Beta Club US History
1/303
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
304 Terms
George Washington
(1) 1789-1797
The first President unified the new nation and shaped the chief executive's duties. He refused to run for a third term.

John Adams
(2) 1797-1801
He was the first president to live in the White House.

Thomas Jefferson
(3) 1801-1809
Considered the most brilliant president who wrote the Declaration of Independence. He was an architect, farmer and scientist

James Madison
(4) 1809-1817
He is considered the father of the Bill of Rights.
He presided over the War of 1812 with Britain, during which the White House was burned. The war ended in a draw.

James Monroe
(5) 1817-1825
He lived out his retirement in poverty.
His term is called the "Era of Good Feeling" because there was little partisan fighting. He formulated the ***** Doctrine, which declared the Americas off-limits to European meddling.

John Quincy Adams
(6) 1825-1829
He and John Quincy Adams were the first father and son to have served as Presidents. Accused of winning the White House through corruption, he was plagued by accusations of misdeeds throughout his presidency.

Andrew Jackson
(7) 1829-1837
He was the first President to ride on a train. Though he was a rich planter, he was considered the common people's friend. Dubbed "Old Hickory" because he was so tough, he greatly expanded the powers of the Presidency.

Martin Van Buren
(8) 1837-1841
He was the first President to be born an American citizen, rather than a British subject.
His Presidency was marred by an economic depression that led to bank failures and food riots. He was easily defeated for reelection.

William Henry Harrison
(9) 1841
He delivered a marathon inaugural speech during which he caught a cold. He died a month later.
He was the first President to die in office and he served the briefest term.
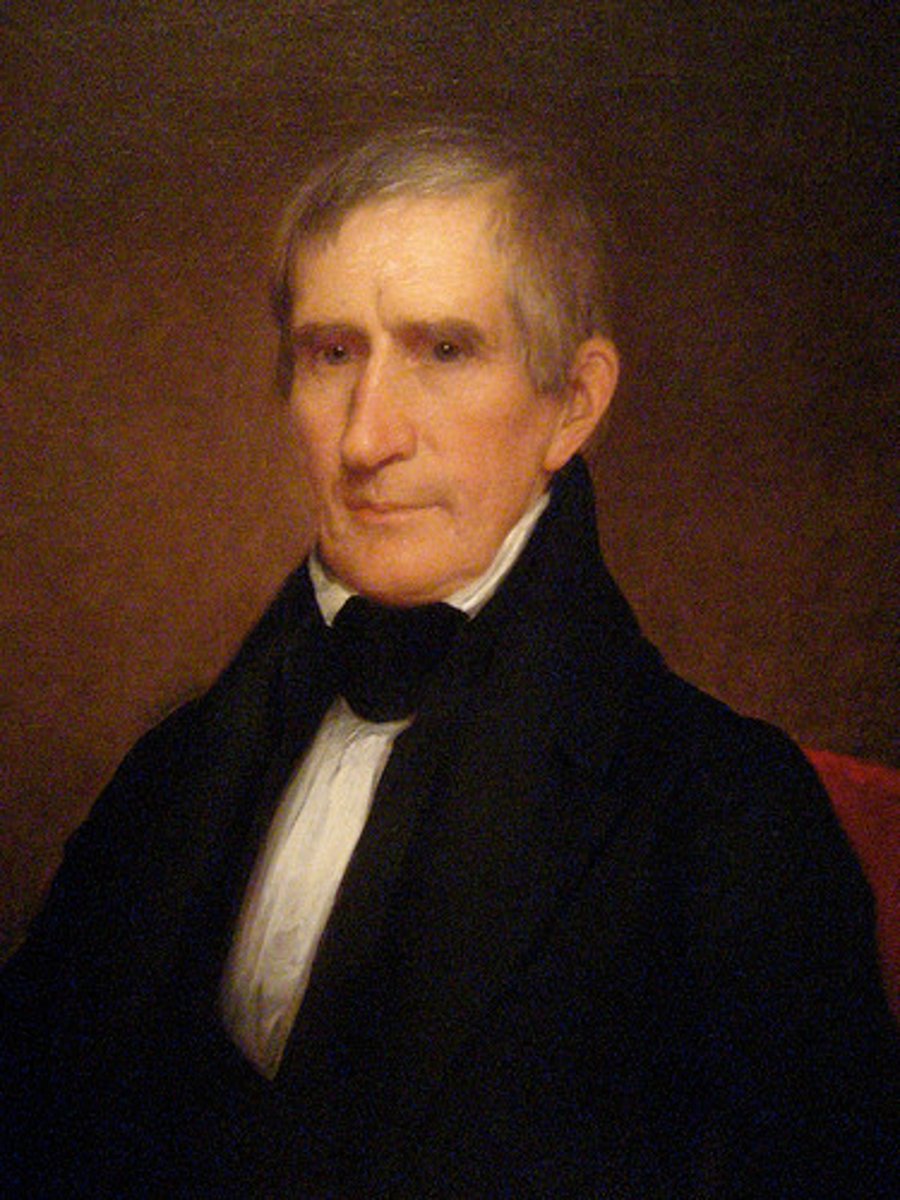

John Tyler
(10) 1841-1845
He had 15 children, more than any President. He was expected to be a passive "acting President" while he finished Harrison's term. But he refused to be passive. He made enemies in Congress and was the first President to be threatened with impeachment. The effort failed.
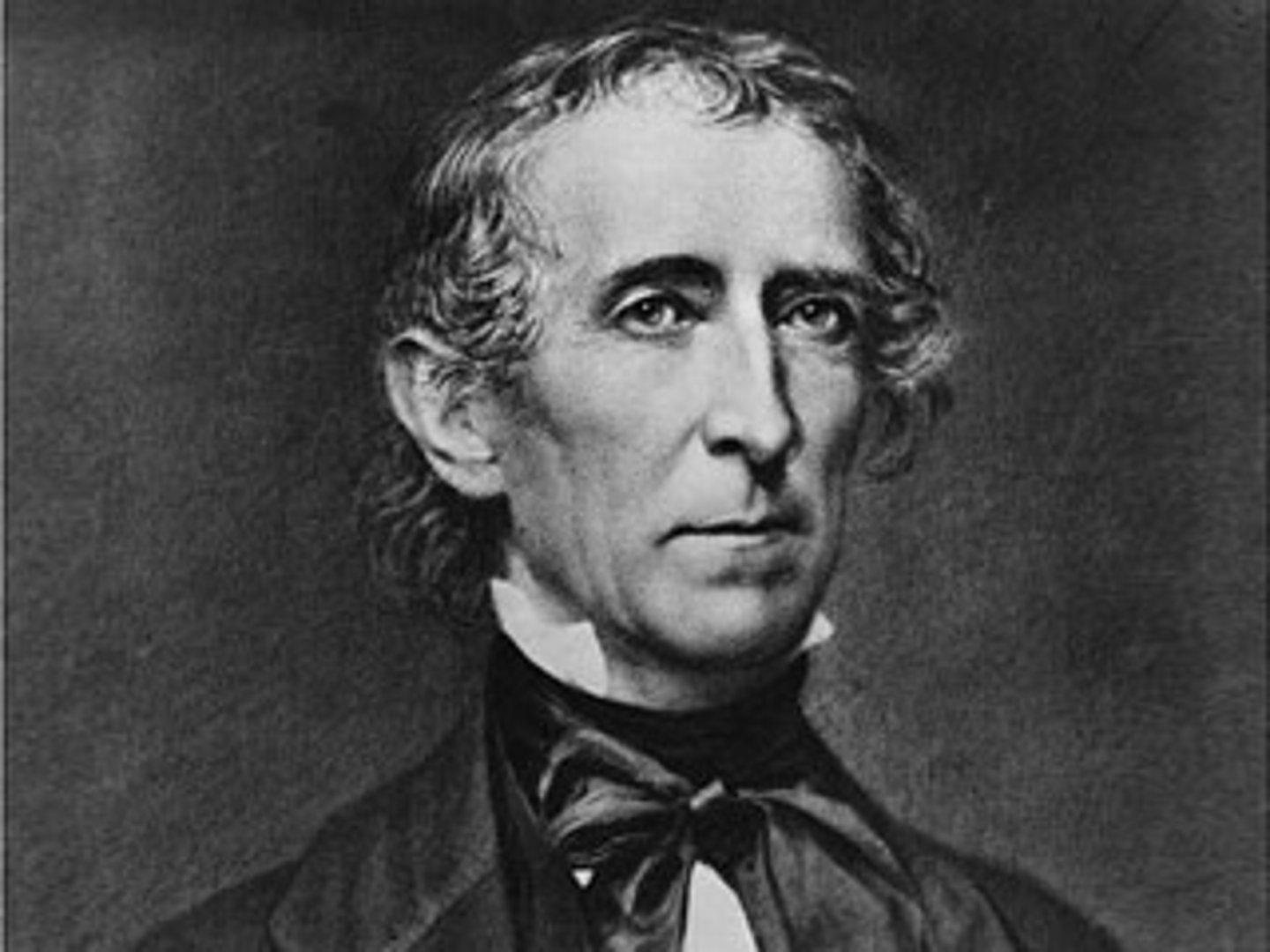

