BIO319-FINAL-SPRING-2025
1/410
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
411 Terms
Naegleria fowleri
Brain-eating amoeba in the Percolozoa phylum.
Point mutation
Single nucleotide change in DNA sequence.
Silent mutation
No change in amino acid sequence.
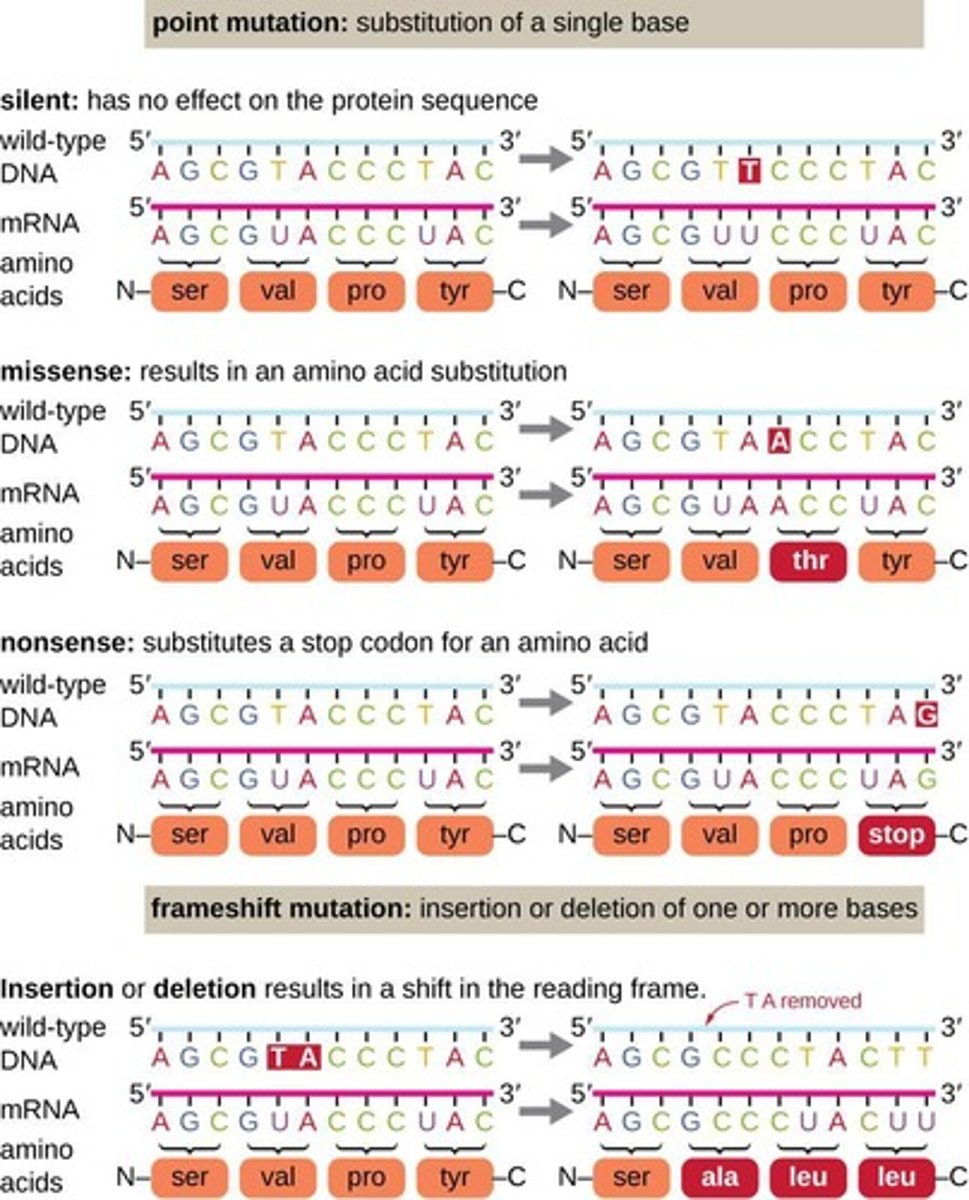
Missense mutation
Change in one amino acid in protein.
