Advanced Separations and Mass Spectrometry
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
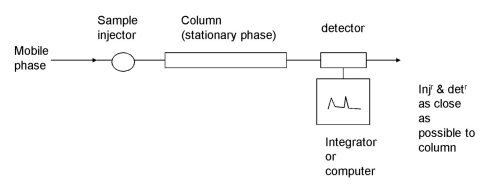
What is the apparatus used for chromatography?
A sample is injected into the mobile phase, which then passes through the column (containing the stationary phase) and arrives at a detector.
The sample added is the eluent.
The mixture that passes out the column is the eluate.
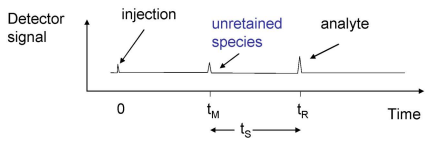
What does a chromatogram look like?
The sample is injected at time 0.
tM represents the unretained species that doesnt interact with the column at all, also called void time.
tR represents the retention time of the analyte.
tS is the time between tM and tR, it represents the strength of the interaction between the sample and the stationary phase.
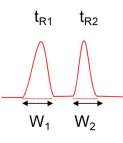
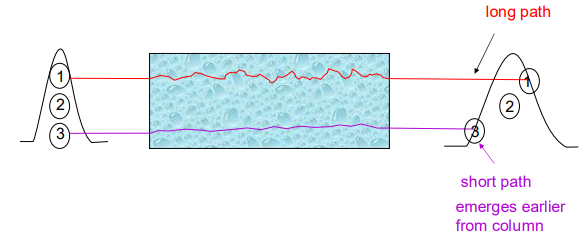
What is resolution?
It is how well you can tell the peaks apart.
Defined in terms of retention times and peak width:
ΔRs = ΔtR / Wav or Rs = 2(tR2 - tR1)/W2+W1
Where Wav is the average of the peak widths at the base.
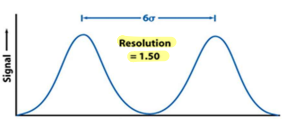
What is the desired Rs value for baseline resolution?
1.5
This is the smallest resolution at which the signal is able to go to 0 before the next peak begins.
What is the capacity factor?
k’ is the amount of time the solute spends in the stationary phase relative to the amount of time the solute spends in the mobile phase.
The longer the component is retained by a column, the greater k’.
How do you calculate k’?
An ideal range is 1-5, however it is often around 0.5-20.
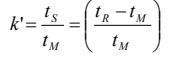
What is the selectivity factor?
α is the selectivity factor, it is the ratio of the capacity factors.
For separation to occur, the analytes must have different capacity factors.
How do you calculate α?
It should always be above 1.

How do you rearrange the k’ equation to incorporate the equilibrium constant K?
If the column runs slowly enough at equilibrium, CS/CM is the equilibrium constant K.
Because the ratio of phase volumes is constant for a given column and mobile phase, k’ is directly proportional to K.
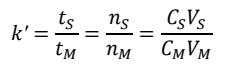
What is migration velocity?
The speed of movement through the column, it depends on the distribution of the analyte between the mobile and stationary phase.
If more analyte is in the mobile phase, net velocity is higher.
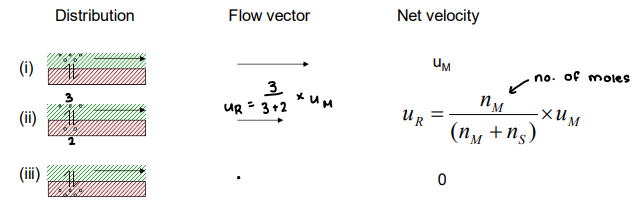
How do you calculate the velocity of the retained species?
uR is the velocity of the retained species.
nM is the number of moles of mobile species.
nS is the number of moles of stationary species.
uM is the velocity of the mobile species.
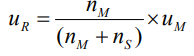
How do you rearrange the k’ equation for uR and uM?
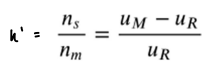
How do you rearrange the k’ equation for velocity in terms of column length and elution time?
Column length is L.
Elution time is t.
Velocity= L/t.
