Musculoskeletal Diagnostic Imaging
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering essential vocabulary and definitions for musculoskeletal diagnostic imaging and related conditions.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
Epiphysis
The end of a long bone which connects to joints.
Metaphysis
The region between the epiphysis and diaphysis that grows during childhood.
Diaphysis
The tubular midportion of the shaft of a long bone.
CT Scan
A detailed examination of bones that can pick up fractures missed by X-rays.
MRI
Imaging technique used to evaluate soft tissues such as tendons and ligaments.
Open Reduction Internal Fixation (ORIF)
A surgical procedure used to stabilize and heal fractured bones.
Subluxation
An incomplete or partial dislocation of a joint.
Dislocation
An injury where a bone is displaced from its proper position.
Osteoarthritis
Chronic degeneration of articular cartilage, common in weight-bearing joints.
Osteoporosis
Loss of bone density over time, commonly seen in postmenopausal women.
Malignant Bone Tumors
Tumors with poorly defined margins; can disrupt cortical bone.
Benign Bone Tumors: Osteochondroma
The most common benign bone tumor, painless and usually found incidentally.
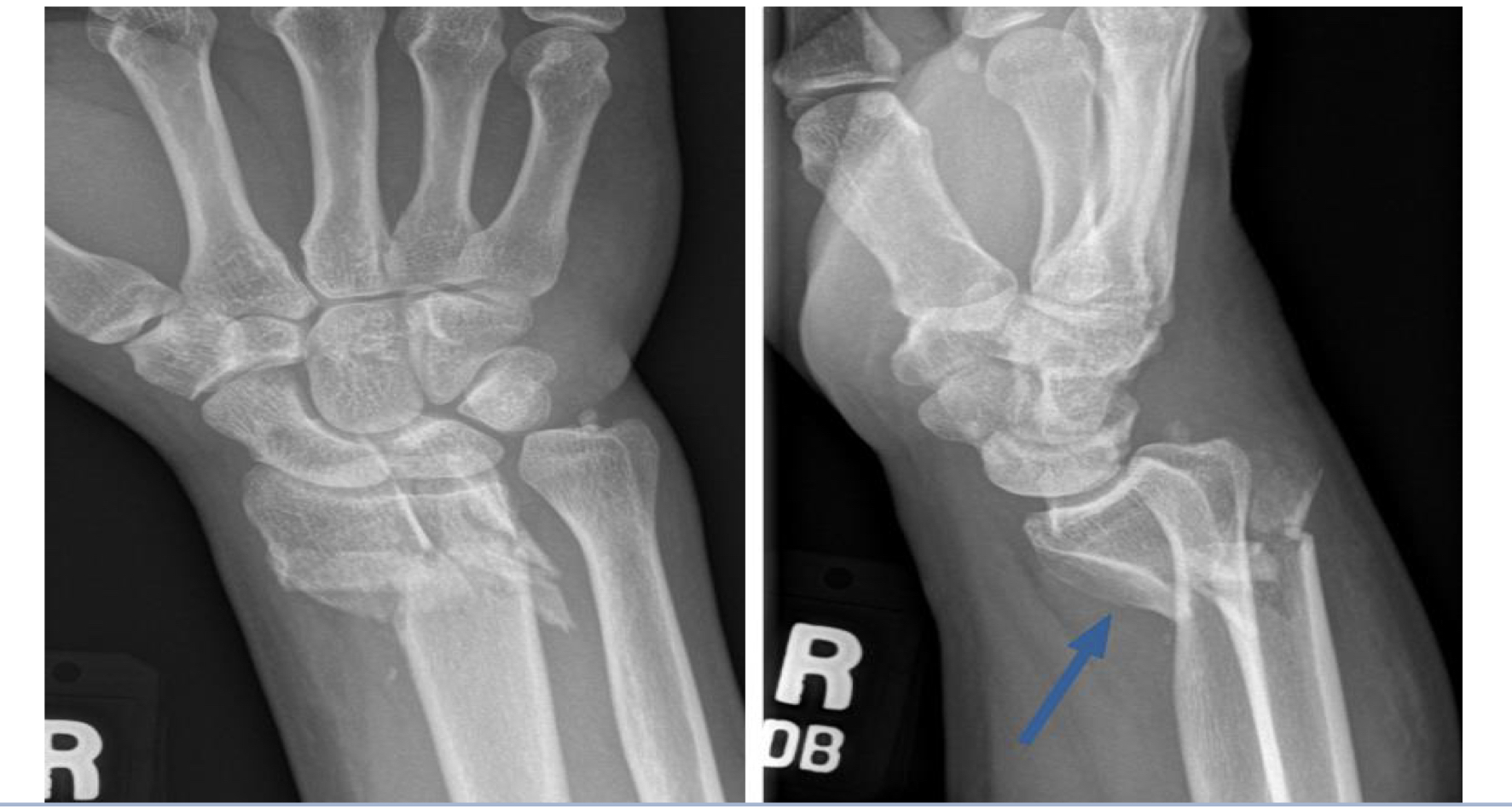
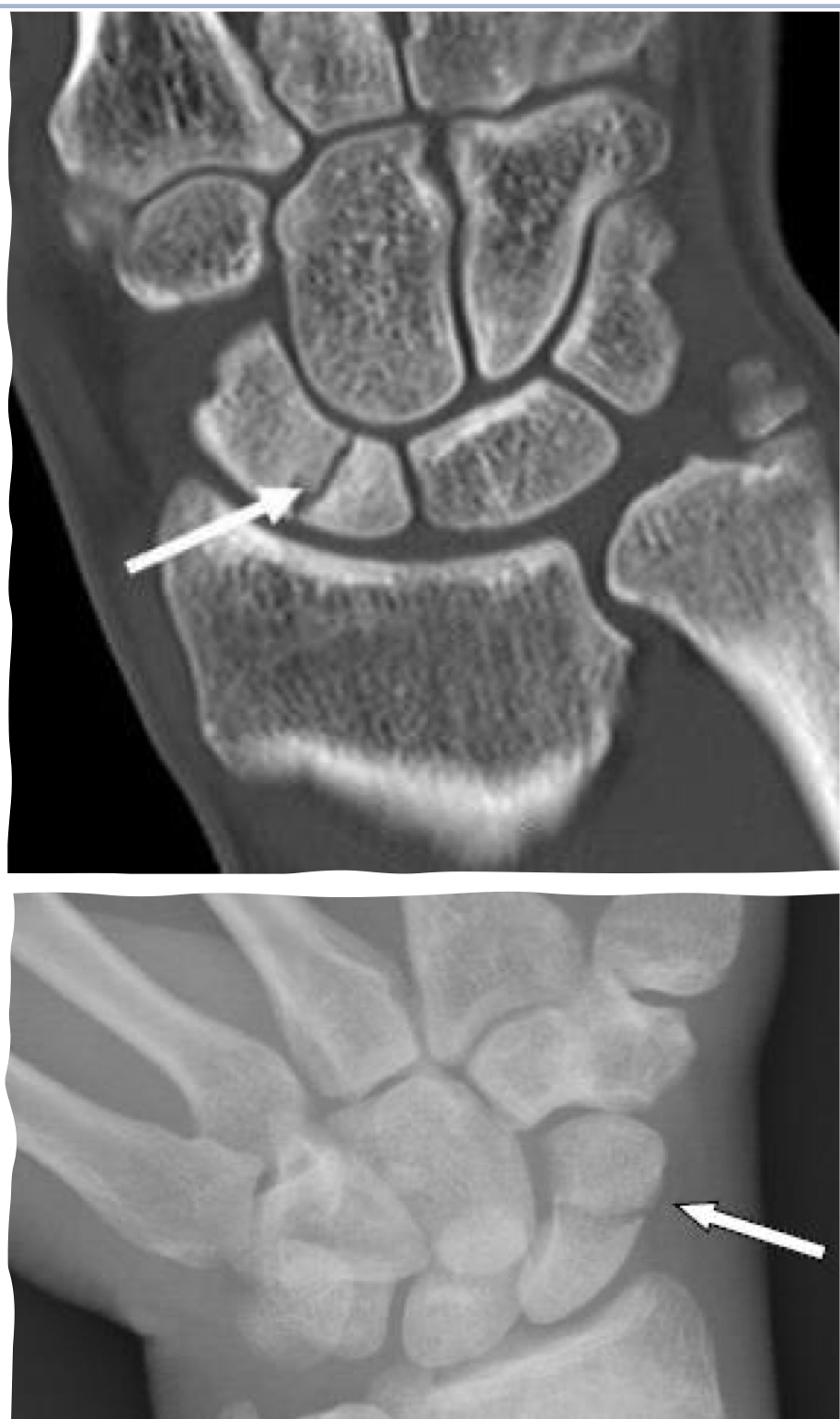
Scaphoid Fracture
Typically caused by a fall on an outstretched hand; can lead to avascular necrosis.
Colle's Fracture
Fracture of the distal radius with dorsal displacement, commonly seen in elderly.
Buckle Fracture
