Section 15 (last section - Skeletal muscles)
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
What are the 3 main types of muscles?
Smooth muscle:
Found in internal organs and blood vessels, allow substances to travel with reduced friction
Cardiac muscle:
Found in the heart
Skeletal muscles:
Muscles attached to the bone, they work as antagonistic muscles (while one contracts, the other relaxes)
The contracting muscle shortens and pulls on the attached tendon
The tendon pulls on the bone, causing movement at joint
The relaxing muscle lengthens to allow movement
Microscopic muscle structure background info:
Skeletal muscles are made from bundles of muscle fibers.
A single muscle fiber is made of specialised cell organelles (myofibrils)
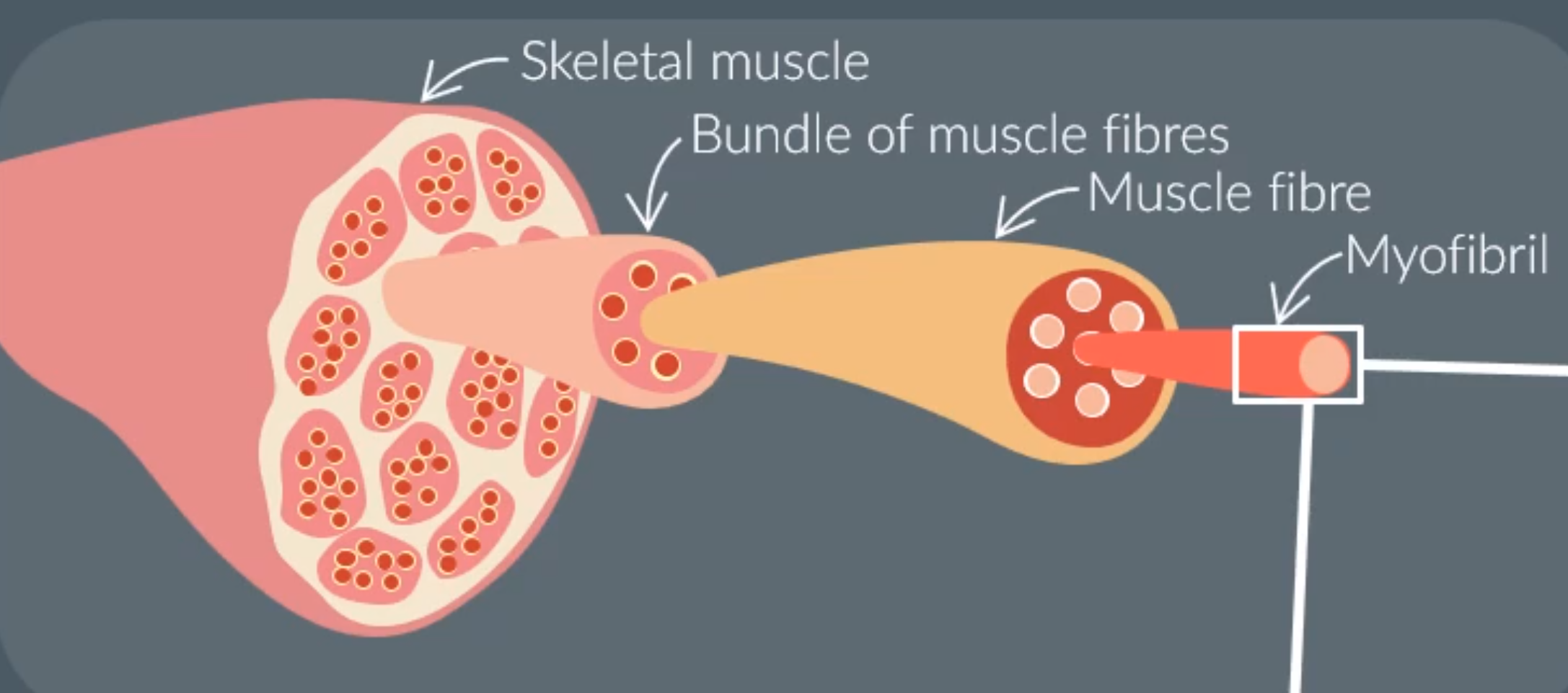
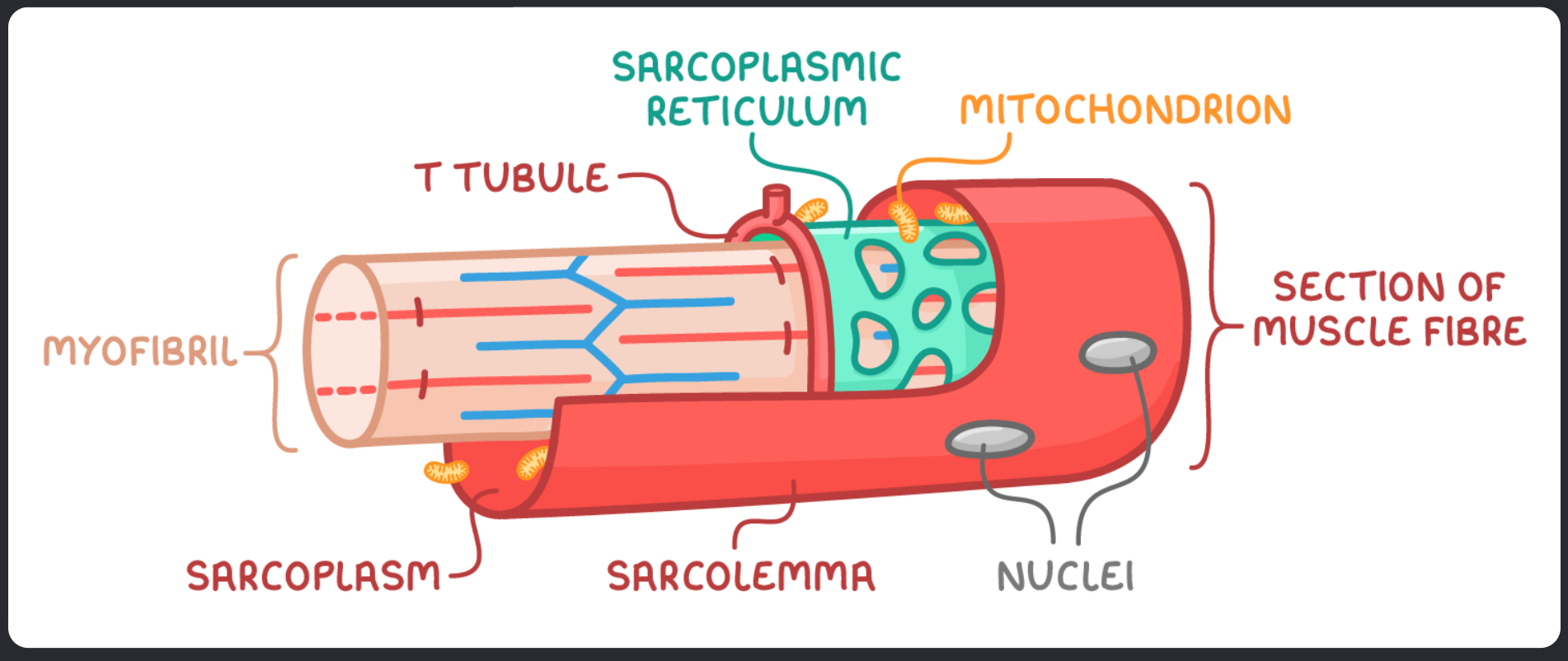
Structure of the Mycrofibril:
Sarcolemma - the cell surface membrane of muscle fibre
Sarcoplasm - The cytoplasm of a muscle fibre
Transverse tubules (T tubules) - Extensions of the sarcolemma that transmit electrical signals, so entire muscle recieves and contracts simultaneously
Sarcoplasmic reticulum - Specialised endoplasmic reticulum that is responsible for storing and releasing calcium ions