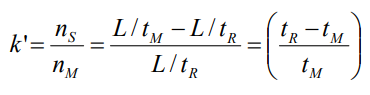
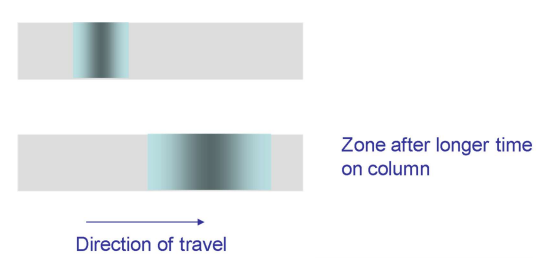
How does the band shape change over time?
The shape of the band changes over time, however the total area under the peak remains constant.
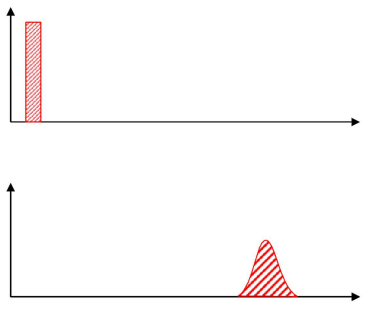
What is the rate theory of chromatography?
As the particles move through the column, they do not move evenly. This causes a symmetrical spread of velocities around a mean value.

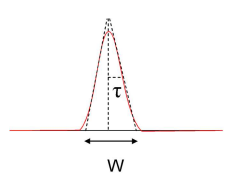
What are Gaussian shaped peaks?
Band broadening for Gaussian shaped peaks is a statistically random process.
σ is standard deviation (length units)
τ is standard deviation (time units)
τ = W/4
σ2 = τ2, this represents variance.
68% of peak area is in the range tR ± τ
How does diffusion cause band spreading?
The diffusion coefficient measures the rate at which a substance moves randomly from a region of [high] to a region of [low].
σ2 = 2Dt
t is measured in seconds.
How does the partition coefficient K affect band shape?
A Gaussian bandshape occurs when K is independent of the concentration of the solute on the column.
Skewing occurs when K is dependent on concentration.
What is fronting?
When overloading occurs as too much solute is added.
Can be corrected by using a smaller sample or diluting.

What is tailing?
When small quantities of solute are retained more strongly than large quantities.
Can be corrected by masking strong adsorption sites on the stationary phase.
What is plate height?
The constant of proportionality between the variance of the band and the distance it has travelled.
Can be thought of as the length of the column required for one equilibrium of solute between mobile and stationary phase.
Has units of length.
How does variance relate to plate height?
The standard deviation for diffusive band spreading is √2Dt. If a solute has travelled a distance x at linear flow rate ux, then it has been on the column for t = x/ux. This can then be rearranged.
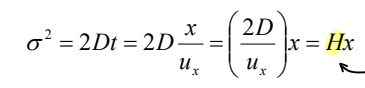
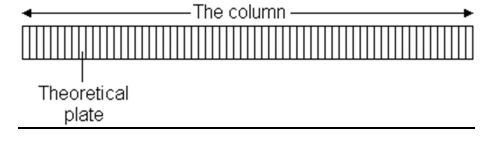
What is the plate model?
A column contains a large number of separate layers (plates). The analyte moves down the column by transfer of the equilibrated mobile phase from one plate to the next.
How does plate height relate to variance?
H = σ2 / L
Small σ means a small H
Large σ means a large H
Why do different solutes have different plate heights?
They have different diffusion coefficients.
What plate height is desirable?
A smaller plate height means a narrower bandwidth, so a small H is good.
What is efficiency?
The theoretical number of plates.
N = L/H
It is dimensionless, however a big N is desired.
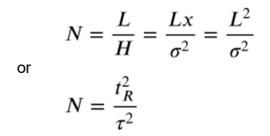
What factors are used to describe column performance?
Efficiency, N: Large is desired.
Plate height, H: Small is desired.
Peak asymmetry
k’
How can resolution be linked to band broadening?
As Rs = ΔtR / Wav, W = 4τ, and tR / τ = N1/2:
Therefore Rs is proportional to √N.
