Gluconeogenesis and Glycogen
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
What is the role of gluconeogenesis?
Generates glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors during fasting.
What is the function of glucose-6-phosphatase?
Converts glucose-6-phosphate to free glucose in liver and kidney.
Why is glucose-6-phosphatase essential?
Allows glucose export into blood to maintain normoglycemia.
What tissues rely heavily on glucose?
Brain, erythrocytes, renal medulla.
What is the order of fuel use during fasting?
Glucose → glycogen → gluconeogenesis.
What are key gluconeogenic substrates?
Lactate, glycerol, alanine, other glucogenic amino acids.
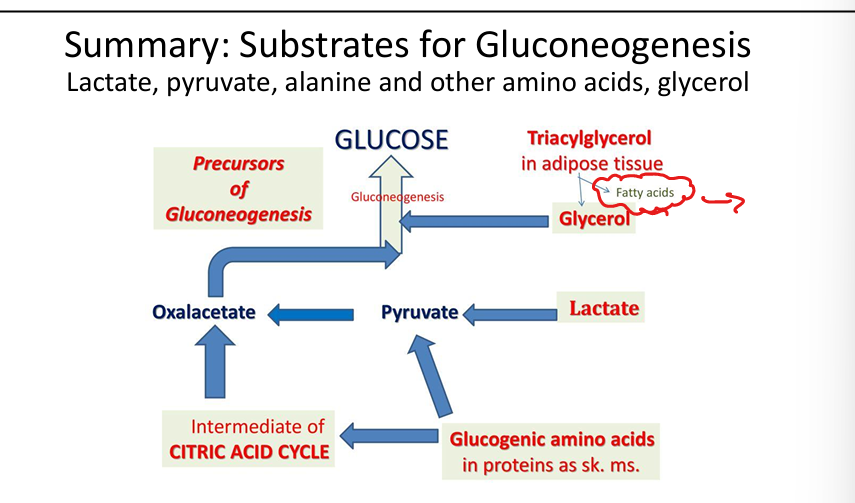

How does lipid metabolism support gluconeogenesis?
FFA oxidation provides ATP; glycerol enters gluconeogenesis. (TAG=triacylglycerol)

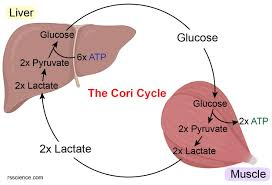
What is the Cori cycle?
Lactate from muscle is converted (oxidized to pyruvate) to glucose in liver.

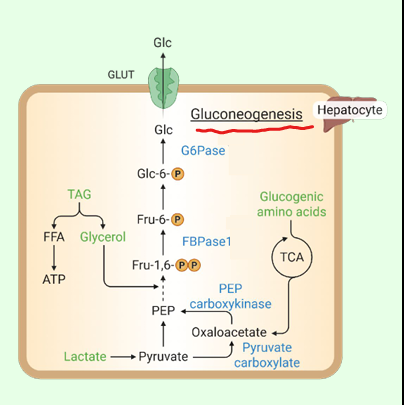
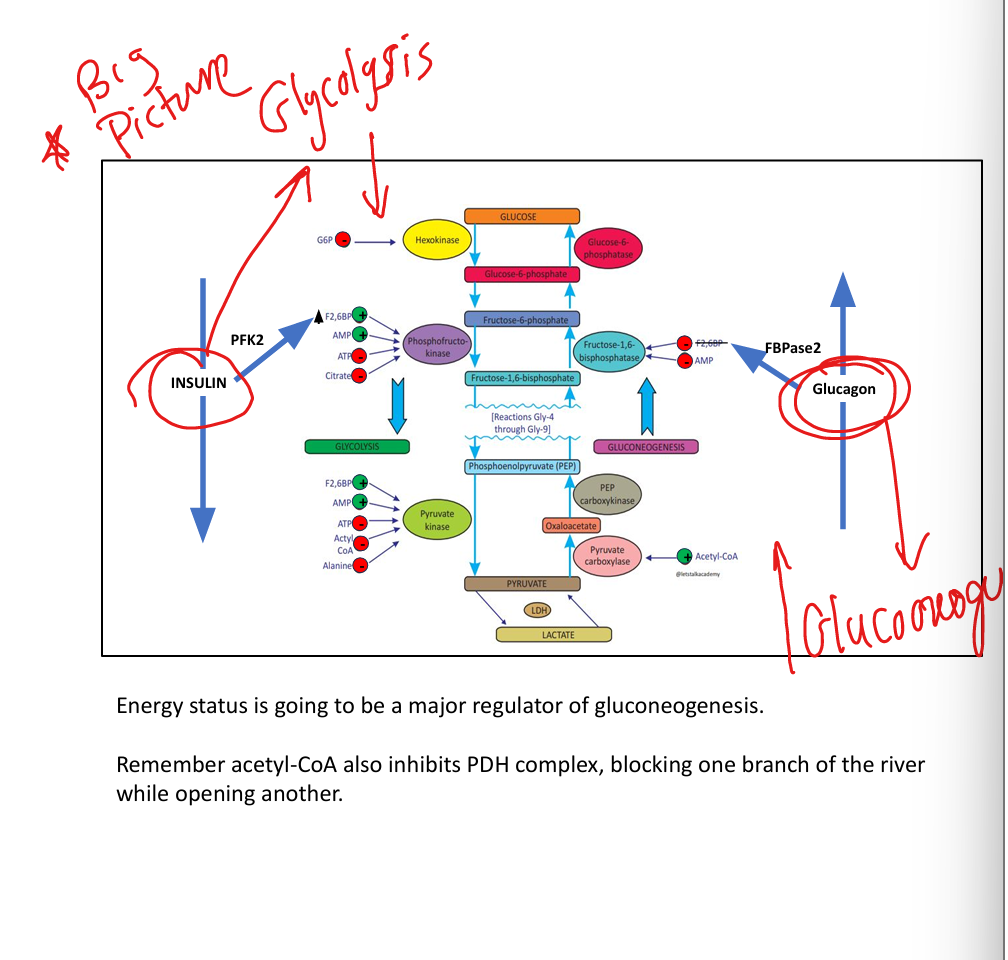
Which glycolytic enzymes are bypassed in gluconeogenesis? (These are just the RLS of glycolysis)
Pyruvate kinase, PFK-1, hexokinase/glucokinase.


What enzymes bypass pyruvate kinase?
Pyruvate carboxylase and PEP-carboxykinase.
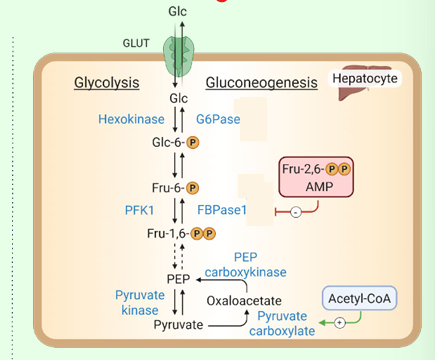

What activates pyruvate carboxylase?
Acetyl-CoA.
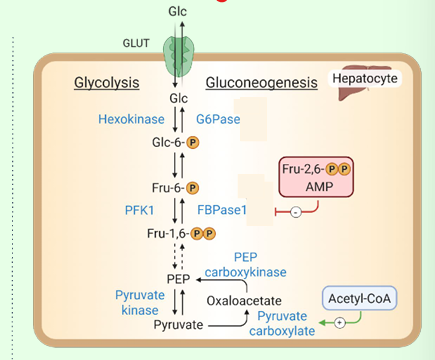

What enzyme bypasses PFK-1?
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase.
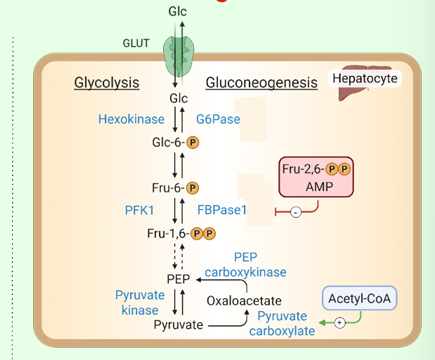

What inhibits FBPase-1?
AMP and fructose-2,6-bisphosphate.
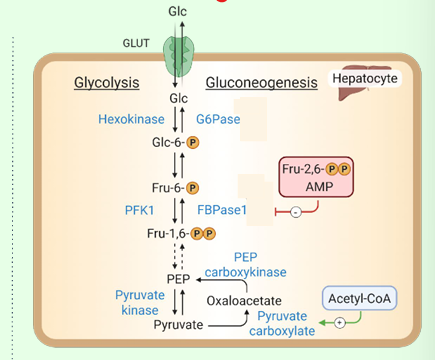

