Genetic Engineering Tools and Editing
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What does a restriction endonuclease do
enzymes (eg EcoR1) which cut DNA at a specific sequence of bases called a restriction site
Make staggered cuts leaving unpaired single stranded ends
Exposed bases form H-bonds to base pair with complementary sticky ends produced by same restriction enzyme
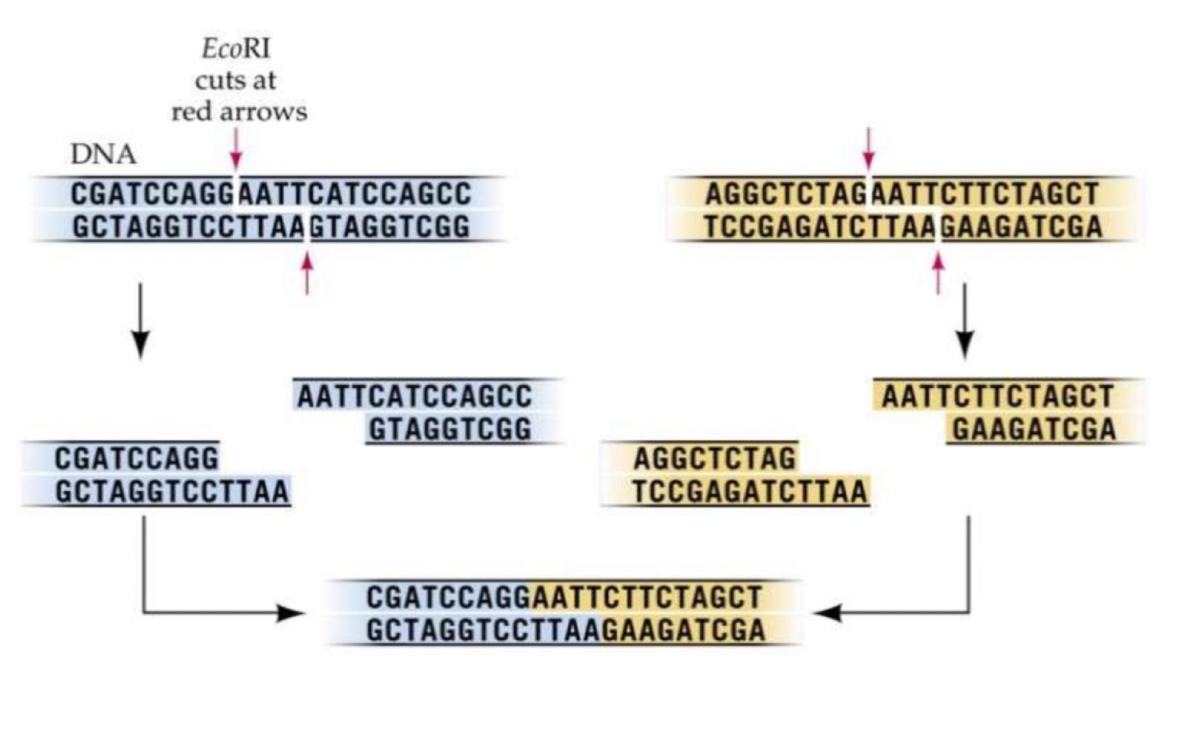
What is an example of a sequence recognised by restriction endonucleases
often palindromic

What are the 3 ways by which genes can be obtained
extracted directly from donor organism using restriction endonucleases
Synthesised chemically from nucleotides
Synthesised from the mRNA of a donor organism
Eg extract mRNA for insulin from the β cells of the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas
How can genes be obtained using mRNA
extract correct mRNA identified by size (eg for insulin from the β cells of the islets of Langerhams in the pancreas)
Use enzyme reverse transcriptase to produce a single stranded cDNA copy
Then add DNA polymerase to make this double stranded.
