CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND DERIVATIVES
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
How do you name carboxylic acids?
name from the carboxylic end
end in -oic acid
if there are 2 carboxylic groups it will be -dioic acid
What type of acids are carboxylic acids?
weak acids in water and slightly dissociate
strong enough to displace carbon dioxide from carbonates
How soluble are carboxylic acids in water?
smaller carboxylic acids dissolve in water, however solubility decreases when the length of the chain increases, as they can no longer make hydrogen bonds
How are carboxylic acid salts stabilised?
by delocalisation
makes dissociation more likely
delocalised ion has equal C-O bond lengths and if delocalisation didn’t occur, the C=O bond would be shorter than the C-O bond
pi charge cloud has delocalised and spread out, making it more stable and more likely to form
What effects the strength of carboxylic acids?
number of alkyl groups
number of electronegative elements
How does the number of alkyl groups affect the strength of carboxylic acids?
increasing the chain length pushes electron density on the COO- ion making it more negative and less stable
this makes it less strong
How does having electronegative atoms affect the strength of carboxylic acids?
electronegative atoms withdraw electron density from the COO- ion making it less negative and more stable
this makes the acid more strong
What forms when a carboxylic acid and a metal react?
acid + metal → salt + hydrogen
What forms when a carboxylic acid and an alkali react?
acid + alkali → salt + water
What happens when a carboxylic acid and a carbonate react?
acid + carbonate → salt + water + carbon dioxide
How can you test for carboxylic acids?
add a carbonate
effervescence due to carbon dioxide produced
What happens when carboxylic acids react with alcohols?
in the presence of a strong acid catalyst
forms esters and water
heat under reflux
How do you name esters?
the alcohol which joined (the O-C) section ends with -yl
the carboxylic acid containing the C=O bond is -anoate
What’re uses of esters?
sweet smelling compounds used for perfumes and flavourings
used as solvents for polar organic substances
used as plasticisers for polymers
What’re properties of esters?
don’t react with water
used in perfumes
non-toxic
soluble in solvent
volatile
don’t form hydrogen bonds
lower boiling point than hydrogen-bonded carboxylic acids
insoluble in water
What’re the 2 ways to hydrolyse esters?
heating with acid
with sodium hydroxide
How are esters hydrolysed using acid?
reagents - dilute acid
conditions - heat under reflux
reverse reaction of ester formation
forms a carboxylic acid and an alcohol
does not give a good yield of the products
How are esters hydrolysed using sodium hydroxide
reagents - dilute sodium hydroxide
conditions - heat under reflux
reaction goes to completion
using excess sodium hydroxide ensures the ester is completely hydrolysed
forms a sodium salt and alcohol
addition of a strong acid to the salt will convert it to a carboxylic acid
What’re the steps in hydrolysing ethyl benzoate?
liquid ethyl benzoate can be hydrolysed by sodium hydroxide by heating under reflux for 30 mins
allow the mixture to cool to room temperature
add hydrochloric acid
a precipitate of benzoic acid will be produced that can be filtered off using suction filtration
benzoic acid can be purified
Why is sodium benzoate soluble in water but benzoic acid isnt?
benzene ring is non-polar
What’re fats and oils?
esters of glycerol and long chain carboxylic acids (fatty acids)
vegetable oils and animal fats can be hydrolysed to give soap, glycerol and long chain fatty acids
What is glycerol?
propane-1,2,3-triol
forms hydrogen bonds very easily
readily soluble in water
used in cosmetics, food and glues
How does soap work?
long chain carboxylic acids produced by the hydrolysis of fats
polar CO2- end is hydrophilic and mixes with water
long non-polar hydrocarbon chain is hydrophobic and mixes with grease
allows grease and water to mix and be washed away
What is biodiesel?
mixture of methyl esters of long chain carboxylic acids
How can vegetable oils be converted into biodiesel?
by the reaction with methanol in the presence of a strong alkali catalyst
How is biodiesel produced from vegetable oils carbon-neutral?
any carbon dioxide given off when the biofuel is burnt would’ve been extracted from the air by photosynthesis when the plant grew
doesn’t take into account any energy needed to irrigate plants, extract the oil, heat the reaction with methanol mixture or process the fuel
What’re acyl chlorides?
more reactive than carboxylic acids
Cl is classed as good leaving groups
ends with -oyl chloride
mostly give off HCl
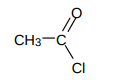
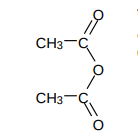
What’re acid anhydrides?
similar reactivity to acyl chlorides
mostly give off RCOOH
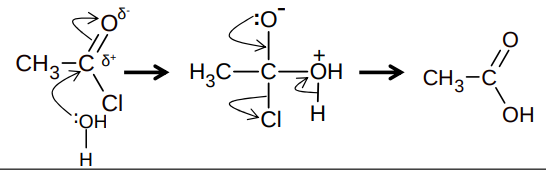
What happens when acyl chlorides react with water?
form a carboxylic acid
reagent - water
conditions - room temp
observation - steamy white fumes of HCl
What happens when acid anhydrides react with water?
form a carboxylic acid
reagent - water
conditions - room temp
What is nucleophilic addition elimination mechanism between water and an acyl chloride?
