oxygen
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
oxygen
what it is: colorless, odorless, tasteless gas; basic need for life
no oxygen(hypoxia) = cell metabolism slows → cells die → brain damage & death in minutes if breathing stops
oxygen therapy: ordered by health care provider (amount given, device given on, and when given), it helps prevent/relieve hypoxia and must be closely monitored by the nurse, or any licensed specialist
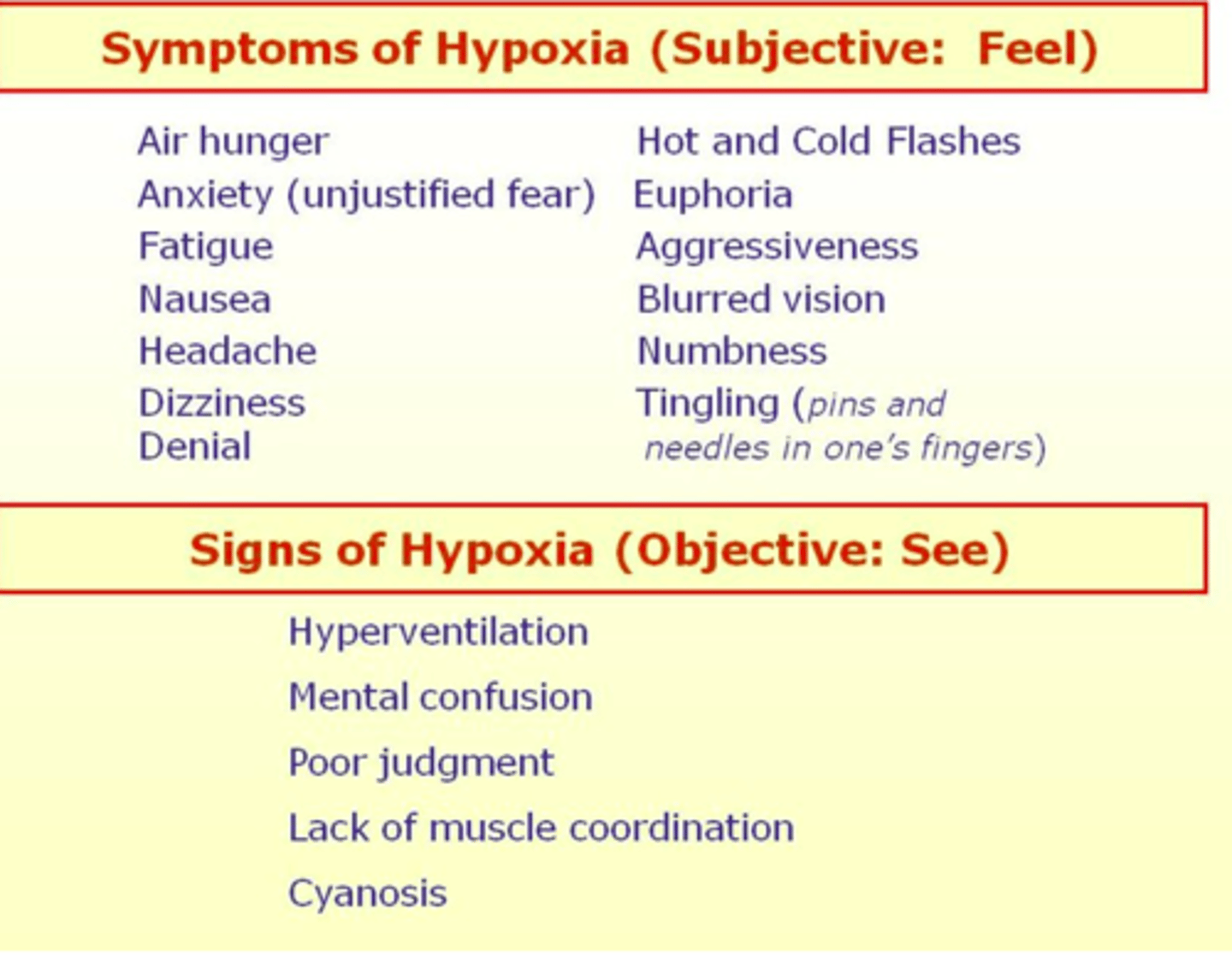
hypoxia signs/symptoms
definition: reduced oxygen content in tissues and cells; cell metabolism slows and cells begin to die
key signs and symptoms:
apprehension, anxiety, restlessness (EARLY!!)
