Unit 3: The Human Immune System (BIO205)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/139
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Includes: Innate Immune System, Adaptive Immune System , and Immune Disorders
Last updated 1:24 AM on 3/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
140 Terms
1
New cards
What is the function of the __lymph system__?
– return extracellular fluids to circulatory system via muscle contractions
– acts as a drain-off system for inflammatory response
– network for immune cell transport
– acts as a drain-off system for inflammatory response
– network for immune cell transport
2
New cards
What __organs/tissues__ are associated with the lymph system?
– bone marrow = birthplace of all immune cells
– lymph nodes = immune system headquarters (armpits, groin, and neck)
– thymus = where T cells mature
– spleen = filters blood
– appendix
– tonsils
– GALT = gut-associated lymphoid tissue
– MALT = mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue
– Peyer’s patch (small intestine)
\
– lymph nodes = immune system headquarters (armpits, groin, and neck)
– thymus = where T cells mature
– spleen = filters blood
– appendix
– tonsils
– GALT = gut-associated lymphoid tissue
– MALT = mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue
– Peyer’s patch (small intestine)
\
3
New cards
**Degranulate**
secretion of antimicrobial chemicals and immunocytokines
4
New cards
3 types of granulocytes =
Eosinophils, basophils + mast cell, and neutrophils
5
New cards
Basophils
degranulate; involved in allergic responses (histamine release); found in mucosal and connective tissue of the skin and respiratory tract
6
New cards
Eosinophils
degranulate; production of toxic proteins against certain parasites; som e phagocytosis; involved in parasitic infections and allergies; found in the xgut, mammary glands, uterus, thymus, bone marrow, and adipose tissue
7
New cards
Neutrophils
Phagocytosis, form an extracellular trap (aka NET), and degranulate; eat to death and form pus (pyogenic); found mostly in blood; migrate through capillary wall into tissue to surround, engulf, and digest microbes
8
New cards
Monocytes
play a role in both the inflammatory and anti-inflammatory processes that take place during an immune response; a type of white blood cell (leukocytes) that reside in your blood and tissues to find and destroy germs ; made in the bone marrow; once they enter tissue they mature to form macrophage
9
New cards
Macrophages
found within tissues and organs; involved with wound healing and antigen presentation; aka the clean up crew after infections
10
New cards
Dendritic cells
capture, process, and present antigens to lymphocytes to initiate and regulate the adaptive immune response.; aka antigen presenting cells (APC) found in epithelial tissue and linings of nones, lungs, stomach, and intestines
11
New cards
What is __phagocytosis__?
The process by which a phagocyte (a type of white blood cell) surrounds and destroys foreign substances (such as bacteria) and removes dead cells; used to engulf and ingest foreign invaders and cellular debris
12
New cards
List the order of events during phagocytosis.
1. **Chemotaxis & attachment: chemical attraction of phagocytes to bacterial products, complement proteins, and other chemokine chemicals; phagocyte then attaches to flagella, peptidoglycan, LPS, complement proteins or antibodies; toll-like receptors or immune cells bind to pathogen-asociatedmolcular patterns (PAMPs)**
2. **Ingestion**: phagocyte encircles the pathogen, forms a vesicle (phagosome) & ingests it
3. **Formation of phagosome:** a sac which becomes acidic and hydrolytic enzymes are activated
4. **Fusion**: phagosome merges with a lysosome (a vesicle containing digestive enzymes) to form a phagolysosome
5. **Digestion**: pathogens inside phagolysosome are digested
6. **Residual bodies**: indigestible material in transported to the all membrane
7. **Discharge**: phagosome fuses with cell membrane and releases waste contents to outside of cell
13
New cards
List the major __microbial attachment sites__ (ie. Flagella, etc) which phagocytes recognize and attach to
Pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) including: flagella, lipopolysaccharides, peptidoglycan; can also attach to complement proteins and antibodies found bound to microbes
14
New cards
__Chemotaxis__
the migration of cells toward attractant chemicals or away from repellents
15
New cards
__Margination__
the movement of particles in flow toward the walls of a channel. (describes the behavior of white blood cells (WBCs) and platelets in blood flow)
16
New cards
__Diapedesis__
the process in which white blood cells come out of the blood vessels into the surrounding area in case of injuries
17
New cards
**Vasodilation**
when blood vessels in your body widen (increase in diameter), allowing more blood to flow through them
18
New cards
**Examples of chemical substances that trigger it**
histamine, carbon dioxide, nitric oxide, acetylcholine, and prostaglandins.
