Ch. 1 -3 Nuc Med I
1/192
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
193 Terms
Clinical applications involve the administration of radioactive tracers (radiopharmaceuticals) to provide diagnostic information regarding disease states
What is nuclear medicine
therapeutically
Some isotopes can also be used _______ to treat certain diseases
gamma ray or high energy photon
When the radionuclide decays it emits a ________.
True
True or False: The energy level of these photons are high enough that a significant number can leave the body without attenuating or being scattered in the body.
a gamma-ray or positron emitting radionuclide
What is a compound labeled with in nuclear medicine?
radiopharmaceutical or tracer
The radiolabeled compound is also called
single photon imagaing and positron imaging
Two classes of nuclear medicine imaging
gamma-ray emission
What type of radionuclide decay does single photon imaging use
positron emission
What type of radionuclide decay does positron imaging use
Tc 99m
What radionuclide decays by gamma ray emission, typically used in single photon imaging
Single Photon Emissions Computed Technology
SPECT
short
Positrons have a ______ lifetime
annihilates; electron; two
During positron Imaging, the positron interacts with and _____ an ______ to emit _____ high energy photons
tomographic
What type of images are formed in positron imaging
False
True or False: Tomographic images in Positron Imaging are form from on angle
biological or physiologic
Nuclear medicine provides _______ information whereas other modalities provide outstanding anatomic images
tissue perfusion, glucose metabolism, somatostatin receptor status of tumors, density of dopamine receptors in the brain and gene expression
examples of the diverse biological processes that can be measured by nuclear medicine include
Ture
True or False: Nuclear medicine is more specific compared to CT/US/MRI
metabolic process
Exams in nuclear medicine have tailor made pharmaceuticals which allow us to specifically target the ________ in the body that is called into question.
FDA
What governing organization has approved safe radiation doses for each compound?
planar; one
A ____ image is obtained by taking a picture of the radionuclide distribution in the patient from ______ particular angle
Henri Becquerel 1896
Discovery of radioactivity - who and when
Marie Curie 1898
Discovery of Radium - who and when
Wilhelm Roentgen 1895
Discovery of x-rays - who and when
Blumgart & Weiss 1927
first human study using radioactive tracers - who and when
Earnest Lawrence 1930
Invention of the Cyclotron
Hal Anger 1958
Invented the first nuclear medicine gamma camera for imaging - who and when
Paul Harper 1964
Implemented the use of 99mTc in Nuclear Medicine
Benedict Cassen 1951
Developed the Rectilinear scanner
Moly Cow
Mo-99/Tc-88m generator is also called
Mo-99; Tc-99m
Moly Cow - Saline Solution flows through ____ sample collecting ______,
True
True or False: Nuclear medicine is the only modality that has the capability of incorporating other radiology scanners
PET/CT
Gives great physiological information paired with CT’s anatomical data for scans
PET/MRI
Studies are still being done to determine proper protocols for imaging and scanning. Has the potential to have the best technology for soft tissue pathologies.
Quantities
Physical properties such as time and energy that can be measured in units, such as seconds and joules.
Quantity
Describes what is measured
Unit
Describes how much
Base Quantity
the given standard that everything is measured to, i.e. the original distance (m), mass (kg) and time (sec)
Derived Quantities
Are combinations of base quantities
Particulate radiation
Atomic or subatomic particles that carry energy in the form of kinetic mass in motion
Electromagnetic Radiation
Energy is carried by oscillating electrical and magnetic fields traveling through space at the speed of light
waves; photons
Electromagnetic radiation behaves as ____ but can also be labeled as _____
high energy and short wavelengths
Why do X-ray and Gamma radiation behave differently from other types of radiation
atom
the smallest unit that any chemical element can be broken down into without losing its chemical identity
John Dalton
an atom was hypothesized as to its exact theoretical structure
Nucleus
