Key words - cell structure
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Carrier protein
A protein on the surface of a cell that helps to transport molecules and ions across a plasma membrane.
Centrifugation
Process of separating out particles of different sizes and densities by spinning them at high speeds in a centrifuge.
Cholesterol
Lipid that is an important component of cell-surface membranes.
Chromatid
One of the two copies of a chromosome that are joined together by a single centromere prior to cell division.
Chromosome
A thread-like structure made of protein and DNA by which hereditary information is physically passed from one generation to next.
Crossing over
The process whereby chromatid breaks during meiosis, rejoins to chromatid of its homologous chromosome (similar/corresponding features) so that their alleles are exchanged.
Differentiation
The process by which cells become specialised for different functions.
Diffusion
The net movement of molecules/ions from an area where they are at a higher concentration to areas where they are at a lower concentration.
Eukaryotic cell
A cell that has a membrane-bound nucleus and chromosomes.
Facilitated diffusion
Diffusion involving the presence of carrier protein molecules to allow the passive movement of substances across plasma membranes.
Glycoprotein
Substance made up of carbohydrates and proteins. Allows wbc to move around the body and initiate immune responses as it identifies other cells.
Glycolipid
Lipids with a carbohydrate attached by a glycosidic bond. They maintain the stability of the cell membrane and they facilitate cellular recognition.
Granum
Stack of thylakoids(sacs bound to membrane) in a chloroplast that resembles a pile of coins, this is the site of the light-dependent reaction of photosynthesis.
Guard cell
One of a pair of cells that surround a stoma in plant leaves and controls its opening and closing.
High-density lipoprotein (HDL)
Compound of protein and lipid molecules found in blood plasma, transports cholesterol from other cells to the liver.
Intrinsic proteins
Proteins of cell-surface membrane that completely span the phospholipid bilayer from one side to another.
Ion
An atom or group of atoms that have lost or gained one or more electrons.
Ion channel
A passage across a membrane, it is made up of a protein that spans the membrane and opens/closes to allow ions to pass in/out of the cell.
Isotonic
Solutions that possess the same concentration of solutes and therefore have the same water potential.
Isotope
Variations of chemical element, same number of protons/electrons but different number of neutrons.
In vitro
Refers to an experiment that is carried out outside of the living body - test tubes.
In vivo
Refers to an experiment that is being carried out within living bodies.
Kinetic energy
Energy that an object possesses due to its motion.
Low density lipoprotein (LDL)
Compound containing both protein and lipid molecules that occurs in blood plasma and lymph, carries cholesterol from liver to other body cells.
Meiosis
Type of nuclear division in which number of chromosomes is halved.
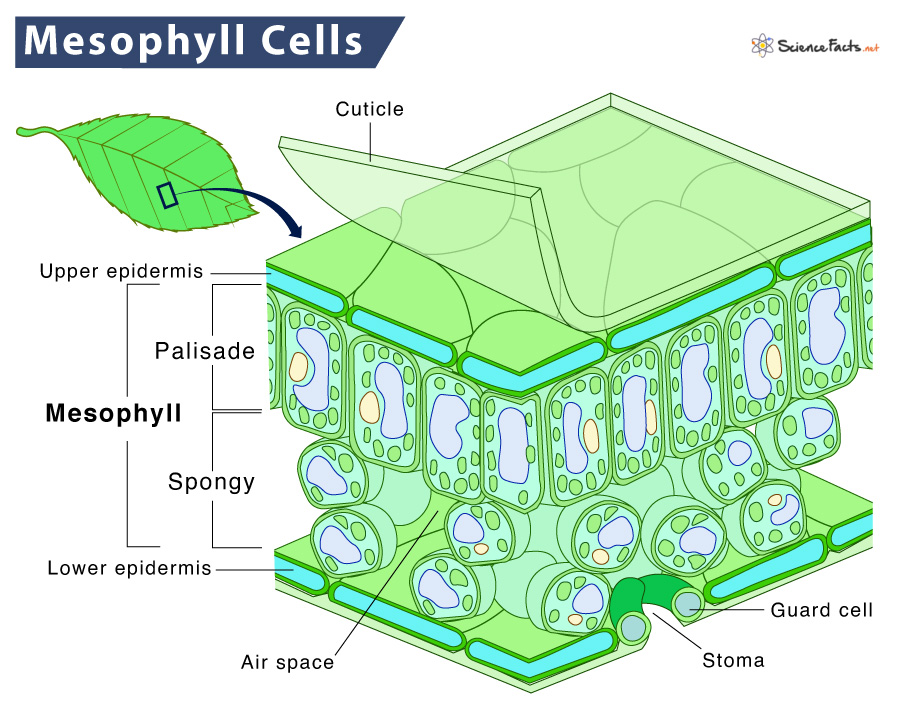
Mesophyll
Tissue found between two layers of epidermis in a plant leaf, compromising of an upper layer of palisade cells and a lower layer of spongey cells.
