OPT 114 EYEBROWS
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
SCALP
skin
connective tissue (sense)
aponeurosis (muscle)
loose connective tissue
periosteum
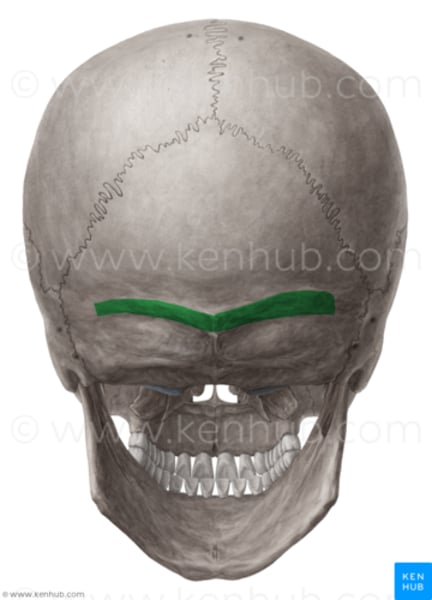
superior nuchal line
runs horizontally from external occipital protuberance
skin
functions as a barrier to the outside environment by preventing microbes from causing infections in underlying tissues
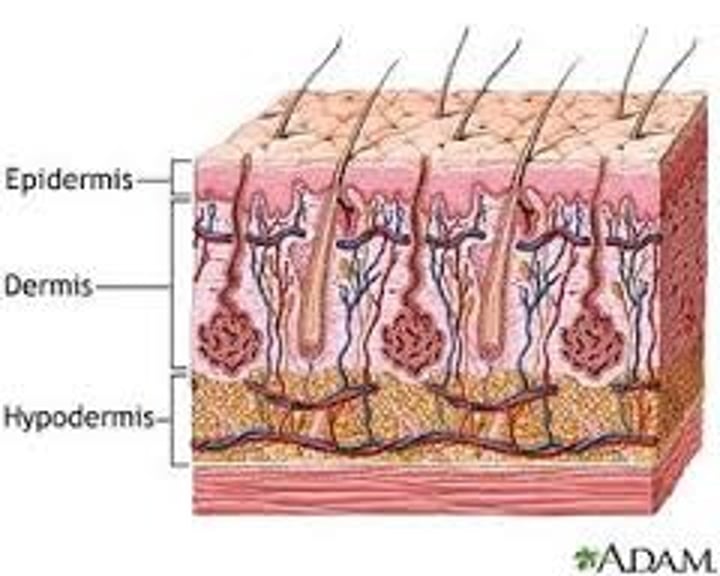
Three layers of skin
epidermis, dermis, hypodermis
Epidermis
outer layer of skin, mostly composed of keratinocytes (90% of cells in epidermis)
