Exam 3
1/217
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
218 Terms
control of hormone secretions
hypothalamus
reproductive maturation, body rhythms
pineal gland
hormone secretion by thyroid, adrenal cortex & gonads; growth
anterior pituitary
water & salt balance
posterior pituitary
growth & development, metabolic rate
thyroid
salt & carb metabolism; inflammatory rxns
adrenal cortex
emotional arousal (epinephrine)
adrenal medulla
Neural and hormonal chemical communication differ:
hormones act in gradual fashion
Hormones often have pulsatile secretion – in bursts
Some hormones are controlled by circadian clocks
how do neural & hormonal responses differ in terms of spatial extent?
neural : precise
hormonal: diffuse
short string of amino acids
peptides
modified version of a single amino acid
monoamines (amines)
- derived from cholesterol, made of 4 rings of Carbon
steroids
peptide hormones
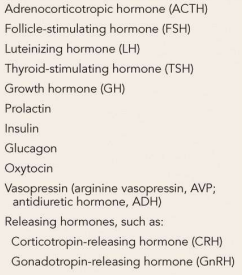
amine hormones

steroid hormones

_____ & ____ bind to receptors on the cell surface to activate second messengers.
Peptides and Amines
(metabotropic)
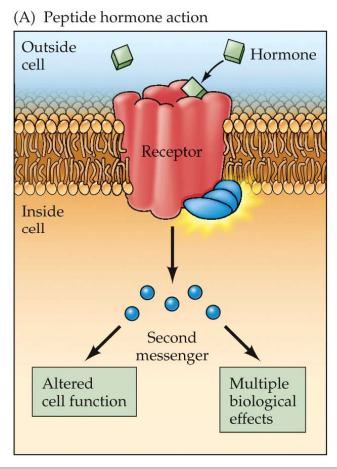
Steroids cross the cell membrane and bind to receptors inside the cell, which act as _______ (control expression of specific genes).
transcription factors
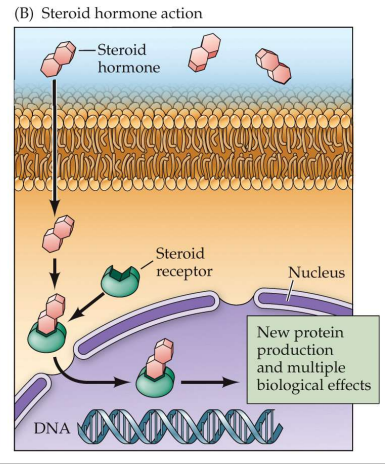
______ cells in the hypothalamus produce and store two hormones which affect social behaviors in the posterior pituitary.
Neuroendocrine
the posterior pituitary secretes two hormones:
• Vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone)- raises blood pressure and inhibits urine formation water conservation, pair-bonds
• Oxytocin- reproductive & parenting behavior (maternal bonding), uterine contractions, milk letdown reflex
The sensory signal from nipple stimulation is sent to the ________, which is routed to the hypothalamus leading to neuroendocrine cells sending action potentials to the_________ to release oxytocin, which contracts mammary glands
somatosensory cortex
posterior pituitary
_____ hormones from hypothalamus control pituitary’s release of tropic hormones
Releasing
_______hormones pituitary hormones that affect other endocrine glands
tropic (trOHpic)
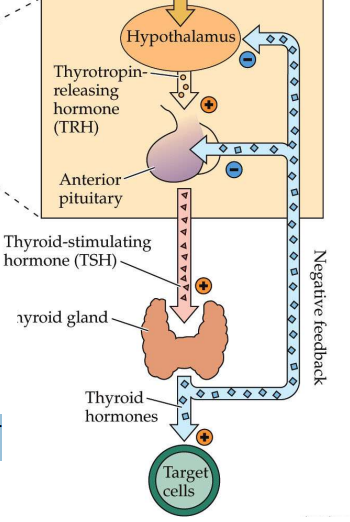
thyroid hormone pathway
1) Hypothalamic neurons synthesize releasing hormones
2) Releasing hormones are then secreted into local blood vessels
3) Releasing hormones float to anterior pituitary, which releases hormones
Vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone (ADH))
raises blood pressure, inhibits urine formation
Emotions, especially fear
oxytocin
maternal behavior / bonding. Autism?