A type of stable fracture typically occurring in children from axial loading.
Salter Harris Fractures
Fractures of the growth plate in children, classified into five types.
Ewing's Sarcoma
A bone tumor occurring mostly in younger patients, often mimics osteomyelitis.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
A chronic autoimmune disease causing joint inflammation and destruction.
Osteomyelitis
An infection and inflammation of the bone, often due to underlying conditions.
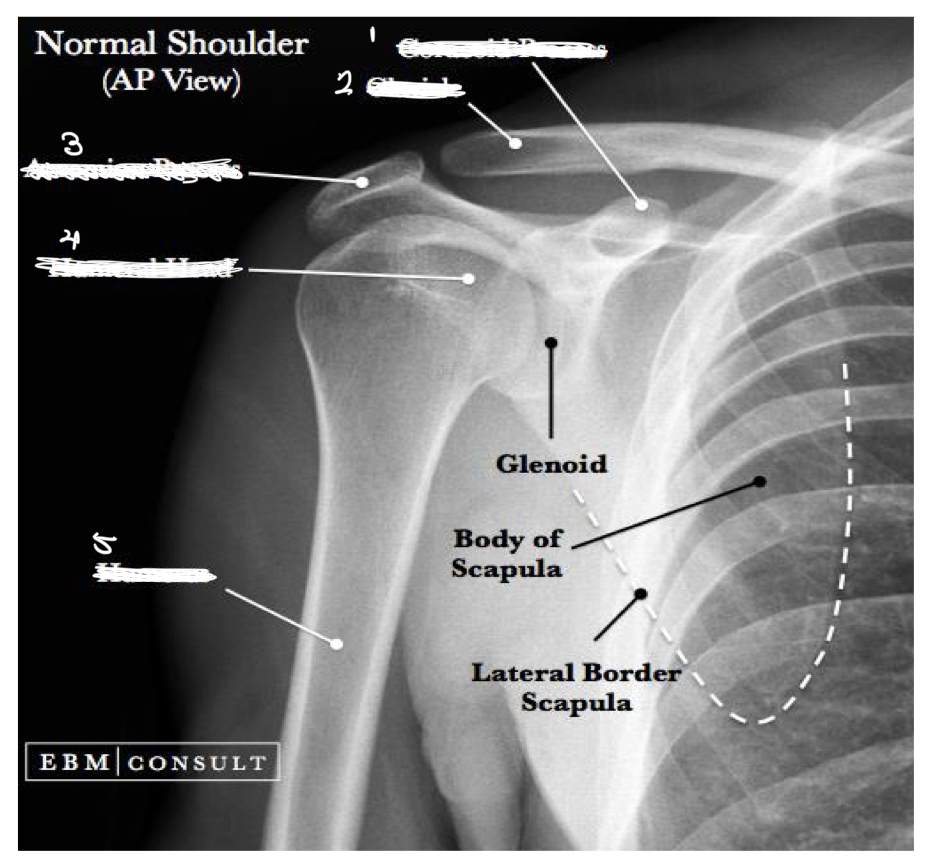
1- corocoid process
2- clavicle
3- acromion process
4- head of humerus
5- humerus
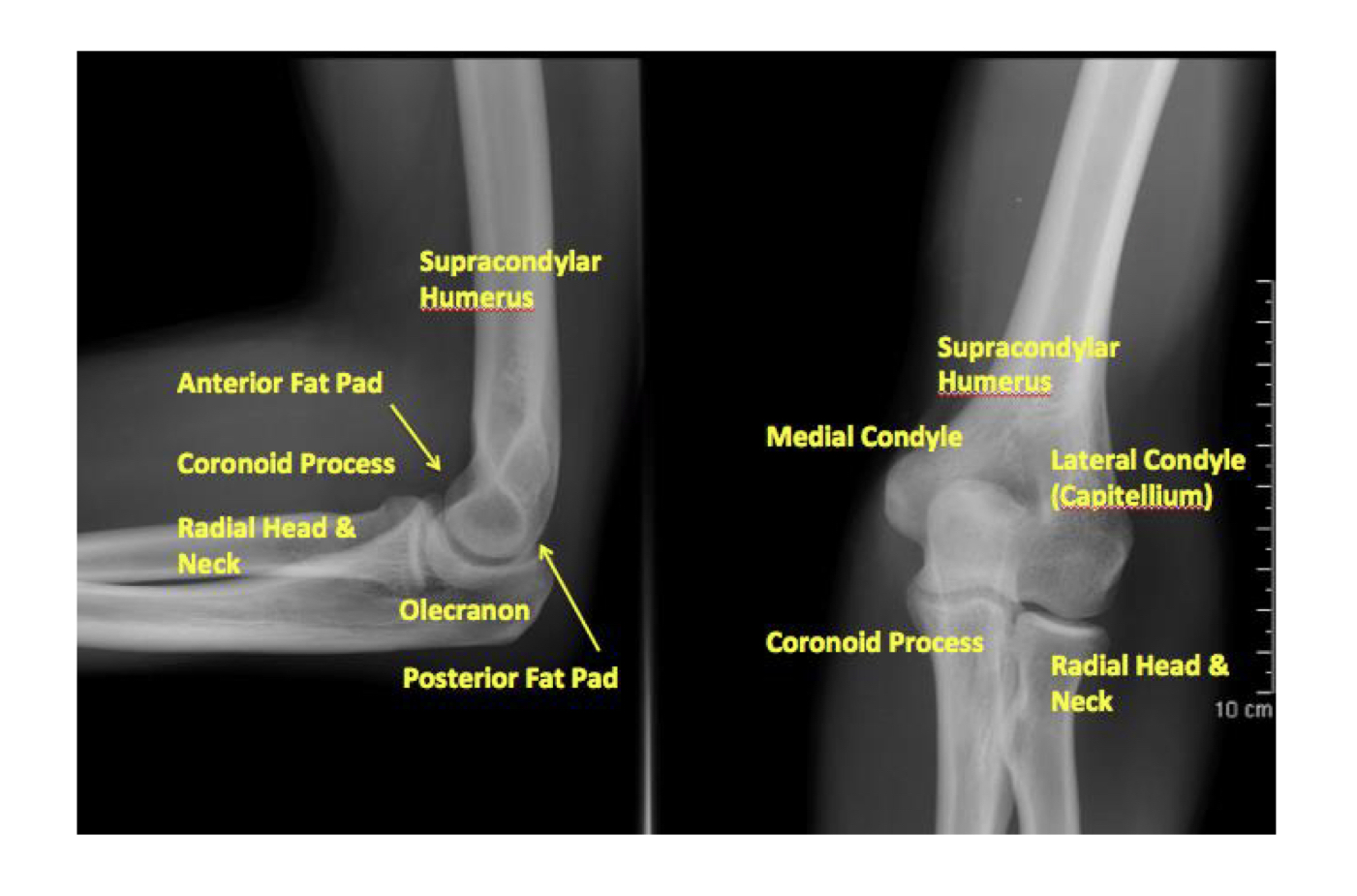
Know condyles
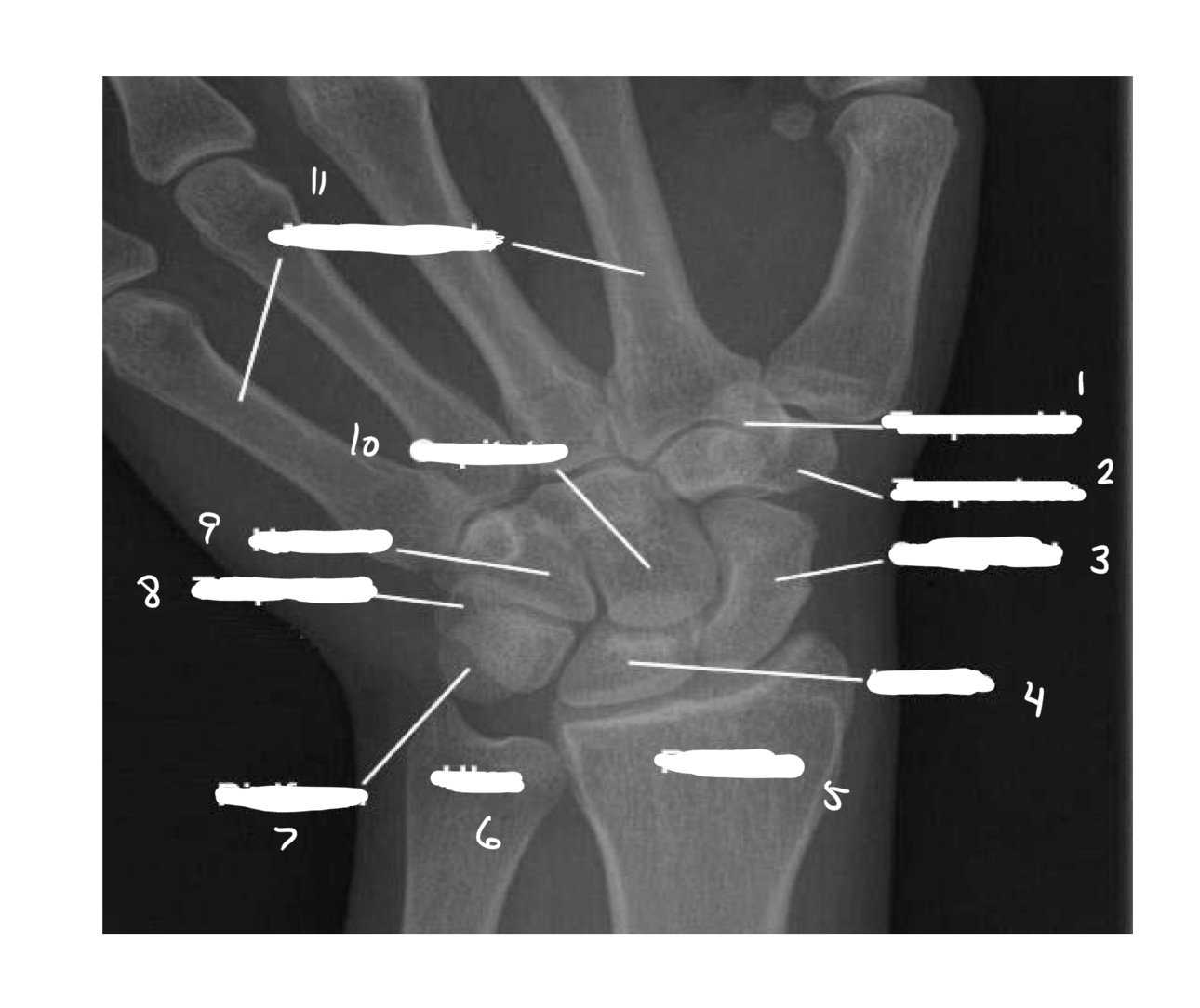
1- trapezoid
2- trapezium
3- scaphoid
4- lunate
5- radius
6- ulna
7-pisiform
