lecture 7 radiation saf
1/183
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
184 Terms
0.5 mm lead apron reduces exposure by at least a factor of [...]
10
A [...] usually disrupts many molecular bonds and produces visible chromosomal damage
hit
Acute deterministic radiation syndromes include? [...]
Local tissue damage, Hematologic depression and cytogenic damage
Acute Radiation Lethality
Mega-radiation levels – like Hiroshima or Chernobyl
LD 50/30 is the lethal dose to kill 50% of the population in about 30 days
Humans LD is [...] to [...] rads
300 to 400 rads

Acute Radiation Lethality
Less than 100 dose (rad) is not lethal
More than 100 is [...] death
More than 1,000 is [...] death
More than 10,000 is [...] death
hematologic
gastrointestinal
central nervous system
look at stages below
Age
Highest risk is [when?]
Younger patients have more rapidly dividing cells and higher metabolic rates so they are associated with more radiation damage
Increases again when you get older
before birth

Age
Law of Bergonie & Tribondeau
Greater maturity of cells (adulthood) increases resistance against radiation
Things that increase radiosensitivity (all associated with childhood)
Increased [...]
Increased [...]
Increased [...]
metabolic activity
cell proliferation rate
tissue growth rate

ALARA stands for [...]
As Low As Is Resonably Achievable
All unnecessary exposure must be avoided and all absorbed doses be kept [...]
As Low As Is Resonably Achievable
Anoxic environments are [...]
more protected from radiation
Average dose for extremity exam of hand or foot is [...] mSv
0.001 mSv
Biologic tissue is [more or less] sensitive under aerobic conditions
more
Biological tissue is more sensitive under [...]
aerobic conditions
Cataract Formation
Acute threshold
Probably about [...] Gy
Fractionated threshold
As high as [...] gy
Indicates fractionating the dose (breaking up the dose over a set period of time) is safer for cataracts
Latent period
15 year average (but reported from 5 to 30 years)
May be dose related – 8 years following 2.5 to 6.5 Gy doses
2 Gy
10 Gy
Latent period
[...] year average (but reported from 5 to 30 years)
May be dose related – [...] years following 2.5 to 6.5 Gy doses
15
8
Cataract Formation
lens radiosensitivity is [dependent on what]
Len shield is not necessary usually, unless working with fluoroscopy
age dependent
Len shield is not necessary usually, unless working with [...]
fluoroscopy
greater effect and shorter latent period with older age
different effect than normal (old age usually protects you)
Cataract Formation
[what type of effect?]
[threshold?]
[linear?]
Deterministic
threshold
nonlinear
Cataract Formation
[greater or lesser] effect and [longer or shorter] latent period with older age
greater
shorter
[...]
halogenated pyrimidines
[...]
contains -SH- group which competes with O2 for free radical binding
Protects the patient
Radiosensitizers
Radioprotectors
Congenital abnormalities
[...]% increase in congenital abnormalities from the normal averages following a 100 mGy (10 rad) fetal dose
Normally, 5% of all live births exhibit congenital abnormality
1%
Lower than 1% increase if the dose is lower

Cytogenic Damage
2 types
[...]
At very low radiation doses
Linear
non-threshold
dose-response
[...] – the most significant latent human damage
At high doses: frequency increases when dosages increase 100 rad
Nonlinear
non-threshold
dose response
Results in
Rings – from multi-damage on the same chromosome
Dicentrics – reciprocal translocations from adjacent hits
single hit
multi hit aberrations
Cytogenic Damage
2 types
Single hit
At very low radiation doses
[linear or nonlinear]
[threshold?]
[dose response?]
Multi hit aberrations – the most significant latent human damage
At high doses: frequency increases when dosages increase 100 rad
[linear or nonlinear]
[threshold?]
[dose response?]
