The pelvis and the hip (joints)
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
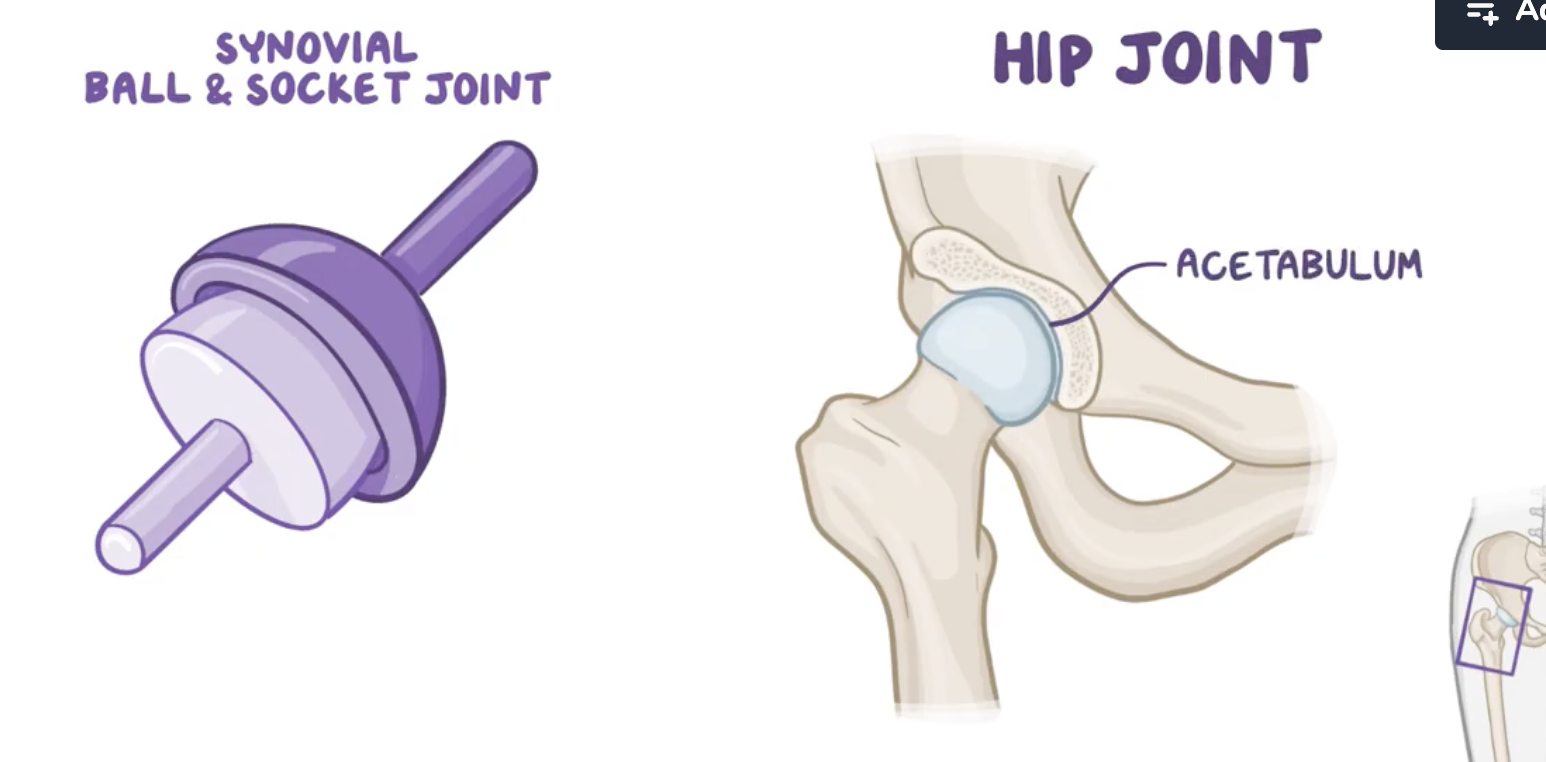
Characteristics of the hip joint
Synovial
Enarthrosis (ball and socket). 2/3 of the ball fitted in the acetabulum
Multiaxial

Pelvic girdle joints
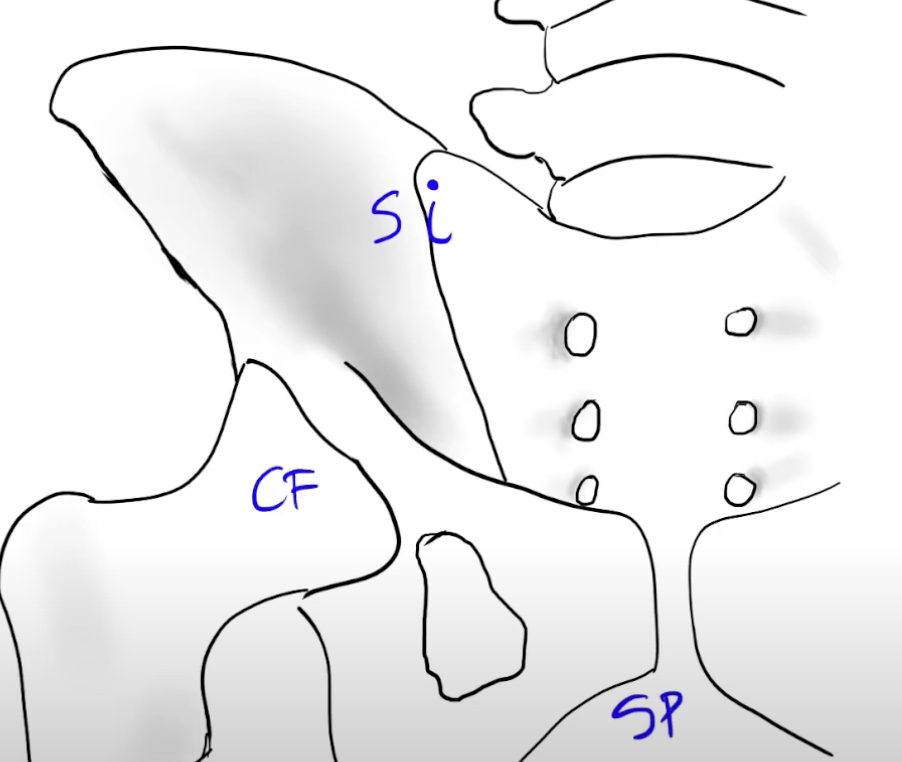
sacroiliac joint
coxofemoral joint
Pubic symphysis
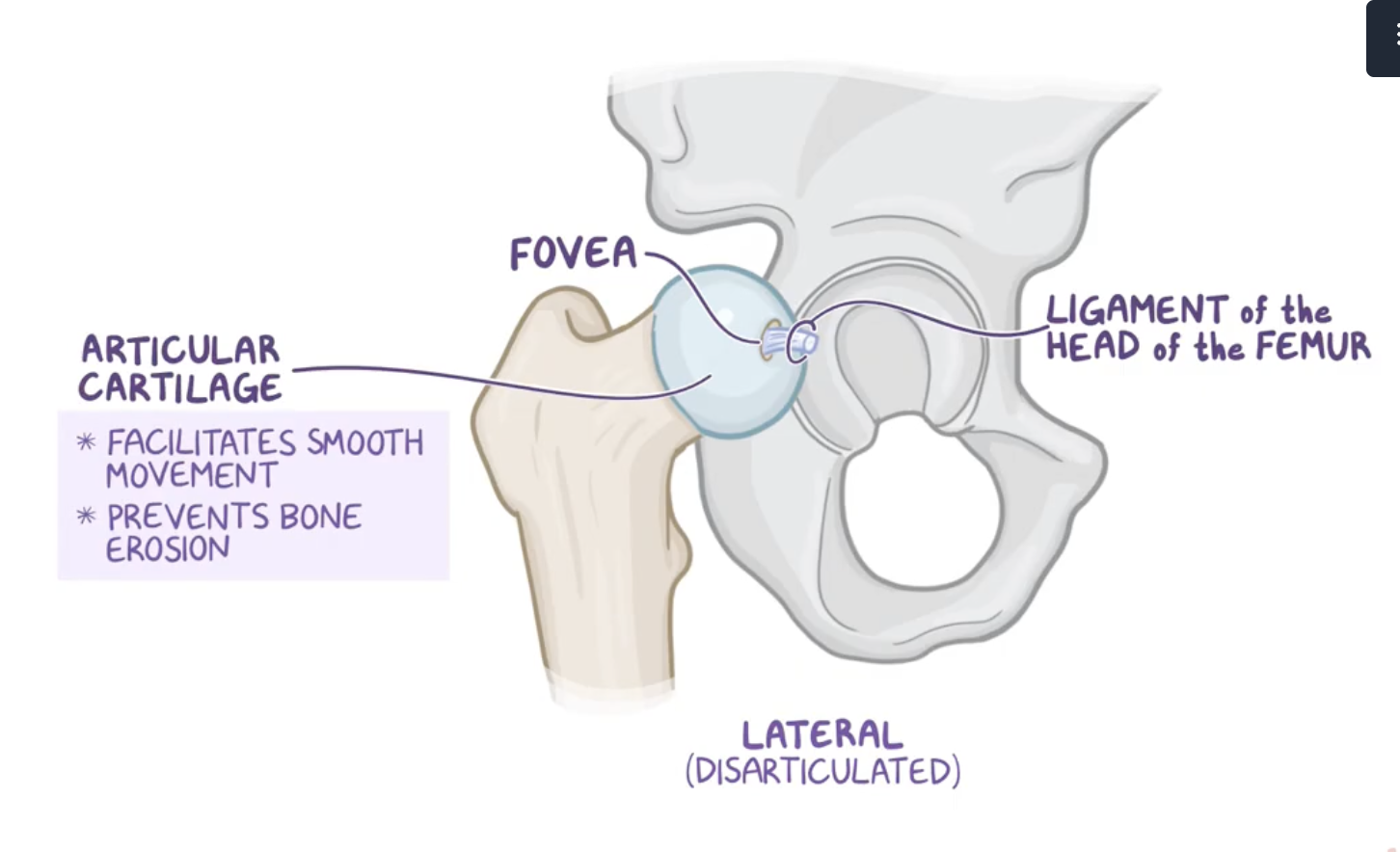
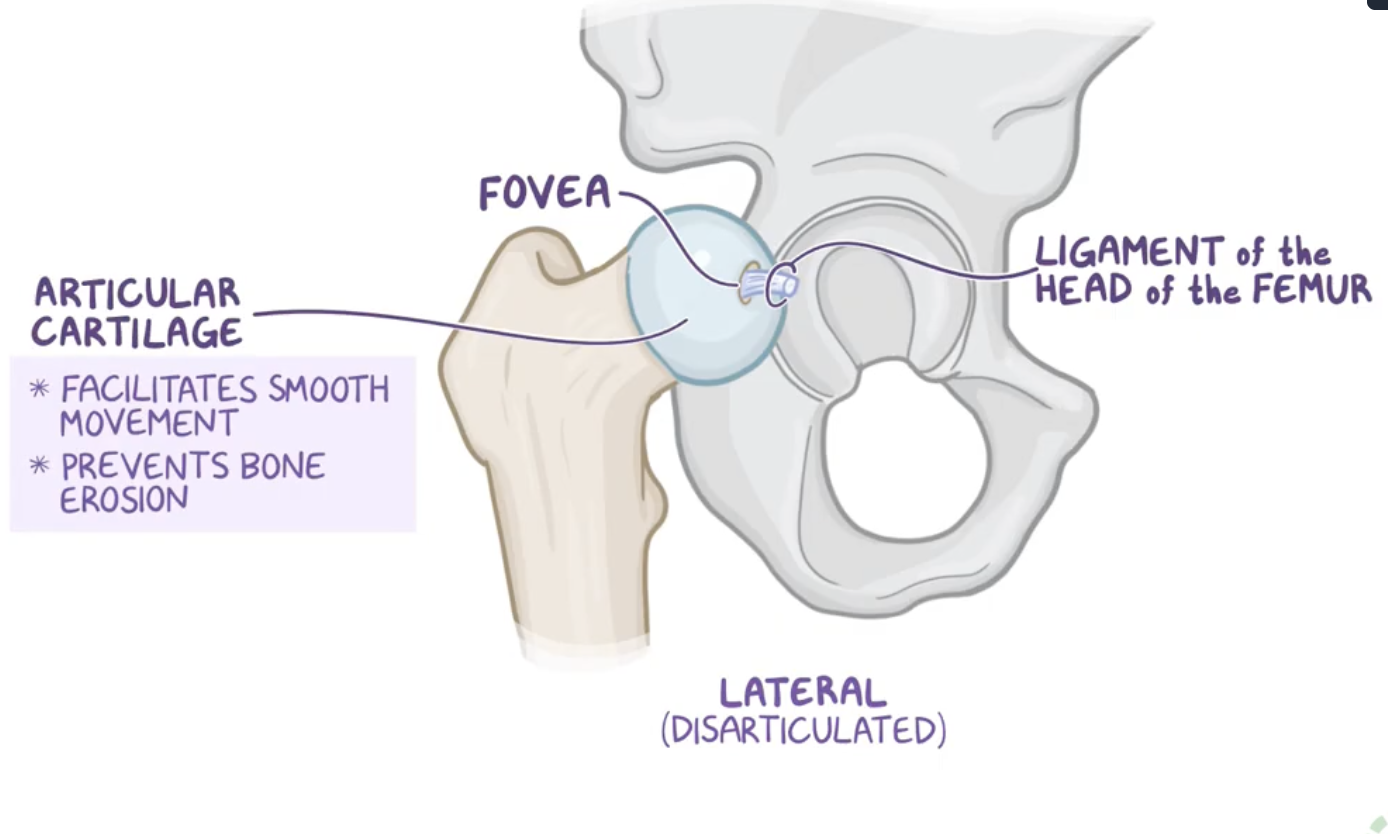
Characteristics of the femur head
it has depression on top of it which is called the fovea for the ligament of the head of the femur.
Except for the fovea, the femoral head is also covered entirely in articular cartilage which facilitates smooth movement and prevents bone erosion as it slides within the acetabulum.