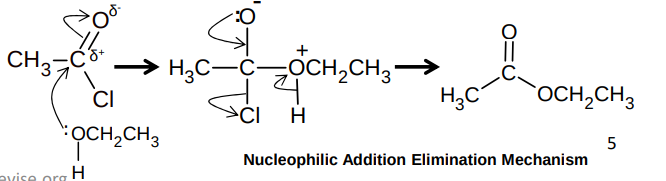
What happens when an acyl chloride reacts with alcohol?
forms an ester
reagent - alcohol
conditions - room temp
observation - steamy white fumes of HCl
What happens when acid anhydrides react with alcohol?
forms an ester
reagent - alcohol
conditions - room temp
What is the nucleophilic addition elimination mechanism between an acyl chloride and an alcohol?
Why is it preferred to make esters from acyl chlorides compared to carboxylic acids?
quicker reaction
not a reversible reaction
What happens when acyl chlorides react with ammonia?
forms a primary amide
reagent - ammonia
conditions - room temp
observation - white smoke of NH4Cl
What happens when acid anhydrides react with ammonia?
forms a primary amide
reagent - ammonia
conditions - room temp
What is the nucleophilic addition elimination reaction between an acyl chloride and ammonia?
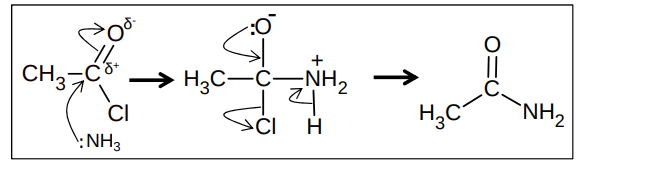
How do acyl chlorides react with primary amines?
forms a secondary amide
reagent - primary amine
conditions - room temp
How do acid anhydrides react with primary amides?
forms a secondary amide
reagent - primary amine
conditions - room temp
What is the nucleophilic addition elimination mechanism between an acyl chloride and a primary amine?
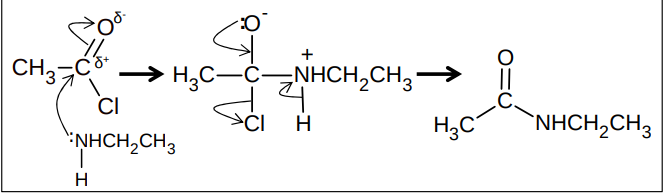
Why are acid anhydrides used instead of acid chlorides?
cheaper
less corrosive
less vulnerable to hydrolysis
less dangerous to use
What’re the steps involved in purifying aspirin?
dissolve the impure compound in a minimum volume of hot solvent
hot filter the solution through filter paper quickly
cool the filtered solution by inserting a beaker in ice
suction filtrate with a buchner flask and funnel to separate out crystals
wash the crystals with distilled water
Why do you use a minimum volume of hot solvent?
appropriate solvent is one which will dissolve both compound and impurities when hot and one in which the compound doesn’t dissolve well when its cold
minimum volume is used to obtain a saturated solution and enable crystallisation on cooling
Why do you hot filter the solution?
removes any insoluble impurities and heat will prevent crystals reforming during filtration
Why do you cool the solution using ice?
crystals reform but soluble impurities remain in solution as they’re present in small quantities
ice will increase the yield of crystals
Why do you suction filtrate?
reduces the pressure and speeds up filtration
Why do you wash crystals with distilled water?
removes soluble impurities
How is the yield lost due to recrystalisation?
crystals lost when filtering or washing
some product stays in solution after recrystallisation
other side reactions occurring
What happens to the melting point if impurities are present?
melting point will be lowered
sample will melt over a range of temperatures
How do you find the melting point of a substance?
place the substance in a capillary tube
place a thermometer in some heating oil
heat slowly near the melting point
measure the point which it melts
How do you verify the degree of impurity?
compare the experimentally determined melting point value with one quoted in a data source