Chapter Six – Skeletal System
1/82
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A comprehensive set of flashcards capturing key concepts, facts, and definitions from the lecture on the skeletal system.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
What is mindset as defined in the lecture?
The driving force in the quest for success and achievement, combining discipline, strength, confidence, and ambition.
How many major bones are there in the human skeleton?
206 major bones.
What are the two parts of the skeletal system?
The appendicular (appendages) and the axial (bones of the midline of the body).
What are the primary functions of the skeletal system?
Structural support, storage of minerals, blood cell production, protection of underlying organs, and leverage to keep the body upright.
What are the six classifications of bones by shape?
Sutural bones, short bones, flat bones, long bones, sesamoid bones, and irregular bones.
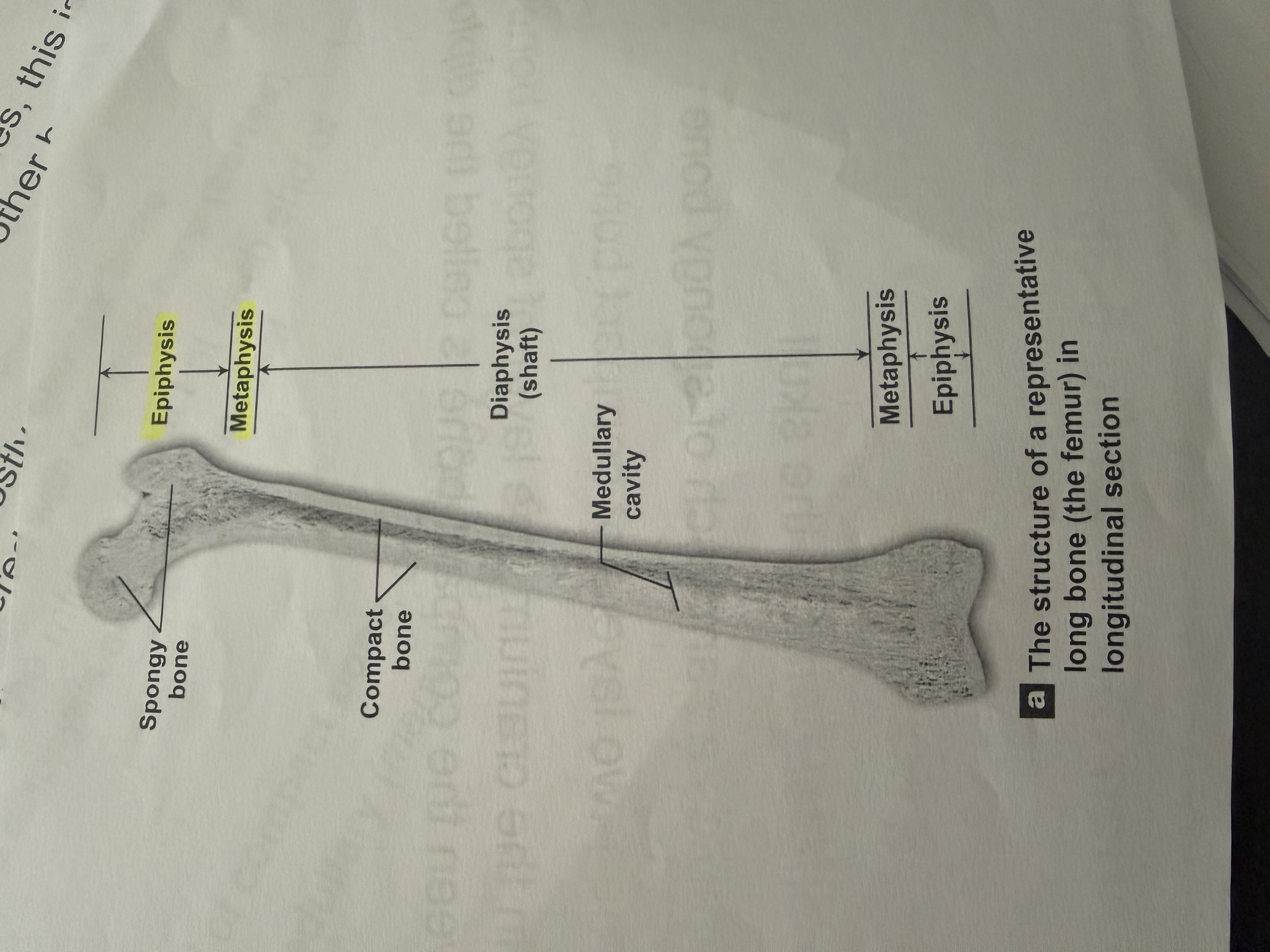
What type of bone is primarily composed of spongy bone and surrounded by compact bone?
