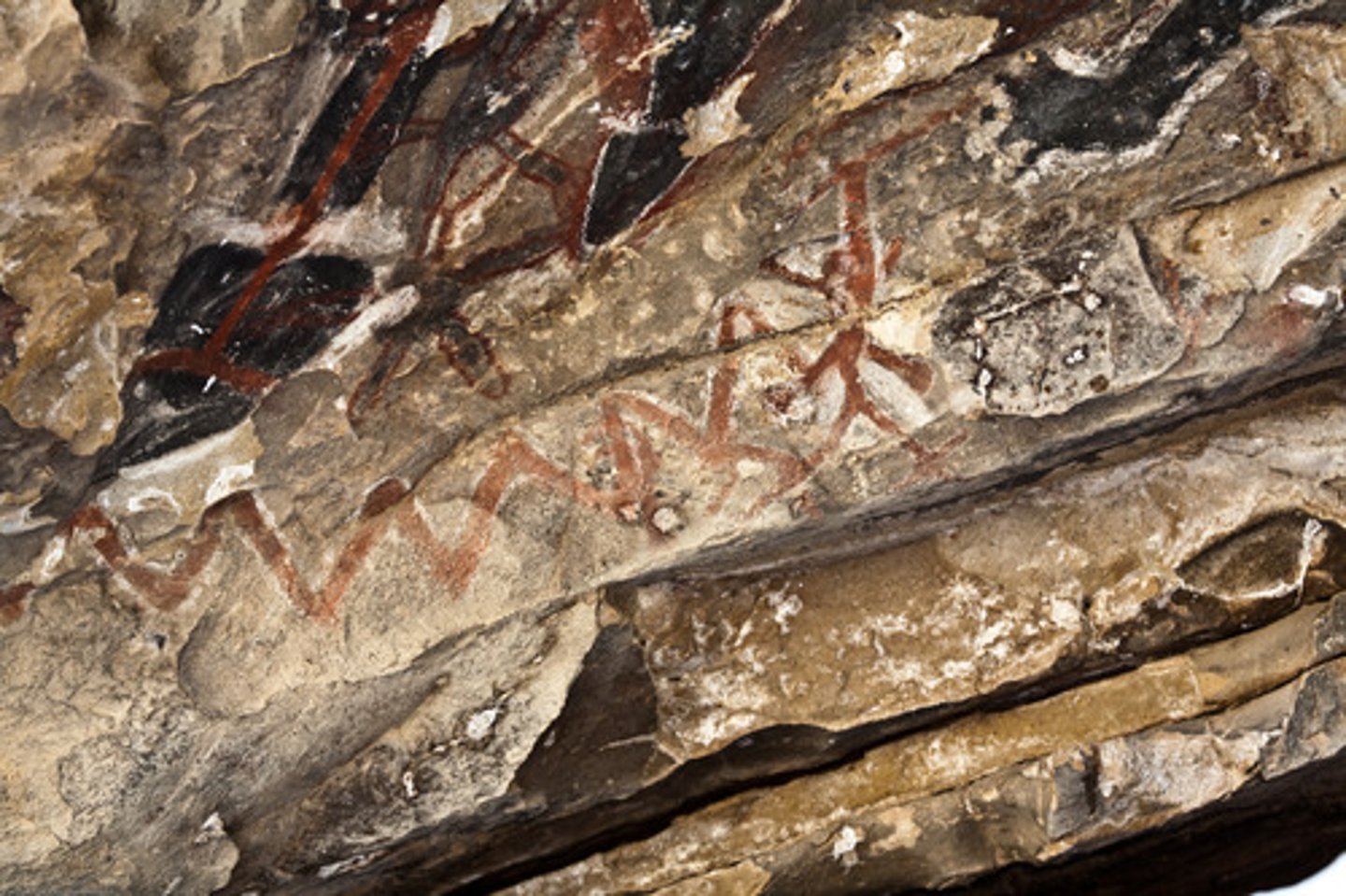
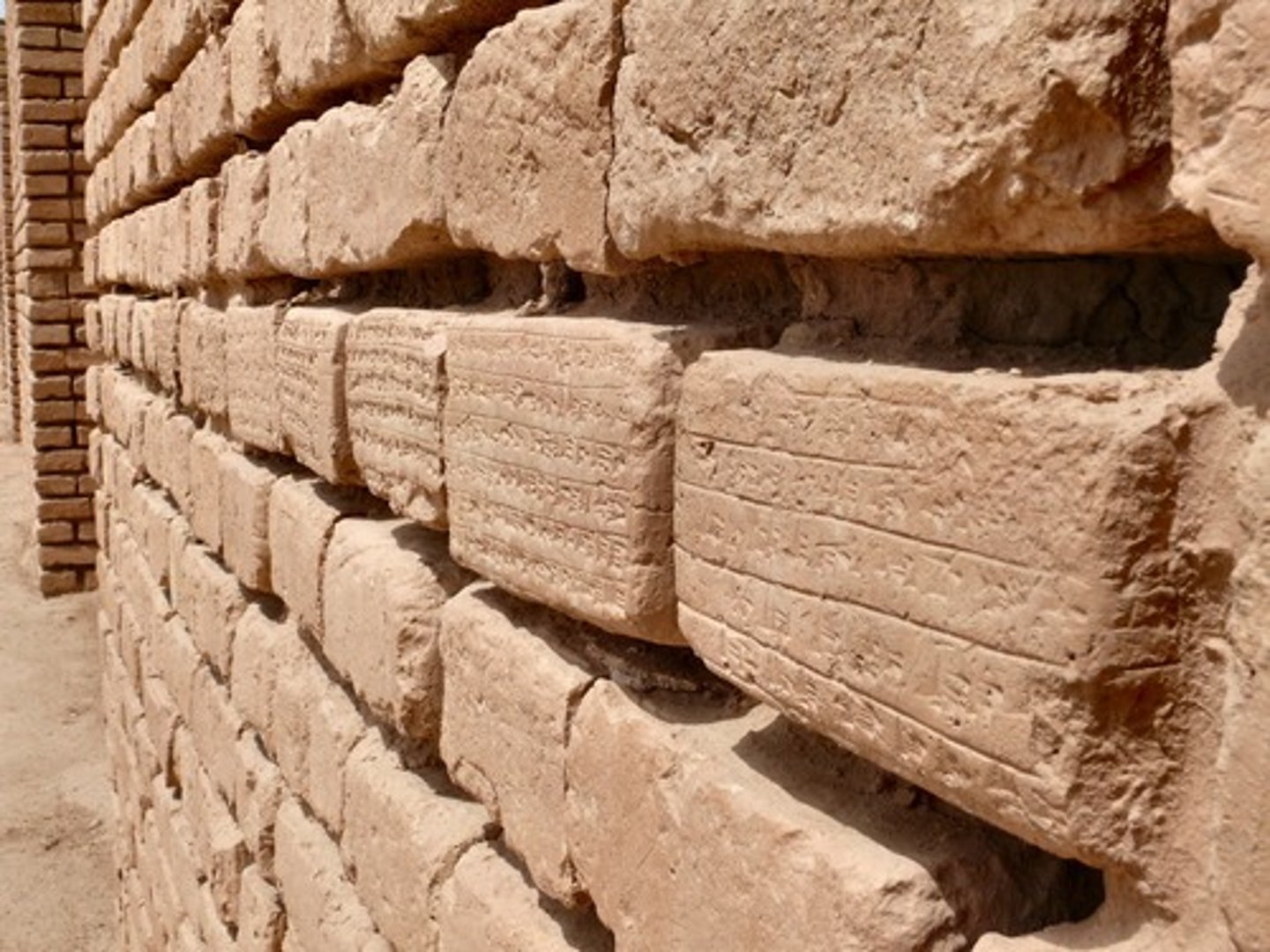
cuneiform
The earliest known form of writing, which was used by the Sumerians. The name derives from the wedge shaped marks made with a stylus into soft clay. Used from the 3000s BCE to the 100s BCE.