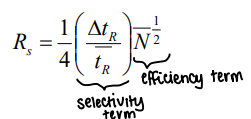
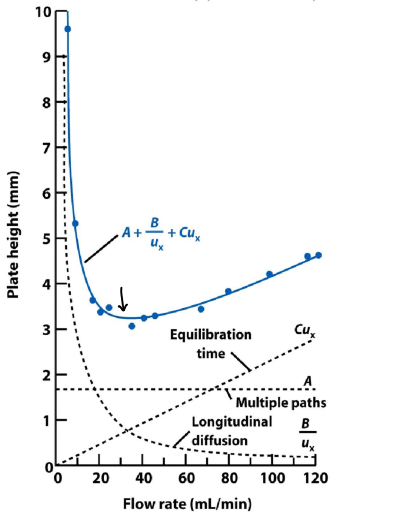
What is the van Deemter equation?
Links plate height and flow rate.
H = A + B/u + Cu
A represents multiple flow paths.
B represents longitudinal diffusion.
C represents mass transfer/equilibration time.
What is A (multiple flow paths)?
A measure of bandspreading. Bandspreading occurs as sample particles have multiple flow paths through the column.
Can be reduced by using smaller stationary phase particles.
Effect is absent in open tubular columns.
What is longitudinal diffusion (B/u)?
A measure of how the sample diffuses over time as it spends longer in the column.
Can be reduced by having a faster linear flow.
What is mass transfer (Cu)?
There is a finite time for the analyte to equilibrate between mobile and stationary phases.
Reduced by decreasing the stationary phase thickness/column radius, or increasing temperature.
How does H vary with u?
The extent of band broadening depend on the length of time the mobile phase is in contact with the stationary phase, therefore it depends on flow rate.
Cu increases with flow rate.
B/u decreases with flow rate.
The optimal flow rate gives the lowest value of H, in this example it is around 30mL/min.
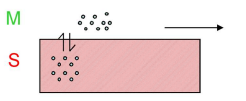
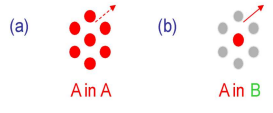
How do analytes elute in gas chromatography?
Analytes elute in order of their boiling points.
Molecules with similarity to the stationary phase are retained more strongly.
e.g. in case (b) the molecule is less strongly retained so has a higher tendency to escape into the vapour phase.
How do you find ΔG0 for the gas-liquid equilbirum?
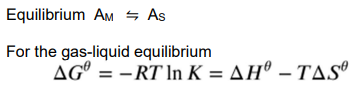
What is van’t Hoff’s isochore?
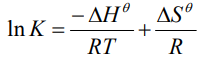
What is Trouton’s rule?
It shows that the standard entropy of vaporisation is approximately constant.
It is around 85 Jmol-1K-1 for many compounds.
How is boiling point linked to retention (via equation)?
ΔGθvap = 0 at b.p. (Tbp)
ΔHθ = TbpΔSθ
This can be substituted into the van’t Hoff isochore.
The k’ equation can be substituted into this equation.

How does k’ change with boiling point for homologous series of analytes?
lnk’ scales with TBP
k’ increases as TBP increases.
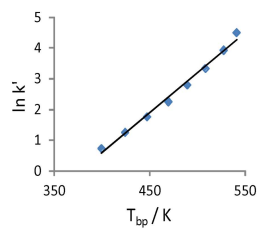
How does k’ change with boiling point for all analytes?
lnk’ scales with 1/T
k’ decreases as T increases.
How can retention time be controlled by varying T?
You can use a programmed temperature range to elute analytes with a wide range of boiling points.
e.g. a programmed temperature between 50-250oC at a ramp rate of 8oC/min
What are packed columns?
A column which is packed with a compound such as zeolite or alumina, creating high flow resistance.
Has a shorter length, around 2-3m.
Has a high phase ratio (VS/VM)
Has low efficiency.
No overloading possible.

What are open tubular columns?
A column that has an open centre, similar to a capillary.
Has low flow resistance.
High length, around 15-100m.
Low phase ratio.
High efficiency.
Can be overloaded if too much analyte is injected.

What is the order of elution in reverse phase liquid chromatography?
Analytes elute in order of their hydrophobicity, most hydrophobic analytes elute last.
HPLC has a polar MP and non-polar SP.
What is eluent strength?
Elution occurs when solvent displaces solute from the SP.
Eluent strength (ε°) is the solvent adsorption energy (defined as 0 for pentane on bare silica).
As ε° increases, solutes elute more rapidly.
How does eluent strength vary with solvents?
As solvent strength increases, ε° increases.
e.g. MeOH has a smaller ε°, and THF has a higher ε°.
In RP, ε° is higher for less polar solvents.
How do you control k’ in LC?
