IB Bio Study Guide units 1,2,3
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This is flascard set is based off the study guide I received
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
hydrogen, carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorous, and sulfur
commonly occuring elements in biology
lipids, proteins, carbohydrates and nucleic acids
commonly occuring biomolecules
Buoyancy
Allows animals to float or sink in water depending on their density sunfish use this to change depths quickly in the ocean
Cohesion
water’s property to stick to itself creates surface tension and allows animals to glide across the water also allows plants to draw water from the ground using xylems.
Adhesion
water’s property to stick to other things allows things to dissolve and allows for water to transport molecules; capillary action in narrow spaces
Condensation
the process of changing monomers to polymers by combining then with covalent bonds and creating polymers
Hydrolysis
adding a water to a polymer to break it a part into monomers
Catabolism
the destructive metabolism process
Anabolism
the creation process of metabolism
Metabolism
all the chemical reactions that happen in a living organism
High Specific heat
water can absorb/release heat with changing temp, organisms use water to stabilize temperature
High Heat of vaporization
absorbs great amount of heat when vaporizing allows body to sweat to release heat
Acidosis
too much acid or too little base causing acid to rip through body and kill you
Alkalosis
too much base or too little acid causing base to rip through body and kill you
Function of Lipids
long term energy storage, membrane structure, hormonal regulation and thermal regulation
function of carbohydrates
short term energy storage and structure
function of Nucleic Acids
store information and participate in protein synthesis
proteins
catalyze reactions, hormonal regulation, transmit information, participate in structure, and transport things.
Lipid
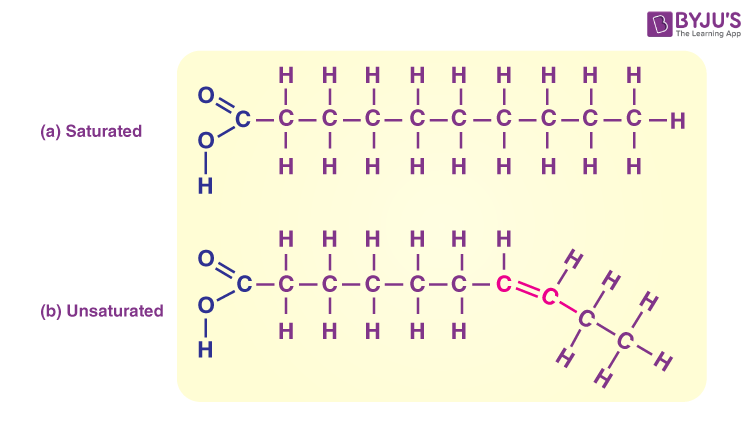
Saturated fats
more unhealthy fats that have all Cs with Hs
Unsaturated fats
fats that have double bonds between C and H and are more healthy
Transcription
DNA is turned into RNA
Translation
RNA is converted into amino acid chain
Factors that affect functionality of proteins
Acidity, Substrate Concentration, and Temperature
Primary structure
A polypeptide chain without links
Fibrous Proteins
Secondary structure used for structure, amine and carboxyl group are linked together
Globular Proteins
Tertiary structure, first functional stage of protein folding
Prosthetic
Inorganic compounds involved in Quaternary stage of folding
5’ to 3’
connection of DNA nucleotides to each other
Silent
point mutation: it produces the same amino acid despite the base change Ex: KAT compared to CAT
Missense mutation
point mutation: changes the base, producing a different amino acid Ex: CAT compared to BAT
Nonsense mutation
point mutation: it changes something to a stop and it doesn’t make sense anymore
Insertion mutation
frame shift: adds a base where it is not meant to be pushing everything back + messing it upp
Deletion Mutation
it deletes a base pulling all bases forward and out of place messing it up