Enzyme regulation
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What are enzyme inhibitors
Molecules that decrease enzyme activity
Some are natural and some are synthetic
Reversible inhibition
Inhibitor binds non-permanently to the enzyme
Enzyme function can be restored
Often resembles enzyme’s substrate
Can bind to free enzyme (prevent substrate binding) or to ES complex (prevent reaction completion)
Irreversible inhibition
Inhibitor permanently alters the enzyme
Forms covalent bonds
Making it nonfunctional
Competitive inhibitors
Compete with substrate for active site
Structurally similar to substrate
Reduces substrate binding
Does not affect catalysis
Uncompetitive inhibitors
Bind at separate site than active site
Binds after substrate has attached to enzyme
Prevents enzyme from catalysing reaction
Mixed inhibitors
Binds to both free enzyme and ES complex
Inhibits both substrate binding and catalysis
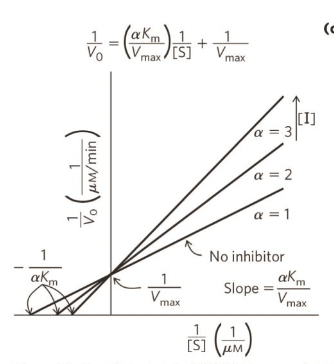
Competitive inhibition plot
Vmax (maximum reaction velocity) - remains unchanged (substrate can outcompete the inhibitor and saturate the enzyme)
Km - increases (enzyme affinity for substrate decreases), higher Km means lower affinity
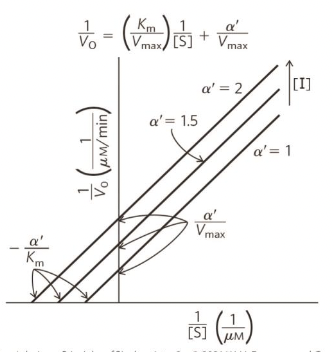
Uncompetitive inhibition plot
Km - decreases (higher affinity as enzyme holds substrate better as it is locked in place)
Vmax - decreases (inhibitor prevents reaction, fewer enzymes available to convert substrate to product, therefore can’t reach full speed)
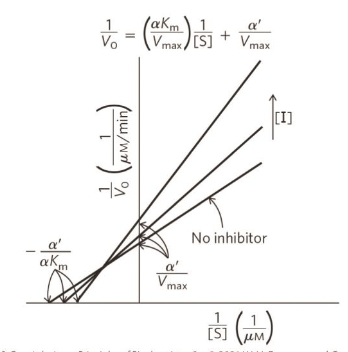
Mixed inhibition plot
Vmax - dcreases (always reduced the number of function enzymes, slows down reaction)
Km - unpredictable (if bind to free enzyme → Km increases like competitive inhibition, or bind to ES complex → Km decreases like uncompetitive)
Allosteric modulation
Enzyme activity is controlled by molecules that bind to a site other than active site
Positive (increase activity) or negative (decrease activity)
Homotropic (modulator is substrate) or heterotropic (modulator diff molecule)
Covalent modification
Enzyme regulated through addition/removal of chemical groups
Phosphorylation
Can activate or inactivate enzymes
Phosphate group is added to protein or enzyme
Enzymes involved - kinase (add phosphate) and phosphatase (remove phosph)
Basic reaction -
Protein + ATP → Phosphorylated protein + ADP
Phosphate group comes out of ATP
Zymogen
Inactive form of an enzyme
Requires cleavage of spcific speptide bonds to become active
Helps prevents premature enzyme activity, rapid activation and regulation
Zymogen activation
Proteolytic cleavage - small part of protein is cut off, causing conformational change that activates enzyme
Some examples include digestive enzymes
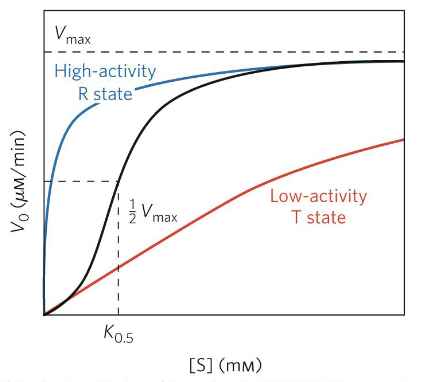
Phosphorylation ACTIVATES enzyme
Phosphorylated enzyme has higher activity
Curve is shifted upwards (higher Vmax)
Enzyme reaches Vmax faster at lower substrate concentration
Km might decrease → higher affinity
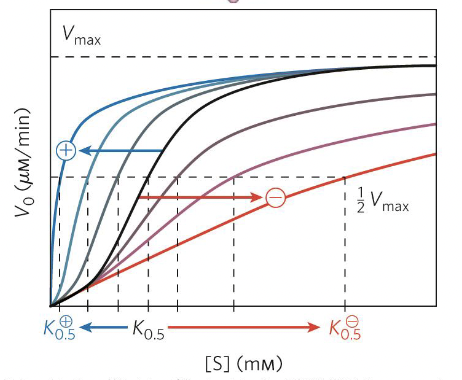
Phosphorylation INHIBITS enzyme
Phosphorylated enzyme shows lower activity
Curve is lower (lower Vmax)
Needs more substrate to reach half maximal velocity (higher Km, lower affinity)