Metabolism
All the chemical processes that take place in living organisms.
Microvilli
Tiny finger-like projections from the cell-surface membrane of some animals.
Middle lamella
Layer made up of pectins and other substances found between the walls of adjacent plant cells.
Mitosis
Type of nuclear division in which daughter cells have same number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
Mono-unsaturated fatty acid
Fatty acid that possesses a carbon chain with a single double bond.
Polyunsaturated fatty acid
Fatty acid that possesses carbon chains with many double bonds.
Osmosis
The passage of water from a region of high water potential to a region where it’s water potential is lower, through a partially permeable membrane.
Palisade cells
Long, narrow cells packed with chloroplasts that are found in the upper region of a leaf - carries out photosynthesis.
Peptide bond
Chemical bond formed between two amino acids during condensation.
Phagocytosis
Mechanism by which cells engulf particles to form a vesicle or a vacuole.
Phloem
Plant tissue that transports the products of photosynthesis from a leaf to the rest of the plant.
Phospholipid
Triglycerides in which one of three fatty acids is replaced by a phosphate.
Plasmid
A small circular piece of DNA found in bacterial cells.
Prokaryotic cells
A cell that does not have a nucleus or membrane bound organelles.
Protoplast
Living portion of a plant cell - nucleus and cytoplasm.
Recognition site
Nucleotide sequences that is recognised by a restriction endonuclease and to which it attaches.
Receptor
Cell adapted to detect changes in environment.
Saturated fatty acid
Fatty acid where there are no double bonds between carbon atoms
Unsaturated fatty acid
Fatty acid where there are one or more double bonds between carbon atoms.
Sodium-potassium pump
Protein channels across membrane that use ATP to move sodium ions out of the cell in exchange for potassium ions that move in.
Stem cell
Undifferentiated dividing cells that occur in embryos and in adult animal tissues that require constant replacement.
Stoma
A pore, mostly in the lower epidermis of a leaf, where gases diffuse in and out of the leaf.
Stroma
Matrix of a chloroplast where the light-independent reaction of photosynthesis takes place.
Supernatant liquid
The liquid portion of a mixture left at the top of the tube when suspended particles have been separated out during centrifugation.
Thylakoid
Series of flattened membranous sacs found in the chloroplasts that contain chlorophyll and the associated molecules needed for the light-dependent reaction of photosynthesis.
Triglyceride
Lipid made of glycerol and three fatty acids.
Ultrafiltration
Filtration, in the kidney, to remove products like urea, glucose, water etc. from the blood - assisted by blood pressure.
Voltage-gated channels
Protein channels across a membrane that opens and closes according to changes in the electrical potential across the membrane. (Difference in charge on either side of cell membrane as there may be a slight excess of ions, potential ranges from -80mV to -40mV).
Water potential
The pressure created by water molecules, it is the measure of the extent to which a solution gives out water.
Xerophyte
A plant adapted to living in dry conditions.
Xylem vessels
Dead, hollow, elongated tubes with lignified side walls and no end walls, that transport water in most plants.