Nonsense mutation
Creates a premature stop codon.
Insertion mutation
Addition of nucleotides in DNA sequence.
Deletion mutation
Removal of nucleotides from DNA sequence.
Frameshift mutation
Disruption of reading frame due to insertions/deletions.
Inversion mutation
DNA fragment flipped in orientation.
DNA polymerase
Enzyme that synthesizes new DNA strands.
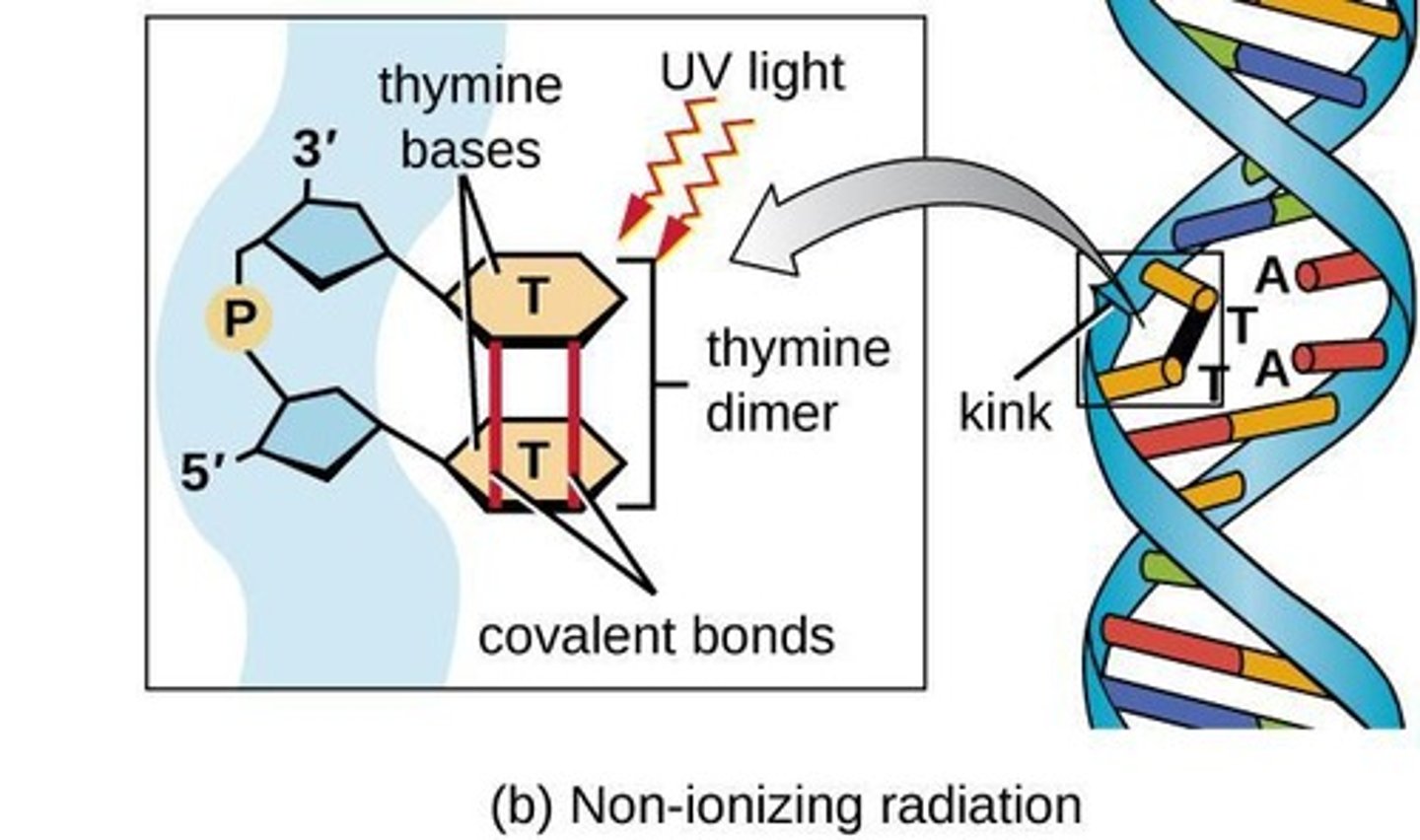
Pyrimidine dimers
DNA damage caused by UV radiation.