James Polk
(11) 1845-1849
He is the only President to have served as Speaker of the House. He was the first "dark horse" or little-known nominee to become President. He presided over the Mexican War, which added Texas, California, and other territory to the United States.
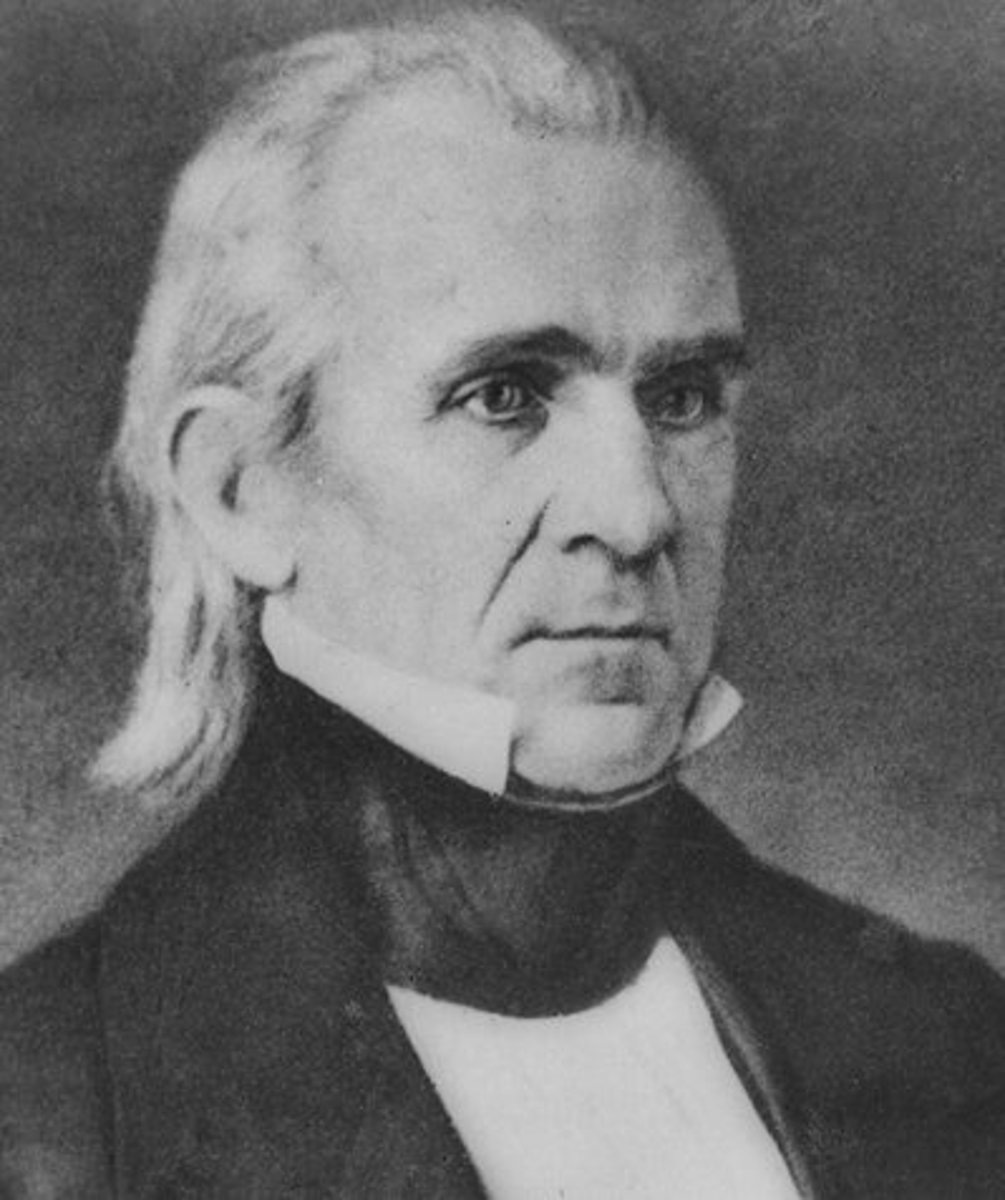

Zachary Taylor
(12) 1849-1850
He won fame as a general in the Mexican War. His soldiers called him "Old Rough and Ready." He threatened to use force to keep the South from leaving the Union. After his death, a compromise allowed slavery to continue in the South.
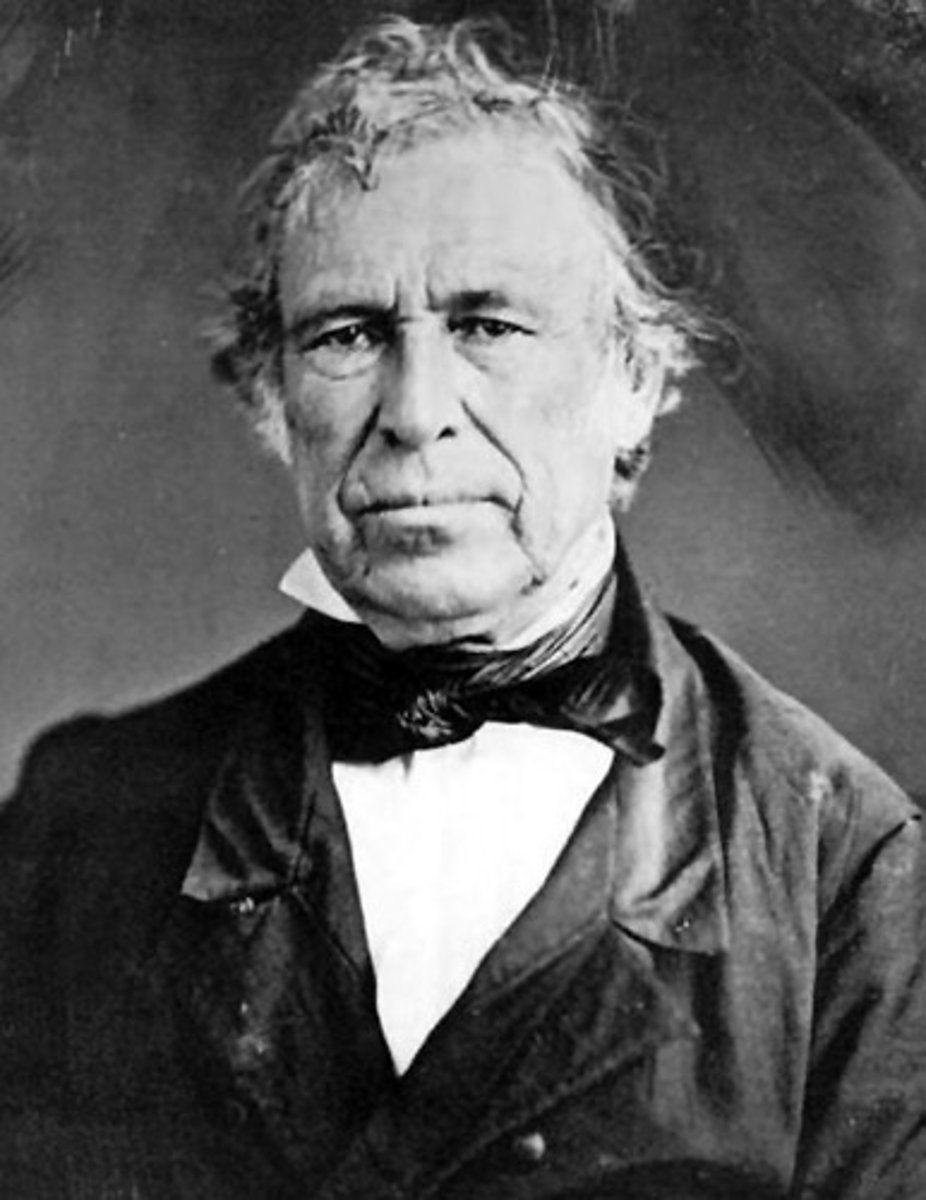

