general chemistry
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Law of Conservation of mass
“building blocks” cannot be created or destroyed, but are rearranged in reactions
Law of definite proportion
“building blocks” form into specific ratios for different compounds
Atomic Theory
combines the law of conservation of mass and the law of definite proportions
Law of Multiple proportion
atoms combine into ratios of simple integers
Avogadro’s Hypothesis
at the the same temperature and pressure the same volume of gas containes the same number of particles
J.J Thompsons cathode ray experiment
measured the charge-to-mass ratio of electrons, bending electrons with electric and magnetic field
What Dalton’s Atomic Theory got wrong
Atoms are indivisible and indestructible
mass of atoms determines the identity of atoms
Oil Drop Experiment
Significant because it measured the charge of an electron
Gold foil experiment
Discovery of the nucleus (no more plum pudding!!)
Mass spectrometry
Discovery of Isotopes
Protons
Charge of +1
In the nucleus
determines the identity of atoms
the number of them determines the atomic number
Neutrons
neutral
in nucleus
“glue” that holds nucleus
Electrons
-1 charge
To find the charge of a chemical symbol #protons-#electrons
Blackbody
Energy level is quantized (in specific amounts)
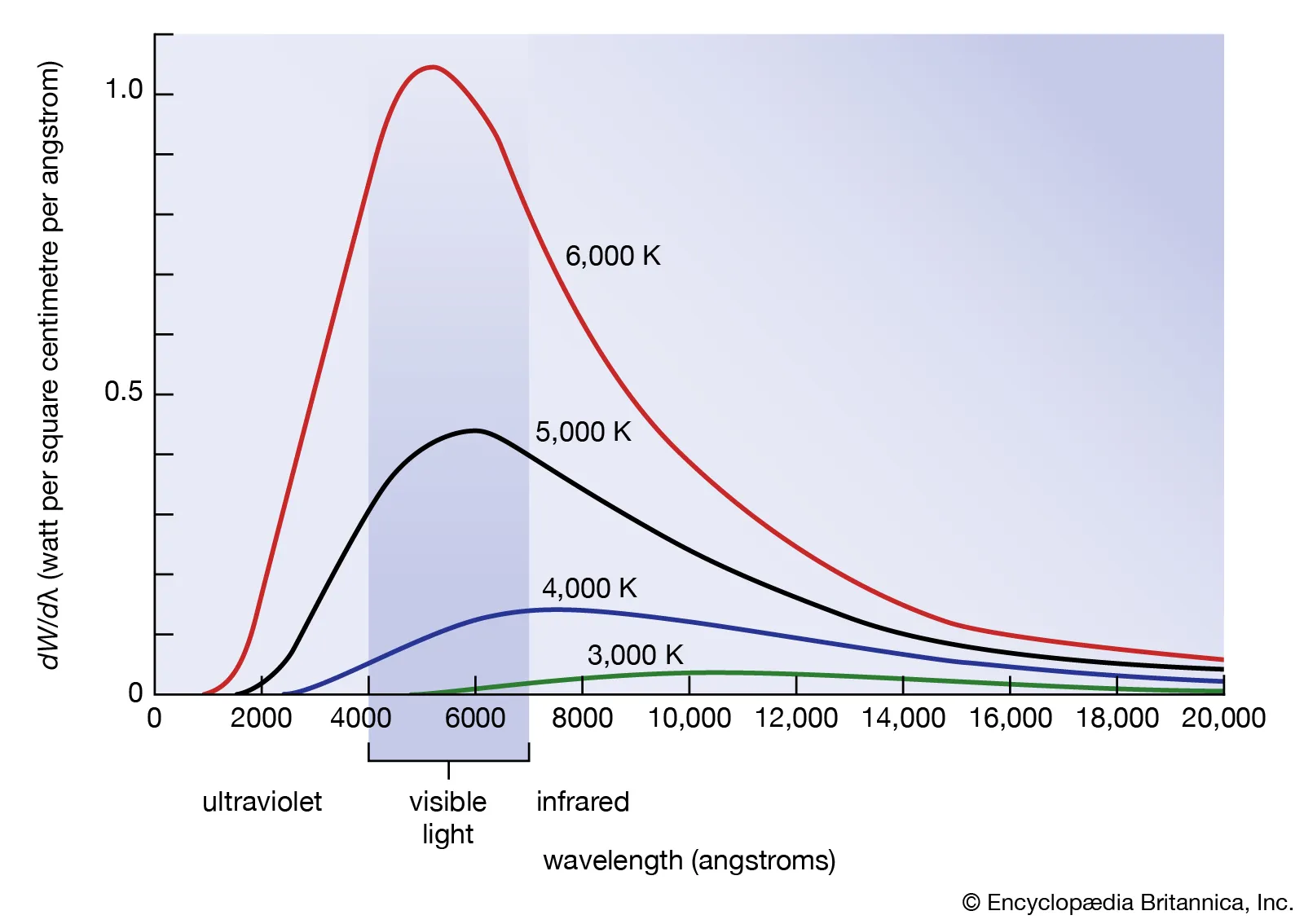
Ultraviolet catastrophe
classical physics says that a blackbody emits infinite amounts of energy at high frequencies. This is physically impossible
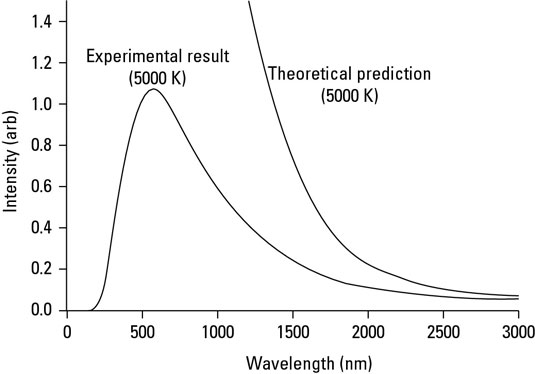
Quantum Mechanics and blackbody
The black body can only absorb or emit energy in specific energy packets or “quanta”
Photoelectric effect
Discovery of the photon
experimental observations explained that increased intensity leads to more electrons ejected but kinetic energy stays the same
below the threshold frequency electrons cannot be ejected
below the threshold frequency photons do not have have enough energy to eject electrons
An increased frequency of light means an increase in kinetic energy
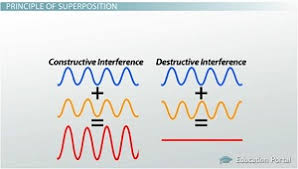
Two-slit experiment with electrons
Shows that electrons have wave like behavior
Electrons + two slit= interference pattern