Base excision repair
Removes specific damaged DNA bases.
Methyl mismatch repair
Corrects mismatched bases using methylation patterns.
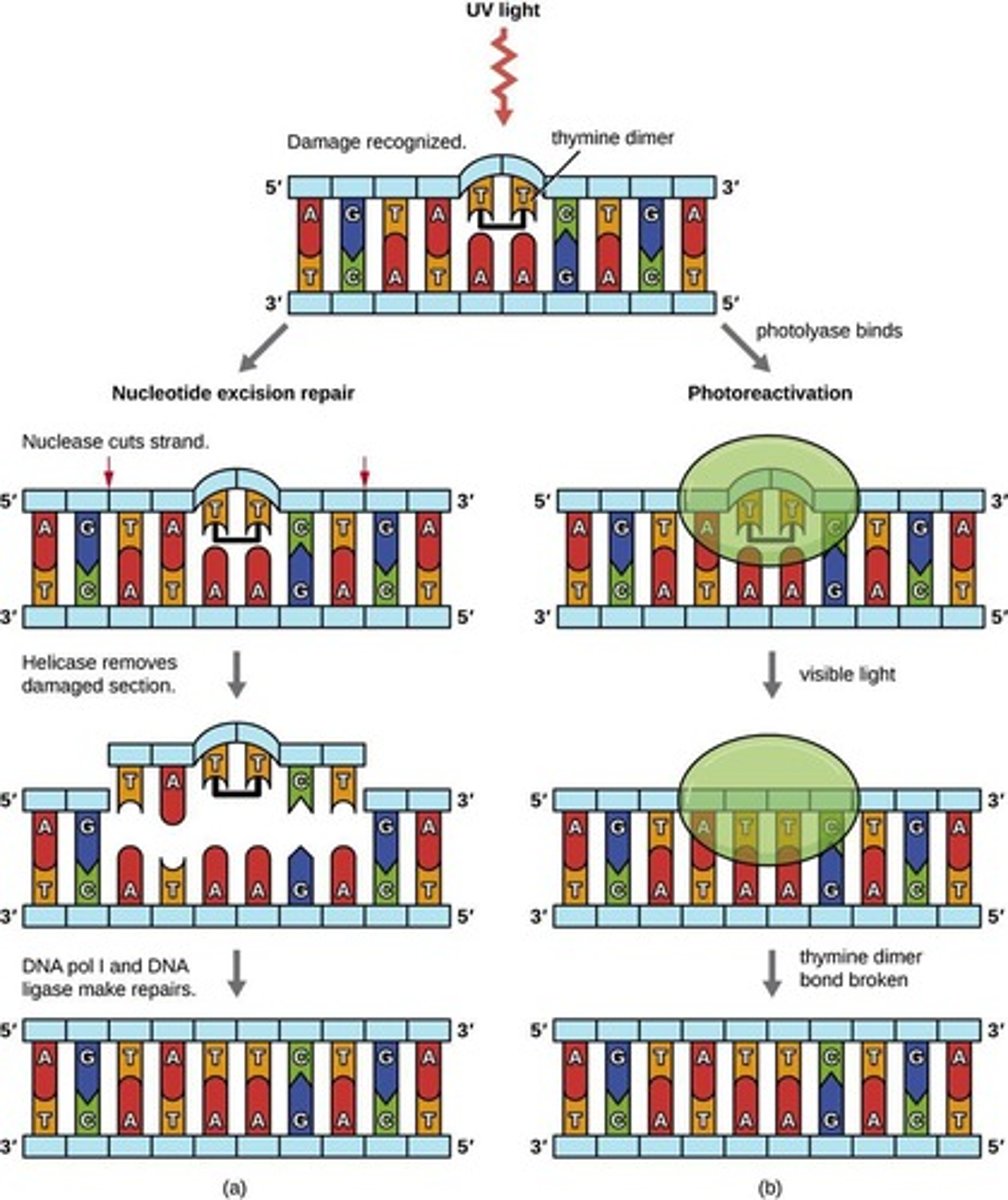
SOS repair
Cellular response introducing mutations to save cell.