Keratinocytes
produce keratin- provides structure and water resistant properties
4 layers of keratinocytes
stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum corneum
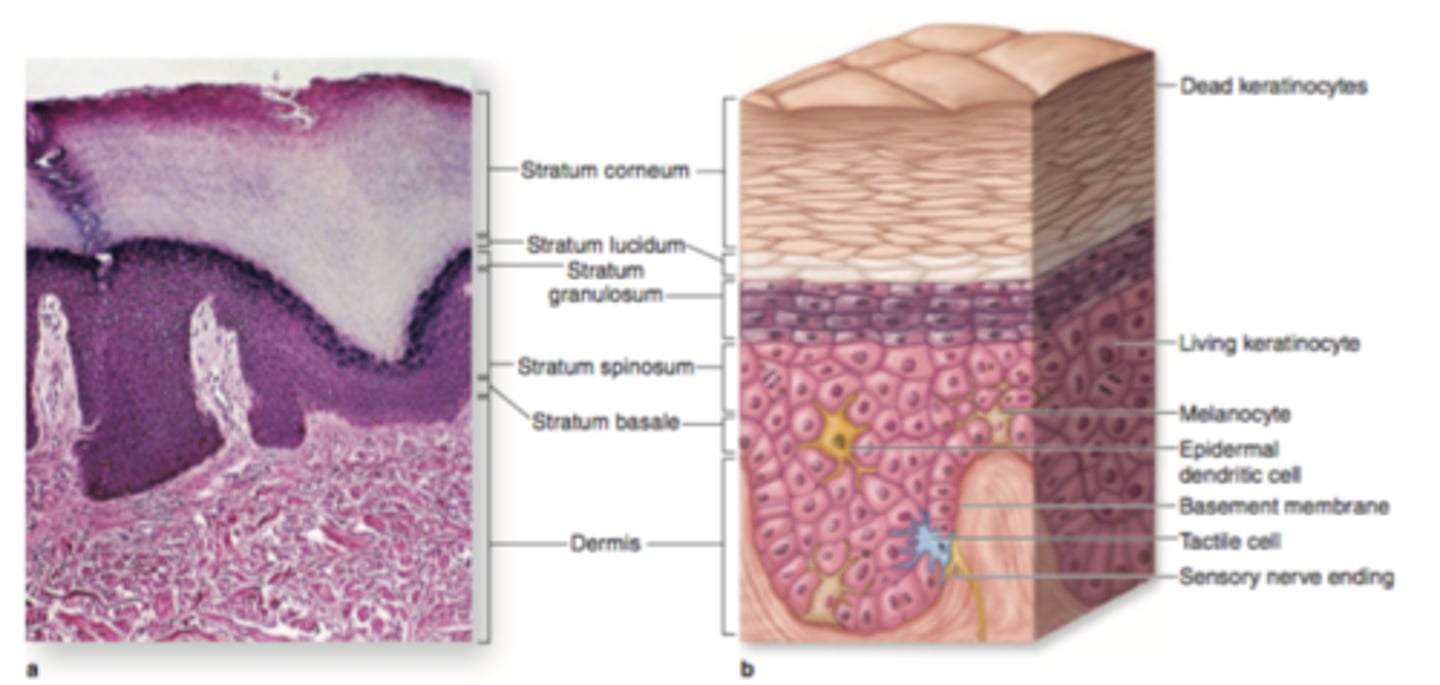
stratum basale
innermost layer, only these cells undergo mitosis and then migrate through the other layers
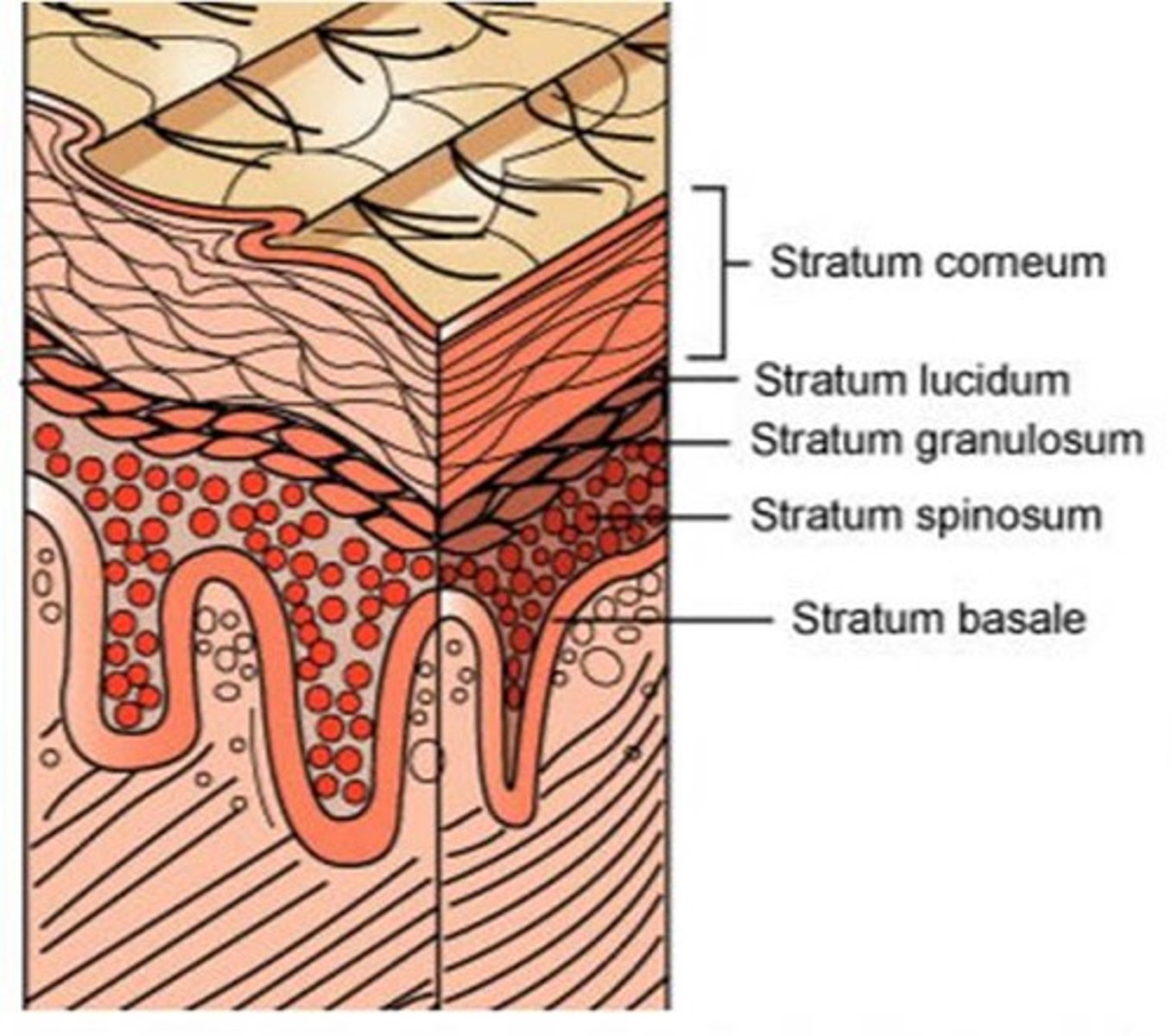
Stratus Granulosum
cells lose their nucleus and become more flattened
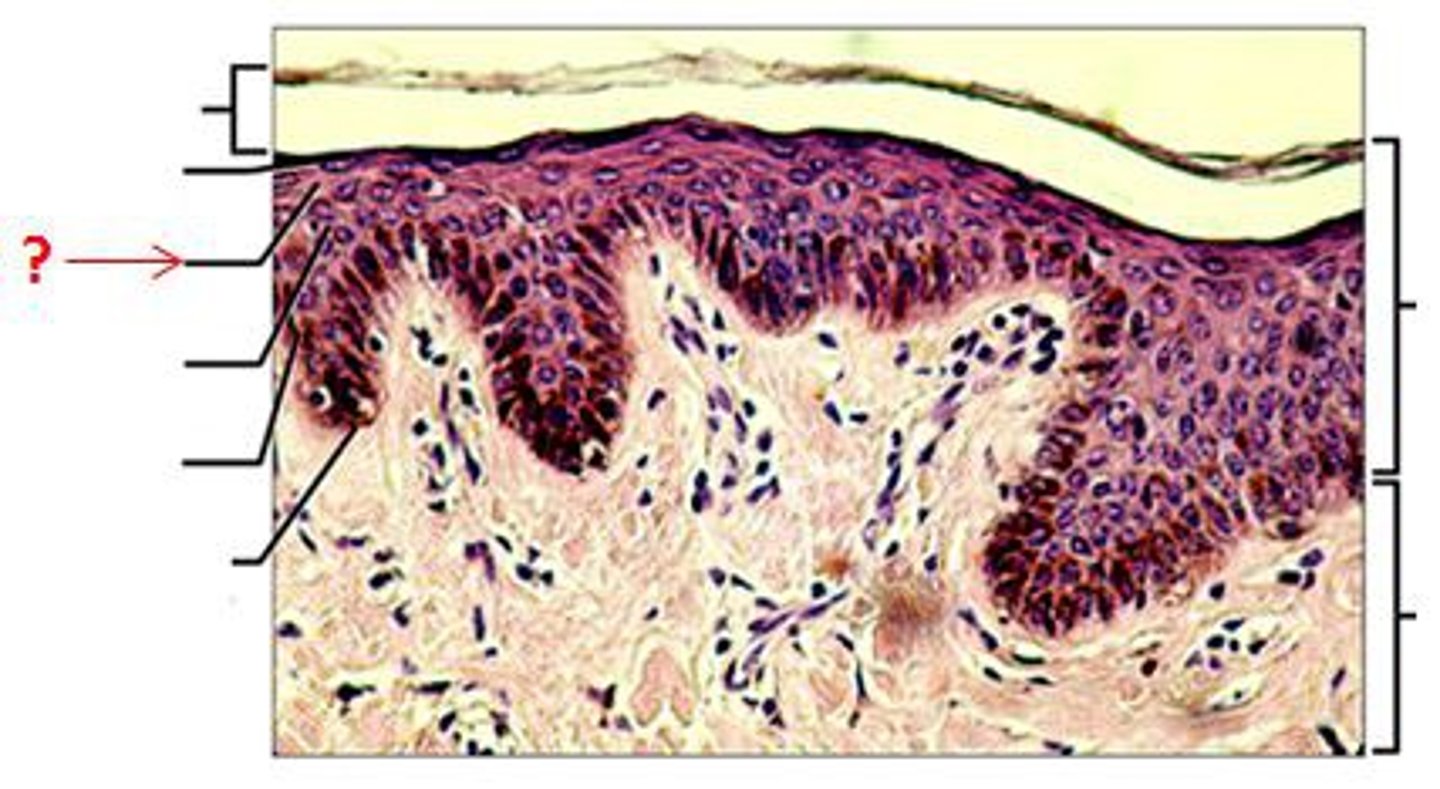
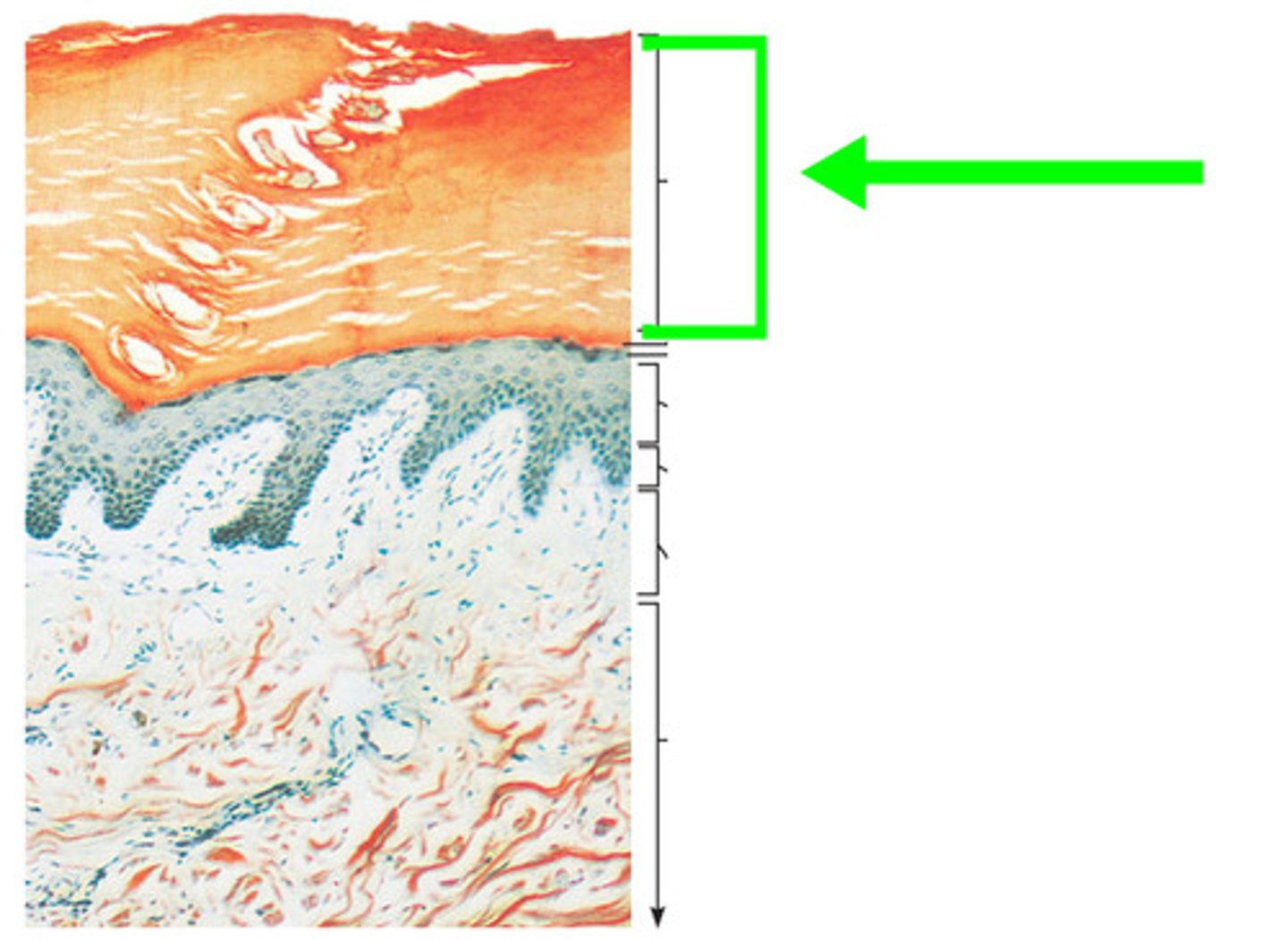
stratus corneum