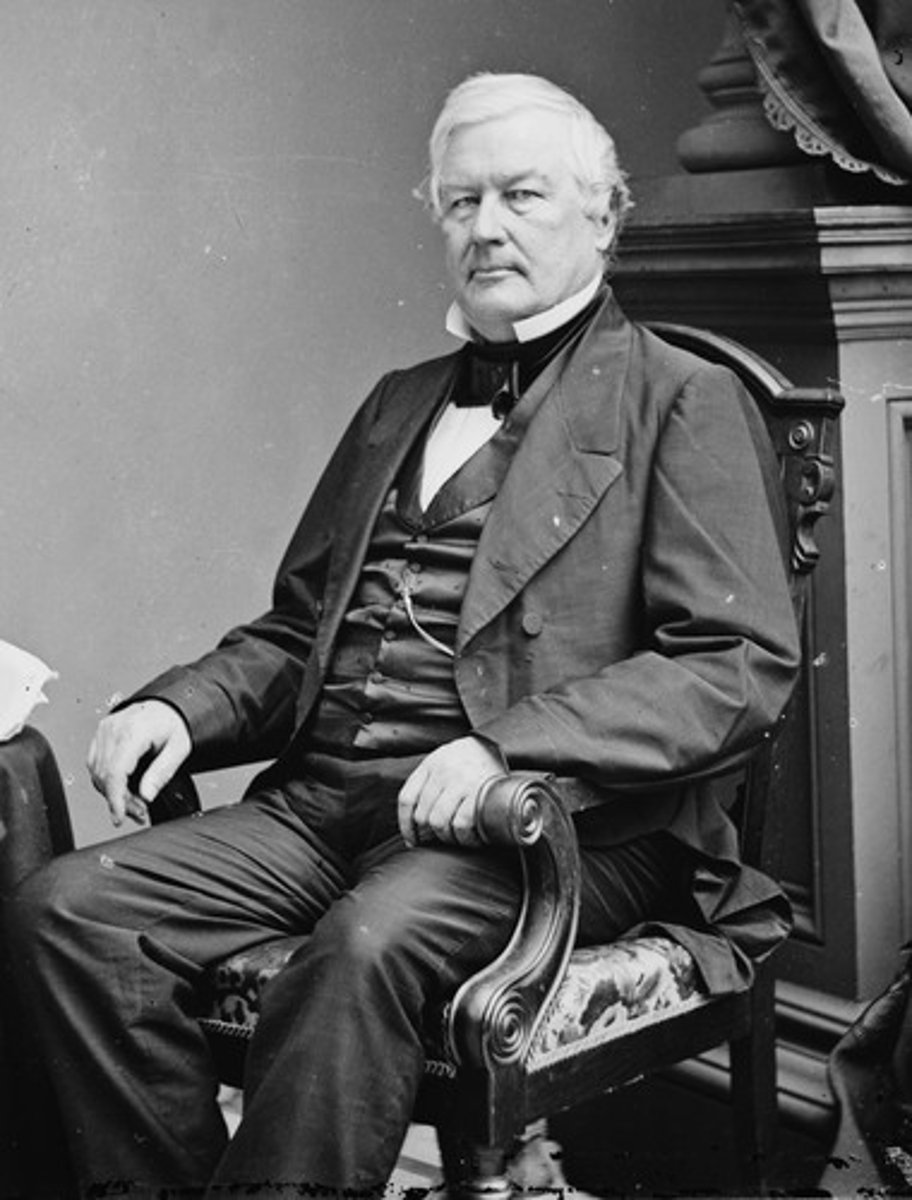
Millard Fillmore
(13) 1850-1853
He approved the Compromise of 1850, allowing slavery in the South. But neither the North nor the South was happy with it, and he was blamed for the law's failure.

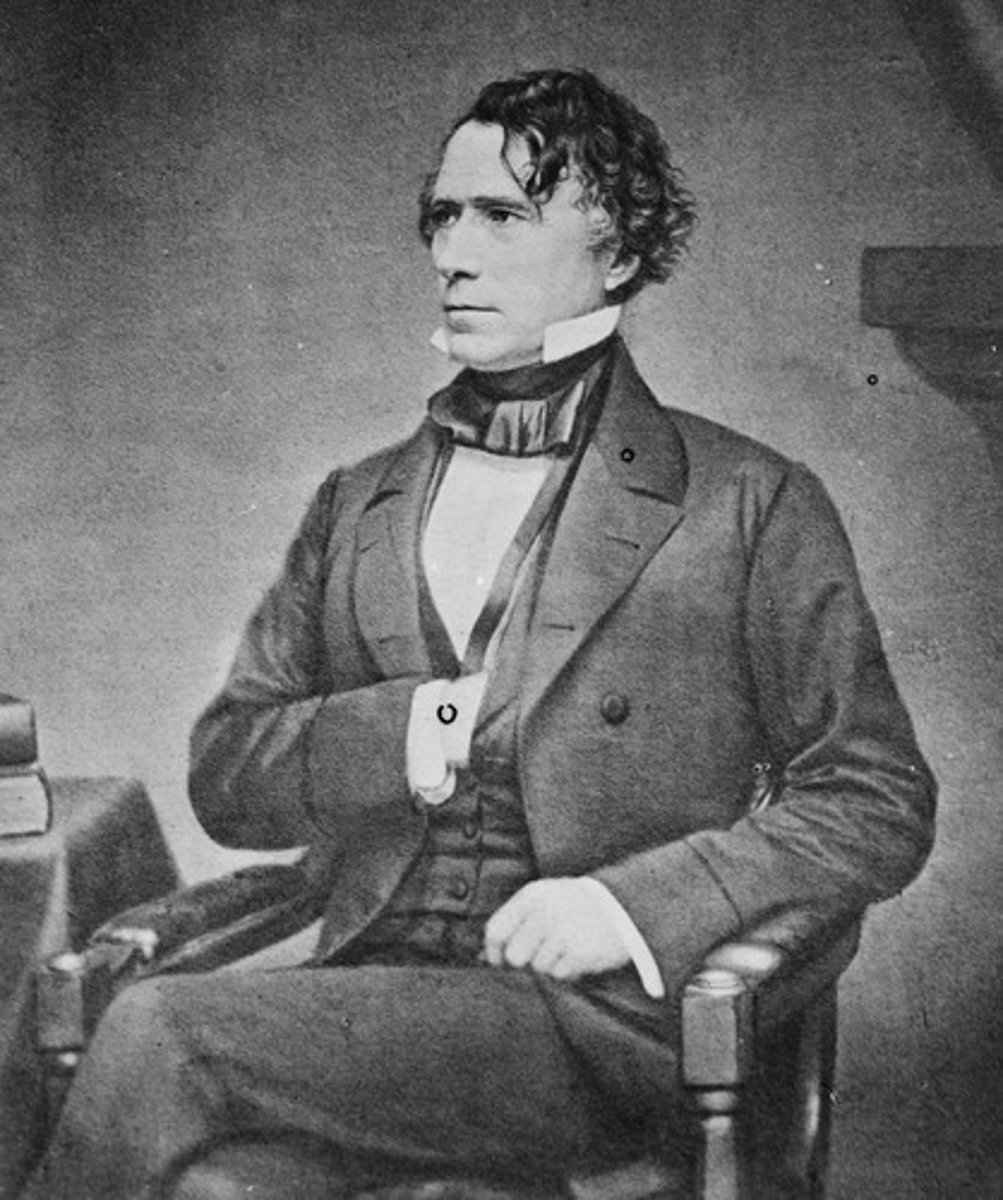
Franklin Pierce
(14) 1853-1857
His wife hated Washington, D.C., so much, that she fainted when she found out he had been nominated for President.

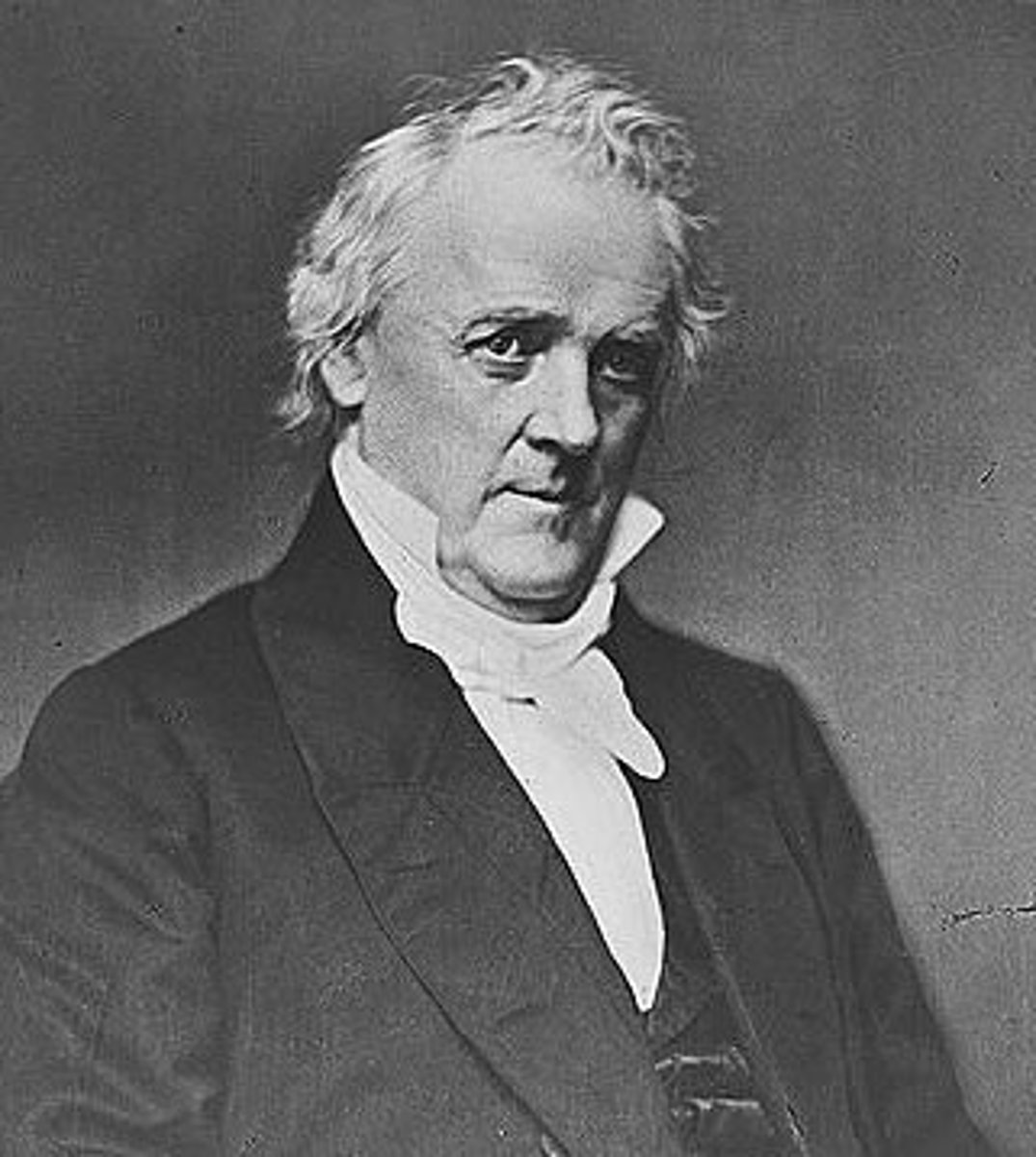
James Buchanan
(15) 1857-1861
He was the only bachelor to ever serve in the White House. He tried in vain to find a compromise to keep the South from seceding from the Union, but failed.