What enzyme bypasses hexokinase?
Glucose-6-phosphatase (in ER).
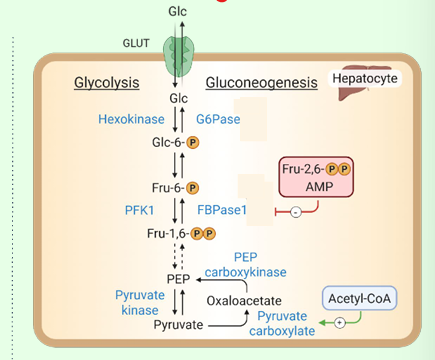

What is the energy cost of gluconeogenesis?
6 ATP and 2 NADH per glucose.
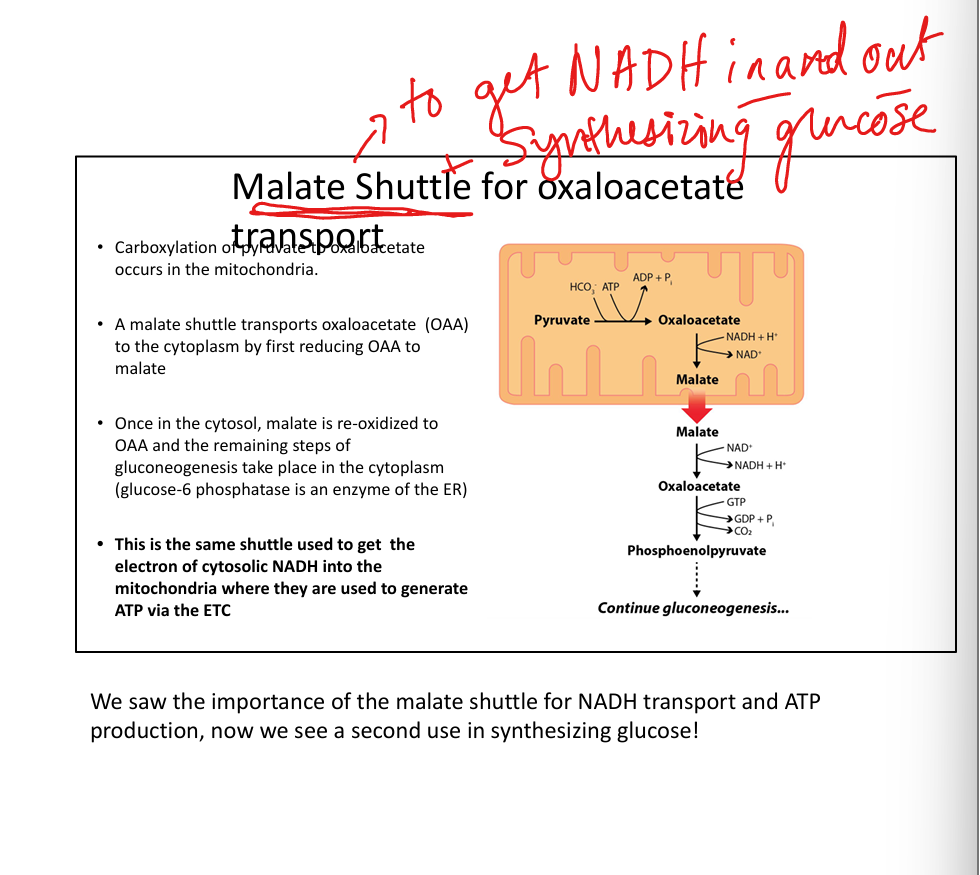
What is the malate shuttle?
Transports oxaloacetate from mitochondria to cytosol as malate.

What does fructose-2,6-bisphosphate do?
Activates PFK-1, inhibits FBPase-1.
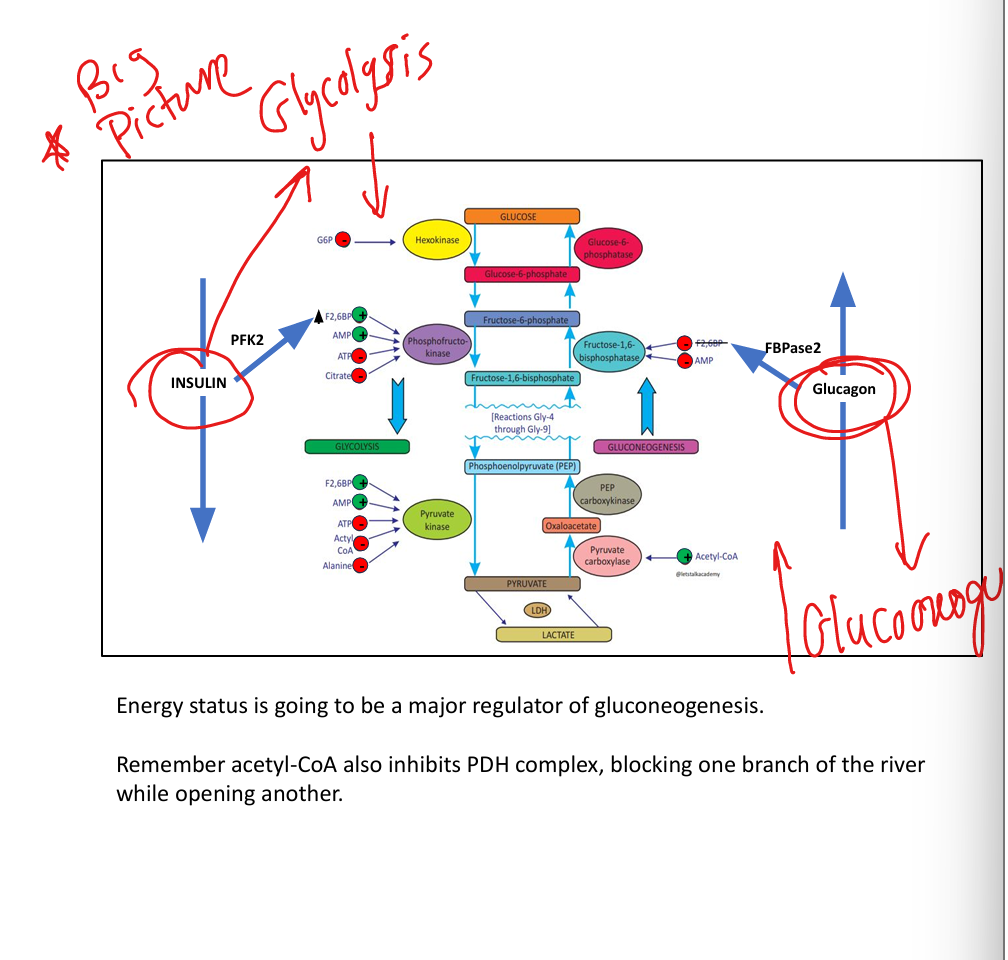

How does insulin regulate glycolysis?
Promotes PFK-2 → ↑ F2,6BP → ↑ glycolysis.
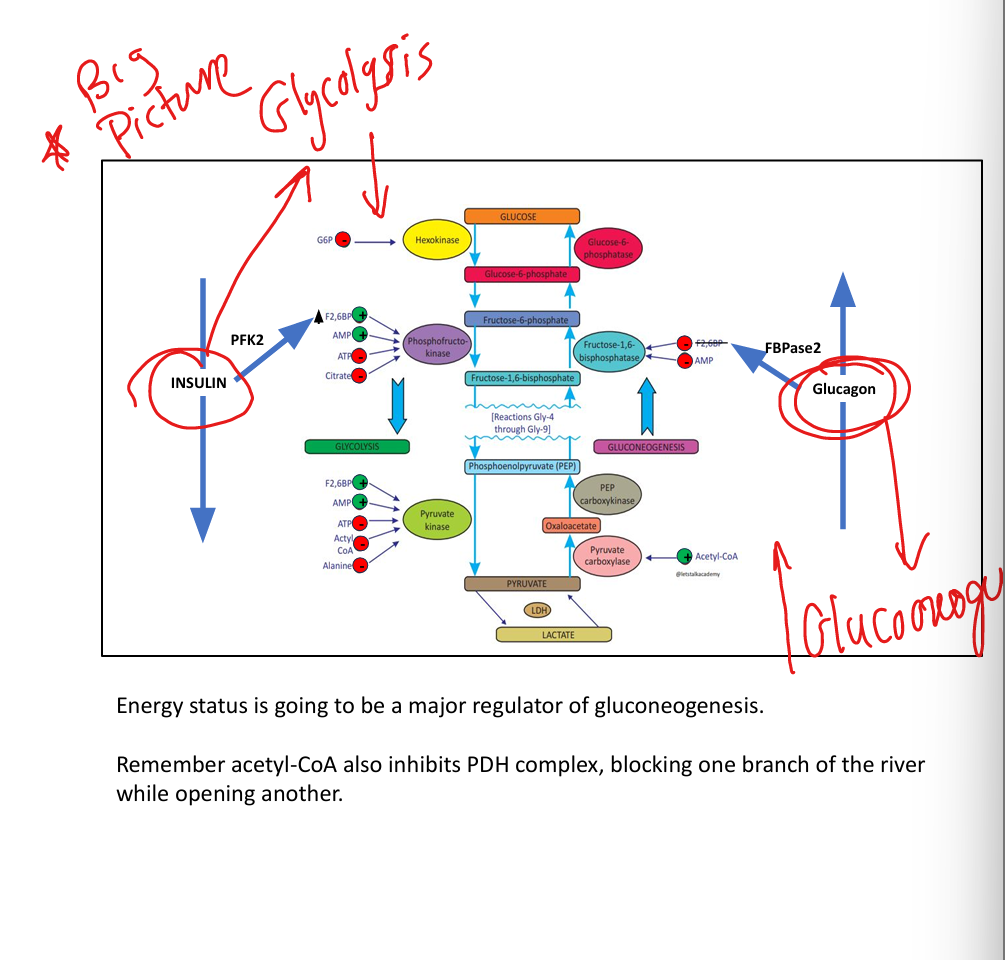

