Earth Science || 1st Semester || Midterms
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
Geosphere
the solid part of the earth consisting of the crust and outer mantle
Atmosphere
A thin layer of gases surrounding Earth
Hydrosphere
All the water on earth
Biosphere
the part of Earth where life exists
Inner core
solid iron and nickel at the center of Earth
Outer core
molten iron and nickel that surrounds the inner core of Earth
Lower Mantle
-soft rocks
-less ductile
-gutenberg discontinuity
Upper Mantle
-solid rocks
-malleable
-mohorovicic discontinuitty
asthenosphere
"weak sphere" is the soft layer of the mantle on which the tectonic plates move
lithosphere
the rigid outer part of the earth, consisting of the crust and upper mantle.
oceanic crust
earths crust located under the ocean
continental crust
A solid, thin outermost layer of Earth
age of star
star must be at least 3 Ga to give life an ample time to evolve
Stable planetary habitable zone
"Goldilocks zone" shell-shaped region of space surrounding a star where the temperature is just right
High metallicity
presence of heavier elements (heavier than H & He)
Low stellary variation
fluctuation in the star's luminosity
Distance from a star
planet must be in a comfortable distance from a star
Terrestrial
planet must be large enough to retain the atmosphere and have a molten core
Orbital eccentricity
elliptical orbit
Axial tilt
the angle at which a planet's axis tilts (23.5 degrees)
Rotation
The spinning of Earth on its axis
Geochemistry
planet should have elements most vital to life
Pangea
term for the super continent which contained all the plates together