tachycardia, dysrhythmias, increased BP (early); later → bradycardia
dyspnea, increased rate & depth of respirations; later → shallow, slow, apnea
cyanosis, pallor
decreased ability to concentrate, increased loss of consciousness
increased fatigue
digital clubbing (with chronic hypoxia)
vertigo
nursing interventions for hypoxia and positioning
position: high-fowlers or semi-fowlers
orthopneic position = difficultly breathing patients
apply oxygen as ordered, check device and flow rate
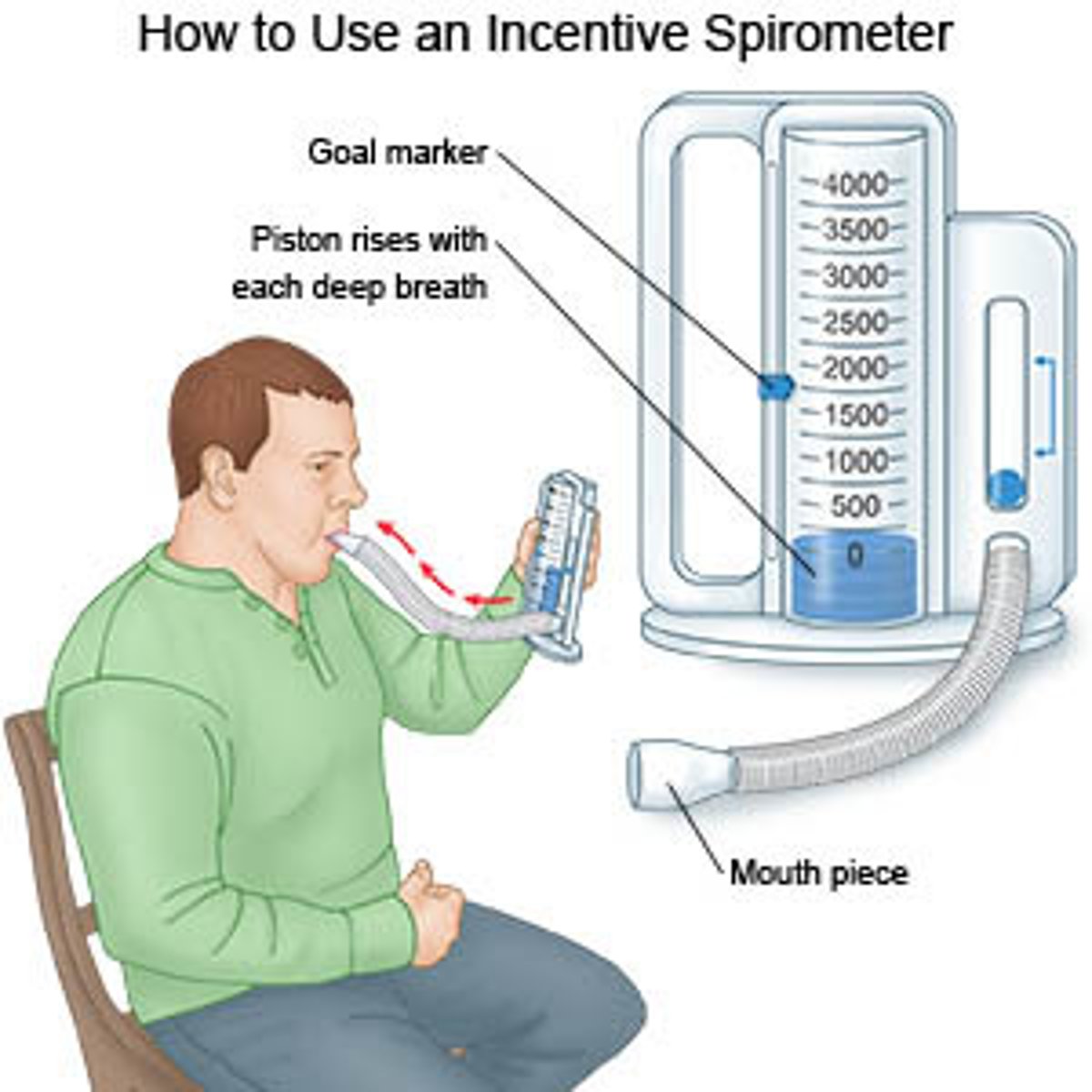
encourage deep breathing and coughing; use incentive spirometer if ordered
monitor pulse oximeter, respirations, lung sounds, and mental status
suction if needed to clear airway (trach/oral/nasopharyngeal)
abnormal respiratory patterns
tachypnea: RR > 20/min – EARLY sign of hypoxia
bradypnea: RR < 12/min – LATE sign of hypoxia
apnea: no breathing – code blue!
