Grade 12 Biology; Photosynthesis
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
;Photosynthesis Equation
6H20 + 6CO2 + Sunlight ----> C6H1206 + 602
6 Water + 6 carbon dioxide +sunlight ----> glucose + oxygen
Chlorophylls
Absorb red and light, reflect green light
Carotenoids
Absorb blue and green light, reflect yellow, orange, red
What happens when a photon of light hits a photosystem
Stage 1: sunlight strikes the antenna molecules, the antenna molecules absorb the light energy and pass it around until it reaches the reaction
Stage 2: reaction center absorbs the energy and becomes excited
Stage 3: electrons are passed from the reaction center to the primary electron acceptor
Pigments
compounds that absorb certain wavelengths of light
Light dependent reactions
Absorb photons of light
reactants: H2O, light, NADP+, ADP
Products: O2, ATP, NADPH
water is split to release electrons and oxygen, electrons move along the ETC to make NADPH and ATP. Oxygen is released to the environment
Calvin Cycle
reactants: ATP, NADPH, CO2
products: glucose
use the energy in ATP/NADH
to convert CO2 into glucose
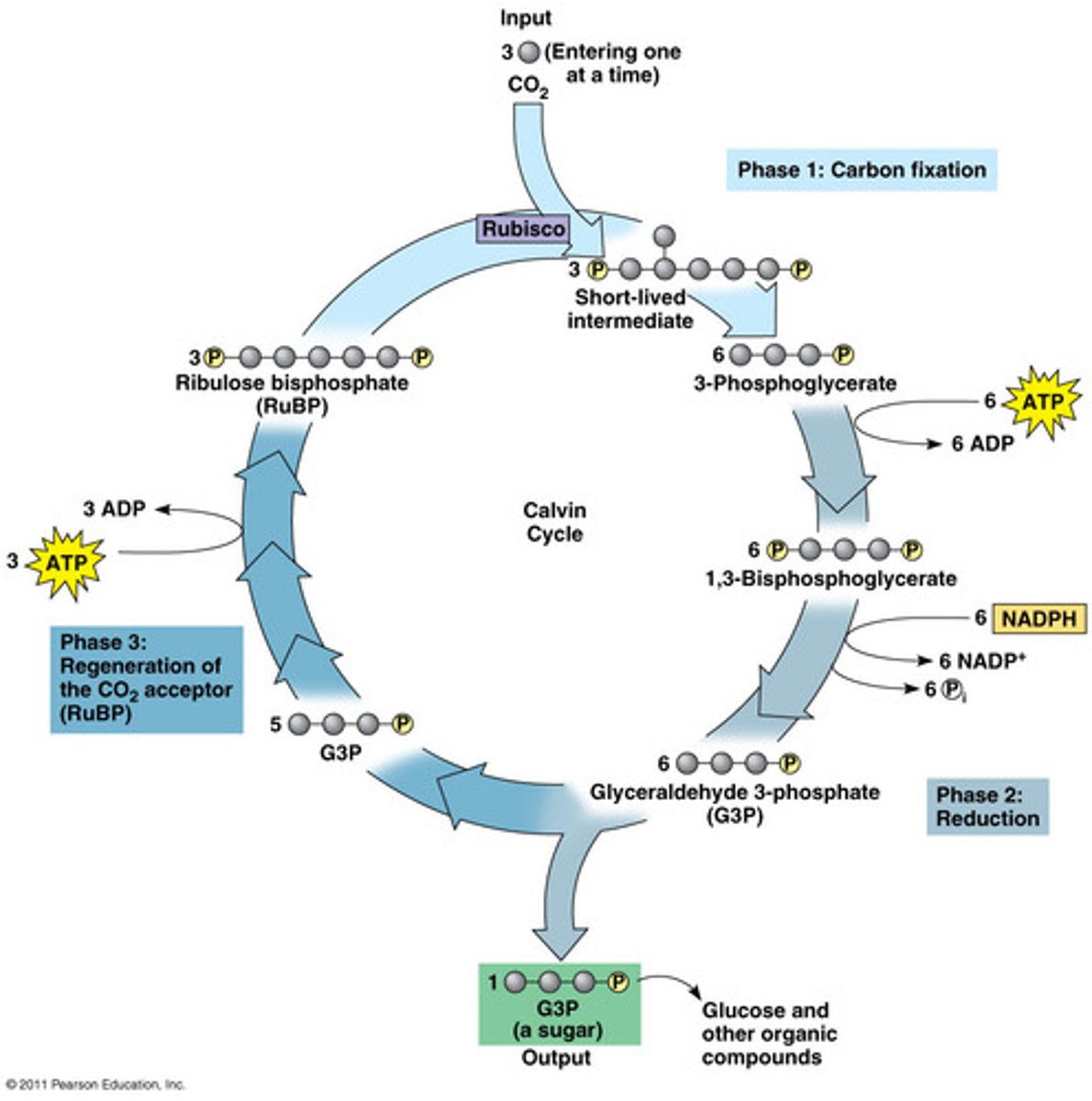
Calvin Cycle Diagram
For 1 glucose molecule this cycle has to happen twice
uses a total of:
6 CO2
18 ATP
12 NADH
Leaf Anatomy Diagram
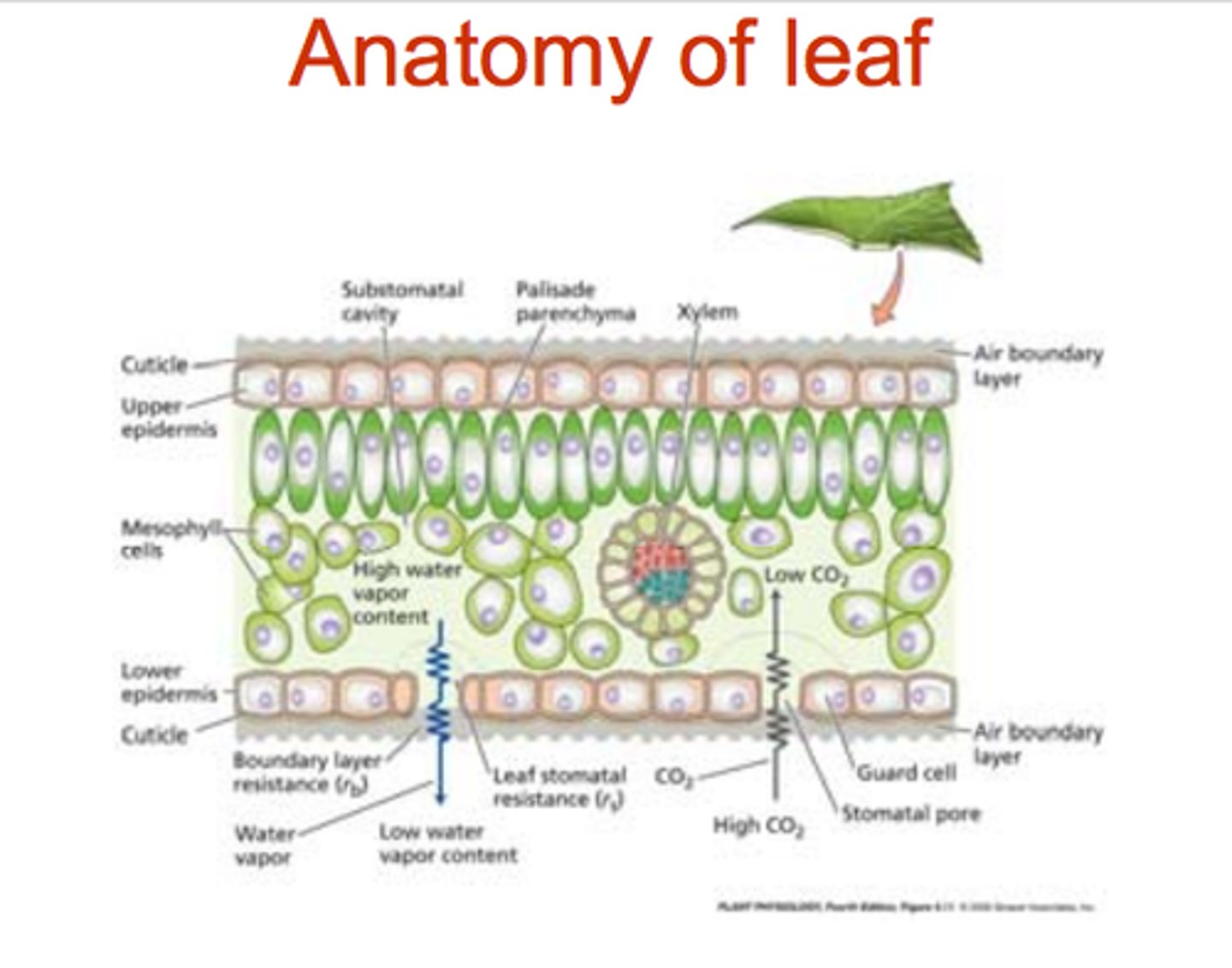
Palisade Mesophyll
Where photosynthesis occurs
Spongy Mesophyll
Photosynthesis also happens here, but it is also designed for gas exchange
Phloem (veins)
transports sugar, proteins and other organic molecules
delivers sugar to root or grain
Xylem
transports water and other water-soluble nutrients
delivers water from soil
stomata function
CO2 and H20 to enter
02 to exit