Troposphere
clouds
Stratosphere
ozone layer
Mesosphere
meteoroid
Thermosphere
aurora
ionosphere
highly ionized gas
exosphere
outermost layer fo the earth's atmosphere
ecosysytem
biotic and abiotic enviroment
Biomes
large ecosystems classified according to the vegetations
Aquatic biome
includes freshwater and marine biomes
Forest biome
tropical, temperate and boreal (taiga)
Grassland biome
dominance of grass
Desert biome
low rainfall
tundra biome
coldest biome
Grassland biome
dominance of grass
Biomes
radioactive decay
unstable atoms emit energetic particles and gamma rays that heat the surrounding rock
planetary differentiation
more dense materials of a planet sink to the center, while less dense materials stay on the surface.
Geologist
a scientist who studies the earth
Petrology
study of rocks
Stratigraphy
the study of rock layers and the sequence of events they reflect
Paleontology
the study of fossils
Igneous Rocks
rocks formed by the cooling of molten rock (either magma or lava)
Sedimentary Rocks
rock that forms when sediments such as muds, sands, or gravels are compressed by overlying sediments
Metamorphic Rocks
forms when other rocks are heated and squeezed together; requires heat and pressure
Relative Dating
places rocks in their chronological sequence or order of occurence without knowing their actual age
Principle of Original Horizontality
layers of sediment are generally deposited in a horizontal position
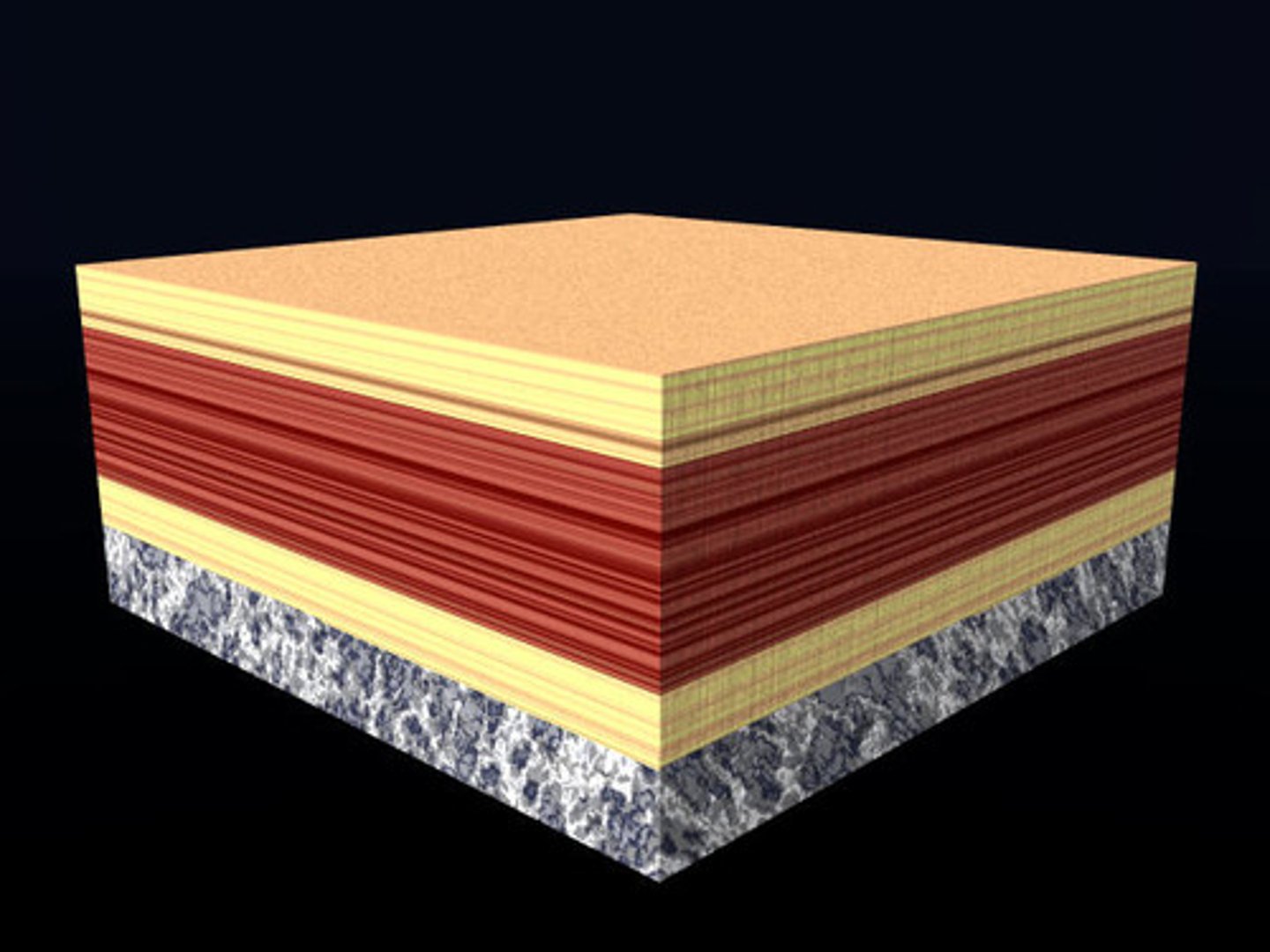
Principle of Superposition
states that in undisturbed rock layers, the oldest rocks are on the bottom and the rocks become progressively younger toward the top