Can add an organic modifier.
log k’ = log k’w – SΦ
Φ is the volume fraction of OM in the mobile phase and S is related to the type of OM (solvent strength).
k’w is k’ in water.
log k’ decreases linearly with volume of OM.
How can you vary MP composition in HPLC and why?
By varying the MP, the magnitude of k’ can change by up to 4 orders of magnitude. This can make peaks clearer and k’ more of a reasonable value.
Change of solvent composition in HPLC is similar to change of T in GC.
Can vary MP composition by gradient elution, e.g. vary % of OM over a set time.
Isocratic elution is keeping the same composition throughout.
How can phase volume be changed in HPLC?
Can use porous vs non-porous silica.
A porous silica has a high surface area and high carbon loading. The SP bonds to the internal pores.
A non-porous silica has a lower surface area and low carbon loading. This means the phase ratio is much lower, and k’ decreases. The SP can only bond to the external surface.

What is plate height like in LC and why?
Transverse diffusion is slow in LC, therefore H is much smaller compared to GC.
In LC, there is a parabolic flow profile due to pressure driven flow. This is because the liquid in the centre of the column moves faster than the liquid near the walls.
This means fast equilibration is needed in the direction transverse to the flow to counteract broadening.
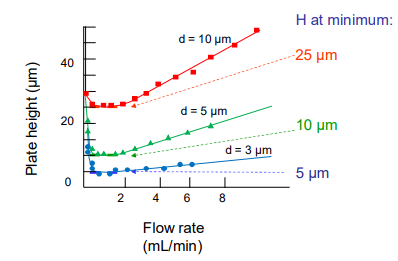
How does plate height change as a function of particle diameter in LC?
Reducing the particle size (dp) reduces the plate height.
H = A + B/u + Cu
A increases with dp as there is a less uniform flow through the column.
C increases with dp as it takes longer to diffuse through the inner pores.
What are the benefits and limitations of using a smaller particle diameter in LC?
A small diameter means a smaller plate height.
However, a small diameter means there is a higher resistance to solvent flow.
What is UHPLC?
Ultra-High Pressure Liquid Chromatography.
The use of a higher pressure to make elution time faster.
This is used alongside a smaller particle size to gain higher efficiency.
How do you calculate column efficiency in HPLC?
N = L/H
N is typically around 104
How does efficiency in HPLC compare to GC?
Plate height is lower in GC by a factor of around 10-100 due to faster diffusion.
Efficiency is higher in capillary GC by a factor of around 10 , this is due to a long column being used.
How do you optimise efficiency in LC?
Use a packed column with a particle diameter as small as possible consistent with pressure limitations.
Minimise any broadening effects.
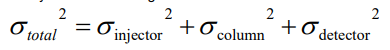
How do you determine minimum selectivity required for baselines peak separation?
For baselines resolution, Rs > 1.5. Rs is proportional to √N
Use 1.5 as the value for Rs to find minimum selectivity.
Multiply by 100 to find the percentage.
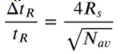
What is the key objective of chromatography?
To fully resolve all peaks in minimum analysis time.
If there is no separation, what should be changed?
In GC, change the stationary phase.
In LC, change the stationary or mobile phase.
If only partial separation is obtained, what should be changed?
Increase efficiency:
Increase column length.
Change flow rate.
Reduce SP thickness.
Increase T.
For a packed column, decrease particle diameter.
Why is MS used alongside chromatography?
Can tell you the mass of the parent ion and the fragmentation pattern.
How do you increase the signal to noise ratio in MS?
Use selected ion monitoring with the spectrometer bringing only ions of the desired mass to the detector
What are the basic 5 steps of mass spec?
Sample introduced via an inlet system
Vapourise/ionise molecules
Separate ions by m/z
Ion detection
Data processing
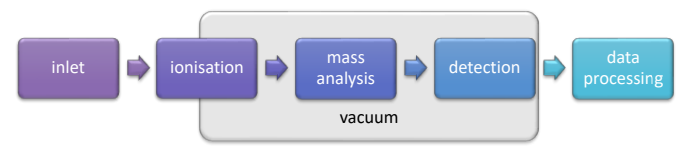
What is a quadrupole mass analyser?
A device with an even number of cylindrical rods arranged parallel to each other. Opposing rods are electrically connected as a pair.