dead, flattened cells filled with keratin. these cells are shed every few weeks in desquamation
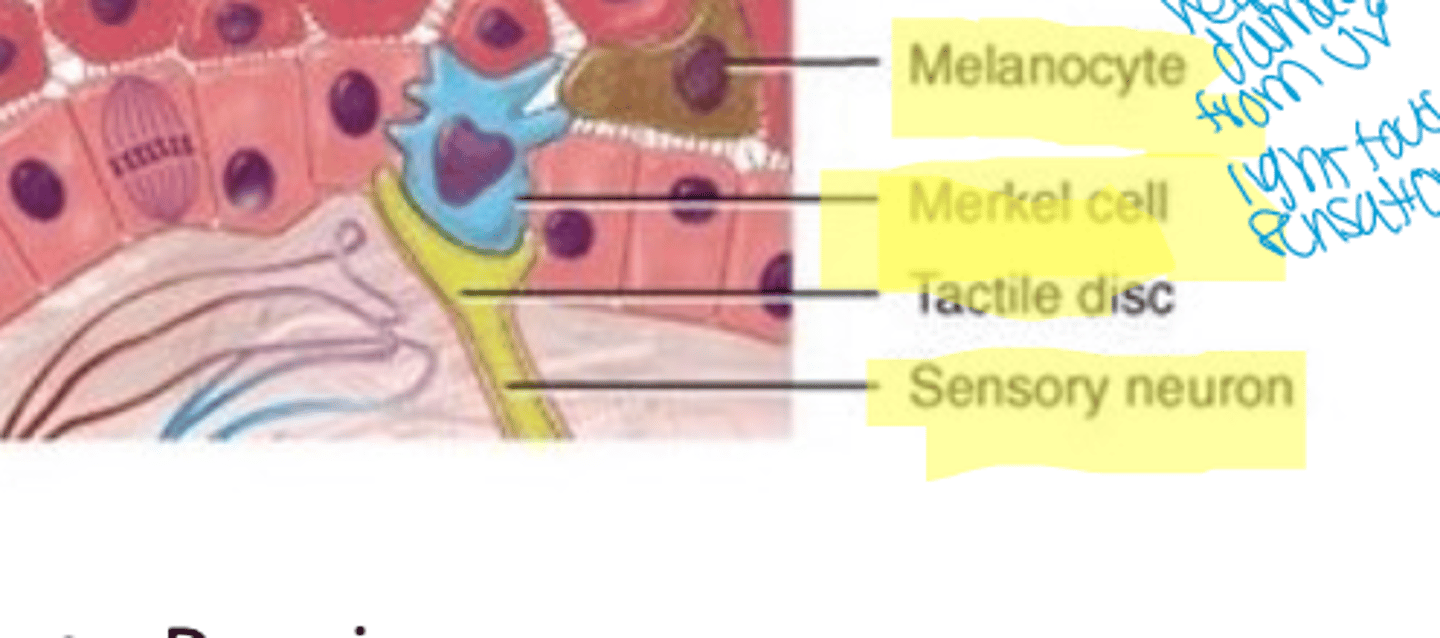
Melanocytes
produce melanin that filters UV light
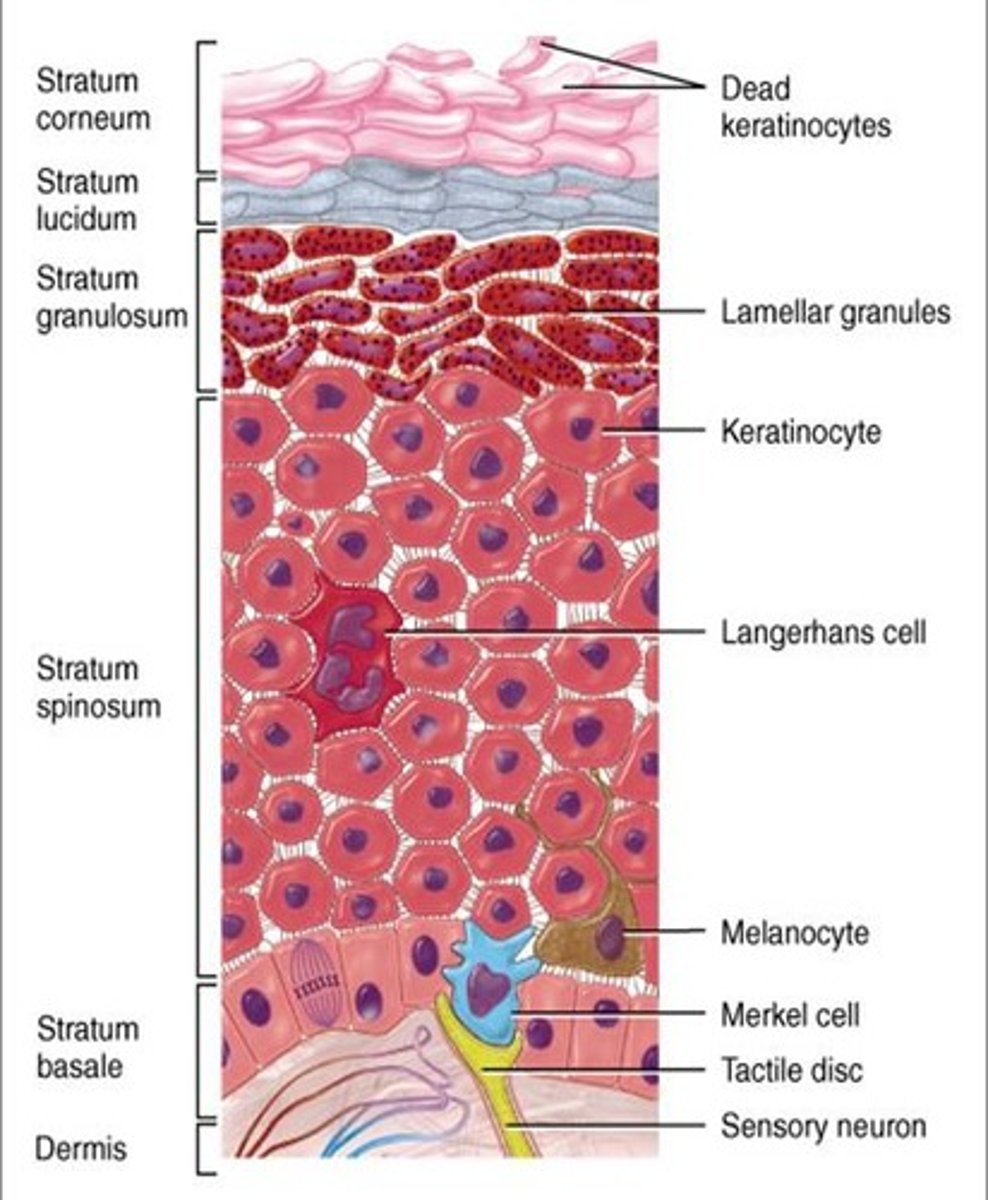
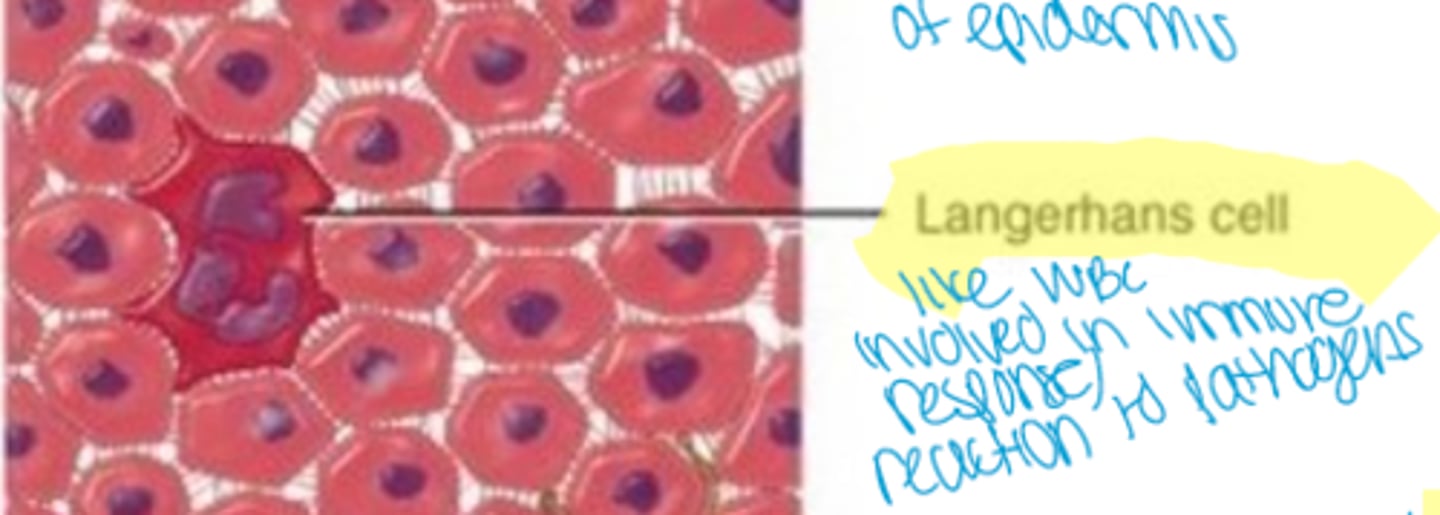
Lamgerhans cells
considered a type of white blood cell and play a role in immune response
Merkel cells
attach to nerve endings to form "light touch" receptors
The epidermis is avascular
relies on dermis for blood supply
basement membrane
Cells at the base of an epithelial layer are attached to this.
