america 1920 - 1973: opportunity and equality (copy) for mock (copy)
1/143
Earn XP
Description and Tags
dosnt include: - prohibiton - the red scare - the kkk - migration of african americans - popular culture after the new deal
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
144 Terms
what are the 2 types of government in the USA
central federal government
state government
whats the central federal government
based in Washington D.C.
run by president (elected every 4 years), a cabinet of advisors and congress
oversees matters that affect the whole country
whats the state government
based in capitol of each state
each state has its own laws, police and court system and its own governor in charge
what are the 2 main political parties in the USA
republican party
democratic party
who are the republican party
more likely to preserve traditions and follow laissez - faires
dont support high taxes - pleases rich business people
has more support in the industrial + richer north
more conservative (traditional)
who are the democratic party
more of the ‘ordinary peoples’ party and will intervene in people daily life if needed
help the vulnerable (e.g. poor/elderly)
more support in southern states
more liberal (prepared to change things + accept change)
whats the policy of isolationism
where a country focuses on its own affairs and avoid getting involved in international conflicts or alliances
what were all 5 causes of the economic boom
ww1
the republican government
consumer society
mass production
new ways to buy and sell
how did the policy of isolationism benefit america during ww1
policy of isolationism meant america didnt join war until 1917
as a result, US banks loaned money to GB and its allies which would be repayed later
these loans were used to buy food, equipment + weapons from USA which created jobs and money
how did ww1 benefit america
war disrupted economic growth of those who were fighting → by the end of war USA led the world in the production of medicines, dyed and other goods
only major nation without huge wartime debts
how did electricity and consumerism help create the economic boom
number of us homes grew rapidly in 1920s
meant people could now buy new elctric powered gadgets (radios, telephones, refrigerators)
as america became a consumer society how many consumer goods were being bought between 1919 and 1929
cars:
1919 : 9 million
1929 : 26 million
radios:
1919 : 60,000
1929 : 10 million
telephones:
1919 : 10 million
1929: 20 million
what were the 3 new ways to buy and sell products
billboards
catalogues
a hire purchase plan
how did billboards encourage people to buy and sell
effective advertising campaigns urged people to buy the latest gadgets and keep up with their neighbors
how did catalogues encourage people to buy and sell
for those who didn’t live near large shopping centre - could order goods
how did a hire purchase plan encourage people to buy and sell
‘buy now,pay later’ meant buyers could pay for goods in small instalments over a fixed period of time - meant majority of Americans could now buy expensive goods
what were the 4 republican policies that helped create the economic boom
laissez faire
rugged individualism
low taxation
tarrifs
how did laissez faires help create the economic boom
businesses were left alone to get on with creating wealth
how did tariffs help create the economic boom
putting taxes on imports made foreign goods more expensive than american goods
how did low taxation help create the economic boom
with lower taxes, people had more money to spend on helping industrial growth
what new method of car production did Henry Ford introduce in 1913
the assembly line which was a conveyor belt which carried partly assembled cars past workers who did one or two small jobs repeatedly e.g. fitting wheels / doors
how did the assebly line improve car production
made car production quicker so prices fell
1911: $800
1928 : $295
what was the impact of cheaper cars due to mass production
people no longer had to live near offices / factories as they could drive into work
how did the stock market boom work
to set up a company you need money for wages, equipment etc
most companies got money from investors and in return investors own a share of the company (become shareholders)