19
New cards
Briefly describe how __anti-inflammatory drugs__ reverse the effects of inflammation
Anti-inflammatory drugs inhibit synthesis of certain immunocytokines and chemicals to reduce inflammation
20
New cards
List __two__ categories of anti-inflammatory drugs.
1. NSAIDS (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) = fast and short acting, blocking prostaglandin production (ex: aspirin & ibuprofen)
2. Steroids (glucocorticoid) = slower and longer acting, black production of many immunocytokines (ex: hydrocortisone)
21
New cards
**Pyogenic**
involving or relating to the production of pus (Neutrophils are found in pus)
22
New cards
Pyrogenic
induce fever; raise thermostat temp.
23
New cards
endogenous pyrogens
made by immune cells such as macrophages (substances, which originate inside the body and which are capable of inducing fever by acting on the hypothalamic thermoregulatory centre)
24
New cards
exogenous pyrogens
infectious agents (substances, which originate outside the body and which are capable of inducing interleukins)
25
New cards
hypothalamus
area of the brain that controls internal thermostat/body tempo. (98.6)
26
New cards
Ferritins
restrict microbe access to iron
27
New cards
Peroxides (found inside white blood cells)
damages DNA, proteins, and membranes (kills pathogens)
28
New cards
Lysozyme (also found inside white blood cells)
breaks down peptidoglycan (kills Gm+ bacteria)
29
New cards
Interferon (IFN)
activate the synthesis of enzymes which degrade mRNA in the host cell; protect the host cell from becoming infected by blocking viral replication
30
New cards
Interleukins (IL-1 and IL-6)
allow communication between leukocytes; IL-1 (fever) and IL-6 (mainly inflammation)
31
New cards
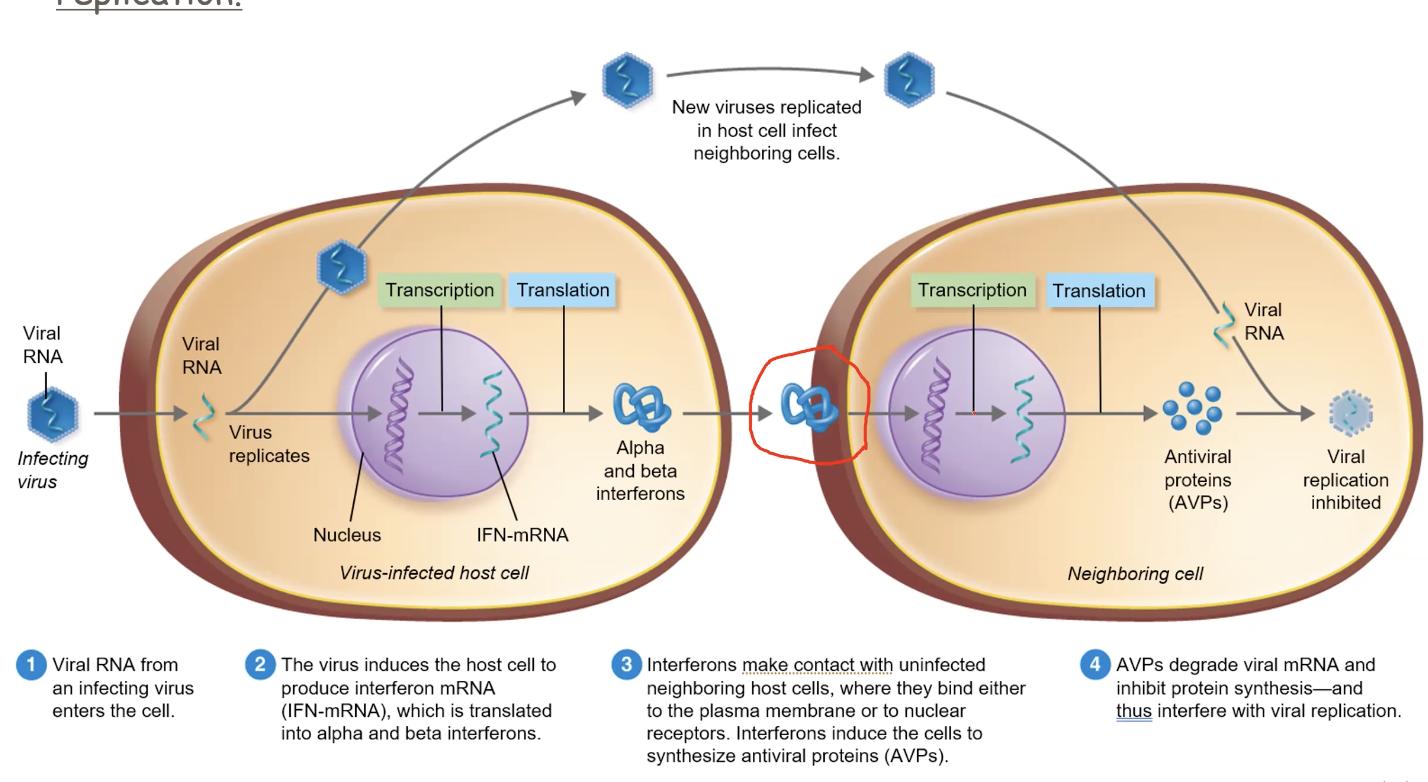
How i__nterferon__ regulates the spread of __viral infections__.
1\.) viral RNA from an infecting virus enters the cell
2\.) the virus induces the host cell to produce interferon mRNA (IFN-mRNA), which is translated into alpha and beta interferons.