hypoventilation: slow, shallow, sometimes irregular respirations
hyperventilation: rapid, deeper than normal respirations
dyspnea: difficult, labored, or painful breathing
cheyne-stokes: gradual increase rate & depth → then become shallow & slow → period of apnea (10–20 sec)
orthopnea: difficulty breathing when lying flat
kussmaul’s respirations: very deep and rapid; often seen with metabolic acidosis
cyanosis: bluish discoloration due to low oxygen
thick secretions: nursing interventions and prevention
ensure adequate hydration = non caffeinated, low sugar, avoid dairy excess
humidify oxygen to prevent drying and thin mucus; only use distilled water and fill every 24 hours
encourage cough deep breath
use incentive spirometer
ambulte/sit the patient out of bed and elevate head of bed
suction (nasopharyngeal,trach,oral) as needed using sterile technique for invasive suctioning
use bronchodilators/steroids as ordered = COPD or asthma
pulse oximetry
measures oxygen saturations = percentage of hemoglobin that is carrying oxygen in arterial blood
normal is 95%-100%
(for most patients COPD often have a lower goal percentage per order)
sensor sites: finger,toe,earlobe,nose,forehead
- avoid swollen/edema or open skin sores
- if poor circulation to fingers/toes → use earlobe, nose, forehead
- set alarms for continuous monitoring
patient problem statements
inability to clear airway
inability to maintain adequate breathing pattern
inability to tolerate activity
anxiousness, fearfulness, and despair
compromised verbal communication
interventions to help clear airway
cough, deep breathe
raise head of bed as tolerated
get patient out of bed and ambulate
incentive spirometer = help patient take slow deep breaths
bronchodilator, steroid use, and humidifier as ordered
airway clearance devices (vibration vest and acapella)
percussion and postural drainage as ordered
fraction of inspired oxygen
FiO2: flow rate of oxygen is ordered in liters per minute, determines how much oxygen the patient will recieve; however there are different percentages of oxygen
nasal cannula: 1-6 L/min = 24%-44% (low concentration rate)
simple face mask: 5-8 L/min = 35%-55%
non-rebreather 6-15L/min = 70%-100%
1 liter/min = 0.24 it moves in 4s per liter -- 1-6 liters/min

tracheostomy tube
tracheostomy = tube dislodgement and accidental decannulations
keep an extra trach tube at bedside! observe for blood or purulent drainage around stomach
#1 goal is maintain patent airway
trach care: suctioning requires sterile technique intremintently while withdrawling and secure new tracheostomy ties before removing old ones
yankauer
used for oral suction; have unresponsive patient lie on side when oral suctioning

trach suctioning and more care
nursing priority: prevent hypoxia
preoxygenate with 100% FI02!
suction is performed if necessary, but no longer than 10 intermintently while withdrawling seconds causes hypoxia!