DNA recombination
Exchange of genetic material between DNA molecules.
Transcription regulation
Control of gene expression at transcription level.
Translational control
Regulation of protein synthesis initiation.
Post-translational control
Modifications after protein synthesis to regulate activity.
Operon
Gene cluster controlled by a single regulatory region.
Global regulators
Proteins affecting expression of multiple genes.
Vertical gene transfer
Gene transfer during reproduction between generations.
Horizontal gene transfer
Gene transfer between cells of the same generation.
Two-component systems
Mechanism for sensing extracellular environment in bacteria.
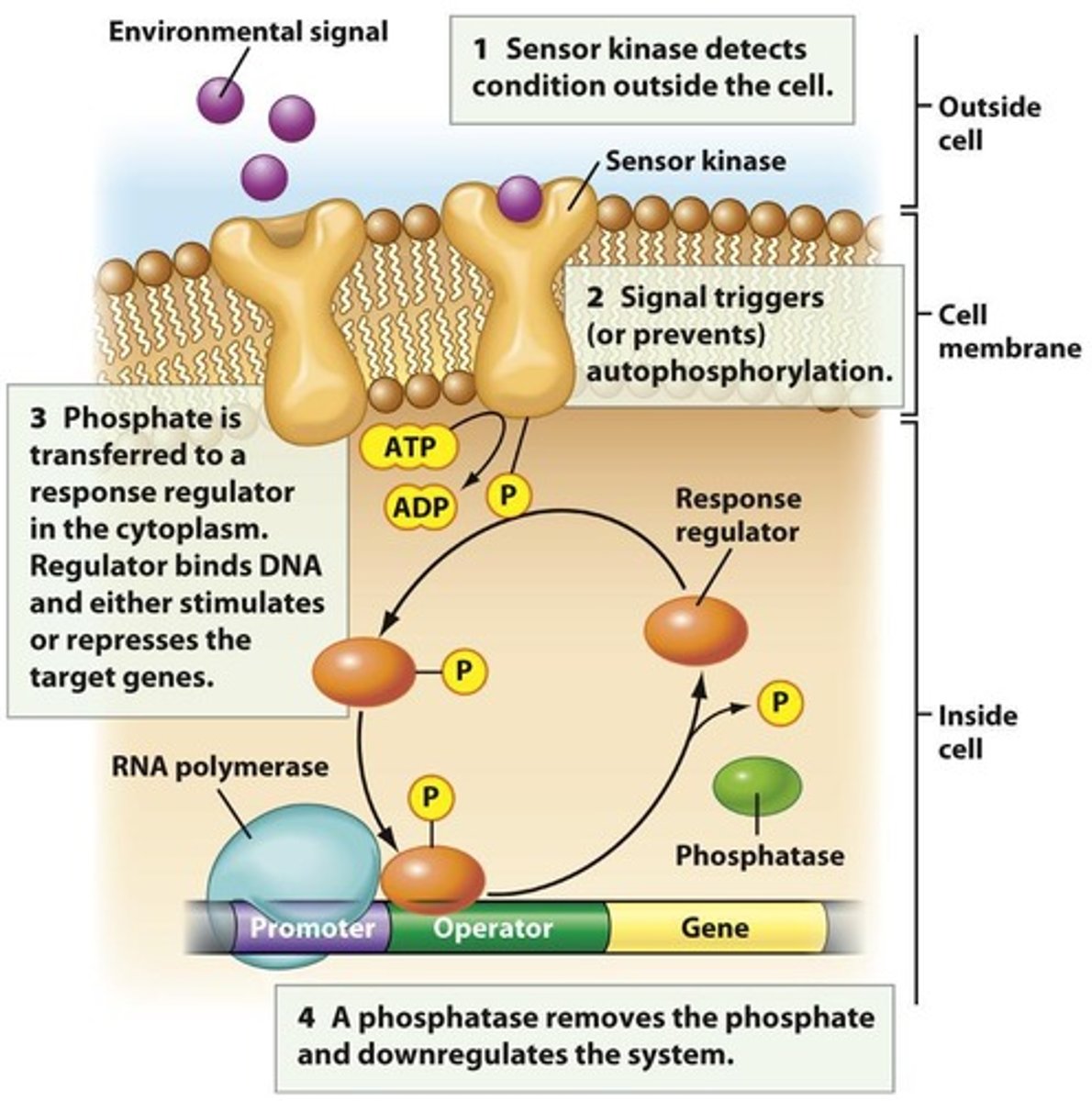
Recombination
Integration of donor genetic material into recipient genome.
F plasmids
Direct synthesis of pili proteins in bacteria.
Resistance plasmids
Carry genes for antimicrobial resistance.
Virulence plasmids
Induce disease symptoms via neurotoxins.
Tumor inducing plasmids
Cause tumor formation in plant cells.
Catabolic enzyme genes
Non-essential genes for bacterial growth.
Bacteriocinogen plasmid
Synthesize bacteriocins that kill other bacteria.
Transposable elements
Genes that move between chromosomes.
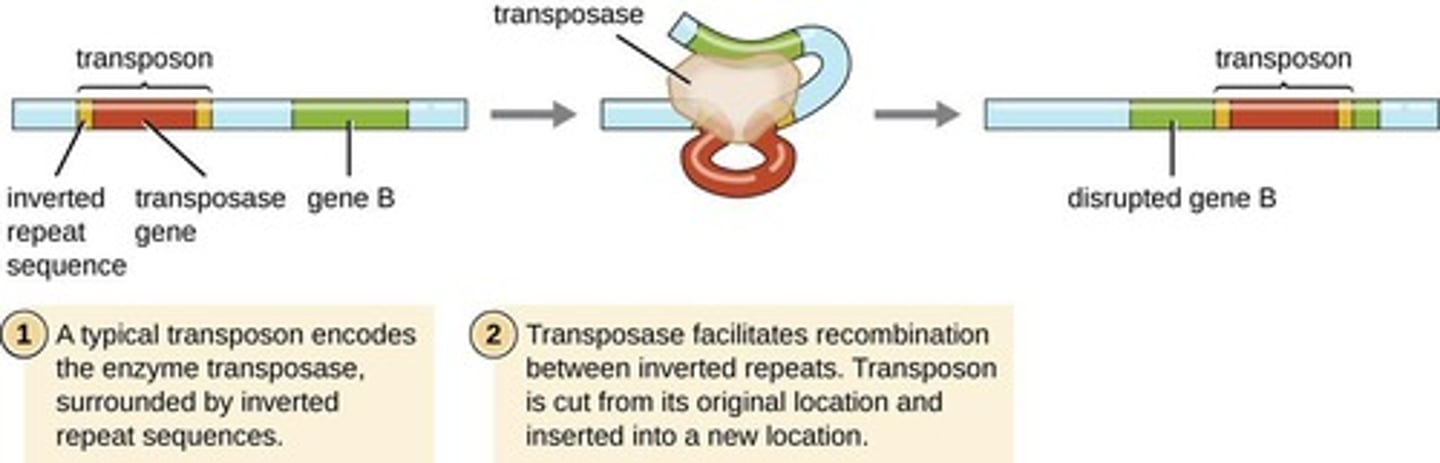
Insertion sequences
Short DNA sequences with transposase genes.