Myofibrils - subcellular strucutres designed for contraction
Multiple nuclei - skeletal muscle fibres have many nuclei because several cells merge to form one muscle fibre
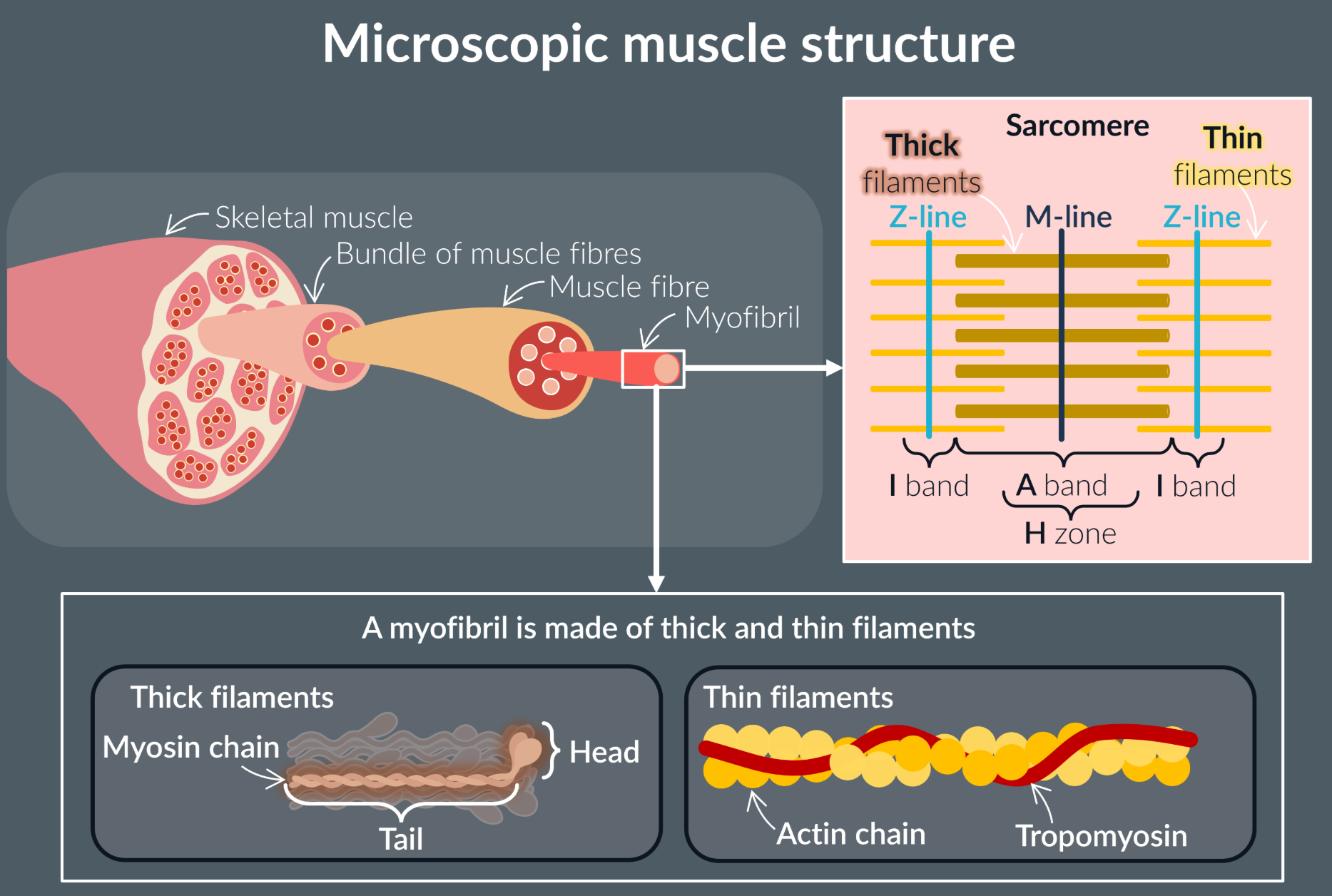
Myofibrils are made of many repeating units …
Myofibrils are made of many repeating units called sacomeres.
Each sacomere:
Thin filaments (two actin filaments with tropomyosin)
Thick filaments (two myosin filaments bundled together with many others)
The steps for sliding filament mechanism:
Calcium ions released by the sacroplasmic reticulum causes the tropomyosin to move away from the actin binding sites.