8- triquetral
9- hamate
10- capitate
11- metacarpals
Sesamoid bone
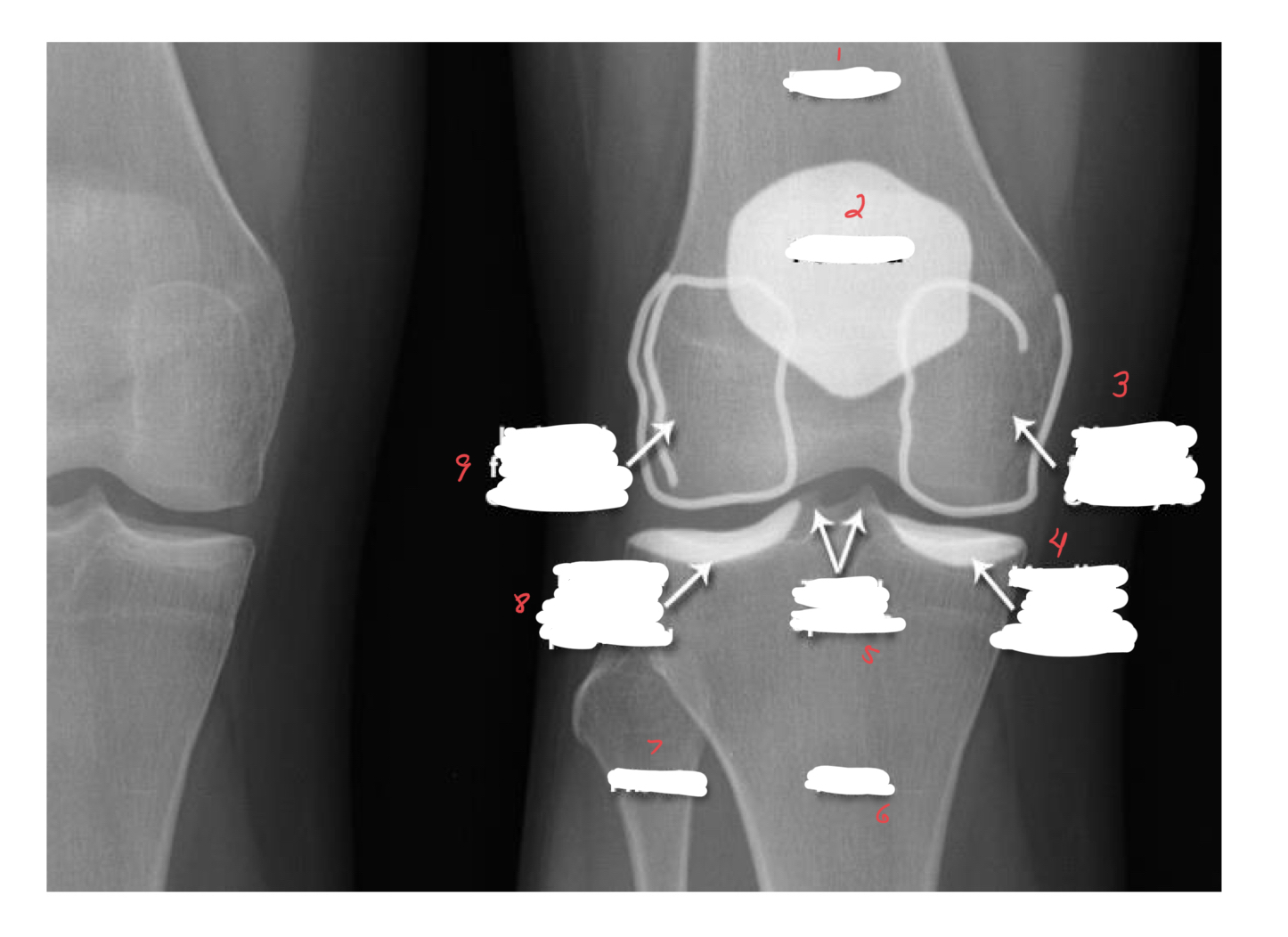
1-femur
2-patella
3-medial femoral epicondyle
4-medial tibial plateau
5-tibial spine
6-tibia
7-fibula
8-lateral tibial plateau
9-lateral femoral epicondyle
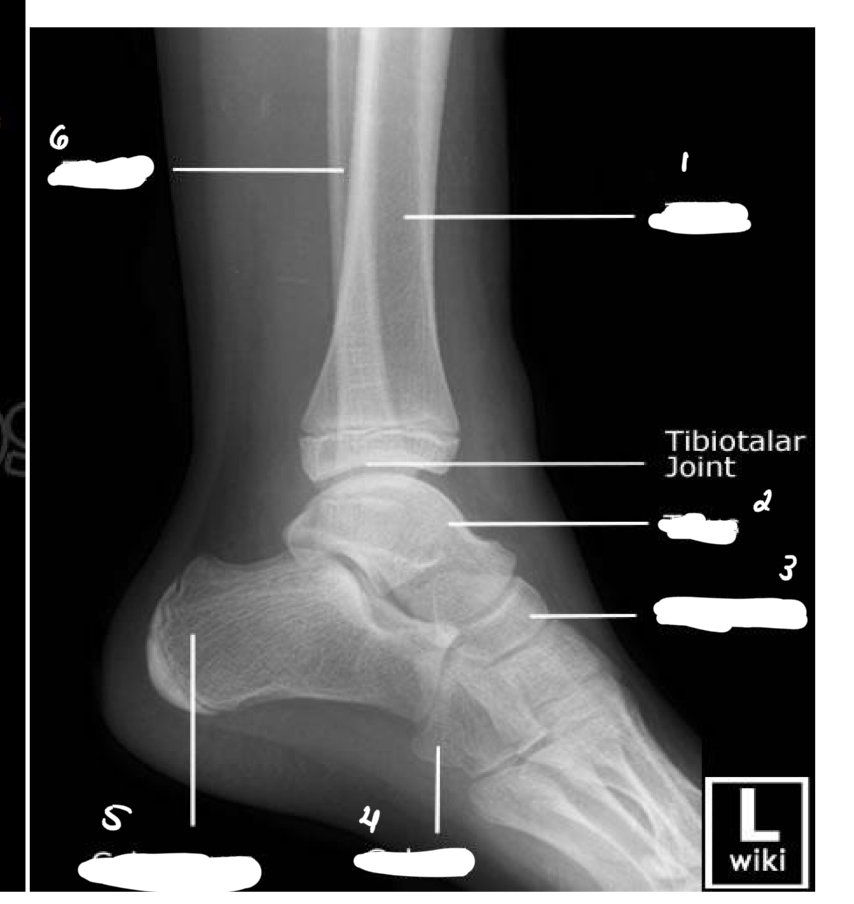
1-tibia
2-talus
3-navicular
4-cuboid
5-calcaneum
6-fibula
Fall on outstretched arm and direct blow
Subluxation of the first finger
Pt fell
Dislocation
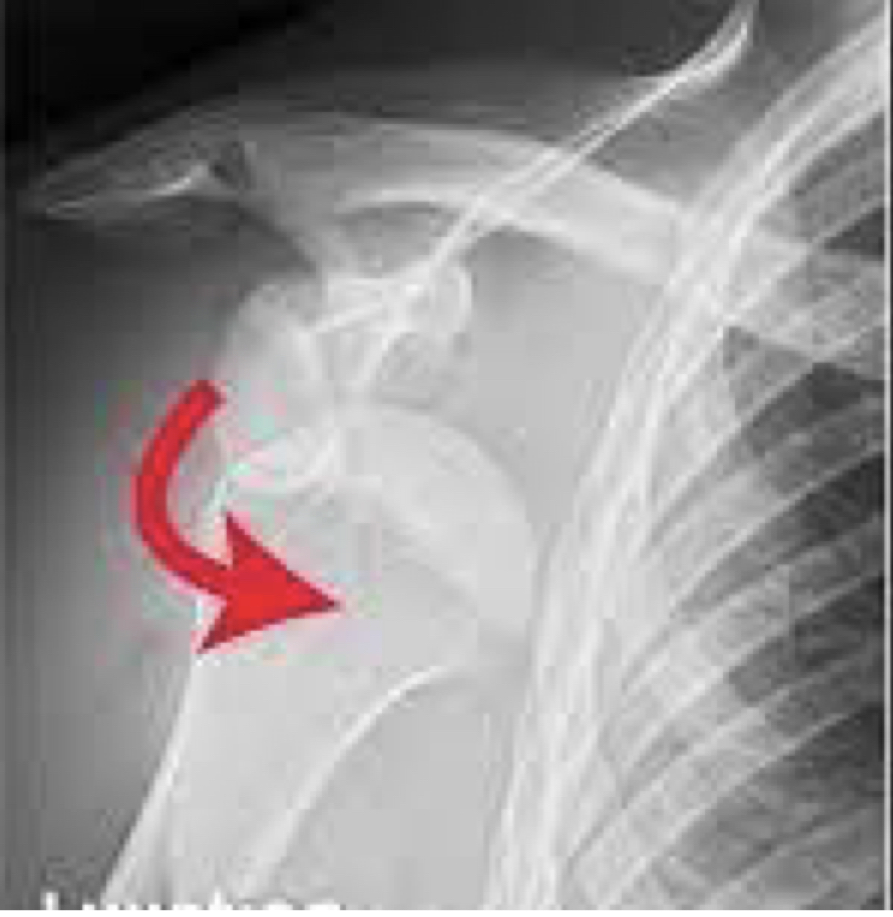
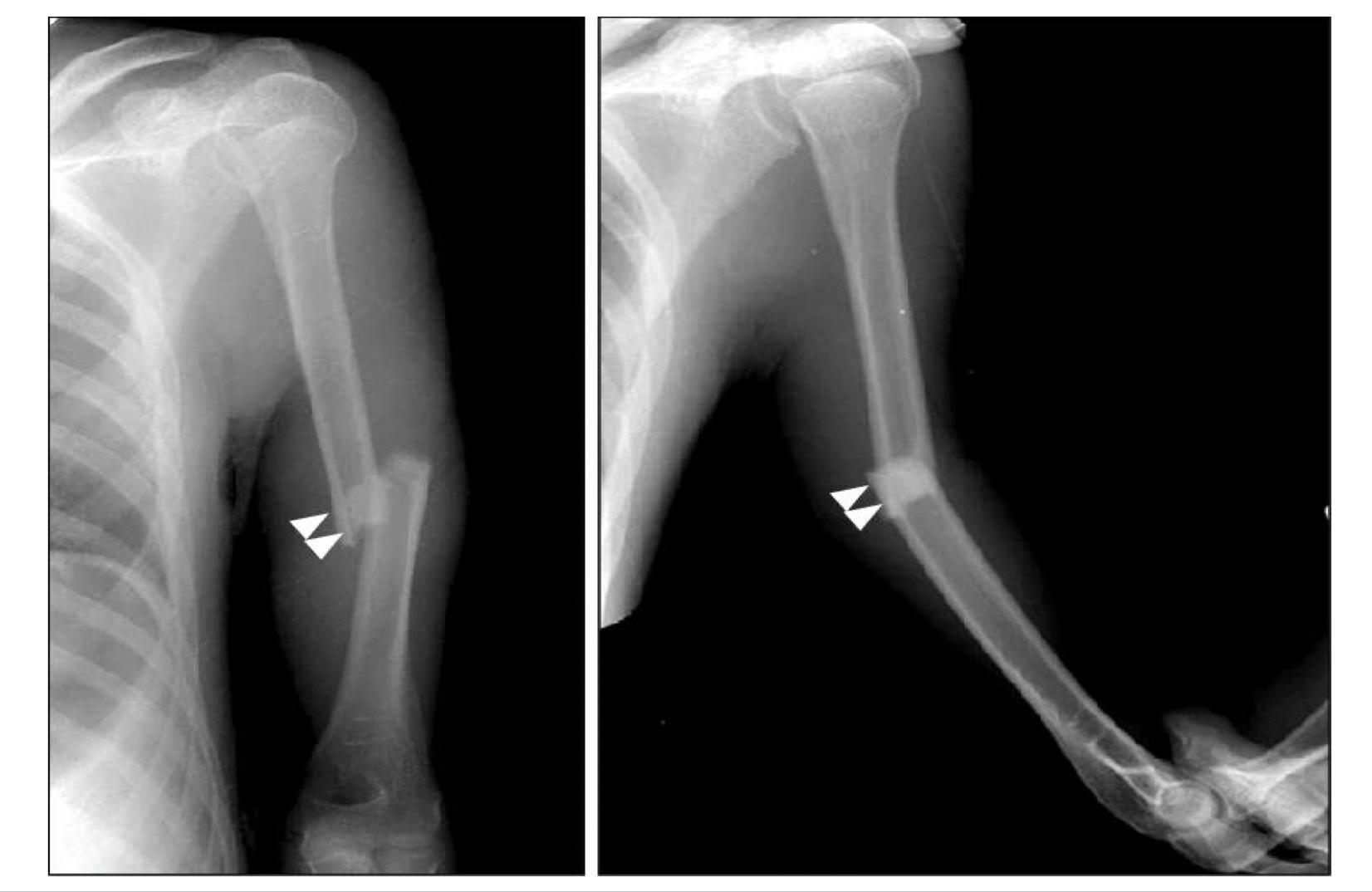
Shoulder dislocation
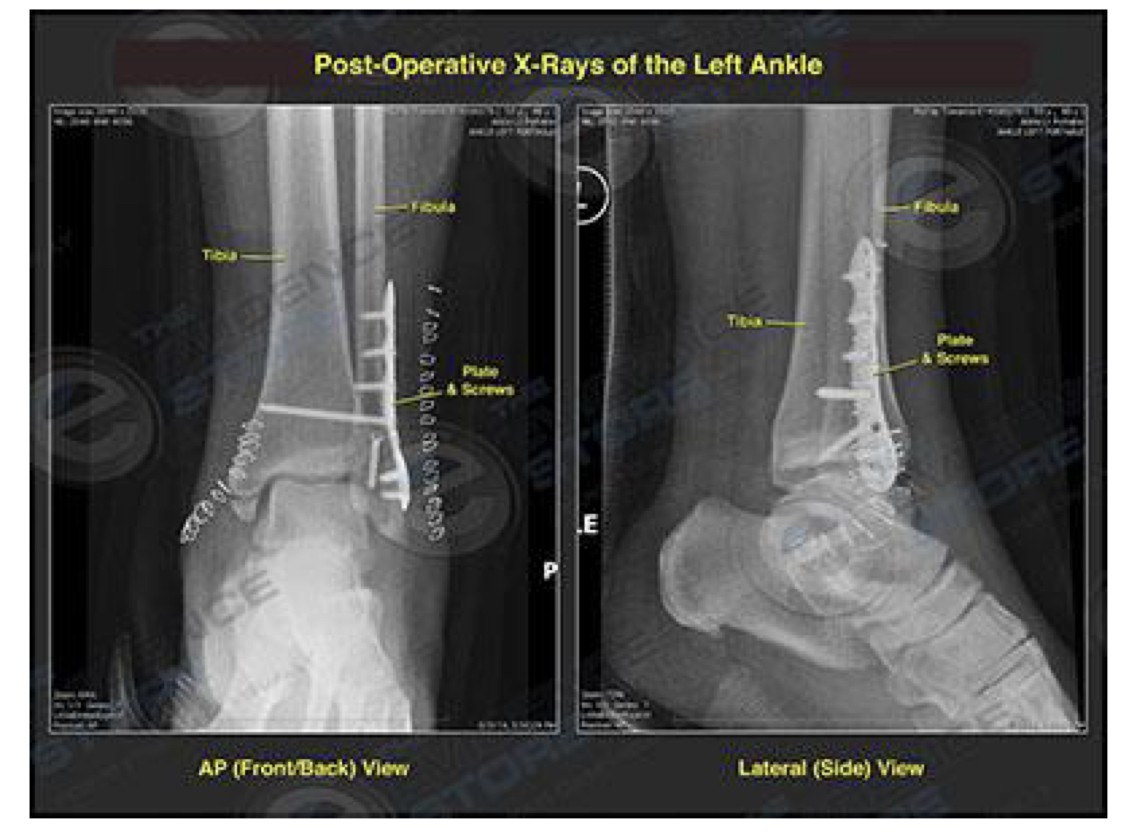
Open reduction, internal fixation
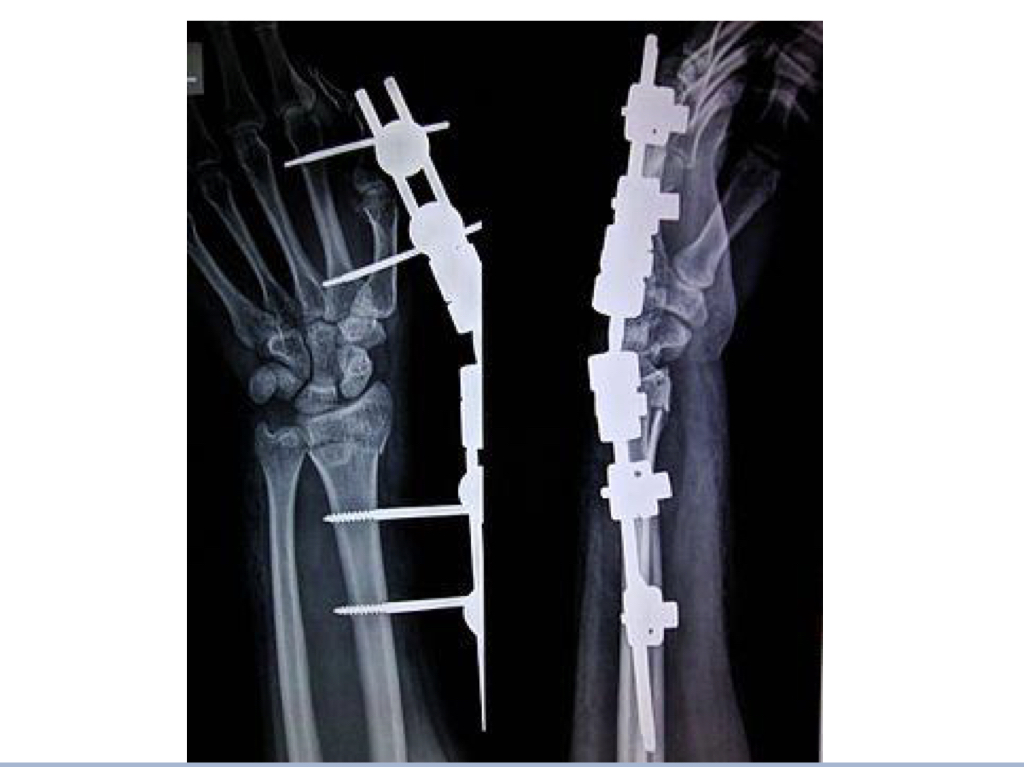
Open reduction external fixation
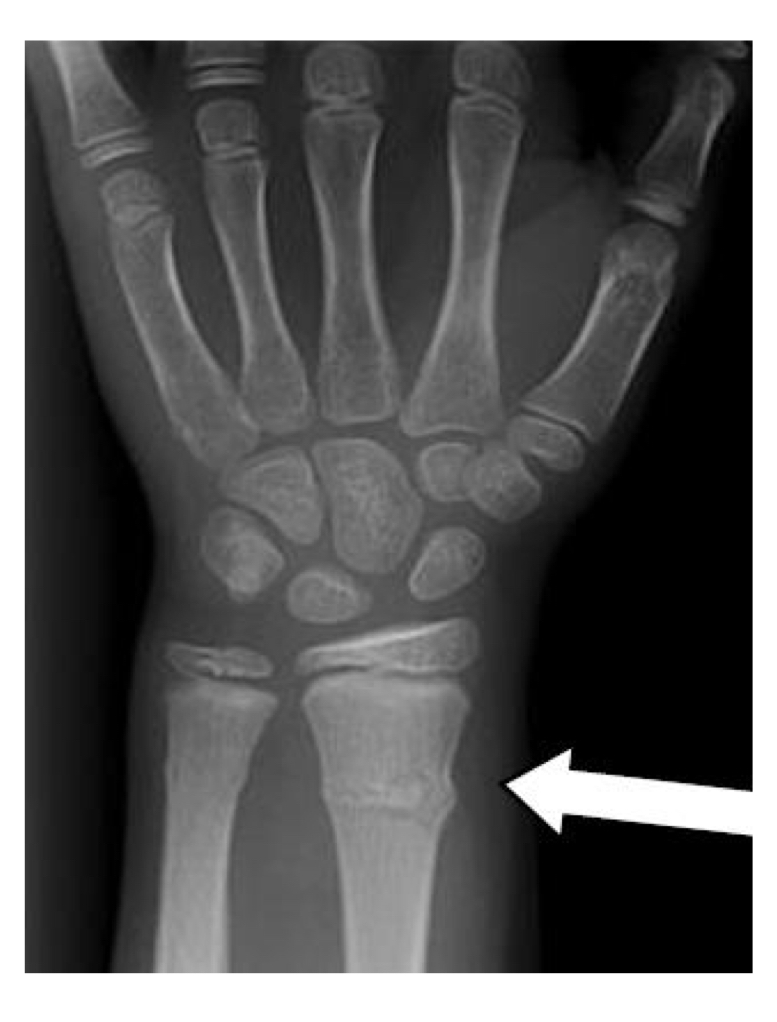
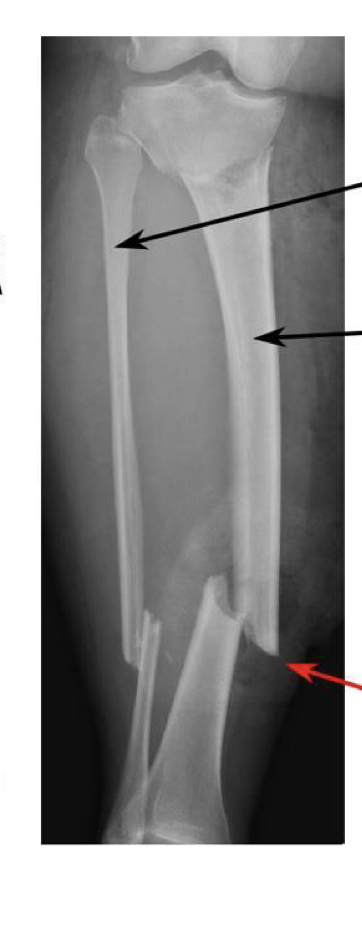