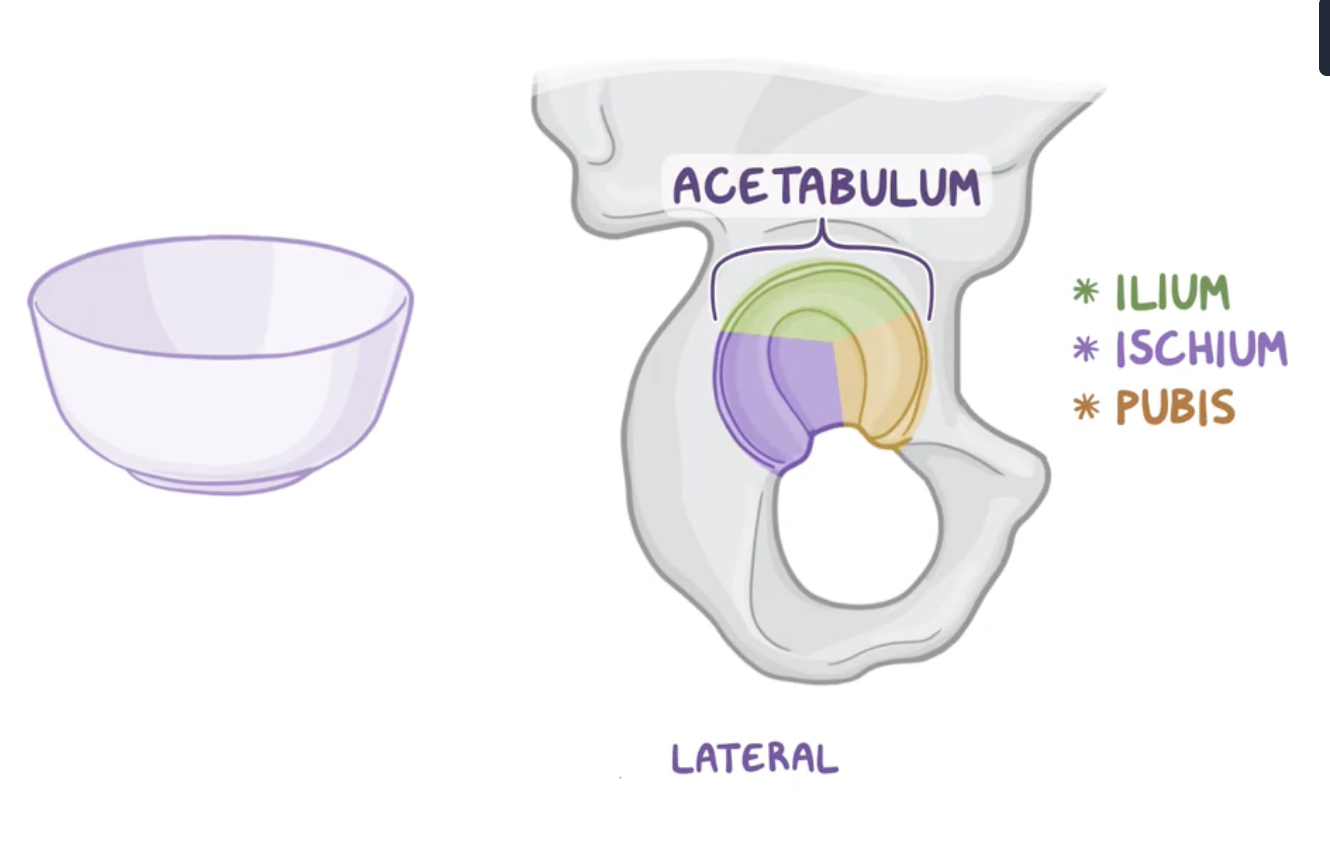
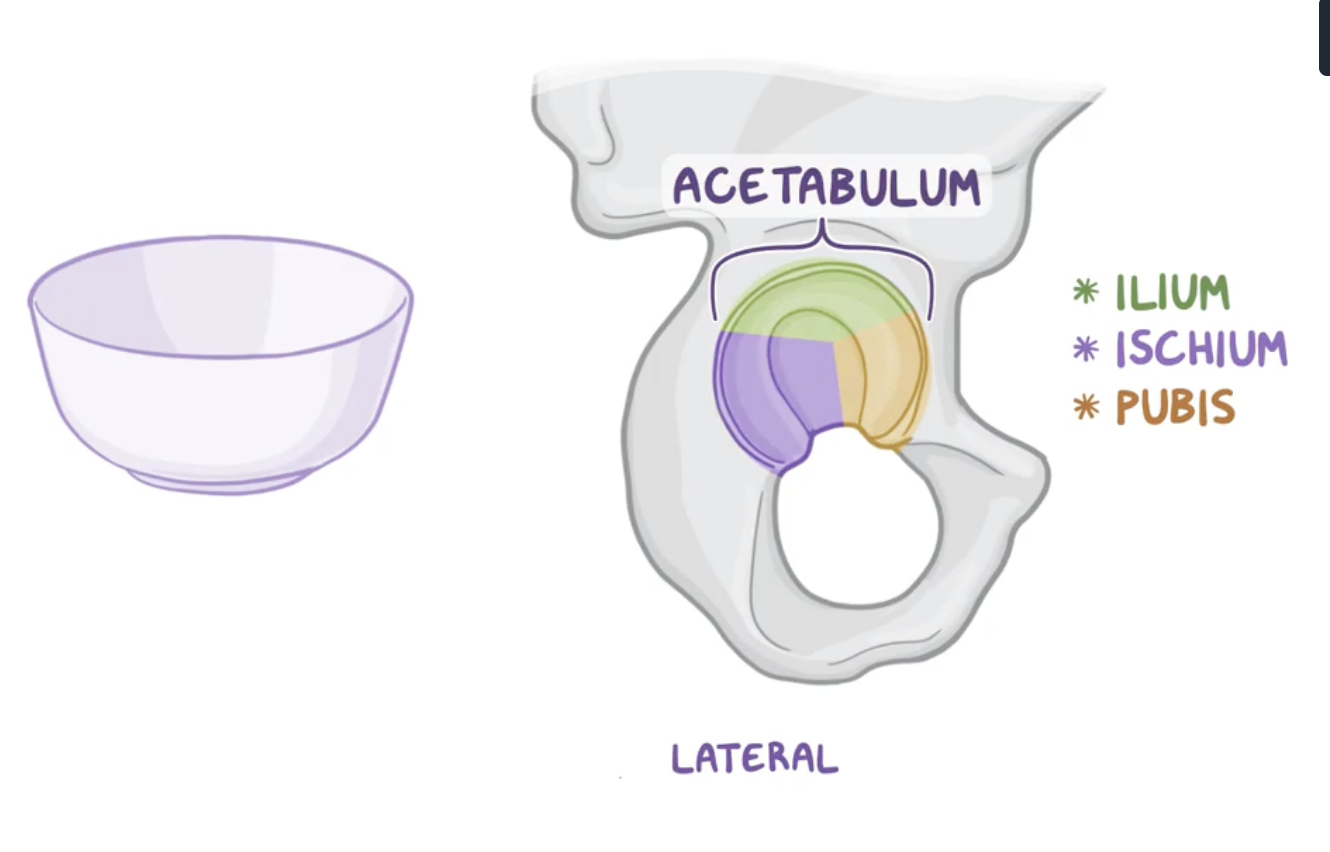
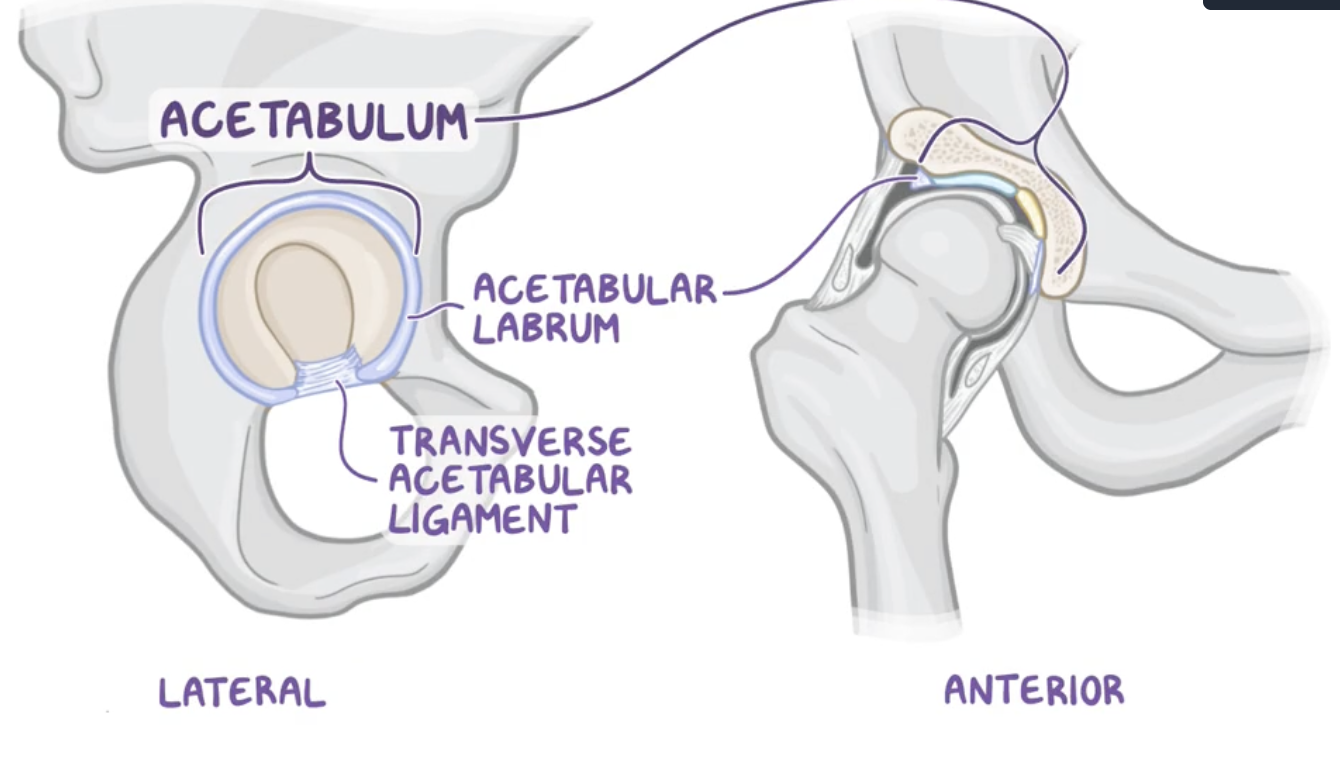
Acetabulum
Bowl shape structure formed by the fusion of:
Ilium
Ischium
Pubis
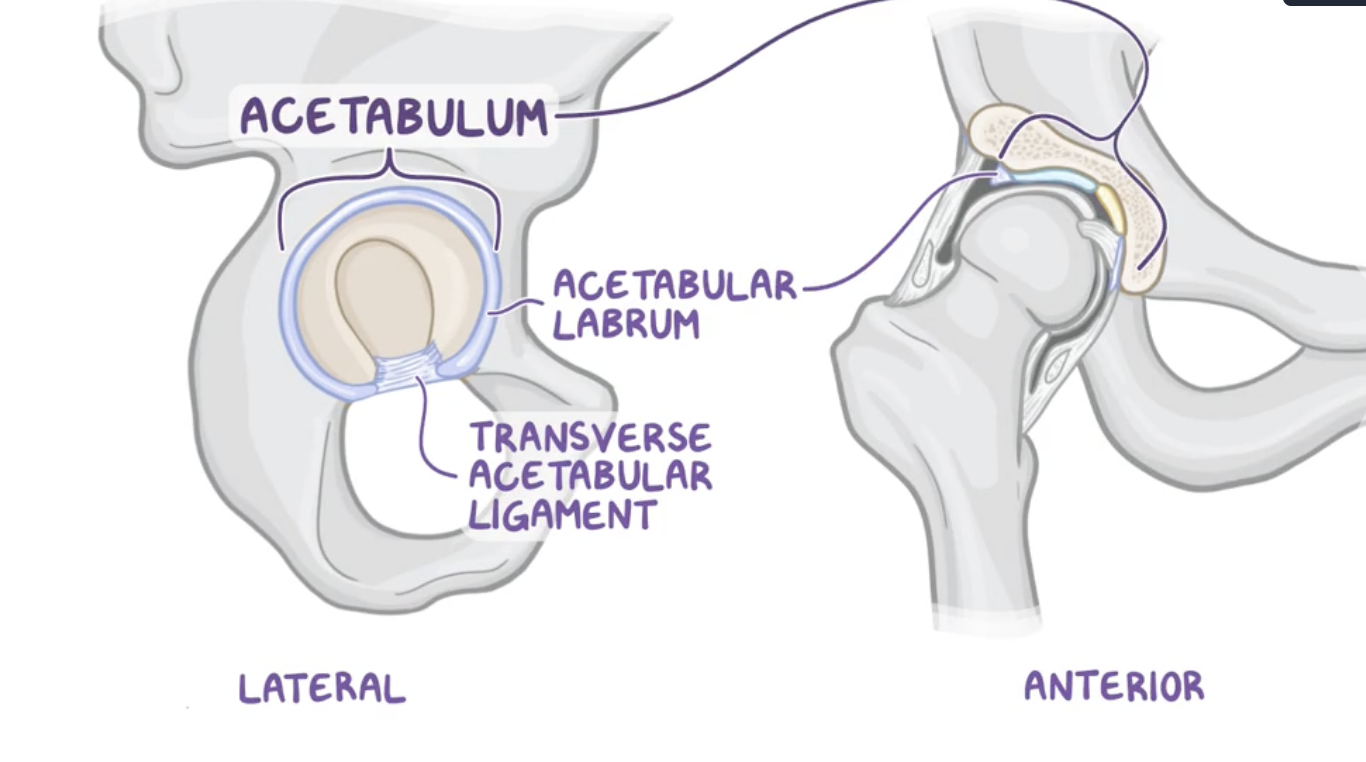
Acetubular labrum
increases the surface area of the acetabulum to allow more than half of the femoral head to fit within the acetabulum for stability.