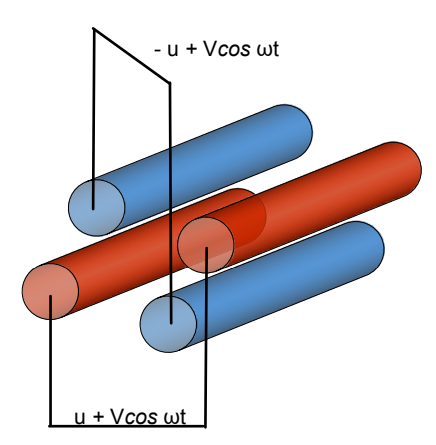
How do quadrupole mass analysers move ions through?
A cation will be pulled towards the negative rod, with ions of lowest KE being affected the most. If the voltage applied is then made positive, the cation will be repelled.
Constantly alternating the electric field at a rapid rate causes ions to zig-zag through the device without touching any rods. Ions with a particular KE will traverse the quadrupole, whereas ions with incompatible KE will collide with the rods and be lost.
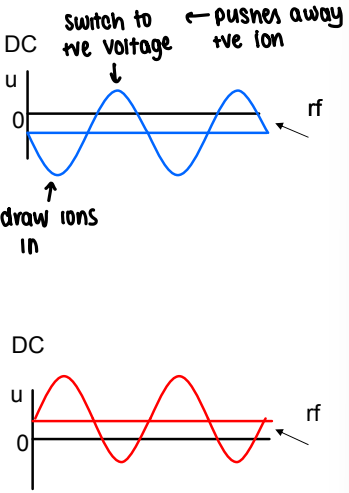
How do quadrupole mass analysers plot data?
If the quadrupole is set to transmit all m/z values, there will be no mass-to-charge separation, but this is used to guide the ions through the vacuum stages of the MS.
For ions of a single m/z value, a specific combination of DC and rf will provide great transmission, and all other m/z values will not make it through.
Different m/z values are scanned through one at a time, giving a stable trajectory for individual m/z values.
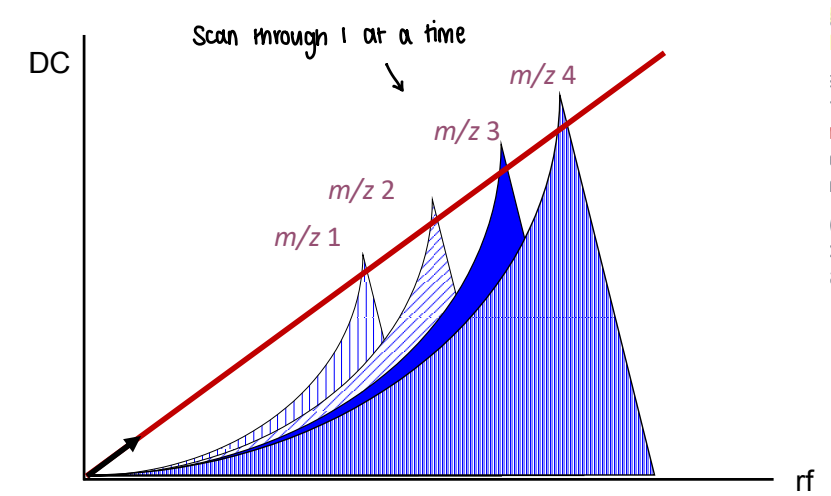
What are quadrupoles most commonly paired with?
Quadrupole: EI & GC
3 Quadrupoles: LC & ESI
What are the advantages of quadrupole mass analysers?
Cheap
Small
Robust
Easy to use
Can be very sensitive with detection limits (as low as pico or femtograms)
Widely used in tandem mass spec.
What are the disadvantages of quadrupole mass analysers?
Limited mass resolving power.
Only able to measure nominal mass.
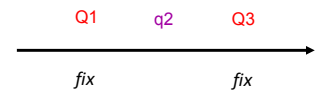
What is a triple quadrupole mass spec (MS/MS)?
Three quadrupoles are connected in a series (a type of tandem mass spec). This allows two sequential stages of mass spec.
The first quadrupole (Q1) is used as a mass analyser or to select/transmit a single ion.
q2 is rf only, therefore it is filled full of gas and ions are pushed through the gas.
Q3 is also used as a mass analyser.
