Plant and Fungi Exam Review
1/90
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Quiz corrections
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
Explain/Name shared characteristics between plant + fungi
Both reproduce sexually and asexually
Are stationary
Cells with a nucleus enclosed in the membranes
Have Cell walls
Explain/Name characteristics that differ between plant + fungi
Plant cell walls are made of cellulose, fungi are made of chitin
Fungi are heterotrophs, and plants are autotrophs
Fungi have a network of tubes with tiny holes in them called conidia
Fungi are more closely related to animals than to plants
Name one important difference between fungi and plants
Fruiting Bodies in fungi are different from plants that are able to produce fruit. The concept of a fruiting body for a fungus instead relates to the appearance of fungi having a stem and capped top. Plants that can bear fruit are called angiosperms.
Concisely explain two advantages that the terrestrial environment provided for first land plants
Advantage 1: Sunlight abundance = more readily available and bright unfiltered sunlight
Advantage 2: Plentiful CO2 and soil minerals = CO2 is more readily available in the air than in water, and soil minerals are essential for plant growth.
Which evolved first, fungi or land plants?
Fungi
What is the age estimate for fungi and land plants?
Fungi: ~1,300 MYA
Land Plants: ~500 MYA
What are two major structural adaptations of land plants?
1: Alternation of generations, provided a lifecycle with sporophyte the produces spores and a gametophyte that produces gametes.
2: Apical meristem tissue: involved in growth and found in roots and shoots.
What are the 4 major fungal phyla?
Chytridiomycota, Ascomycota, Basidiomycota, and Glomeromycota
What are all 200 species of Glomeromycota involved in?
symbioses with plants
What fungi is the sac-fungi
Ascomycota
Ascomycota are typified by the production of what?
Ascus or a sac-like structure containing spores
What fungi produce mushrooms?
Basidiomycota
What trait do Chytridiomycota have that led to them being most similar to ancestral fungi, and the only fungi that possess this trait?
A singular Flagellum
Chytridiomycota
Organisms in this phylum are characterized by the production of motile zoospores; these fungi are commonly parasitic and/or decomposers of organic matter in aquatic environments.
Ascomycota
The most species-rich phylum; meiospores are enclosed inside the fruiting body in these fungi.
Glomeromycota
No sexually-reproducing members of this phylum have been discovered; its fungi produce relatively large spores.
Basidiomycota
Known for forming large fruiting bodies with meiospores housed externally in club-shaped structures.
Anatomical/ Reproductive feature that is common in Dikarya
It’s a fungal cell/ mycelium that contains two genetically distinct but unfused nuclei
Occurs after plasmogamy and before karyogamy
Fruitification of sexual morphs:
Formation of specialized fruiting structures
Common name for a bryophyte
Moss
Common name for a seedless vascular plant
Ferns
Common name for a gymnosperm
Conifers
Common name for a angiosperm
Apple trees
How are Gymnosperms distinguished?
Has naked seeds exposed in cones
How are Angiosperms distinguished?
Have seeds enclosed in a fruit
First vascular plalnts; produce microphylls
lycophytes
Have a dominant gametophyte generation
Bryophytes
Make flowers and seeds
Angiosperms
A pine tree and a ginko are plants in this group
Gymnosperms
Have spore-based reproduction and vascular tissue:
Monilophytes
Two major organ systems of vascular plants
shoot system (leaves, stems, flowers and fruits)
Root system
3 major differentiated types of tissue in a vascular plant
dermal
vascular
ground tissue
Name the most common plant cell type
parenchyma cells
The major tissue systems in plants are dermal, parenchyma, and ground tissue, and all three are found in roots, stems, and leaves.
False, dermal, vascular, and ground tissue are the three major tissue systems
All plant cells have chloroplasts, but only some plant cells contain a primary cell wall.
False: Chloroplasts are not in each cell, only in ones that receive sunlight.
In a single plant cell, vacuole volume has been estimated to be as little as 25% of the total cell volume and as much as 90% of the total cell volume.
True
In both roots and shoots, vascular tissue forms a central cylinder called a stele
True
Primary vs Secondary growth
Primary - adds length to the platn stem and cells are able to undergo cell division
secondary - adds girth to stem and unable to undergo constant cell division
Accurately describe a key feature of primary growth in roots
Occurs at the root tip, where apical meristem cells divide to produce the root cap and elongate cells.
In a cross-section of an herbaceous dicot stem, vascular bundles are arranged in a ring. Accurately describe the vascular bundles.
Embedded within ground tissue and contain xylem, phloem, and a layer of vascular cambium.
Distinguishing feature of palisade mesophyll from the spongy mesophyll in a typical dicot leaf
Palisade mesophyll cells are columnar and densely packed near the upper surface for efficient light capture, while spongy mesophyll cells are irregular and spaced out to allow gas exchange
What best describes the function of endodermis in roots?