Transposase
Enzyme that facilitates DNA element movement.
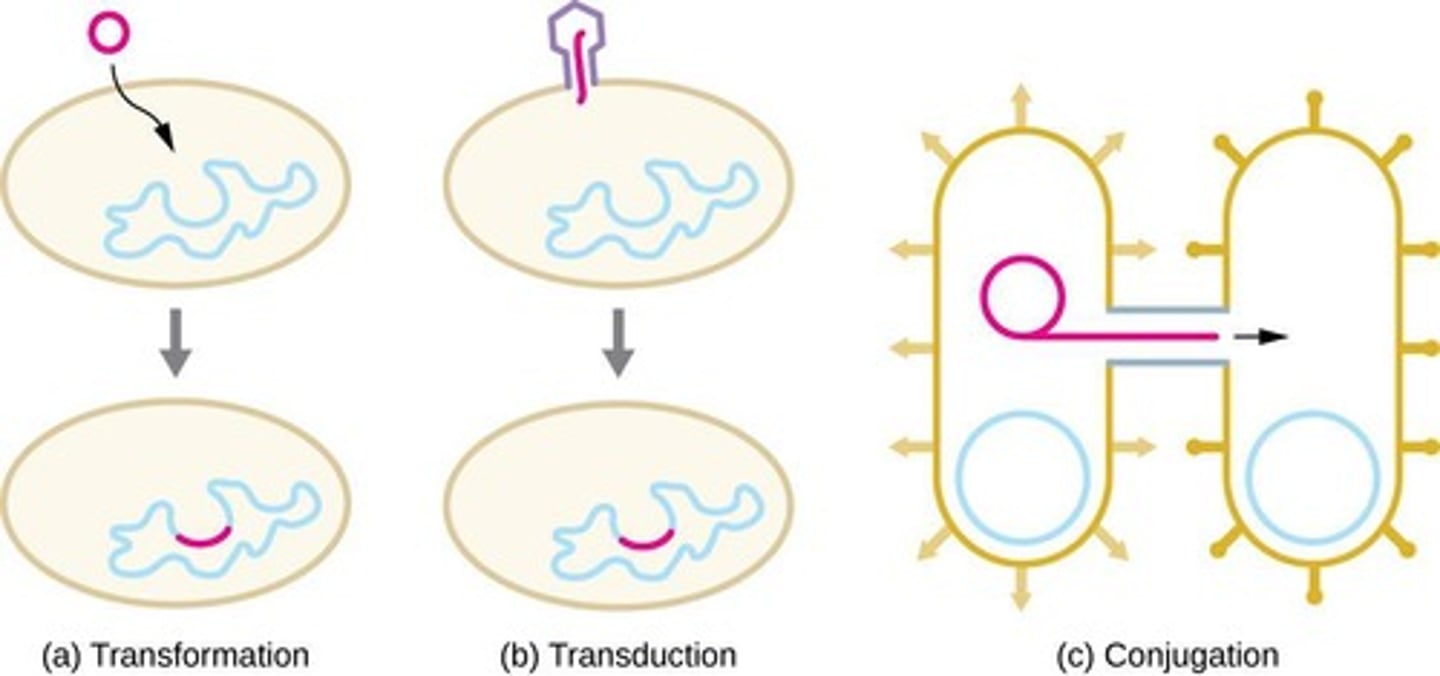
Natural transformation
Bacteria uptake free DNA from environment.
Transformasome
Protein complex enabling natural transformation.
Competent bacteria
Bacteria capable of natural transformation.
Bacteriophage
Virus that infects bacteria, transferring DNA.