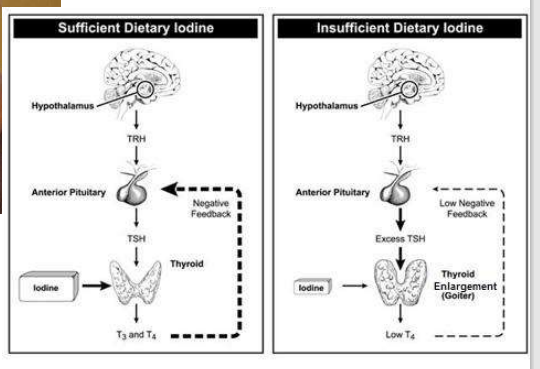
Thyroid hormone contains ________- and depends on its supply
iodine
A _____ is swelling of the thyroid gland from iodine deficiency
goiter
____________ is inadequate thyroid hormone production in newborn infants
Congenital hypothyroidism (CH)
iodine TSH interaction
_______ results from long-term excess glucocorticoids, with fatigue and depression
Cushing’s disease
The hypothalamus controls gonadal hormone production by releasing _______ into the median eminence
gonadotropin releasing-hormone (GnRH)
GnRH stimulates the anterior pituitary to release one or both gonadotropins:
+ follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
+ luteinizing hormone (LH)
in males:
the testes sense LH & produce & secrete the _______, a steroid hormone
testes also sense FSH & (do what..)
androgen testosterone
produce sperm
in females:
Ovaries sense FSH, which stimulated the ________
LH stimulates the follicles in the ovary to_________
maturation of egg containing follicles and the secretion of estrogens
rupture releasing the egg and form a corpus luteum to secrete progesterone
Oral contraceptives exerts negative feedback on the hypothalamus, inhibiting _____
GnRH
Without GnRH, no FSH or LH is released, and the ovary does not release an egg for fertilization.
levels of sex determination:
Chromosomal Sex (XY, XX, XXY, etc.)
Gonadal Sex (testis, ovaries)
Internal Sex Organs (prostate, uterus)
External Sex Organs (penis, vagina)
Brain Sex
Gender Identity
Gender Preference
Developmental event that decides whether embryo will be male or female gonadally:
SRY gene – sex-determining region on Y chromosome – is responsible for development of testes
Without an SRY gene, an ovary forms
_____ Direct Sexually Differentiation
Gonadal Hormones
____ effects mostly occur prenatally or shortly after birth
Organizing
• They affect brain and body structure and are lifelong (e.g., genitals)
____ effects occur at any time in life
Activating
• Come/go with hormone fluctuation or are long-lasting, but reversible (e.g., muscle mass, breast development, hair growth)
_____ is main organizing hormone in human brain development
Testosterone
In females, the______ develop into the fallopian tubes, the uterus, and vagina—the ______ shrink.
müllerian ducts
wolffian ducts
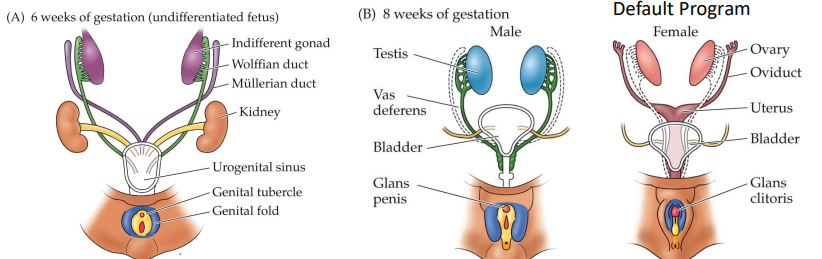
in males, testosterone promotes the______ to develop into the epididymis, vas deferens, and seminal vesicles, while _______ directs the müllerian ducts shrink.