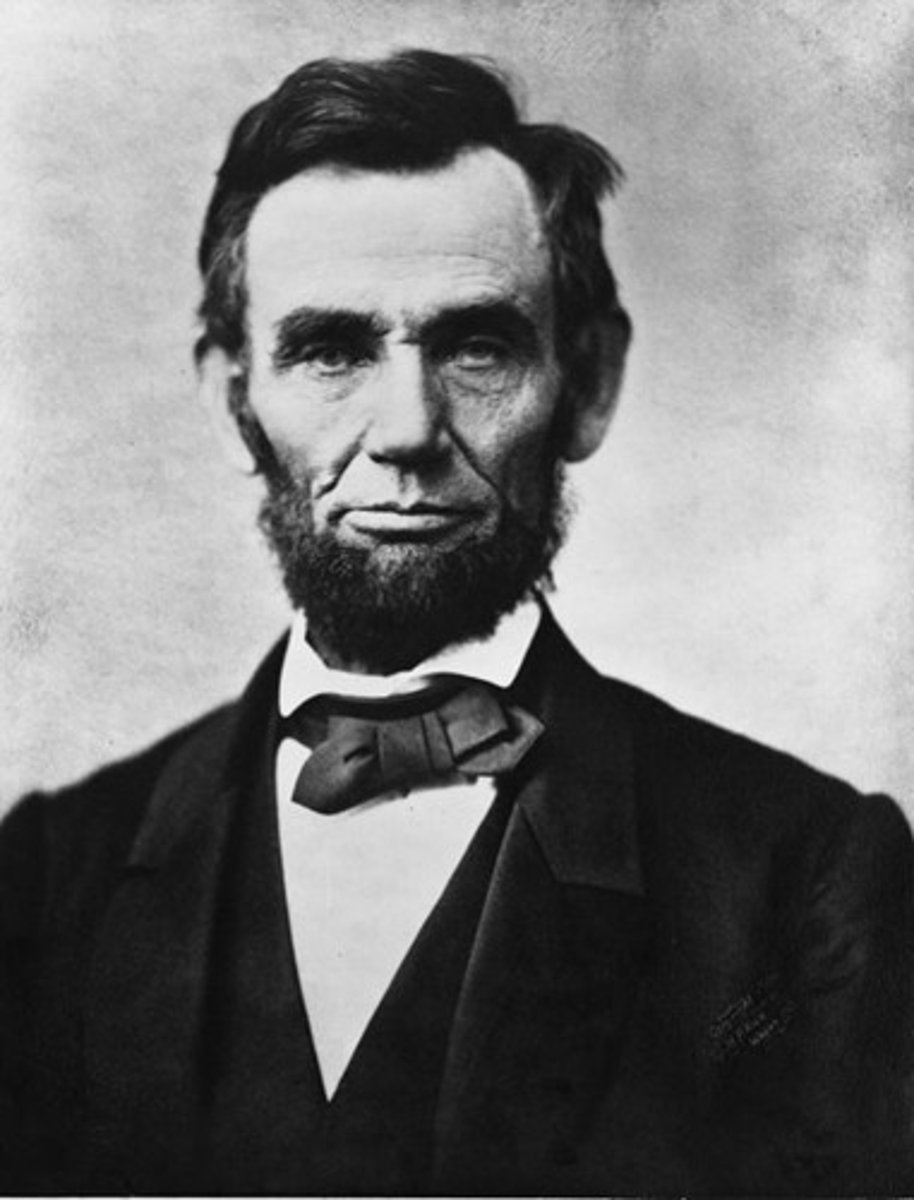
Abraham Lincoln
(16) 1861-1865
He led the Union into the Civil War to preserve the nation and end slavery. He was assassinated just five days after the Confederate armies surrendered. Polls show that he is the most admired President

Andrew Johnson
(17) 1865-1869
Succeeding Lincoln, Johnson found himself in bitter battles with Congress over Reconstruction. He was impeached and tried by the Senate, but was acquitted by one vote. He was the only southern senator to stay loyal to the Union.

Ulysses S. Grant
(18) 1869-1877
He was the top Union military hero of the Civil War. His two terms were marred by scandals. His name was changed due to an error on his application. He liked his initials so much that he kept that name

Rutherford Hayes
(19) 1877-1881
He is one of only three Presidents to lose the popular vote but win the office. He won the election by one electoral vote. His wife, Lucy, was the first First Lady to graduate from college.

James Garfield
(20) 1881
He set out to reform the "spoils system" by which politicians gave their friends low-level political offices. He was assassinated by a disappointed office seeker. He was the first left-handed President.

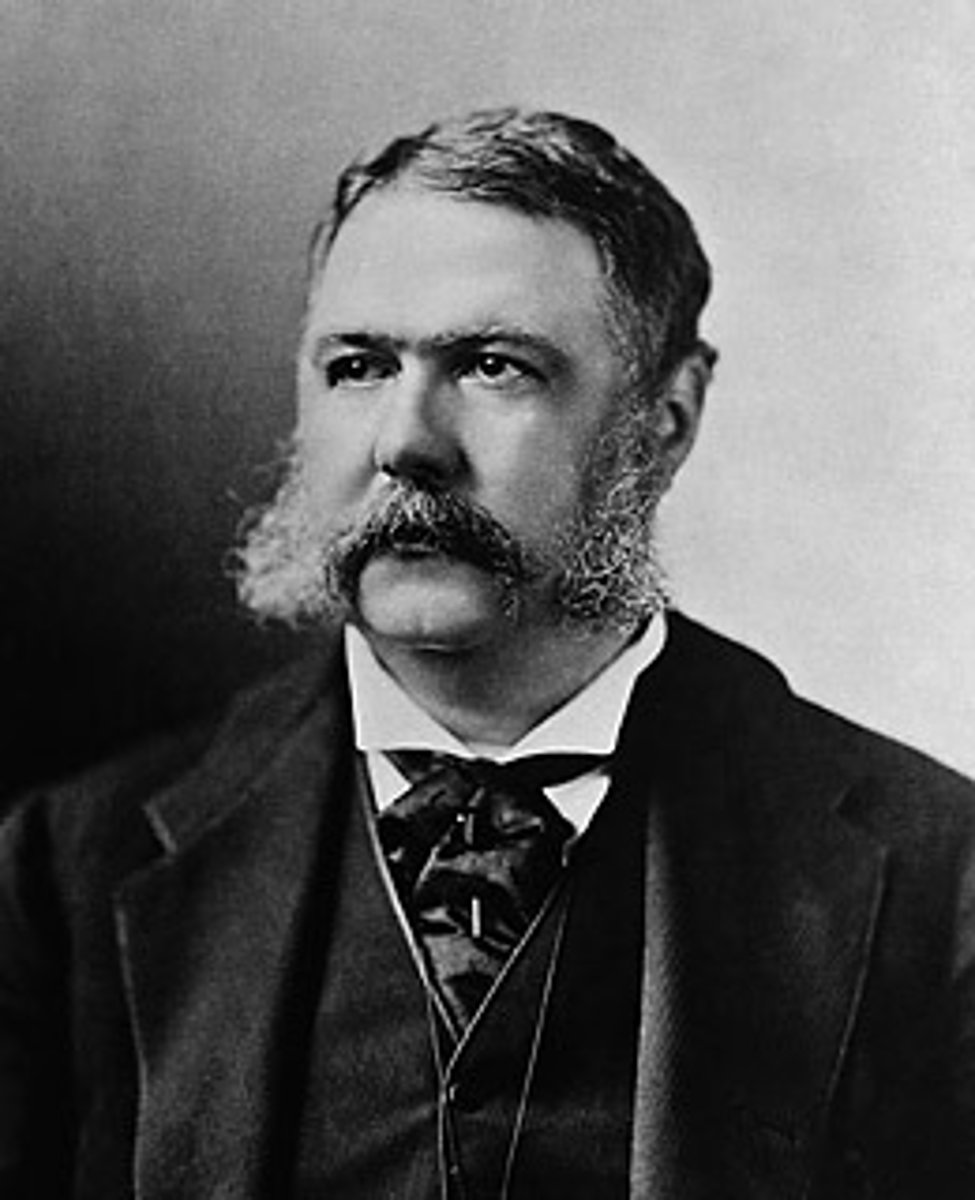
Chester Arthur
(21) 1881-1885
He was unknown before being elected, but surprised people by being honest and responsible. He helped create the Civil Service. As a lawyer, he defended a black woman who had been abused on a streetcar. He won the case, which led the streetcar companies to integrate.