ideograms
A character or figure in a writing system in which the idea of a thing is represented rather than it's name (example: Chinese)

Sumer
The world's first civilization, founded in Mesopotamia, which existed for over 3,000 years.

Xia
A legendary Chinese dynasty that was not believed to exist until relatively recently. Walled towns ruled by area-specific kings assembled armies, built cities, and worked bronze. Created pictograms which would evolve in to the first Chinese script.
Shang Dynasty
An early Chinese dynasty. Not a unified Chinese state. Instead rulers and their relatives gave orders through a network of cities. Earliest evidence of Chinese writing comes from this period.

Zhou Dynasty
Succeeded the Shang dynasty. Similar to the Shang And Xia dynastic periods in that China was fragmented politically. Yet, despite the lack of true centralization, this was one of the longest Chinese dynasties, lasting about 600 years. It left substantial written records, unlike the preceding dynasties.
Yellow River
Also known as the Huang-He. The second longest river in China. The majority of ancient Chinese civilizations originated in its valley.
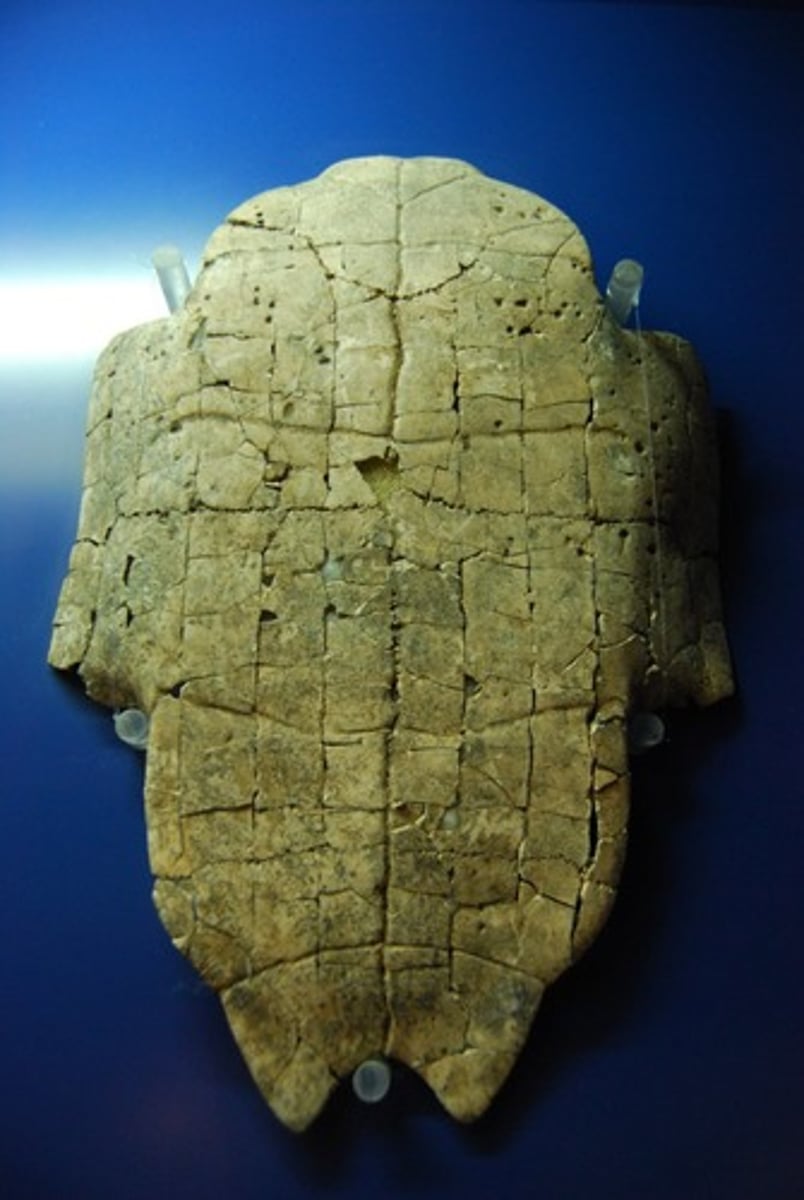
Oracle Bones
The earliest known Chinese writing is found on these from ritual activity of the Shang period.
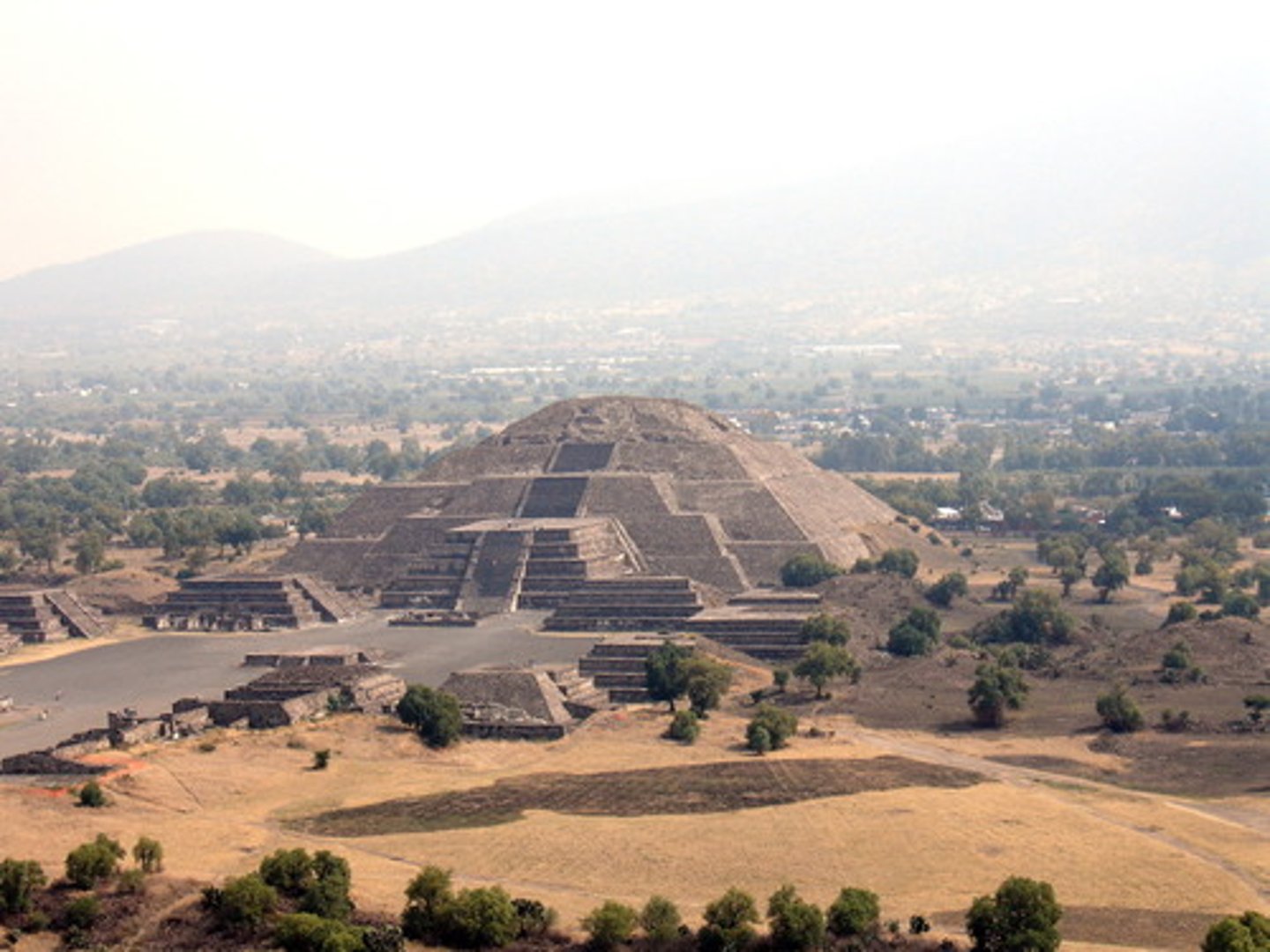
Teotihuacan
A large central city in the Mesoamerican region. Located about 25 miles Northeast of present day Mexico City. Exhibited city planning and unprecedented size for its time. Reached its peak around the year 450.