wolffian ducts
Anti-müllerian hormone (AMH)
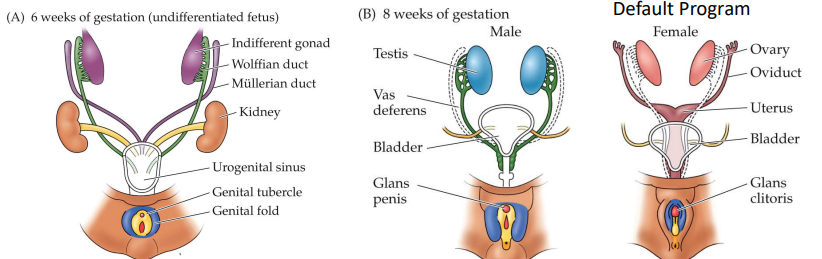
Deficiency in an enzyme 5-α-reductase, which is needed to convert testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (imp for development)
~12 yrs old testosterone surge leads to growth of penis
XY
guevedoces
Signs/Symptoms vary, but often patients with Klinefelter Syndrome have low levels of testosterone
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) during puberty can increase fertility and reverse many signs
chromosomes: ____
XXY
Why do individuals engage in reproductive behavior?
Reproduction (more of us)
DNA shuffling (but not exactly us)
It’s fun (uniquely human- no)
how is sex like hunger & thirst?
involves arousal & satiation
hormonal control
controlled by specific areas of the brain
sex is unlike hunger & thirst:
not homeostatic tissue need
individuals don’t require rex for survival (species do)
Gonadal steroids ____ sexual behavior
activate
Estrogen rise before ____ promotes non-human sexual behavior
ovulation
If a female is sexually receptive she is in ____
estrus
human females don’t have estrus – they are complicated (but they are more likely to initiate sex at ovulation)
human sexual response curve
in both men & women:
excitement phase (arousal)
In plateau, arousal levels off
Orgasm (ejaculation)
Resolution, as arousal falls and body returns to normal
_____ Are Necessary for Male Copulation
Androgens
PET imaging of male orgasm shows that primary activation was in …..
ventral tegmental area
Oxytocin releases at ejaculation; promoting bonding?
PET imaging of female orgasm shows activation & inhibition of what?
• Activation of the deep cerebellar nuclei
• Inhibition of orbitofrontal cortex
higher lvl decision making is dampened (animal brain)
Medial amygdala (MeA; in the temporal lobe)
Involved in sex, smell, aggression, and emotions
Medial preoptic area (mPOA of the hypothalamus)
involved in sexual performance
brain areas for sex important for males:
Sexually dimorphic nucleus
Located in mPOA (INH3 in humans) (anterior hypothalamus)
2-3x larger in men
Male sex activity related to its size
Size depends on prenatal exposure to testosterone
brain areas important for sex in females:
ventromedial hypothalamus
(Receptivity to male advances; ‘in the mood’ Increases dendritic trees in response to estrogen)
dopamine (DA) activity in ____ motivates sex behavior in both sexes, esp. in men
• Drugs that increase DA increase sexual activity in humans
• Increasing levels of DA produce erection in males, then ejaculation
mPOA
serotonin (5HT) increases in the _______ during ejaculation- contributing to the refractory period?
• Injecting SSRI into LH increases time before male rats copulate again
• Both men and women complain SSRIs impair their sexual ability
lateral hypothalamus
T/F: women have larger corpus callosum
TRUE
size of corpus callosum correlates with cognitive skills in women
T/F: males have greater asymmetry than females
• right hemisphere is _____ in males than females
TRUE
thicker
Women have greater gray matter in….
dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (think before you act) • superior temporal gyrus (talking/listening)
overall, males have
______ inferior parietal lobule, amygdala, nucleus of anterior hypothalamus, bed nucleus of stria terminals
______ Broca’s area & Wernicke’s area, anterior commissure, hippocampus
larger
smaller
how do sexual dimorphisms develop?