3\.) interferons make contact with uninfected neighboring host cells, where they bind either to the plasma membrane or to nuclear receptors. Interferons induce the cells to synthesize antiviral proteins.
4\.) AVPs degrade viral mRNA and inhibit protein synthesis and thus interfere with viral replication.
2\.) the virus induces the host cell to produce interferon mRNA (IFN-mRNA), which is translated into alpha and beta interferons.
3\.) interferons make contact with uninfected neighboring host cells, where they bind either to the plasma membrane or to nuclear receptors. Interferons induce the cells to synthesize antiviral proteins.
4\.) AVPs degrade viral mRNA and inhibit protein synthesis and thus interfere with viral replication.
32
New cards
Do Complement proteins participate in the 1st, 2nd or 3rd line of defense?
* 2nd line of defense
* Complement proteins are secreted by the liver and macrophage
* Complement proteins are secreted by the liver and macrophage
33
New cards
What are the **three** **major functions** of the complement proteins (state which complement proteins are involved)?
a) Stimulate and recruit WBCs by C3a and C5a (chemotactic and vasoactive) → inflammation
b) Opsonization (process of coating microbes with protein molecules to enhance phagocytosis) by C3b → phagocytosis
c) Lysis of microbes = membrane attack complex (MAC) by C5b-C9
b) Opsonization (process of coating microbes with protein molecules to enhance phagocytosis) by C3b → phagocytosis
c) Lysis of microbes = membrane attack complex (MAC) by C5b-C9
34
New cards
Antigen
foreign substance that stimulates an immune response; found on microbes such as spikes, flagella, LPS, peptidoglycan & other major structures which are not found on host cells.
35
New cards
Epitope (mugshot)
piece of the antigen that triggers immune response & is recognized directly by antibodies → most peptides, some sugars, few lipids or nucleic acids (DNA/RNA)
36
New cards
What is the function of major histocompatibility complex I (MHC I)?
MHCI displays __self or abnormal epitopes__ to __Cytotoxic T-cells__ (CD8)
(they kill themselves)
(they kill themselves)
37
New cards
What is the function of major histocompatibility complex II (MHC II)?