Principle of cross cutting relationship
younger features cut across older features
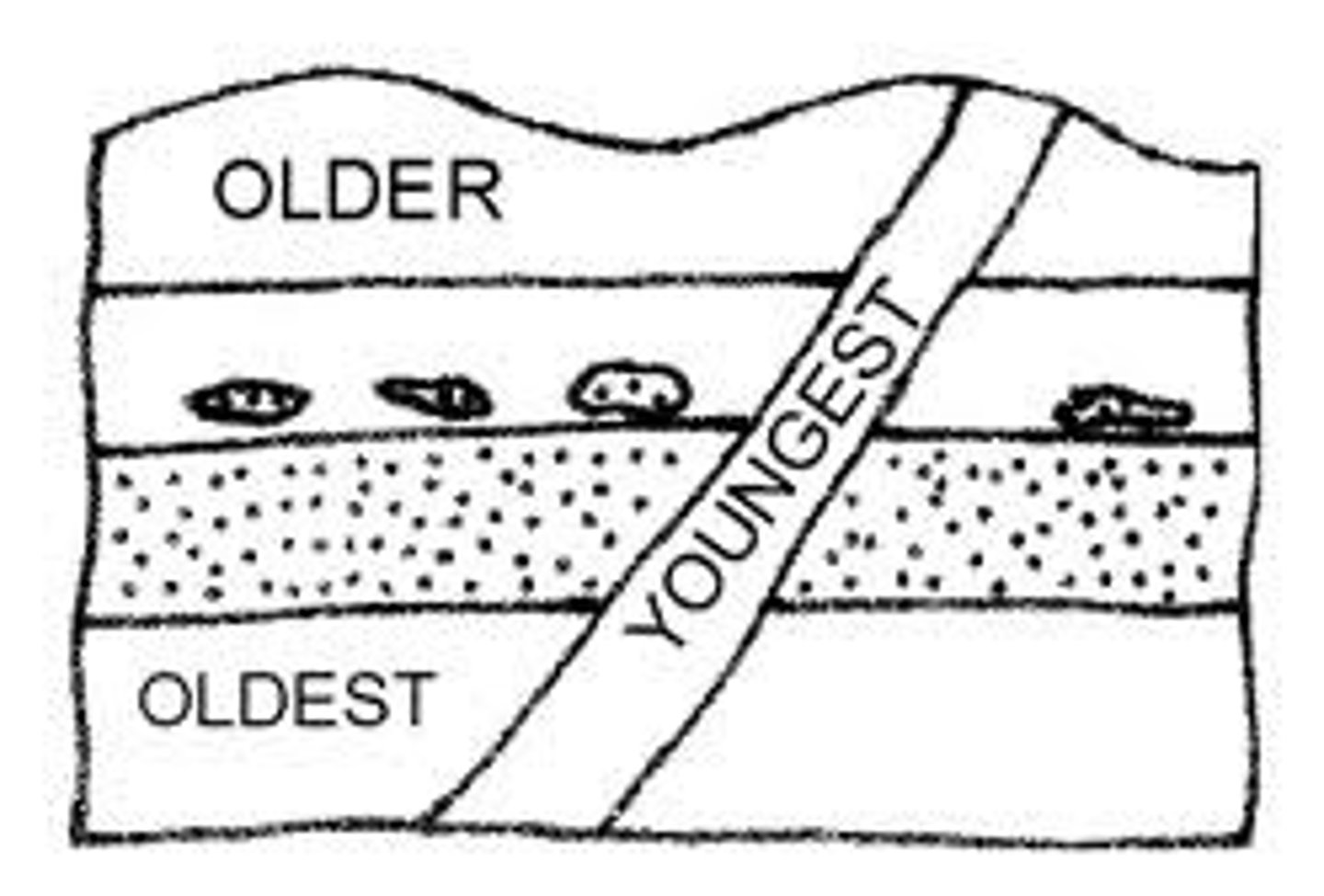
Principle of inclusion
rock bodies are younger than inclusions within them

Unconformity
corresponds with a gap in sedimentation resulting from nondeposition or erosion
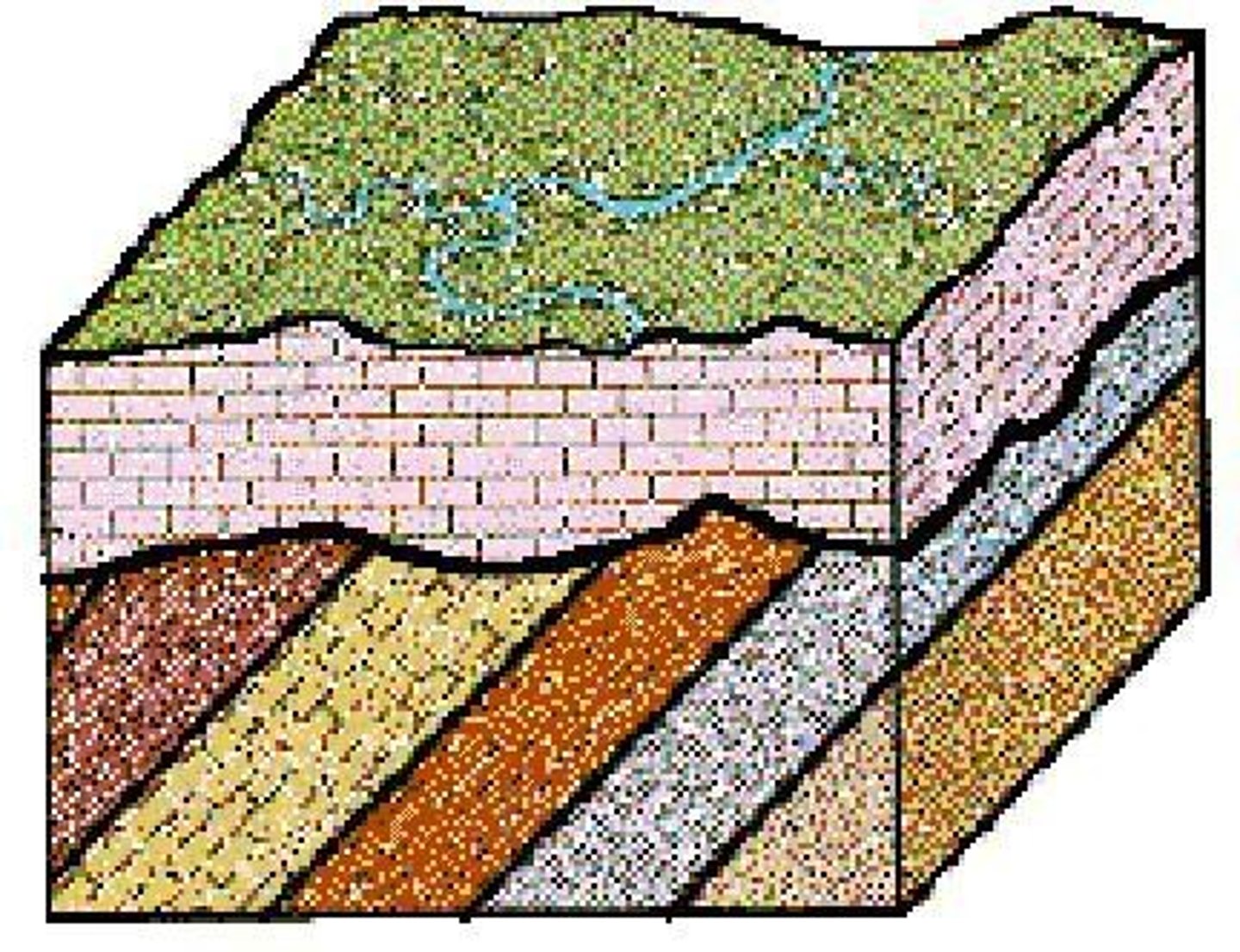
Angular unconformity
tilted rocks are overlain by flat-lying rocks
Disconformity
beds above and below are parallel
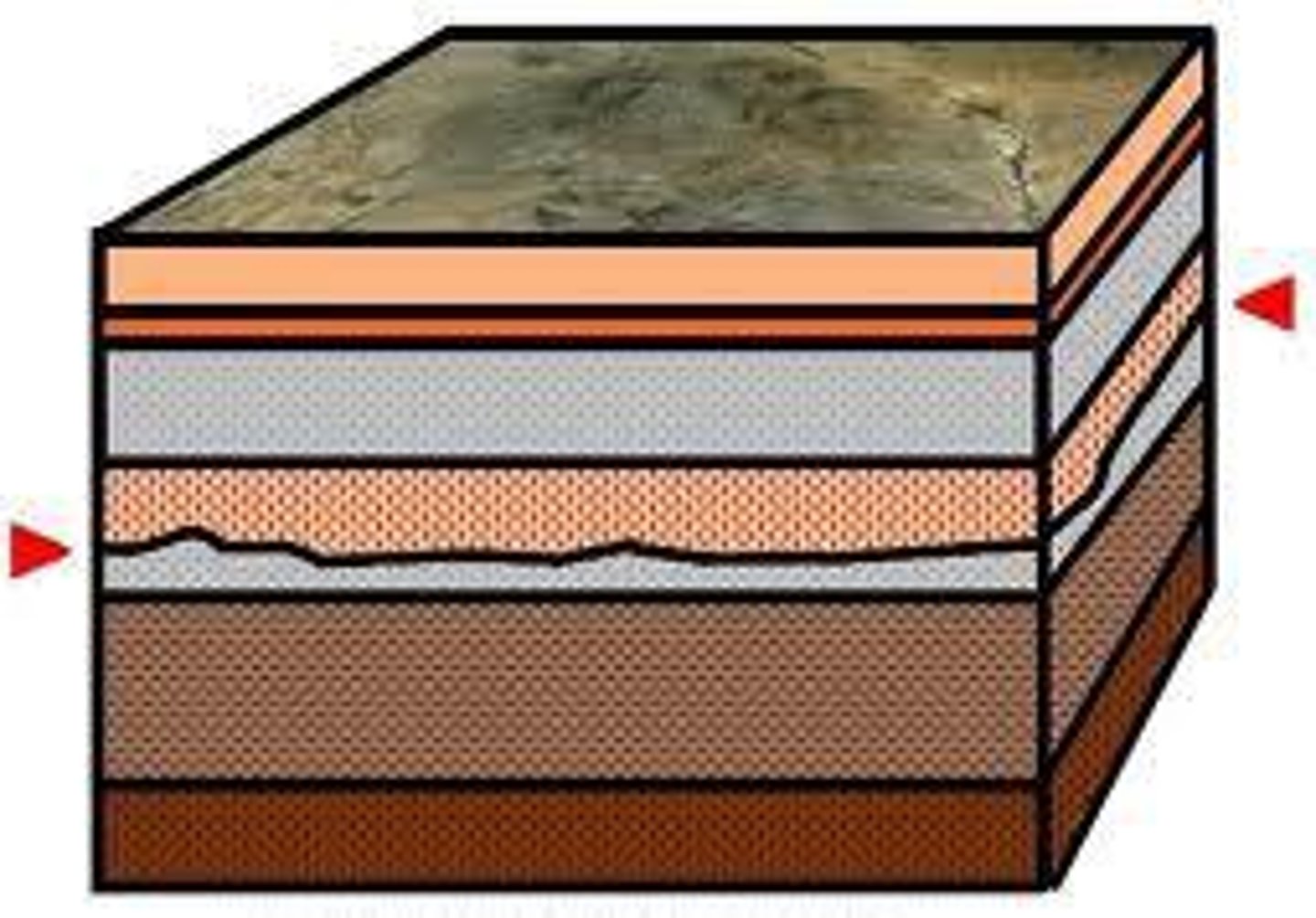
Nonconformity
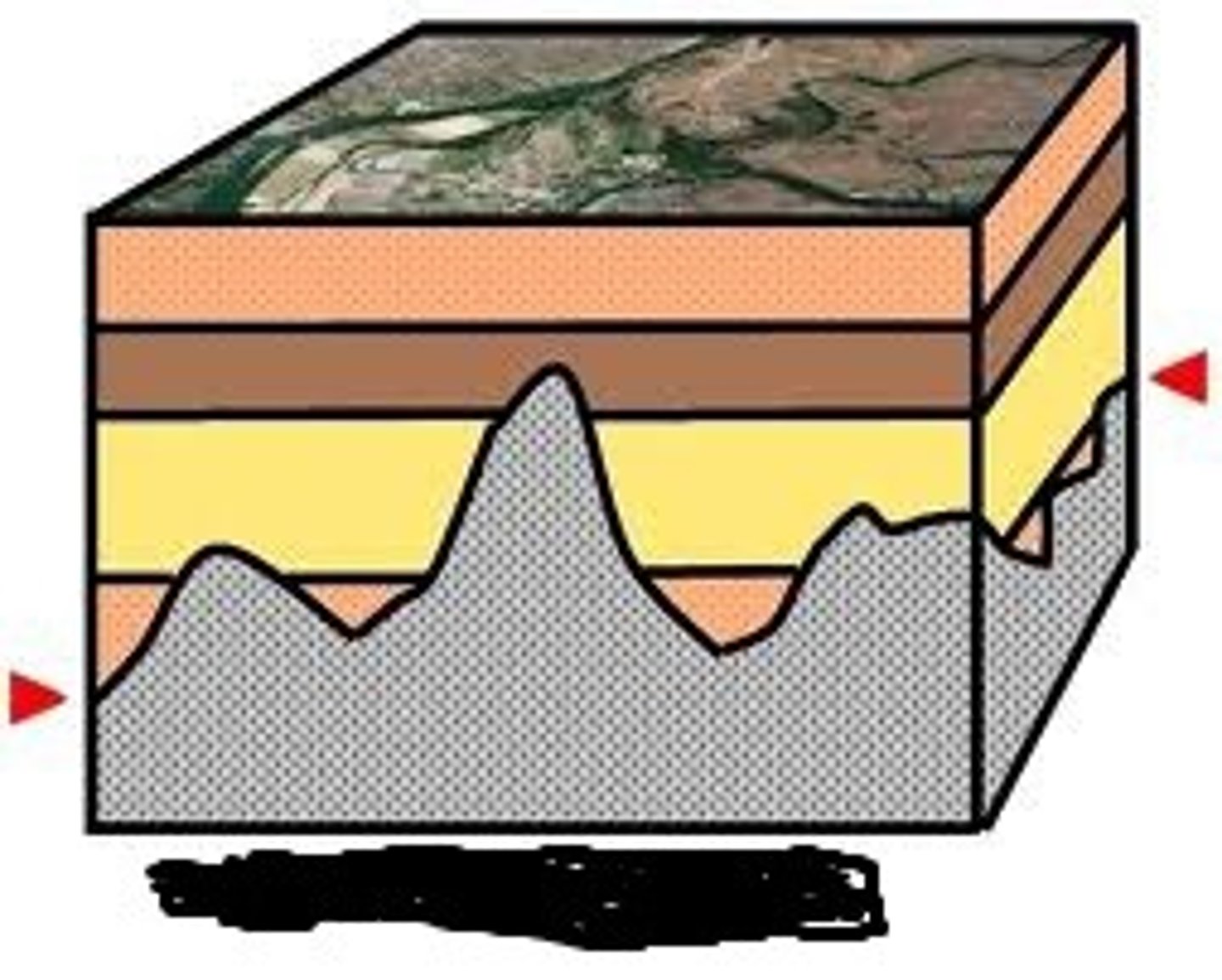
Absolute Dating
places the actual ages of rocks
radiometric dating technique
process that gives numeric date when an event occured
Half Life
time for the nucleus of the atom of a redioactive element to decay
decay rate