Dermis
middle layer of skin, composed of connective tissue
Fibroblasts
cells that produce collagen and elastin
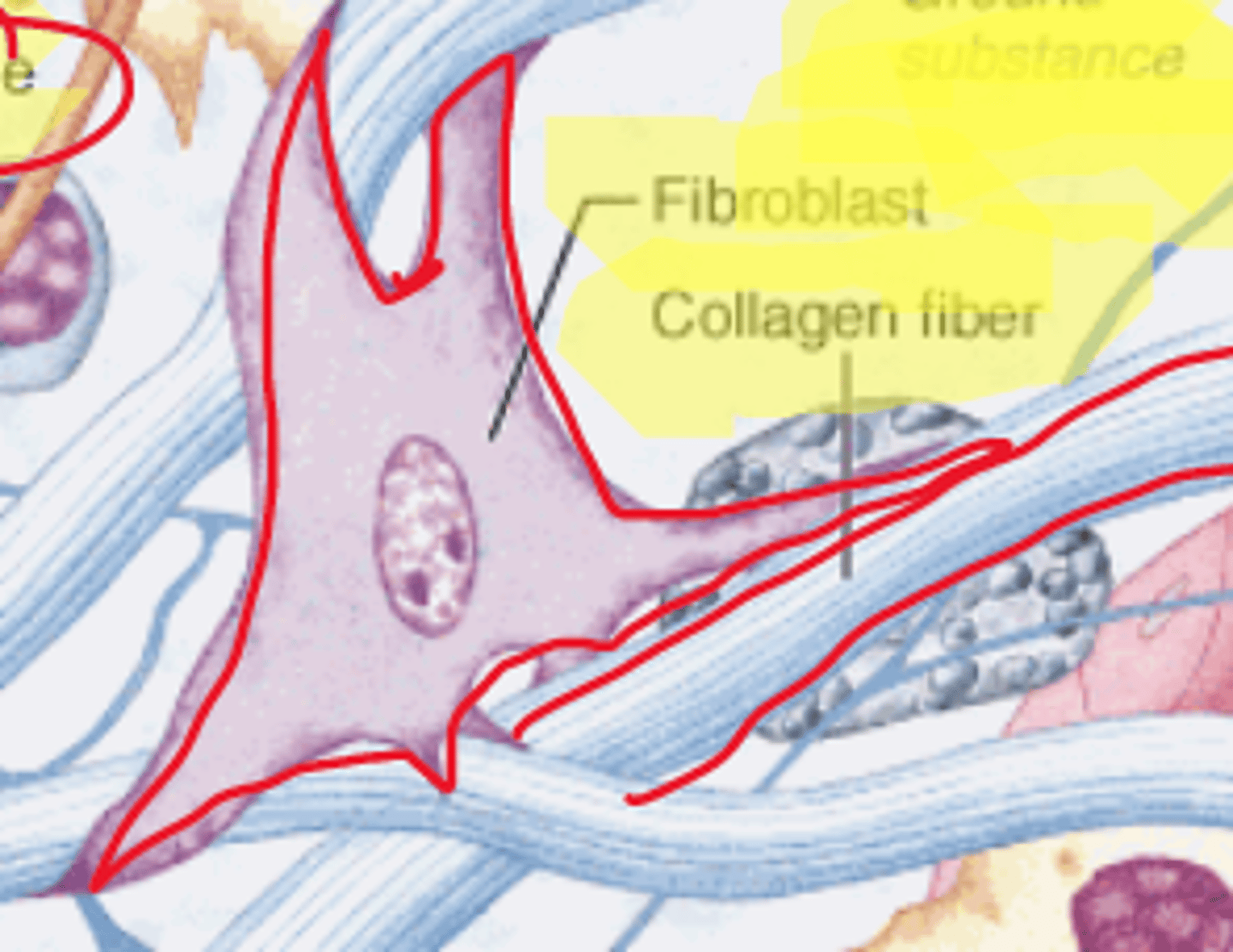
Collagen
proteins that provides structure and tensile strength
Elastin
protein that provides elasticity , enabling movement
ground substance
transparent gel composed of water, glycosaminoglycans and proteoglycans
white blood cells
involved in immune response
Adnexal structures include:
hair follicles, hair, sebaceous glands, sweat glands
first body hairs formed during embryological development?