MHCII displays __foreign epitopes__ to __helper T-cells__ (CD4)
(they go kill microbes)
(they go kill microbes)
38
New cards
What is the purpose of co-stimulation in the immune response?
activates white blood cells; T-cell dependent activation; necessary for T-cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival.
39
New cards
What 2nd line cell activates the 3rd line lymphocyte T-helper generals?
Dendritic Cells
40
New cards
What are the TWO requirements for co-stimulation to occur?
epitope & chemical activation
41
New cards
Co-stimulation between WBCs requires ___ and ___.
epitopes and cytokines
42
New cards
Where are T and B lymphocytes __produced__ and where do they __mature__?
They both are produced in the bone marrow, but B lymphocytes remain in the marrow to mature, while T lymphocytes travel to the thymus to mature.
43
New cards
__Define__ __**clonal expansion**__
where epitope reception & hormones activate lymphocytes to undergo mitosis, producing thousands of clones (proliferation)
44
New cards
Identify the function of __each type of T cell or chemical__ involved in the specific immune response.
1. **T helper 1 cells**: activate __Killer T cells (aka cytotoxic T cells)__ cells to kill infected or cancerous cells
2. **T helper 2 cells:** activate __B-cells__ to produce antibodies
3. Cytotoxic T cells: kill infected HOST cells (not the microbes)
4. Memory T cells: provide long-term protection (months to years)
5. Do T-cells **secrete** antibodies? No
45
New cards
What is the function of Natural Killer (NK) cells? Do they require activation by CD4+ T cells?
* function = cytotoxic attack
* respond independently to other WBCs (though do not require costimulation)
* have the ability to recognize stressed cells in the absence of antibodies and MHC, allowing for a much faster immune reaction
* respond to: cells with too few, fake, or no MHC I receptors, stressed cells, and abnormal cells
* They do not require activation by CD4+T cells
* respond independently to other WBCs (though do not require costimulation)
* have the ability to recognize stressed cells in the absence of antibodies and MHC, allowing for a much faster immune reaction
* respond to: cells with too few, fake, or no MHC I receptors, stressed cells, and abnormal cells
* They do not require activation by CD4+T cells
46
New cards
Identify the function of __B cells & plasma cells__ in the specific immune response and state whether they are **active or inactive** after clonal selection.
1. Plasma cells = an immune cell that makes large amounts of a specific antibody (active)
2. Memory B cells = memorize the characteristics of the antigen that activated their parent B cell during initial infection (inactive)
3. Do B cells **secrete** antibodies? Yes
47
New cards
Clonal selection
**a process by which the body produces B and T cells to respond to infections**. These cells each have unique receptors that allow them to identify specific pathogens.
48
New cards
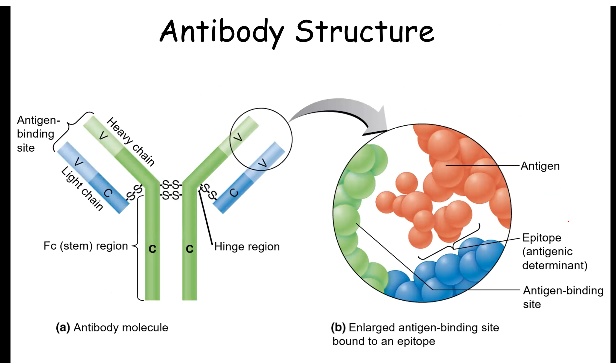
Draw the structure of an antibody and identify which part binds to the antigen & which part binds to macrophages and other WBCs.
* Stem region bind to WBCs and macrophages
* Hinge region binds to antigens
* Hinge region binds to antigens
49
New cards
Agglutination (function of antigen)
1. reduces the number of infectious units to be dealt with; immobilized microbes or toxins by creating clumps of the immune complex; rapid and efficient
50
New cards
Neutralization
1. blocks adhesion of bacteria and viruses to mucosa; blocks attachment of toxic; no longer threat and can’t do harm!