How does glucagon regulate gluconeogenesis?
Activates FBPase-2 → ↓ F2,6BP → ↑ gluconeogenesis.
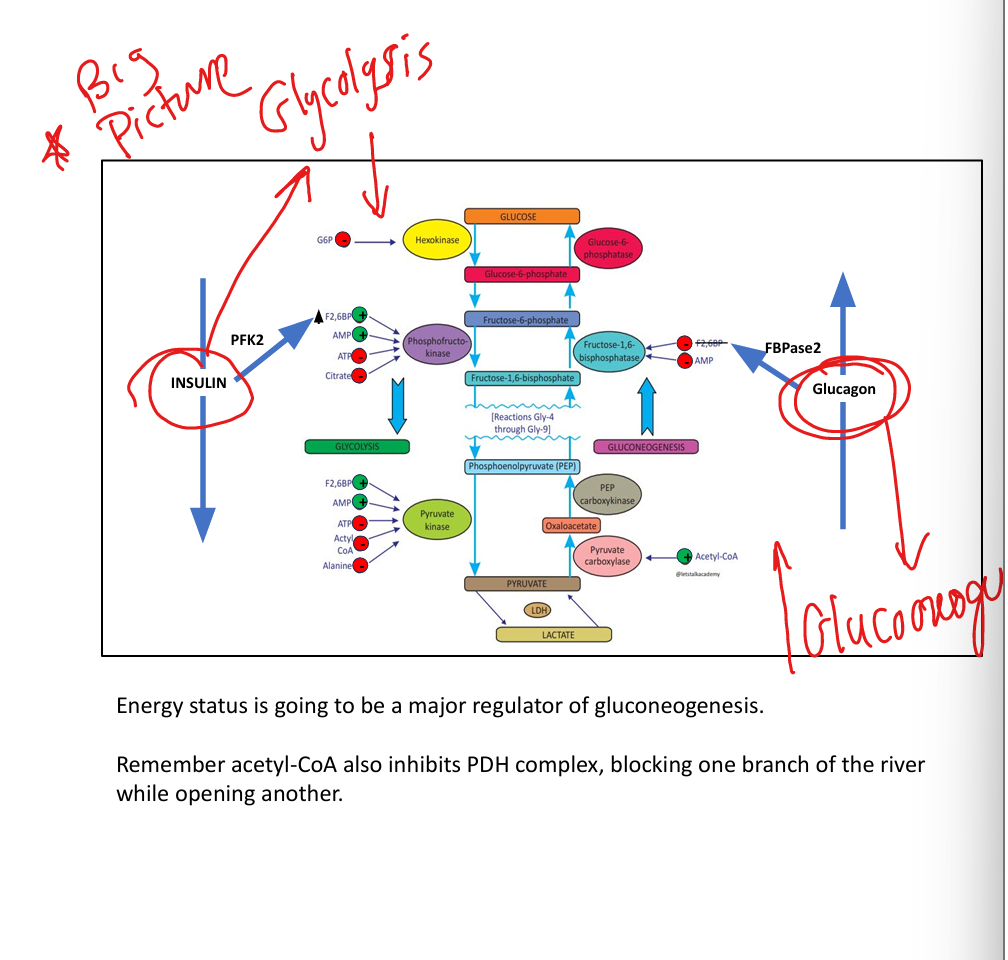

What does acetyl-CoA do?
Activates pyruvate carboxylase, inhibits PDH.
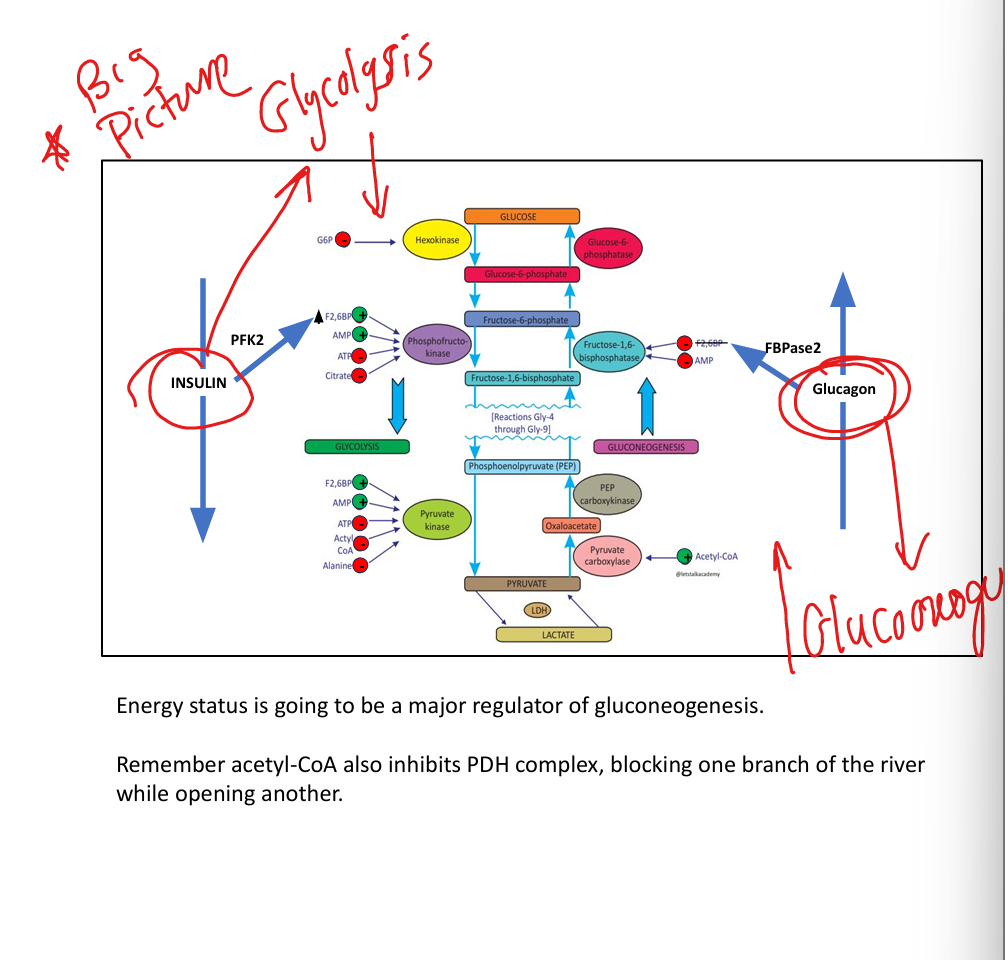