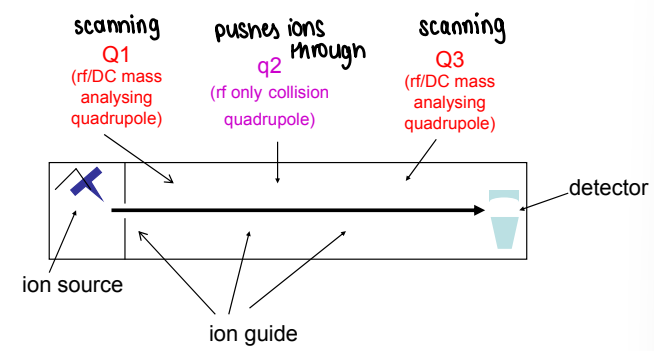
Why is tandem MS used?
It aims to controllably isolate an ion of interest, break it apart and measure the fragment ions, therefore giving information on structure.
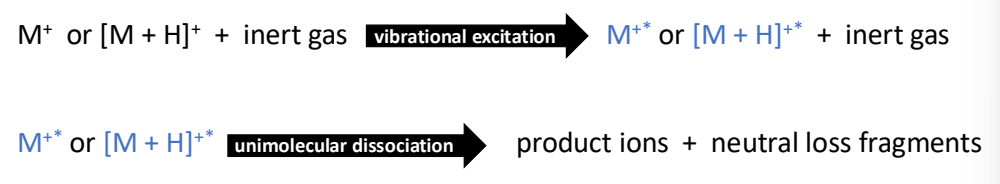
How are fragments made via collision-induced dissociation?
Accelerate ions and collide them with neutral gas molecules (e.g. Ar, He or N2).
Some KE is converted to internal energy.
Ions become vibrationally excited which leads to unimolecular dissociation.
Fragments include the product ion (retaining the charge) and the neutral loss.
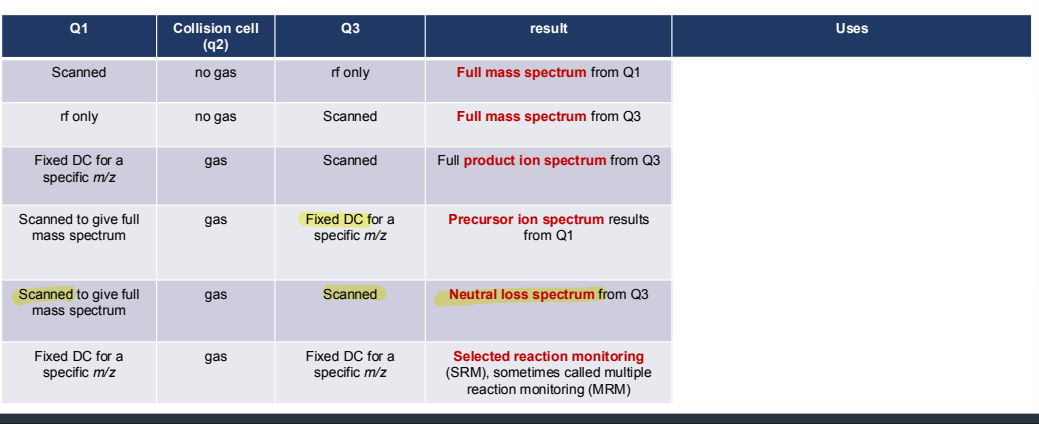
What are the uses of different scan modes possible with a triple quadrupole?
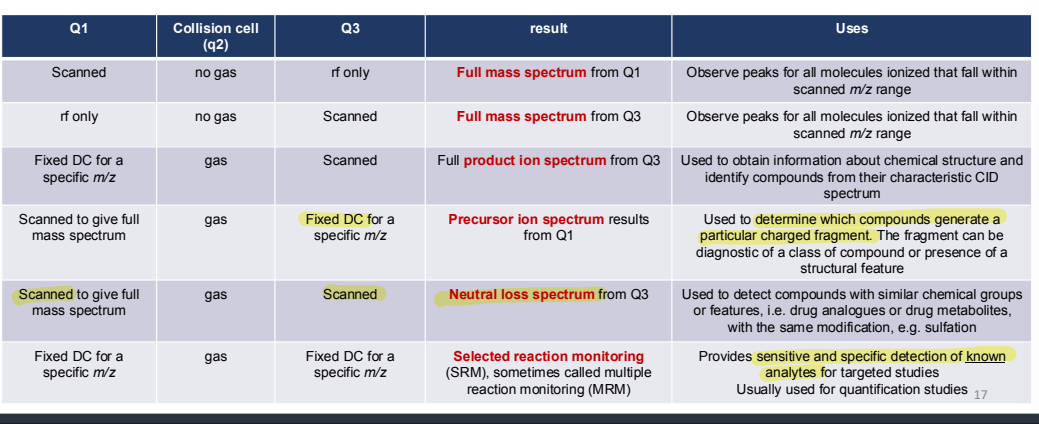
What are full scan MS?