Jenne-Jeno
One of the first urbanized centers in western Africa. A walled community home to approximately 50,000 people at its height. Evidence suggests domestication of agriculture and trade with nearby regions.
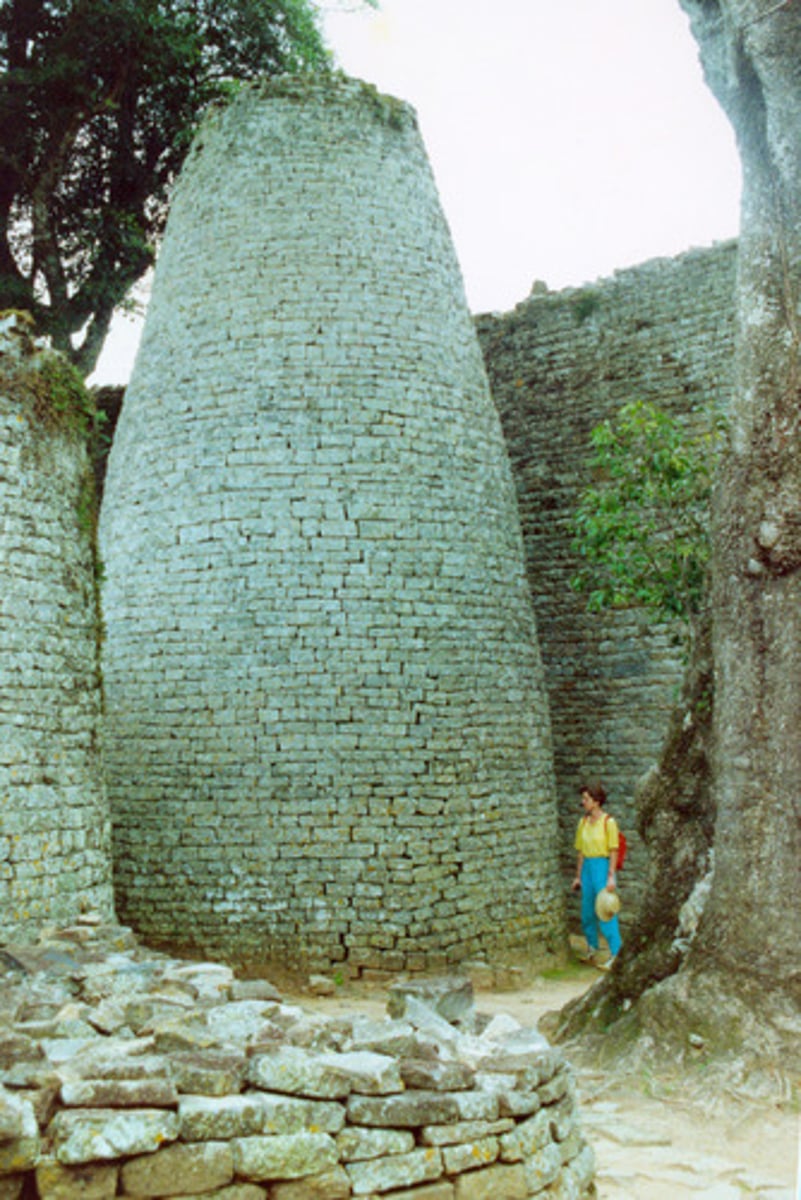
Great Zimbabwe
A stone-walled enclosure found in Southeast Africa. Have been associated with trade, farming, and mining.

Hammurabi
The first king of the Babylonian Empire. Best known for his legal code.
Code of Hammurabi
A collection of 282 laws. One of the first (but not THE first) examples of written law in the ancient world.
Hittites
An ancient Anatolian group whose empire at largest extent consisted of most of the Middle East. Some of the first two-wheeled chariots and iron.