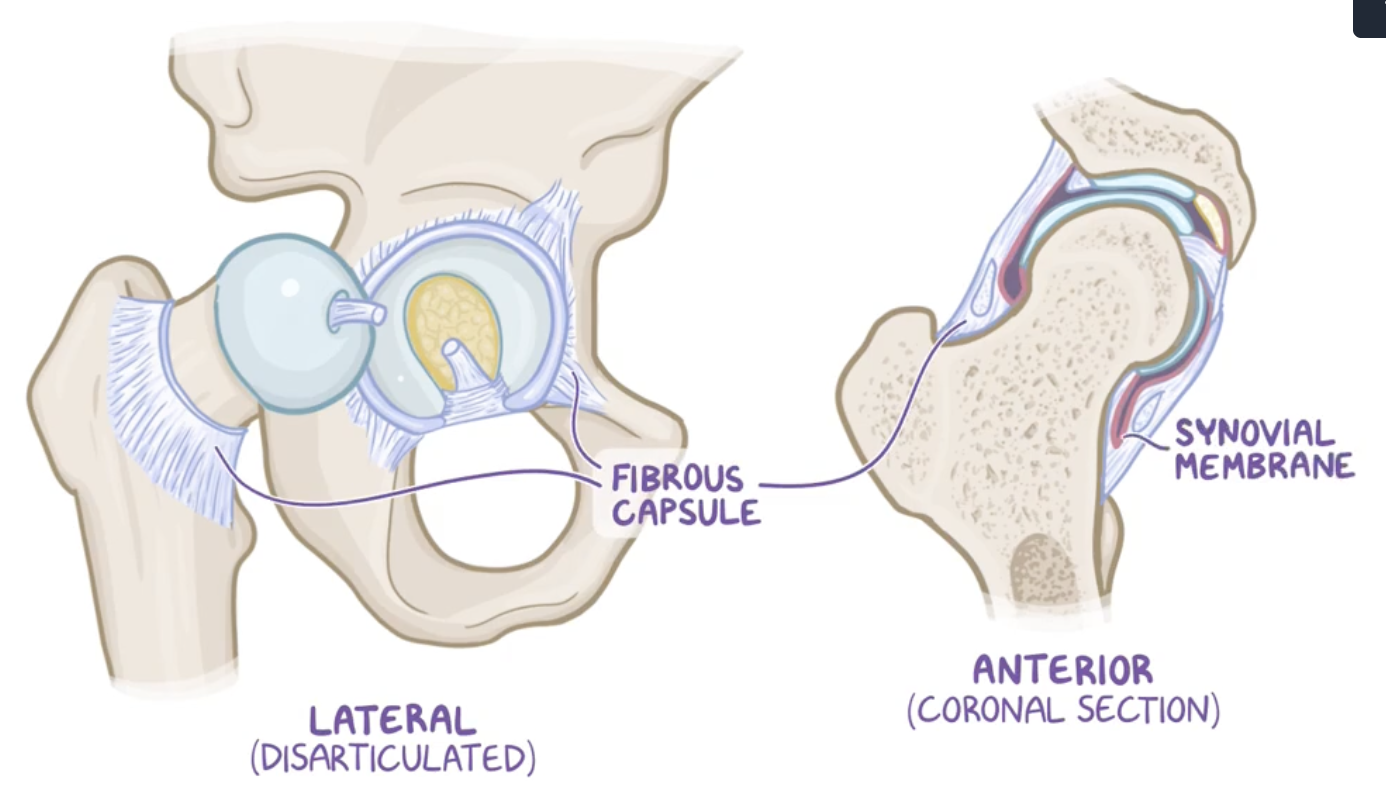
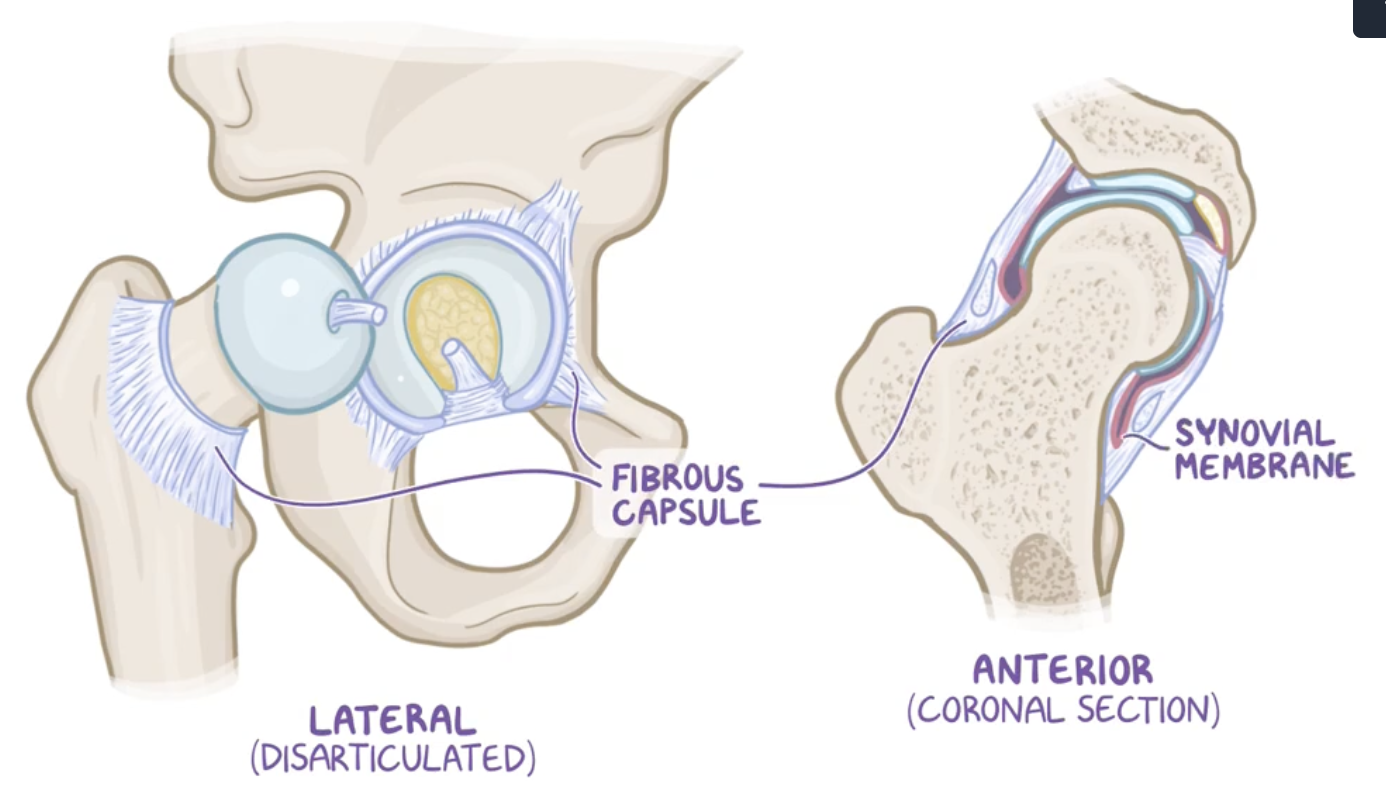
Fibrous capsule and synovial membrane
fibrous capsule: strong joint capsule formed by an external fibrous layer,
synovial membrane : internal layer.
Ligaments of the hip
Intracapsular
Capsular
Capsular ligaments
Iliofemoral
Pubofemoral (anterior)
Ischiofemoral (posterior)
Most of these ligaments’ fibers has an spiral shape
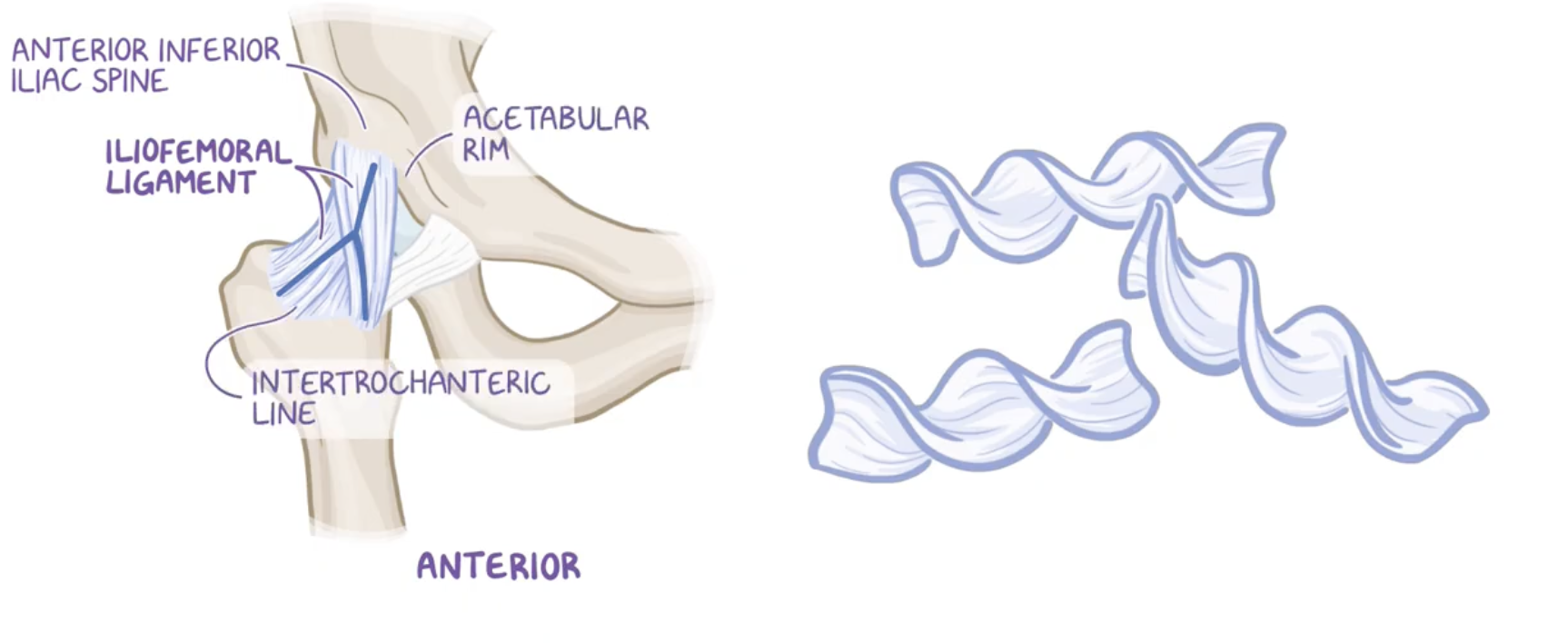
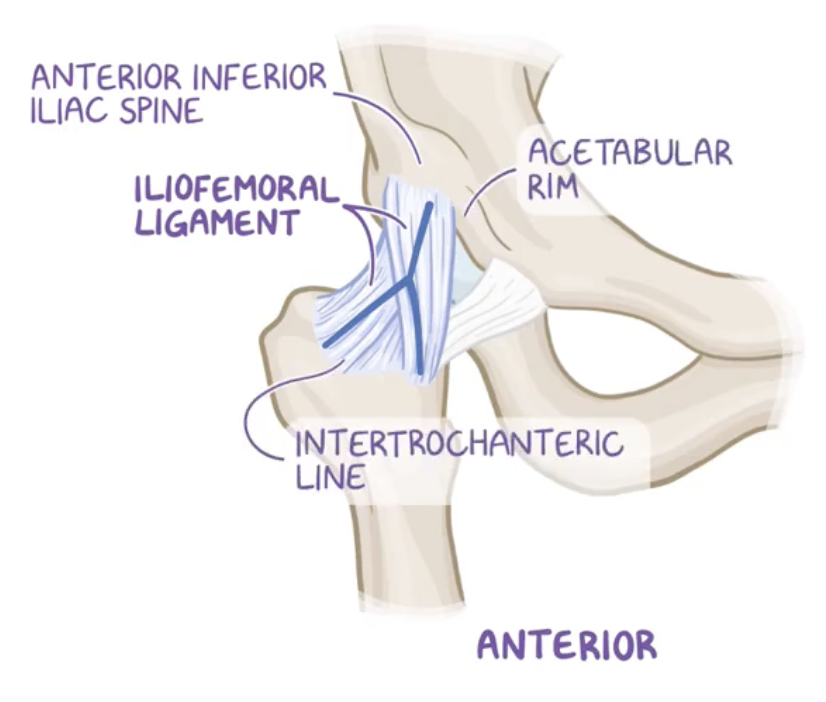
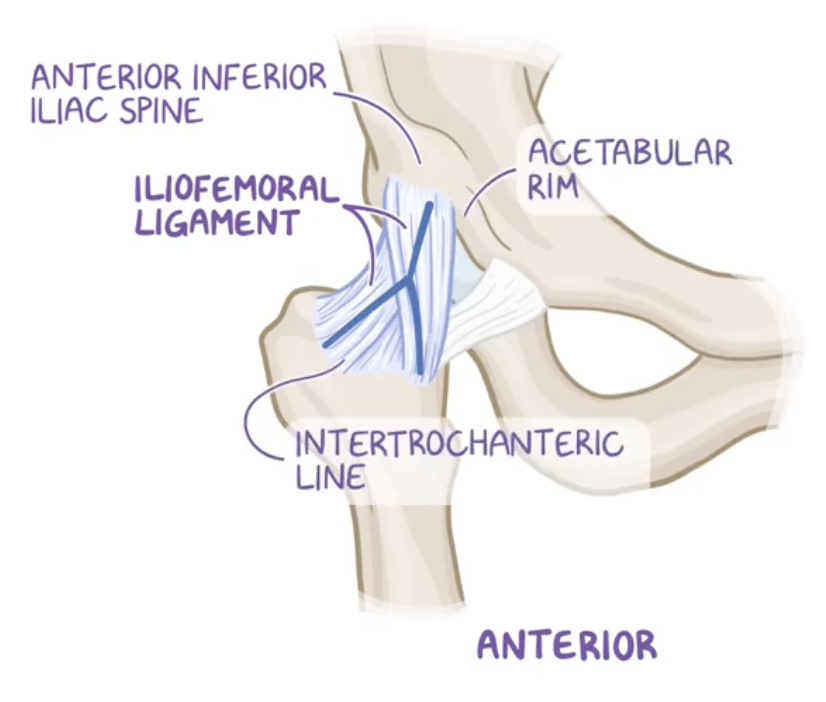
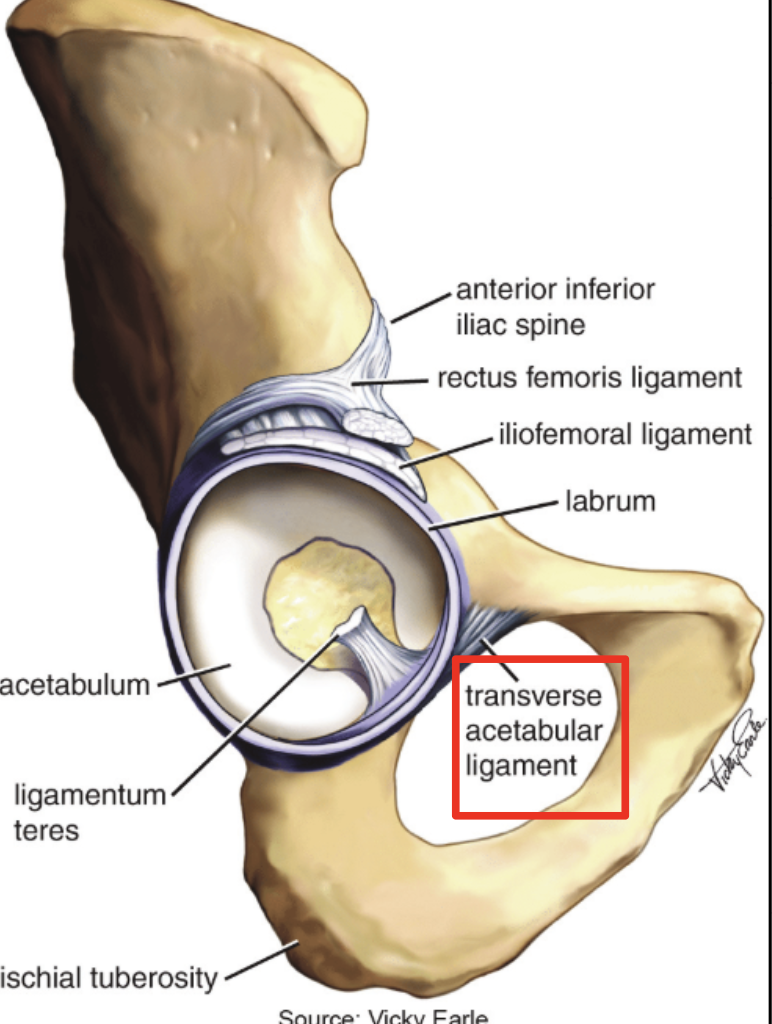
Iliofemoral ligament
Origin: anterior inferior iliac spine (AIIS) of the pelvis and acetubular margin
Insertion: intertrochanteric line of the femur.
