HOSA Occupational Therapy study guide 2024-2025
1/644
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
645 Terms
Occupation
The occupational functioning in life roles that are important to the individual patient or client
Occupational Therapy Practice Framework: Domain
and Process, 2nd Edition (OTPF-2)
-Outlines the unique focus of the profession and delineates the issues that OT should address.
-The purpose is to identify
clearly the factors that the OT and occupational therapy assistant (OTA) should consider
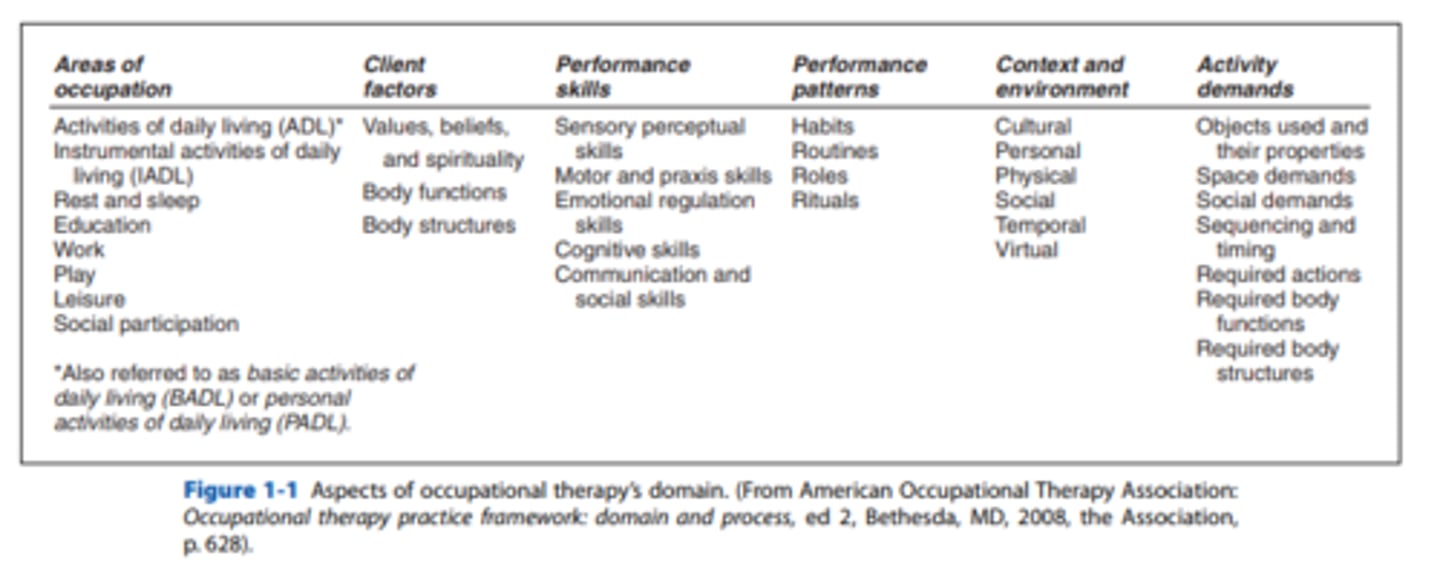
Areas of Occupation
ADLs, IADLs, rest and sleep, education, work, play, leisure, social participation
Performance Skills
are the building blocks of performance in occupation. These skills
Patterns
Such as habits, routines, rituals, and roles. Patterns help to make performance more automatic and thus less demanding of conscious attention.
Activity Demands
Take into account all of the parameters of a specific activity.
Figure 1-1
Frame of Reference
-Provides structure to organize thoughts
-Theoretical
Components of MOHO
Habituation
Occupation
Environment
PERSON
Three subsystems of human occupation
Volition
Habituation
Performance Capacity
MOHO: Volition
Personal Causation -Beliefs about personal effectiveness
Values - Internalized images of what is important and meaningful
Interests- Things a person finds enjoyable or satisfying (liking football more than baseball)
MOHO: Habituation
Habits
Internalized roles
Habits
-Automatic routines or patterns of activity
-Completed with little conscious awareness
-Habits and environment are interdependent
Internalized Roles
-Personalization of typical occupational roles
-May reflect values and interests
-Role transition occurs over the life span
MOHO: Performance Capacity
The "ability for doing things"
Dependent on body structures and functions
"Lived body"
-Knowledge of the world is developed through the experience of living in a particular body
-Lived body of a person with physical disability provides a different perception and understanding of the world.
Principles of OT intervention Derived from MOHO
-Client change is the focus of therapy
-Only clients can accomplish their own changes
-Therapeutic doing must involved an occupational form
-For achievement of change the doing must be relevant and meaningful
-Change in therapy involves simultaneous an interacting alteration in the person and the environment, and in the relationship of the two.
Biomechanical approach
-Targets populations with lower motor neuron or orthopedic disorders
-Focus is to remediate range of motion, strength, and endurance
-Also applied in ergonomics and work hardening
-Targets performance capacity, body structures, and body functions
Sensorimotor and Motor Learning Approaches
Developed for people who have central nervous system dysfunction
Sensorimotor approaches
- Use neurophysiologic mechanisms
- May use reflex mechanisms
- Controlled input to stimulate specific response
Motor learning approaches
-Acquisition of motor skills through practice and feedback
Rehabilitative Approach
-Concerned with restoration of a purposeful life
-Focus is on abilities rather than disabilities to compensate for physical limitations
-Aim is to minimize the effect of the residual disability on role performance
-May be used in combination with other treatment approaches
Treatment Continuum
Continuum between the onset of illness and the restoration of maximal independence
Four stages
-Adjunctive methods
- Prepare the person to engage in activity
Enabling activities
-Require more active patient involvement
-Are a step toward performing purposeful activities
-Purposeful activity
-Occupational performance and occupational roles
Evidence Based Practice (EBP)
Using research to provides evidence to support practice
OT profession needs more research to support EBP
Considers both the consumer's an the practitioner's perspectives
Occupational therapy assistant (OTA) may contribute to the research process
cardiovascular accident
What does CVA mean?
ischemia
Lack of blood supply
hemorrhagic stroke
occurs when a blood vessel in the brain leaks or ruptures; also known as a bleed
ischemic stroke
Most common type of stroke in older people, occurs when the flow of blood to the brain is blocked by the narrowing or blockage of a carotid artery.
thrombosis, lacunar, embolism
what are the three types of ischemic strokes?