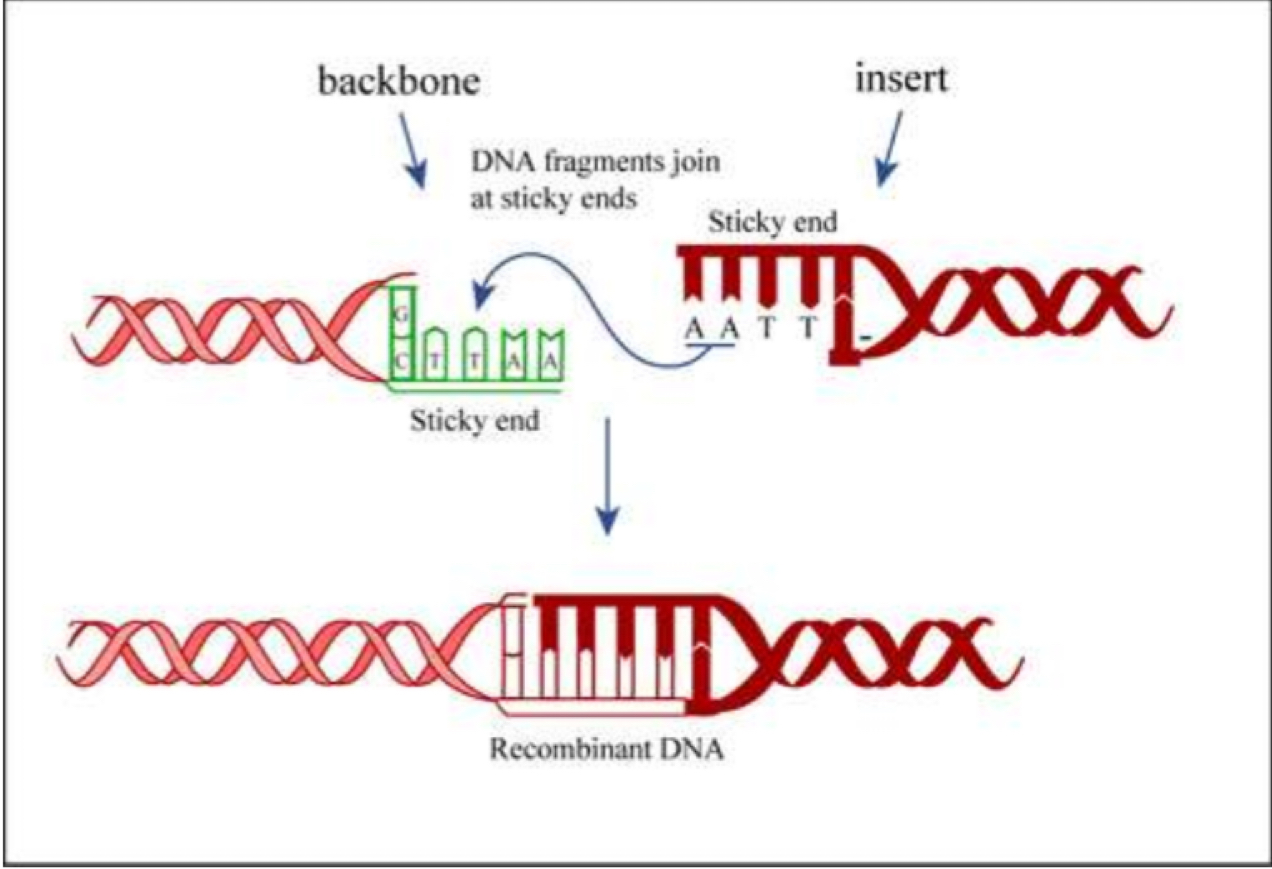
How is a recombinant DNA formed
Recombinant DNA by joining pieces of DNA from two or more different sources
Genes can be transferred from one species to another different species to form a transgenic organism because the genetic code is universal, so any gene can be expressed.
Transgenic organisms can produce a new protein on top of their existing proteome, gaining a new characteristic.
DNA ligase catalyses the formation of phosphodiester bonds to seal the “gap” in sugar phosphate backbone creating the recombinant DNA.