Results in
Rings – from multi-damage on the same chromosome
Dicentrics – reciprocal translocations from adjacent hits
Linear
non-threshold
dose-response
Nonlinear
non-threshold
dose response
[...] – from multi-damage on the same chromosome
[...] – reciprocal translocations from adjacent hits
Rings
Dicentrics
Cytogenic Damage
Damage is usually manifest during the next cellular mitosis
Significant radiation damage can cause chromosomal aberrations in the next 1 to 2 cell divisions (therefore is [what type of] effect)
an acute deterministic
Cytogenic Damage
Damage
[threshold?]
[dose-response?]
Damage is difficult to identify with low doses (less than 5 rads)
Non-threshold
dose-response
(any amount of damage will produce an effect)

Cytogenic damage of acute determinisitic effects we can infer genetic changes, however we are only actually [...]
looking at the physical structure change to DNA
Data from Mega-mouse experiments
Doubling dose
Found the doubling dose for genetic mutation was much [higher or lower] in mice than fruit flies. Since mice are more comparable to humans, this mean the doubling dose is more like [...] or [...].
higher
100 or 200
Governmental standards did not change however since the world was already used to the 5 rad limit, why increase it.
Data from Mega-mouse experiments
Pertinent conclusions
A dose of 1.0 rem per generation increases the natural of spontaneous mutation rate by approximately [...]%
1%
Even though 1.0 rem is a lot of radiation, it actually caused a 1% increase in mutation which is not a lot
Data from Mega-mouse experiments
Pertinent conclusions
Most mutations are harmful
Any dose of radiation, however, small, entails some genetic risk
Number of mutations are proportional to dose
Linear extrapolation from high dose is a [valid or invalid] estimate of low-dose effects
valid
Data from Mega-mouse experiments
Substantial dose rate effect
Since mice, like us, have an ability to heal (unlike fruit flies)
Same dose administered over a period of time results in [more or fewer] mutations than an acute exposure
Dose rate effect in gonads
Chronic irradiation is considerably less effective in inducing mutations in spermatogonia and oocytes
greater in females (oocytes > spermatogonia)
Indicates why spermatogonia are more radiosensitive; because they can’t heal as fast as oocytes
Absolute frequency of radiation induced genetic mutations are very low
fewer
Data from Mega-mouse experiments
Substantial dose rate effect
Since mice, like us, have an ability to heal (unlike fruit flies)
Same dose administered over a period of time results in fewer mutations than an acute exposure
Dose rate effect in gonads
Chronic irradiation is considerably [more or less] effective in inducing mutations in spermatogonia and oocytes
greater in females (oocytes > spermatogonia)
Indicates why spermatogonia are more radiosensitive; because they can’t heal as fast as oocytes
Absolute frequency of radiation induced genetic mutations are very low
less
Data from Mega-mouse experiments
Substantial dose rate effect
Since mice, like us, have an ability to heal (unlike fruit flies)
Same dose administered over a period of time results in fewer mutations than an acute exposure
Dose rate effect in gonads
Chronic irradiation is considerably less effective in inducing mutations in spermatogonia and oocytes
greater in females (oocytes > spermatogonia)
Indicates why spermatogonia are more radiosensitive; because they can’t heal as fast as oocytes
Absolute frequency of radiation induced genetic mutations are very [high or low]
low
Decrease age of tissue/organs = [...]
increase radiosensitivity
Deterministic effects aka Nonstochastic effects
Linear threshold curve
Sigmoid threshold curve
Linear quadratic threshold curve
Linear at first but becomes quadratic (exponential) at higher doses
Examples:
[...]
[...]
[...]
Leukemia
Breast cancer
Heritable damage

Distance
Scatter is generally [...]% of beam entrance skin intensity at 1.0 meter (about 3 feets)
0.1%
Meaning that that the intensity of the scatter is 1/1000th of what it is at the source of the scatter if you get 1 meter away (about 3 feet)
SO most effective means of protection from scatter radiation is distance (for the clinician at least, it doesn’t reduce scatter radiation, just prevents it from hitting you)
Earliest sign of radiation injury is [...]
erythema
Estimates
[...]