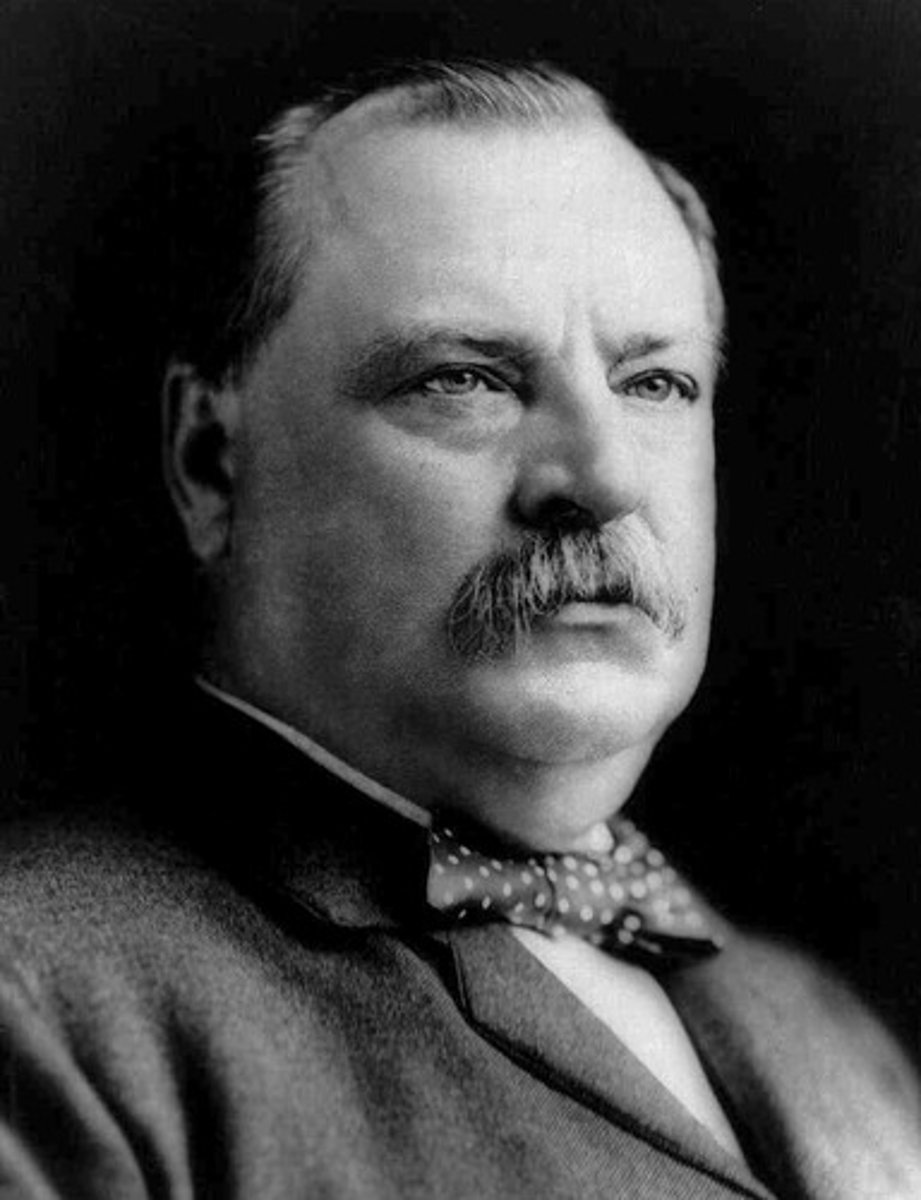
Grover Cleveland
(22) 1885-1889
He is the only President to be elected to two non-consecutive terms.
He expanded the Civil Service and ended wasteful government programs. But an economic depression wrecked his second term

Benjamin Harrison
(23) 1889-1893
He was caught between reformers who were fighting the spoils system and those who wanted to continue it, and was defeated after one term.
His grandfather was President William Henry Harrison.
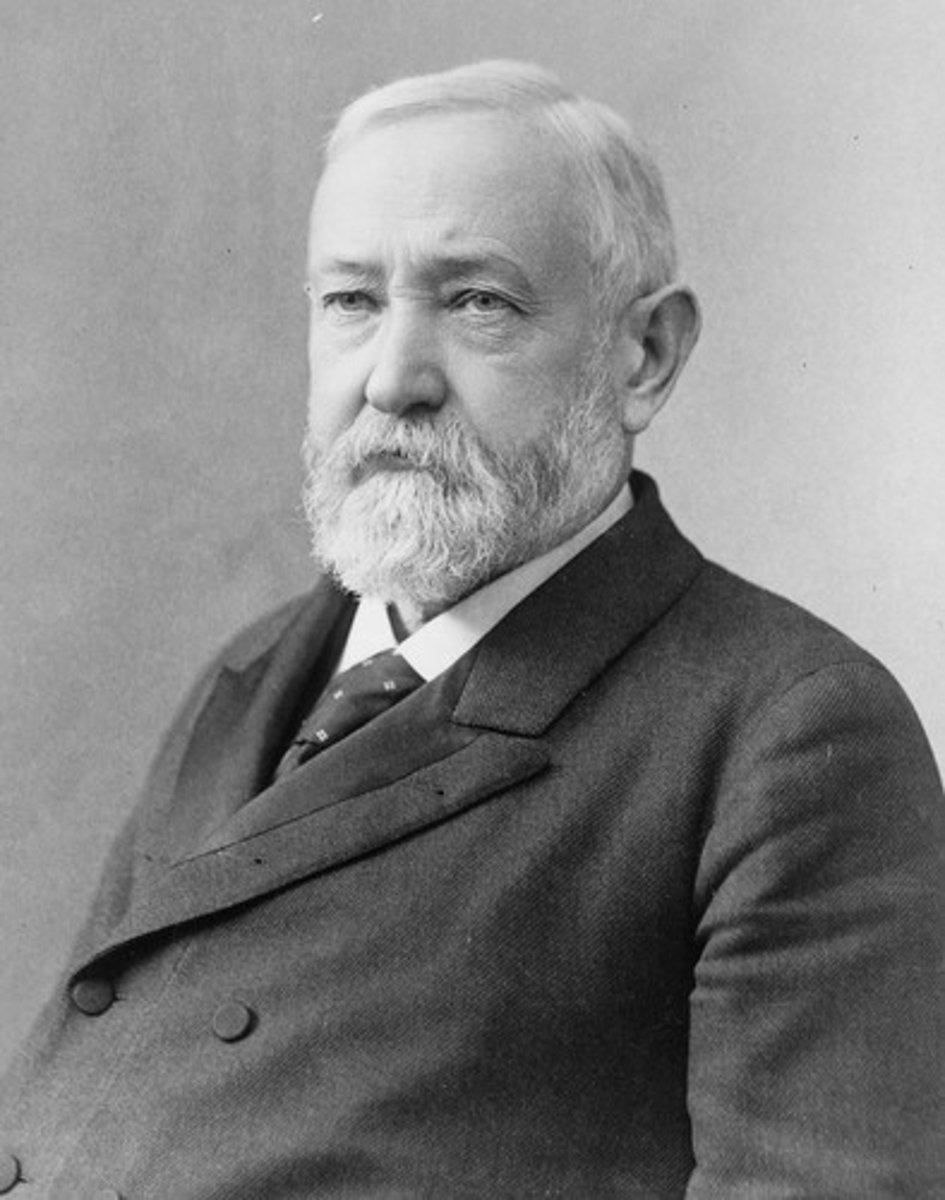
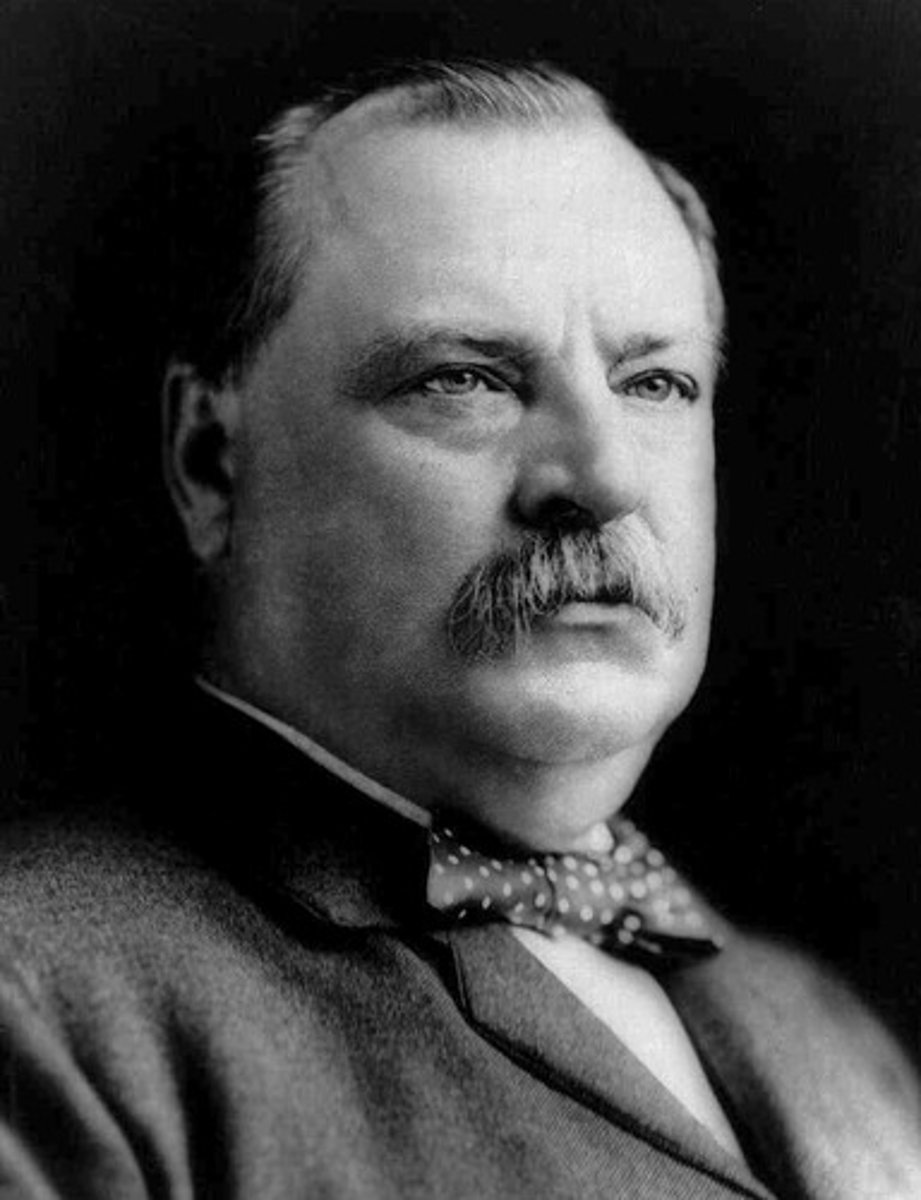
Grover Cleveland
(24) 1893-1897
He is the only President to be elected to two non-consecutive terms.
He expanded the Civil Service and ended wasteful government programs. But an economic depression wrecked his second term