Buckle fracture
Angled buckle fracture
Spiral fracture
Displaced transverse fracture
Impacted fracture
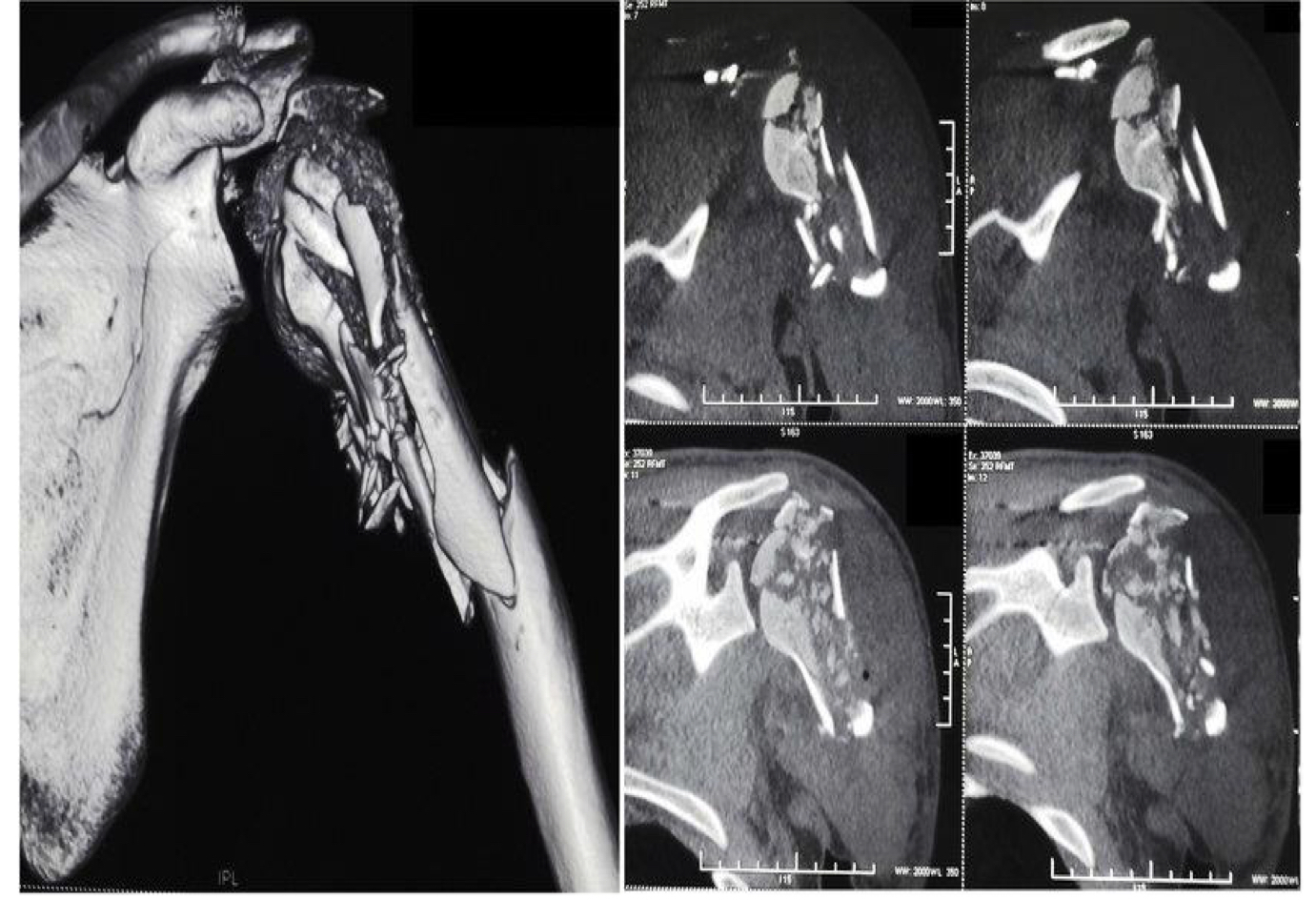
Communited fracture
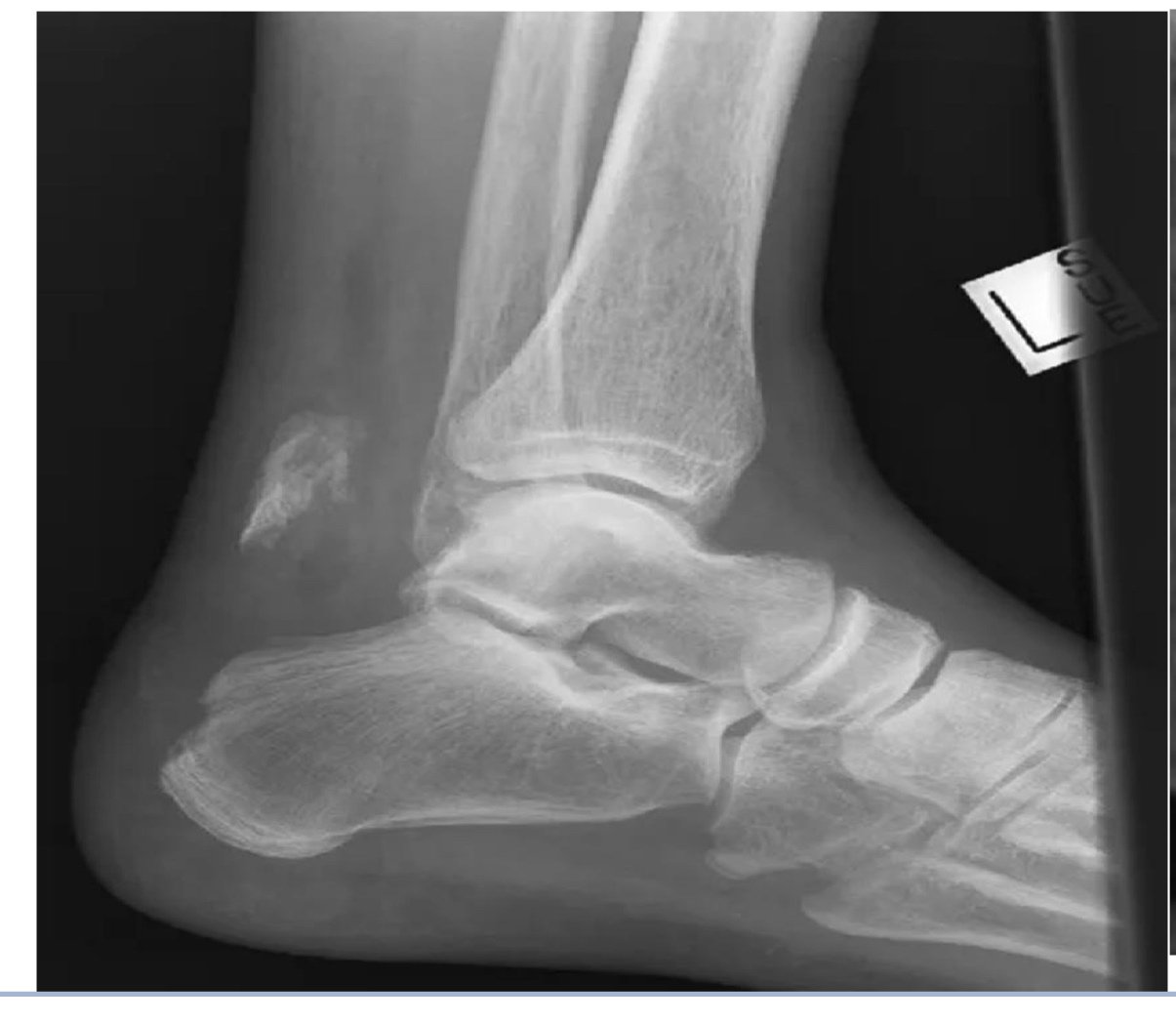
Avulsion fracture
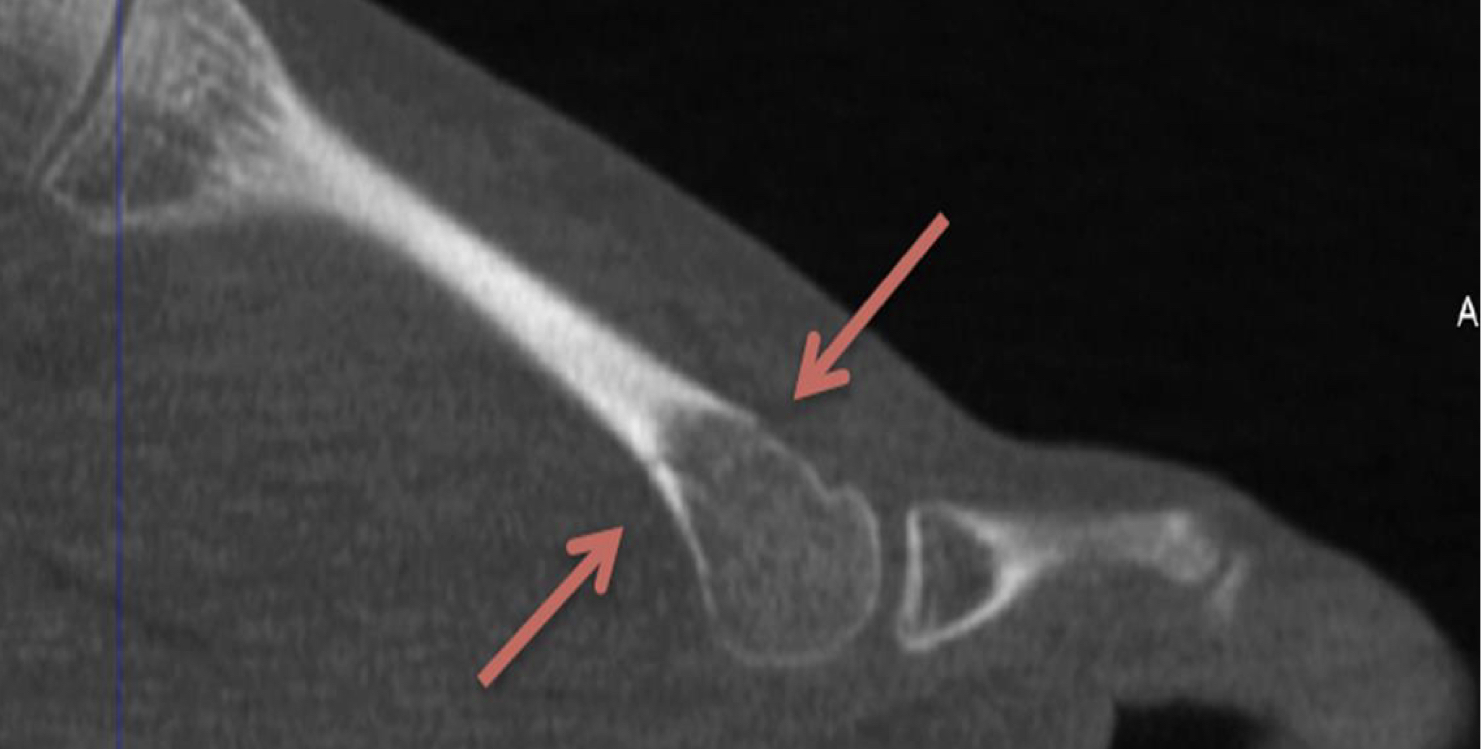
Hairline fracture CT
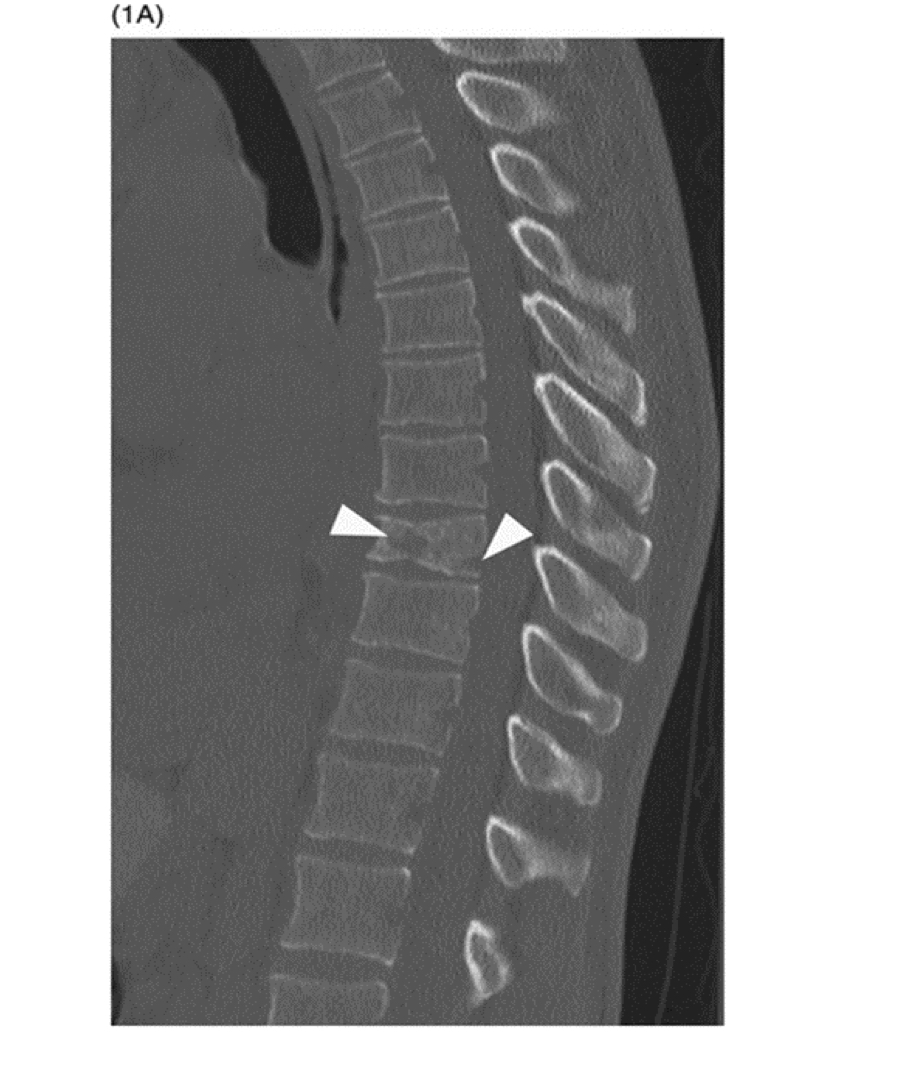
Compression fracture CT
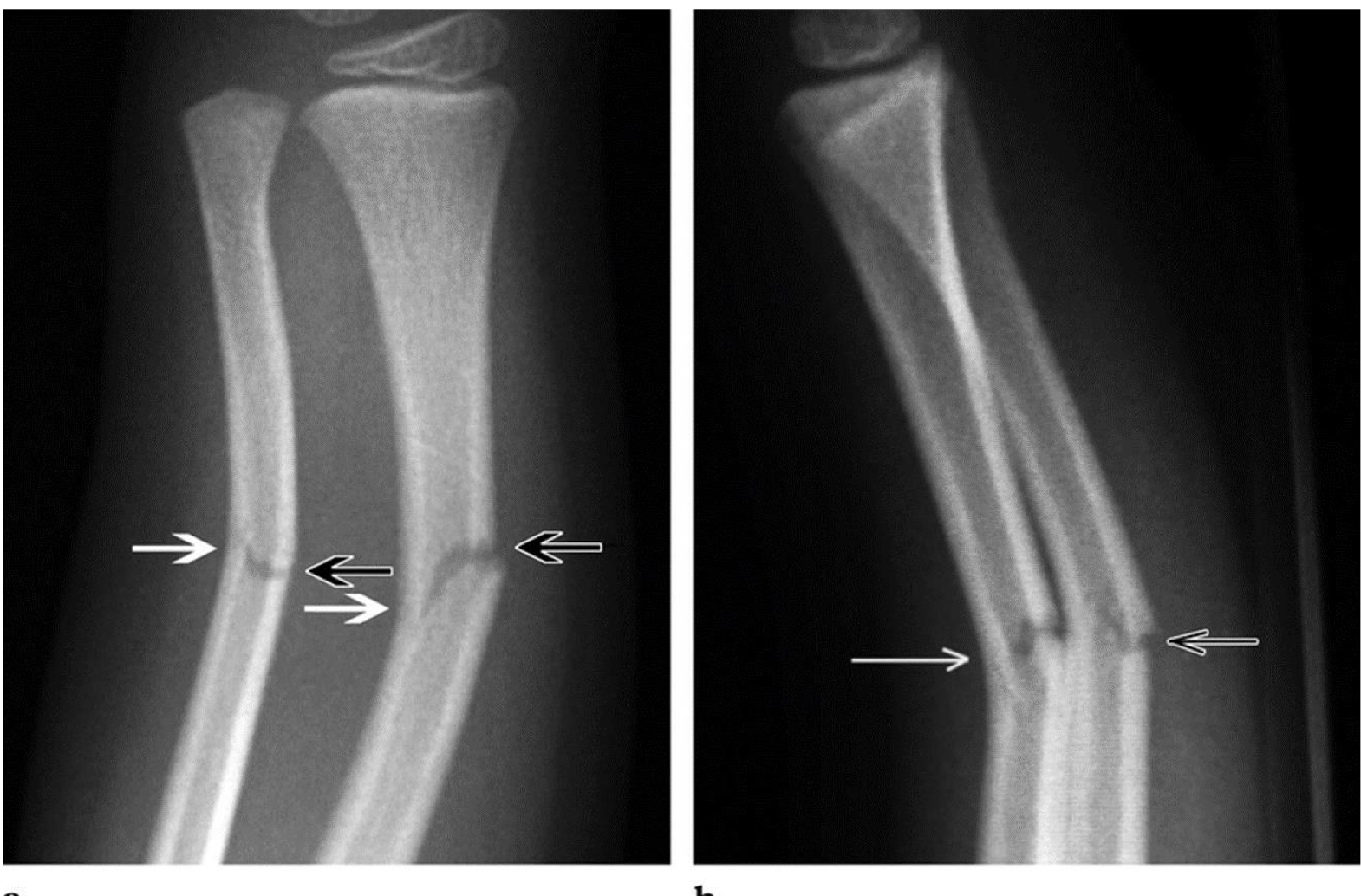
Green stick fracture x ray
Compound fracture
Child has point tenderness over thr epiphyseal plate
X ray can be negative
Salter Harris fracture 1
Non surgical tx
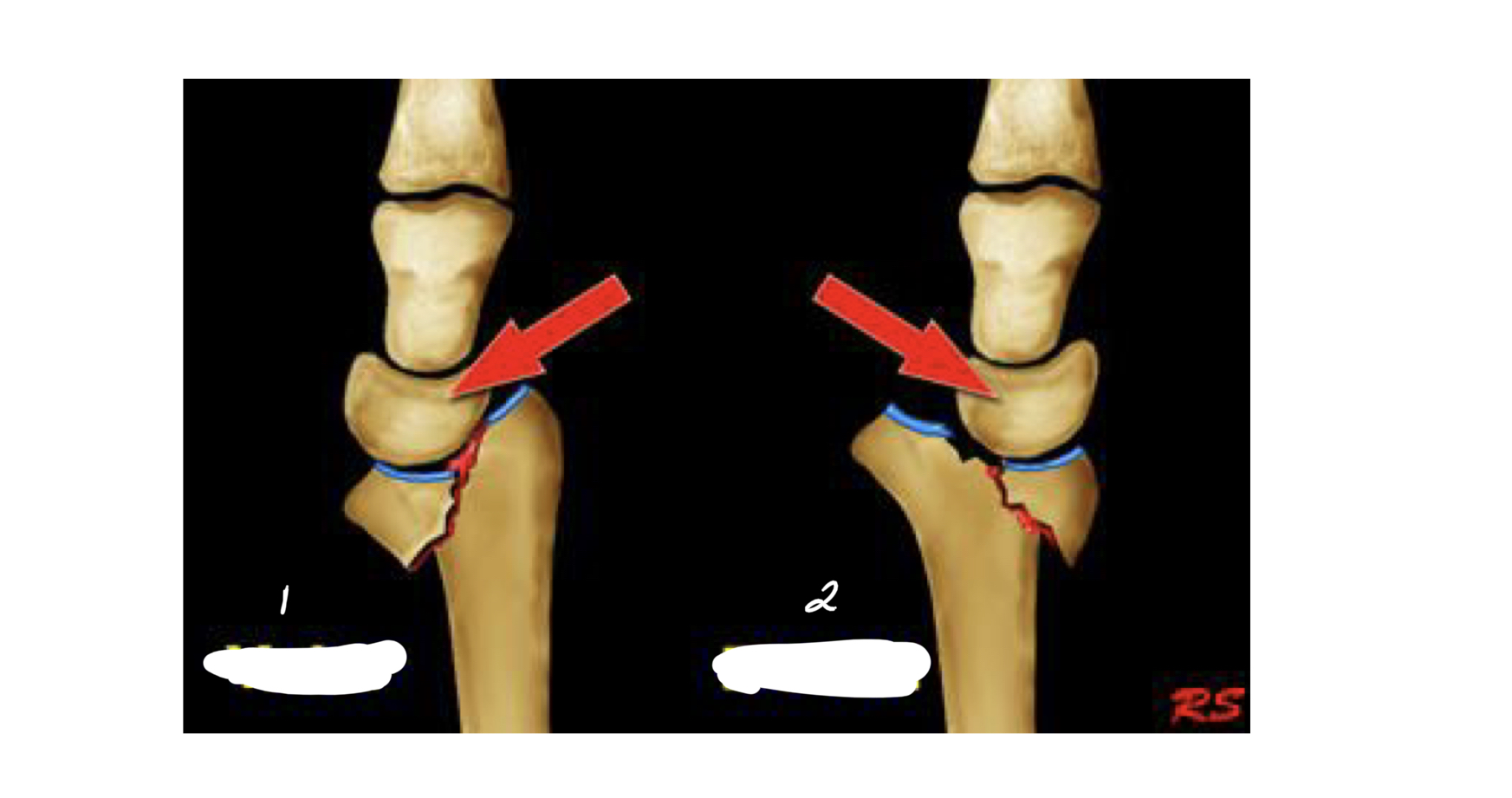
Involves physis and epiphysis
Salter Harris fracture 2
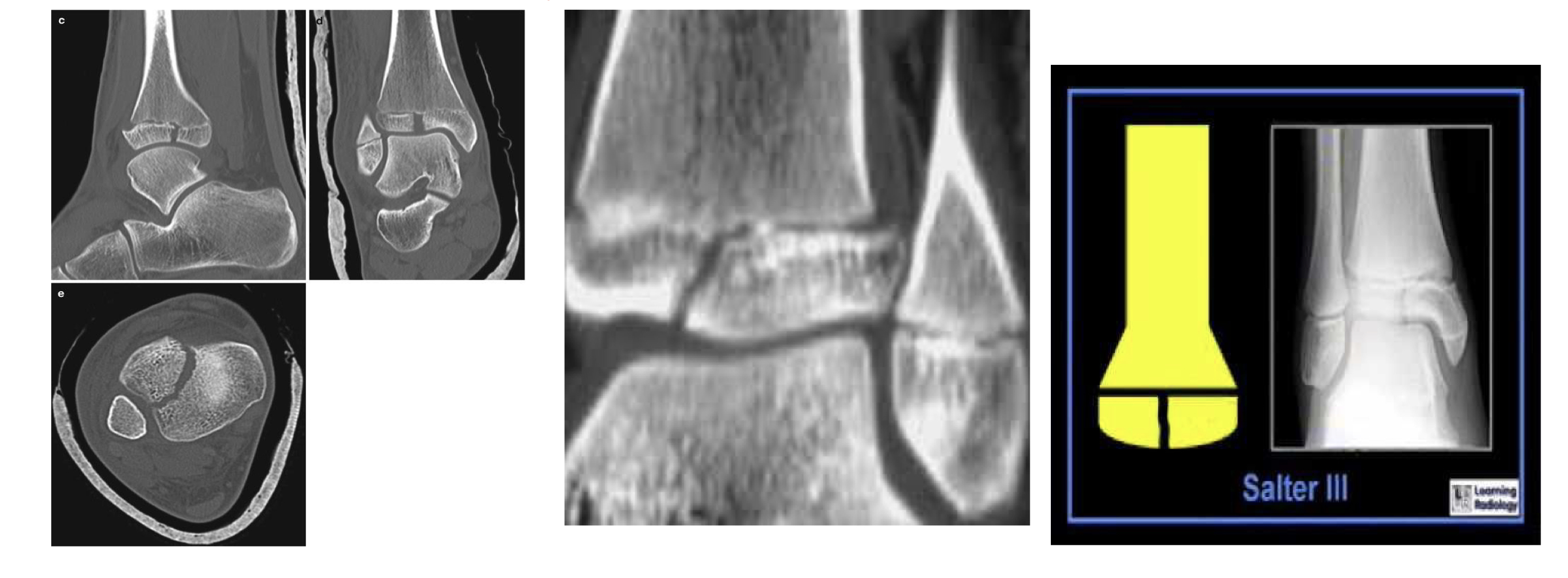
MC SH fracture
Fracture through the physis, epiphysis and metaphysis