51
New cards
Opsonization
1. Coats antigen with antibody enhances phagocytosis, creates WBC binding receptor or surface attachment; creates complement attachment binding site
52
New cards
Complement fixation
causes inflammation and cell lysis; C5b-C9 attaches to antigen-antibody complex in order to destroy the pathogen (MAC attack)
53
New cards
Identify the major class of antibody (IgA, IgE, IgG or IgM) for each description below **AND** state which __**function(s) they perform**__.
1. First type of antibody released during a primary immune response, circulates in the blood (5-10% of circulating antibodies): Igm (neutralizes, opsonizes, agglutinates, and fixes complement)
2. Antibody that provides long-term protection; can cross placenta (80% of circulating antibodies): IgG (long-lasting memory, protecting of developing fetus, neutralizes, agglutinates, opsonizes, and fixes complement)
3. Antibody that is secreted in mucus, saliva, tears and milk (up to 13%): IgA (a dimer, provides specific resistance to microbes in tears and saliva, found in gastrointestinal and respiratory tracts, serves to pass immunity along to a baby, and they are great at neutralization
4. Antibody that is involved in allergic reactions (
54
New cards
Natural passive
antibodies pass from mother to fetus via placenta or to infant via the mother’s milk (ex: breastfeeding where antibodies and memory cells are given)
55
New cards
Natural active
antigens enter the body naturally; body induces antibodies and specialized lymphocytes (ex: getting sick and your body produces antibodies on it’s own)
56
New cards
Artificial passive
preformed antibodies in immune serum are introduced by injection (antibody injections that are given to you)
57
New cards
Artificial active
antigens are introduced in vaccines; body produces antibodies and specialized lymphocytes (ex: flu or covid vaccine and following this antibodies are produced on it’s own)
58
New cards
What is a __primary immunodeficiency__?
Present at birth or become evident during infancy and childhood
59
New cards
What parts (B cells, T cells, etc) of the immune system are affected in the following immunodeficiencies?
1. SCIDS – B and T cells combined
2. DiGeorge - T cells (lymphocytes)
3. Agammaglobulinemia – B cell (lymphocytes) and antibodies
60
New cards
What is a __secondary immunodeficiency__?
Disorders acquired later in life and often result from use of a drug, cancer or an infectious disease, like HIV/AIDS. They are dramatically more common than congenital immunodeficiency disorders. This includes many types of cancer, particularly those of the bone marrow and blood cells (leukemia, lymphoma, multiple myeloma), and certain chronic infections.
61
New cards
What immune system cell (be specific) is affected in HIV/AIDS? Explain how HIV targets and infects this cell type (describe the spikes used). What causes a decrease in the number of these immune cells?
* Immune system cell affected in HIV/AIDS are CD4 cells (white blood cells)
* HIV attaches to CD4 and CCR5 or CXCR4 receptors primarily on Helper T cells, macrophages, & microglial (brain dendritic cells)
* gp120 spike binds to CD4 and the gp41 spike component binds to CCR5 or CXCR4 coreceptors.
* Attachment → fusion → entry
* Cytotoxic T cells are going to decrease amount helper T cells over time → becoming immunocompromised
* HIV attaches to CD4 and CCR5 or CXCR4 receptors primarily on Helper T cells, macrophages, & microglial (brain dendritic cells)
* gp120 spike binds to CD4 and the gp41 spike component binds to CCR5 or CXCR4 coreceptors.
* Attachment → fusion → entry
* Cytotoxic T cells are going to decrease amount helper T cells over time → becoming immunocompromised
62
New cards
allergen
a substance that causes an __allergic__ reaction
63
New cards
wheal & flare = type 1 allergic reaction;
it includes swelling, produced by the release of serum into the tissues (wheal), and redness of the skin, resulting from the dilation of blood vessels (flare).
64
New cards
anaphylactic shock
an extreme, often life-threatening __allergic__ reaction to an __antigen__ to which the body has become __hypersensitive__.