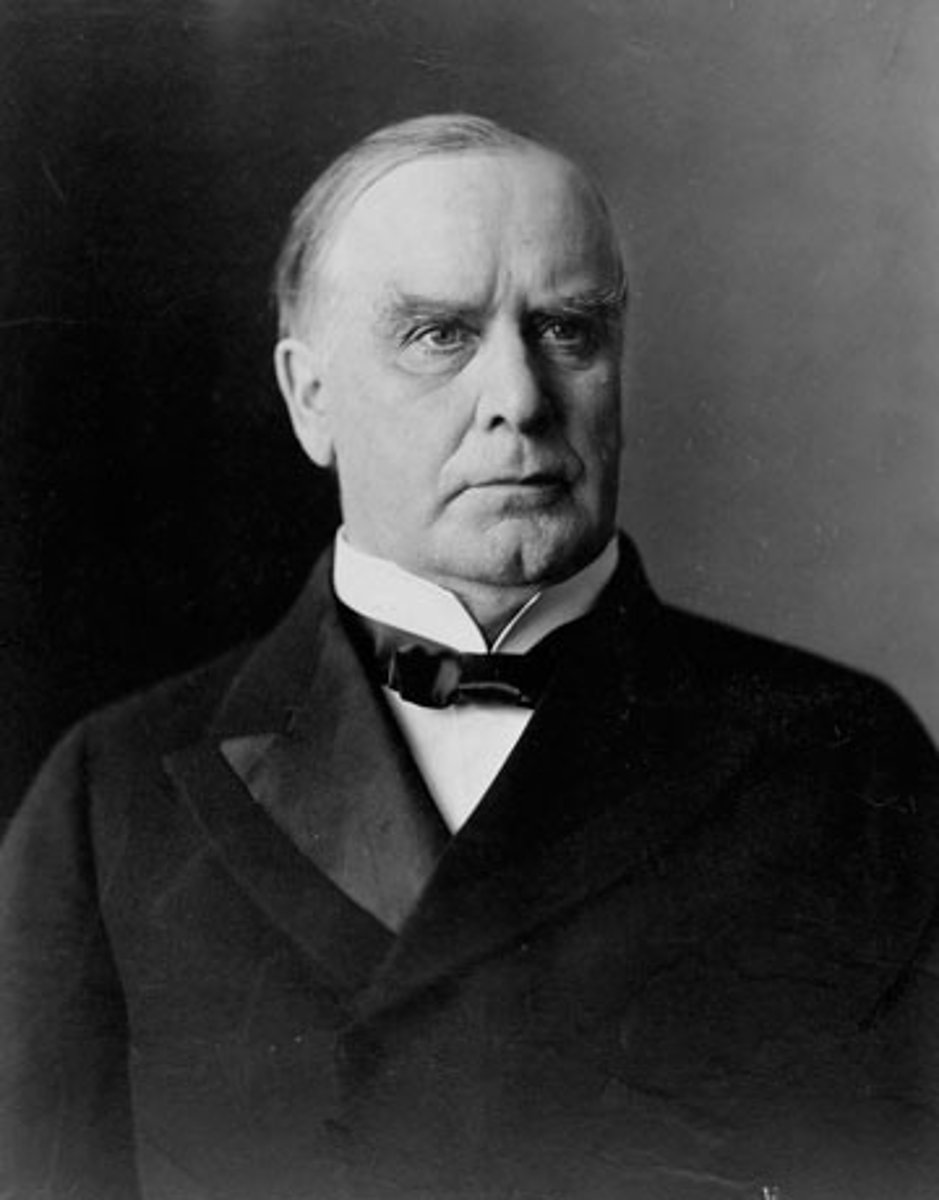
William McKinley
(25) 1897-1901
He led the United States during the Spanish-American War. The United States won several important overseas colonies.
Only moments after handing a girl his "lucky" red carnation, he was assassinated

Theodore Roosevelt
(26) 1901-1909
He was one of the most activist Presidents. His many accomplishments included the building of the Panama Canal, cracking down on business monopolies, and creating many national parks.
He was the first President to visit a foreign country while in office.
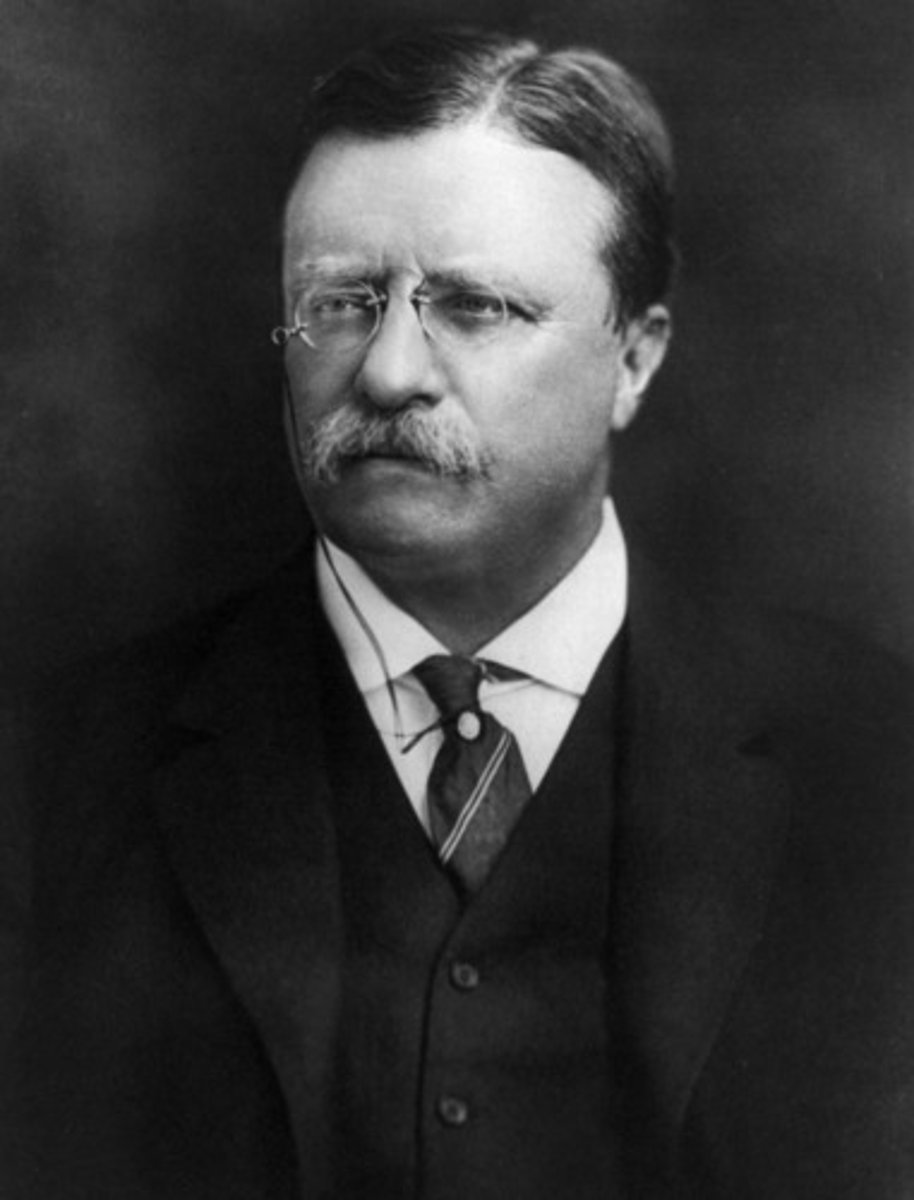