eyebrow hairs
Hypodermis
the layer of skin beneath the dermis, which is primarily composed of adipose and loose connective tissue
dense connective tissue
connects the skin to underlying muscle and contains arteries, veins, and nerves supplying the eyebrows
4 muscles innervating eyebrows
-Frontalis
-Corrugator
-Procerus
- Orbicularis Oculi
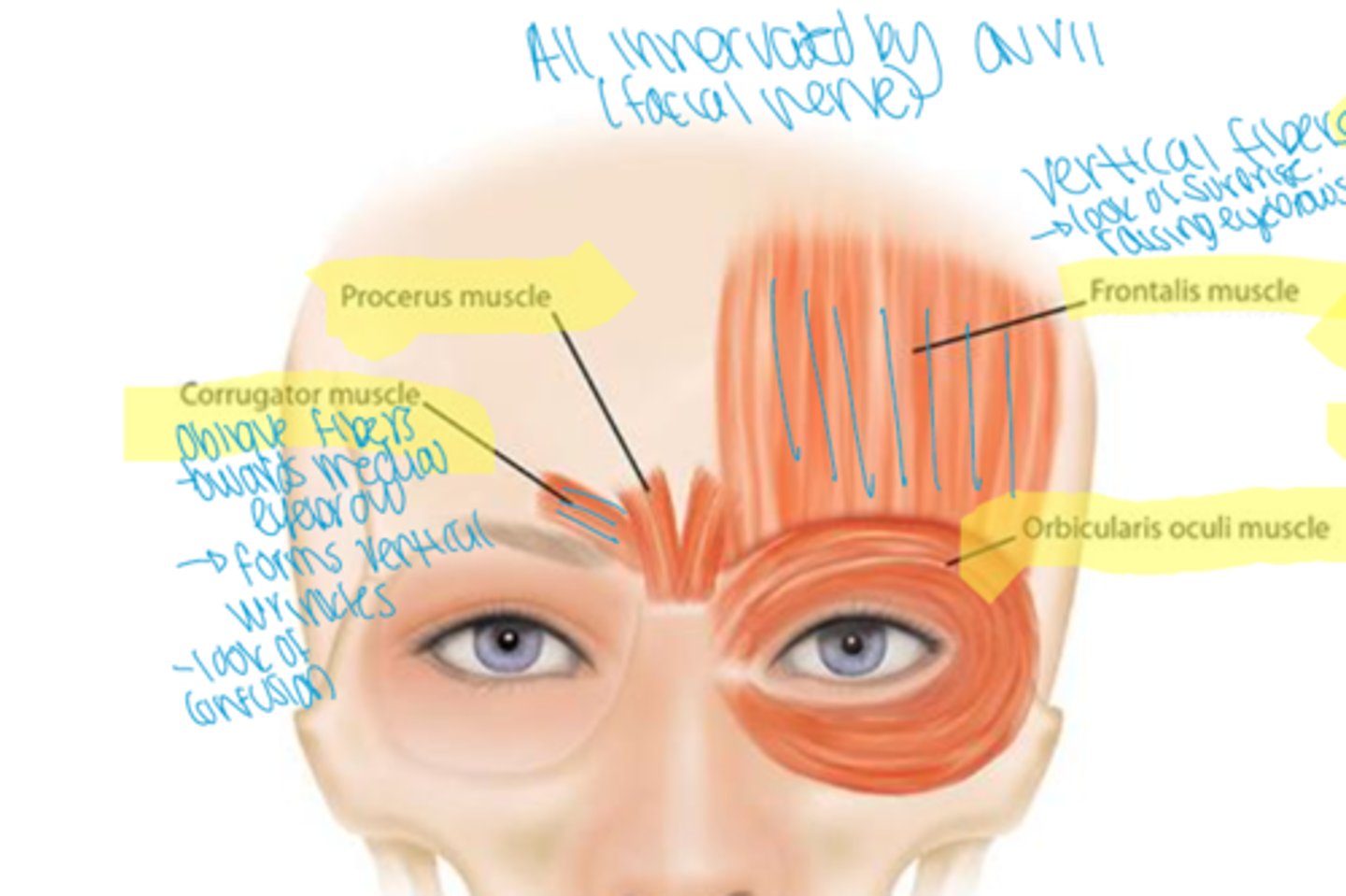
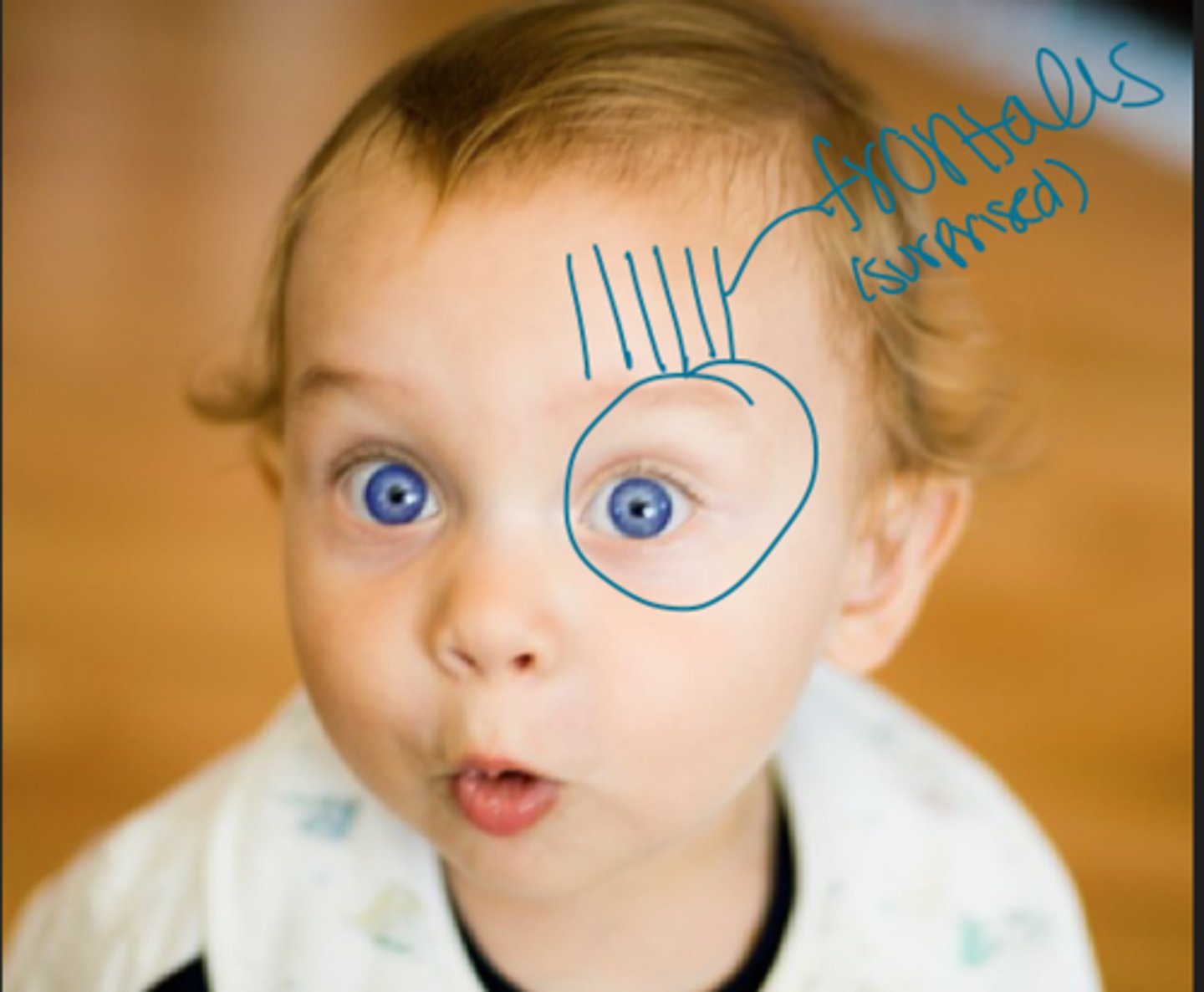
Frontalis
vertical fibers originate high on the scalp and insert near supraorbital margin
-elevates the brows
What muscle is associated with the look of surprise?