Epiphysis.
What is ossification?
The process of bone formation, which includes endochondral ossification and intramembranous ossification.
What are the roles of osteoblasts and osteoclasts in bone homeostasis?
Osteoblasts build bone, while osteoclasts recycle bone.
What mineral is most abundant in the body and vital for the skeletal system?
Calcium.
What is osteoporosis?
A condition characterized by severe bone loss and affects normal function, typically occurring in individuals over the age of 45.
What is the role of calcitonin in calcium regulation?
Calcitonin decreases calcium ion levels by inhibiting osteoclast activity and increasing calcium excretion at kidneys.
What are the four steps in the repair of fractures?
- Formation of a blood clot. 2. Formation of a callus by cells of the endosteum and periosteum. 3. Osteoblasts repair the ends of the bone. 4. Remodeling of the fracture by osteoblasts and osteocytes.
What are the effects of aging on the skeletal system?
Bones become thinner and weaker, leading to conditions like osteopenia and osteoporosis.
What is osteosarcoma?
The most common malignancy of bone in adolescents, characterized by bone pain and may present as a 'sun burst' appearance on radiography.
What distinguishes endochondral ossification from intramembranous ossification?
Endochondral ossification ossifies bones that originate as hyaline cartilage, while intramembranous ossification occurs in the dermis and produces dermal bones.
What factors influence bone growth and maintenance?
Exercise, nutrition, and hormonal factors.
What is the function of the periosteum?