Specialized transduction
Specific gene transfer by modified bacteriophages.
Hfr cells
High-frequency recombination cells in conjugation.
Genetic variation
Diversity in genetic traits among organisms.
Promiscuous plasmids
Plasmids that can transfer between different bacteria.
Mutualism
Both populations benefit from the relationship.
Amensalism
One population is harmed, the other unaffected.
Commensalism
One population benefits, the other is unaffected.
Neutralism
Both populations remain unaffected by each other.
Parasitism
One population benefits at the expense of another.
Genetic Recombination
Exchange of genes between DNA molecules.
Vertical Gene Transfer
Gene transfer during reproduction across generations.
Transformation
Importing free DNA from the environment into bacteria.
Transduction
Gene transfer mediated by bacteriophage vectors.
Plasmids
Circular, extrachromosomal DNA that self-replicates.
F Plasmids
Direct synthesis of proteins for pili formation.
R Plasmids
Carry genes for antimicrobial resistance.
Virulence Plasmids
Cause disease symptoms in host organisms.
Tumor Inducing Plasmids
Induce tumor formation in plant cells.
Transposons
Mobile genetic elements that cannot replicate independently.
Insertion Sequences
Short DNA sequences that facilitate transposition.
Transposase Gene
Enzyme that moves transposable elements between DNA.
Competent Bacterial Cells
Cells capable of taking up foreign DNA.
Electroporation
Method using electrical pulses to introduce DNA.
Transgenic
Organisms with genes from different species.
Gene Linkage
Study of genes on the same chromosome.
Conjugation
Direct gene transfer between bacterial cells.
Hfr Cells
Cells with integrated F plasmid into chromosome.
F Plasmid
Plasmid that facilitates bacterial conjugation.
Genetic Variation
Diversity in genetic makeup among organisms.
Genetic Diversity
Variety of genetic characteristics in a population.
Self-Transmissible Plasmids
Plasmids that can transfer themselves between cells.
Promiscuous Plasmids
Plasmids that can transfer between different species.
Restriction Endonuclease
Enzyme that cuts DNA at specific sequences.
Palindrome Sequence
DNA sequence that reads the same forwards and backwards.
EcoR1
Restriction enzyme from Escherichia coli.
Gel Electrophoresis
Technique for separating DNA fragments by size.
DNA Recombination
Process of combining DNA from different sources.
Gene Fusion
Joining of two genes to create a new function.
Transposition
Movement of genes within the chromosome.
Sterilization
Destruction of all living cells and viruses.
Disinfection
Killing of disease-causing organisms on surfaces.
Antisepsis
Removal of pathogens from living tissues.
Sanitation
Reducing microbial population to safe levels.
Microbial Load
Amount of microorganisms present on a surface.
Biosafety Levels
Ranking of pathogens by disease severity and transmission.
Microbial Control
Methods to reduce or eliminate microorganisms.
Cidal agents
Kill microbes, including bacteria and viruses.
Static agents
Inhibit or control microbial growth.
Bactericidal
Specifically kills bacteria.
Fungicidal
Specifically kills fungi.
Virucidal
Specifically kills viruses.
Bacteriostatic
Inhibits bacterial growth.
Fungistatic
Inhibits fungal growth.
Virustatic
Inhibits viral growth.
Microbial death curve
Evaluates effectiveness of microbial control protocols.
Decimal reduction time (DRT)
Time to kill 90% of organisms.
Thermal death time (TDT)
Time to kill all bacteria at specified temperature.
Moist heat
Effective method for killing microbes.
Micropore filters
0.2 µm filters remove microbial cells, not viruses.
Organic load
Presence of organic material that inhibits disinfectants.
Standard autoclave conditions
121°C at 15 psi for 20 minutes.
Factors influencing microbial control
Population size, composition, agent concentration, exposure duration.
Micropore Filters
Filters with 0.2 µm pores; remove microbial cells.