Frontalis

What nerve innervates the frontalis muscle?
CN VII (facial nerve )
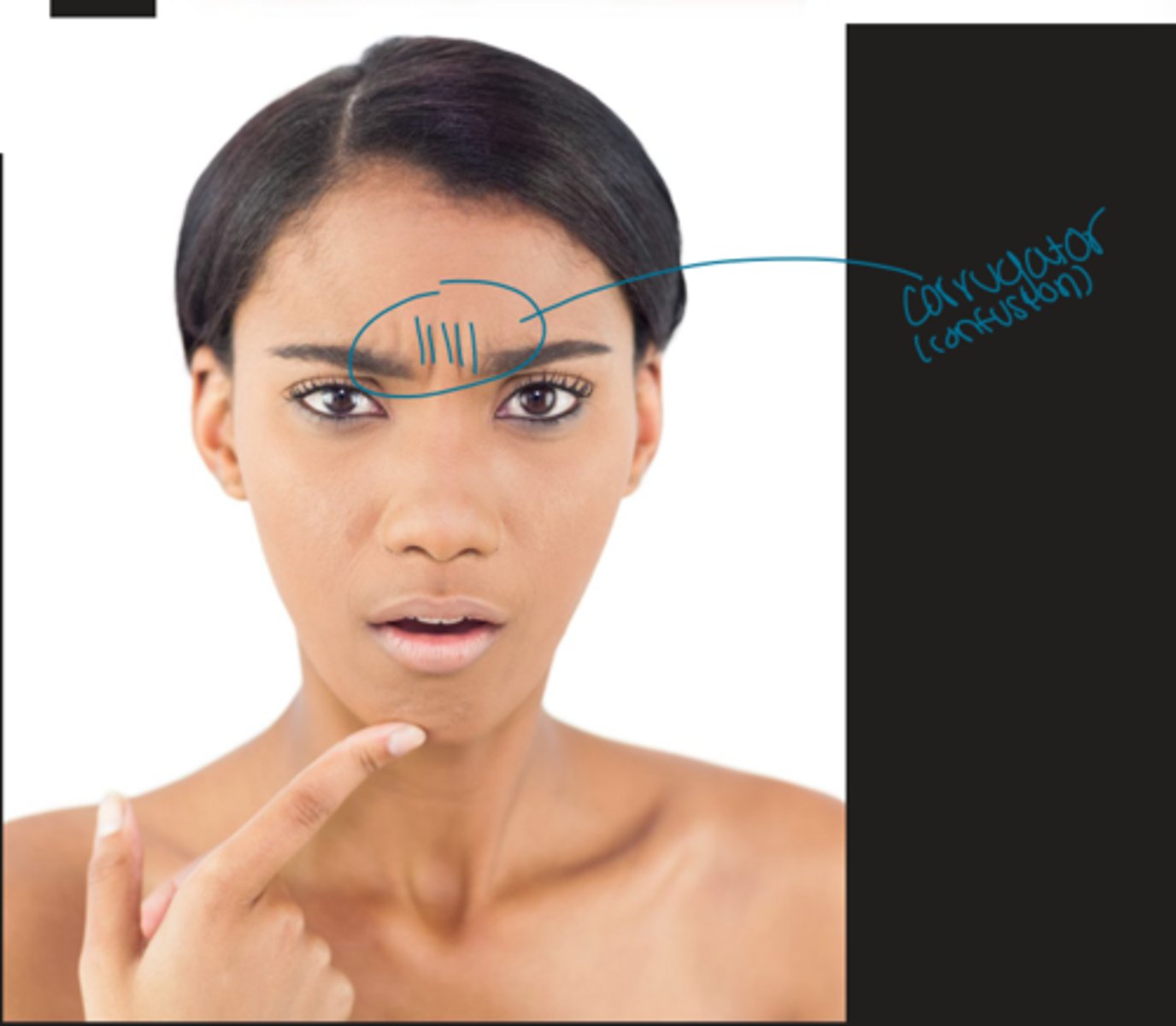
Corrugator
oblique fibers originating from the supracilliary arch and insert into the medial forehead
- depresses medial brows forming vertical wrinkles
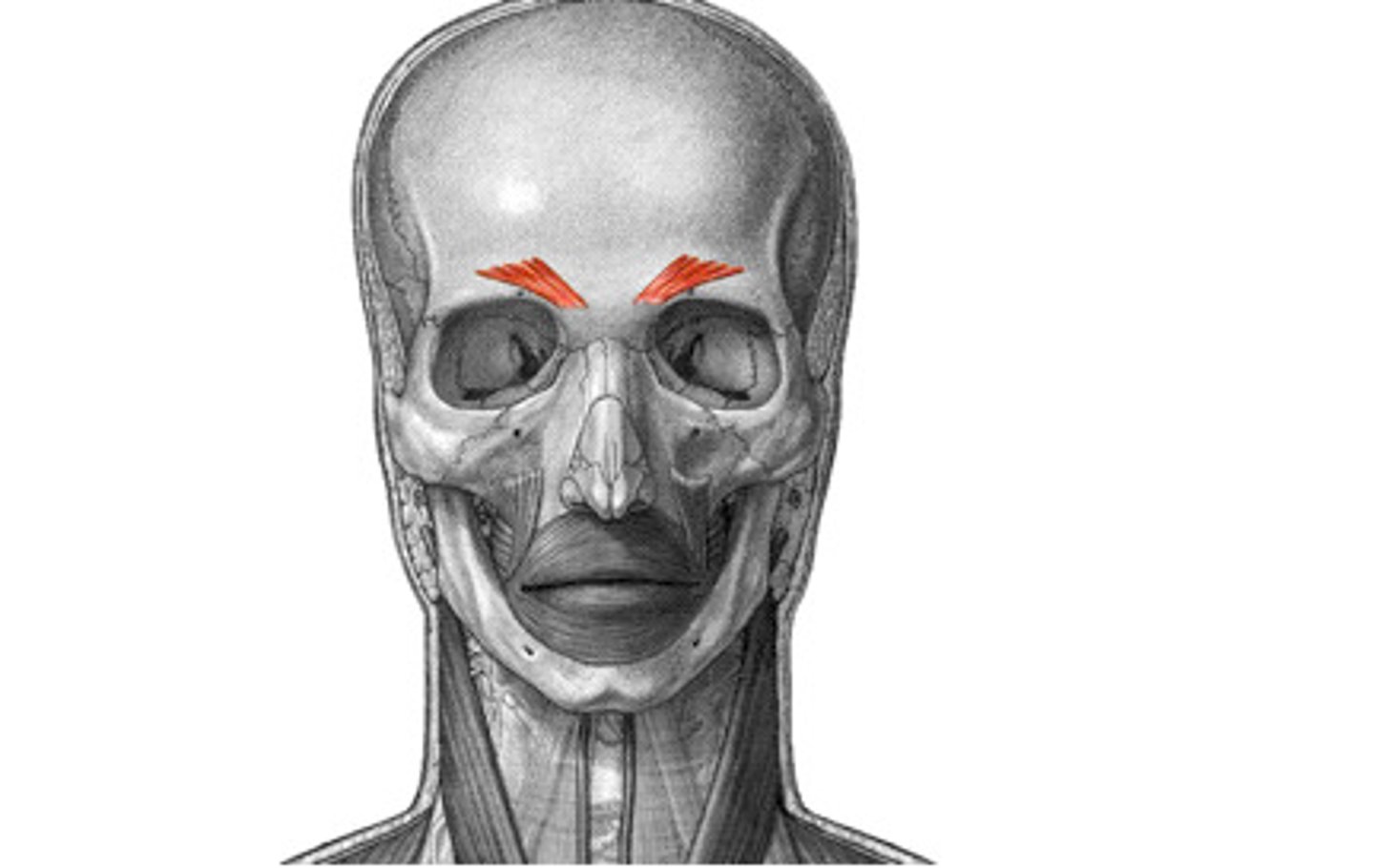
What muscle is associated with the look of trouble/confusion?