It forms a selective barrier that regulates the movement of water and solutes into the vascular cylinder
Describe the strongly supported hypothesis for how water/nutrients move in a plant using one concise sentence
The cohesion-tension theory explains that water and nutrients move up a plant due to water's cohesive properties, adhesion to xylem walls, and transpiration creating tension that pulls water upwards.
Describe one major effect that auxin has on growth and/or development using one concise sentence
Auxin influences plant growth by promoting cell elongation and causing plants to bend towards light, a process known as phototropism; auxin facilitates this by concentrating on the shadier side of the plant, stimulating cell growth there.
Describe cohesion-tension hypothesis in three concise sentences or fewer
Water and nutrients ascend in plants due to water’s cohesive nature and adhesion to xylem walls. Transpiration creates a tension that pulls water upwards. This comprehensive process allows plants to efficiently transport essential substances.
Concisely describe one major difference between angiosperm and gymnosperm reproduction with a single sentence
Angiosperms reproduce through flowers, resulting in seeds enclosed in fruits, and gymnosperms reproduce via cones, with naked seeds unenclosed.
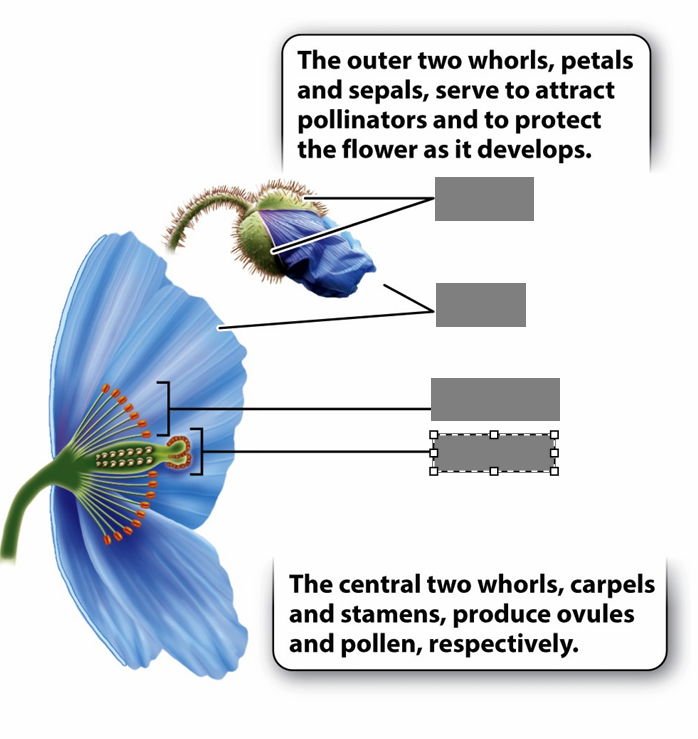
What are the 4 parts of a flower
Septals = calyx
Petals = corolla
Stamen
Carpel
Gymnosperm microsporangia
Male cones
Gymnosperm Megasporangia
Female cones (ovule)
Angiosperms microsporangia
Anther
Angiosperms megasporangia
Carpel (ovule)
Concise sentence to describe one major pollination difference between gymnosperms and angiosperms
Gymnosperms rely on wind for pollination, while angiosperms utilize a variety of methods, including insects, birds, and mammals.
One structural feature of fungal cells that is unique to fungi
Cell walls made of Chitin
Septa
Walls that divide fungal hyphae into sperate cells, often with small pores
Filamentous
Describes fungi that grow in long threads or filaments rather than as single cells
Mycelia
A mass of branching, thread-like structures that forms the main body of some fungi
Yeast
Describes a unicellular form of fungi that reproduces by budding or fission
Hypha
A single long thread-like fungal cell that may branch
What does saprobe mean?
Saprobes are fungi that are heterotrophs and not able to photosynthesize. Instead, they’re able to break down dead organic matter for nutrients, making them saprobes.
Describe pressure-flow hypothesis in three concise sentences or fewer
The pressure-flow hypothesis explains how plants transport nutrients. It says that sugar production creates high pressure, pushing sap through phloem. This sap moves from source to sink, delivering nutrients to plant parts.
what is a similarity between sporangiospores and conidia?
Both produce spores
what is a difference between sporangiospores and conidia?