monitor pulse oximetry
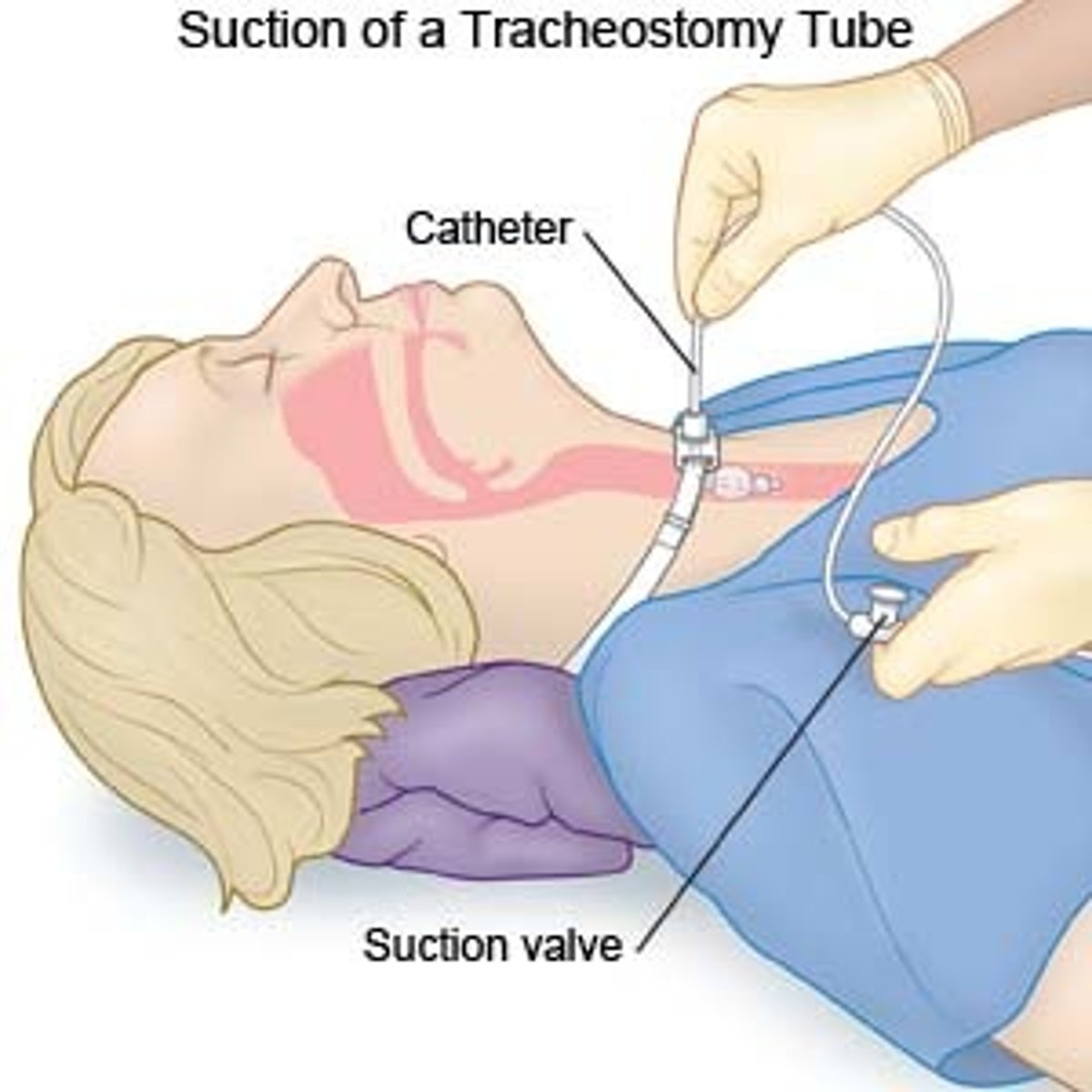
tracheostomy care continued
prevent infection in buildup of exudate
suction patient first before trach care
insert catheter = no suction
withdrawling catheter = suction
suction catheter discarded after each use!
CLEAN ONLY INNER CANNULA = HYDROGEN PEROXIDE
NORMAL SALINE FOR CLEANING TRACH SITE
complications of oxygen therapy
respiratory drive = increase in C02 levels
patients with COPD = hypoxic drive (given oxygen the presipratory drive may be diminished)
oxygen should be carefully titrated around 88%-94%
oxygen toxicity: causes scarring of respiratory tract and even blindness with prolonged high FiO2
safety measures of oxygen
oxygen does not burn or explode = avoid smoking use of electrical appliances
avoid and restrict flammable products
patient safety and comfort for oxygen
ventilation: semi-fowlers and high-fowlers
check for skin breakdown where tubing or mask touches
use padding or change devices if needed
provide mouth care and humidification to prevent dryness
ensure patient can communicate needs with trach
aspiration precautions: nursing interventions