a shareholder makes money by either receiving a share of company profits or selling the share for a higher price than they payed for it → if company does well its hares become more valuable but if its doing badly the shareholder could be stuck with a share no one wants to buy
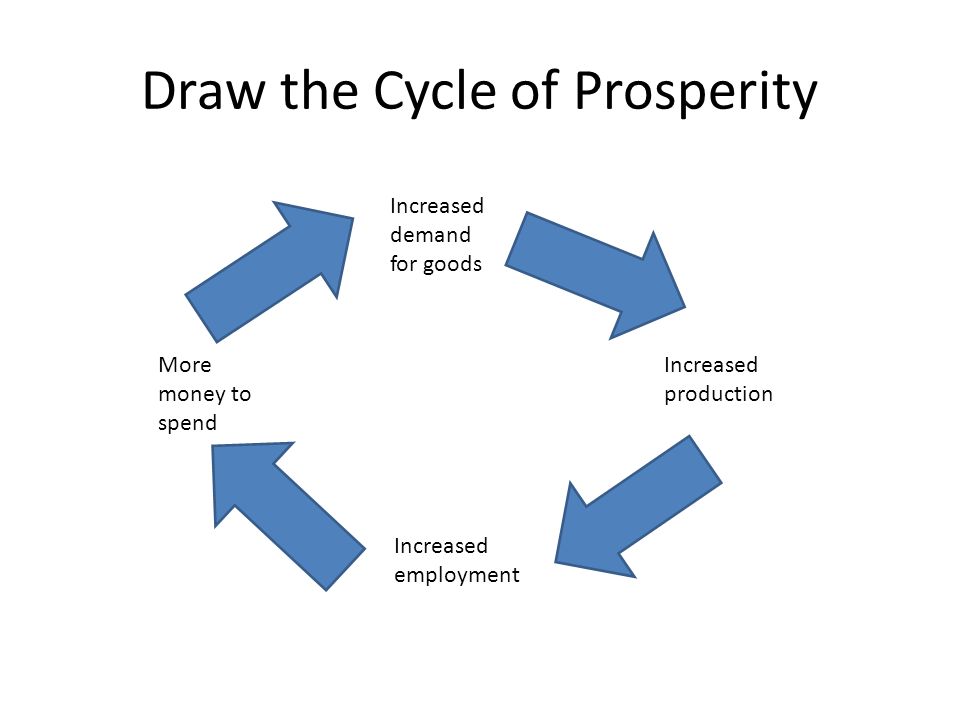
what was the cycle of prosperity
increased demand for goods → increased production → increased employment → more money to spend
what was ‘buying on the margin’
a way of purchasing shares with money borrowed from the bank which they would then pay off with the profits they made when the shares were sold
what caused poverty in the countryside in the 1920s
after ww1, less demand in europe for american exports
countries taxed us products making them more expensive and more difficult to sell overseas
how did high tech farming machinery increase poverty in the countryside
high tech farming machinery produced more food to sell - prices fell and farmers became poorer
some farmers borrowed money for the machinery which they could now not afford to pay back - many had to sell their farms / were evicted from land
around 600,000 farmers lost their farms in 1924 alone
why did older industry (coal+ cotton) start to suffer in the 1920s
Coal industry suffered as new power was used – oil, gas, electricity.
Too much coal was produced, which meant the price fell and mines closed.
The same thing happened in the cotton and textiles industries.
In the 1920s, 60% of people lived below the poverty line.
what happened to African american workers when farms started to close in the 1920s
they made their way to cities to find work however they could only find low pay jobs
what happened to american indians in the 1920s
their land was seized by mining companies
were forced to move to reservations but quality of soil was poor it was impossible to grow crops
american Indians lived in extreme poverty , were poorly educated and had a lower life expectancy
how did music change during the 1920s
jazz came from the southern states of america but when African Americans started to travel north in search of work more white people were exposed to it
it became popular in bars and nightclubs in cities e.g. new york
provided opportunities for black musicians like Louis Armstrong and Benny Goodman
how did the star system help change the movie industry in the 1920s
studios introduced the ‘star system’ to promote their main actors- made sure the media had access to the star e.g. magazine interviews photo shoots, radio shows + public appearances
how did talkie films help change the movie industry in the 1920s
until 1927 films were silent and words appeared on the screen with a piano player playing the background music
‘the jazz singer’ was the fist movie with sound
boosted audience figures and people wanted to see how their favourite movie stars spoke
how did sport change in the 1920s
sports people became celebrities
radios, newspapers and magazines help bring sports events to a mass audience
what were women like before the war
couldn’t vote
middle - upper class women expected to behave politely at all times and had to wear sensible clothing
relationships with men strictly controlled
poorer women had to settle for poorly payed jobs e.g. cleaning, factory or secretary work
what were women like during ww1
women took over jobs of men who went to fight
they worked just as well as men and the income gave them a sense of independence
what caused women to become flappers
given the right to vote in 1920s
had a new sense of freedom from their jobs in ww1 which meant they no longer had to rely on their husband
what was a flapper
mainly middle and upper class women from northern states
dressed in revealing clothes, smoked + drank in public and had sex before marriage
they shocked traditional members of society
an anti flirt league formed to protest against their behaviour
how did ordinary women’s lifes change in the 1920s
domestic machines brought as husbands made more money
fridges , radios + washing machines made their lives easier
many women kept jobs from ww1 - Independence
did all womens lifes change during the 1920s
no as women in poorer southern states life went on as before
also didn’t have money to buy luxuries
what was the wall street crash
The Wall Street Crash 1929, was a severe financial crisis that occurred in the United States.