The myosin head then attaches to one of the binding sites on actin (actinomyosin bridge)
ADP and Pi are released from the head, causing a power stroke where myosin head moves actin to M line
The myosin head binds to new ATP molecule and dettaches from actin
Myosin head hydrolyses the ATP and returns to starting position
The picture steps are most accurate

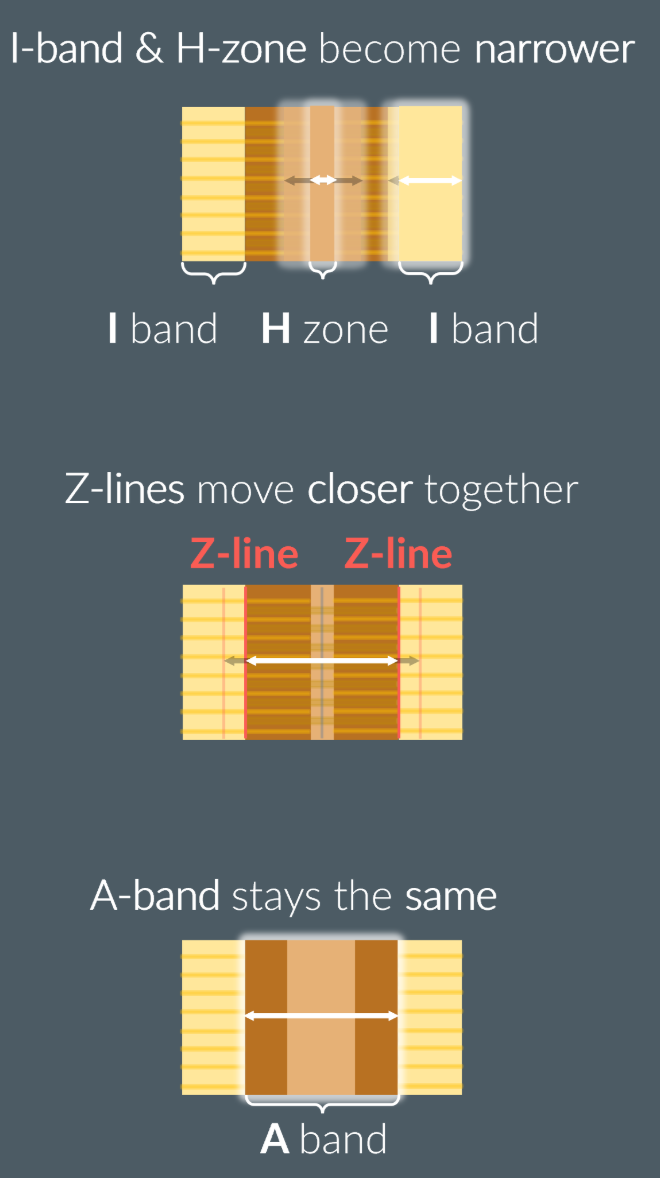
The proof of sliding filament theory:
The I band and H zone shorten due to an increased overlap of actin and myosin filaments
The A band remains at constant length, as the myosin filaments remain stationary, but the heads are the only ones moving
How do the calcium ions find their way into tho the myofibril?
Action potential arrives at the end of neurone
Triggers opening of calcium ion channels and calcium ions enters the neurone
The acetylcholine vesicles release their contents into the synaptic cleft
Acetylecholine diffuses across the synaptic cleft
Acetylcholine binds to the receptors on sarcolemma leading to opening of sodium ion channels
This results in depolarisation of sarcolemma.
The depolarisation extends through the T tubles, which interact with sacroplasmic reticulum and release calcium ions into the sacroplasm.

