MedChem Exam 1
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lectures 1-8
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
What is Medicinal Chemistry?:
a) The organic chemistry of drug design, drug development, and drug action
b) How the chemistry of a drug defines drug receptor interactions
c)How the chemistry of a drug defines its absorption, transport, and distribution properties
d)How the chemistry of a drug defines the metabolic transformations of drugs into other chemicals
e) all of the above
e) all of the above
Which of the following is the strongest interaction?:
a) Ionic (electrostatic) interactions
b) Ion-Dipole Interactions
c) dipole-dipole interactions
d) hydrogen bonding
e) hydrophobic interactions
f) Van der Waals interactions
a) Ionic (electrostatic) interactions
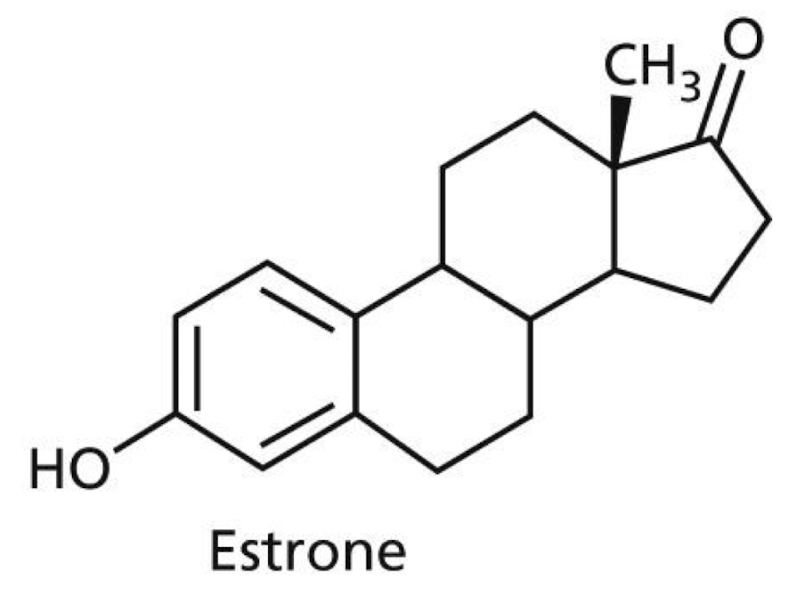
Which intermolecular interactions are possible with estrone?:
a) VDW, H-bond, Dipole-Dipole
b) Ionic, Dipole-Dipole, H-bond
c) Hydrophobic, Ionic, VDW
d) H-bond, VDW
a) VDW, H-bond, Dipole-Dipole
Which, in general, is the most important bonding interaction in protien tertiary structure?:
a) Covalent bonds
b) H-bonds
c) Ionic bonds
d) Van der Waals
b) H-bonds
Which of the following statements is not true about protein tertiary structure?:
a) Proteins fold up into a tertiary structure such that most amino acids with hydrophilic residues are exposed to the aqueous surroundings
b) Proteins fold up into a tertiary structure such that most amino acids with hydrophobic residues are in the center and hidden from the aqueous surroundings.
c) Proteins fold up into a tertiary structure such that most amino acids with hydrophobic residues are exposed to the aqueous surroundings
d) interactions between amino acid residues are important in protein tertiary structure
c) Proteins fold up into a tertiary structure such that most amino acids with hydrophobic residues are exposed to the aqueous surroundings
Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding transport proteins?
a) They are present in all cell membranes
b) they serve to carry polar molecules across the hydrophobic cell membrane
c) they are required to transport amino acids across acids across cell membranes
d) they are required to transport steroids across cell membranes
d) they are required to transport steroids across cell membranes
Serine (Ser, S)
Polar, Hydrophilic
Thyronine (Thr, T)
Polar, Hydrophilic
Tyrosine (Tyr, Y)
Polar, Hydrophilic
Asparagine (Asn, N)
Polar, Hydrophilic
Glutamine (Gln, Q)
Polar, Hydrophilic
Histidine (His, H)
Polar, Hydrophilic, Positively charged
Lysine (Lys, K)
Polar, Hydrophilic, Positively charged
Arginine (Arg, R)
Polar, Hydrophilic, Positively charged
Aspartate (Asp, D)
Polar, Hydrophillic, Negatively charged
Glutamate (Glu, E)
Polar, Hydrophilic, Negatively charged
Alanine (Ala, A)
Nonpolar, Hydrophobic
Valine (Val, V)
Nonpolar, Hydrophobic
Isoleucine (Ile, I)
Nonpolar, Hydrophobic
Leucine (Leu, L)
Nonpolar, Hydrophobic
Methionine (Met, M)
Nonpolar, Hydrophobic
Phenylalanine (Phe, F)
Nonpolar, Hydrophobic
Tryptophan (Trp, W)
Nonpolar, Hydrophobic
Which of the following amino acids acts as an acid-base catalyst in catalyzed reaction mechanisms?