raise head of bed
check ability to swallow; consult speech therapy
thickened liquids or special diets
small bites, slow sips, no talking while eating
suction equipment at bedside for high-risk patients
monitor for coughing, wet voice, drooling, or pocketing food
assessment and interventions
assessment: respirations, pattern, depth, abnormal breathing problems
pulse oximetry, heart rate, and blood pressure
skin color = palor/cyanosis
mental status and fatigue
breathe sounds (clear or adventitious)
prescence of secretions/ cough effectivness
devices in use and flow rate
interventions:
postioning, cough/deep breathe, incentive spirometry
apply/titrate oxygen per order/check equipment
suction when needed --pre oxygenate with 100% of Fi02, limit to less than 10 seconds
provide humidification, fluids, and mouth care
reasess and document
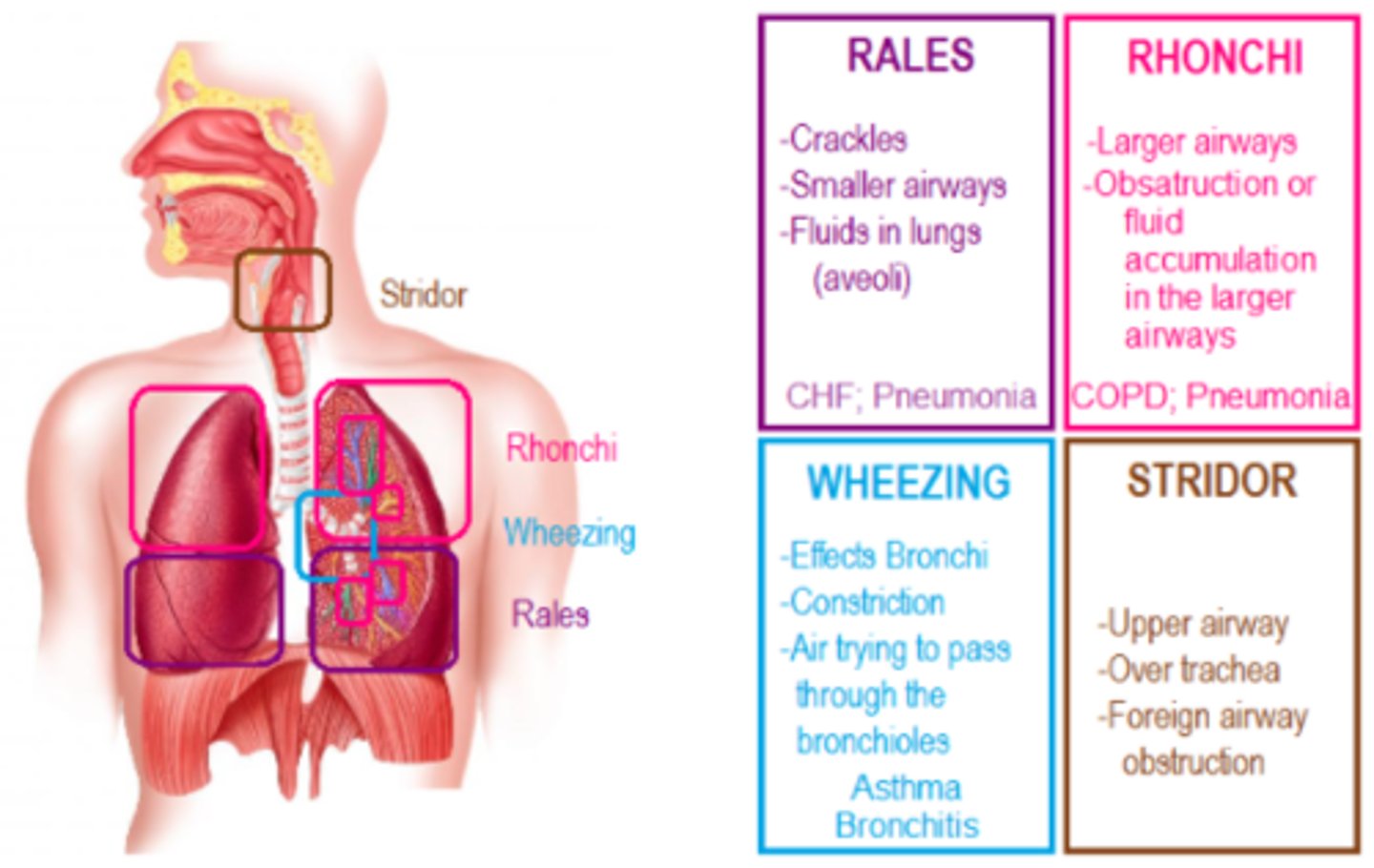
adventitious lung sounds
crackles (rales): popping, bubbling; fluid in alveoli (CHF, pneumonia)
wheezes: high-pitched musical; narrowed airways (asthma, COPD)
rhonchi: low-pitched snoring; thick secretions in larger airways
stridor: harsh, upper airway obstruction: EMERGENCY