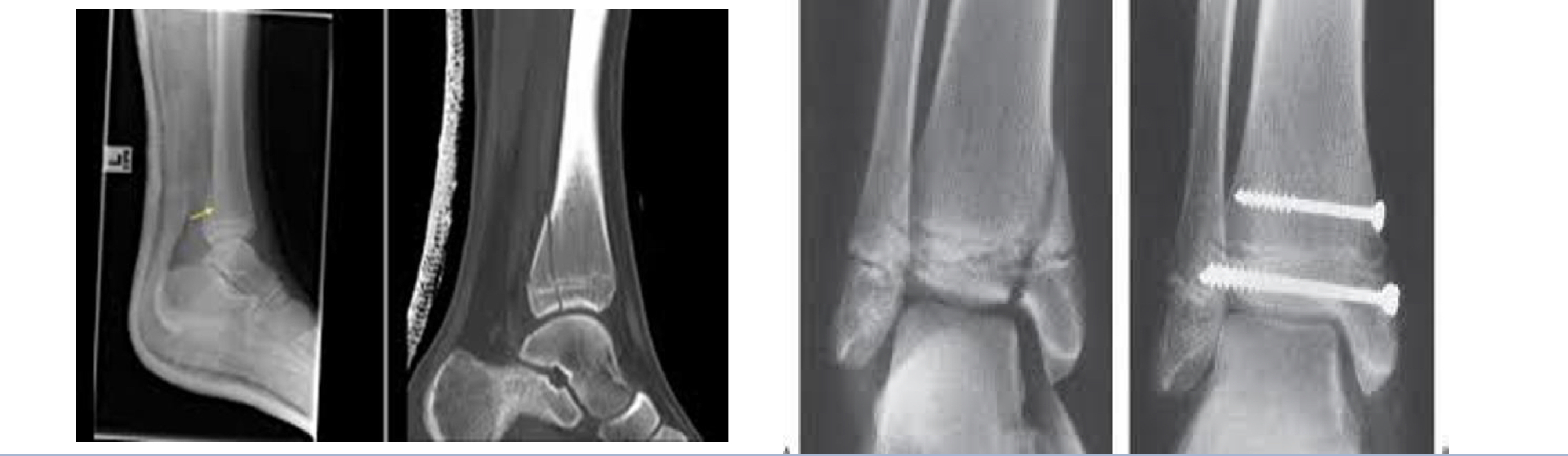
Salter Harris type 4
Can cause abnormalities
Fracture through the physis and epiphysis
Salter Harris fracture type 3
Tx surgery
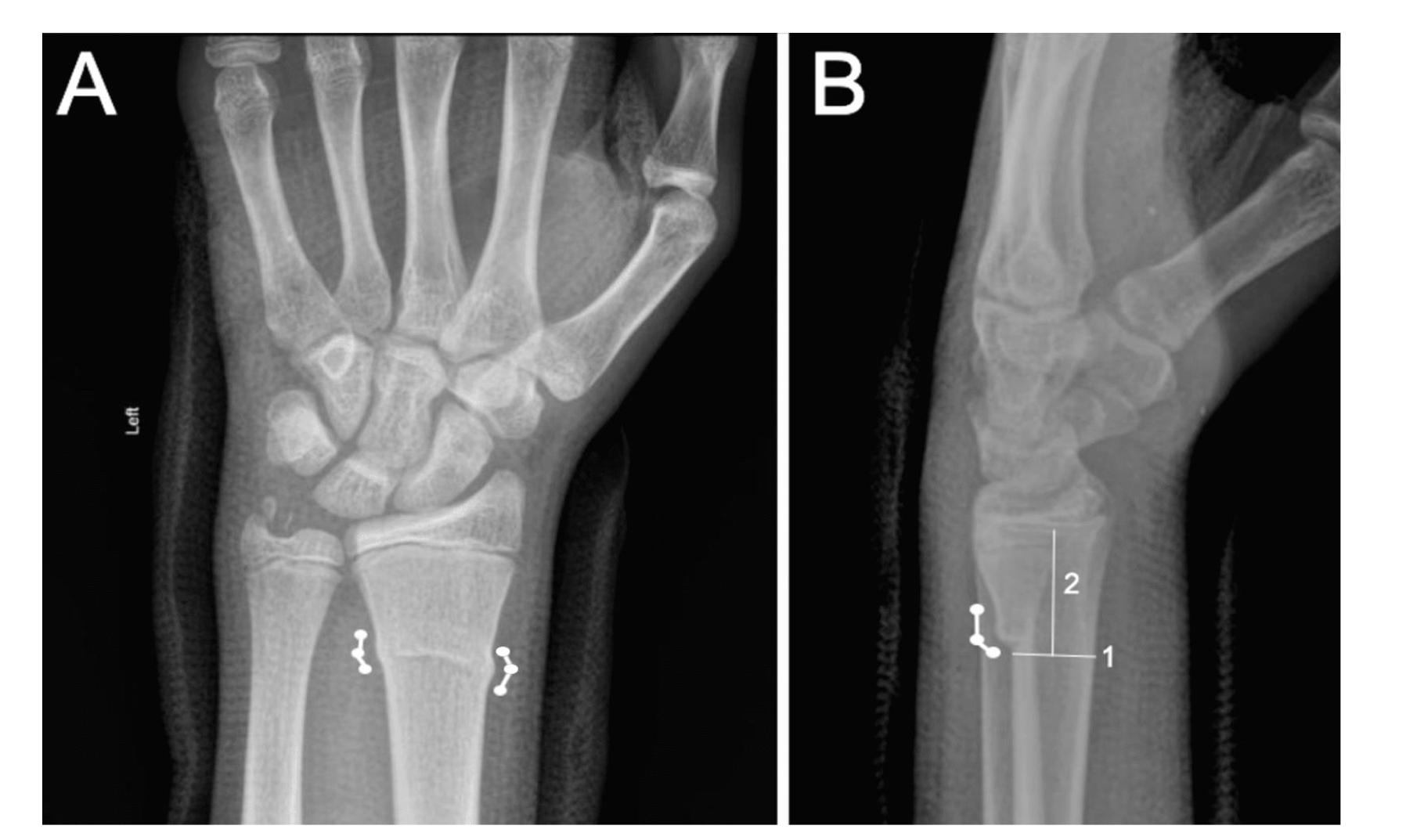
1- Voltar
2- dorsal
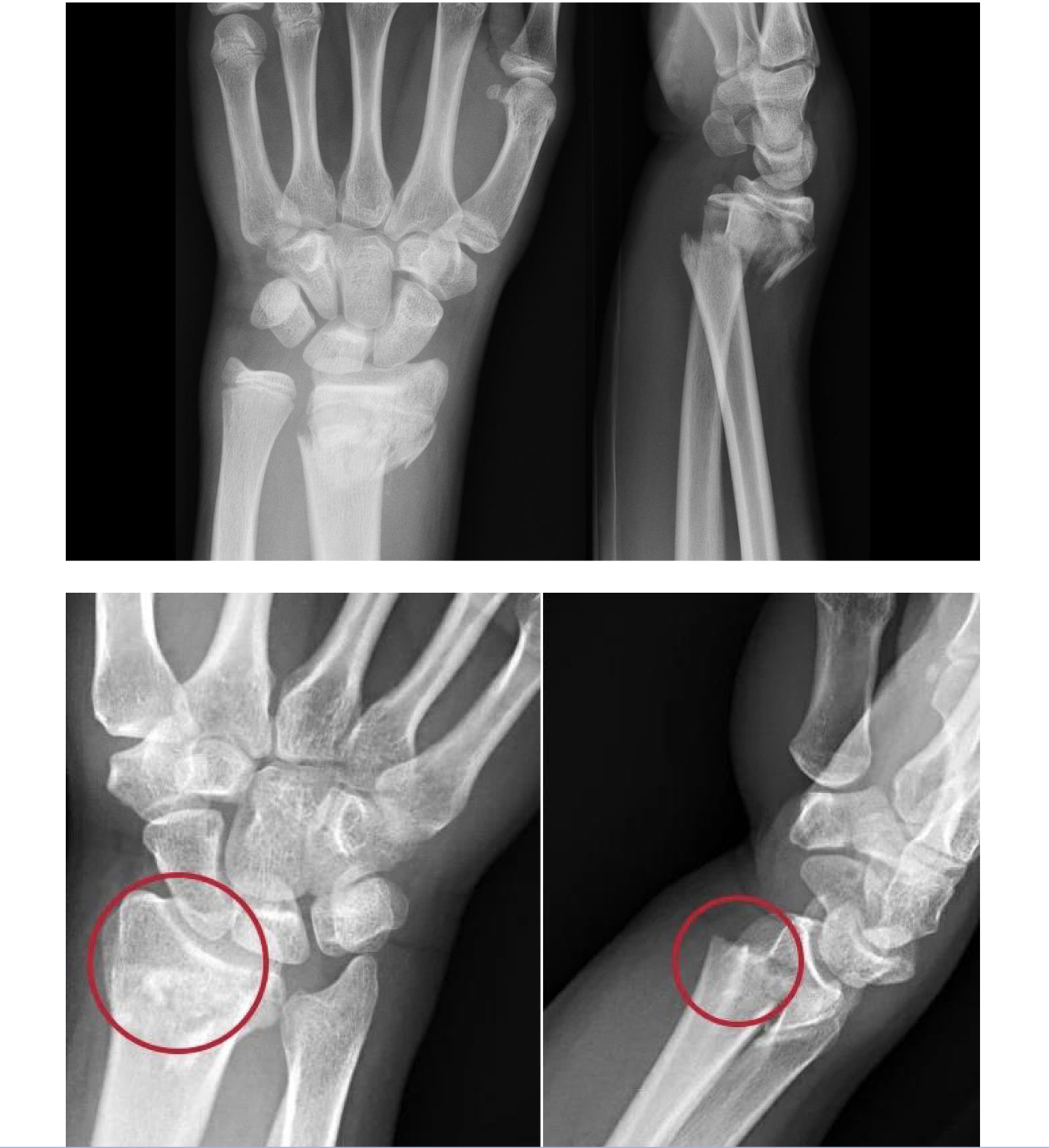
Colees fracture
Silver fork deformity
Velar displacement
Smith fracture
Anatomical snuffbox tenderness
Scaphoid fracture
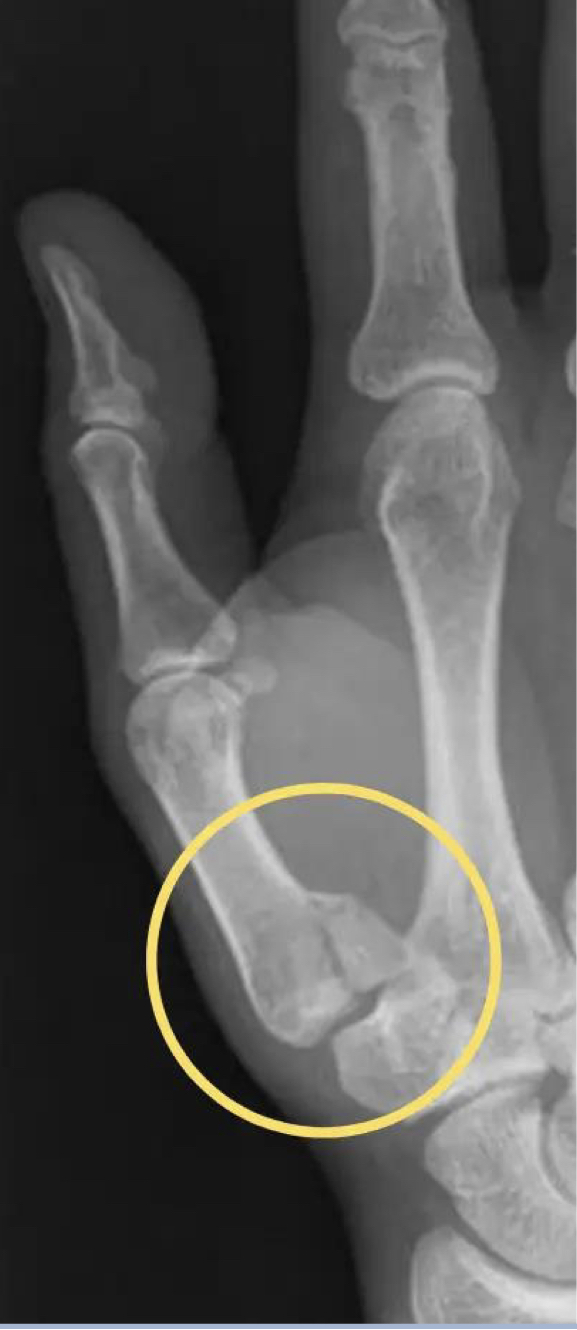
Bennet fracture
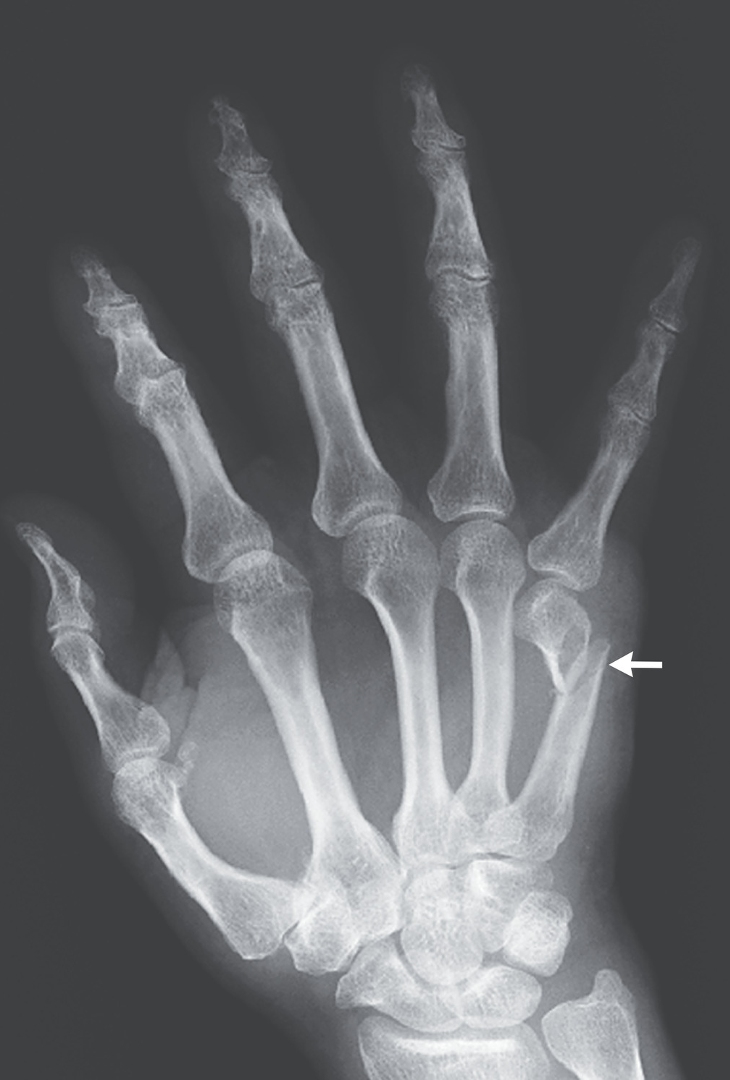
Boxers fracture
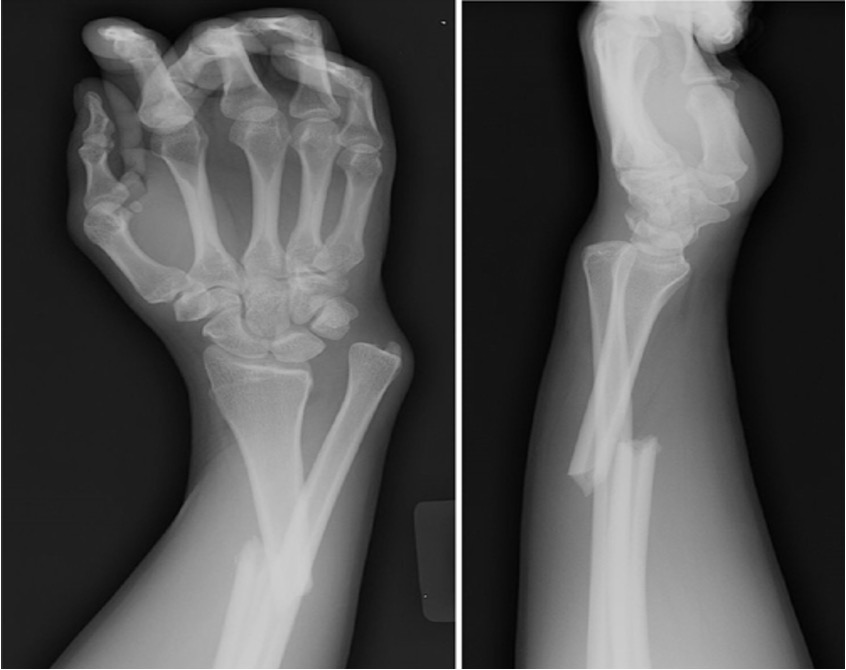
Galeazzi fracture
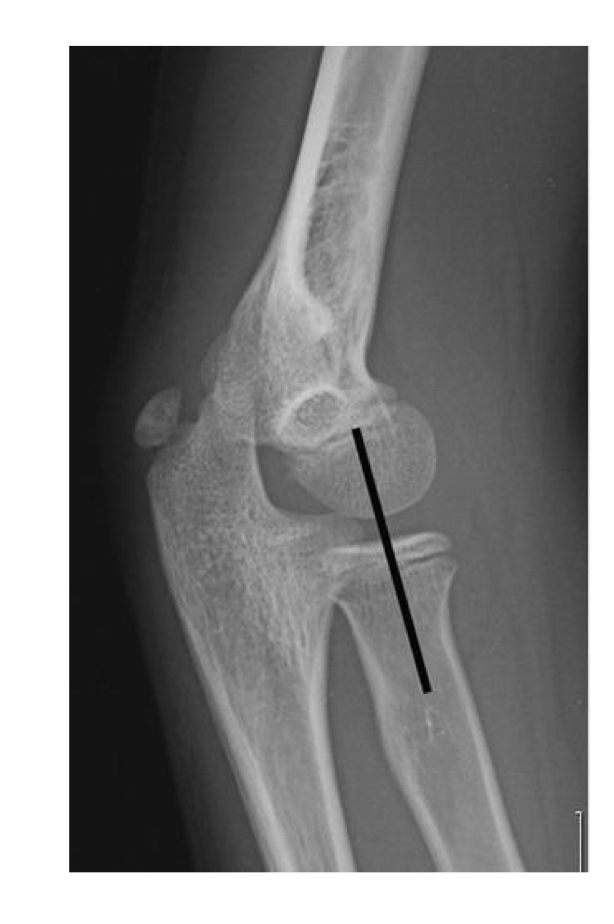
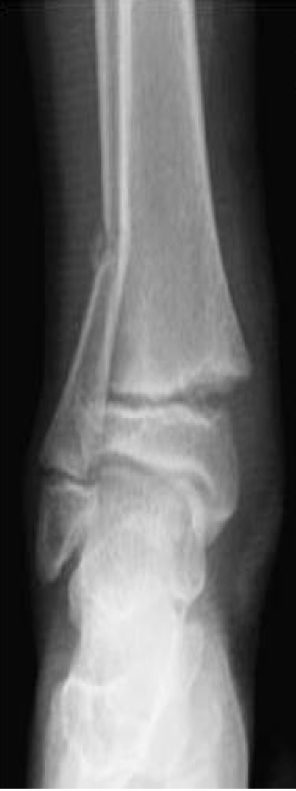
Nursemaids elbow
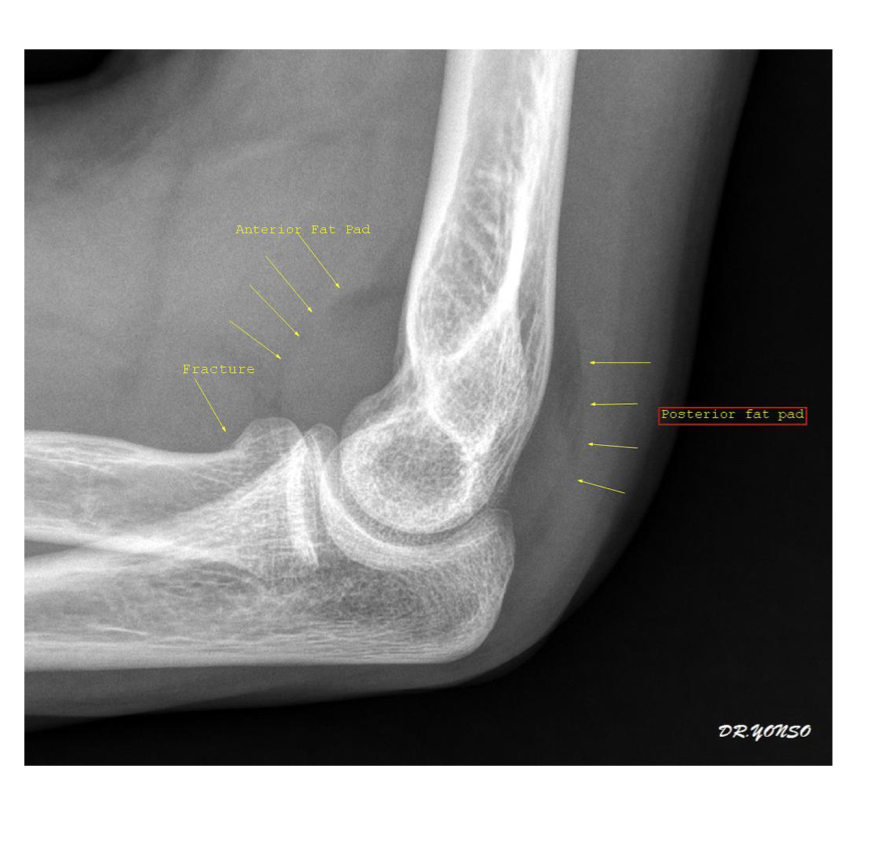
Fat pad sail sign
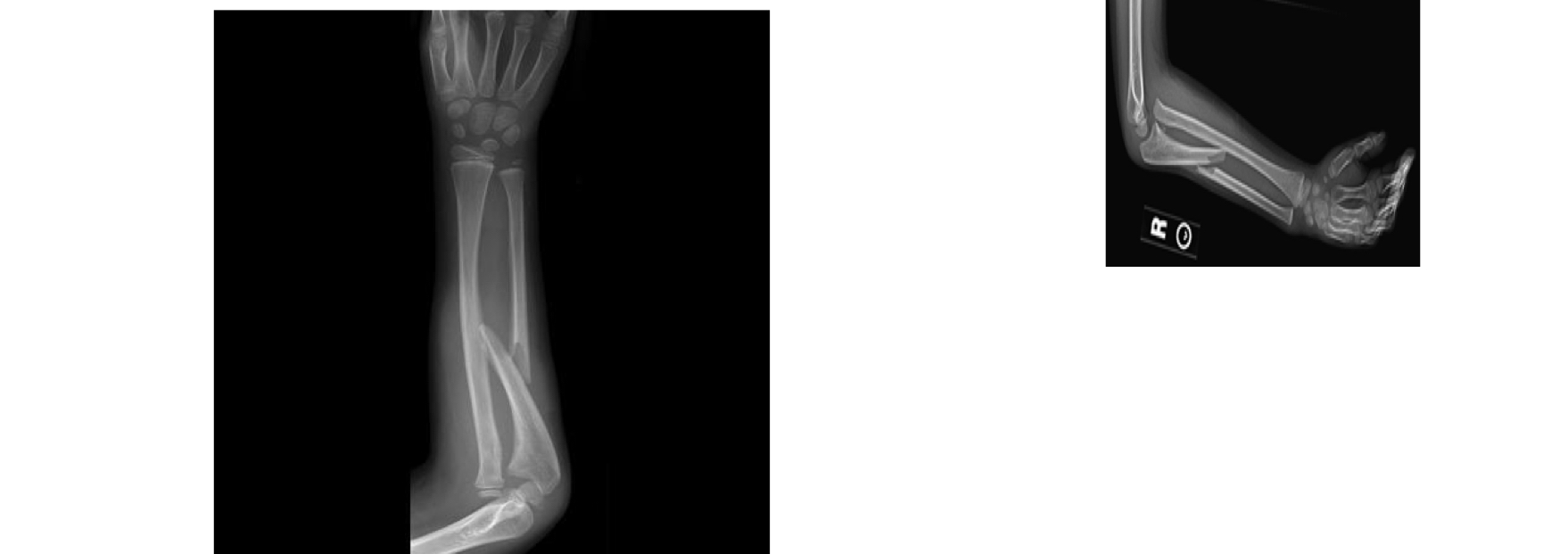