William Howard Taft
(27) 1909-1913
He continued many of Roosevelt's policies. A conservative, he alienated the progressive wing of his party and lost reelection.
He is the only President who became a Supreme Court Justice.
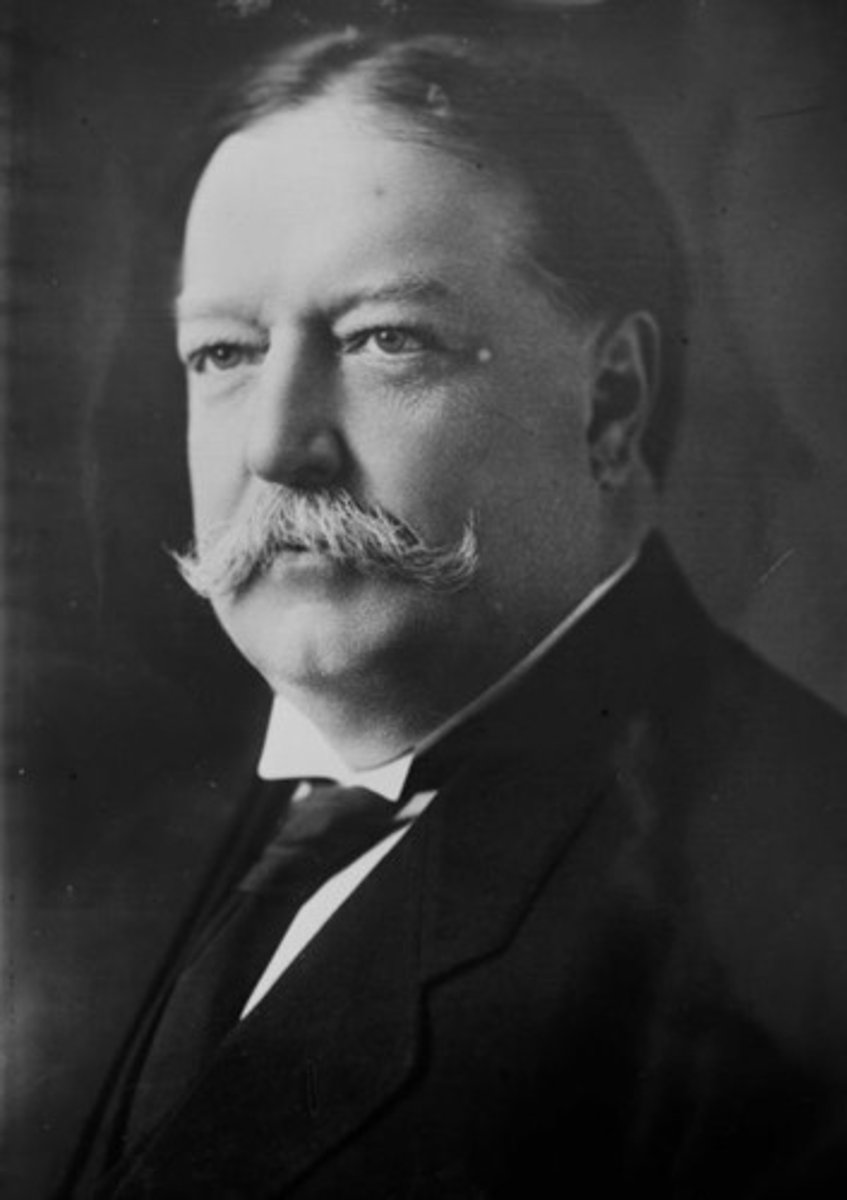

Woodrow Wilson
(28) 1913-1921
After initially opposing World War I (1914-1918), He led the United States into the war and drafted the peace plan that ended it. Wilson then fought to create the League of Nations, the forerunner of the United Nations. He was the first President to hold a news conference.
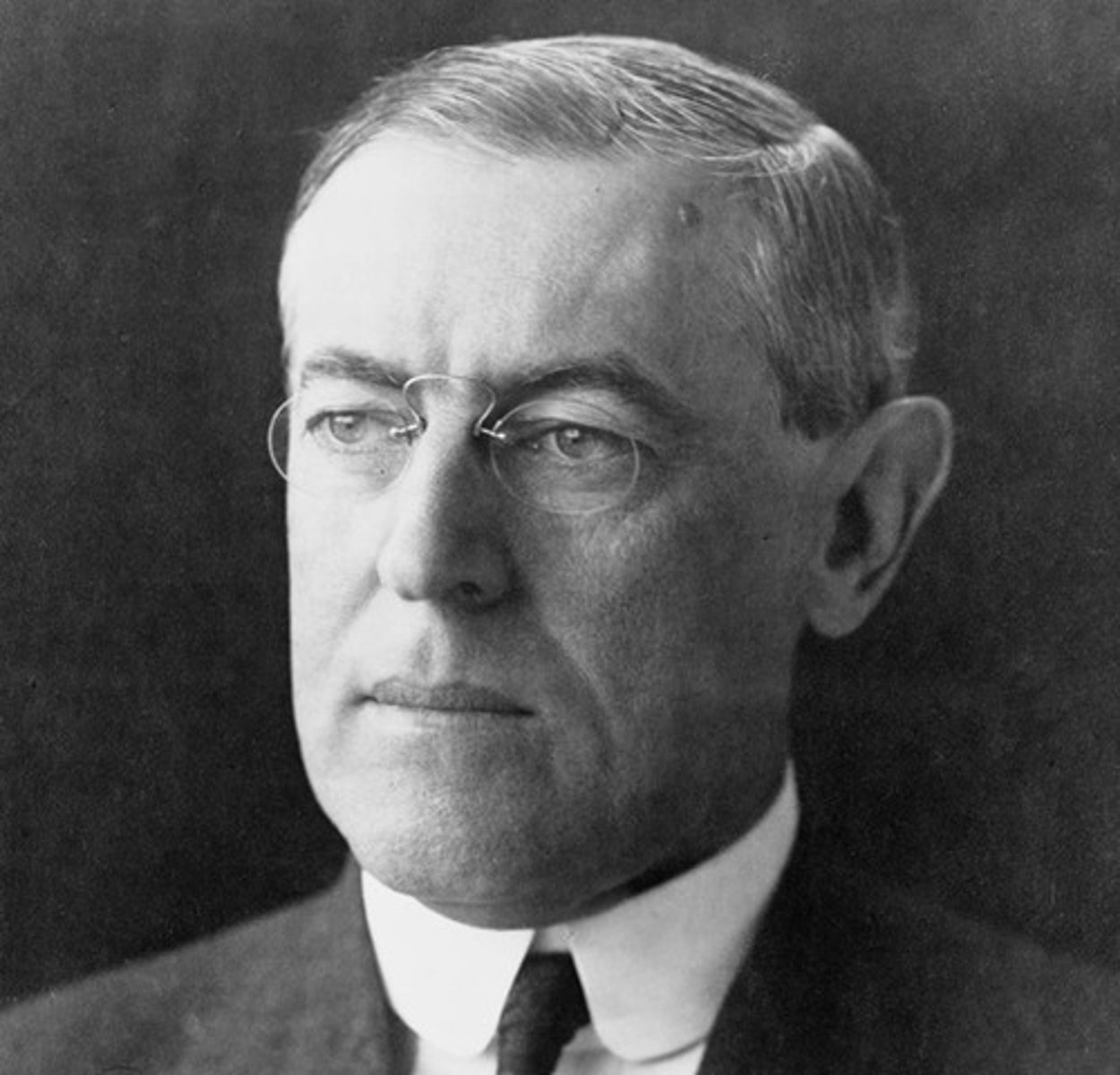

Warren G. Harding
(29) 1921-1923
He died in office, just as massive corruption in the Teapot Dome scandal was about to become public. Harding's election was the first in which women voted.
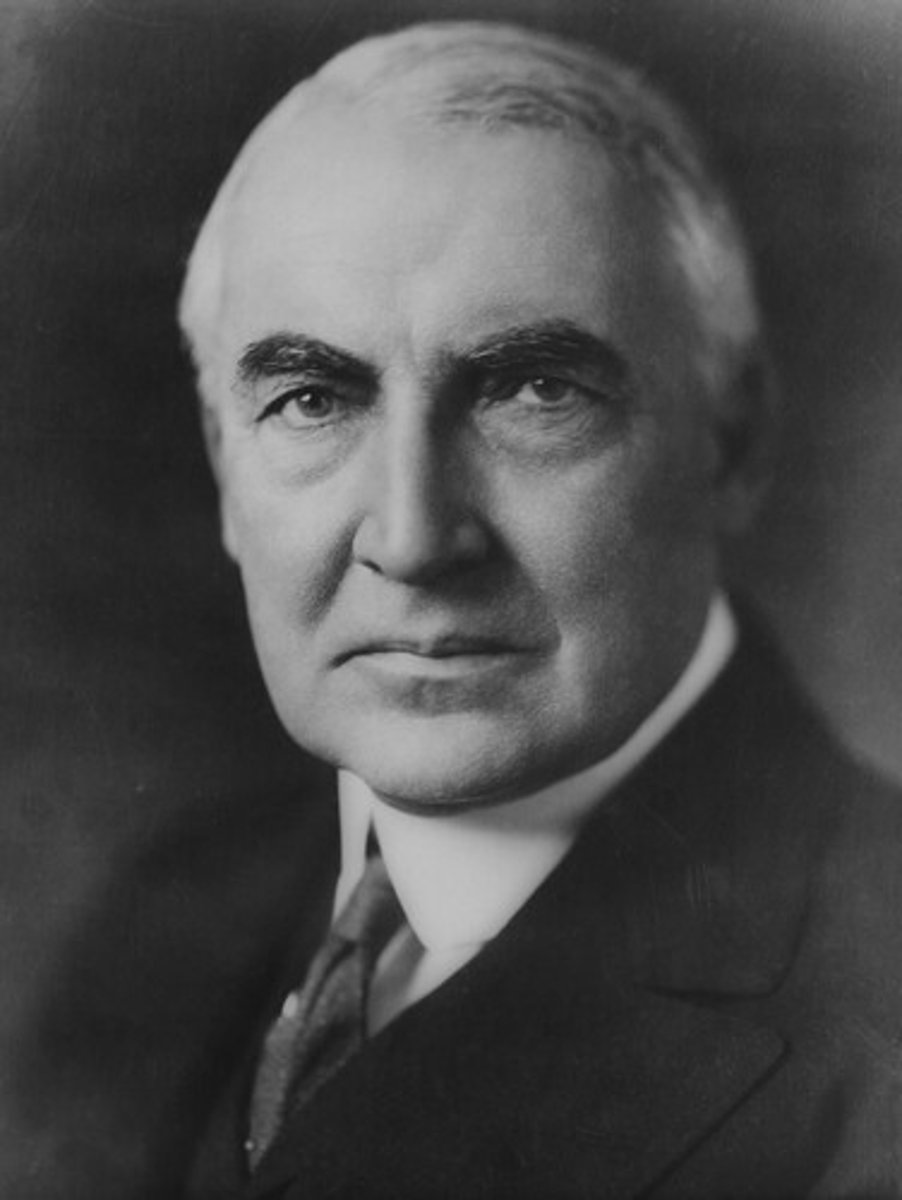

Calvin Coolidge
(30) 1923-1929
His term was marked by economic prosperity. However, he ignored signs that the stock market was likely to collapse.