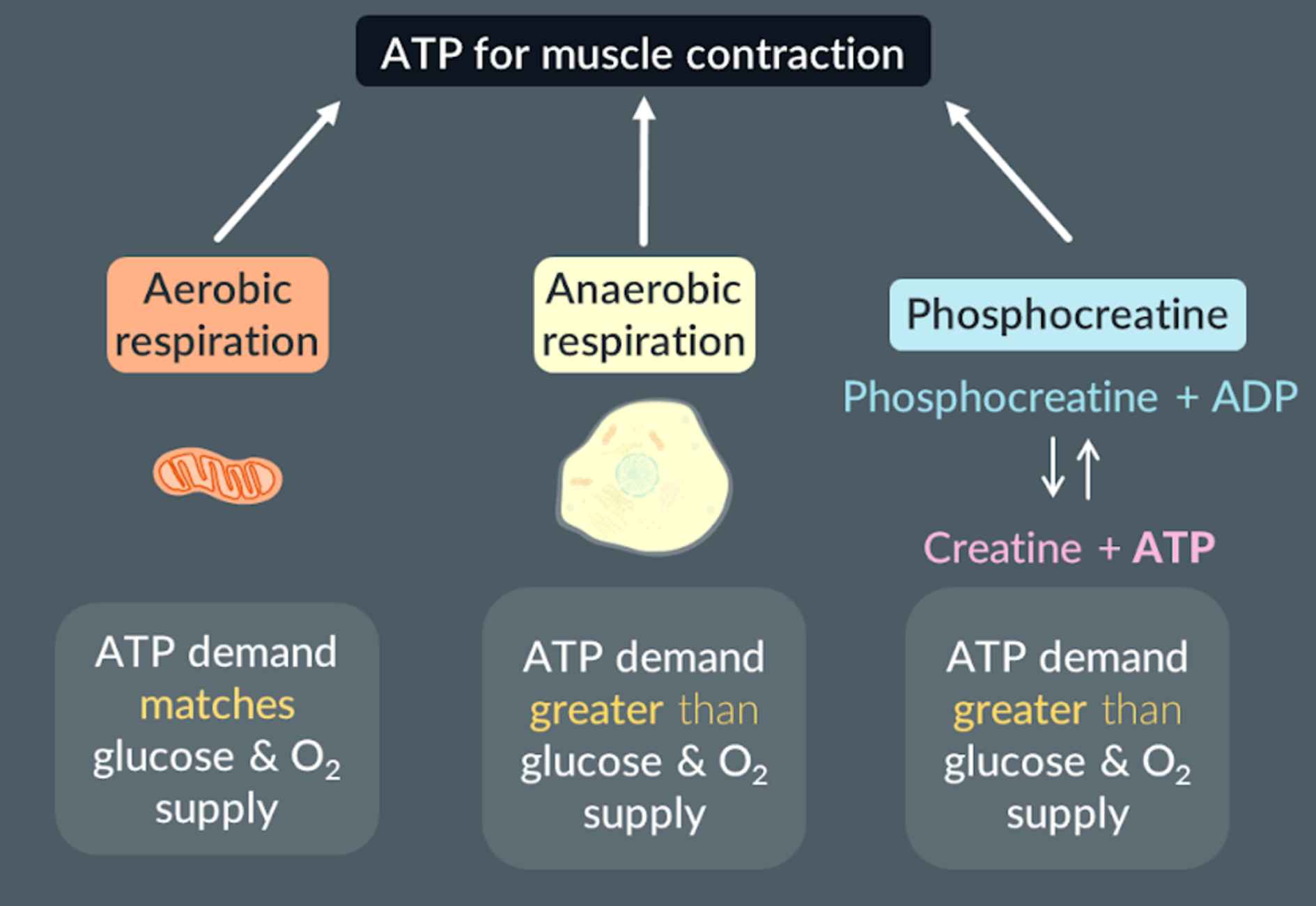
The three types of ATP sources from muscles
Aerobic respiration: when the ATP demand matches the oxygen and glucose supply
Anaerobic respiration: when the ATP demand does not match the oxygen and glucose supply
Phosphocreatine + ADP → Creatine + ATP: when the ATP demand does not match the oxygen and glucose supply
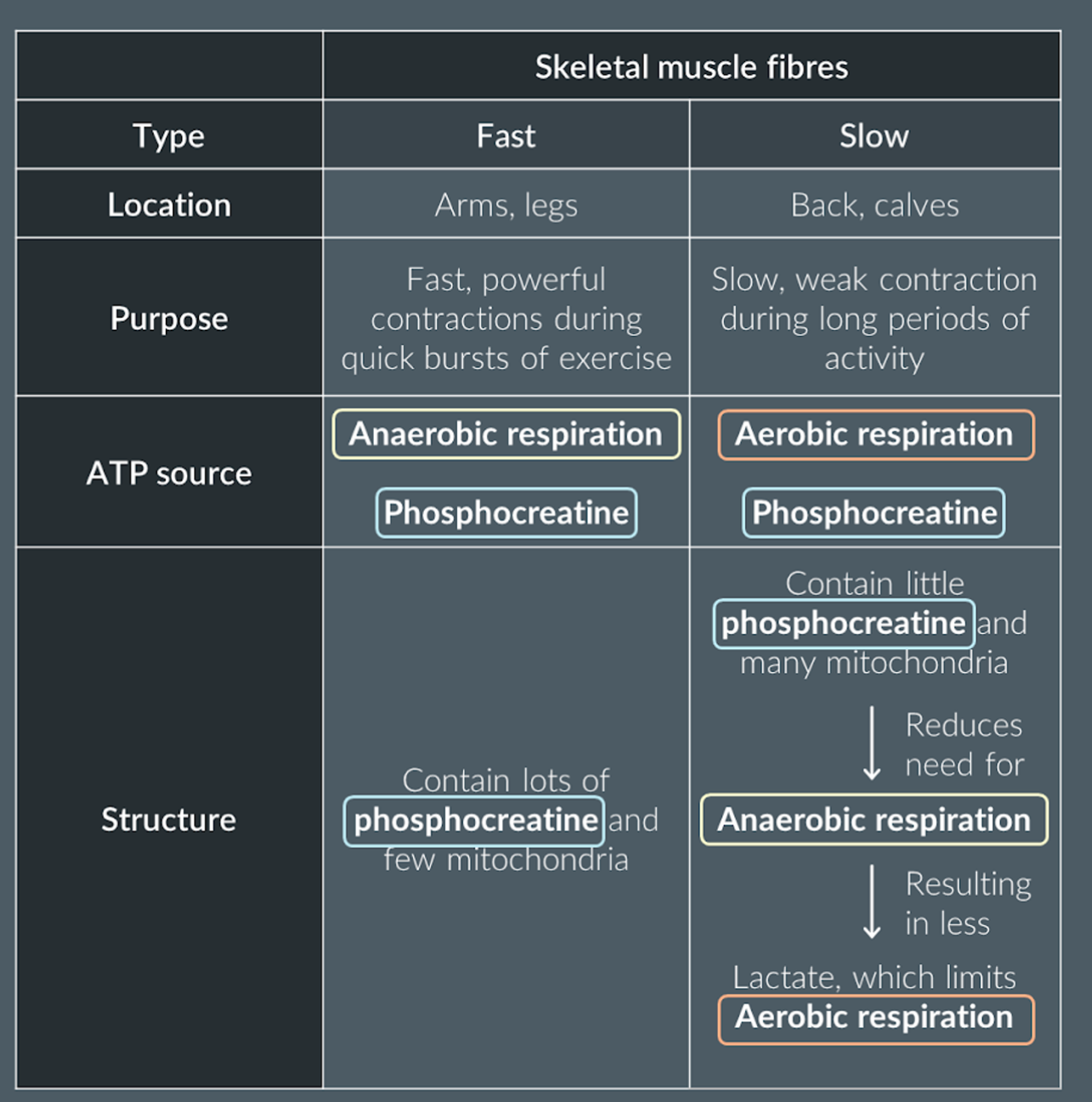
The difference between slow-twitch and fast-twitch muscles:
Slow-twitch fibers, contain large store of myoglobin (a bright red colour that stores oxygen) + rich blood supply to deliver oxygen and glucose for respiration + many mitrocondria
What is the difference between neuromuscular junction and cholinergic synapse?
Neuromuscular junction only links only links neurons to muscles, but cholinergic synapse links neurons to neurons (or neurons to other effector organs)
For neuromuscular junction action impulse ends here, but for cholinergic synapse a new action impulse may be produced along another neuron
In neuromuscular junction acetylcholine binds to muscular membrane (sarcolemma), but for cholinergic synapse acetylcholine binds to the post synaptic membrane