described in terms of half life
isotopes
atoms that has the same number of protons and but different number of electrons
Carbon 14
used to measure the age of prehistory plants and animals
age
millions of years
epoch
tens of millions of years
period
one hundred million years
era
several hundred million years
eon
half a billion years or more
Precambrian
the oldest and longest span of geologic time
Hadean Eon
Earth's first eon with hellish conditions
Archean Eon
oldest fossil (apex chert and stromatolites)
Proterozoic Eon
fossil of a bacteria and b-g algae
Cambrian Period
marine shelled invertebrates
Ordovician Period
first vertebrates
Silurian Period
first land plants
Devonian Period
first amphibians and forest
Carboniferous Period
large nonflowering plants and amphibians
Permian Period
reptiles became dominant
Triassic Period
first dinosaur appeared
Jurassic Period
age of dinosaurs
Cretaceous Period
first mammals and extinction of dinosaurs
Paleocene Epoch
first primates evolved
Eocene Epoch
primitive horse branced out
Oligocene Epoch
apes, primates, and elephants became dominant
Miocene Epoch
grasses became abundant
Pliocene Epoch
flowering plants became abundant
Pleistocene Epoch
rise of man and mammals
Holocene Epoch
man and vegetation flourished (current era)
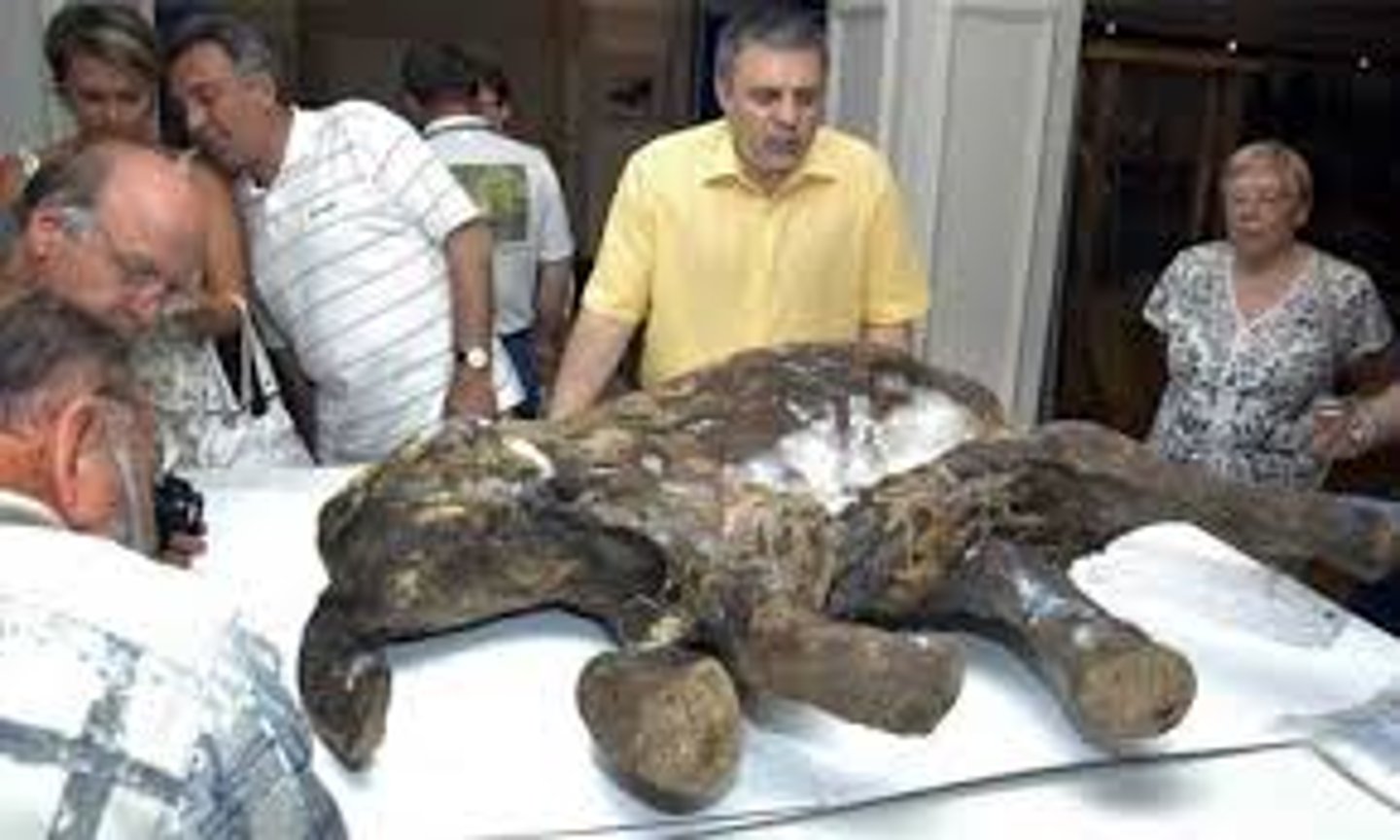
true form fossils
when the whole organism has been preserved

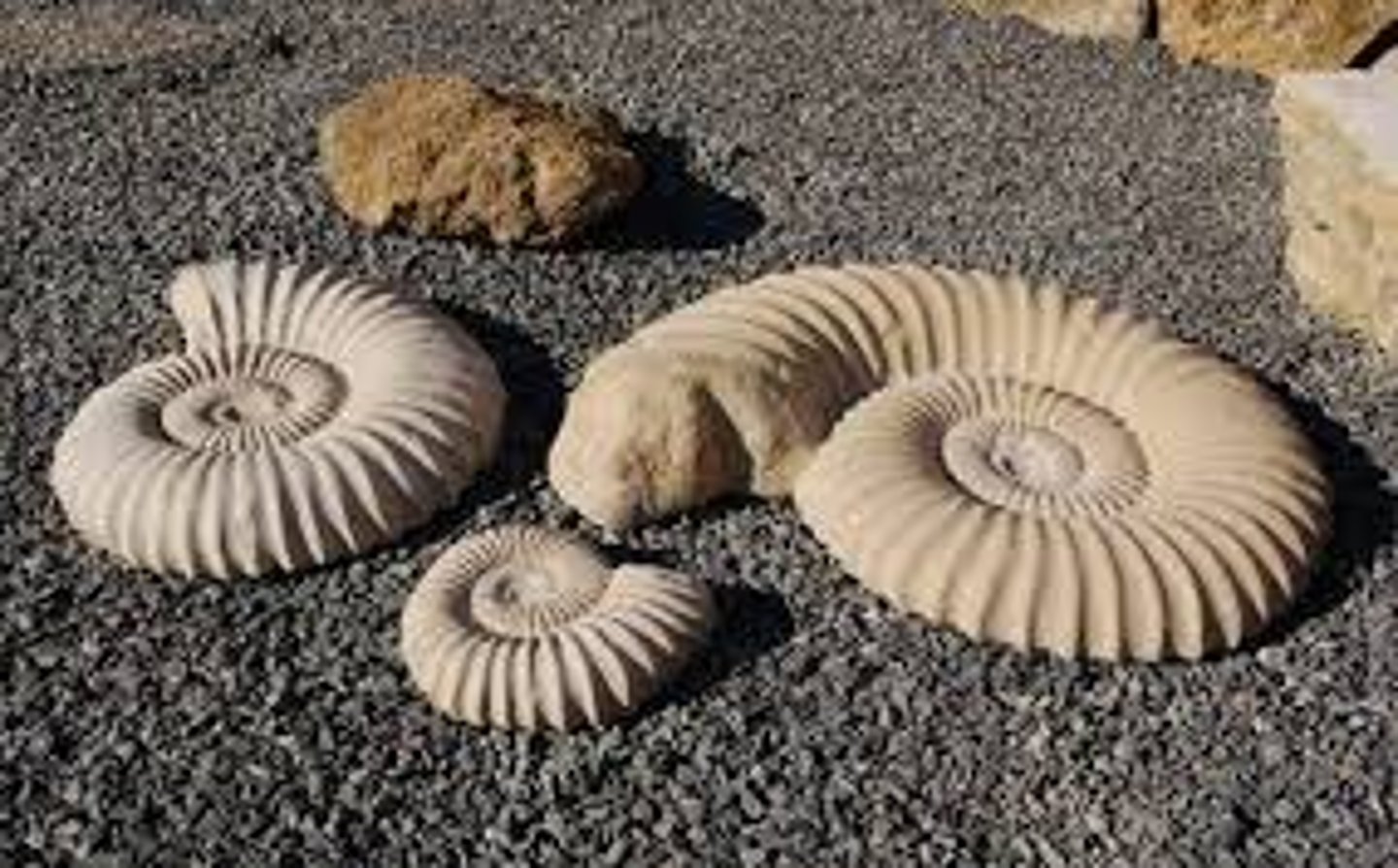
mold fossils
hollow impressions of a living thing in a rock

cast fossils
formed when a mold is filled in

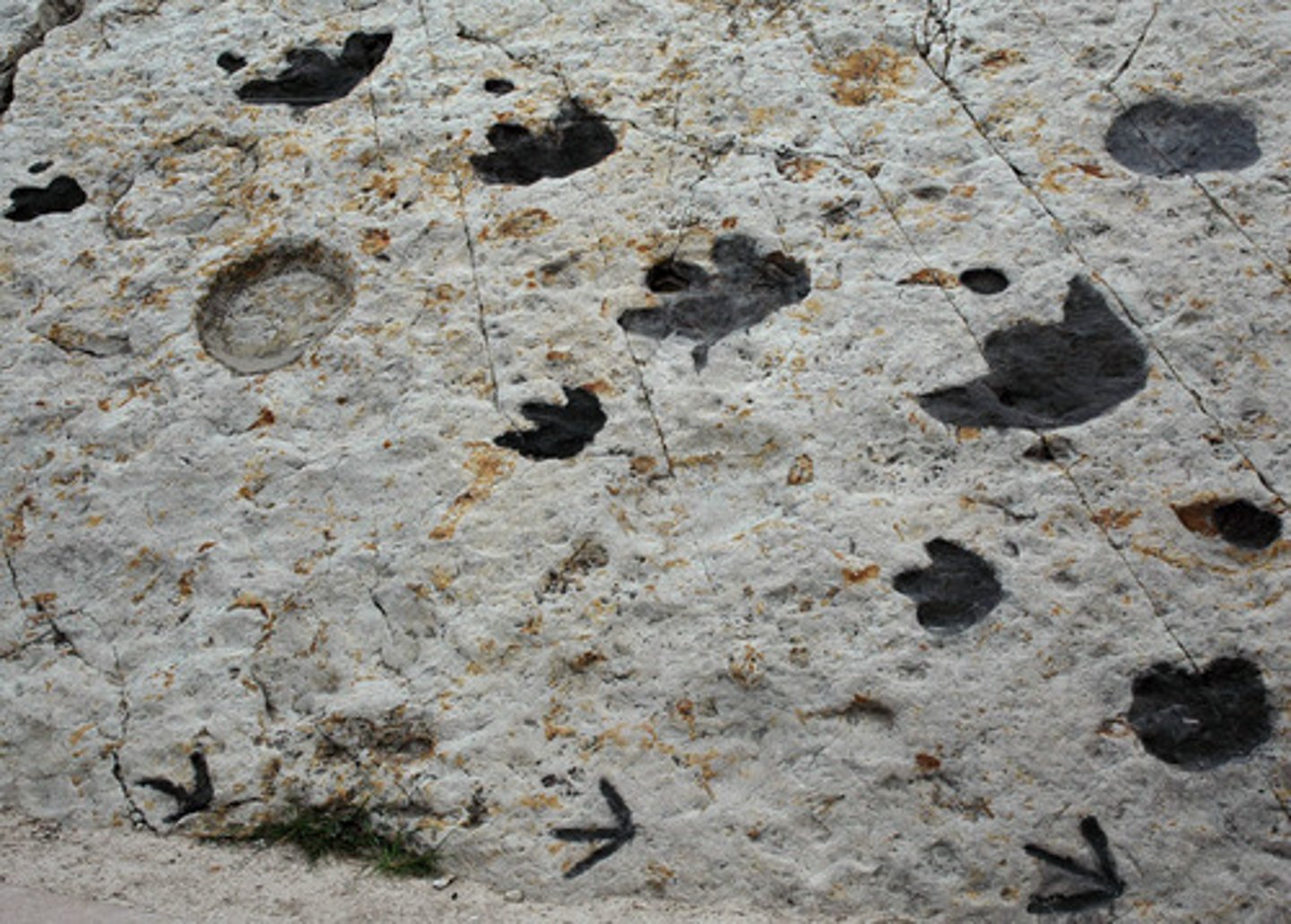
Trace fossils (ichnofossils)
rocks that show certain animal activities

William Smith (1769-1839)
- different rock layers contain different fossils
- created first geological map
- these concepts of geology became known as uniformitarianism or actualism
principle of fossils
fossil organisms succeed each other in an order that is definite and determinable according to
index fossils
a fossil that is useful for dating and correlating the strata in which it is found.
Cosmology
study of the universe
Religious Cosmology
Many world religions have origin beliefs that explain the beginnings of the Universe and life
Biblical cosmology
God created the heavens and the earth
Mormon cosmology
there was a pre-existing or pre-mortal life
Hindu cosmology
sees the universe undergoing cycles of creation and destruction
Islamic cosmology
Allah created the universe