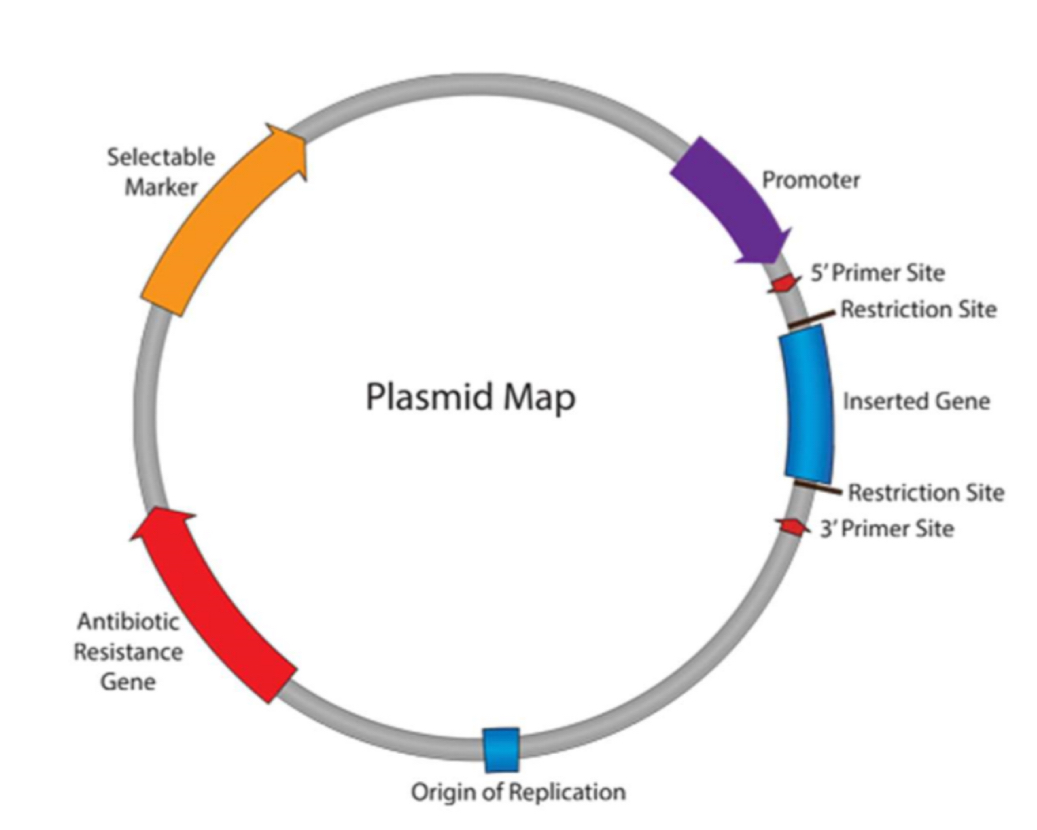
What is a plasmid and explain its structure
small, circular piece of DNA which replicates independently of the main chromosome
Small - easily taken up by bacteria
Circular - stable
Contain origin of replication - can replicate independently and produce large numbers of plasmids
Restriction sites - genes can be added
Marker genes (eg antibiotic resistance or GFP) - transformed bacteria can be identified
What are examples of vectors used to move genes into another organism
plasmids
Viruses (eg retroviruses)
Liposomes - tiny spheres of lipid containing DNA
How can bacteria be forced to take up plasmid vectors
by being placed int concentrated calcium ion solution and ‘heat shocked’ - put in very hot environment, then cold, then hot etc. the bacteria become transformed
How can plasmids be inserted into plant cells, and what type of plasmid
specific bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Ti plasmids
What are GFPs and what can it be used as
Green fluorescent proteins, as a selectable markers
How do GFPs work as selectable markers
transformed cells produce the protein which is fluorescent under UV light
Use a gene which produces an enzyme which converts colourless substrates into colourless ones therefore a small quantity of protein can produce a visible result.
What is the danger of using antibiotic resistant genes as marker genes
Gene could be transferred into other species of potentially pathogenic bacteria
What needs to happen to a gene to produce their protein and what is it controlled by
needs to be expressed, controlled by the promoter region where RNA polymerase binds.
What is needed to transfer genes from eukaryotes to prokaryotes
an expression vector (ie plasmid with relevant promoter) so that desired gene is expressed
How was the gene for human insulin expressed in bacteria
enzyme β-galactosidase only expressed in the presence of lactose
Insulin gene was inserted next to the β-galactosidase gene so they shared a promoter.