65
New cards
Isograft
* between identical twins (matching HLAs)
* ex: skin or organs, like kidney transplants
* ex: skin or organs, like kidney transplants
66
New cards
Autograft
* within an individual (own HLAs)
* ex: burn on patient’s skin (skin from thigh taken and put on burn site)
* ex: burn on patient’s skin (skin from thigh taken and put on burn site)
67
New cards
Allograft
* between non-identical individuals
* ex: skin or organs, like kidney transplants
* most transplants fall under this category
* HLAs must match as loosely as possible
* Usually, blood relatives are preferred as donors
* ex: skin or organs, like kidney transplants
* most transplants fall under this category
* HLAs must match as loosely as possible
* Usually, blood relatives are preferred as donors
68
New cards
Xenograft
* between species (ex: between pigs and humans)
69
New cards
1st line PHYSICAL BARRIERS __block entry__ of microbes (skin)
* intact skin **CANNOT** be penetrated by most microbes
* epidermis contains keratin and collagen
* dermis is made up of fibrous connective tissue (macrophages and fibroblasts) with blood vessels (RBCs & WBCs)
* epidermis contains keratin and collagen
* dermis is made up of fibrous connective tissue (macrophages and fibroblasts) with blood vessels (RBCs & WBCs)
70
New cards
1st line PHYSICAL BARRIERS __block entry__ of microbes (Respiratory Tract)
* mucous membranes line the digestive, genitourinary, respiratory tracts
* **mucus** = a thick film that helps trap and remove microbes (4 cups/day)
* **cilia** = tiny hairs that sweep mucus out of respiratory tract
* coughing and sneezing help remove microbes trapped in mucus
* **mucus** = a thick film that helps trap and remove microbes (4 cups/day)
* **cilia** = tiny hairs that sweep mucus out of respiratory tract
* coughing and sneezing help remove microbes trapped in mucus
71
New cards
1st line PHYSICAL BARRIERS __block entry__ of microbes (Eye)
movement of eyelids = flushing action removes microbes
72
New cards
1st line PHYSICAL BARRIERS __block entry__ of microbes (digestive system)
* mucus membrane
* mucus
* vomiting and defecation (diarrhea) help remove microbes trapped in mucus
* mucus
* vomiting and defecation (diarrhea) help remove microbes trapped in mucus
73
New cards
1st line CHEMICAL BARRIERS __block entry__ of microbes (skin)
* Dermcidin = a type of antimicrobial peptide (AMP) which is a positively charged chain of amino acid that kill fungi, Gram + bacteria & Gram - bacteria (secreted in sweat)
* Salt = secreted in sweat; contains hypertonic environment
* lysozyme = an enzyme that destroys Gram + bacteria by digesting peptidoglycan in bacterial cell walls
* sebaceous gland secrete sebum, which keeps skin pliable and most resistant to breaking and tearing
* Salt = secreted in sweat; contains hypertonic environment
* lysozyme = an enzyme that destroys Gram + bacteria by digesting peptidoglycan in bacterial cell walls
* sebaceous gland secrete sebum, which keeps skin pliable and most resistant to breaking and tearing
74
New cards
1st line CHEMICAL BARRIERS __block entry__ of microbes (Respiratory Tract)
* mucus containing the enzyme lysozyme
* oil glands contains fatty acids, which lower in pH of the skin to a 5, which is inhibitory for many pathogenic bacteria
* oil glands contains fatty acids, which lower in pH of the skin to a 5, which is inhibitory for many pathogenic bacteria
75
New cards
1st line CHEMICAL BARRIERS __block entry__ of microbes (eye)
lacrimation = tears contain lysozyme (enzyme that destroys gram + bacteria by digesting peptidoglycan in bacterial cell walls)
76
New cards
1st line CHEMICAL BARRIERS __block entry__ of microbes (diggestive system)
* mucus and saliva contain lysozyme
* hydrochloric acid = pH of 20 kills most bacteria
* salmonella is acid-resistant and can survive in the stomach and digestive tract
* bile (liver) and enzymes (pancreas) get released into small intestine and disrupt microbial membranes