Corrugator

What nerve innervates the corrugator?
CN VII (facial nerve)
Procerus
vertical fibers originating from the nasal bone and insert into the medial forehead
-depresses medial brows furrowing horizontal wrinkles across bridge of nose
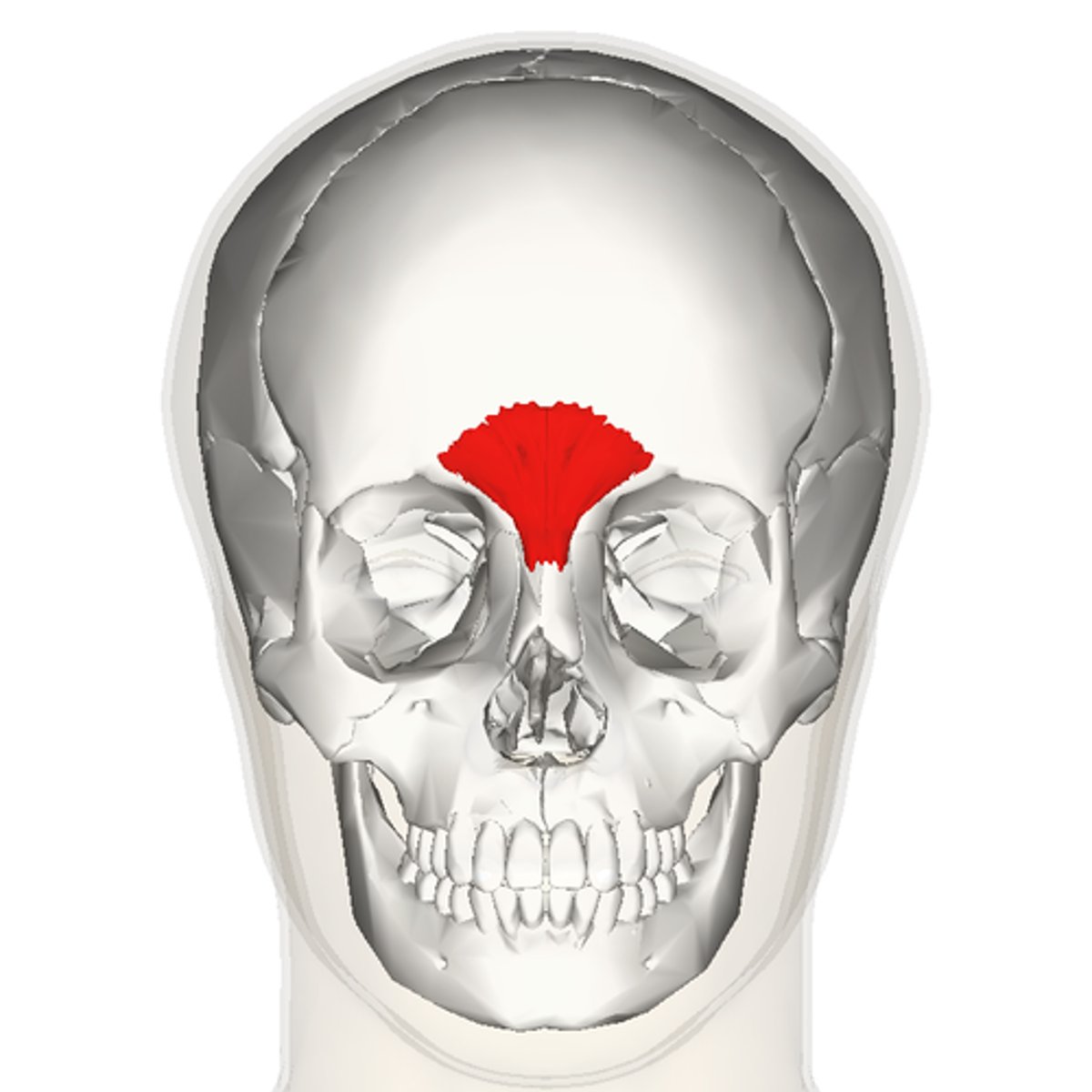
What muscle is associated with the look of menace or anger?