This ligament is the strongest ligament of the hip joint (and of the body), providing stability and preventing hyperextension.
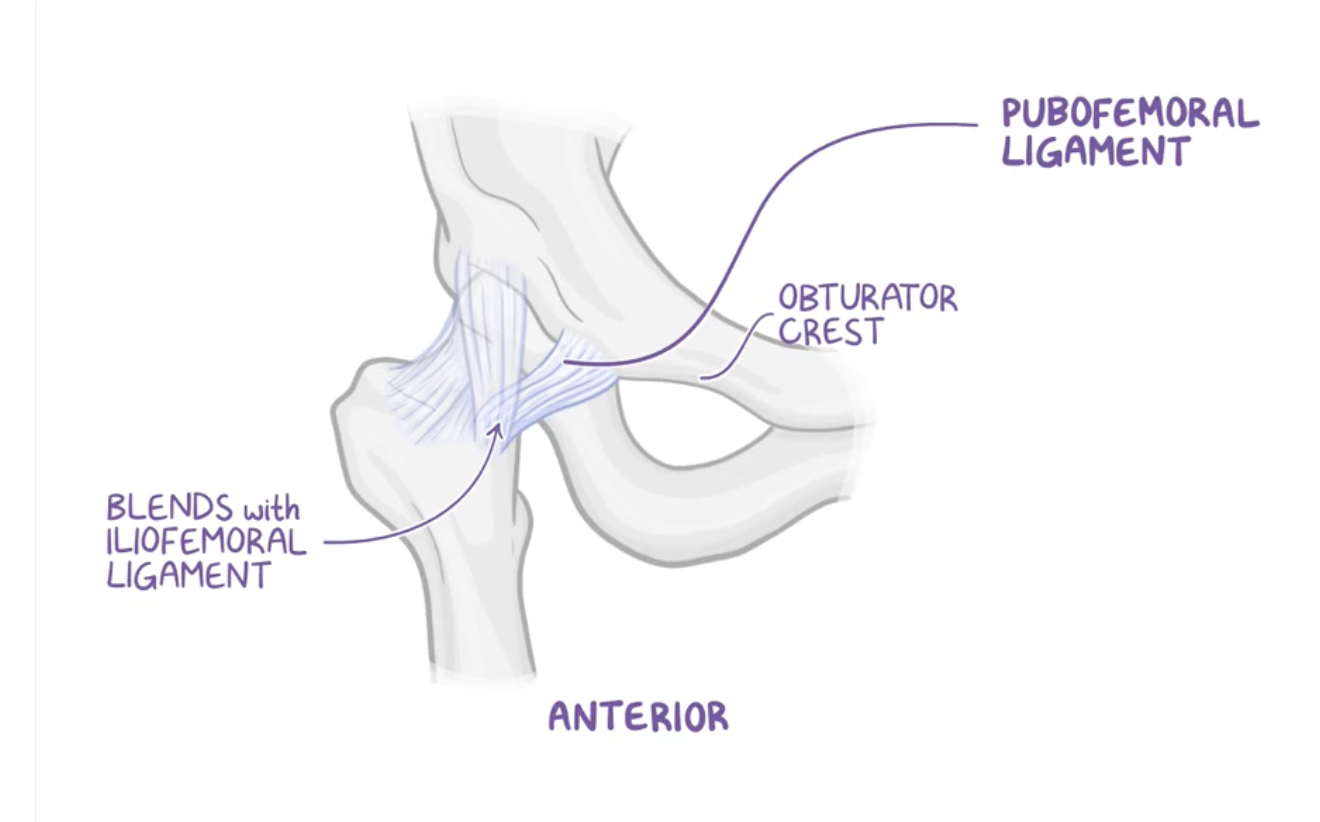
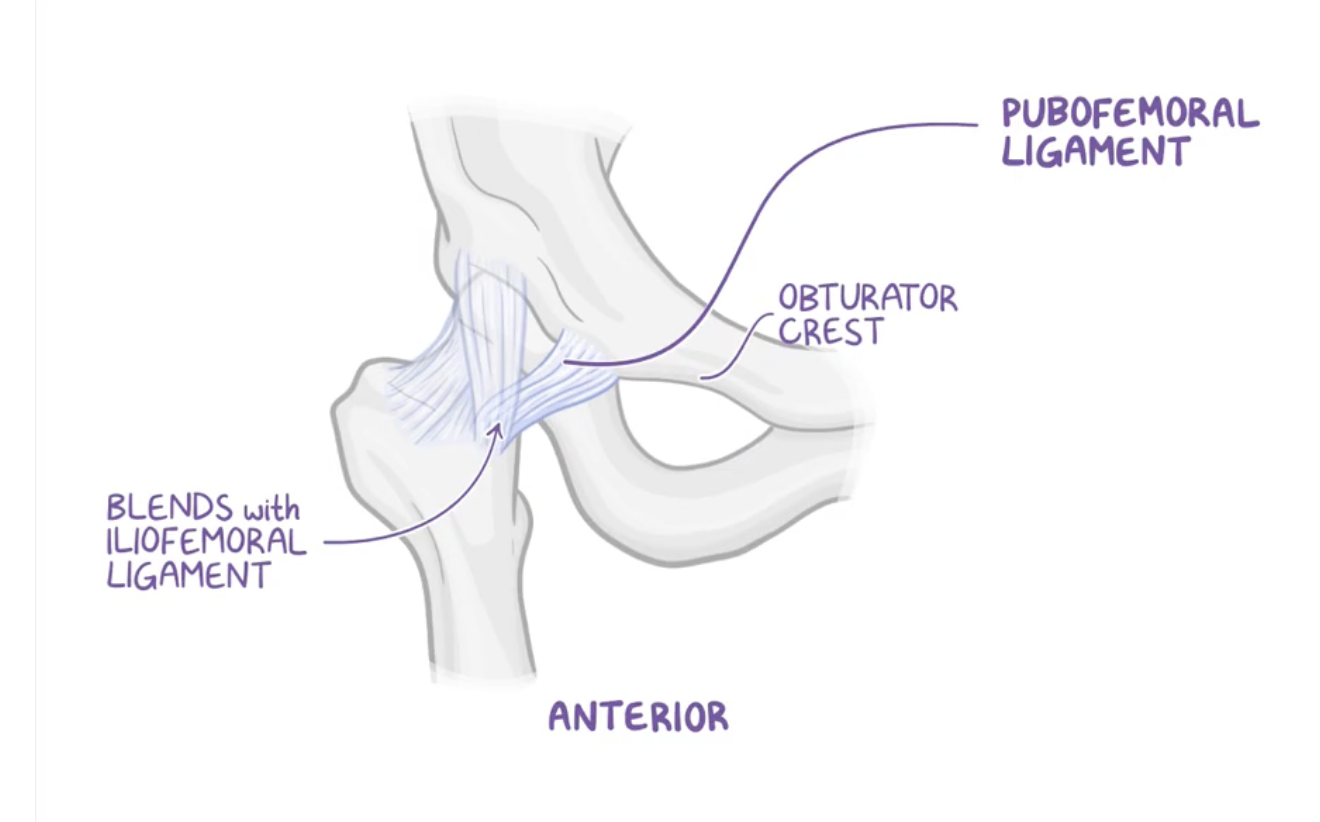
Pubofemoral ligament (anterior)
Origin: pectineal crest and pectineal pubis
Insertion: intertrochanteric line
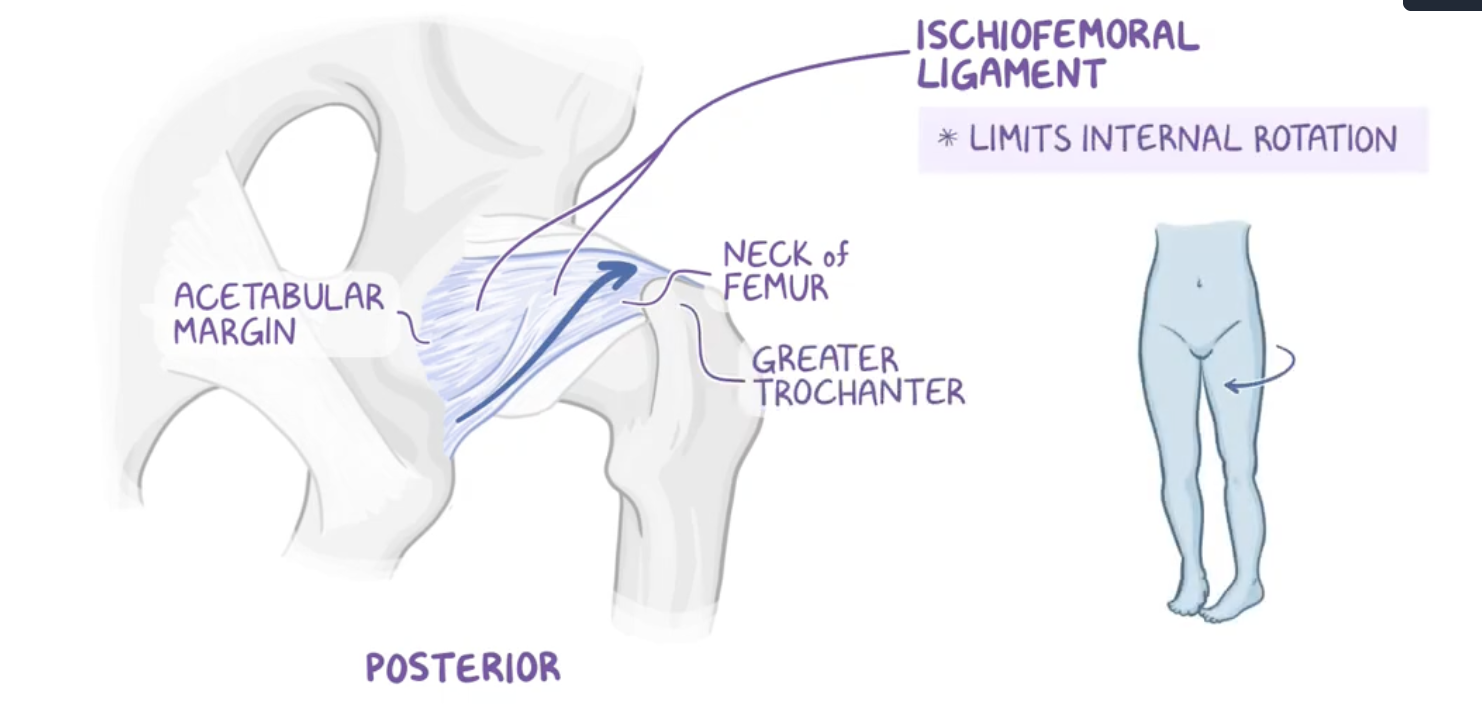
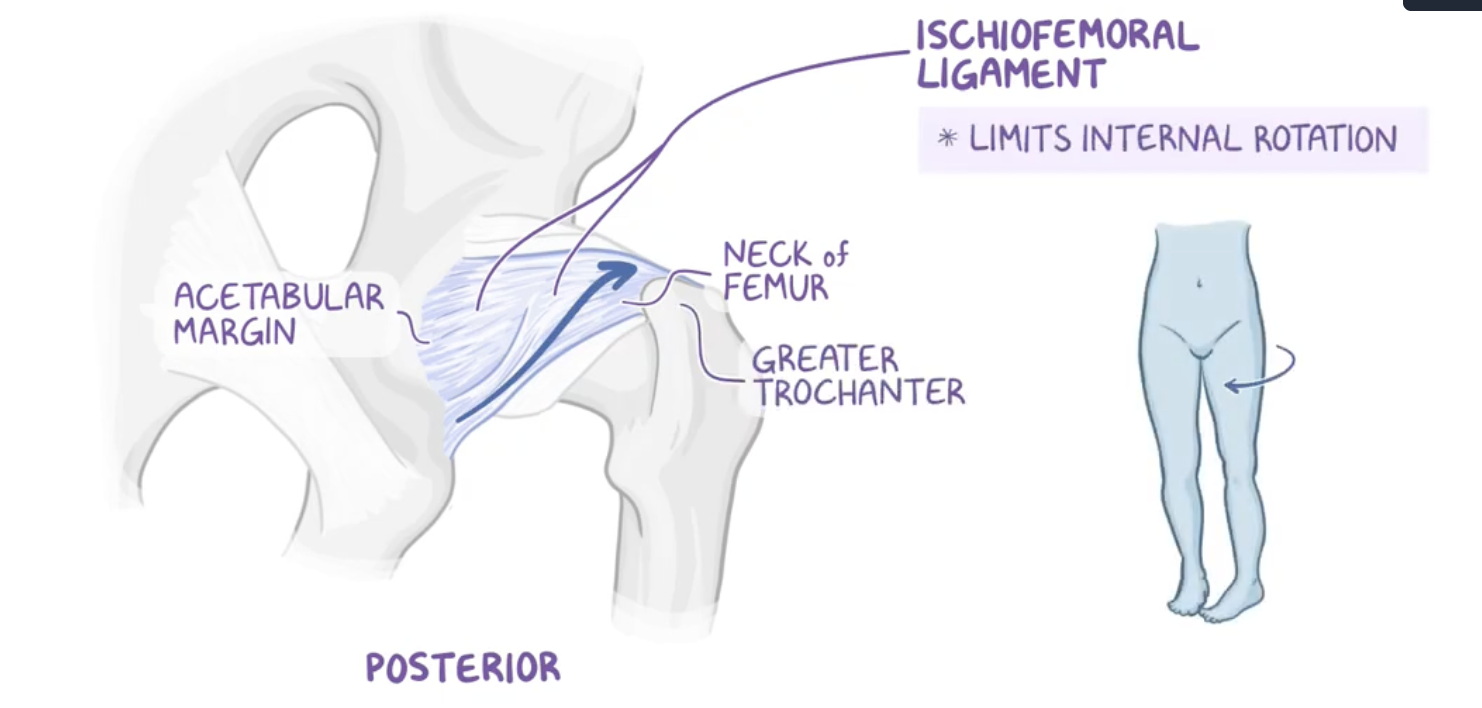
Ischiofemoral ligament (posterior)
Origin : ischium
Insertion : intertrochanteric line (not crest)
limits internal rotation
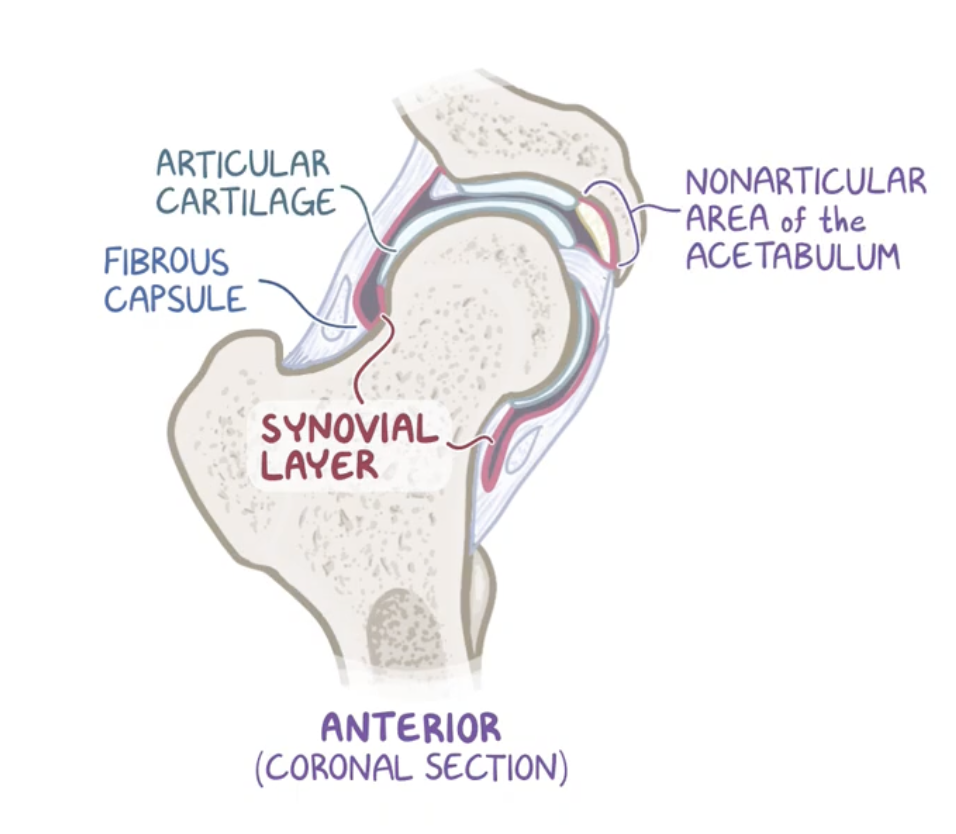
Synovial layer
Covers the ligementum teres (ligament of the head of the femur) and acetabular fossa producing synovial fluid to lubricate the joint.