A spectrum that can see everything that is ionised by the chosen ionisation technique and polarity.
What are product ion scans?
Used to discover information about chemical structure. Can be used to confirm the identity or target compounds through their characteristic CID spectra, or to elucidate unknown compounds.
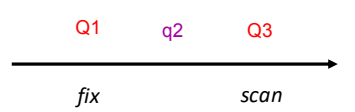
What are precursor ion scans?
Used for screening experiments where a group of related compounds all give the same product ion.
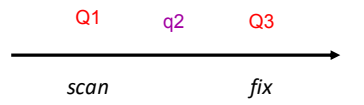
What are neutral loss scans?
Used for screening experiments where a group of related compounds lose the same neutral fragment.
What is selected/multiple reaction monitoring?
Used to filter out one specific precursor ion which fragments to give one or more specific product ions.
Why is selected reaction monitoring used?
Greatly improves sensitivity (no chemical noise).
Great selectivity.
Great specificity.
Very reproducible.
Peak area is quantifiable.
What is quantification?
The measurement of a known analyte relative to the measurement of a standard analyte of known concentration.
Typically has a linear relationship.
What is dynamic range?
The concentration level over which linearity, accuracy and precision are acceptable.
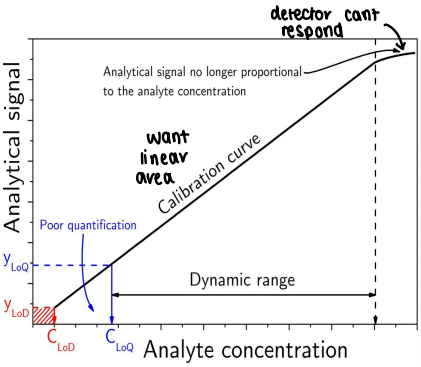
What is the limit of detection (LoD)?
The lowest amount of analyte that can be distinguished from the blank.
Often 3x the signal intensity of the blank.
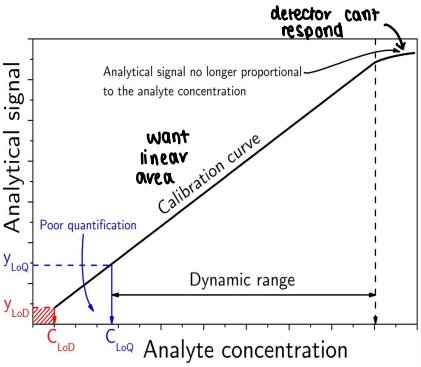
What is the limit of quantification (LoQ)?
The lowest concentration of analyte that can be reliably measured.
What are matrix effects?
The matrix effect can cause peak areas to be very different even though concentrations are the same.
Samples for quantification can be complex mixtures, therefore matrix effects occur when something in the rest of the sample affects the response of the technique to the analyte.
Can cause an increase/decrease in the signal
What is external calibration?
The measurement of a reference material externally to the measurement of a target analyte.
Prepare a series of standards containing increasing concentrations of the targeted analyte.
How do you carry out an external calibration?
Prepare a series of standards containing increasing concentrations of the targeted analyte.
Measure:
Each of the dilution series.
The sample of interest.
A reagent blank.
Create a calibration curve using the concentrations of the dilution series and read of the concentration of the unknown sample.
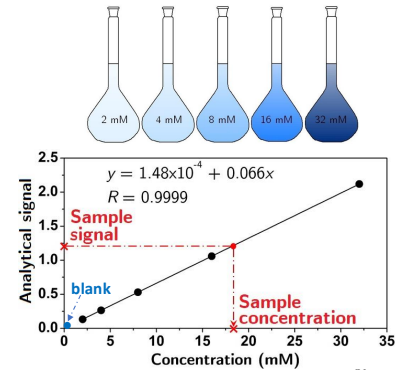
What is a con of using external calibration?