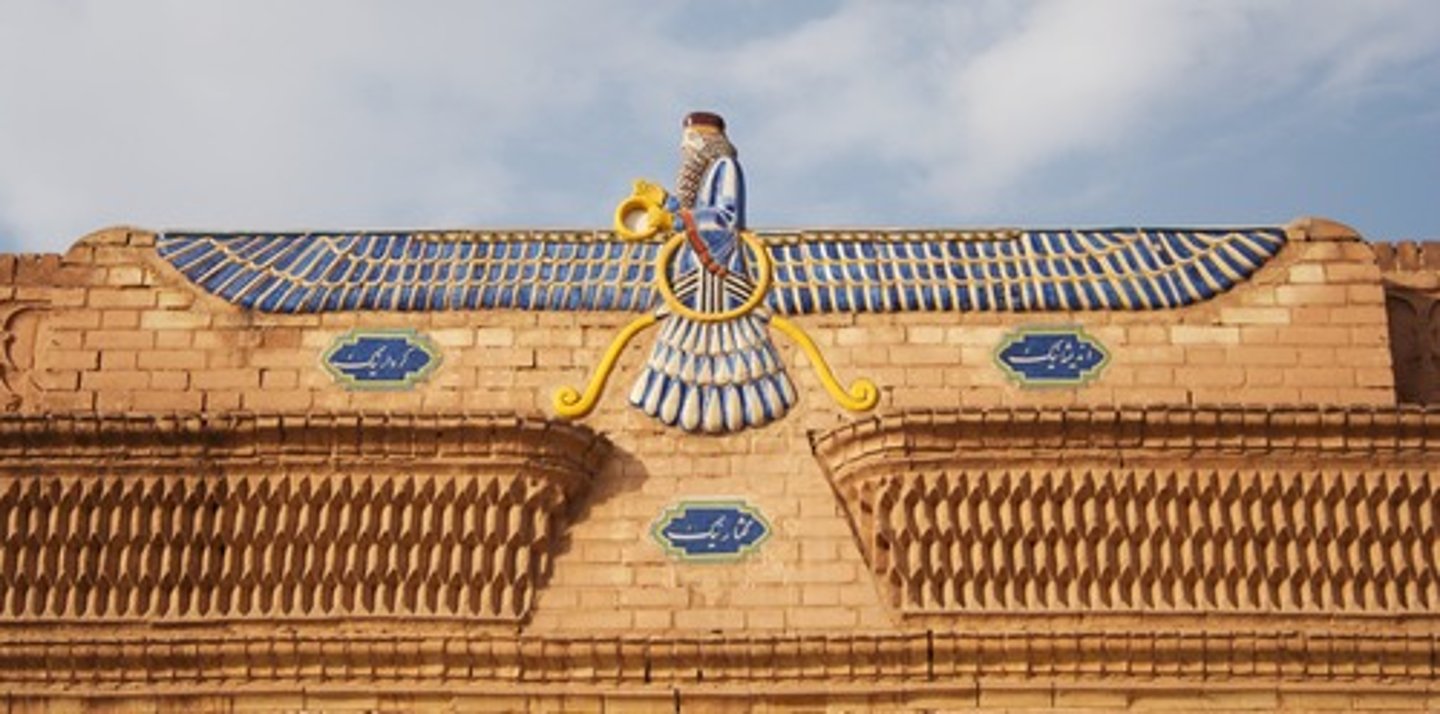
Zoroastrianism
One of the first monotheistic religions, particularly one with a wide following. It was central to the political and religious culture of ancient Persia.
Zoroaster
The founder of Persia's classical pre-Islamic religion.