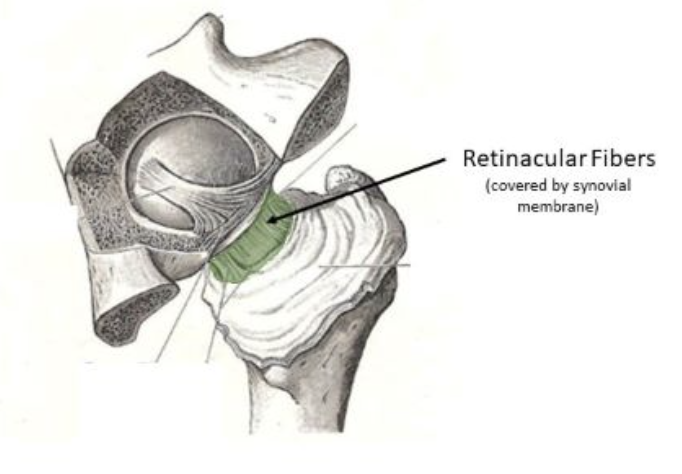
Retinacula of the synovial membrane
Vascular plexus for the femoral head
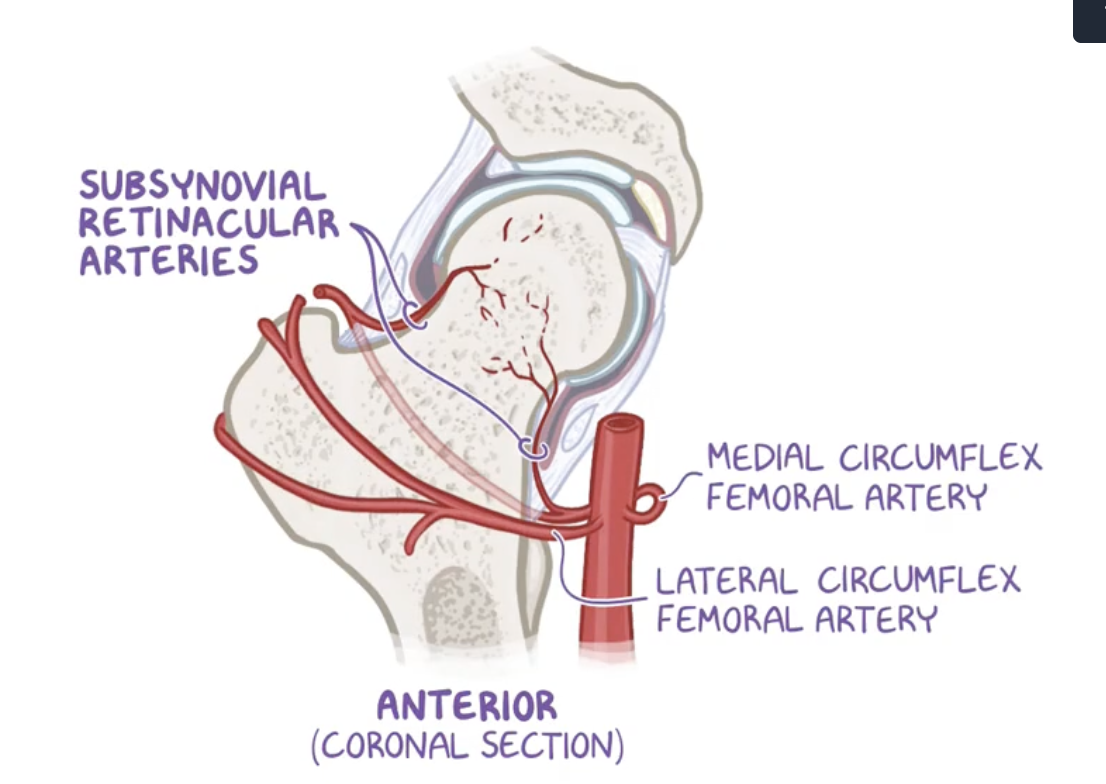
Intracapsular ligaments
Transverse acetabular ligament
Ligamentum teres
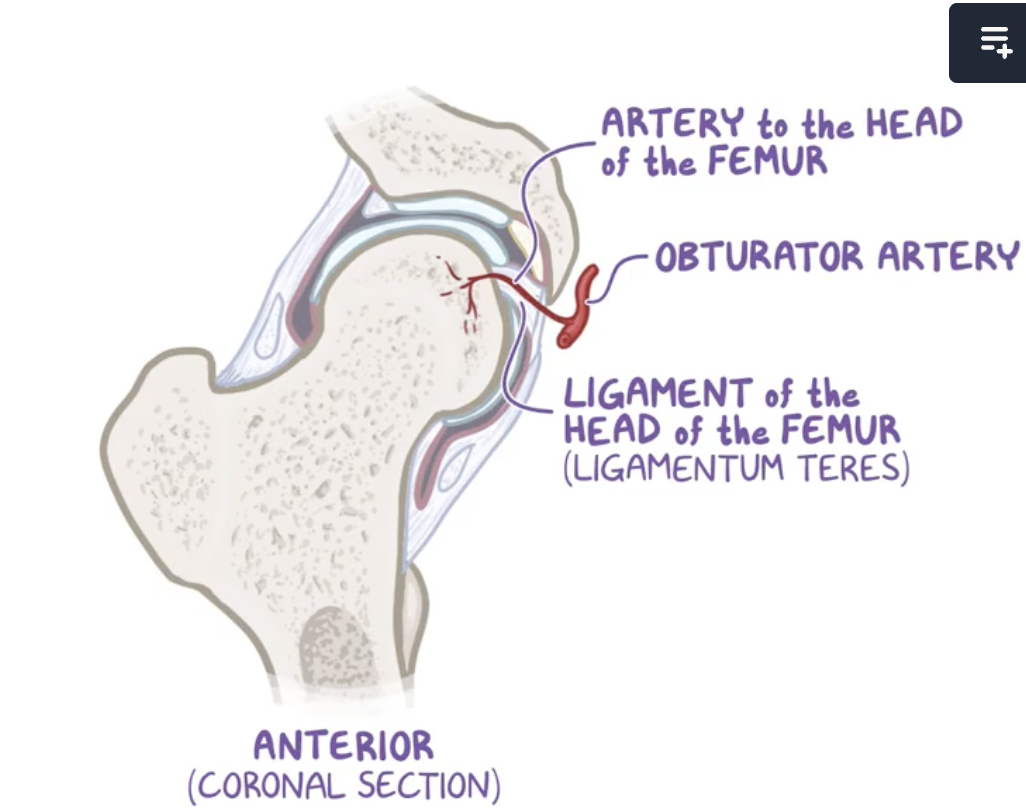
Ligamentum teres
ligament of the head of the femur, which houses the artery to the head of the femur, a branch of the obturator artery.
Origin: margins of the acetabular notch along with the transverse acetabular ligament,
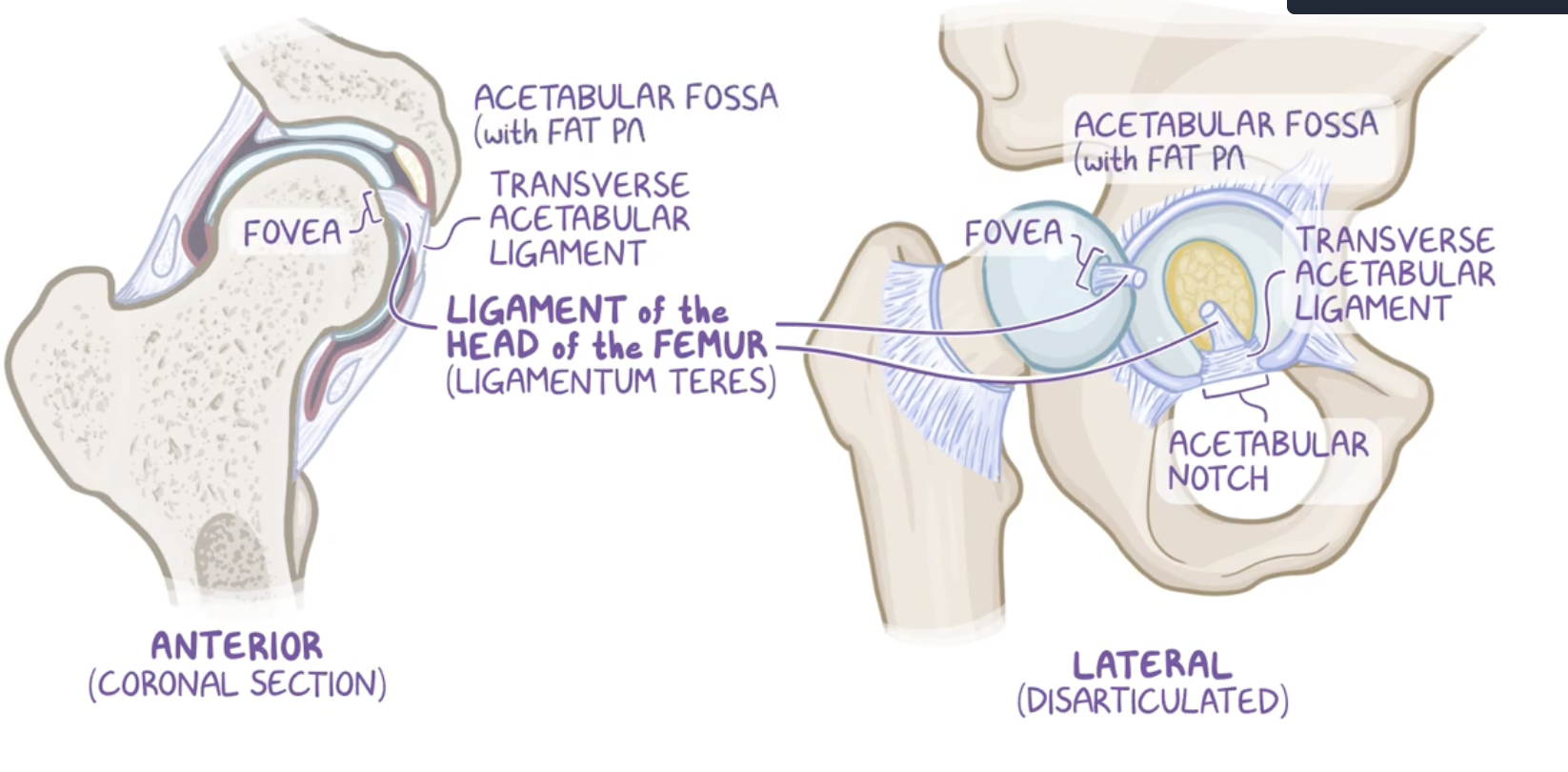
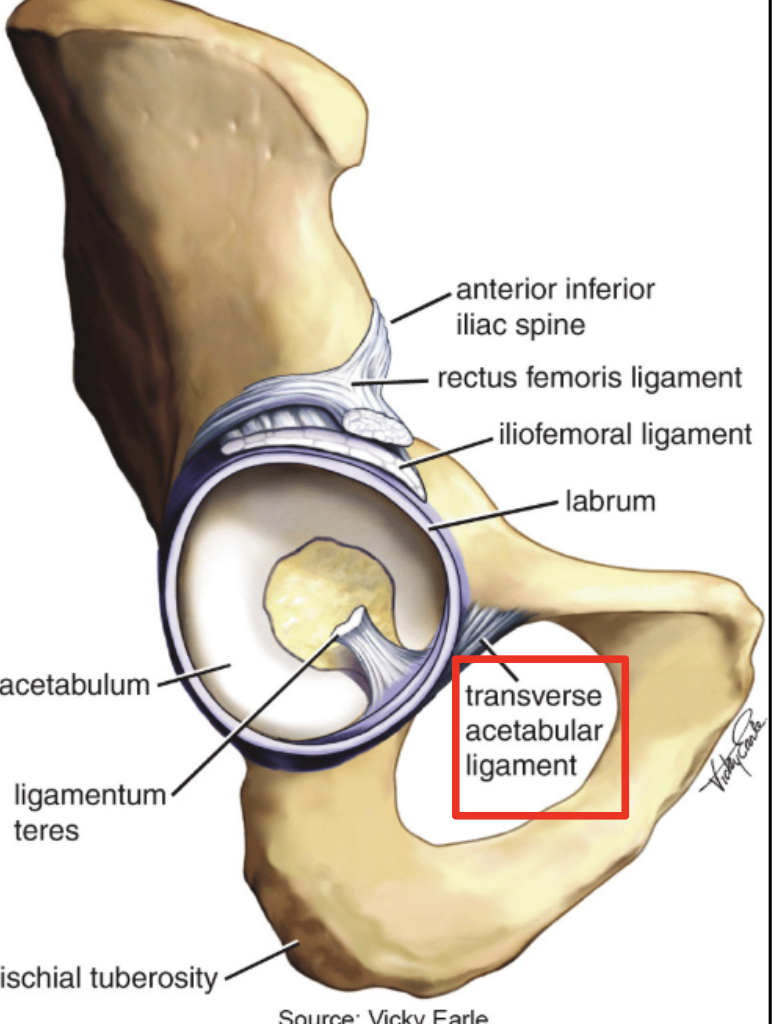
Transverse acetabular ligament
attaches to the edges of the acetabular notch
Movements of the hip
Flexion-extension
abduction-adduction
rotation, medial (internal) and lateral (external)
circumduction (combination of previous movements)

Sacroiliac joint type
synovial type.
primarily responsible for transferring weight and forces between the upper body and lower limbs.