Herbert Hoover
(31) 1929-1933
The stock market crashed a few months into his term. The Great Depression that followed was widely and some say unfairly blamed on him.

Franklin Roosevelt
(32) 1933-1945
He led the nation during the Great Depression of the 1930s and to victory in World War II (1941-1945). He also greatly expanded the size and role of the federal government through his New Deal social programs. He is the only President elected four times.

Harry S. Truman
(33) 1945-1953
He made the fateful decision to drop the atomic bomb on Japan. World War II ended days later. Truman also led the United States during the Korean War (1950-1953).

Dwight D. Eisenhower
(34) 1953-1961
A former World War II general and hero, he helped end the Korean War and steered a moderate course during the Cold War.

John F. Kennedy
(35) 1961-1963
In 1962, the United States and the Soviet Union hovered on the brink of nuclear war during the Cuban Missile Crisis. He eventually forced the Soviets to back down. He was assassinated in the third year of his term

Lyndon B. Johnson
(36) 1963-1969
He passed sweeping antipoverty and civil rights programs. However, he also involved the United States in the unpopular Vietnam War. Antiwar protests caused him to drop a reelection bid.
He was sworn into office on an airplane after the Kennedy assassination.

Richard Nixon
(37) 1969-1974
During his first term, he improved relations with the Soviet Union and China and wound down the Vietnam War. But the Watergate scandal forced Nixon to resign before Congress could impeach him. He is the only U.S. President in history to resign his office.

Gerald Ford
(38) 1974-1977
He became Vice President after Nixon's Vice President resigned in disgrace, and President after Nixon resigned. His pardon of Nixon was unpopular, probably costing him reelection.
He is the only President never elected President or Vice President.

James Carter
(39) 1977-1981
He had success promoting Middle East peace. But soaring oil prices, high inflation, and the Iran hostage crisis made him look weak and ineffectual. Since leaving office, he has traveled the world doing charity work.

Ronald Reagan
(40) 1981-1989
He is credited with reviving national pride after the turmoil of the 1960s and 1970s. He enjoyed great popularity, though his conservative policies were controversial. He is the only President to survive after being wounded by a would-be assassin.

George H. W. Bush
(41) 1989-1993
During his term, the Soviet Union collapsed and the Cold War ended. He also led the United States in the 1991 Gulf War against Iraq. But economic troubles at home cost him his reelection bid. He was the first sitting Vice President to be elected President since Martin Van Buren.

Bill Clinton
(42) 1993-2001
He achieved goals such as passage of the NAFTA trade agreement and cuts in the budget deficit. But his popularity was uneven and his second term was marred by scandal.

George W. Bush
(43) 2001-2009
Just eight months after being sworn in, President had to unite a mournful country after the September 11th terrorist attacks. A self-proclaimed wartime commander-in-chief, like his father, led the United States into war against Iraq.

Barack Obama
(44) 2009-2017
He gained national recognition after he delivered the keynote address at the Democratic National Convention in 2004. He served as the U.S. Senator for Illinois from 2005 to 2008. He is the first African American president of the United States.

Donald Trump
(45) 2017 -
Before entering politics, he was a businessman and television personality.

The Declaration of Independence
Document asserting the thirteen American colonies' independence from British rule (1776).
The American Revolution
Conflict between the thirteen colonies and Great Britain (1775-1783) leading to independence.
The Civil War
Conflict between the Northern states (Union) and Southern states (Confederacy) over issues including slavery (1861-1865).
Emancipation Proclamation
Executive order by President Lincoln freeing slaves in Confederate-held territory (1863).
Reconstruction
The period following the Civil War focused on rebuilding the South and integrating freed slaves into society (1865-1877).
The Louisiana Purchase
Acquisition of the Louisiana territory from France, doubling the size of the U.S. (1803).
Manifest Destiny
The 19th-century belief that the U.S. was destined to expand across the North American continent.
The Monroe Doctrine
Policy opposing European colonialism in the Americas (1823).
The Gold Rush
Mass migration to California following the discovery of gold in 1848.
The Great Depression
Severe worldwide economic downturn (1929-1939) that led to widespread unemployment and hardship.
The New Deal
Series of programs and reforms enacted by President Franklin D. Roosevelt to combat the Great Depression.
World War I
Global conflict involving the U.S. and allies against the Central Powers (1914-1918), with U.S. involvement starting in 1917
World War II
Global conflict involving the U.S. and allies against the Axis Powers (1939-1945), with major events including Pearl Harbor (1941) and D-Day (1944).
The Cold War
Political tension and military rivalry between the U.S. and the Soviet Union after WWII, characterized by nuclear arms race and proxy wars (1947-1991).
The Civil Rights Movement
Movement aimed at ending racial discrimination and ensuring equal rights for African Americans (1950s-1960s).
The Vietnam War
Conflict between North Vietnam (supported by communists) and South Vietnam (backed by the U.S.), with significant anti-war protests in the U.S. (1955-1975).
Marbury v. Madison
Established judicial review (1803).
Brown v. Board of Education
Declared racial segregation in public schools unconstitutional (1954).
Roe v. Wade
Affirmed women's right to choose abortion (1973).
George Washington
First President and a Founding Father.
13th Amendment
Abolished slavery (1865).
14th Amendment
Granted citizenship and equal protection under the law (1868).
19th Amendment
Granted women the right to vote (1920).
The Boston Tea Party
Protest against British taxation (1773).
The signing of the Treaty of Paris
Ended the Revolutionary War (1783).
Attack on Pearl Harbor
Led to U.S. entry into WWII (1941).
The Articles of Confederation
The first constitution of the United States, later replaced by the current Constitution.
The Federalist Papers
Essays promoting the ratification of the Constitution, written by Hamilton, Madison, and Jay.
The Whiskey Rebellion
A violent tax protest in 1794 against the federal excise tax on whiskey.
The Trail of Tears
Forced relocation of Native American nations from their homelands in the Southeastern U.S. (1830s).
The Seneca Falls Convention
First women's rights convention held in 1848, advocating for women's suffrage.
The Gilded Age
Period of rapid economic growth and industrialization in the late 19th century.
The Progressive Era
Time of social activism and political reform in the U.S. from the 1890s to the 1920s.
The Spanish American War
Conflict between the U.S. and Spain in 1898, resulting in U.S. territorial gains.
The Great Migration
Movement of African Americans from the rural South to urban centers in the North (1916-1970).
The Harlem Renaissance
Cultural movement celebrating African American arts and culture in the 1920s.
The New Frontier
President John F. Kennedy's domestic program aimed at improving the economy and civil rights.
The Civil Rights Act of 1964
Landmark legislation prohibiting discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex, or national origin.
The Voting Rights Act of 1965
Legislation aimed at overcoming barriers to voting for African Americans.
The Watergate Scandal
Political scandal leading to President Nixon's resignation in 1974.
The Iranian Hostage Crisis
444 days during which American diplomats and citizens were held hostage in Iran (1979-1981).
The Gulf War
Conflict in 1990-1991 to expel Iraqi forces from Kuwait.
The War on Terror
Global military campaign launched by the U.S. after the September 11 attacks.
The Affordable Care Act
Health care reform legislation aimed at increasing health insurance coverage (2010).
Imperialism
Policy of extending a country's power and influence through diplomacy or military force.
Isolationism
A foreign policy of remaining apart from the affairs or interests of other groups.
Nativism
The policy of protecting the interests of native-born or established inhabitants against those of immigrants.
Liberalism
A political philosophy advocating for civil liberties, political rights, and social justice.
Conservatism
A political philosophy promoting traditional institutions and practices.
Battle of Bunker Hill
Early battle in the American Revolution (1775). Where the British won and Colonel William Prescot led the colonial forces and famously said.
Battle of Gettysburg
Turning point battle in the Civil War (1863).It resulted in a significant Union victory and marked the beginning of the end for Confederate hopes in the war.
Battle of Normandy (Day)
Allied invasion of German-occupied France (1944).
Thomas Jefferson
Author of the Declaration of Independence and third President.
Frederick Douglass
Abolitionist and former enslaved person who advocated for civil rights.
Susan B. Anthony
Women's rights activist and key figure in the suffrage movement.