Isolates bone from surrounding tissues, provides a route for circulatory supply, and participates in bone growth and repair.
How does vitamin D3 affect the skeletal system?
It is necessary for the synthesis of calcitriol, which helps absorb calcium and phosphorus from the digestive tract.
Bone Cells make up what percentage of bone mass?
2%
Storage of Minerals of Ca+
salts, which is the most abundant mineral of the body. The way body regulates blood serum Ca+ levels.
Blood cell production
makes RBC’s and WBC’s in the bone marrow of long bones
protection of underlying organs
Hard bones around the brain, thoracic cavity and reproductive organs
leverage to keep the body upright
The heaviest bones are centrally located to keep the organism, centrally balanced
bones are classified by
Shape
Internal tissue
Bone markings
sutural bones
small irregular bones found between flat bones of the skull.
short bones
These are boxy shaped examples of these are ankle, ankles, and wrist bones
flat bones
Thin, broad bones found in the skull sternum ribs and scapula. These allow for muscle attachments and greater surface area.
parietal bones of skull
bone tissue - osseous
dense, supportive, connective tissue
Contain specialized cells
Produces solid matrix of calcium salt deposits
Long bones
Appendages
long & thin
phalanges, humorous, femur, tibia/fibula, radius/ulna
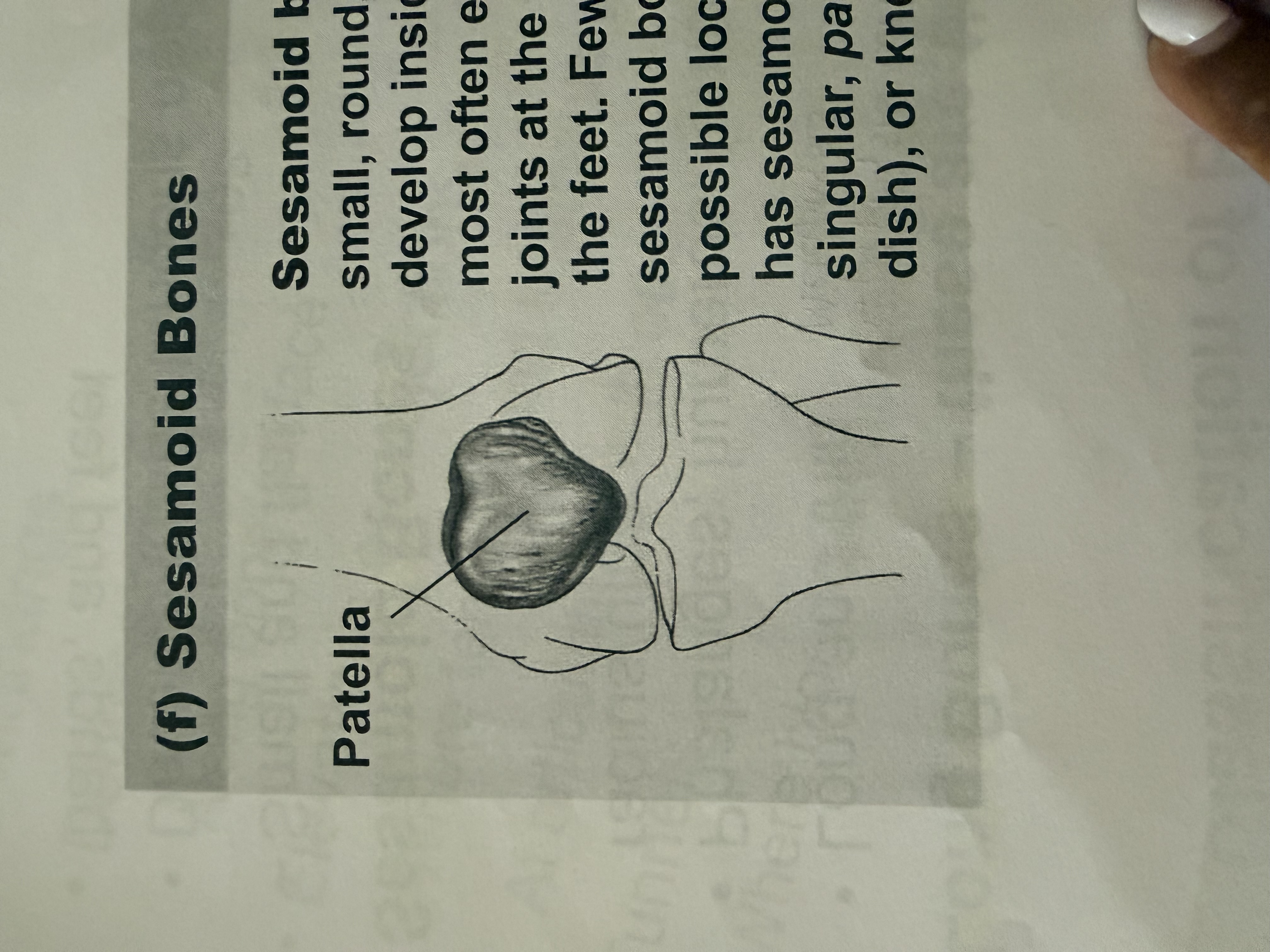
sesamoid bones
small flat bones
develop inside tendons near joints of knees, hands, and feet

irregular bones
Irregular bones have complex shades with short flats, notched, or rigid surface
bone markings
Depressions or grooves along bone surf