Articular surfaces of the sacrum and ilium
Flat with irregularities
Cartilage is thick
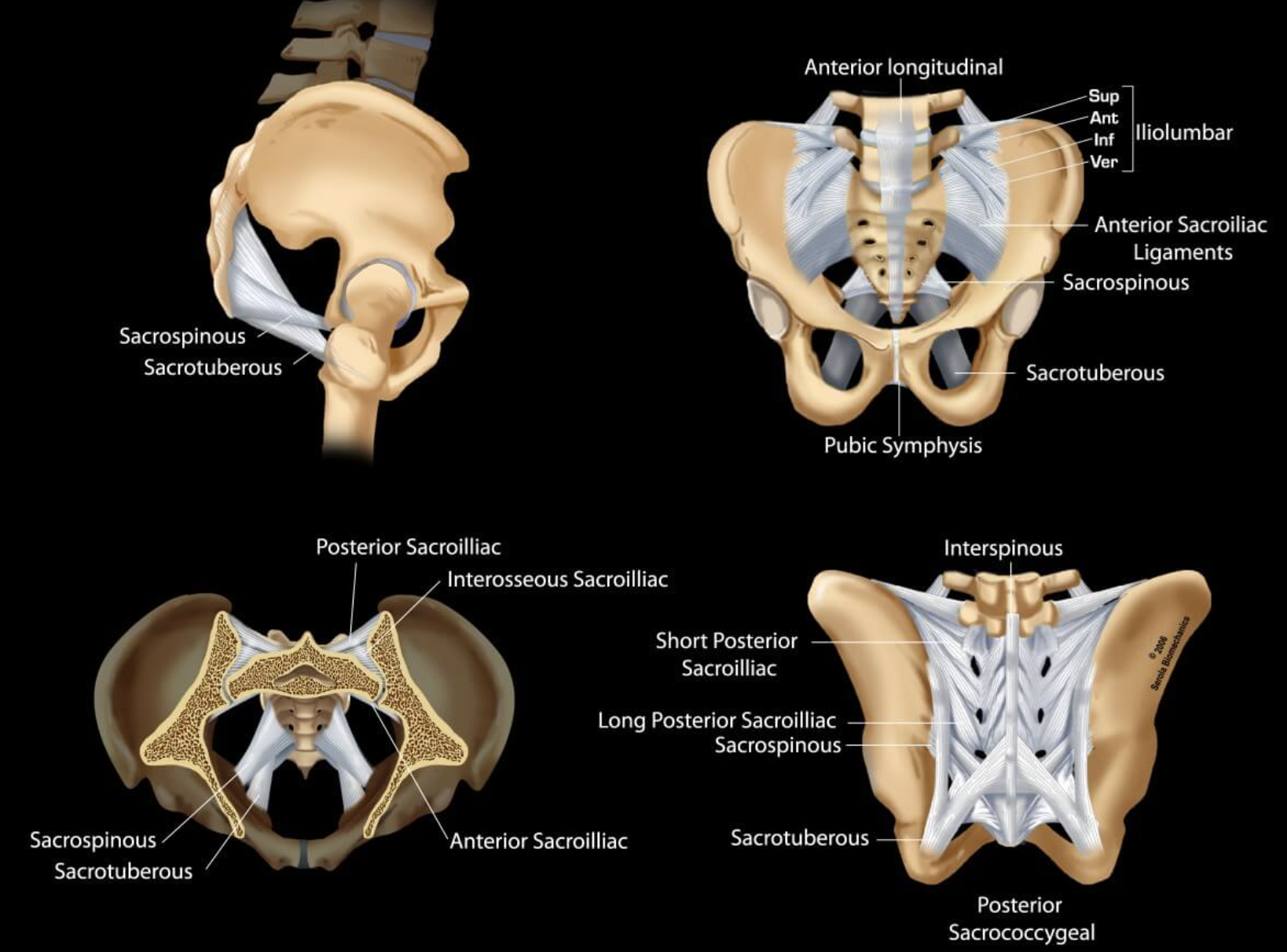
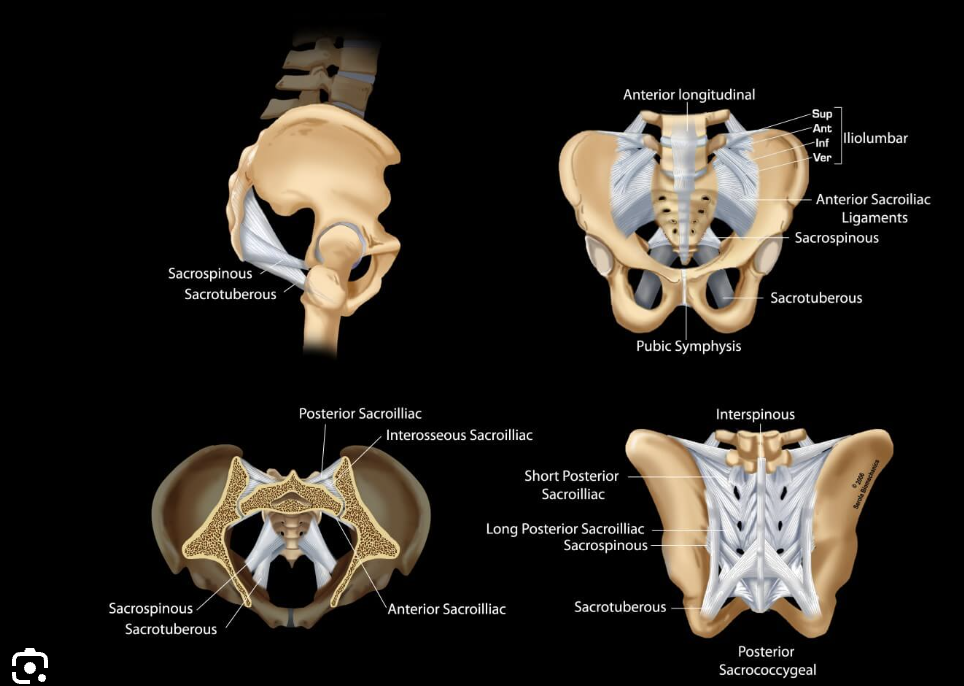
Ligaments of the sacroiliac joint
anterior
interosseous
posterior
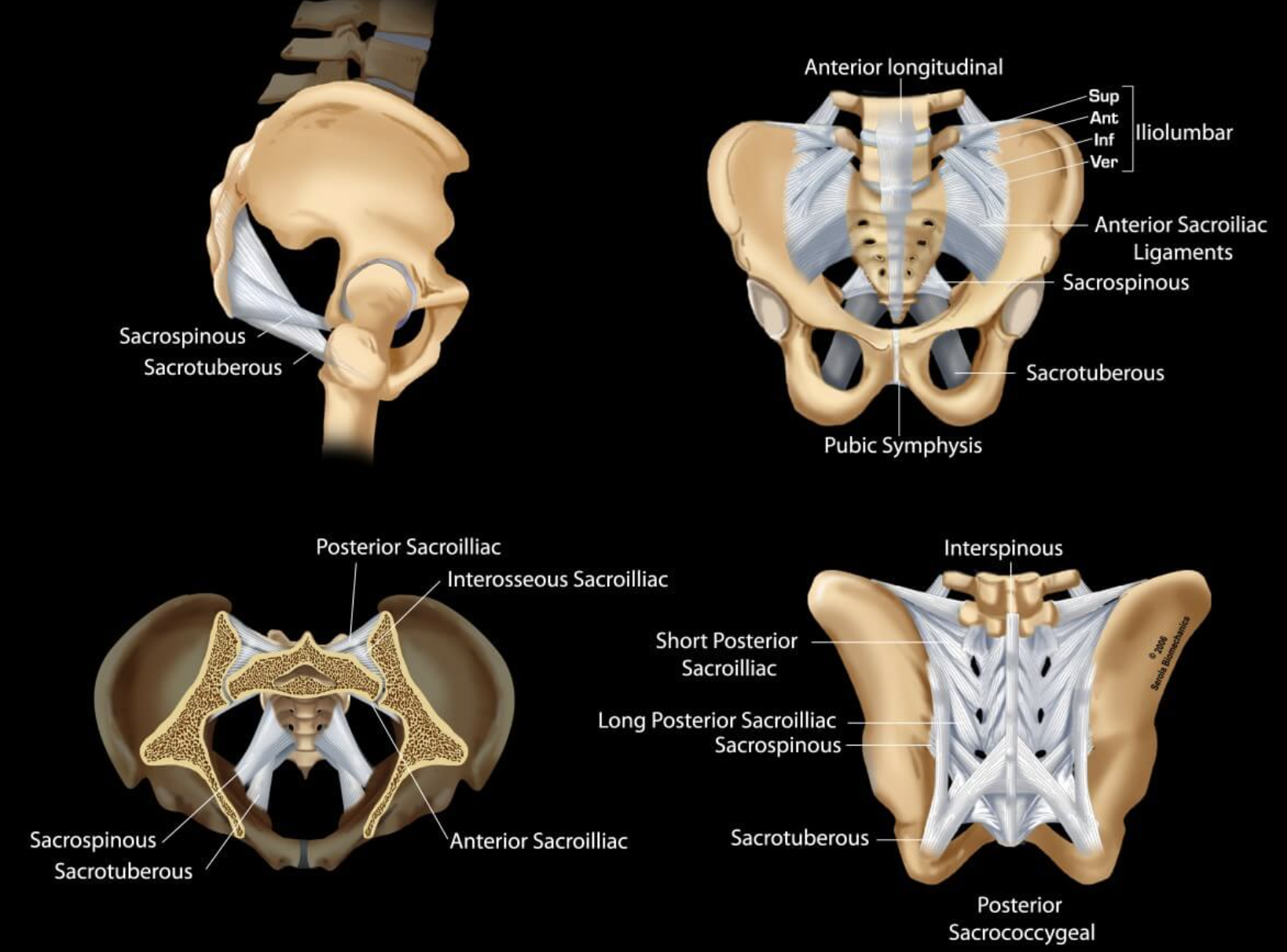
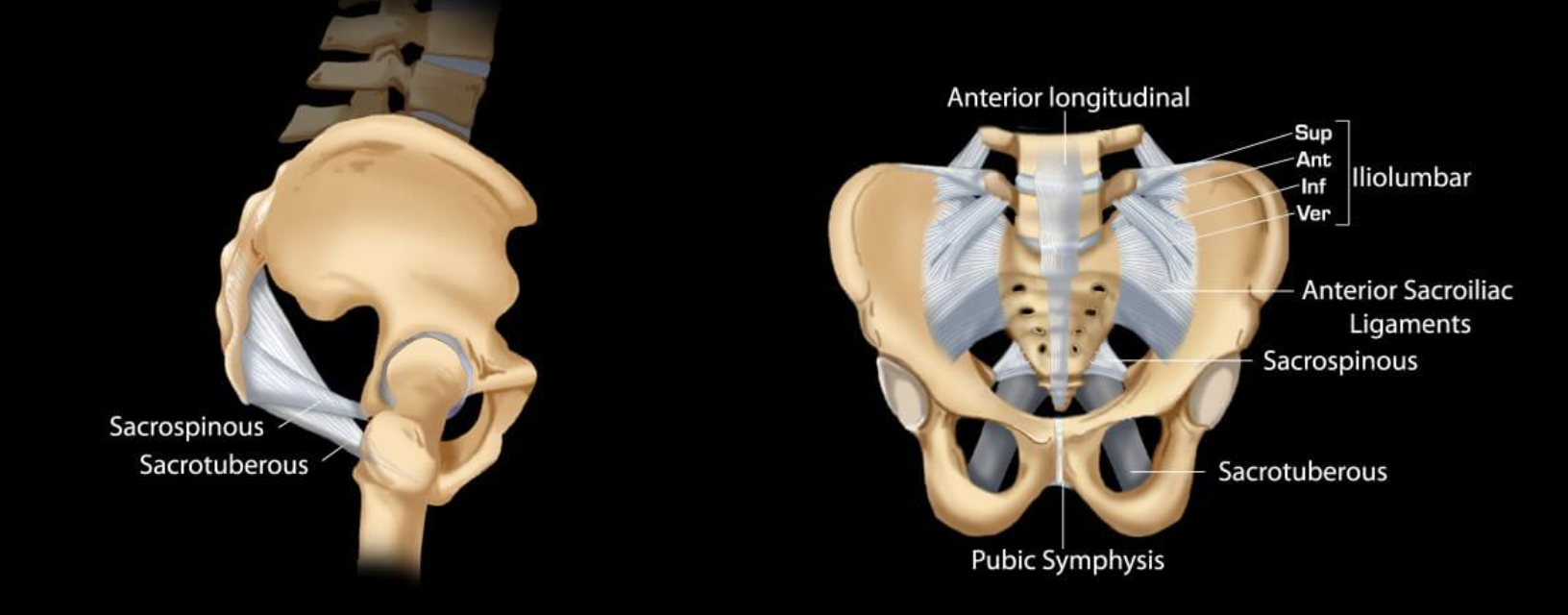
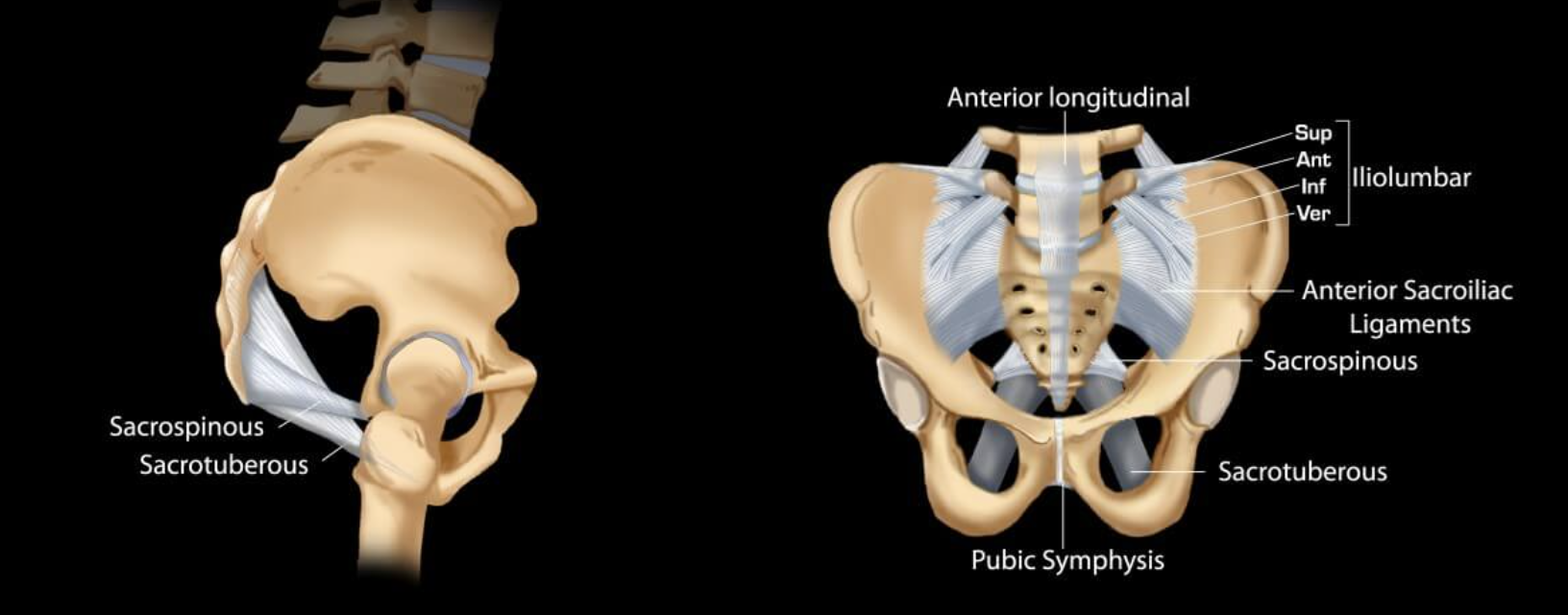
Accesory ligaments of the sacroiliac joints
sacrospinous
sacrotuberous
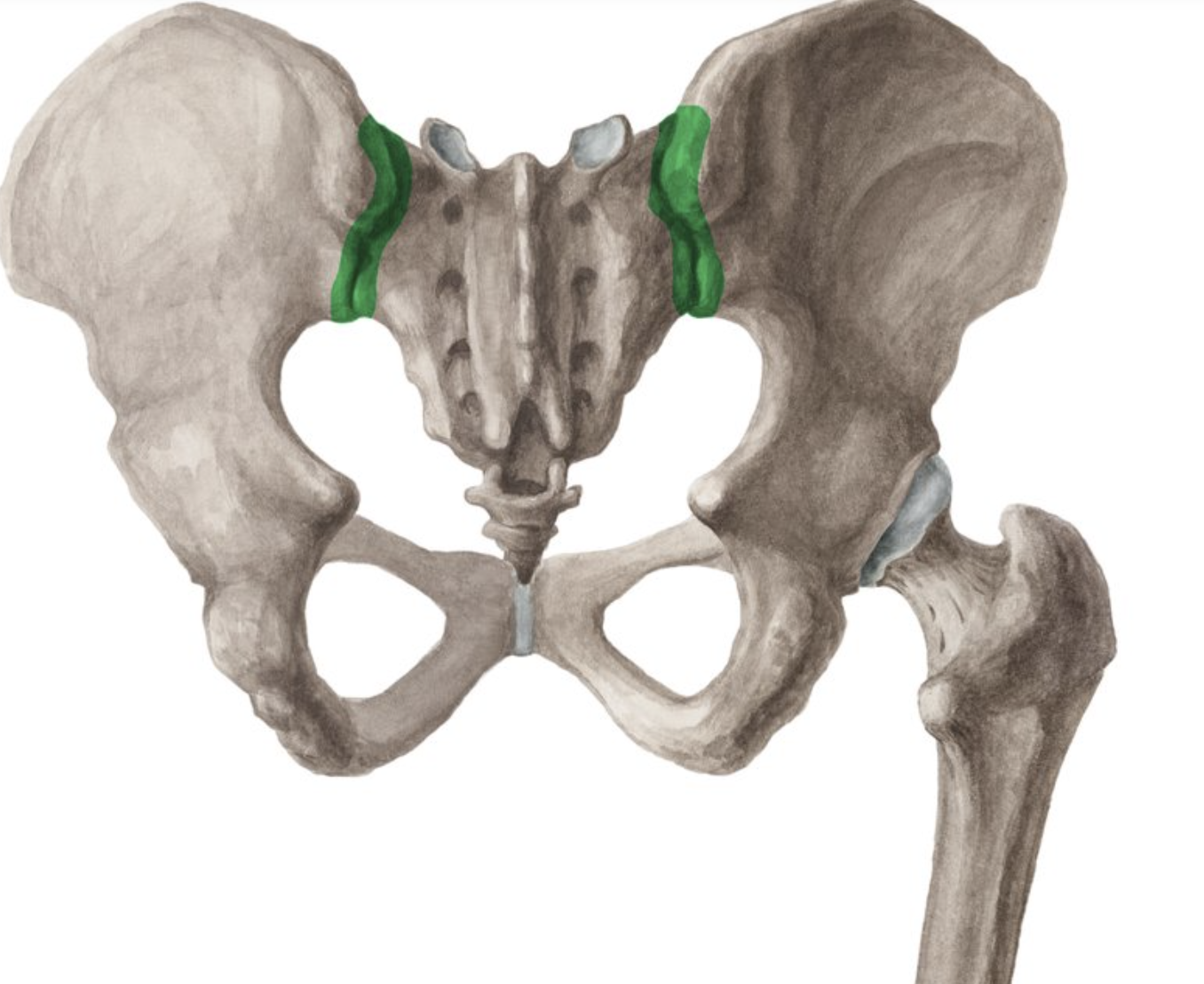
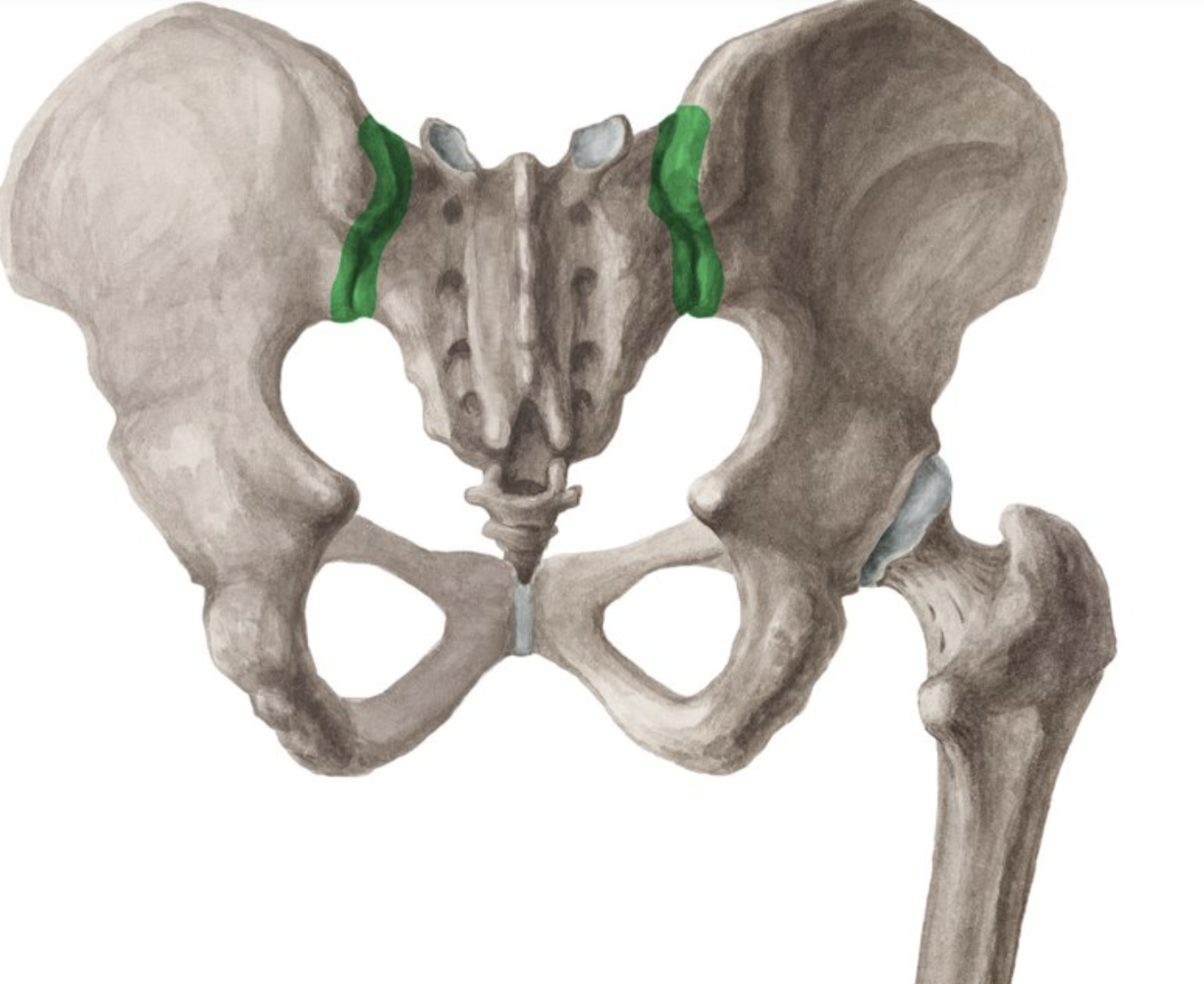
interosseous sacroiliac joint