This event marked the beginning of the Great Depression
how were inequalities of wealth a factor of the wall street crash
some Americans couldn’t afford the goods factories produced
limit to number of radios, telephones, cars and fridges people needed to buy
american factories were overproducing and profits began to fall
what was overproduction
when factories were making more goods than they could sell them so profits began to fall
how were foreign tarrifs a factor of the wall street crash
companies struggled to sell their goods abroad because foreign governments had outs taxes (tarrifs) on us made goods
this was a way of encouraging citizens to buy local goods
how did lack of confidence in shares contribute to the wall street crash
some shareholders began to doubt weather the companies they invested in would make profits
people began to sell their shares
why did more and more people start to sell their shares
word spread about the falling profits of us companies
shareholders realised their shares were only valuable if someone wanted to buy them
as they tried to sell their shares they dropped the price to attract a buyer
what happened in the wall street crash on 24 october 1929
5 times as many shares sold as on a normal day
share prices in companies continued dropping
some called this black thursday
why did banks go bankrupt during the wall street crash
many Americans had borrowed money from banks to buy shares in the hope that they would pay them back when their shares rose in price
investors then couldn’t sell their shares for enough to be able to pay the bank back
the banks went bankrupt and people lost their savings
how many banks closed between 1929 and 1933
10,000
how many businesses went bankrupt between 1929 and 1933
100,000
what was the great depression
in 1930 where the economy started to decline as a result of the wall street crash when factories closed, banks failed and unemployment rose
how were ordinary shareholders affected by the great depression
many lost a fortune
tried to pay banks back loans by selling valuables
some people struggled to pay rent and faced homelessness
how were farmers affected during the great depression
over farming and drought turned farms dry (called dust bowls) and drove farmers off their land
farmers couldn’t pay mortgages /debts for equipment and sacked workers and lost their farms
how were businessmen and their workers affected by the depression
factories had been overproducing
people had less money to spend after the crash so fewer goods were sold (under consumption)
factory owners cut production, wages and then jobs
these closures affected local businesses too e.g. restaurants and these had to close too
how were the very rich affected by the great depression
members of upper classes lost wealth from shares / owned fcatrories that closed
had property + land to fall back on
sacked chauffeurs + cleaners and started doing work themselves
how were bank mangers affected by the great depression
when banks went bust bank managers and staff lost their jobs
how many people had lost their jobs in 1932
around 13 million - 25% of us workforce
what were hobos
the unemployed who travelled the country looking for work
what were hoovervilles
named after President Hoover's insufficient relief during the crisis
people who had been evicted for not paying mortgages took to the streets and built shacks with scrap metal and cloth
these were called hoovervilles and were temporary dwellings for the homeless
who was americas president at the start of the great depression
Herbert Hoover
what actions did herbert hoover take during the great depression
believed in rugged individualism and that america would recover by itself
he did try and improve some things:
lent money to businesses and farms in trouble
a huge damn and road building scheme provided some jobs
made $300 dollars available for states to help unemployed but only $30 million of it was actually used
1930 Hawley-Smoot Tariff Act, which increased tariffs imported items. The act aimed to help industry sell more home-produced goods by making foreign goods more expensive. However, foreign countries retaliated by taxing American goods, so trade fell even further.
how did people react to Herbert hoovers response to the great depression
Herbert hoover wasn’t very popular
his ideas of rugged individualism made him look incaring
the economy didn’t get back on track and people
Hoover was increasingly mocked and blamed for the continued hardships
who were the 2 main candidates for the 1932 presidential election
hervert hoover
franklin delano rooselvelt
who was herbert hoover and what did he believe in
belonged to the republicans
believed in lassaiz faires
believed in rugged individualism
what was rugged individualism
idea of people who could overcome any problem without help and achieve success through their own hard work
what happened in Herbert hoovers early life that made him believe in rugged individualism
orphoned aged 8 and raised by 2 uncles
made his fortune in the mining industry
became a self made multi millionaire by the age of 40
retired from mining to enter politics
what was herbert hoovers political career
excellent early career in politics during first world war
elected as president in 1928 during economic boom
what party did Franklin Delano Roosevelt belong to
democratic party
what was Franklin Delano Roosevelts backround
privately educated only child from very rich family
what was FDRs political career
helped organise navy during WW1
contracted polio in 1921 and used a wheelchair for the rest of his life which attracted people has he still git on with it and thought it would give him compassion
reentered politics in 1928 and became govener of new york
what were FDRs ideas for dealing with the depression during the election
the 3 Rs
relief - help for old, sick, unemployed + homeless