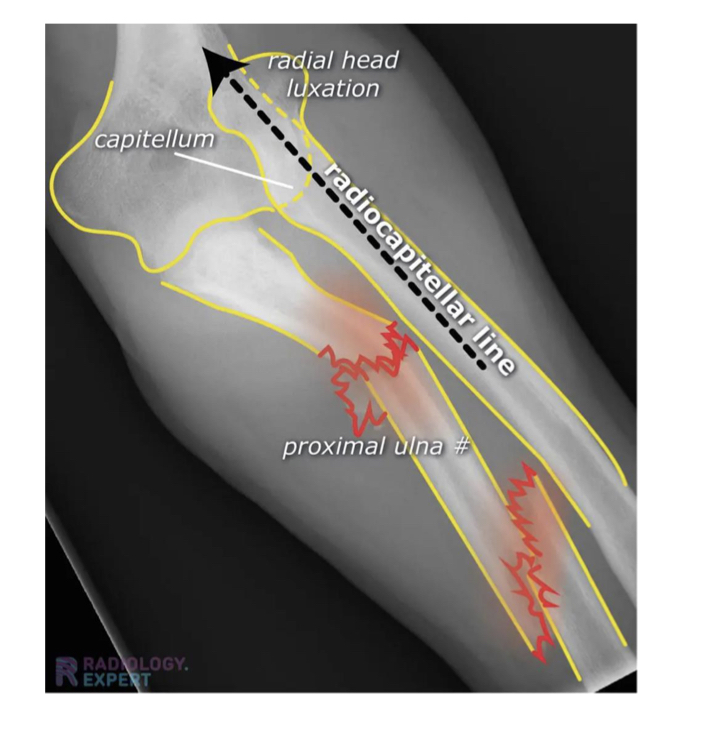
Proximal and middle ulna dislocation of the radial head
Monteggia syndrome
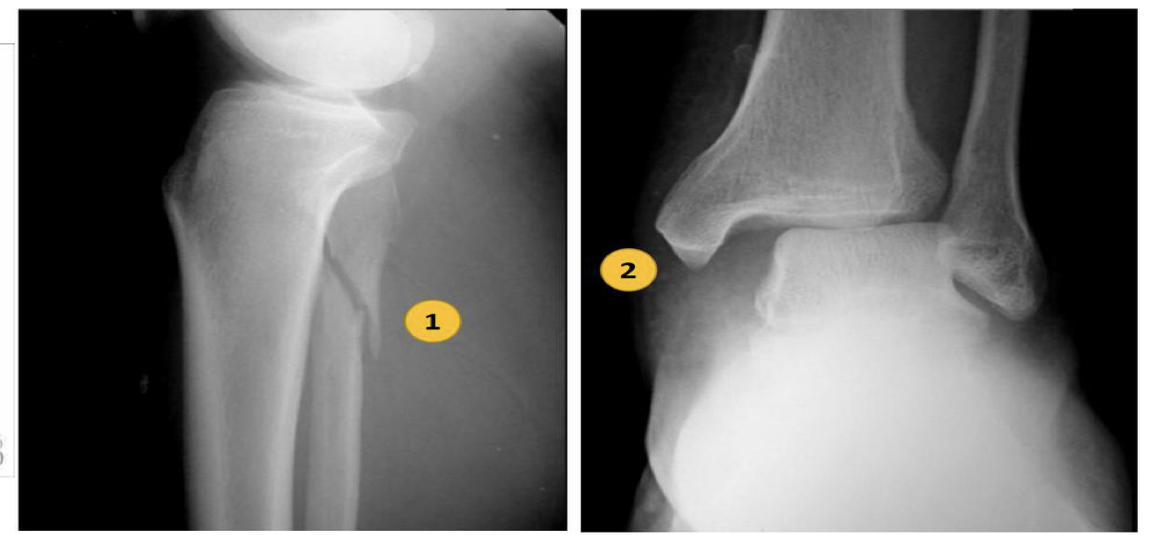
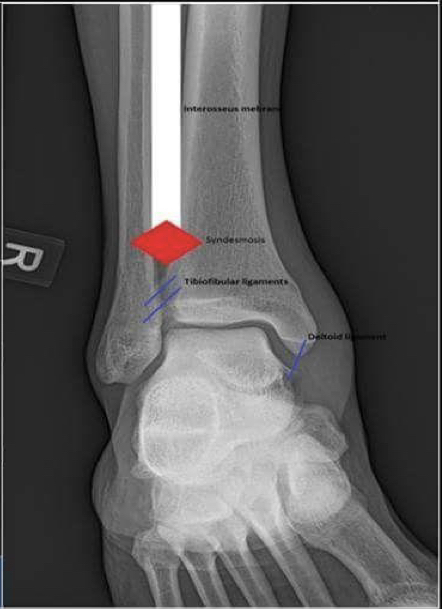
Maisonneuve fracture
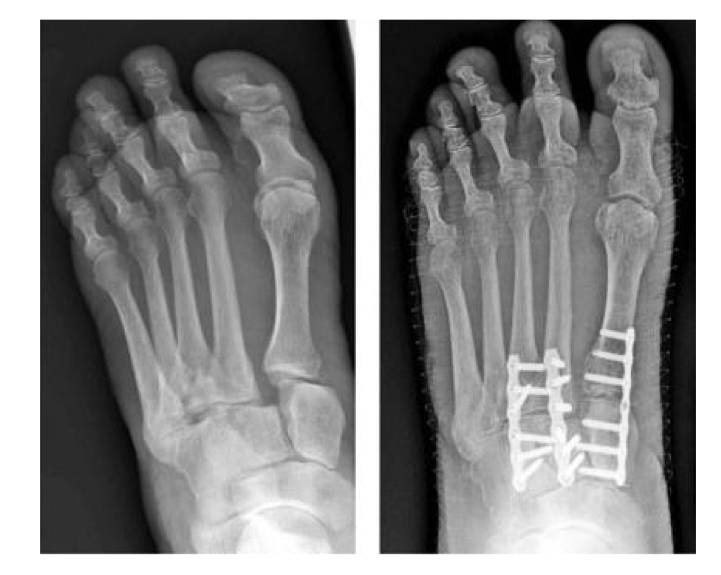
Lisfranc fracture
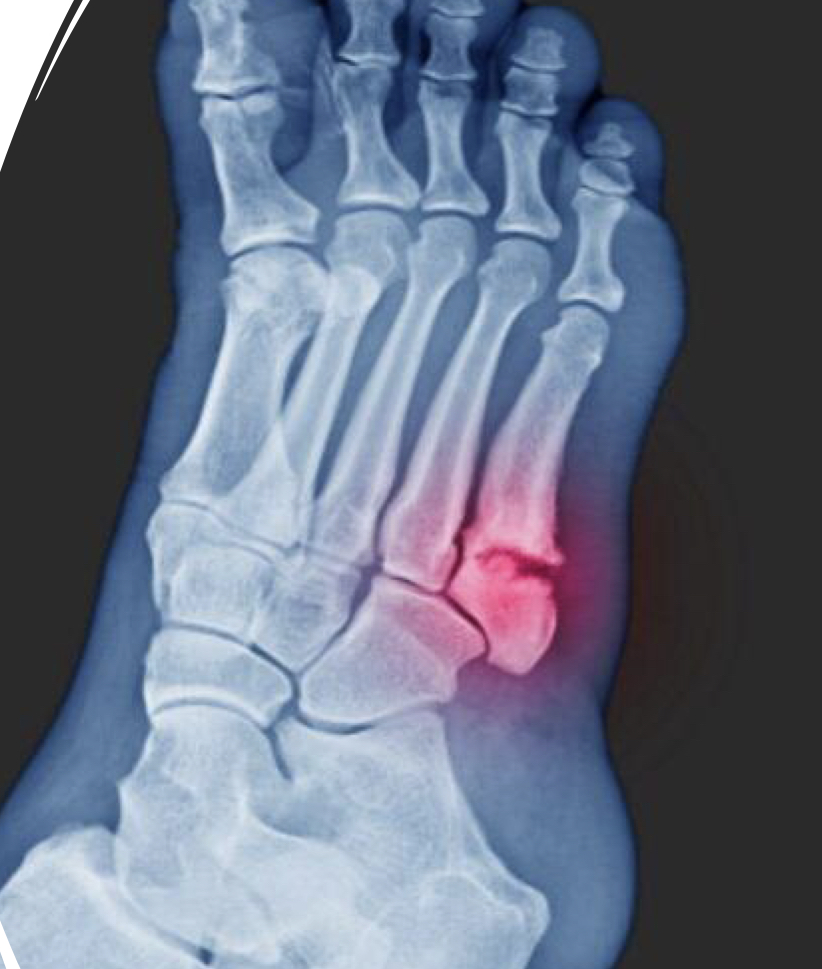
Jones fracture
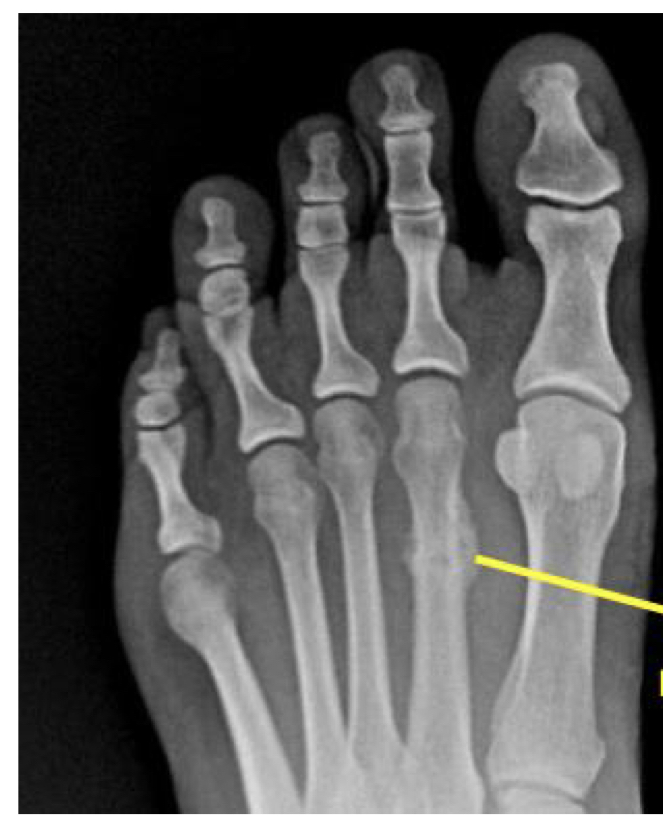
Stress fracture
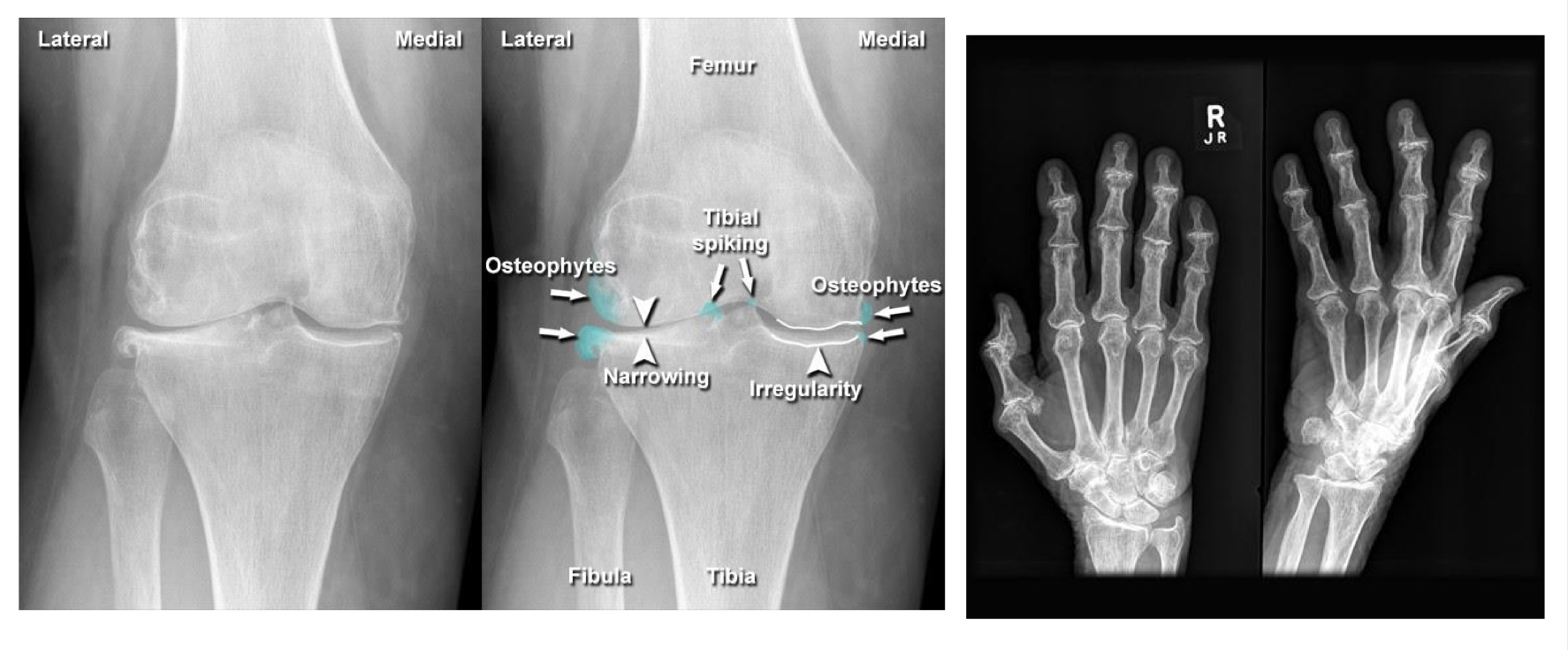
Osteoarthritis
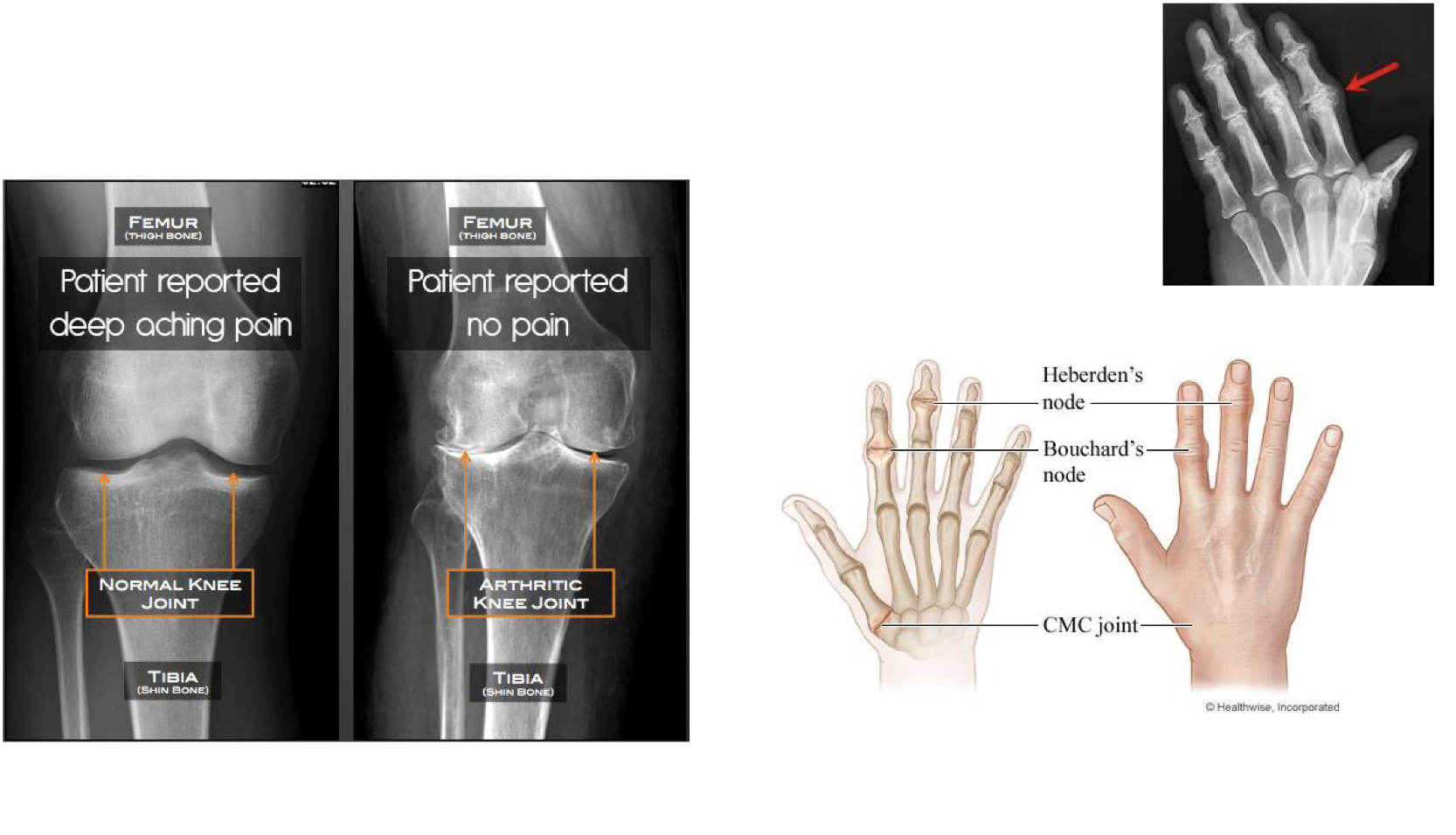
Osteoarthritis
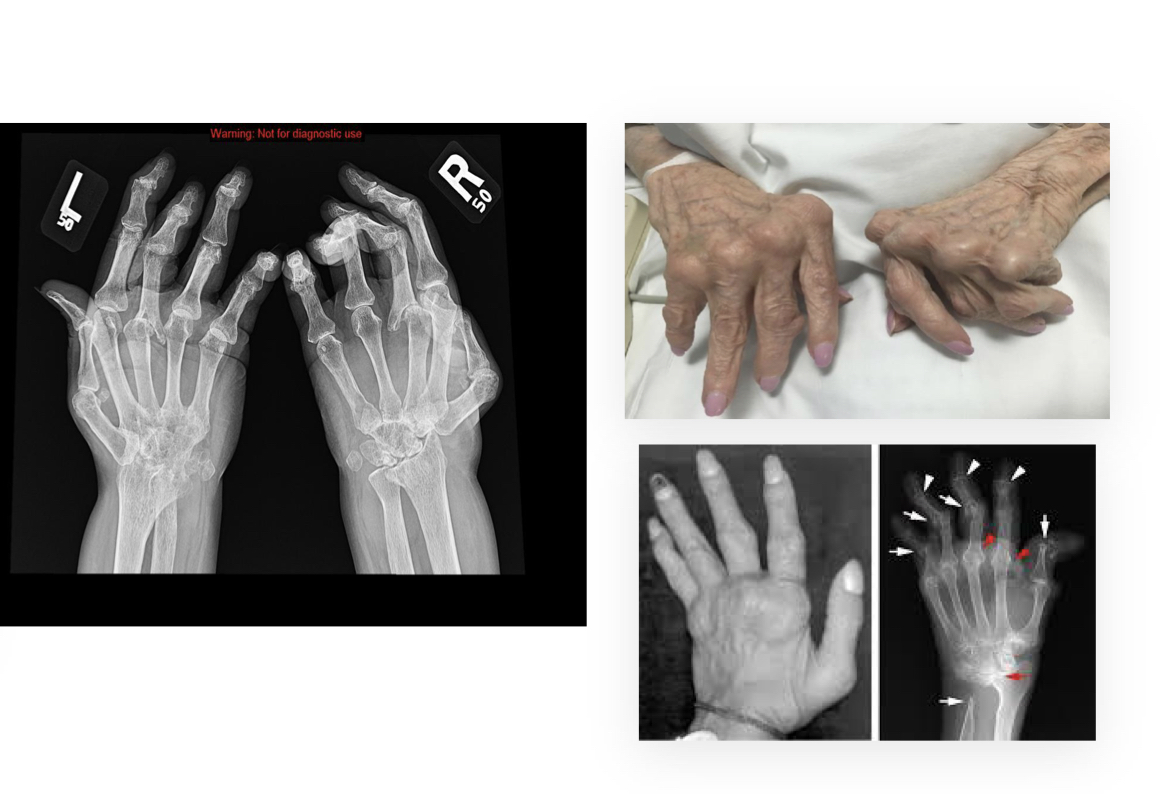
Rheumatoid arthritis
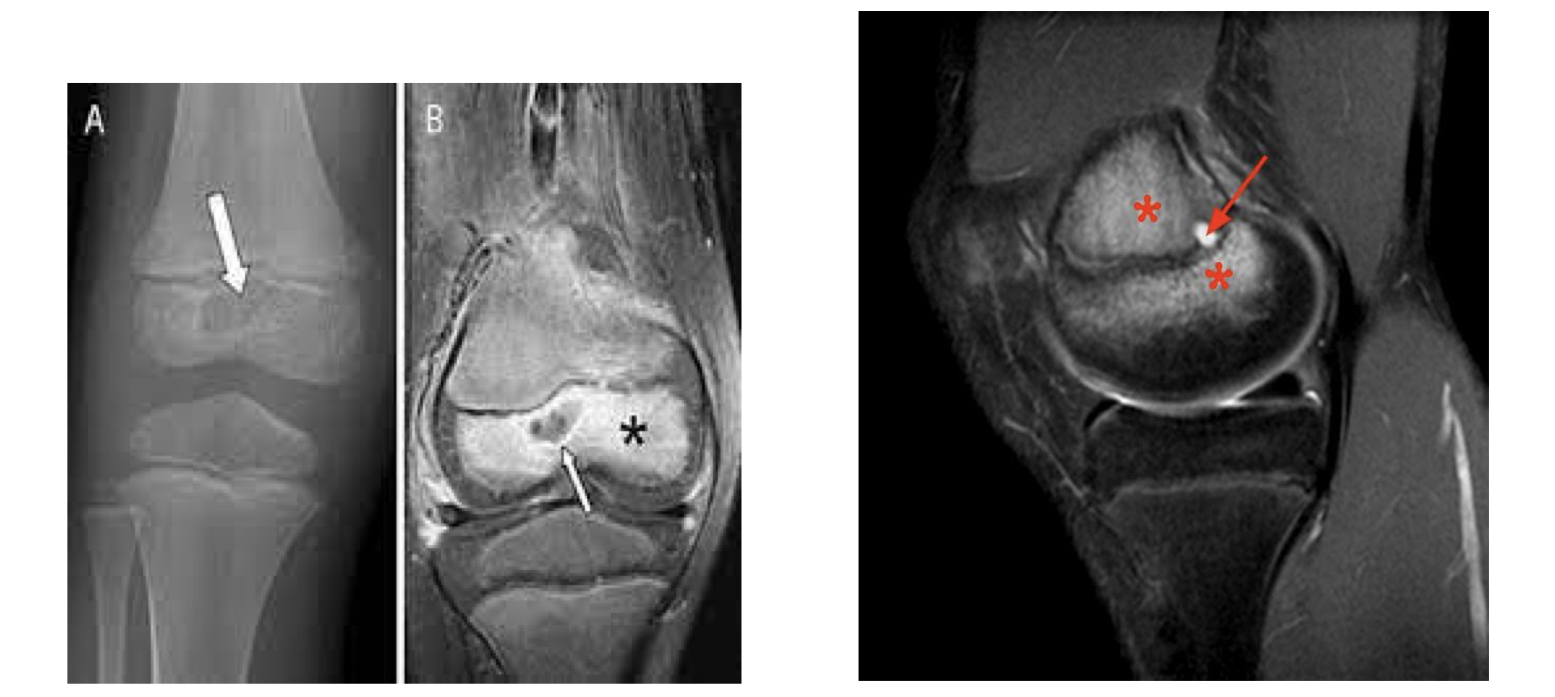
Osteomyelitis
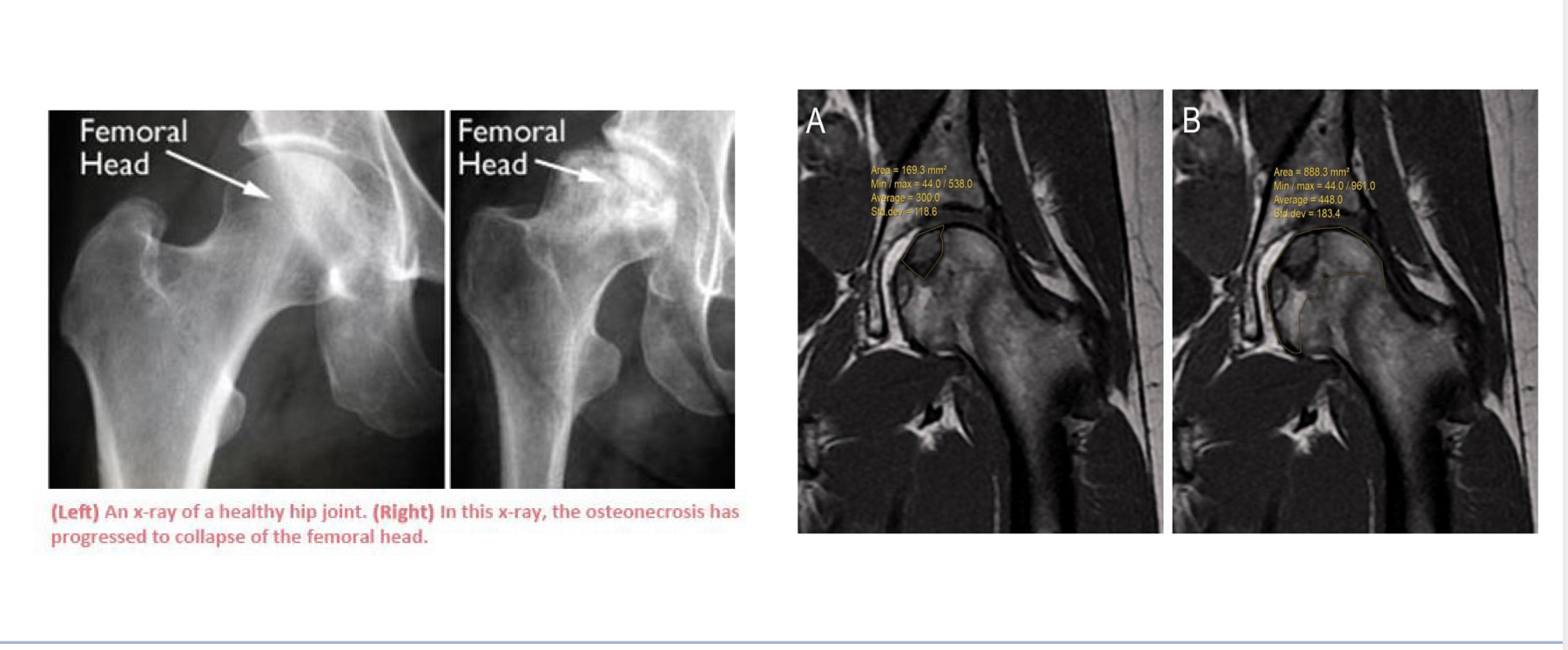
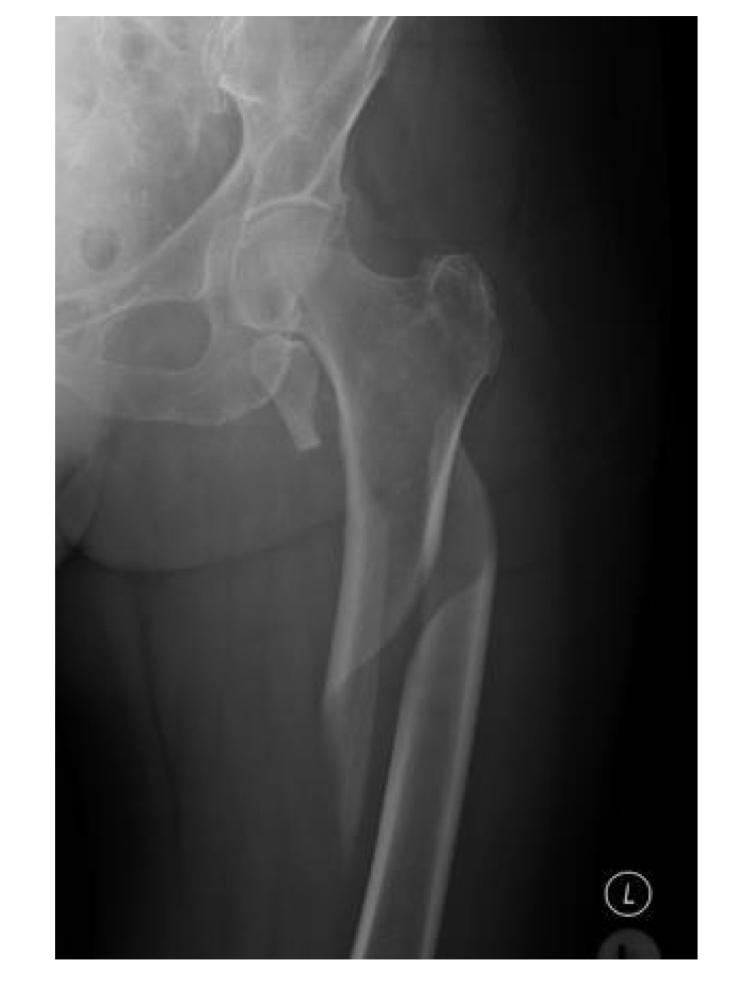
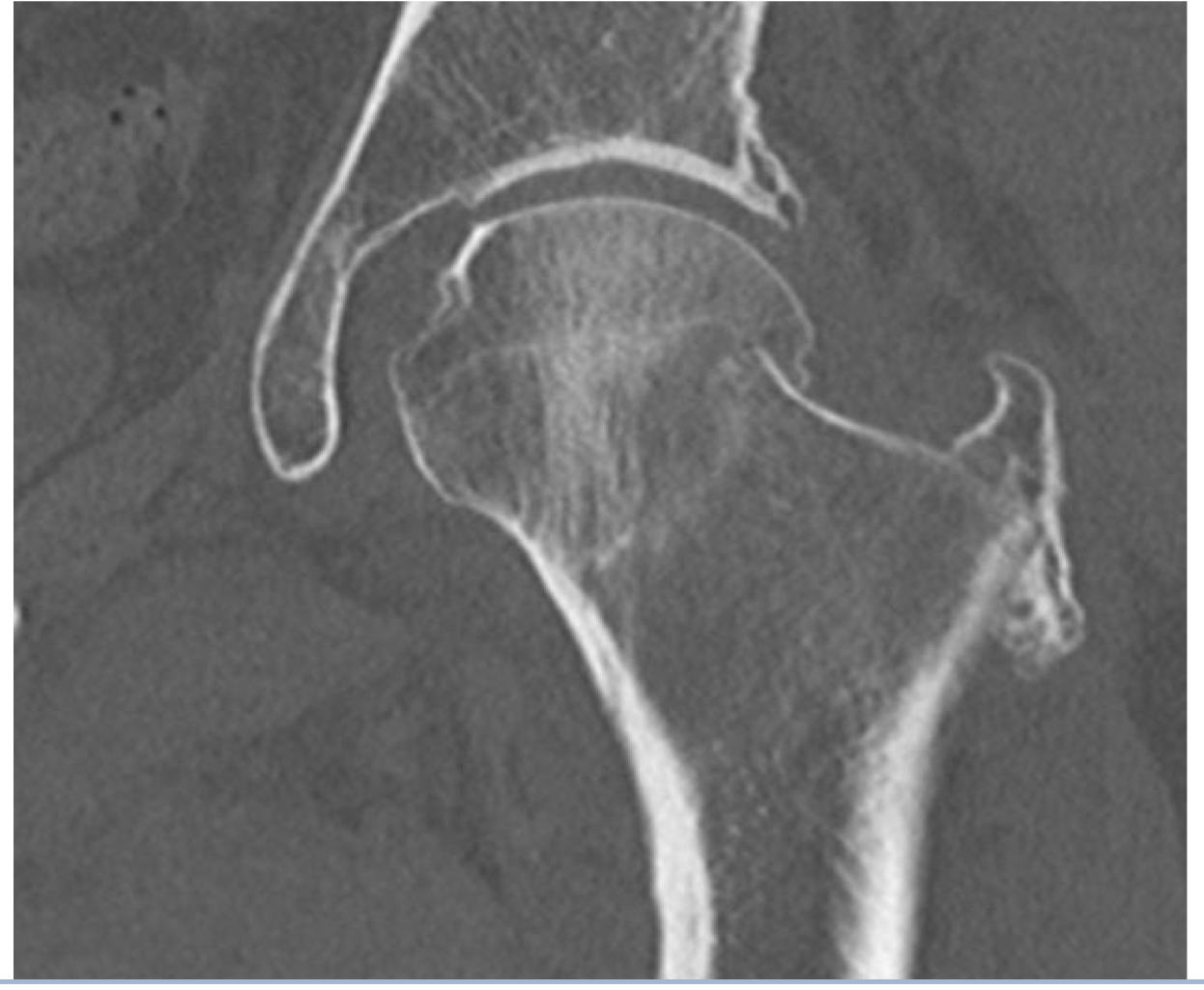
Osteonecrosis