A type of joint connection between the sacrum and ilium, characterized by strong ligaments that stabilize the pelvis during movement.
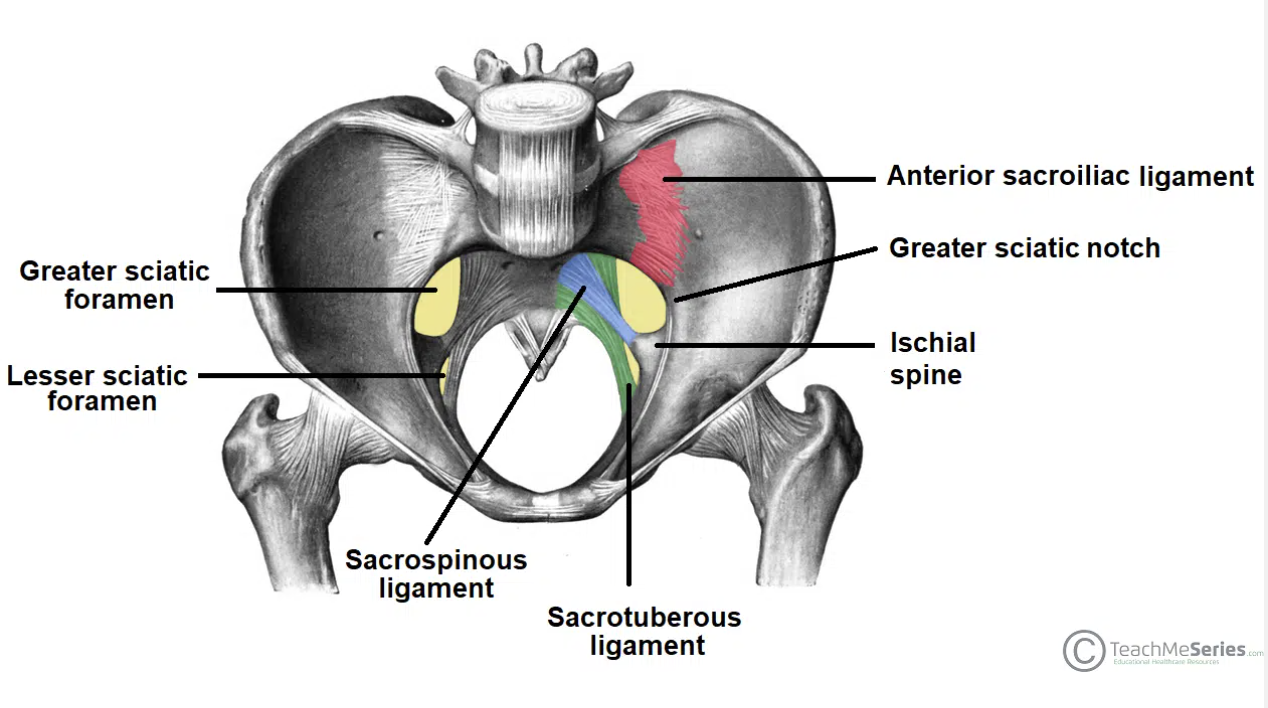
Sciatic foramina
Greater sciatic foramen
Lesser sciatic foramen
Static foramina
The sciatic foramina are two openings in the posterior pelvis that allow important nerves, vessels, and muscles to pass between the pelvis and gluteal region. They are formed by the greater and lesser sciatic notches of the pelvis and the sacrospinous and sacrotuberous ligaments.