Slope of linear dose response
[...]
Observed cases – expected cases
[...]
Observed cases : expected cases
Absolute risk
Excess risk
Relative risk
Relative risk
Ex: if I expect to see 10 cases of a given cancer, but I see 30, then that’s a 3:1 ratio increase in relative risk
Estimates
Absolute risk
Slope of linear dose response
Excess risk
[...] cases – [...] cases
Relative risk
[...] cases : [...] cases
Observed cases – expected cases
Observed cases : expected cases
Relative risk
Ex: if I expect to see 10 cases of a given cancer, but I see 30, then that’s a 3:1 ratio increase in relative risk
Exposure reduction principles
Minimize [...]
Maximize [...]
Employ [...]
time
distance
shielding
Exposure time
Exposure rate x time
Scatter exposure rate expressed in [...]
mR/hr
Factors affecting scatter
Field size = (irradiated voxel)2
This is something we can actively control by using [...]
proper collimation
Increasing area the x-ray beam can come out of, increases the dimensions of the x-ray beam and increases the field size
Purpose of collimation
Lowers patient dose by restricting the volume of irradiated tissue
Safe and improves image contrast by decreasing scatter

Factors affecting scatter
Field size = ([...])2
This is something we can actively control by using proper collimation
irradiated voxel
Increasing area the x-ray beam can come out of, increases the dimensions of the x-ray beam and increases the field size
Purpose of collimation
Lowers patient dose by restricting the volume of irradiated tissue
Safe and improves image contrast by decreasing scatter

Factors affecting scatter
Orientation of body part and tube – you want the body part to be [...]
parallel
Factors affecting scatter
Thickness of body part
[thicker or thinner] body parts have more scatter radiation
Thicker
Foot is pretty thin but the ankle might give off some scatter
Abdomen is thick and gives off a lot of scatter
Fetal Effects
1st trimester is the most sensitive!
High risk of prenatal death, congenital deformities and neonatal death
Risk of [...] extends to the 2nd trimester
leukemia

Fetal Effects
[...] trimester is the most sensitive!
1st
Fetal exposure
2nd to 10th week = period of [...]
If radiation dose is sufficiently high:
Temporary growth retardation
Early in the period = severe skeletal anomalies
Later in the period = congenital abnormalities
major organogenesis
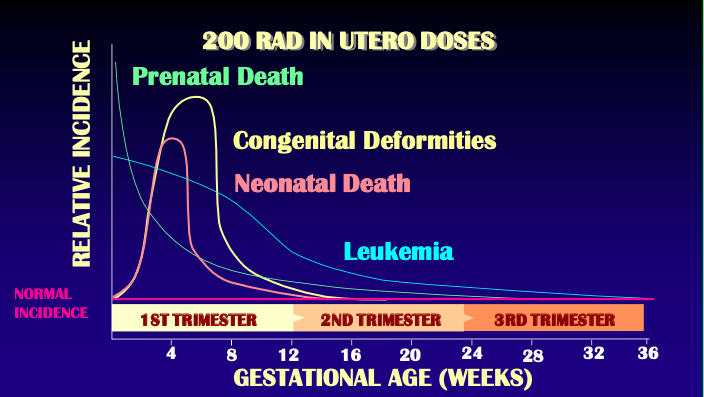
Fetal exposure
2nd to 10th week = period of major organogenesis
If radiation dose is sufficiently high:
[...]
Early in the period = [...]
Later in the period = [...]