What does citrate do?
Inhibits PFK-1.
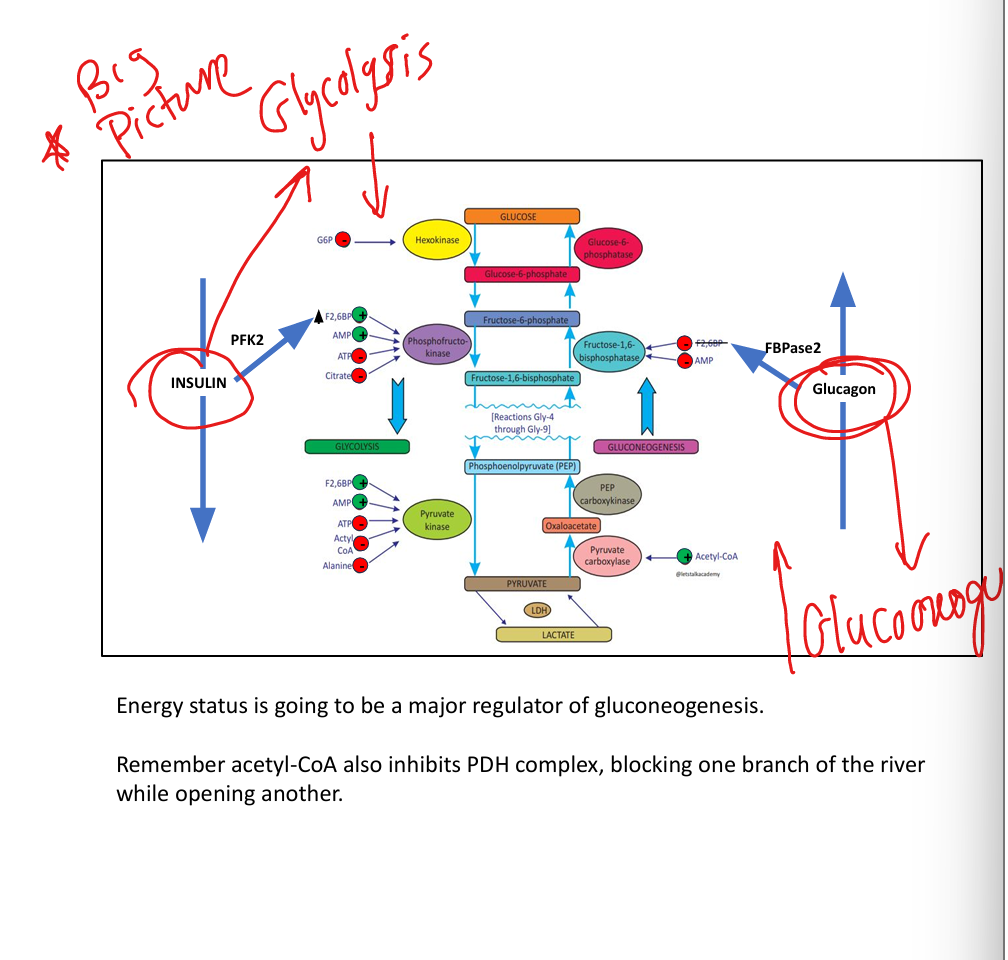

How do ATP and AMP regulate glycolysis?
ATP inhibits glycolysis; AMP activates glycolysis and inhibits gluconeogenesis.
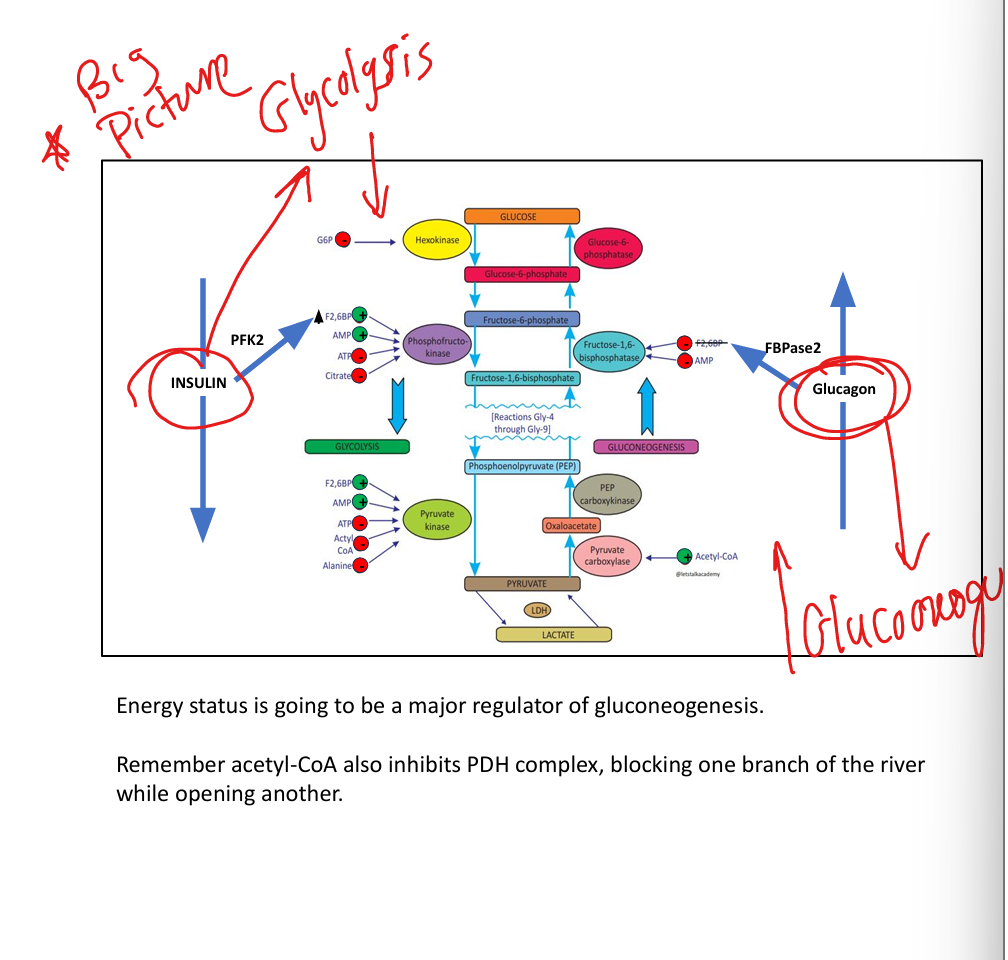

What does glucose-6-phosphate do?
Inhibits hexokinase.

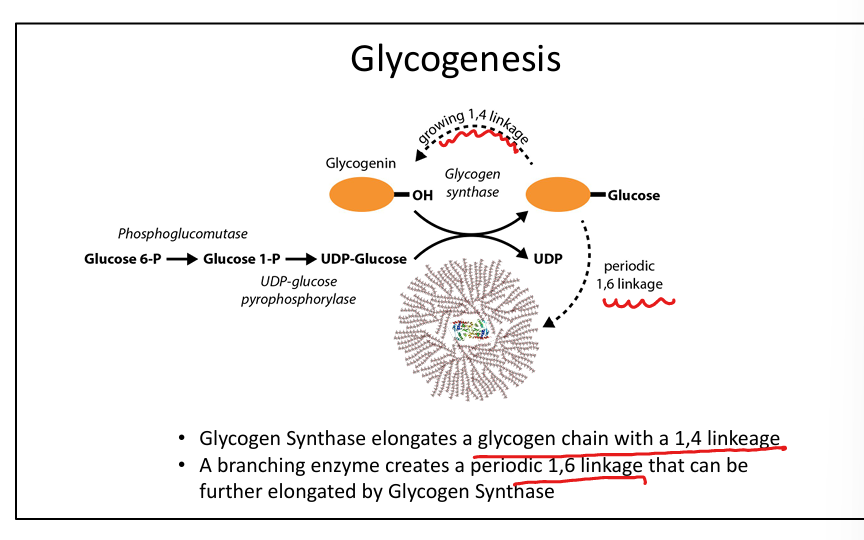
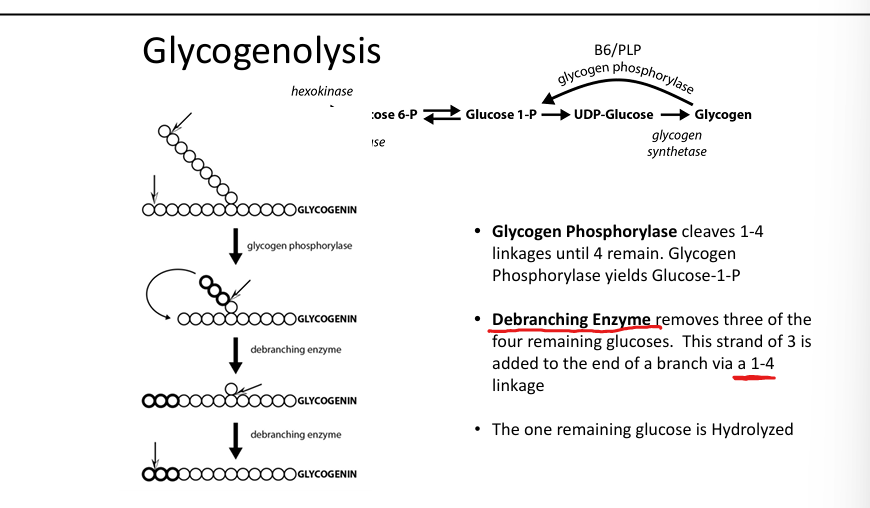
What enzyme synthesizes glycogen?
Glycogen synthase (α1-4 linkages).
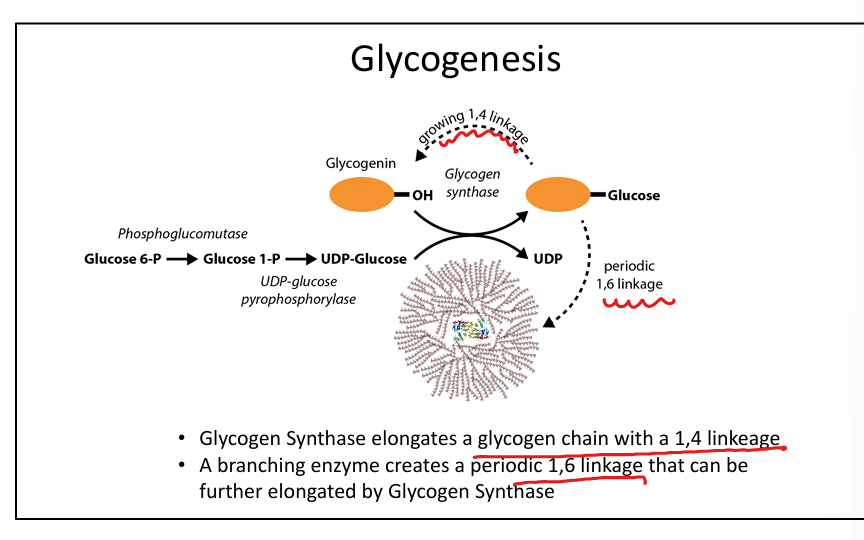