Sporangiospore production is internal while conidia are external
Define Homothallic
They can switch mating type
Define heterothallic
can’t switch mating type
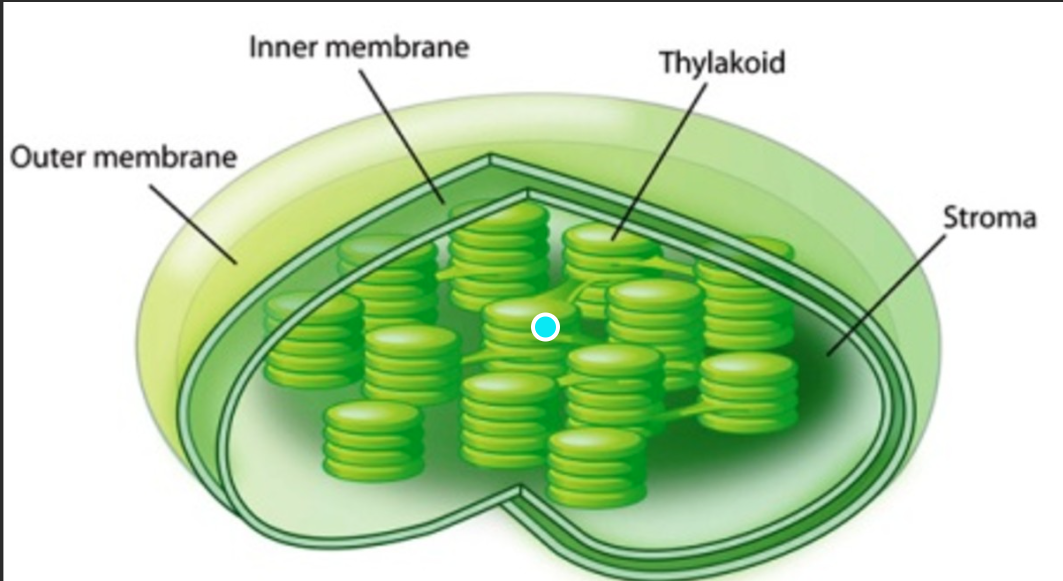
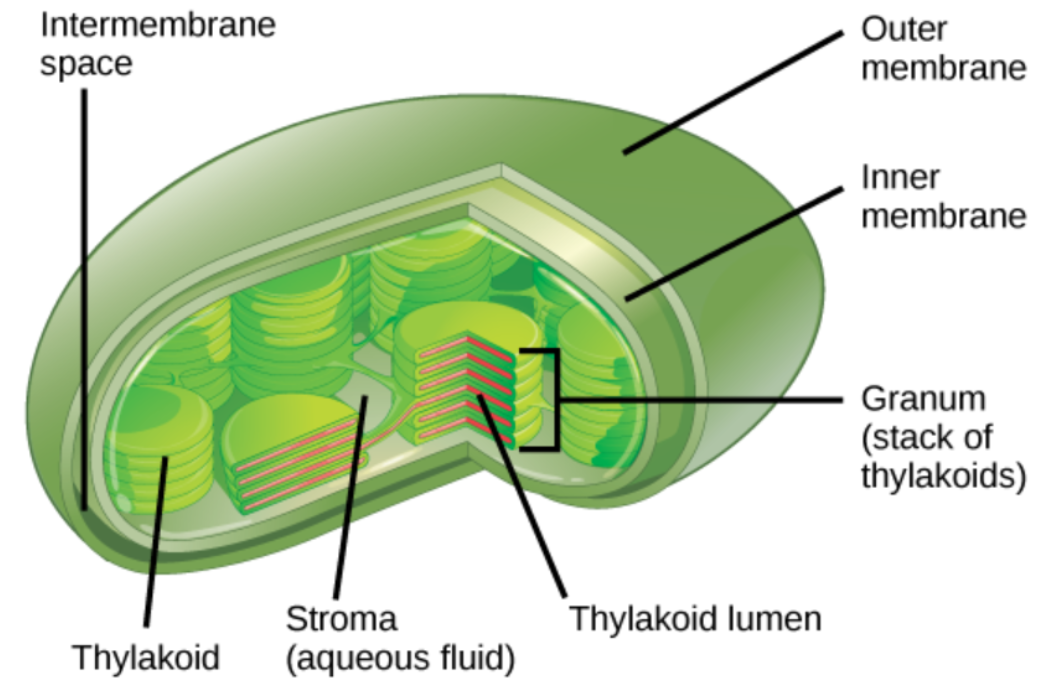
What is depicted in the image?