Temporary growth retardation
Early in the period = severe skeletal anomalies
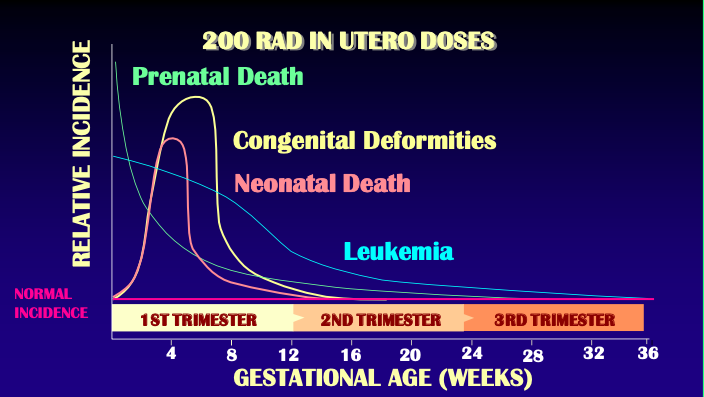
Later in the period = congenital abnormalities
Fetal exposure
After 10th week = period of [...]
Functional CNS disorders
Mental retardation
~4% chance of occurrence per 10 Rads (0.1 Sv)
Structural CNS disorders
Microcephaly
Permanent growth retardation is likely
CNS development
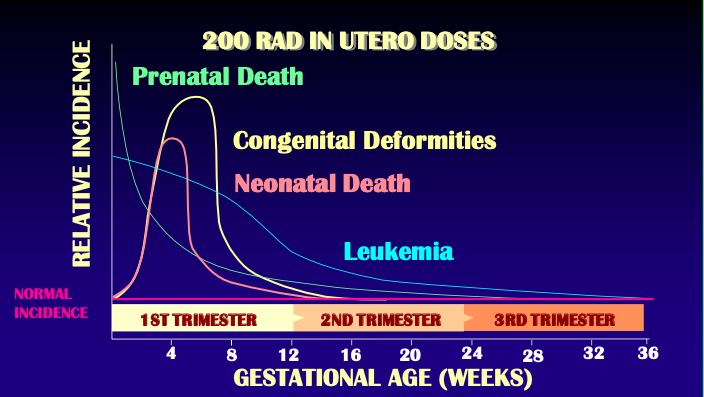
Fetal exposure
After 10th week = period of CNS development
Functional CNS disorders
[...]
~4% chance of occurrence per 10 Rads (0.1 Sv)
Structural CNS disorders
[...]
Permanent growth retardation is likely
Mental retardation
Microcephaly
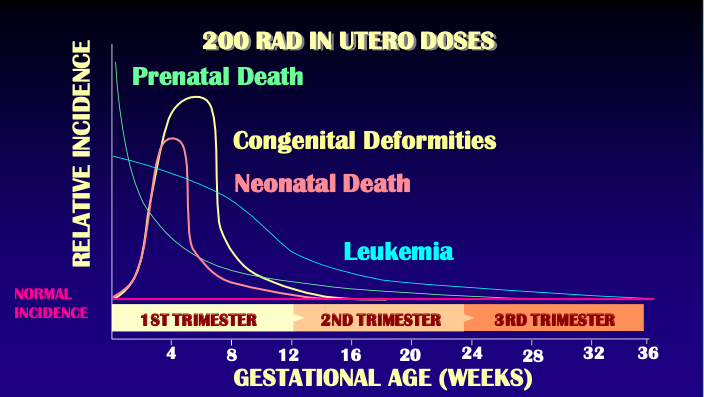
Mental retardation
[...]% chance of occurrence per 10 Rads (0.1 Sv)
~4%
Fetal exposure
First two weeks
High dose (250 mG)
Results in [...] or [...]
Low does
Increased normal incidence of spontaneous abortion by only [...]%
Normal incidence is about 25 to 50%
Very LOW rate
resorption of embryo or spontaneous abortion & death
0.1%
Fetal Risks
Below 50 mGy
[...]
Between 50 to 100 mGy
[...]
After 100 mGy
[...] effects
[...] during organogenesis (2nd to 10th weeks)
[...] (8th to 15th weeks)
Probably no risk of embryonic death or major malformation during organogenesis (2nd to 10th week)
Deterministic
Malformations
Microcephaly/mental defects
Fluoroscopy & Basic Operator Safety
Distancing and Positioning
One step back from the table cuts down exposure rate by a factor of [...]
Shielding
0.5 mm lead apron attenuates scatter factor by a factor of [...]