What enzyme creates branches in glycogen?
Branching enzyme (α1-6 linkages).

What enzyme breaks down glycogen?
Glycogen phosphorylase (cleaves α1-4 linkages).
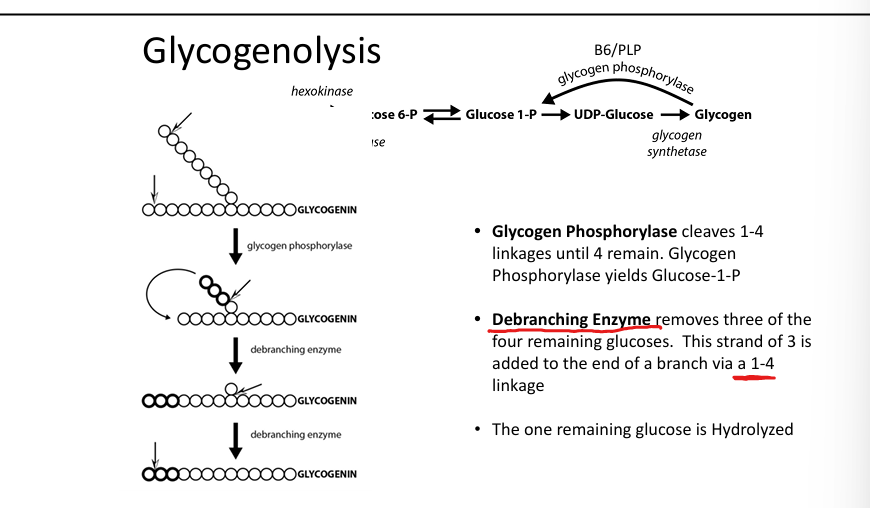

What enzyme removes branches?
Debranching enzyme (transfers and hydrolyzes α1-6 linkages).

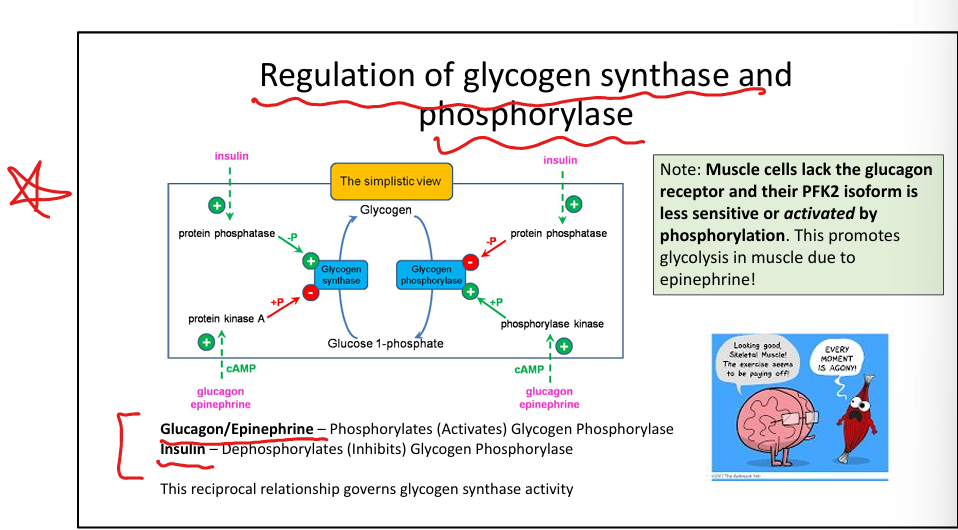
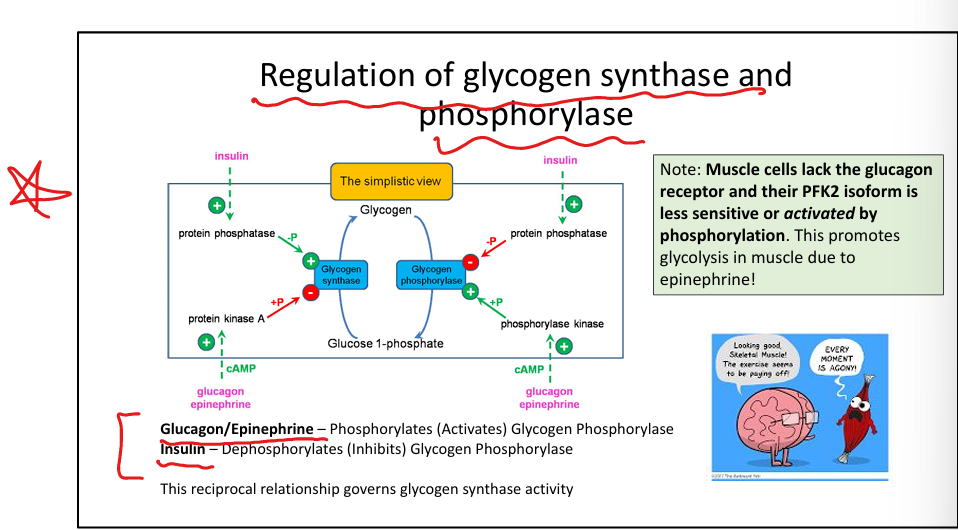
How does insulin regulate glycogen metabolism?
Activates glycogen synthase, inhibits glycogen phosphorylase.
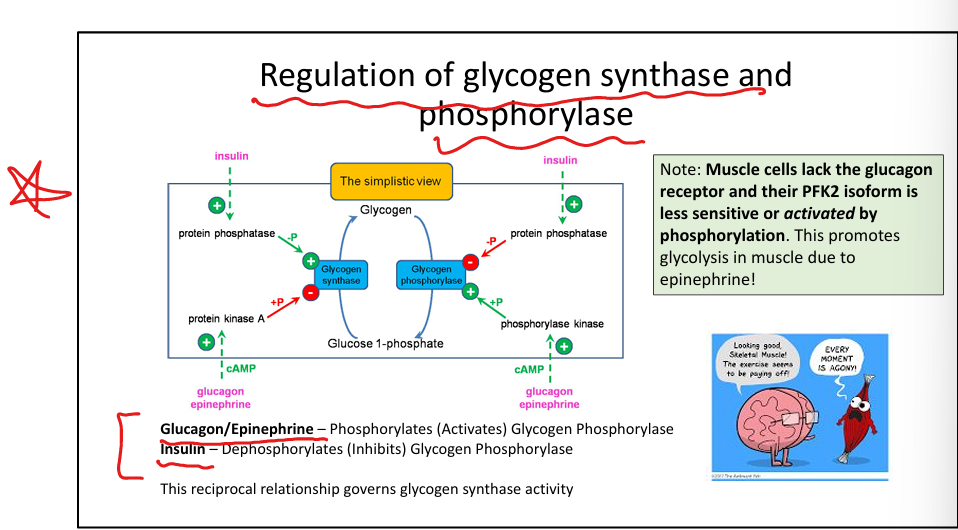

How do glucagon and epinephrine regulate glycogen metabolism?
Activate glycogen phosphorylase, inhibit glycogen synthase.

Which tissues store glycogen?
Liver and skeletal muscle.