Hellenistic
Of or influenced by the Greek Empire. A type of culture typically referred to after the conquests of Alexander the Great.
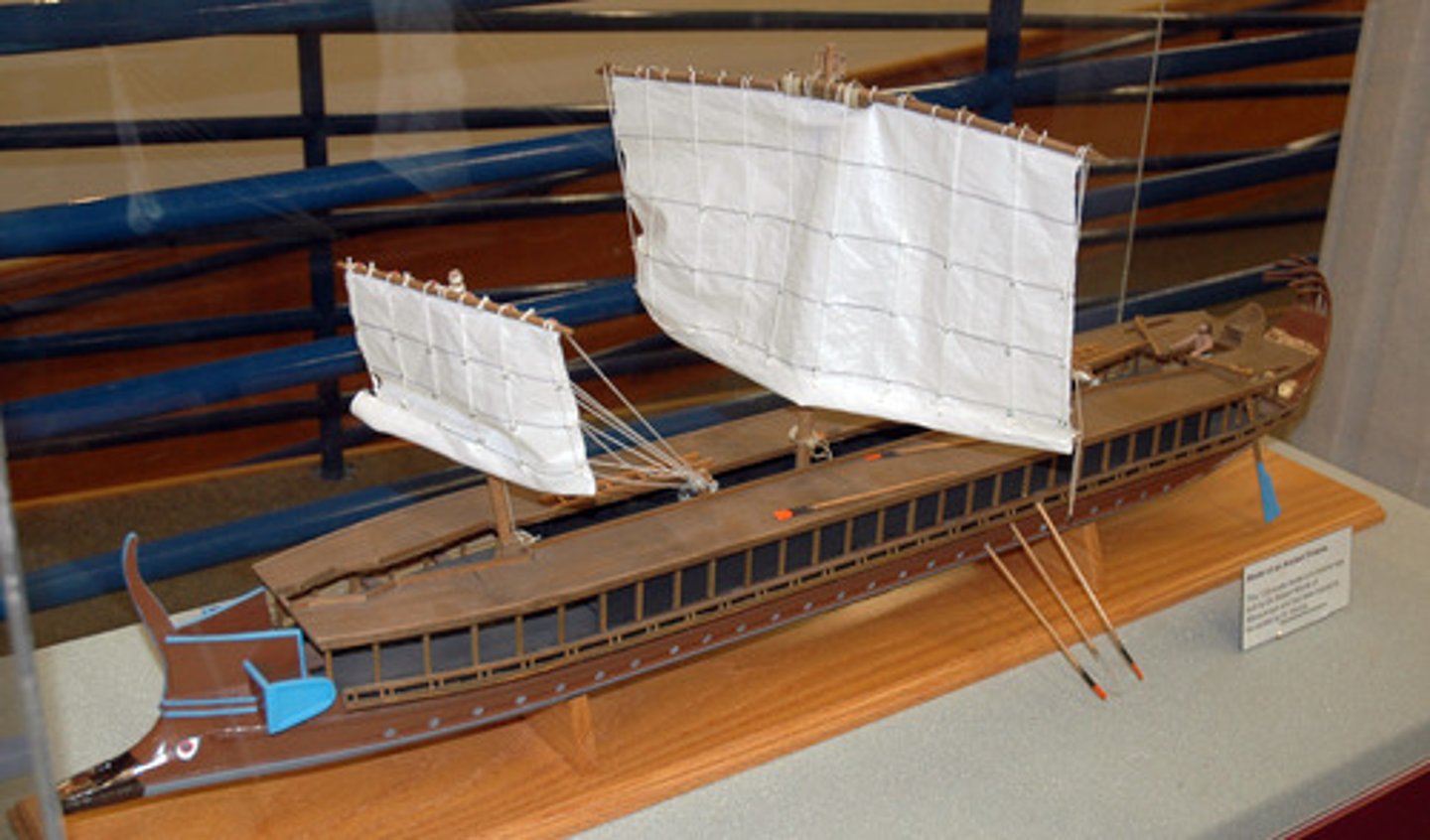
Trireme
Greek ships built specifically for ramming enemy ships.
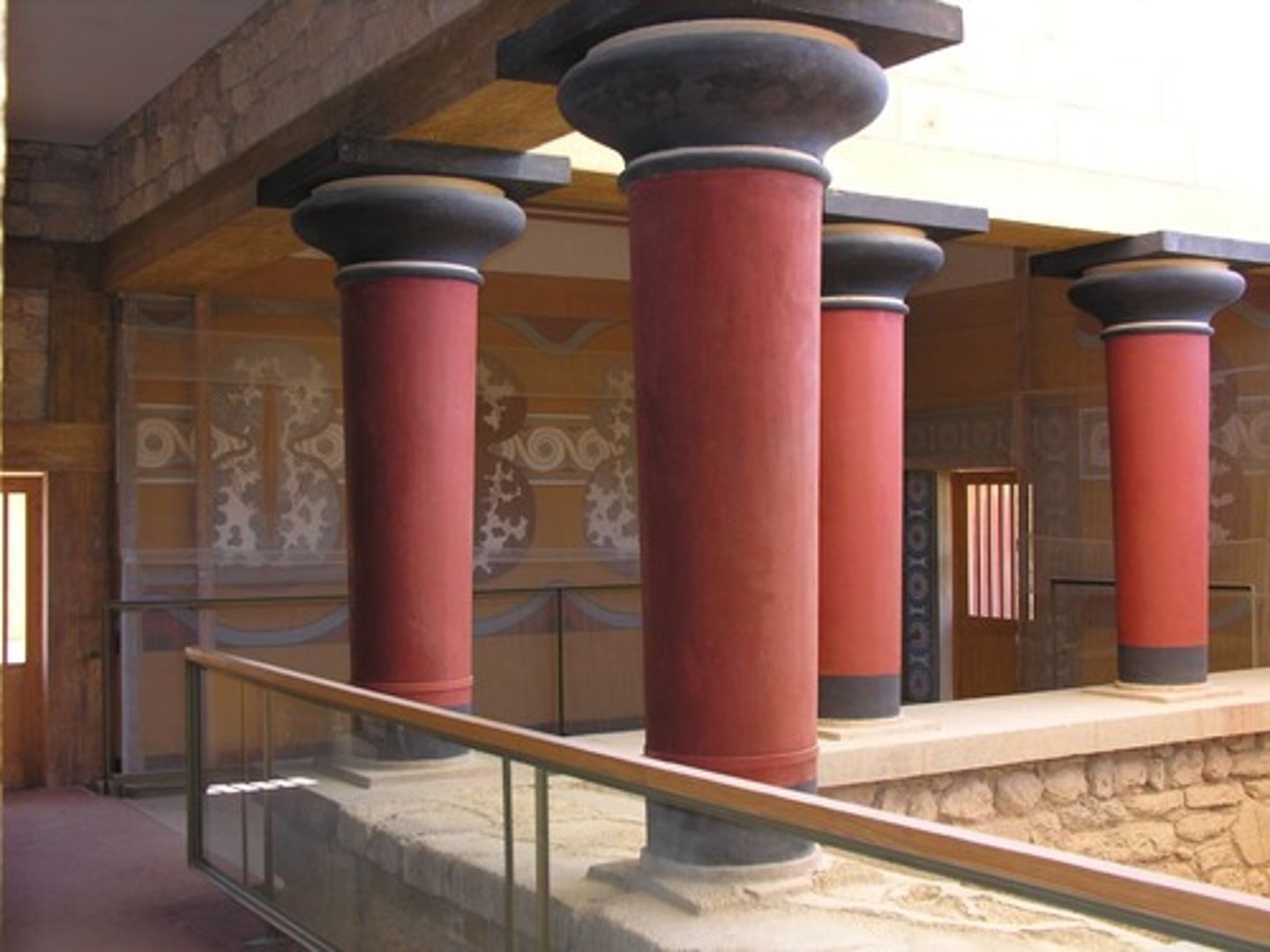
Minoans
One of the early proto-Greek peoples from 2600 BCE to 1500 BCE. Inhabitants of the island of Crete. Their site of Knossos is pictured above.