4
20
Fluoroscopy & Basic Operator Safety
Good rule of thumb:
Getting 1 feet away from the table decreases the dose by [...]
Getting 1 meter away decreases dose by [...]
100
1000
Fluoroscopy & Basic Operator Safety
Orientation of the image intensifier can change the location of the scatter radiation
[...] dose reduction on intensifier side with lateral fluoroscopy
5x
Fluoroscopy & Basic Operator Safety
Time
Use [...] whenever possible
Use [...] fluoroscopy (if designed to reduce dose
Use [...] only when permanent record is required
Do not expose patient unless [...] is viewing image
freeze frame (last image hold)
pulsed
record mode
physician
Fluoroscopy & Basic Operator Safety
Where should you stand?
Most of the scatter radiation is by the [...] so you should stand by the [...]
x-ray tube
x-ray intensifier
Genetic Mutations
Data from drosophila (fruit fly studies)
[linear?] non-threshold curves
[dose rate?] according to fruit fly data
Meaning genetic effects are cumulative; doesn’t matter if it’s a little or a lot or spread out over time
Doubling dose from 5 to 150 rads!
Meaning the natural mutation rate is doubled in as little as 5 rads
Linear
No “dose rate” effect
Doubling dose from [...] to 150 rads!
Meaning the natural mutation rate is doubled in as little as [...] rads
5
5
Greater maturity of cell = [...]
increase resistance
High dose non-specific lifespan shortening groups have [...]
decrease parenchymal cells, decrease in number of fine blood vessels, and increase density of connective tissue
HT = quality factor in [what unit?]
Rems (not rads)
In fluoroscopy where is safer to stand on the image intensifier side or xray tube side? [...]
Image intensifier
Scatter radiation is higher at the tube side
In terms of gonads [...] will decrease the number of spermatozoa, [...] temporary sterility, [...] permanent sterility
10 rads
200 rads
500 rads
Increase cell proliferation rate = [...]
increase radiosensitivity
Increase metabolic activity = [...]
increase radiosensitivity
Increase tissue growth rate = [...]
increase radiosensitivity
Irradiation of macromolecular solutions
Produces many smaller molecules and viscosity decreases describes which irradiation type? [...]
Produces side chains that become sticky, and the viscosity increases describes which irradiation type? [...]
Considered to be the primary mechanism of cellular damage from low dose of radiation accounting for late effects of radiation describes which radiation type? [...]
Main Chain Scission
Cross-linking
Point Lesions
Is radiation an effective cancer-causing agent?
[...]
No! It is not highly effective
For about 300 A-bomb survivors, only one died due to malignancy
Lead glass
[...] mm lead equivalent
The shield should be double the thickness of lead
Lead glass used bc by law, you should be able to see the patient the entire time
1.5 mm
Lead safety garments
[...] mm lead typical for primary beam
[...] mm lead for secondary beam
All gonadal shields should have at least [...] mm of lead
.5
.25
.5
Life span Shortening
Since 1965, radiologic occupations are safe. Mortality is the same as the general population
Currently, we might lose about [...] days due to dealing with radiation
Linear
non-threshold
does response
12
Life span Shortening
Since 1965, radiologic occupations are safe. Mortality is the same as the general population
Currently, we might lose about 12 days due to dealing with radiation
[linear?]
[threshold?]
[dose response?]
Linear
non-threshold
does response
Major forms of DNA damage
Main chain scission
One side rail
[can it be repaired]
Mis-repair possible via [...]
Both side rail
[can it be repaired] & can result in [...]
Main chain scission with cross-linking
Rung breakage
Simple
2 nitrogenous bases separated by an ionizing event
Typically reparable
Base separation/loss of base
Typically irreparable
Results in a frame shift
Often quickly repaired
point mutation
Generally irreparable & can result in frame shift
Rung breakage
[...]
2 nitrogenous bases separated by an ionizing event
Typically reparable
[...]