recovery - government schemed to provide jobs
reform - make america a better place for ordinary people and ensure a depression wouldn’t happen again
what was the new deal
a series of programs and government schemes implemented by FDR in within the first 100 days of his presidency in response to the great depression
what were 3 acts FDR implemented at the start of the new deal
the emergency banking act
the economy act
the beer act
what was the emergency banking act
all banks were closed for a 4 day ‘bank holiday’ so they could be inspected
only honest well run banks with enough cash would be given loans and reopened
what was the economy act
cut the pay of government employees ( army, navy + air force) by 15%
saved nearly a billion dollars which could then be used to help unemployed
what was the beer act
made it legal for people to sell alcohol
put an end to the gangsters and dealings
now alcohol was legal the government could raise money by taxing it
how did FDR make himself known to the american people
fireside chats - every sunday he would broadcast on radio to the nation
what were the alphabet agencies
new organisations FDR created to deal with some of the country’s problems
named alphabet angencies as known by their initials
what was FDR’s ideas behind the alphabet agencies
the government created jobs by spending money
once the workers started earning the waged they bought goods
firms and businesses then would start hiring more workers
more and more people would buy american goods
what did the AAA (Agricultural adjustment agency) do for farmers
paid farmers to produce less and burn produce
food prices would rise as in short supply
farmers incomes doubles
was criticised as food was being destroyed whilst millions went hungry
what was the NRA (national recovery administration)
set fair prices, wages and working conditions and gave workers the right to join trade unions
what was HOLC (home owners loan cooperation)
gave loans to people struggling with their mortgages
what was the FERA ( federal emergency relief agency)
millions of dollars given to states to help homeless and starving people
money spent on soup, kitchens, clothes and nursery schools ( so parents could find work during the day)
why did the rich oppose the new deal
to pay for the new deal FDR raised taxes for rich people which angered them
why did businessmen oppose the new deal
the new deal agencies ‘interfered’ with business giving more rights to workers
the NRA meant people could now join trade unions meaning employees had to pay minimum wages, improve working conditions and set limited hours of work
why did republicans oppose the new deal
believed in lassaiz faires and rugged individualism so were horrified by the way the new deal dominated peoples life
claimed it would make america soft and people wouldn’t be able to stand on their own two feet
why did the supreme court oppose the new deal
claimed the AAA and the NRA alphabet agency was illegal
said that giving help to farmers was for state governments not the federal government
what 3 individuals came up with alternatives to the new deal
huey long
francis townsend
charles coughlin
what was huey longs idea instead of the new deal
‘share our wealth’
fortunes over $5 million confiscated and shared out so family’s could buy, a car , radio and house
would provide food for the poor, free education and minimum wage
what was francis townsends idea instead of the new deal
wanted everyone to reture at 60 to give job oppertunities to younger people
what was charles coughlins idea instead of the new deal
‘ national union for social justice ‘
thought the new deal wasn’t doing enough for the poor
wanted banks to have less power so should be taken over by the government
popularity declined after he made speeches attacking jews and trade unions
what was in FDRs second new deal
1st new deal - focusing on banks and boosting economy - short term
2nd new deal - aimed to change unfairness and improve the lives of ordinary people - long term
name 3 new alphabet agencies in FDRs second new deal
SSA (social security act)
FSA(farm security administration)
NLRA ( national labor relations act)
what was the SSA (social security act ) as part of the second new deal
government pensions provided for old people, widows and disabled. Also established a system for sick and unemployed
what was the FSA (farm security administration) as part of the second new deal
government loans given to tenant farmers (farmers who farm on rented land ) so they could buy their own land
set up camps for poor farming families who lost their farms
what was the NLRA (National Labour Relations Act) as part of the second new deal
Workers were allowed to join trade unions so they could campaign for better pay and conditions.
In the past, some employers, like Henry Ford, had sacked workers who had formed groups or unions.
Now it was hoped that bosses would have to listen if their workforce was unhappy.
The NLRA was seen as a replacement for the scrapped NRA.
why was FDR accused of trying to make america a dictatorship
planned to appoint his supporters as extra judges on the supreme court so his ideas wouldn’t be not allowed as his men would outvote the rest
alarmed Americans as seemed he wanted to become a dictator like Hitler was in germany
how was the new deal a success for workers
alphabet agencies provided work for many skilled and unskilled workers
Roosevelt introduced the Wagner act (officialy called the NLRA) which gave workers the right to join trade unions which gave workers more rights
what was the wagner act ( as NLRA)
The Wagner Act was a labor law passed in 1935 after the NRA was declared illegal by the supreme court. It aimed to protect the rights of employees to organize and bargain collectively with their employers whihc improved working conditons