a) serine
b) phenylalanine
c) histidine
d) tryptophan
c) histidine
Identify an amino acid in an active site whose residue could bind a drug principally by hydrogen bonding
serine
which of the following descriptions best describes a competitive enzyme inhibitor?
a) A drug that binds to an active site and undergoes a reaction
b) A drug that binds to an active site and inhibits the enzyme, but which is displaced by increasing the concentration of substrate
c) a drug that binds to an active site and inhibits the enzyme, but which is not displaced by increasing the concentration of substrate
d) a drug that binds to a different binding site from the active site and affects the activity of the enzyme
b) A drug that binds to an active site and inhibits the enzyme, but which is displaced by increasing the concentration of substrate
Which statement best describes the relevance of an allosteric binding site to medicinal chemistry?
a) it is more hydrophobic that normal binding sites and accepts hydrophobic drugs in prefrence to hydrophilic drugs
b) a larger variety of drug structures will bind to the allosteric site than to the active site
c) drugs can be designed based on the structure of the endogenous chemicals which bind to allosteric sites and control enzyme activity
d) drugs can be designed based on the transition state of the enzyme-catalysed reaction
c) drugs can be designed based on the structure of the endogenous chemicals which bind to allosteric sites and control enzyme activity
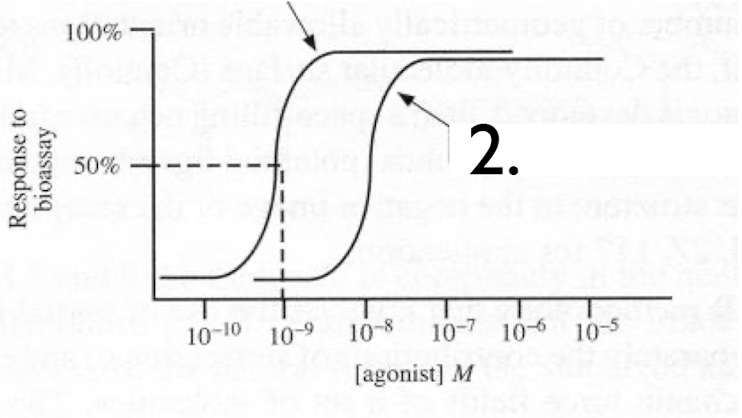
The dose response curve demonstrates
a) full agonist
b) agonist + Competitive Antagonist
c) agaonist + non-competitive antagonist
b) agonist + competitive antagonist
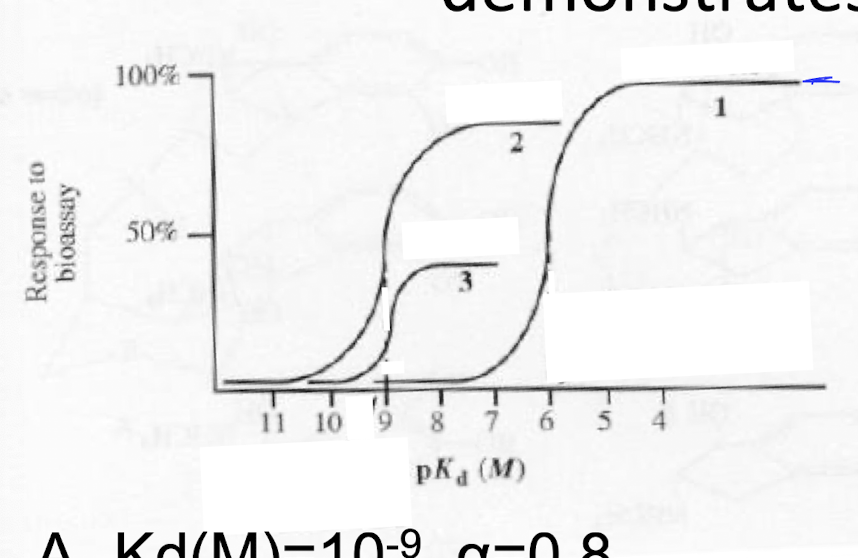
The (1) dose response curve demonstrates
a) Kd(M)= 10^-9, a=0.8
b) Kd(M)= 10^-9, a=0.4
c) Kd(M)= 10^-6, a= 1.0
c) Kd(M)= 10^-6, a= 1.0
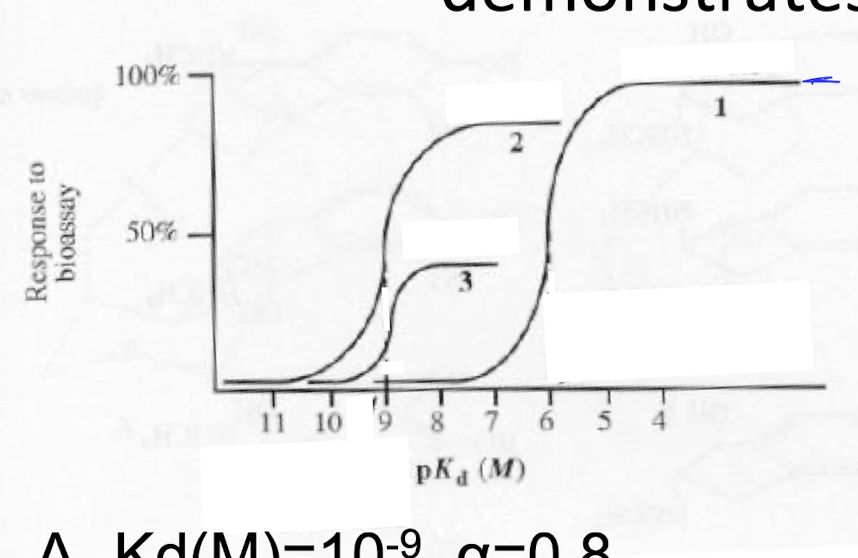
The (2) dose response curve demonstrates
a) Kd(M)= 10^-9, a=0.8
b) Kd(M)= 10^-9, a=0.4
c) Kd(M)= 10^-6, a= 1.0
a) Kd(M)= 10^-9, a=0.8
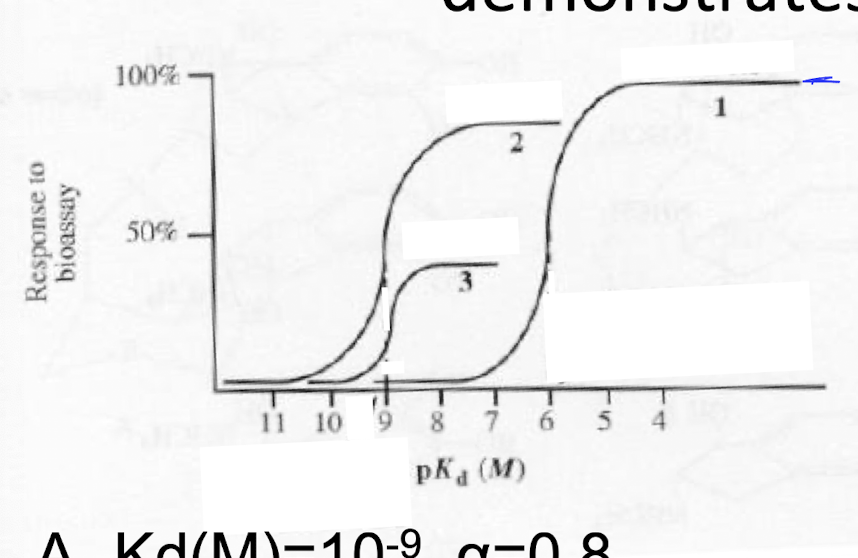
The (2) dose response curve demonstrates
a) Kd(M)= 10^-9, a=0.8
b) Kd(M)= 10^-9, a=0.4
c) Kd(M)= 10^-6, a= 1.0
a) Kd(M)= 10^-9, a=0.8