Acropolis
Greek for "high city". The chief temples of the city were located here.
Plato
Socrates' most well known pupil. Founded an academy in Athens.
Pax Romana
The "Roman Peace", that is, the state of comparative concord prevailing within the boundaries of the Roman Empire from the reign of Augustus (27 B.C.E.-14 C.E.) to that of Marcus Aurelius (161-180 C.E.)
Republic
A state that is not ruled by a hereditary leader (a monarchy) but by a person or persons appointed under the constitution
Centuries - (not the time period)
The smallest units of the Roman army, each composed of some 100 foot soldiers and commanded by a centurion. A legion was made up of 60 of these. They also formed political divisions of Roman citizens.
Consul
Under the Roman Republic, one of the two magistrates holding supreme civil and military authority. Nominated by the Senate and elected by citizens in the Comitia Centuriata, the consuls held office for one year and each had power of veto over the other.
Patricians
land-owning noblemen in Ancient Rome
Plebeians
all non-land-owning, free men in Ancient Rome
Paterfamilias
the head of the family or household in Roman law -always male- and the only member to have full legal rights. This person had absolute power over his family, which extended to life and death.
Twelve Tables
Completed in 449 BCE, these civil laws developed by the Roman Republic to protect individual following demands by plebeians.
Triumvirate
An unofficial coalition between Julius Caesar, Pompey, and Crassus was formed in 60 B.C.E.
Monophysites
The supporters of a doctrine in the early Christian Church that held that the incarnate Christ possessed a single, wholly divine nature. they opposed the orthodox view that Christ had a double nature, one divine and one human, and emphasized his divinity at the expense of his capacity to experience real human suffering.
Julius Caesar
Part of the first triumvirate who eventually became "emperor for life". Chose not to conquer Germany. Was assassinated by fellow senators in 44 B.C.E.

Octavian
Part of the second triumvirate whom the power eventually shifted to. Assumed the name Augustus Caesar, and became emperor. Was the end of the Roman Republic and the start of the Pax Romana.

Diocletian
Roman emperor of 284 C.E. Attempted to deal with fall of Roman Empire by splitting the empire into two regions run by co-emperors. Also brought armies back under imperial control, and attempted to deal with the economic problems by strengthening the imperial currency, forcing a budget on the government, and capping prices to deal with inflation. Civil war erupted upon his retirement.
Bread and Circuses
A Roman bribery method of coping with class difference. Entertainment and food was offered to keep plebeians quiet without actually solving unemployment problems.

Goths
An array of Germanic peoples, pushed further westward by nomads from central Asia. They in turn migrated west into Rome, upsetting the rough balance of power that existed between Rome and these people.
legalism
A school of Chinese philosophy that come into prominence during the period of the Warring states and had great influence on the policies of the Qin dynasty. People following this took a pessimistic view of human nature and believed that social harmony could only be attained through strong government control and the imposition of strict laws, enforced absolutely.
assimilation
The process by which different ethnic groups lose their distinctive cultural identity through contact with the dominant culture of a society, and gradually become absorbed and integrated into it.
Huns
large nomadic group from northern Asia who invaded territories extending from China to Eastern Europe. They virtually lived on their horses, herding cattle, sheep, and horses as well as hunting.
Tang Revival
Continuing the imperial revival started by the Sui Dynasty this dynasty that followed restored the Chinese imperial impulse four centuries after the decline of the Han, extending control along the silk route. Trade flourished and China finally reached its western limits when its forces were defeated by the imperial armies of the Muslim Abbasid Empire at the Talas River--which stopped future expansion by both empires.

Yellow Turban
A 184 C.E. peasant revolt against emperor Ling of Han. Led by Daoists who proclaimed that a new era would be3ing with the fall of the Han. Although this specific revolt was suppressed, it triggered a continuous string of additional outbreaks.
Liu Bang
First emperor of the Han dynasty under which a new social and political hierarchy emerged. Scholars were on top, followed by farmers, artisans, and merchants. He chose his ministers from educated men with Confucian principals.
Aryans
immigrants who arrived at the Ganges river valley by the year 1000 BC
Vedas
compilations of hymns, religious reflections, and Aryan conquests

Mahabharata
the longest single poem in the world, about a war fought between two branches of the same family. One of India's greatest epics written between 1000 and 700 BC