Chloroplast
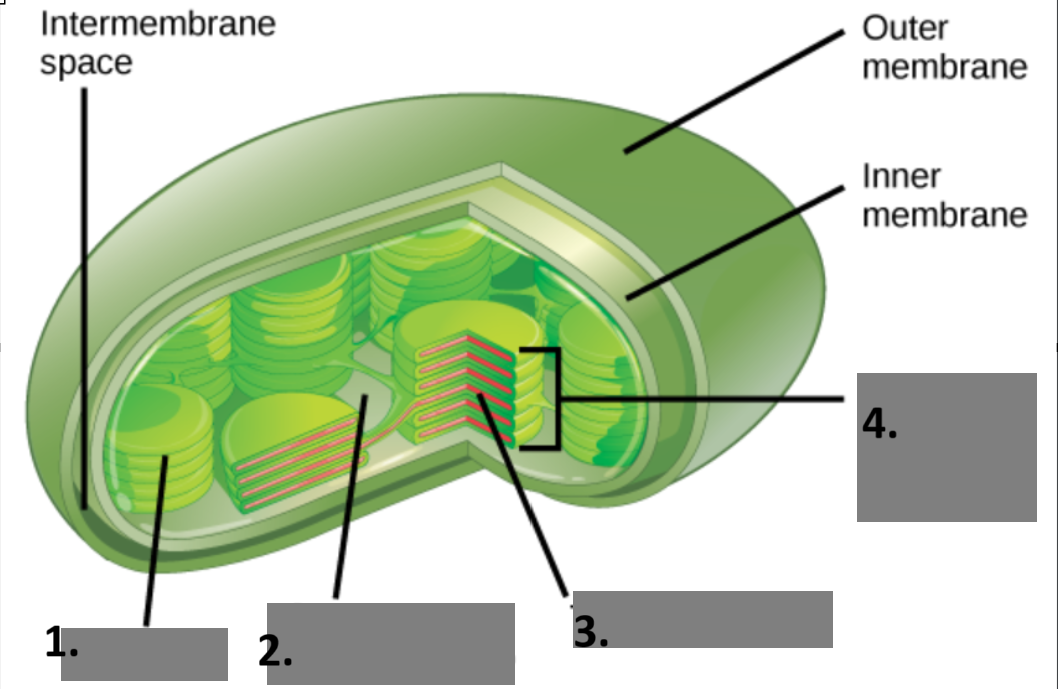
Label the parts of chloroplast
thylakoid
stroma
Thylakoid Lumin
Granium
Describe why too little light can be detrimental to plant growth
Light is essential for photosynthesis, it helps to initiate the process so plants can make glucose
Describe a specific response that plants have when dealing with low light quantity
Increase surface area cause bigger leaves can help to store more nutrients when light is not as abundant
Describe a specific response that plants have when dealing with high light quantity
Produce pigments like carotenoids and anthocyanins to absorb excess light energy and protect chlorophyll from damage. Develop smaller, thicker leaves or increase leaf reflectance by developing a waxy cuticle or leaf hairs
Describe why too much light can be detrimental to plant growth
Leads to radical oxygens that will lead to apoptosis of plant cells
What is the main source of energy in photosynthesis?
Light
What is the main energy source in fungi?
organic molecules
What is the main carbon source in photosynthesis?
Carbon dioxide
What is the main carbon source in fungi respiration
Glucose
Amylases
Amylases break down starch into simpler sugars. Example environment: bread mold growing on starchy bread.
Cellulases
Cellulases degrade cellulose, a major component of plant cell walls. Example environment: fungi decomposing dead plant litter in a forest.
Proteases
Proteases breakdown proteins into peptides or amino acids. Example environment: fungi decomposing animal carcasses in soil.
Lipases
Lipases break down lipids (fats and oils) into glycerol and fatty acids. Example environment: fungi growing on oily seeds or nuts.
Xylanases
Xylanases degrade xylan, a component of plant cell walls. Example environment: fungi breaking down wood in a decaying log.
Pectinases
Pectinases break down pectin, another component of plant cell walls. Example environment: fungi causing fruit rot.
Name the two major types of mycorrhiza
Ectomycorrhizae (EM) and Endomycorrhizae
Difference between the two major types of mycorrhizae
Ectomycorrhizae form a sheath around the root and penetrate between root cells, while endomycorrhizae penetrate root cells, forming arbuscules.
What similarities between Ericoid and Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
Both enhance nutrient uptake and stree tolerance in plants
What difference between Ericoid and Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
Arbusular are found in 70-80% of plants and Ericaceae are found in 1-3% of plants
One way fungi benefit humans
Can make medicine with fungi, like penicillin
One way plants benefit humans
Plants are a valuable resource for food, and clothes, providing essentials for humans
What nitrogen source can all fungi use?
Glutamine/Glutamate
Briefly describe the form and function of Rhizomorph
Form = thread-like or cord-like structure
Function = Act as an absorption and translation organ of nutrients by decaying roots and wood. Can reach areas where food resources are scarce, being an advantageous trait
Briefly describe the form and function of Spitzenkorper
Form = Small vesicles in the hyphal tip
Function = Organizing center for hyphal growth, present in growing hyphal tips, during spore germination, and where branch formation occurs
meiosis in fungi reproduction
involved reductional nuclear division, and produces haploid cells
plasmogamy
protoplasm of two parent cells fuse without the fusion of nuclei. Brings two haploid nuclei close together in the same cell
Karyogamy
Two haploid nuclei fuse to form a diploid nucleus during sexual reproduction in fungi