Elevations or projections
Tunnels were blood and nerves and her bone
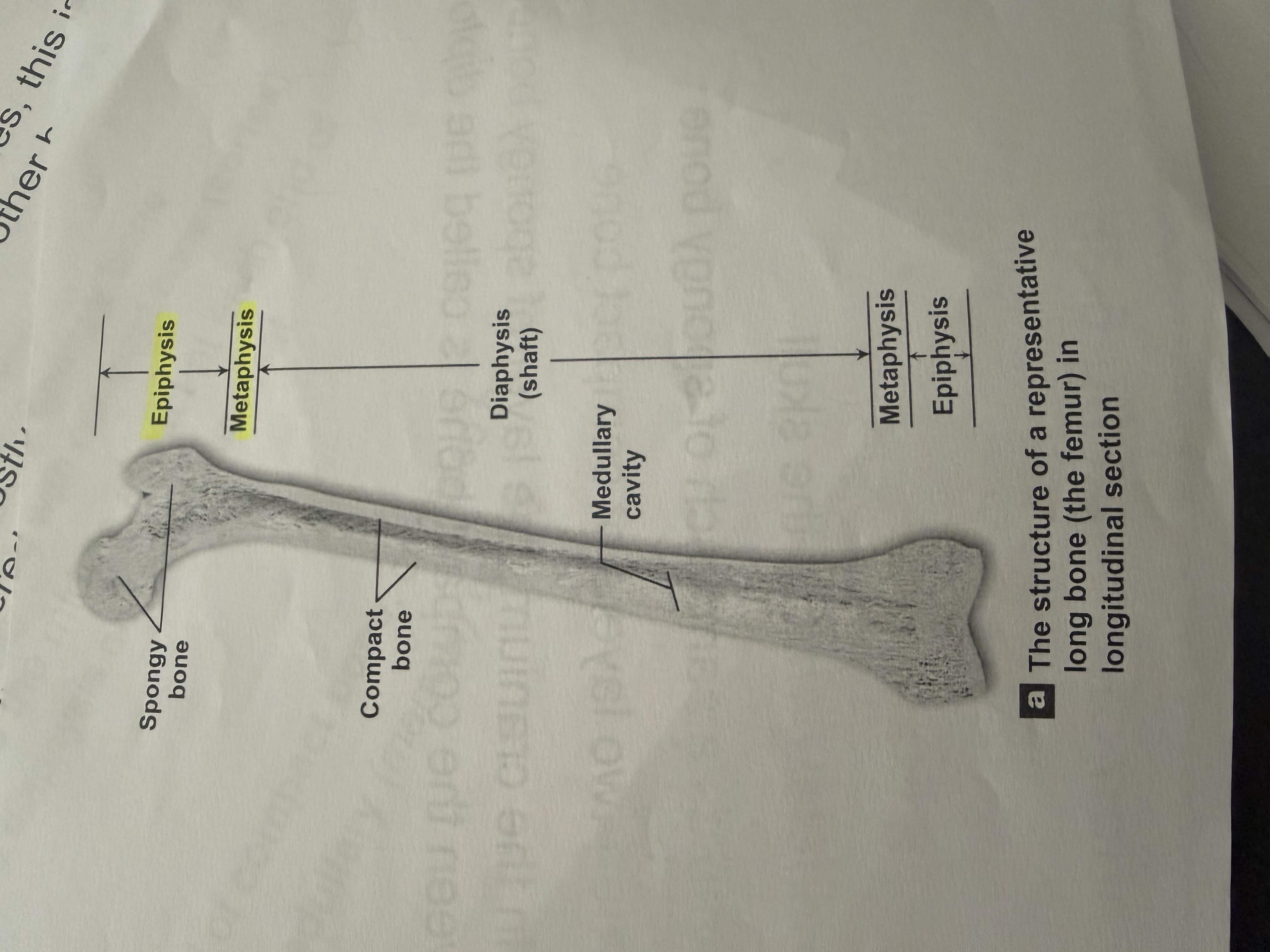
Metaphysis
The middle aspect at each end of the bone.
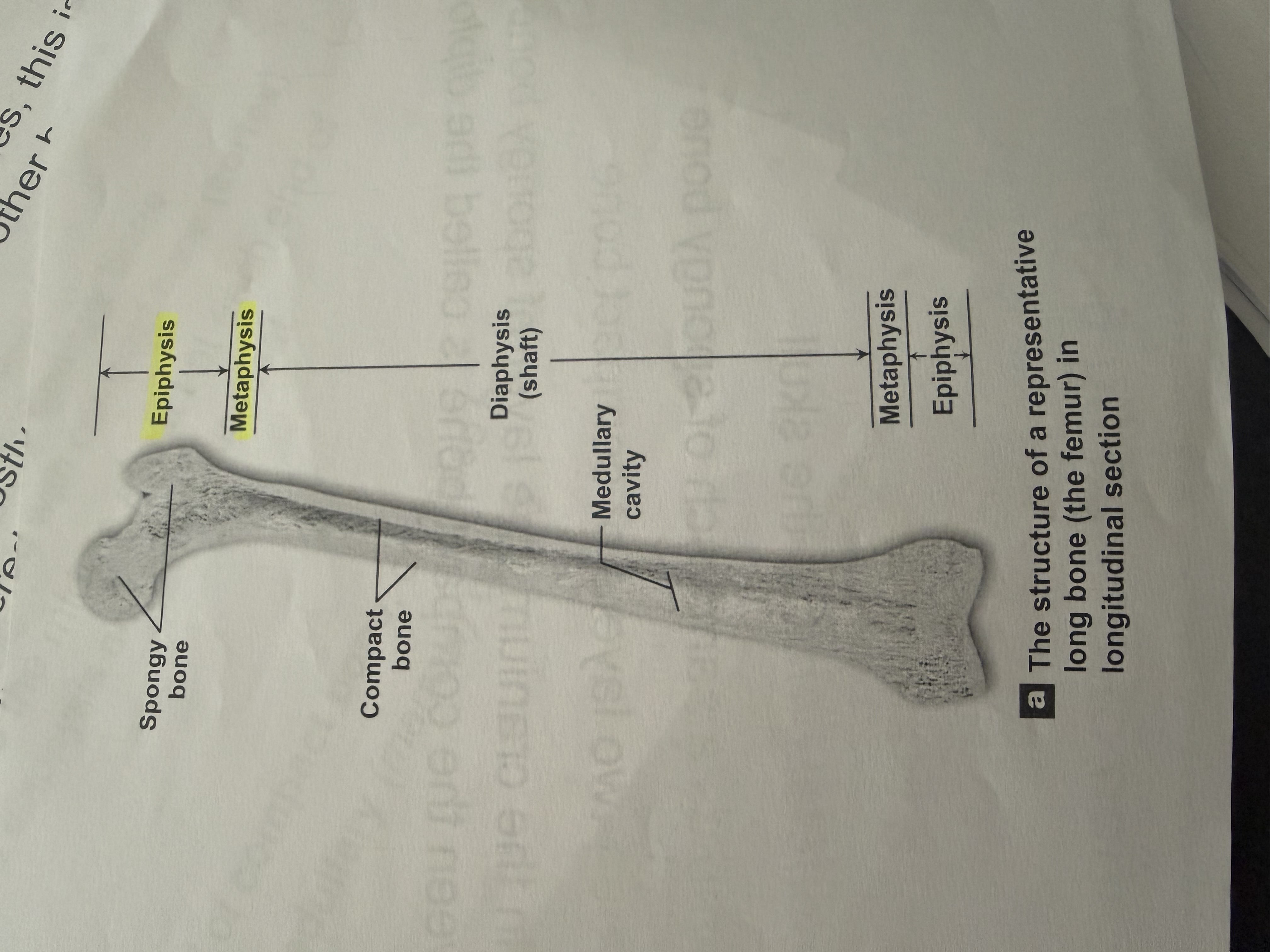
Diaphysis
the shaft
I have a wall of compact bone or dense bone.
Has A central medullary cavity
osteocytes
Mature bone cells forming a pathway to exchange nutrients and waste
containing calcium salts
periosteum
covers outer surfaces of bones
Osteocytes
mature bone cells that maintain the bone matrix
Lives in the lacunae
are between layers lamellae of matrix
2 major functions of osteocytes
maintain protein and mineral
help repair damaged bone
osteoblasts
build bone .
osteoid
osteoblast without calcium
Osteoblast surrounded by the bone then they become osteocytes
osteoclasts
Breakdown bone
osteogenesis cells
mesenchymal stem cells - divide to produce osteoblasts
osteolysis
process to break down bone
homeostasis
Bone building and bone recycling must balance
osteon
basic unit , 1 unit.
osteocytes
arranged in concentric lamellae
perforating canals
perpendicular to the central canal
weight bearing bones
from femur to tibia
transfer weight to hip joint then to knee
transfers kinetic energy forces to compact cone on the medial aspect to support body upright
periosteum
outer layer of bones.
covers all bones except parts enclosed in joint
functions of periosteum
Isolate bone from surrounding tissues.
Endosteum
inner lining of the bone where the medullary cavity is.
appositional growth
100lbs puberty hits for girls . compact bone thickens and strengthens long bone .
epiphyseal line
long bones stop growing after puberty.