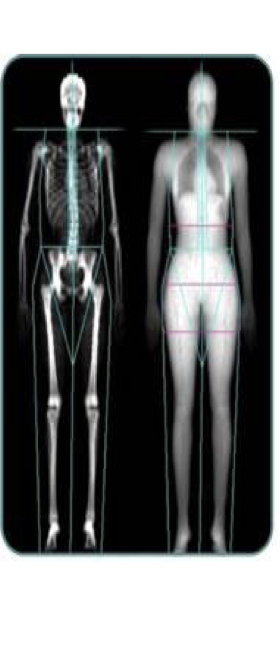
Osteoporosis dexa scan
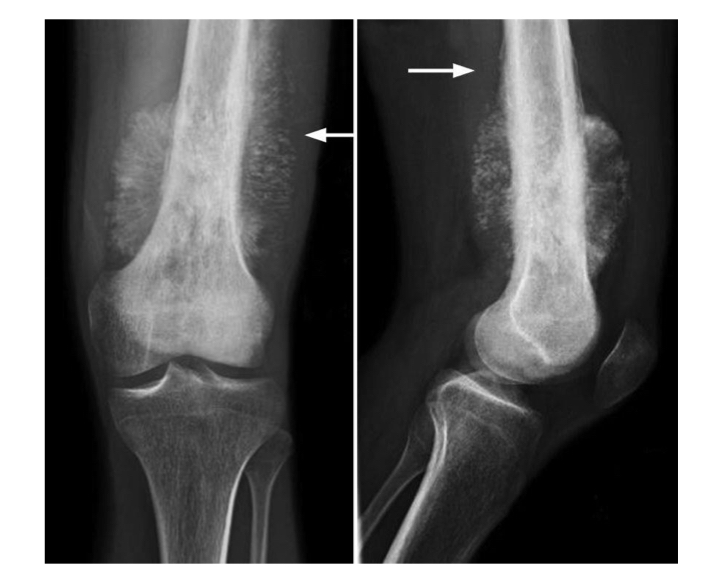
Benign bone tumors osteochondroma
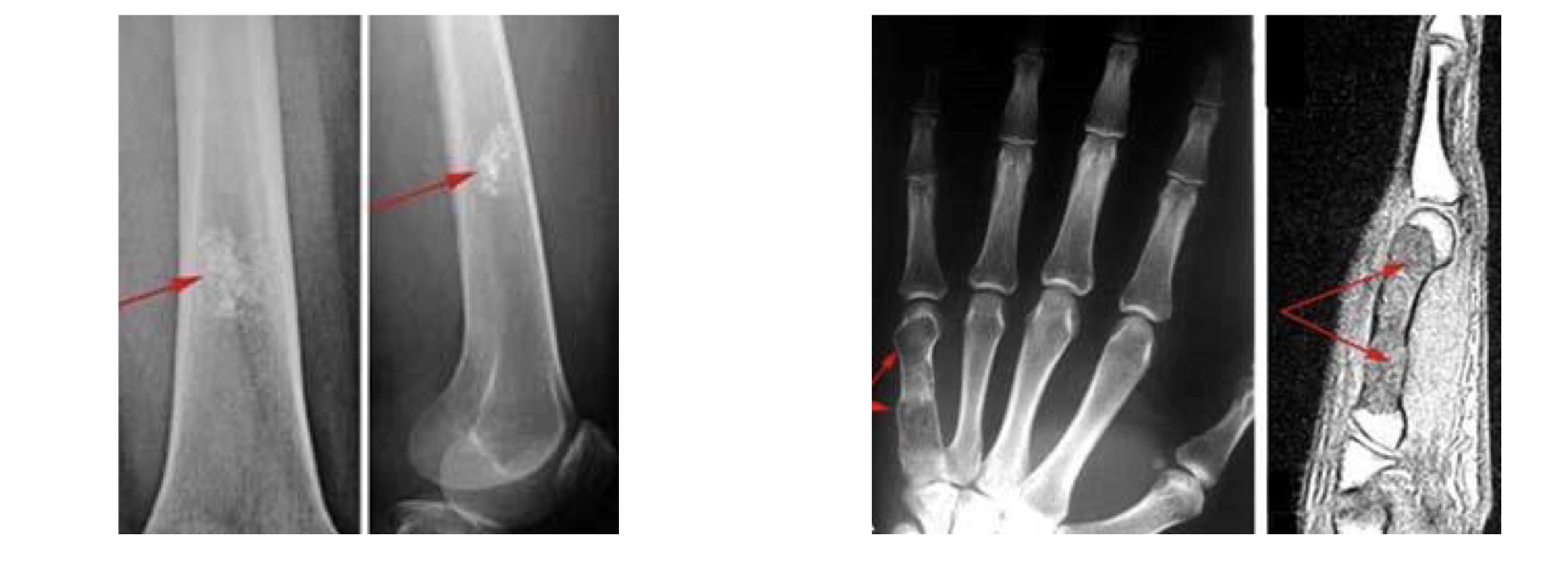
Endochondroma
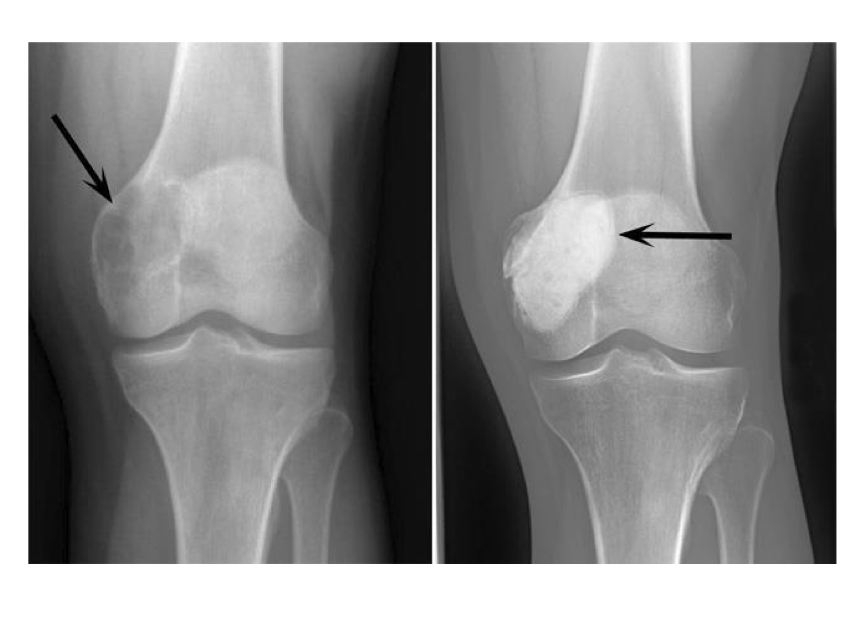
Giant cell
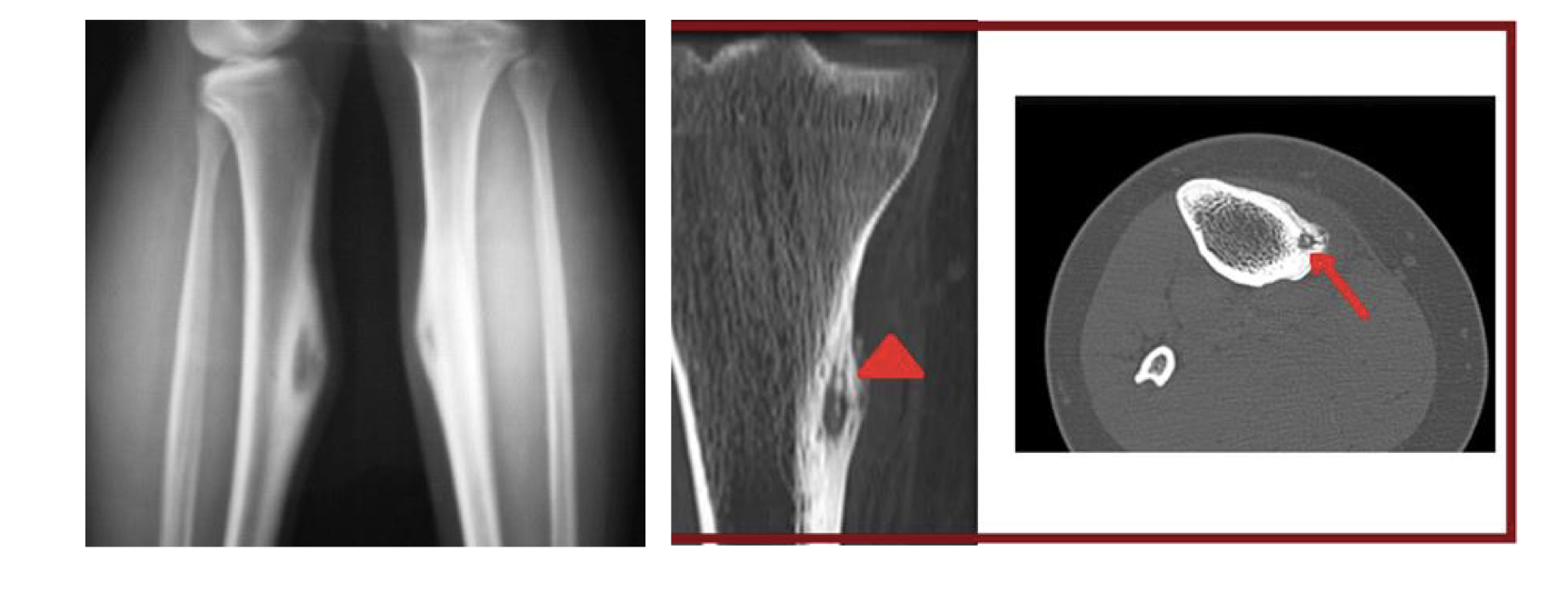
Localized pain more severe at night
Osteoid osteoma
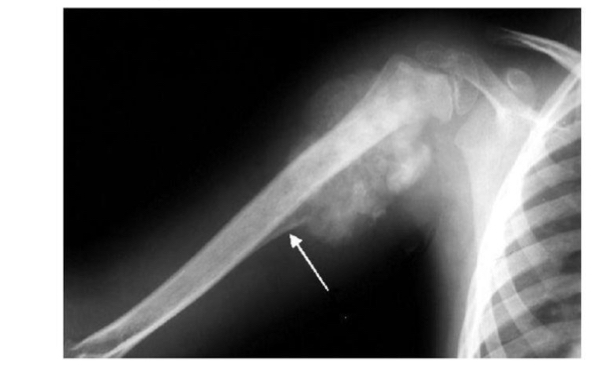
Malignant bone tumor
Codmans triangle
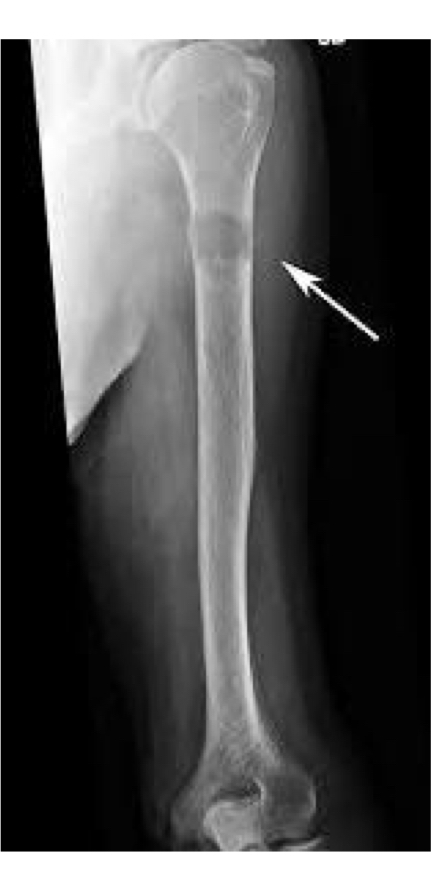
Metastatic bone tumors
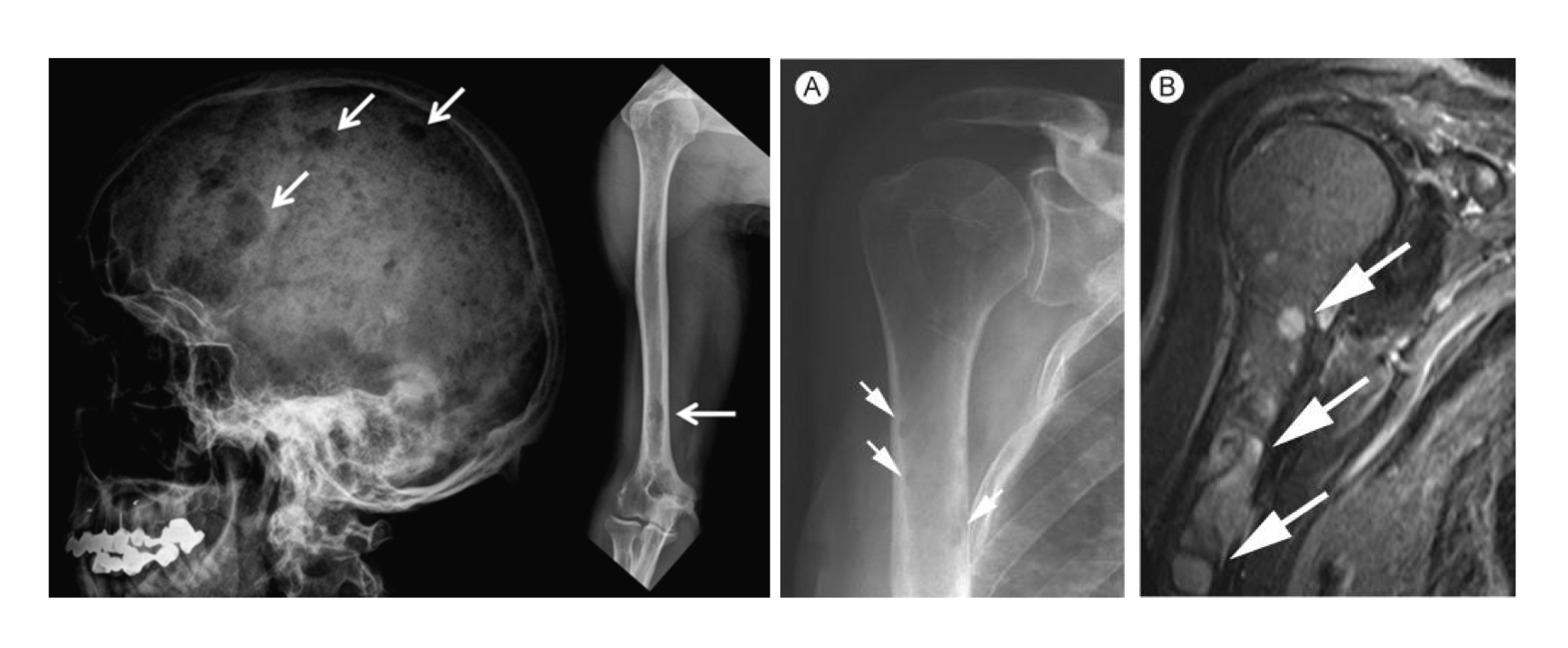
Multiple myeloma with punched out lytic lesions
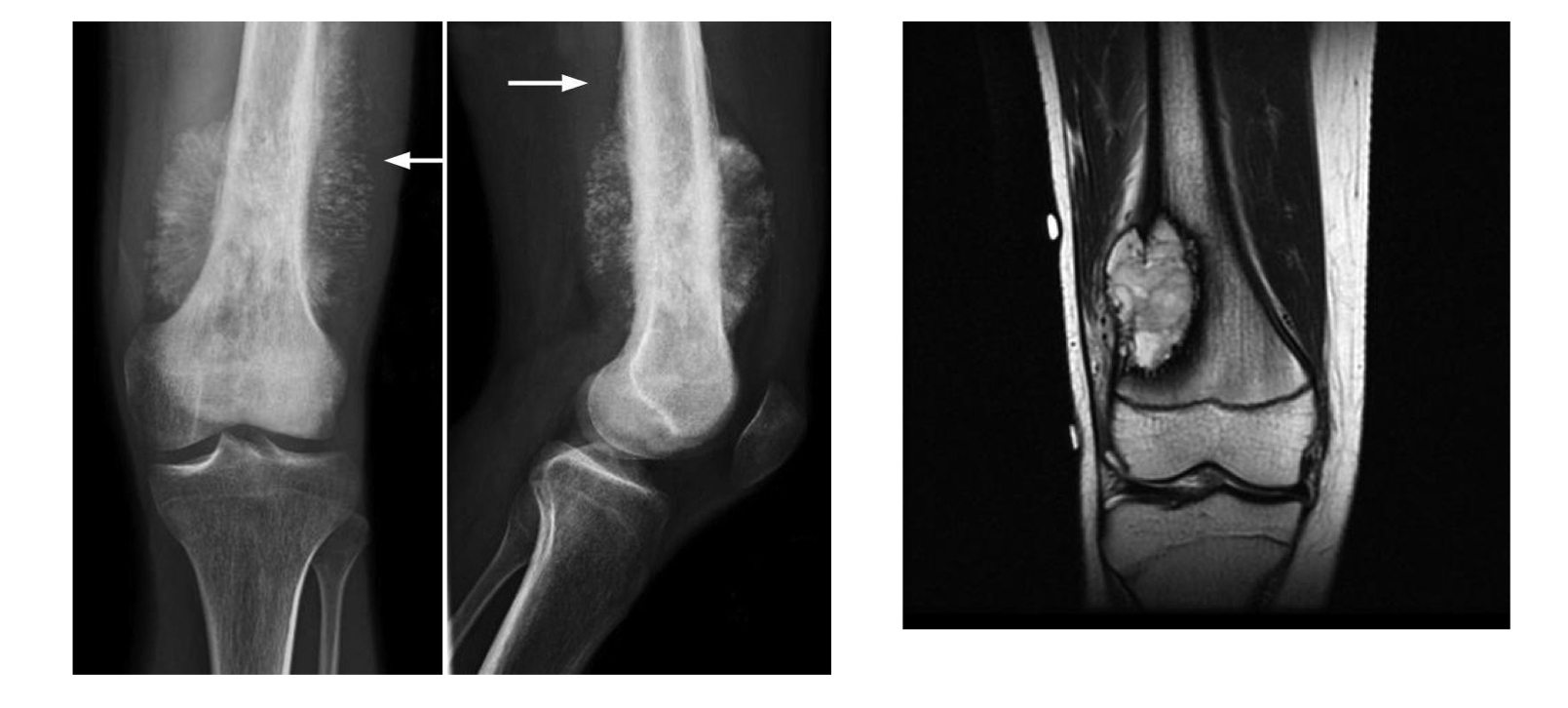
Osteosarcoma
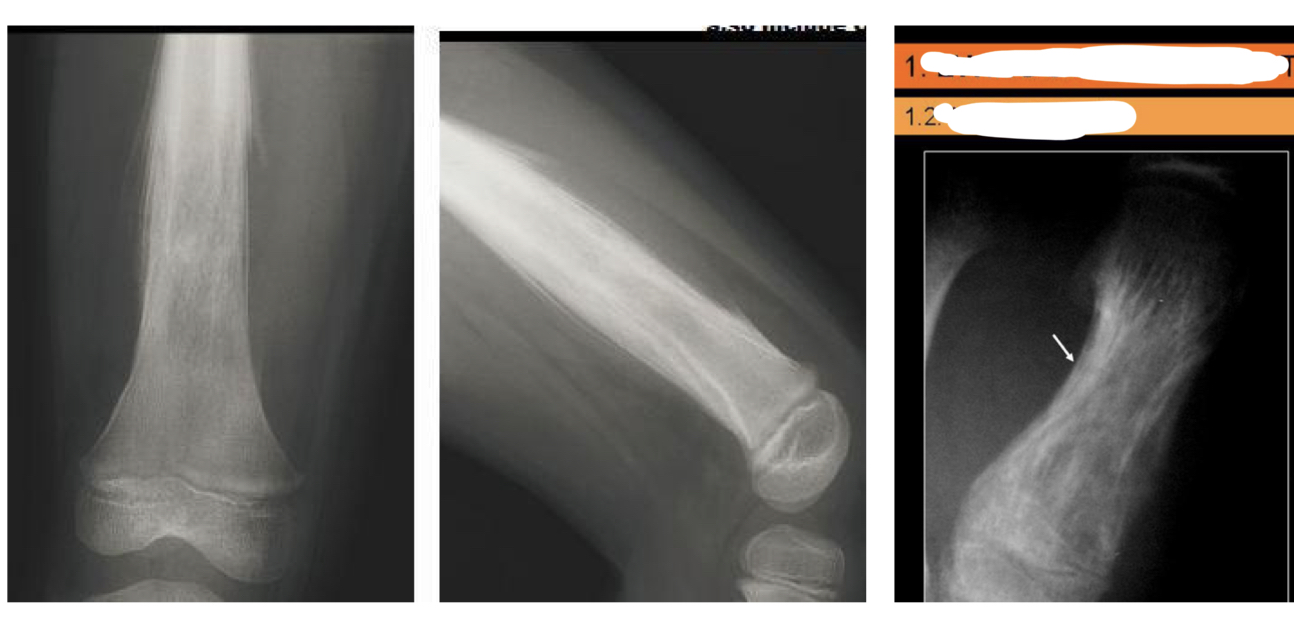
Edwings sarcoma
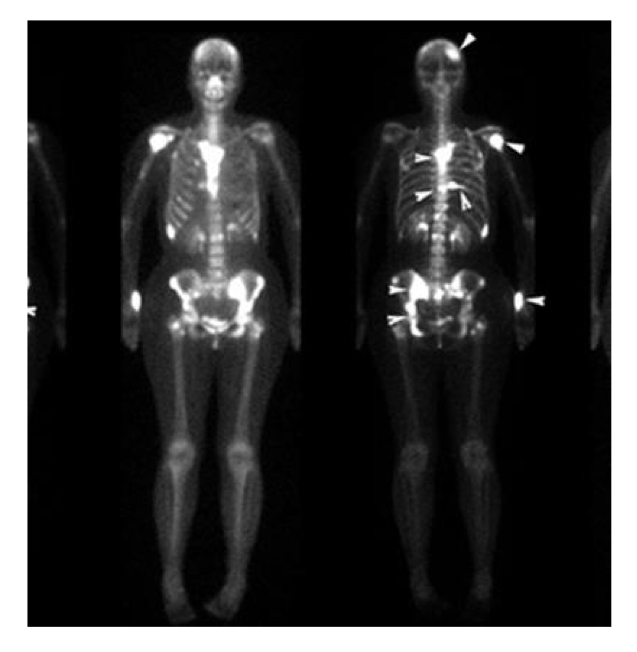
Bone metastasis
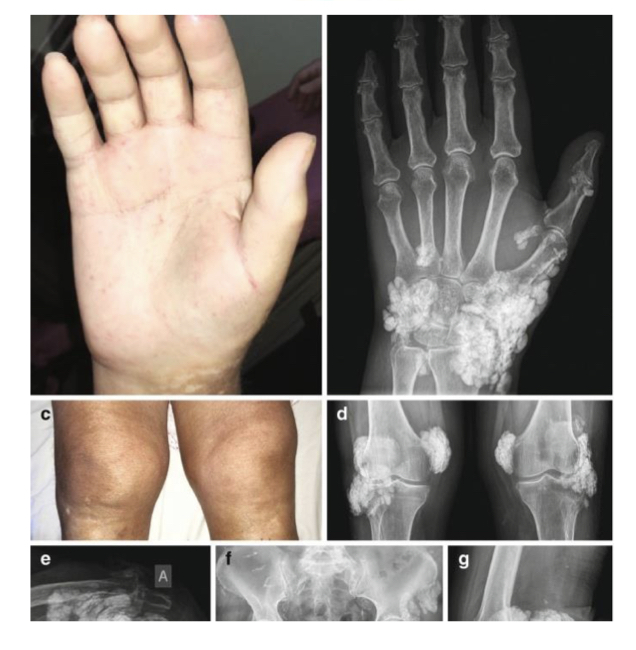
Scleroderma