Which tissues can release glucose into blood?
Liver and kidney (contain glucose-6-phosphatase).
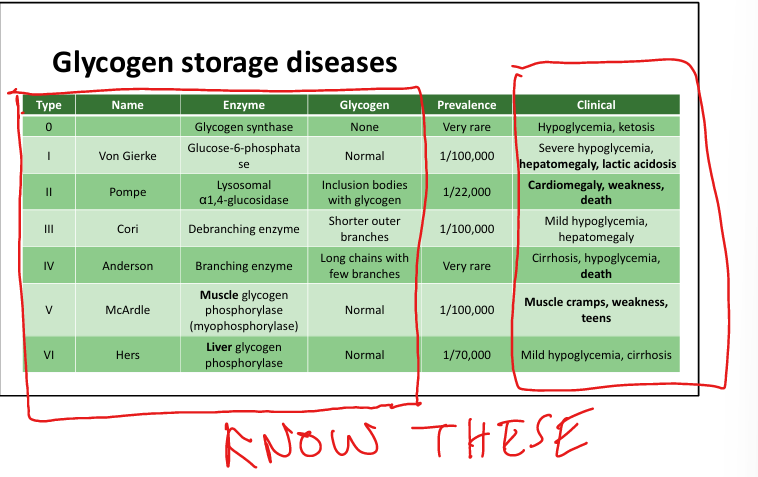
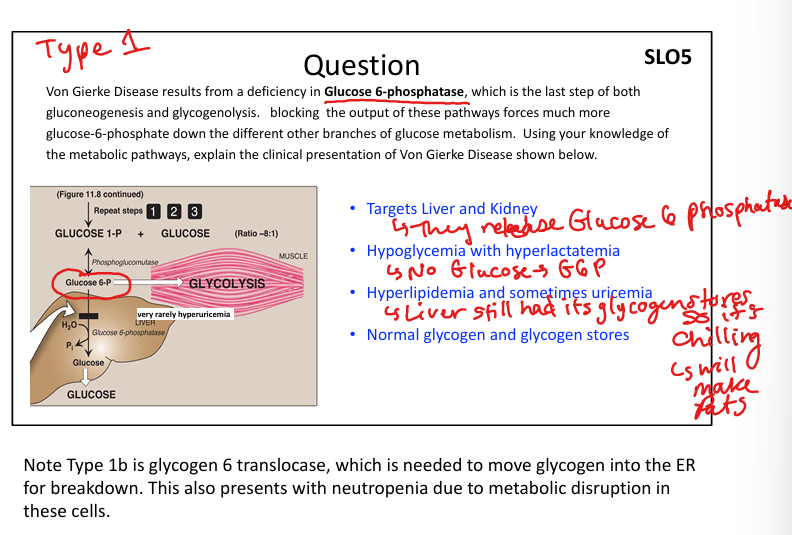
What causes Von Gierke disease (Type I)?
Glucose-6-phosphatase deficiency.
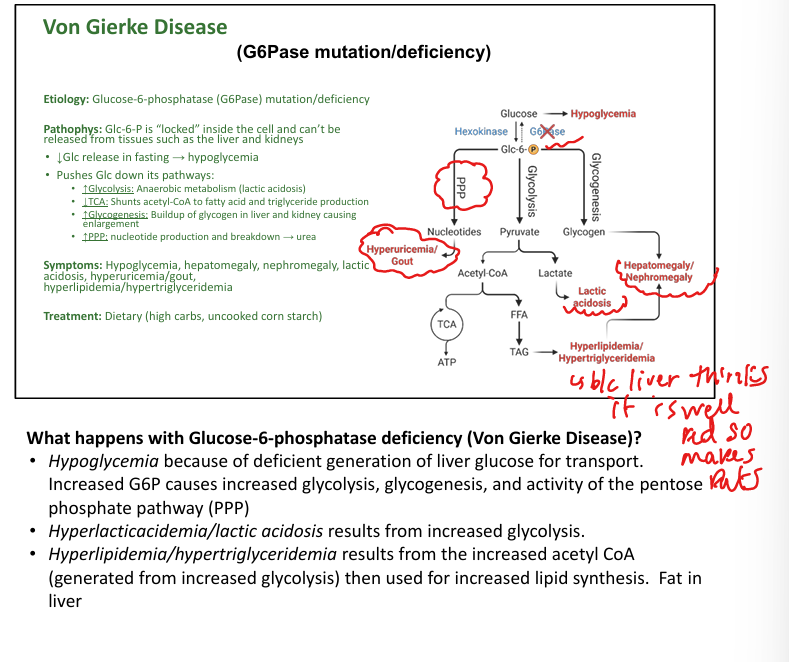

What are symptoms of Von Gierke disease?
Hypoglycemia, hepatomegaly, lactic acidosis, hyperlipidemia.

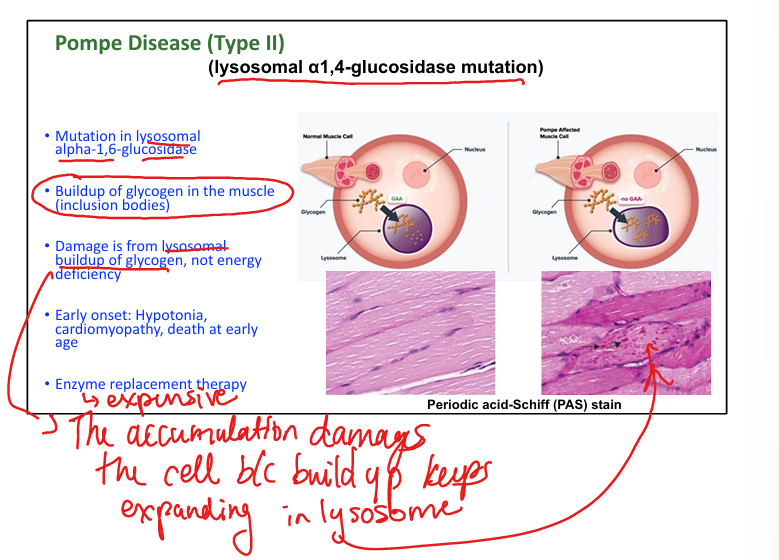
What causes Pompe disease (Type II)? (we can’t destroy Pompeii!)
Lysosomal α1,4-glucosidase deficiency. (can’;t break down glycogen)
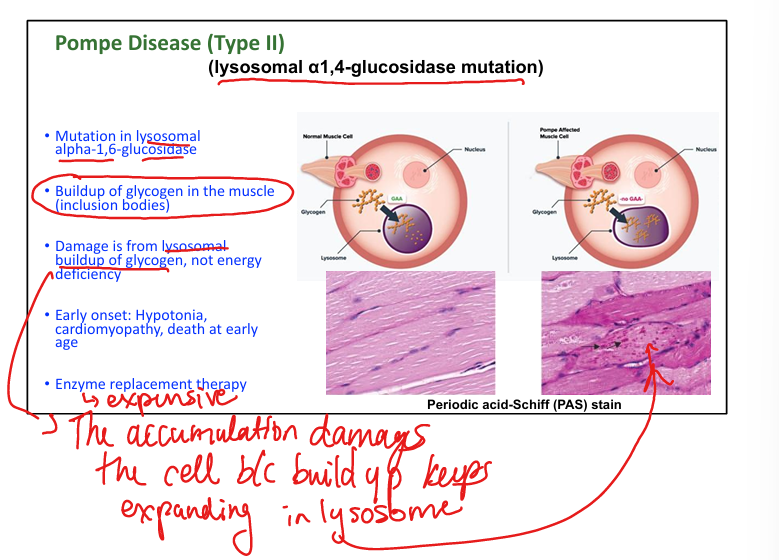

What are symptoms of Pompe disease?
Hypotonia, cardiomegaly, early death.