Only waves can have constructive and destructive interference
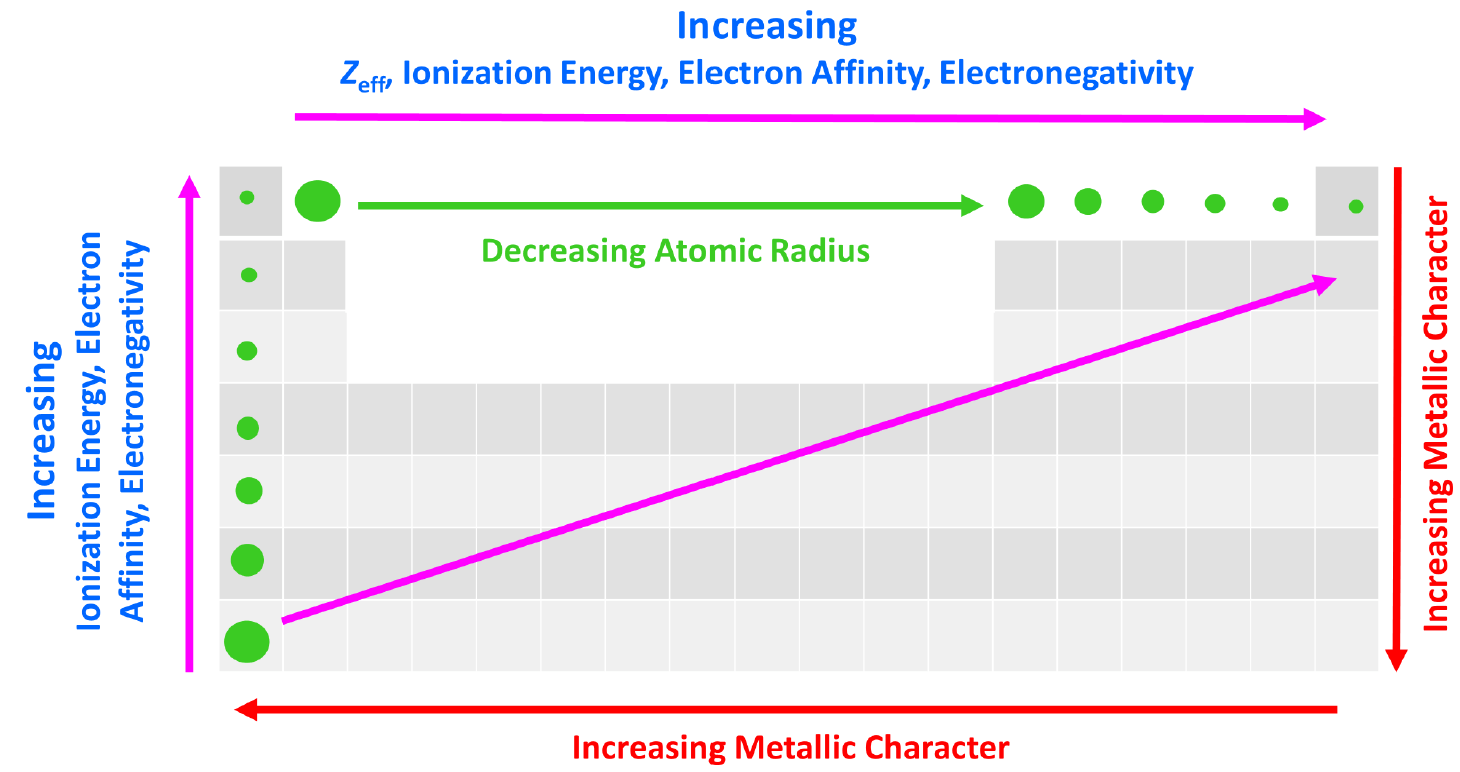
effective nuclear charge
Nuclear charge decreases when there is an increase of shielding
Increase in nuclear charge with an increasing atomic number, number of protons added to the nucleus
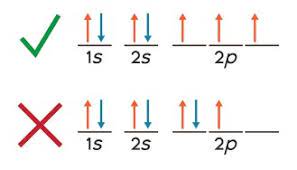
Aufbau Principle
add electrons to the orbitals with lowest energy
Hund’s rule
add electrons to empty orbital with parallel spin rather than pairing up
Ground state
electron configuration obeys all rules
Excited state
electron configuration violates hunds rule or aufbau principle
Atomic Radii
Increases going to the left and down a group
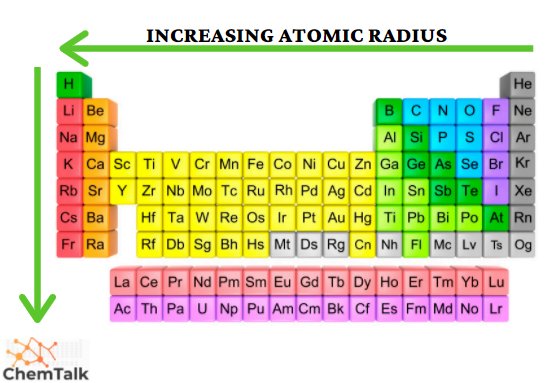
Effective nuclear charge
increases going to the right because electrons are closer to the nucleus
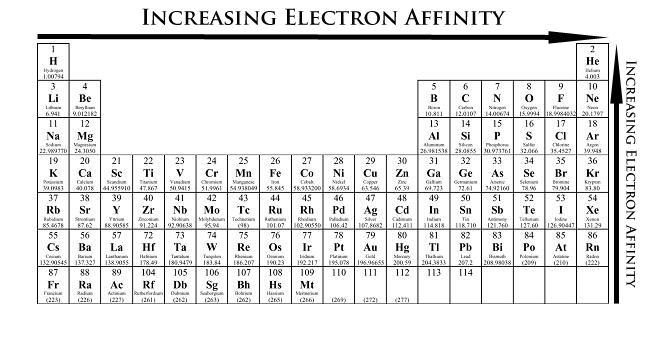
Electron affinity
the energy released when an electron is added
Exceptions in electron configuration
Cr[Ar]4s^13d^5
Cu[Ar]4s^13d^10
Ionization energy
energy required to remove an electron

covalent bonds
when electrons are shared
ionic bonds
when electrons are transferred