* hydrochloric acid = pH of 20 kills most bacteria
* salmonella is acid-resistant and can survive in the stomach and digestive tract
* bile (liver) and enzymes (pancreas) get released into small intestine and disrupt microbial membranes
77
New cards
1st line CHEMICAL BARRIERS __block entry__ of microbes (Normal flora)
secrete lactic acid and bacteriocins that inhibit microbes
78
New cards
1st line PHYSICAL BARRIERS __block entry__ of microbes (Normal flora)
* block attachment of pathogens to host
compete with pathogens for nutrients
compete with pathogens for nutrients
79
New cards
The 4 signs of inflammation are:
Rubor (red), Calor (heat), Tumor (swelling), Dolor (pain)
80
New cards
**Rubor** (red) or discoloration of skin
\
Increased blood flow due to vasodilation
Increased blood flow due to vasodilation
81
New cards
\
**Calor** (heat)
**Calor** (heat)
\
Increased blood flow
Increased blood flow
82
New cards
\
**Tumor** (swelling)
**Tumor** (swelling)
\
Increased permeability of capillaries
Increased permeability of capillaries
83
New cards
\
**Dolor** (pain)
**Dolor** (pain)
\
Due to the release of chemicals
Due to the release of chemicals
84
New cards
Identify the __4 types of hypersensitivities__
1. Anaphylactic Reactions (
85
New cards
**Anaphylactic Reactions (
* Classic allergy – IgE antibodies bind to the surface of mast cells/basophils and combine with non-infectious antigens, called allergens
* Granulocytes release histamine during a process called degranulation
* Ex: hay fever, asthma, and hives
* Granulocytes release histamine during a process called degranulation
* Ex: hay fever, asthma, and hives
86
New cards
**Cytotoxic Reactions (5-12 hours for clinical signs)**
* Antigen bound to host cell surface results in attack by WBCs
* IgM, IgG & complement mediated
* Ex: blood transfusion reactions, erythroblastosis fetalis, drug-induced thrombocytopenia
* IgM, IgG & complement mediated
* Ex: blood transfusion reactions, erythroblastosis fetalis, drug-induced thrombocytopenia
87
New cards
**Immune complex Reaction (3-8 hours for clinical sings)**
* soluble antigen found in serum bind to antibodies and deposit in capillary wall in bone, kidneys, eyes, and major organs
* Agglutination/Immune Complex between IgG, complement & neutrophil mediated
* Complement system and neutrophils attack and destroy tissue
* Ex: Arthus reactions, serum sickness
* Agglutination/Immune Complex between IgG, complement & neutrophil mediated
* Complement system and neutrophils attack and destroy tissue
* Ex: Arthus reactions, serum sickness
88
New cards
**Delayed Cell Mediated (24-48 hours for clinical signs)**
* mediated primarily by T cells
* Ex: transplant rejection, tuberculin test, allergic contact dermatitis, such as poison ivy
* Ex: transplant rejection, tuberculin test, allergic contact dermatitis, such as poison ivy
89
New cards
T cells mature in which location?
Thymus
90
New cards
What do Th2 cells activate?
B-Cells
91
New cards
The perforin-granzyme pathway involves
the production of special cell-killing proteins that act on infected or abnormal cells
92
New cards
After exposure to an antigen, antibodies will be immediately detectable in an individual's serum. True/False
False
93
New cards
Cytotoxic attack on infected cells is performed by _ after co-stimulation by __.
CD8 T cells…CD4 T cells
94
New cards
CD8 T cells…
attack
95
New cards
CD4 cells produce
antibodies
96
New cards
examples of active immunity
immunization and infection
97
New cards
breast milk is considered…
passive immunity (the antibodies are given rather than made)
98
New cards
Exogenous antigens are processed for immune recognition by ________ cells
dendritic and macrophage
99
New cards
List of things involved with apoptosis (programmed cell death).
\n tumor necrosis factor, interferon, perforin, granzyme
100
New cards
Sequence of events in phagocytosis.
Chemotaxis, attachment, endocytosis, fusion, digestion, residual bodies, exocytosis