Typically irreparable
Results in a frame shift
Simple
Base separation/loss of base
Simple
2 nitrogenous bases separated by an ionizing event
Typically reparable
Base separation/loss of base
Typically irreparable
Results in a [...]
frame shift
Maximum permissible dose (MPD)
Cumulative lifetime limit
[...] rem (10 mSv) x age
Ex: if you’re 20 years old, your exposure limit is [...] rems
Got rid of MPD in 1990 and began to use effective dose limits
1 rem
20 rems
Miscellaneous statistics
Newborns are 3 times [more or less] radiosensitive for cancer than a 25 year old
70 year old’s are about 3 times [more or less] radiosensitive than a 25 year old
more
less
Most medical procedures result in a [...] dose distribution within the patient
nonuniform
Most to least cells sensitive to radiation
[...]
[...]
[...]
[...]
[...]
[...]
[...]
[...]
[...]
[...]
Lymphocytes
Erythroblasts (a lot of these are in red bone marrow)
Myeloblasts
Spermatogonia/oocytes
Endothelial cells
Epithelial cells
Bones
Nerve
Brian
Muscle

Multi-hit chromosomal aberration are considered to be the most significant in terms of [...]
latent human damage
Observed / Expected cases = [...]
Relative Risk
Observed cases - Expected cases = [...]
Excess risk
Occupational dose monitoring is required when there is any likelihood that an individual will receive more than [...] the recommended dose limit
1/10
Occurs at very low radiation doses. In the G1 phase of the cell cycle, produces chromatid deletion. Replication during S-phase of mitosis. This describes which cytogenic damage? [...]
Single hit chromosomal abberations
Occurs in higher dose greater than 0.5Gy, generally results from cell death or organ atrophy. Describes those for which incidence and severity depends on dose, but for which there is a threshold dose? [...]
Nonstochastic Effects
Occurs in lower doses less than 0.5Gy. Severity of effect is independent of the dose. Usually no threshold to damage. As dose increases chance of occurrence increases describes? [...]
Non-Deterministic Effects
Once above [...] kVp , you have to put lead in the walls :/
70 kVp
One step back from table can cut exposure rate by a factor of [...]
4
OSLD is [...] can read as low as [...]
most sensitive
1 mrem (0.0001 rem)
Ovaries
Pre-puberty radiation
[...]
[...]
Post-puberty irradiation: (same numbers as the testes)
As little as 10 rads can cause delay or suppression of menstruation
200 Rads – temporary sterility
500 Rads – permanent sterility
Germ cell death
Ovarian atrophy
Post-puberty irradiation: (same numbers as the testes)
As little as [...] rads can cause delay or suppression of menstruation
200 Rads – [...]
500 Rads – [...]
10 rads
200 Rads – temporary sterility
500 Rads – permanent sterility
Overall lifetime cancer risk increases about [...]% for every 10 rad ([...]% natural incidence)
1% for every 10 rad (33% natural incidence)
Overall Quantitative Radiation-Induced Cancer risks -- BEIR committee Report
A single exposure to a lot of radiation (10 rads) [does or doesn't] result in as much excess mortality as does continuous exposure to low doses (1 rad, or 100 mrads)
doesn’t
This describes occupational hazard of the clinician
Overall, females are about [...]% [more or less] radiosensitive to cancer than males
Breast, lung cancer
70% more
Oxygen effect
Biologic tissue is more sensitive under aerobic conditions
Oxygen Enhancement Ratio (OER) = [...] dose / [...] dose
Always takes less radiation to cause damage in an aerobic environment so OER will always be [positive or negative]
OER is LET (linear energy Transfer) dependent – inverse relationship
Greatest for low-LET – max at 3.0
About 1.0 for high-LET radiations
X-rays are low LET
Heavier radiation like alpha particles are high-LET
anoxic dose / aerobic dose
positive
OER is LET (linear energy Transfer) dependent – [direct or inverse] relationship
inverse
Oxygen effect radiation is dependent on [...]
Linear energy transfer