It assumes the measurement is not affected by the matrix.
What is standard addition?
The addition of incremental amounts of the reference material.
How do you carry out a standard addition?
Prepare equal volumes of undetermined sample solution.
All but one are spiked with increasing volumes of pure analyte standard of known concentration.
All vessels are diluted to the same final volume.
Measure the analytical response for each sample.
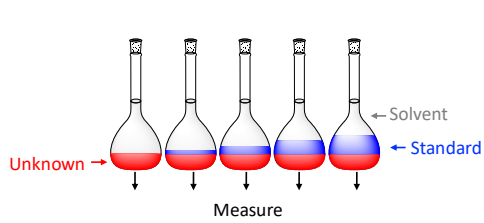
What is an advantage of using standard addition?
It greatly reduces analytical error of the matrix effect as the standard and unknown are affected to the same degree.
What is a disadvantage of using standard addition?
It requires a linear response to the analyte, it is an extrapolation rather than interpolation.
How do you find the concentration of the unknown sample from standard addition?
Measure the signals for the sample + standard and plot against the concentration of the added standard.
The concentration of the sample is given at the x-axis intercept when corrected for the original dilution.
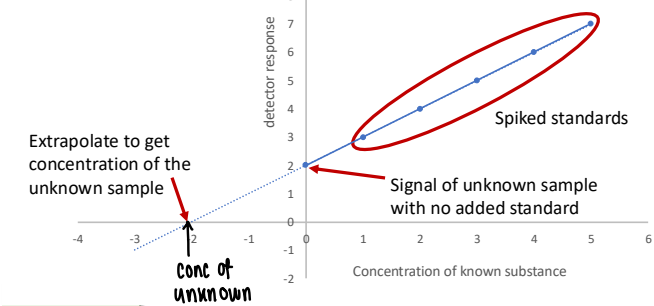
What is internal calibration?
The addition of a fixed and known quantity of a reference material is added to the unknown sample. It relates the signal response for the internal standard and analyte to their respective concentrations.

What are the advantages of using internal calibration?
It is the most precise.
It can minimise signal fluctuations from one analysis to another dye to uncontrollable factors (e.g. temp, pressure)
It can correct for sample losses that may occur during preparation.
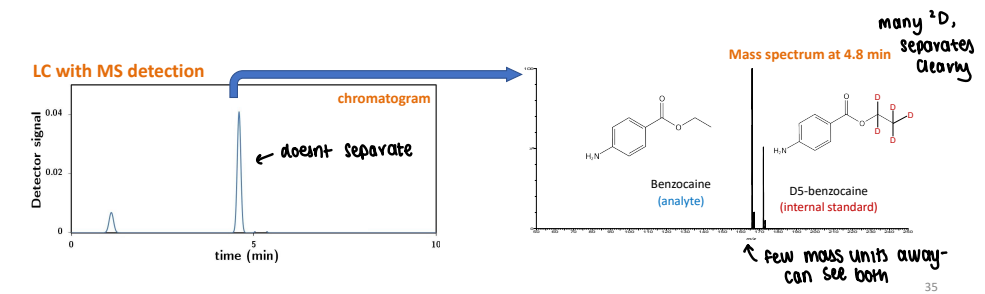
How is internal standard used for MS detection?
The reference material is often an isotopically labelled analogue of the target analyte.
The reference and analyte are assumed to have the same retention time and therefore matrix effect.
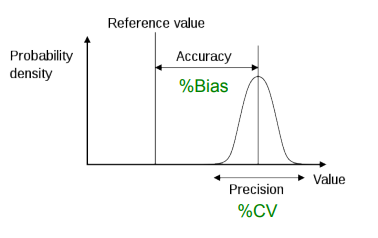
What is accuracy?
A measure of how close the value obtained is to the true value.
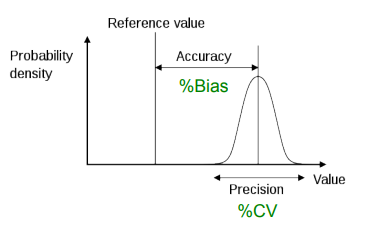
What is precision?
The closeness of multiple measurements of the same sample.
What is an accurate mass measurement?
An experimental determination of the accurate and precise value of m/z of an ion, usually with a view to suggest elemental composition.
What is a mass defect?
The difference between a compounds exact mass and its nominal mass.