The positively charged core of an atom containing protons and neutrons
Electron
the negatively charged particle that is rotating around the Nucleus
Proton
the positively charged particle that is fixed in the nucleus
neutron
the neutral charge particle that helps maintain gravitational balance of the atom
identical
Protons have an _______ energy requirement to Neutrons due to their heavier size
0.511 MeV
energy level of an electron
938.272 MeV
energy level of a proton
938.272 MeV
energy level of a neutron
K , L, M, N
order of energy levels (shells) of an atom
to maintain thermodynamic configuration
Why do stable atom follow configuration that allow them to fill th inner electron levels first and then their outermost shells
increases
The more positive the charge of the nucleus _____ the binding affinity of the electrons
the electromagnetic pull of the charge differentials
why does the binding affinity of the electrons increase with the a more positive charged nucleus
outer shell electrons
which electrons require the least amount of energy to be emitted
outer shell electrons
which electrons are usually targeted when radiation is being emitted
bone scan
example of planar image
radioactivity
process involving events in individual atoms and nuclei
Dalton (Da) or unified atomic mass unit (u)
basic unit of mass of biomolecules
electron volt (eV)
basic unit of energy
electron volt
the amount of energy acquired by an electron when accelerated through an electrical protentional of 1 V
1 eV = 1.6022×10^-19 kg*m²/sec²
conversation of SI energy units to electron volt
931.5 MeV
1u = ______ MeV
radiation
energy in transit
Particulate radiation
consisting of atomic or subatomic particles (electrons, protons, etc.) that carry energy in the form of kinetic energy of mass in motion
Electromagnetic radiation
energy is carried by oscillating electrical and magnetic fields traveling through space at the speed of light
none
What is the mass of a photon
none
what is the charge of a photon
speed of light
speed of a photon
radio; micro; infrared; visible light'; UV; x-rays; gamma
list of EM rays from lowest energy to highest energy
Z
Atomic number symbol
binding energy
The energy required to completely remove an electron from a given shell in an atom
increases
binding energy _______ with the positive charge of the nucleus
the difference in binding energies between the two shells
The energy required to move an electron from an inner to an outer shell is exactly equal to
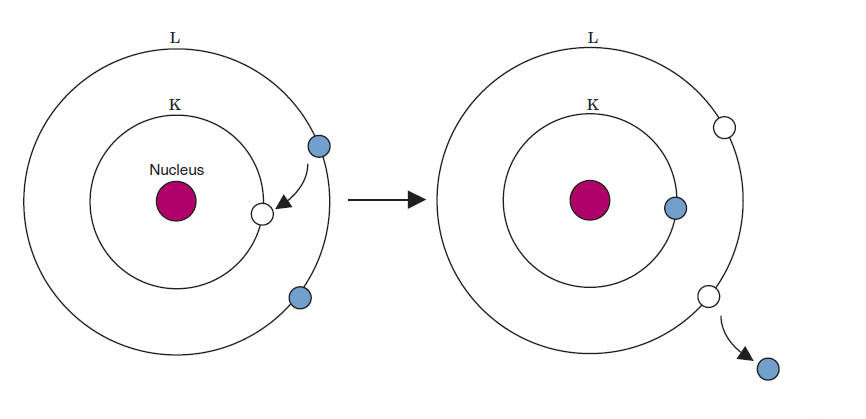
Auger effect
an electron from an outer shell again fills the vacancy, but the energy released in the process is transferred to another orbital electron
When an electron fills a vacancy in a lower energy shell energy emitted from that is characteristic radiation. An auger electron is emitted when an outer shell electron fills an inner shell vacancy the energy released from those transfers to another electron that is then emitted from the atom, that electron is Auger electron
What is the difference between characteristic radiation and an Auger electron
two
how many orbital vacancies exist after the auger effect occurs
fluorescent yield
The probability that a vacancy will yield characteristic x rays
characteristic x-ray
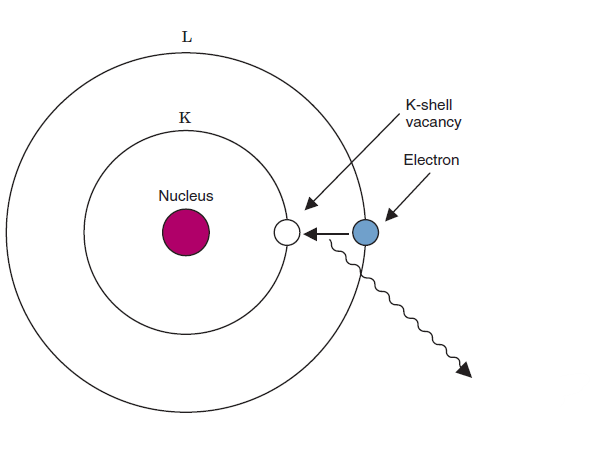
Auger effect
A
atomic mass number symbol
Atomic mass (A) on TOP, atomic number (Z) on bottom
Order of atomic mass and number in the atomic composition
N
neutron number
938.272 MeV
Energy of a proton
isotopes
Nuclides that have the same atomic number Z
125-I, 127-I, and 131-I
examples of isotope families
isobars
Nuclides with the same mass number A
131-I, 131-Xe, and 131-Cs
examples of isobars
isotones
Nuclides with the same neutron number N
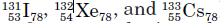
examples of isotones
isotopes have the same number of protons, isotones the same number of neutrons, and isobars the same mass number (A)
mnemonic technique to remember nuclide types
coulombic forces and nuclear forces
Two kinds of forces withing the nucleus
REPULSIVE forces that exist between positively charged protons
what are coulombic forces
ATTRACTIVE forces that exist between two nucleons (neutron/proton)
what are nuclear forces
repulsive coulombic forces between protons
Nuclear forces hold the nucleus together against the
ground state
The most stable arrangement of nucleons