Procerus
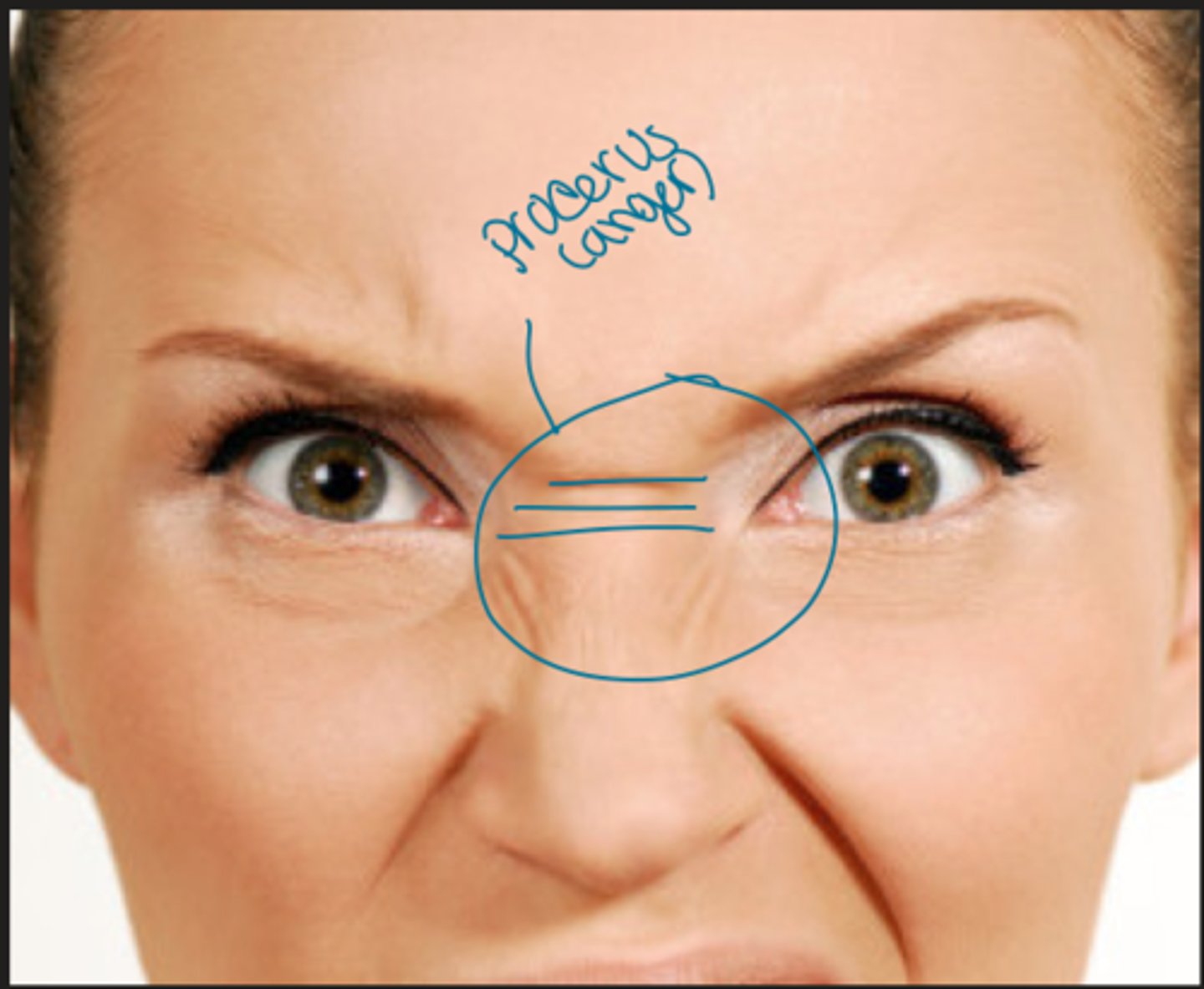
What nerve innervates the procerus muscle ?
CN VII (facial nerve)
orbicularis oculi
Oblique fibers originating from the medial orbital rim to encircle the eye and insert into the lateral palpebral ligament
-depresses the brows and protracts the eyelids
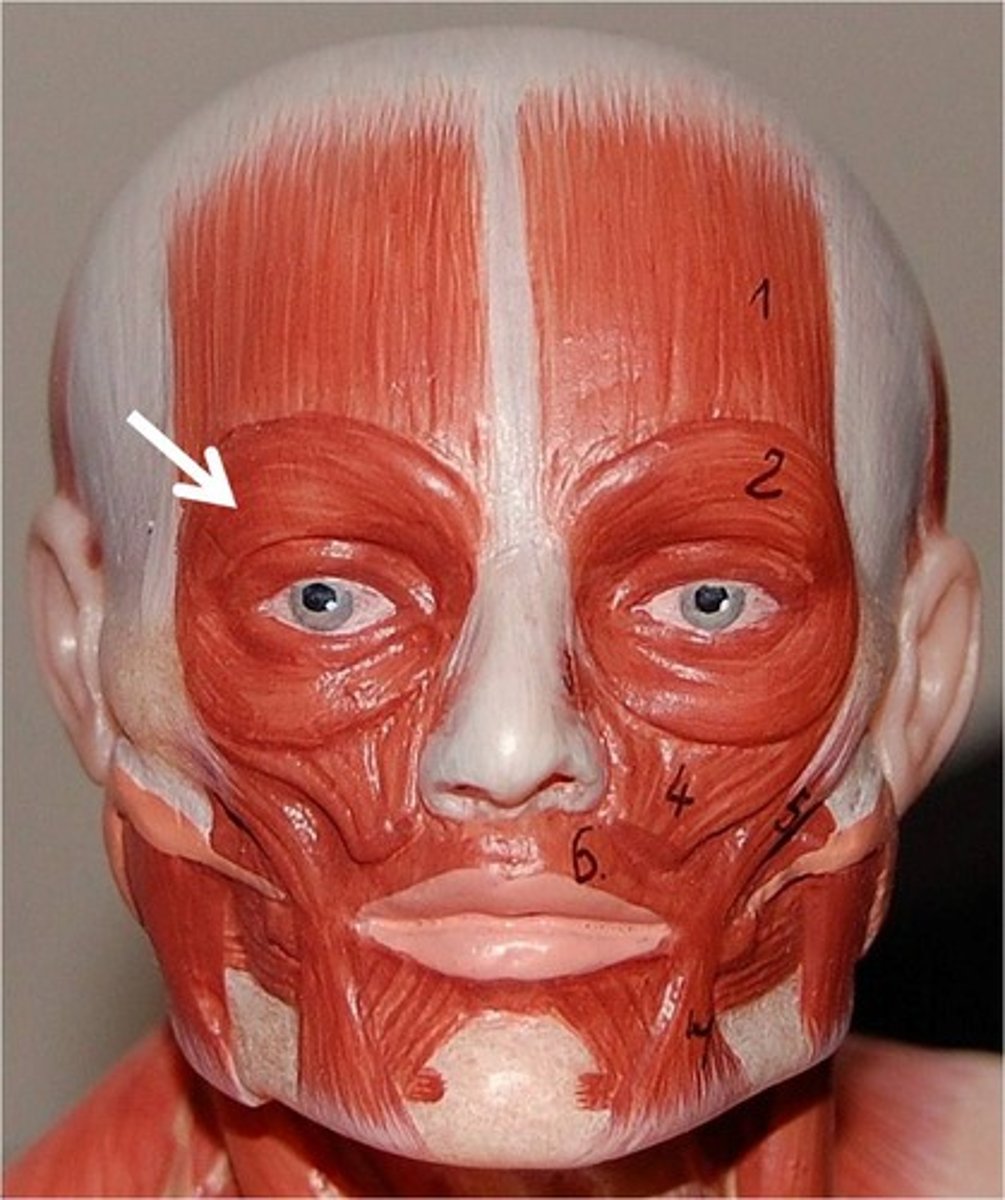
What nerve innervates the orbicularis oculi?
CN VII (facial nerve)
What is loose connective tissue composed of?
fibroblasts, collagen fibers, elastic fibers, adhesive proteins, ground substance
What is the function of loose connective tissue In the skin?
connects the skin, dense connective tissue and the muscles to the underlying periosteum
Why is connective tissue considered the danger zone?
pus and blood can easily spread causing infections to pass into the cranial cavity through veins
What is the periosteum composed of?
dense irregular connective tissue that cover bone
Osteogenic cells
stem cells that divide and differentiate into osteoblasts
osteoblast
form the bone matrix
What are the primary functions of the eyebrows?
- shield liquids from dripping into the eye
-shield from bright light above
-plays role in aging (atrophy and drooping)
-crucial to facial expressions