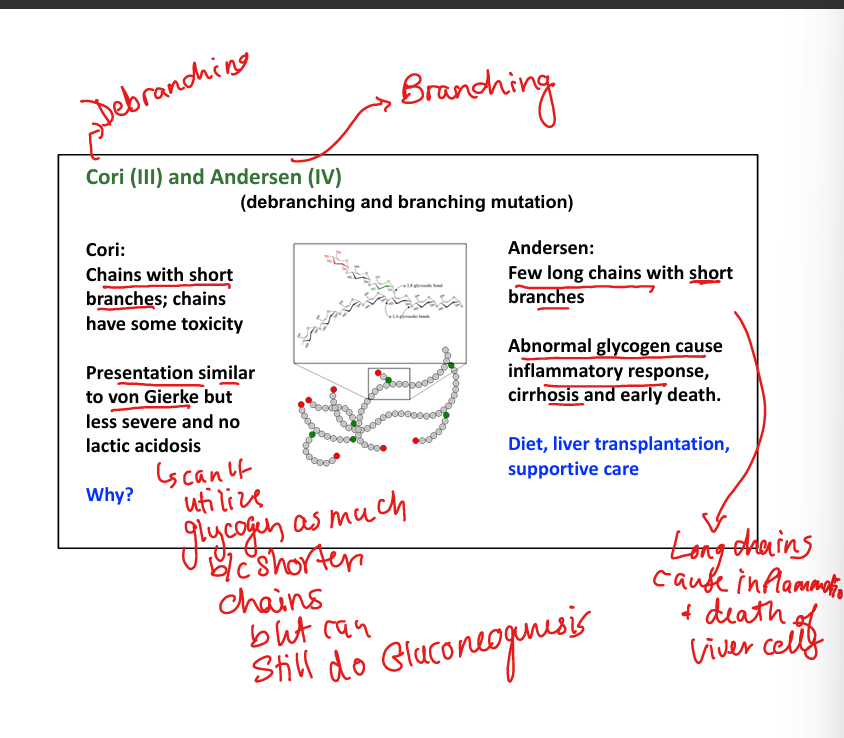
What causes Cori disease (Type III)? Watch for the Small Branch Cori!
Debranching enzyme deficiency.»chains with shorter branches »can’t break down glycogen into glucose well
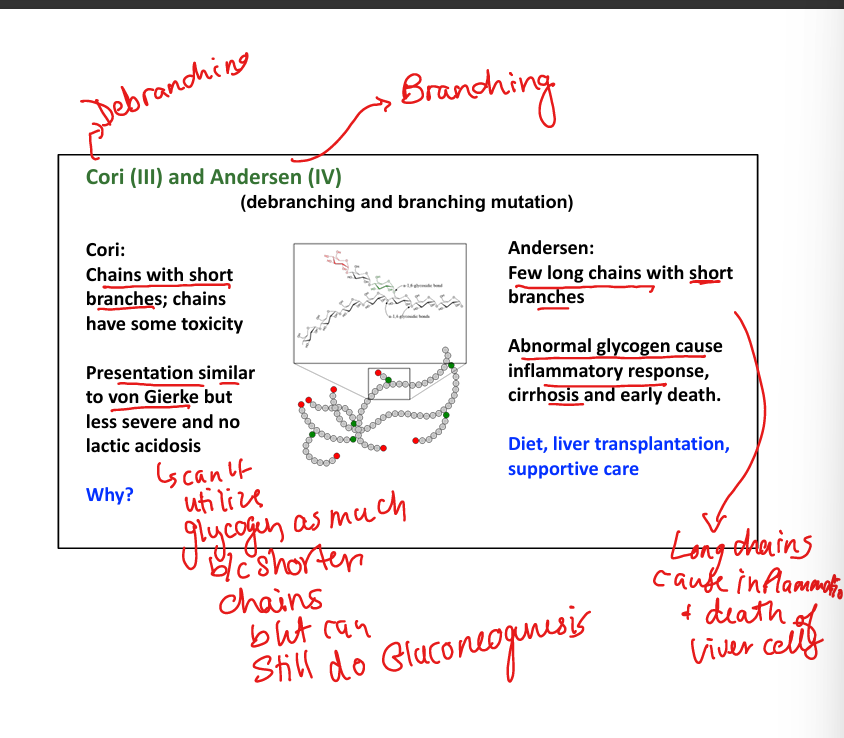

What are symptoms of Cori disease?
Mild hypoglycemia, hepatomegaly, no lactic acidosis.
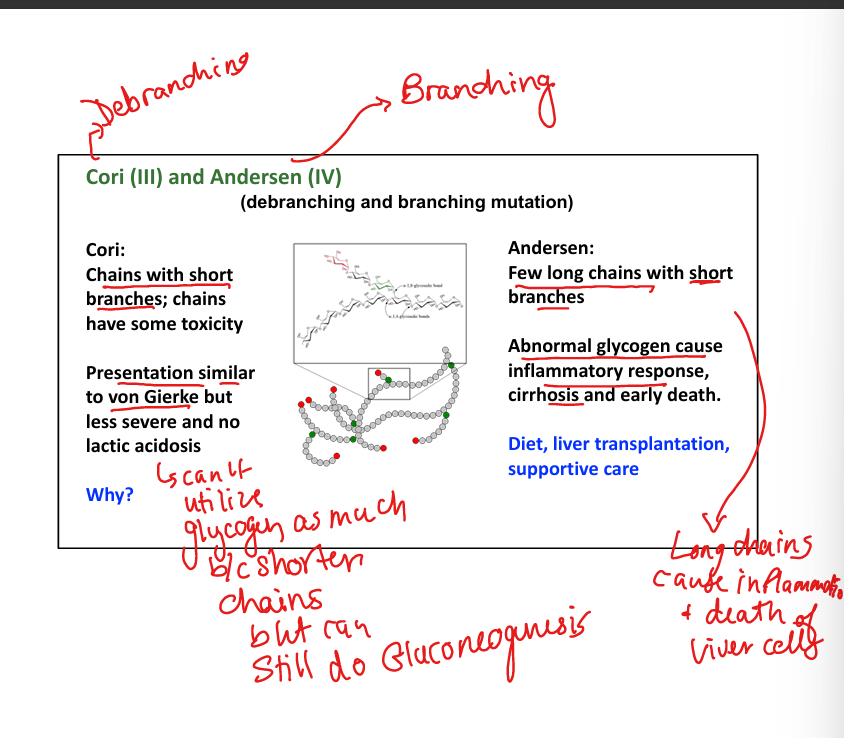

What causes Andersen disease (Type IV)?(A big Branch left a deficiency in my Anderson windows)
Branching enzyme deficiency. Few long chains, with short branches»Abnormal spreading»BAD
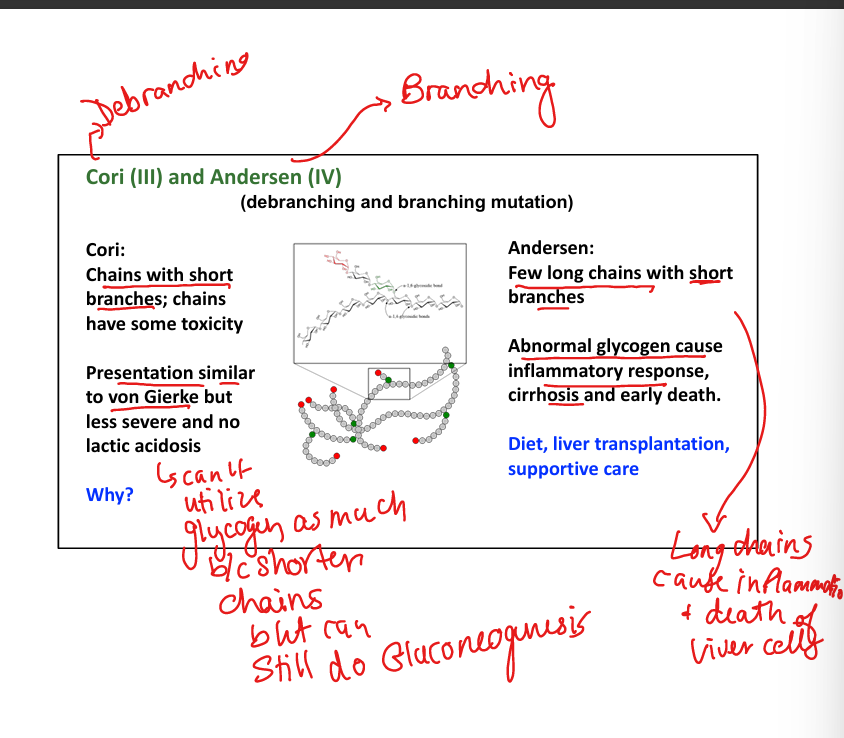

What are symptoms of Andersen disease?
Cirrhosis, liver failure, early death.