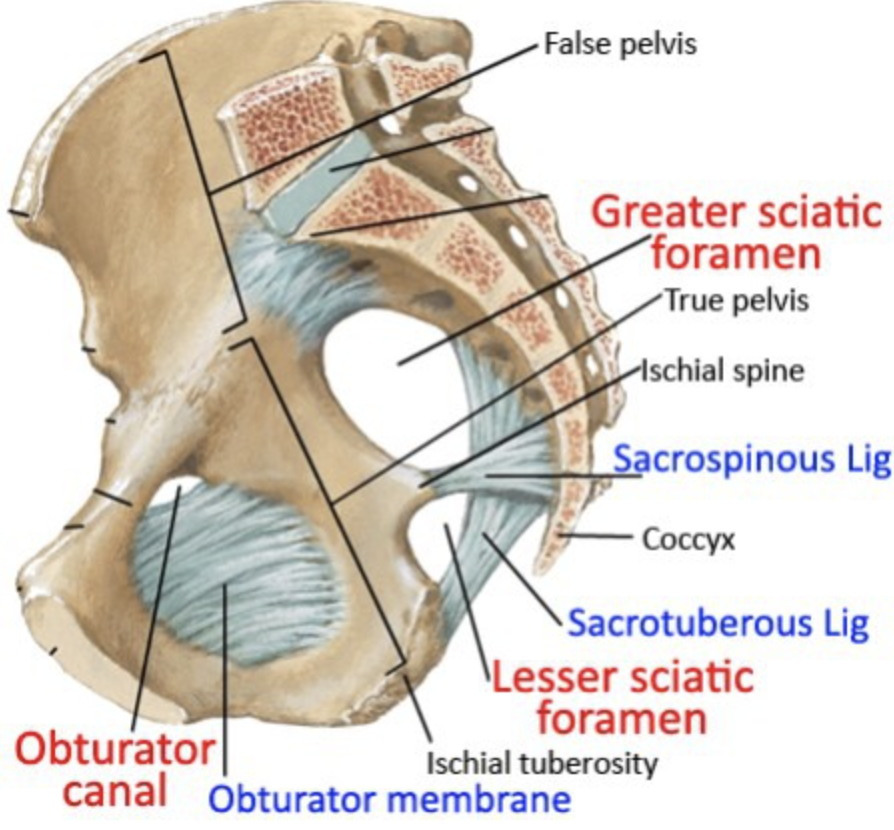
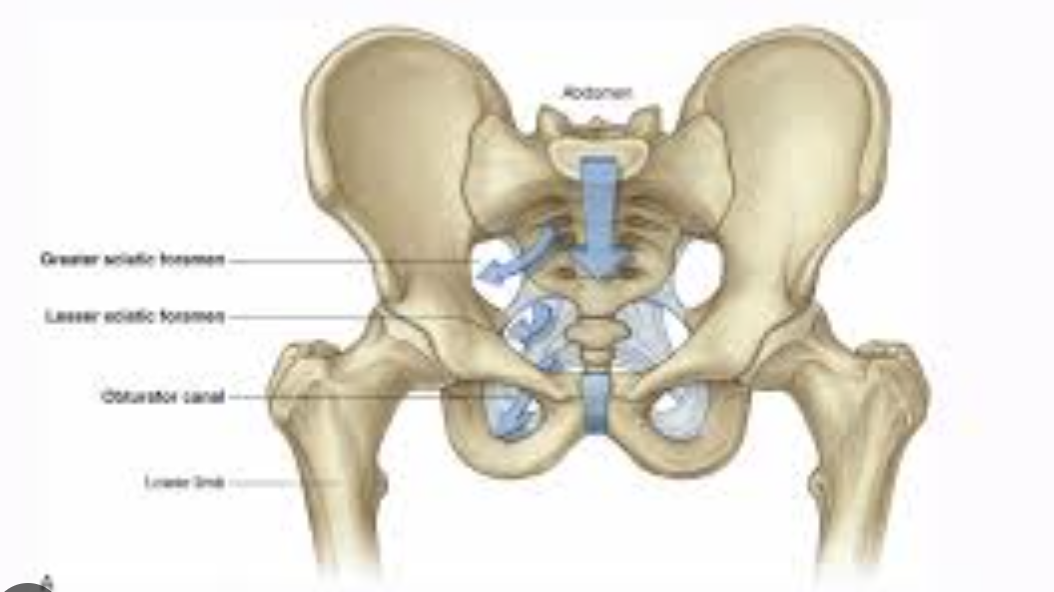
Greater and lesser sciatic foramen
greater: from lesser pelvis to gluteal region
lesser: from perineum to gluteal region
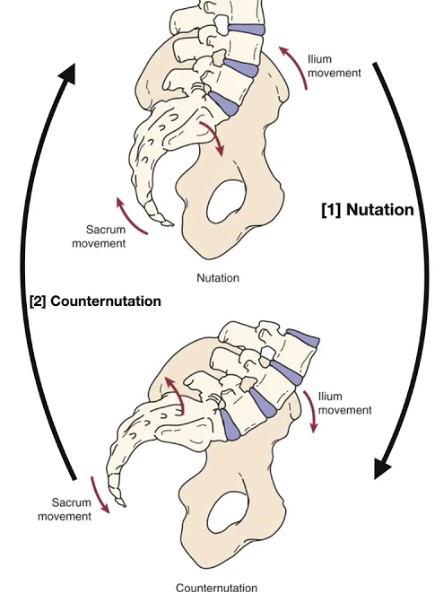
Movements of the pelvis
Important during pregnancy.
Relaxin hormone that helps in pelvic flexibility, relaxing the ligaments
Nutation: standing, the coccyx goes backwards
counter-nutation
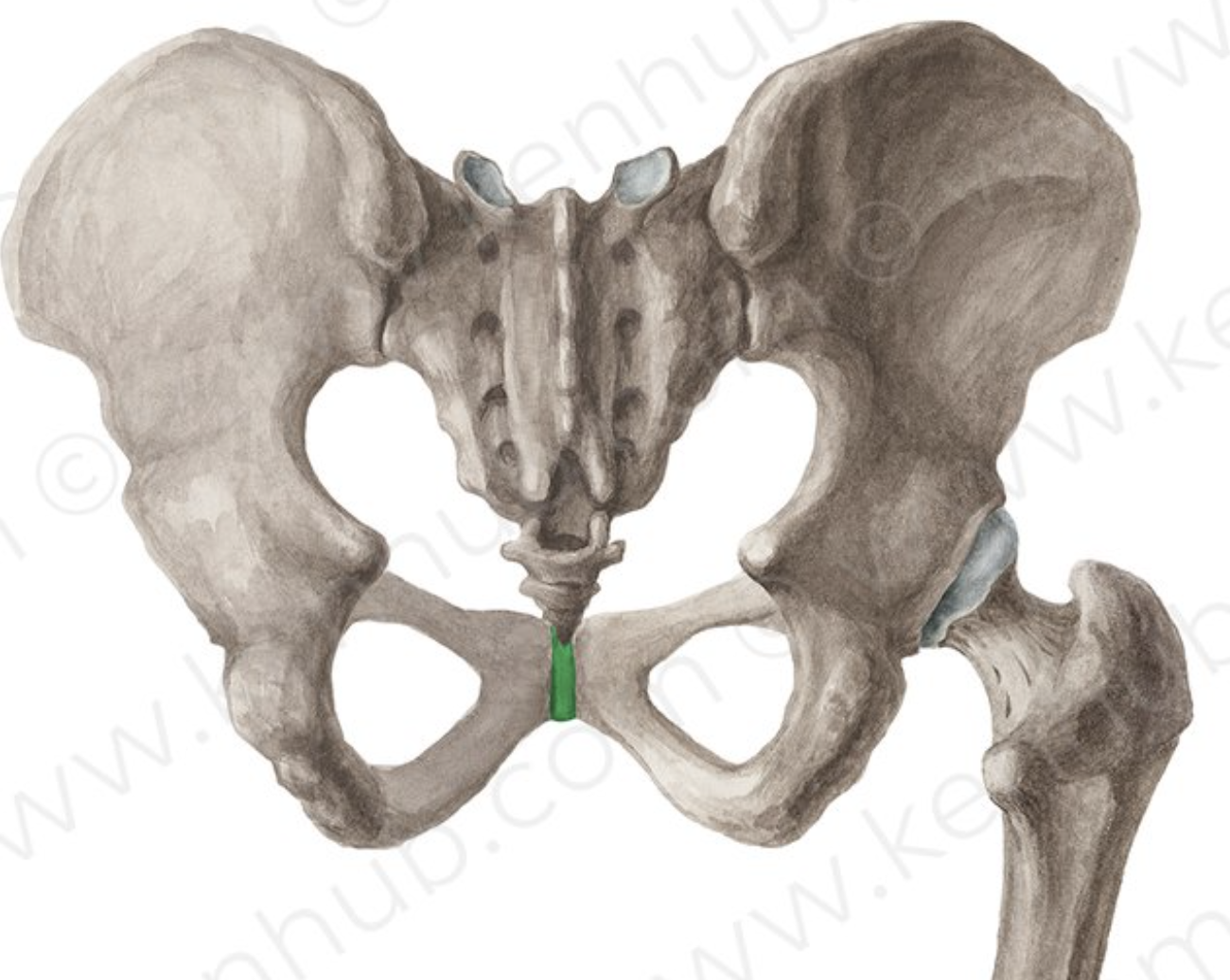
Pubic symphysis
The pubic symphysis is a cartilaginous joint located between the left and right pubic bones in the pelvis, providing slight movement and stability during activities such as walking and childbirth.
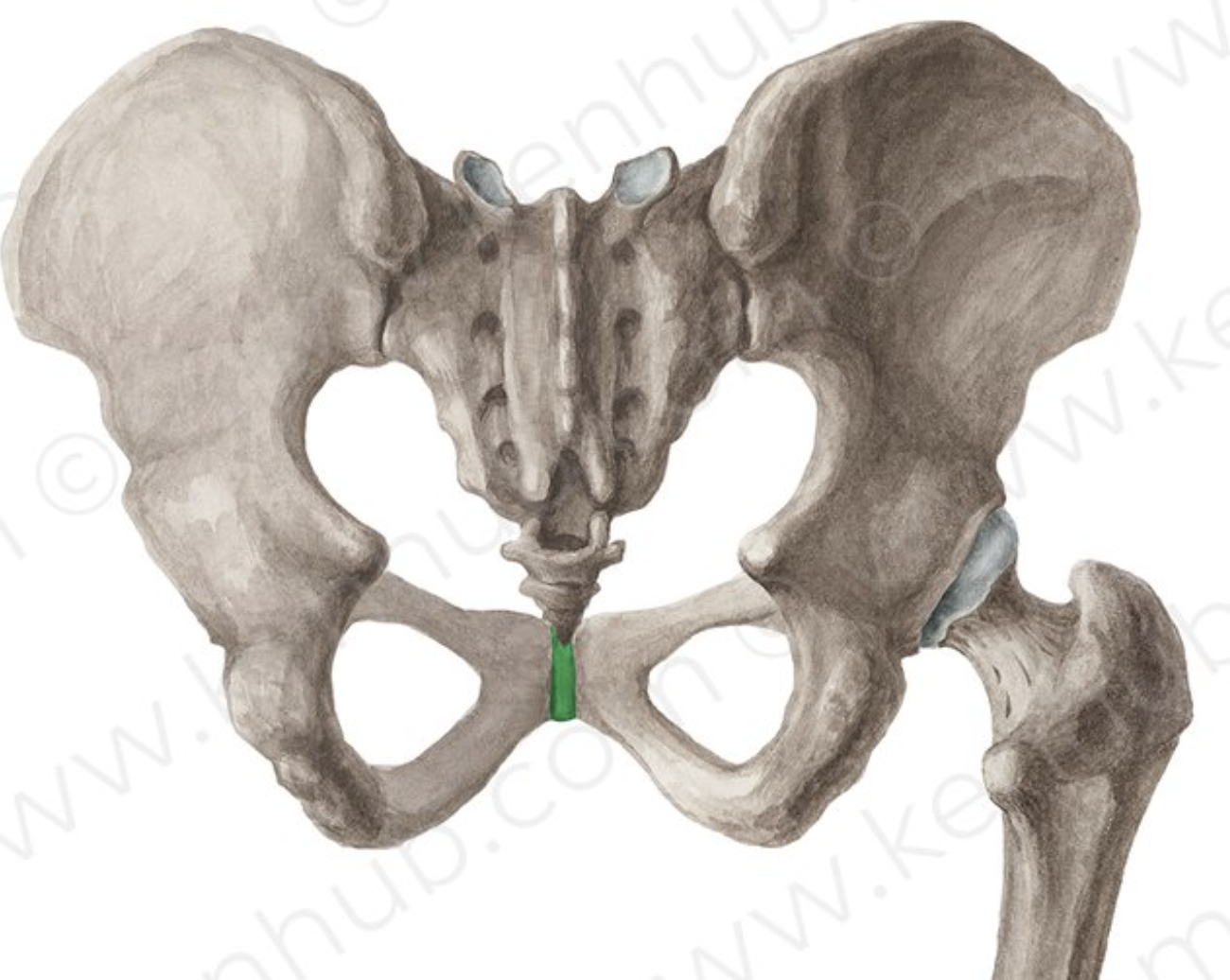
Pubic symphysis articular surfaces
flat but with reciprocal ridges and papillae
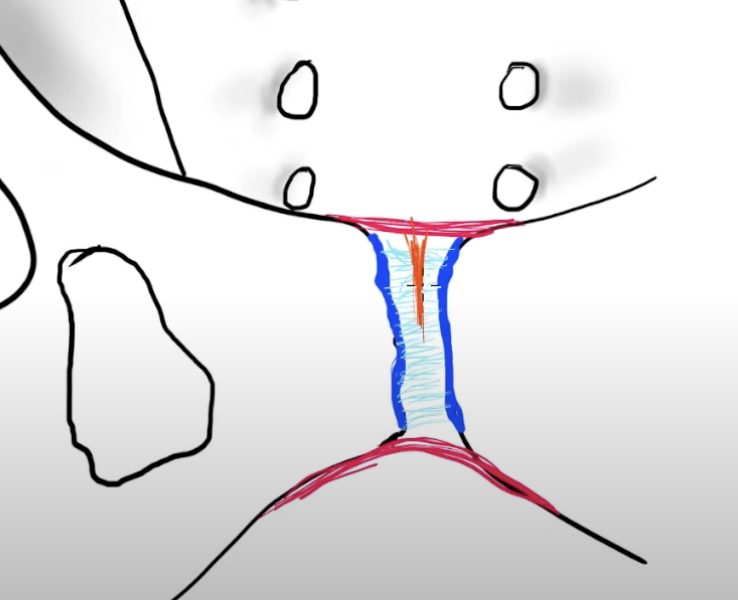
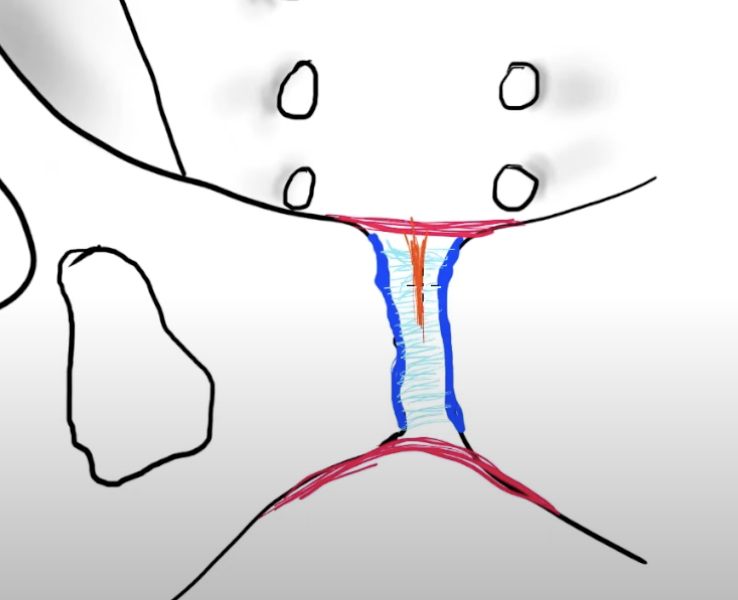
Pubic symphysis
hyalinge cartilage → dark blue
interpubic disc (fibrocartilagenous, shock absorber, not synovial) → light blue
Superior and inferior (arcuate) ligament → red