prenatal hormone exposure or social influence
The _________ was larger in men than in women, and larger in heterosexual men than in gay men
Interstitial Nuclei of the Anterior Hypothalamus
little support for _______, which emphasizes home environment or early seduction as causes of homosexuality
social influence hypothesis
_____ influences- The likelihood that an individual identifies as gay or lesbian is 2-7 times higher among siblings of gay and lesbians than in general population
Genetic
Gay men and heterosexual men have the _____testosterone levels (as adults)
same
Any hormonal influence on a man sexual orientation likely occurs _____
prenatally
Women who identify as lesbians later in life have been shown to have had ____ exposure to fetal androgens than those identifying as heterosexual
more
____ hypothesis- The more older brothers a man has from the same mother, the greater the probability he will identify as being gay, (but only if R handed) - Maternal antibodies to make tissues
Antibody
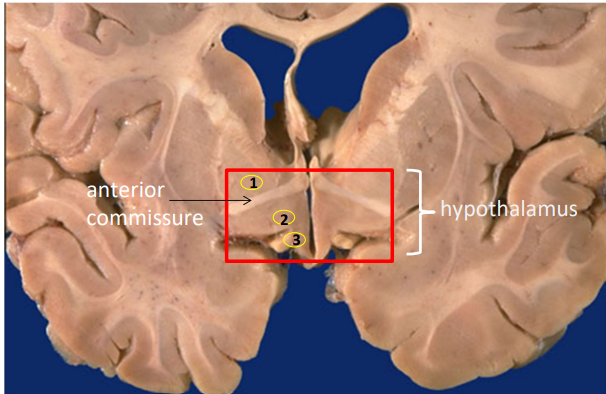
label 1,2,3
1. Bed nucleus of the stria terminalis
2. Sexually dimorphic nucleus (INAH3)
3. Suprachiasmatic nucleus
T/F: gay men have a larger third interstitial nucleus of the anterior hypothalamus
FALSE
it is female sized (smaller)
_______ is larger in gay men than in heterosexual men and contains more vasopressin-secreting cells
Suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN)
_______ is larger in gay men and heterosexual women than in heterosexual me
Anterior commissure (AC)
Larger Right Hemispheres in both ___________________
Symmetric Hemispheres in both _______________
lesbians and heterosexual males
gay males and heterosexual women
Spatial ability is affected by _______________
masculinization
High estrogen level is associated with
• depressed spatial ability
• enhanced speech and manual skill tasks
_______ during 2nd trimester increases cerebral asymmetry via accelerated growth of the right hemisphere
Testosterone
Males low in testosterone in development are impaired in ________________
spatial ability
the maintenance of a stable, balanced, internal environment
homeostasis
___________ systems are the main homeostatic mechanisms
If a desired set point is deviated from, compensatory action begins
negative feedback
factors that initiate, sustain, or direct behavior
motivation “to set in motion”
_______- drive physiological motivation
Homeostatic systems
what are the two internal cues that trigger thirst?
low volume (hypovolemic thirst)
replenish systems
detected by brain, kidney, heart
high [solute] (osmotic thirst)
![<ol><li><p>low volume (hypovolemic thirst)</p><ol><li><p>replenish systems </p><p>detected by brain, kidney, heart </p></li></ol></li><li><p>high [solute] (osmotic thirst)</p></li></ol>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1de0b517-6e90-4fb4-b777-dff57f196f45.jpeg)
______ is the principal fuel for energy
Glucose
_____ is glucose stored for short term in the liver
Glycogen
______: converting glucose to glycogen, using pancreas hormone insulin
Glycogenesis
____, for long-term storage, are stored in fat tissue
Lipids
T/F: Brain integrates insulin and glucose levels with other information to decide when to start/stop eating
true
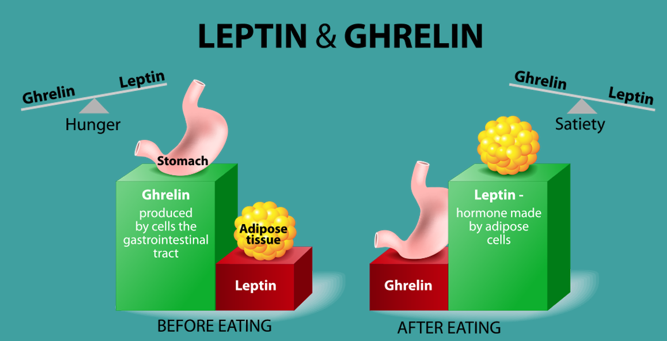
Fat cells produce _____ and secrete it into the bloodstream
leptin
Defects in leptin production or receptor sensitivity give a falsely ____(low or high) report of body fat, causing animals to overeat
low
Obese people are leptin-…..
resistant
Overnutrition inflames the _______ - obesity, diabetes, and heart disease
hypothalamus
Released by stomach endocrine cells
- Appetite stimulant
Rises during fasting; drops after eating
ghrelin
leptin & ghrelin before vs after eating
Ghrelin levels are _________ in Prader-Willi
elevated
___________ usually caused by deletion of a part of chromosome 15.
Defects in the hypothalamus.
Prader-Willi