epiphyseal cartilage disappears
mature bones
osteoclasts enlarge medullary
process of remodeling
bone continually remodels, recycles and replaces..
vitamin C
required for collagen synthesis and stimulation of osteoblast differentiation
vitamin A
Stimulates osteoblast activity
Vitamin K
help synthesize bone proteins
The skeleton as a calcium reserve
Bone store, calcium, and other minerals
Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the body
how much calcium in bone
39%
how much potassium in bone
0.2%
how much sodium in bone
0.7%
how much magnesium in bone
0.5%
how much carbonate in bone
9.8%
how much phosphate in bone
17%
total organic components
67%
organic compounds in bone
33%
bone contains 99% of the bodies?
Calcium
bone contains 4% of the bodies?
Potassium
bone contains 35% of the bodies?
sodium
bones contain 50% of the bodies?
Magnesium
bone contains 80% of the bodies
Carbonate
bone contains 99% of the bodies
Phosphate
fractures
cracks or breaks in bones
caused by physical stress
compression fractures
jumping from high height
epiphyseal fractures
happens in a child before puberty
green stick feacture
tiny nic in the bone, usually younger or older
colle’s fractures
happens in elderly people usually on radius bone
potts fractures
soccer players, ankles bones.
osteopenia
when bone becomes demineralized between ages 30 & 40
Osteoporosis - loss of spongy bone mass
over age of 50
29% of women
18% of men
osteosarcoma
the most common malignancy of bone seen in an adolescent child.
60-70% of patients survive 5 yrs or more
osteoma
benign tumor in children and adolescents. remove with laser