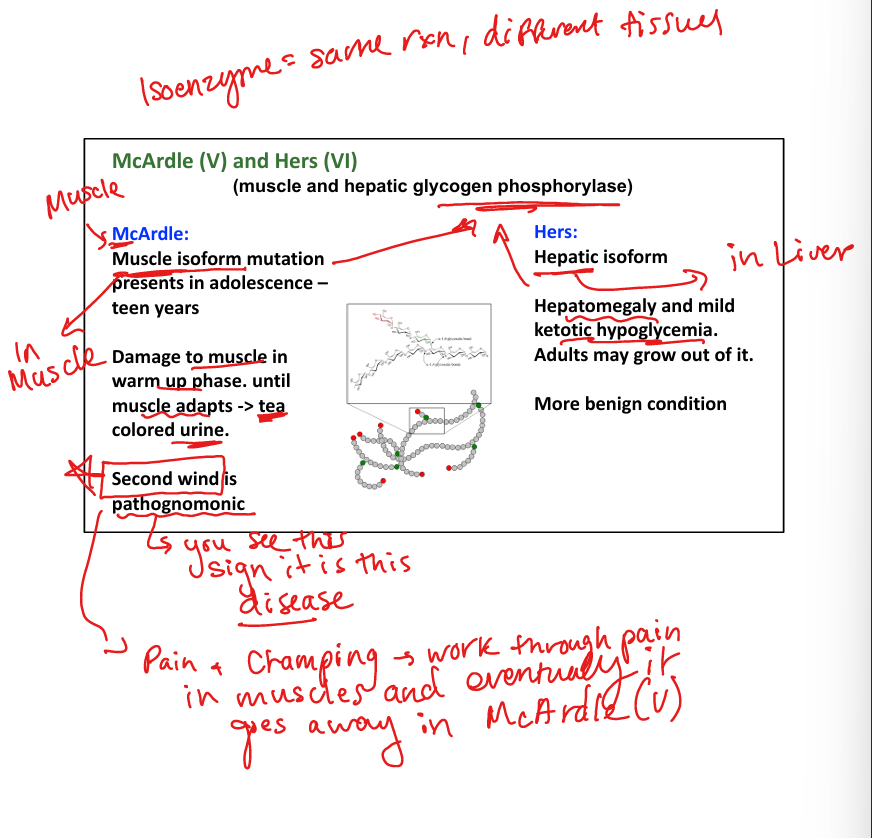
What causes McArdle disease (Type V)? (use my muscles to Warm up and McHurdle over things)
Muscle glycogen phosphorylase deficiency.
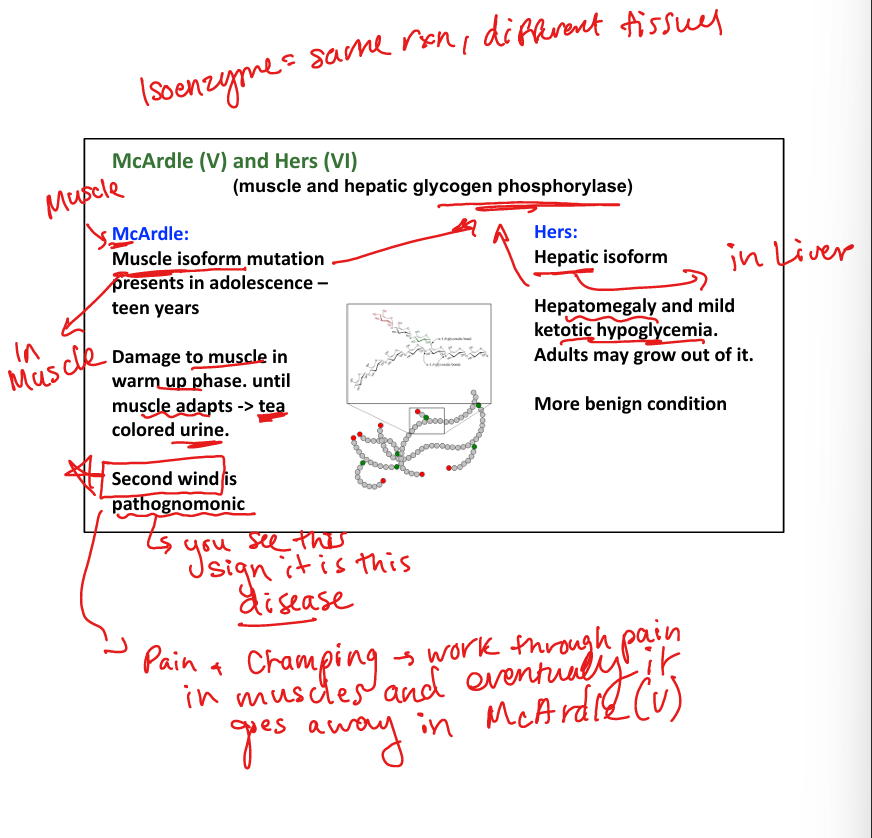

What are symptoms of McArdle disease?
Muscle cramps, tea-colored urine, second wind phenomenon.
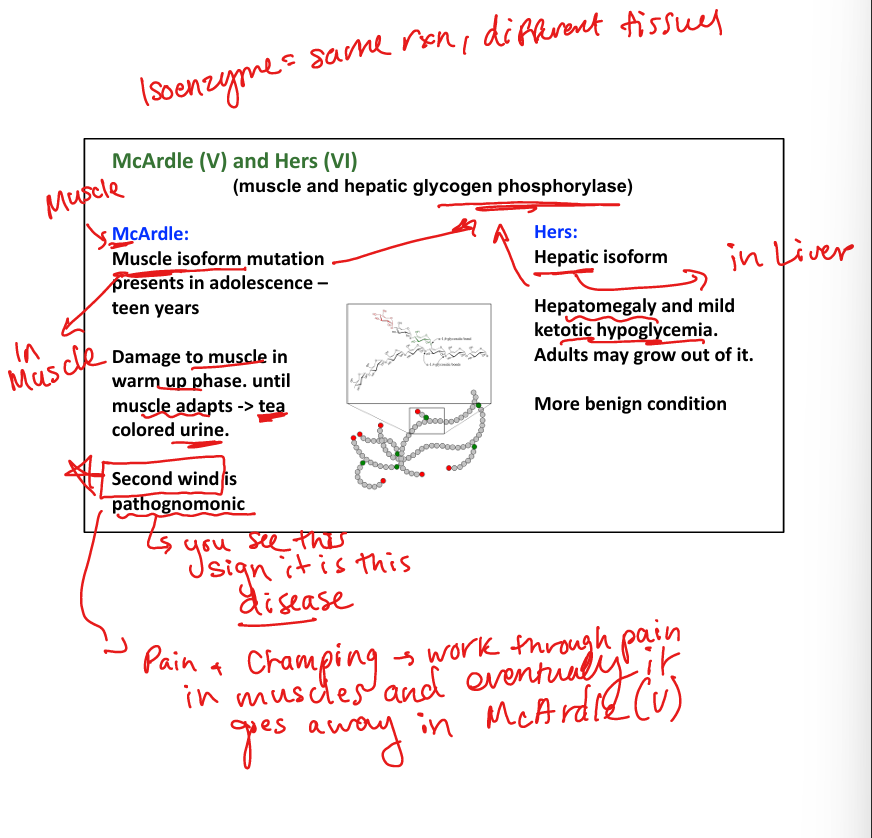

What causes Hers disease (Type VI)? (Her liver sugar defiency)
Liver glycogen phosphorylase deficiency.
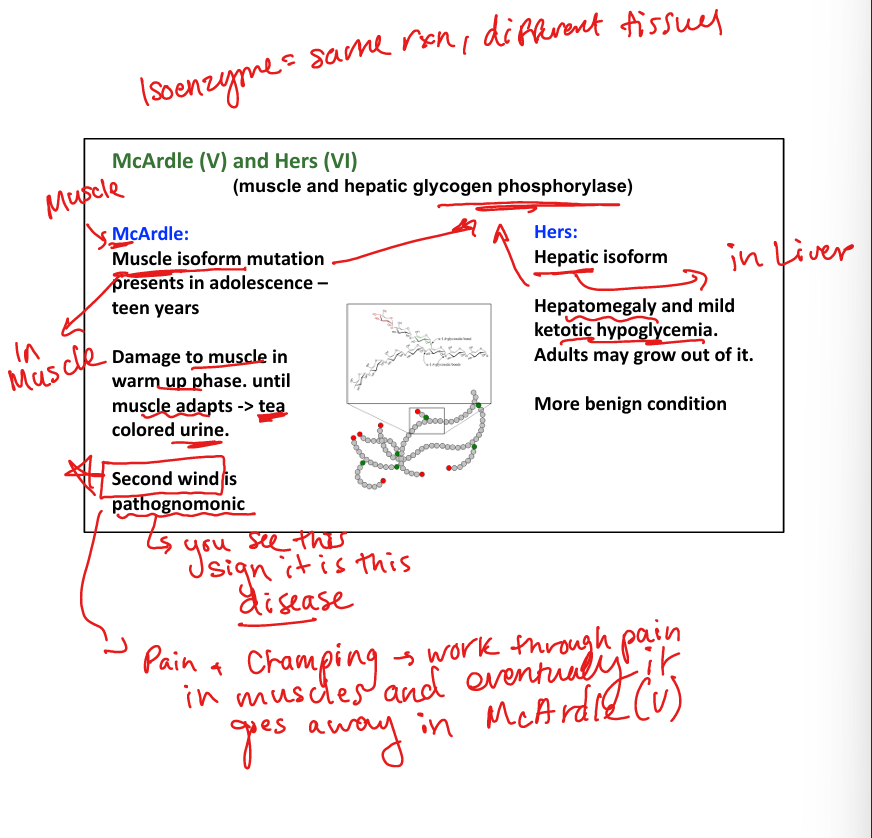

What are symptoms of Hers disease?
Mild hypoglycemia, hepatomegaly, benign course.

All the glycogen storage diseases