By growing bacterium in presence of lactose, both genes would be expressed and insulin produced
What does gene editing allow
genetic material to be added, removed or altered at specific locations in the genome, thus offering the treatment of diseases by cutting out or replacing mutated genes
How does gene editing differ from genetic engineering
Gene editing involves the modification of the existing DNA
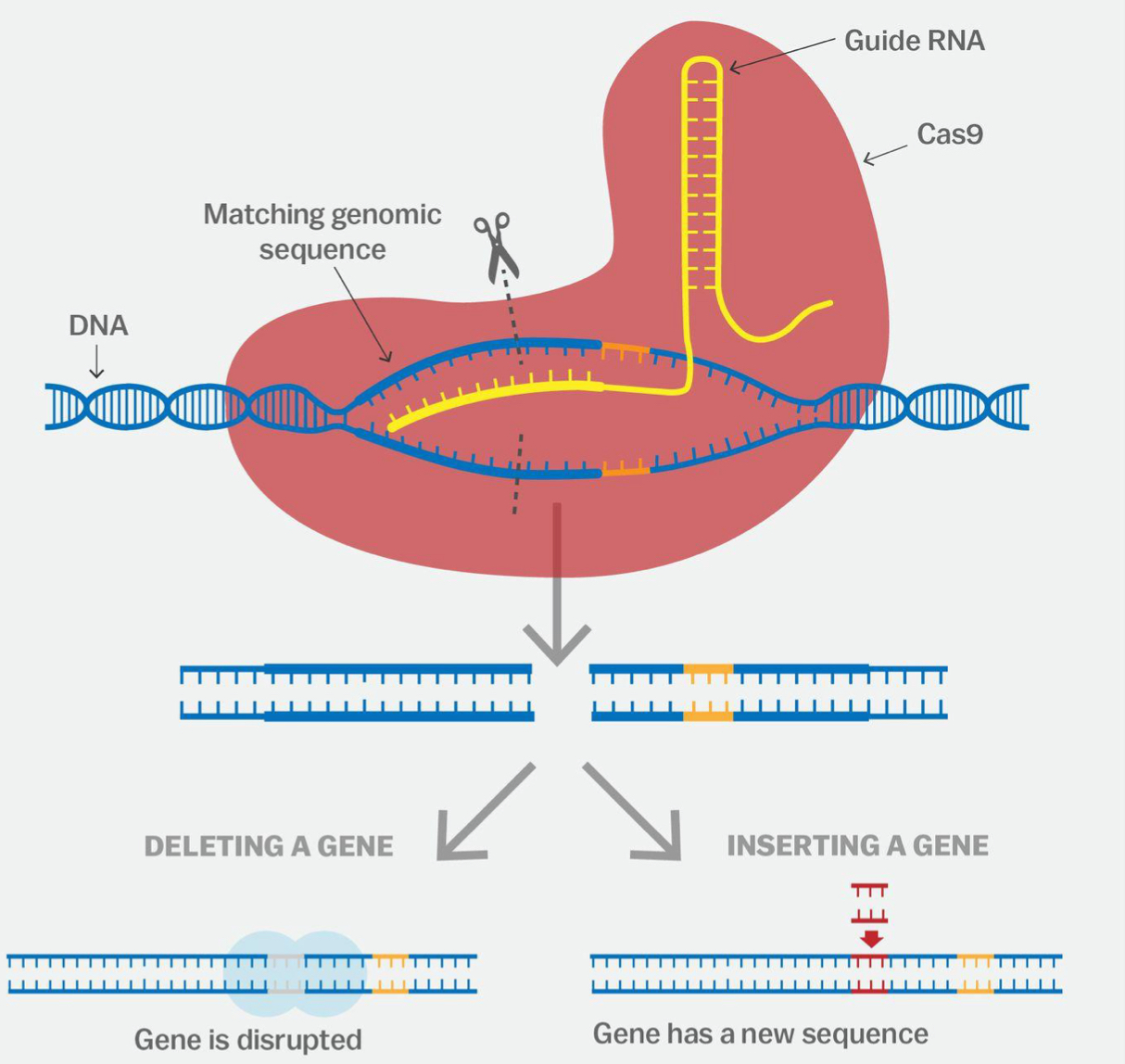
How does the gene editing technique CRISPR work
uses short RNA template which matches the DNA target sequence in the genome
RNA template guides Cas9 enzyme to targeted DNA sequence
Cas9 cuts genome at this point to allow the editing to occur