Janapadas
Political units in India in the years 700-600 BC. They are the major realms or kingdoms of Vedic (Iron Age) India. They are the earliest kingdoms set up by the Indo-Aryans migrants to India.
Guilds
associations of businessmen and producers
Dharma
the fulfillment of social and religious duties in Hinduism
Artha-sastra
characterized inter-state relations in ancient India
Siddhartha Gautama
the founder of Buddhism
Rigveda
a book composed by Brahman priests that contains verses and Sanskrit poetry
Caste system
a social system that separated people by occupation, the caste system in India has virtually no social mobility
Samsara
the cycle of life in Hinduism
Puranas
a collection of ancient stories that feature Hindu gods such as Vishnu and Shiva
Nirvana
release from suffering into a blissful nothingness
Four Noble Truths
suffering is always present in life; desire is the cause of suffering; freedom from suffering can be achieved in nirvana; the Eightfold Path leads to nirvana

Mahayana Buddhism
The more mystical and larger of the two main Buddhist sects, this one originated in India in the 400s CE and gradually found its way north to the Silk road and into Central and East Asia.

Jainism
An ancient religion of India with a small following today of only about 10 million followers. Originated in the 800s BCE. They prescribes a path of non-violence towards all living beings. Its philosophy and practice rely mainly on self-effort to progress the soul up the spiritual ladder to divine consciousness. Any soul that has conquered its own inner enemies and achieved the state of supreme being is called jina (Conqueror or Victor).
Silk Road
connected China, India, and the Middle East. Traded goods and helped to spread culture.
Empress Wu
the only woman to rule China in her own name, expanded the empire and supported Buddhism during the Tang Dynasty.
Mantra
the repetition of mystic incantations in Hinduism and Buddhism.
Mentuhotep I
Egyptian pharaoh who founded the Middle Kingdom by REUNITING Upper and Lower Egypt in 2134 BCE.
Olmec
Mesoamerican civilization in lower Mexico around 1500 BCE to about 400 BCE focused. Most remembered for their large stone heads.
Maya
Extensive Mesoamerican culture that made great advances in astronomy in areas such as their famous calendar

Nazca
South American civilization famous for its massive aerial-viewable formations
Neo-Assyrians
Assyrian resurgence that initiated a series of conquests until a combined attack by Medes and Babylon defeated them
Mycenae
Sea-faring proto-Greek kingdom whose abrupt demise triggered the Greek Dark Ages ca. 1200 BCE-800 BCE
Persia
Mesopotamian empire that conquered the existing Median, Lydian, and Babylonian empires
Polis
Form of government in which power is centralized into a local city-state.
Solon
Early Greek leader who brought democratic reforms such as his formation of the Council of Four Hundred
Pericles
Ruler of Athens who zealously sought to spread Athenian democracy through imperial force
Peloponnesian War
Conflict between Athens and Sparta
Macedonia
Area between the Greek and Slavic regions; conquered Greece and Mesopotamia under the leadership of Philip II and Alexander the Great
Philip II
Macedonian king who sought to unite Greece under his banner until his murder
Ptolemy
Subordinate to Alexander who took over Egypt after his death

Stoicism
Roman philosophy which emphasizes accepting life dispassionately
Qin
1st unified imperial Chinese dynasty

Shinto
"Way of the Kami"; Japanese worship of nature spirits

Rama
Incarnation of Hindu god Vishnu made famous in the Ramayana
Siddhartha Gautama
Indian prince who renounced his worldly possessions and founded Buddhism; Buddha
Apostle Paul
Zealous proponent of Christianity who was instrumental in its spread beyond Judaism
Guild
associations like those of merchants or artisans, organized to maintain standards and to protect the interests of its members, and that sometimes constituted a local governing body.
Epic of Gilgamesh
an epic poem from Mesopotamia, and among the earliest known works of literary writing.
Hieroglyphics
designating or pertaining to a pictographic script, particularly that of the ancient Egyptians, in which many of the symbols are conventionalized, recognizable pictures of the things represented

Jenne-jeno
considered to be among the oldest urbanized centers in sub-Saharan Africa.
Hegemony
leadership or predominant influence exercised by one nation over others, as in a confederation.
Hoplite
a citizen-soldier of the Ancient Greek City-states. They were primarily armed as spear-men.
Iconoclast
Opposing or even destroying images, especially those set up for religious veneration in the belief that such images represent idol worship.

Diaspora
any group migration or flight from a country or region; dispersion.
St. Augustine
one of the most important figures in the development of Western Christianity
Agora
the chief marketplace of Athens, center of the city's civic life.

Realpolitik
political realism or practical politics, especially policy based on power rather than on ideals.
Punic Wars
the three wars waged by Rome against Carthage, 264-241, 218-201, and 149-146 b.c., resulting in the destruction of Carthage and the annexation of its territory by Rome.
Stoicism
An ancient Greek philosophy that became popular amongst many notable Romans. Emphasis on ethics. They considered destructive emotions to be the result of errors in judgment, and that a wise person would repress emotions, especially negative ones and that "virtue is sufficient for happiness." They were also concerned with the conflict between free will and determinism. They were also non-dualists and naturalists.

Balance of Power
a distribution and opposition of forces among nations such that no single nation is strong enough to assert its will or dominate all the others.
Satrapy
Conquered territory in Media and later Perisa, ruled through client kings and governors rather than by direct rule.