Atherosclerosis
Rough, irregular fatty deposits from within the intima and inner media of the arteries and often leads to the generation of a thrombus.
Thrombus
a blood clot attached to the interior wall of an artery or vein
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA)
temporary blockages of an artery, precede actual infarction about have the time, and the risk factors for TIAs are the same as other types of strokes.
Mini Stroke
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) is also known as a ____________________.
thrombosis
cerebral _______________ occurs when a blood clot forms in one of the arteries supplying the brain causing vascular obstruction at the point of its formation.
Lacunar stroke
Small infarctions, usually lying in the deep brain structures, such as the basal ganglia, thalamus, pons, internal capsule, and deep white matter.
True
T/F: Because Lacunar infarctions are so small, minimal neurological symptoms are often present, and many such strokes go undetected.
Ebolism
__________ occurs when a clot has formed elsewhere, breaks off, travels up the bloodstream until it reaches an artery too small to pass through, and blocking the artery.
False
T/F: embolic strokes typically occur during the night times activity.
aneurysm
ballooning of a weakened portion of an arterial wall
intracerebral hemorrhage
Which has a higher percentage of deaths?
a. intercerebral hemorrhage
b. ischemic strokes
subarachnoid hemmorhage
bleeding in the subarachnoid space
True
T/F: Some strokes start as ischemic and transforms into hemorrhagic.
psychosocial factors
which is not a non-modifiable risk factor?
a. age
b. ethnicity
c. psychosocial factors
d. gender
e. genetics
second
CVA is the ____________ leading common cause of death in the world after heart disease.
Cerebral Pasly (CP)
what condition in children is the result of an a stroke at a young are or in the womb?
homonymous hemianopsia
The loss of the right or left half of the field of vision in both eyes.
stroke warning signs
Sudden numbness or weakness of the face, arm, or leg
Sudden confusion or trouble speaking or understanding
Sudden trouble walking, dizziness, or loss of balance or coordination
Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes
Sudden severe headache
Left-sided stroke
LANGUAGE
aphasia
agnosia (unfamiliar objects)
agraphia
alexia (reading issues)
right hemiplegia/hemiparesis
hemianopsia (visual field)
SLOW CAUTIOUS behavior
ANGER/DEPRESSION
right-sided stroke
affects left side, unilateral neglect, safety impulses, uninhibited & have perceptual deficits
anterior cerebral artery stroke
Contralateral hemiplegia, grasp reflex, incontinence, confusion, apathy and/or mutism
vertebrobasilar
Cerebellar and brain stem ischemia and infarction
wallenberg syndrome
a classic brainstem stroke that also is referred to as lateral medullary syndrome as it occurs as a result from a vertebral or cerebellar artery occlusion.
secondary complications of CVA
-Depression (1/3 of stroke patients)
-Seizures (10% of stroke survivors, brain is scarred during seizures, scar tissue remains)
-Infections (trouble swallowing)
-Bowel and bladder incontinence (UTI)
-Pulmonary Embolism (embolism lodged in lungs)
-Shoulder subluxation
-Painful shoulder
-Shoulder hand syndrome (shoulder, elbow, hand does not coordinate)
-Abnormal muscle tone
-Associated reactions and movements
-DVT (lower extremity hot to touch , calves, painful)
subclavian steal syndrome
Occurs when significant stenosis in the subclavian artery compromises distal perfusion to the inferior mesenteric artery.
neural plasticity
The ability of the brain's networks of neurons and their synapses to change. Allows adaptation to chaining life circumstances as well as memory formation (memory can be stored as changes to networks of neurons)
cardiopulmonary
what term means "pertaining to the heart and lungs"?
oxygen
when blood is pumped through the lungs it picks up ____________ and carries it back to the heart and then to the rest of the body.
vital signs
Measurements of the body's most basic functions and useful in detecting or monitoring medical problems.
pulse rate
the number of pulse beats per minute
respiratory rate
number of breaths per minute
blood pressure
the pressure that is exerted by the blood against the walls of blood vessels
hypertension
high blood pressure is also known as _________________.
oxygen saturation
percentage of hemoglobin that is bound to oxygen
270 million
each red blood cell within the body contains ~_________ molecules of hemoglobin.
hypoxemia
decreased level of oxygen in the blood.
hypotension
low blood pressure
Coronary artery disease
this disorder develops when coronary arteries, the blood vessels that supply the heart with blood, oxygen, and nutrients become damaged over time.
atherosclerosis
condition in which fatty deposits called plaque build up on the inner walls of the arteries
True
T/F: CAD typically progresses slowly and worsens over time, often going unnoticed until arteries have narrowed considerably, and blood flow has been significantly restricted.
angioplasty
the technique of mechanically widening a narrowed or obstructed blood vessel
coronary artery bypass graft
surgical technique to bring a new blood supply to heart muscle by detouring around blocked arteries
congestive heart failure
heart is unable to pump its required amount of blood
dyspnea
difficult or labored breathing
COPD
an umbrella term used to describe a group of progressive lung disorders.
emphysema
a condition in which the air sacs of the lungs are damaged and enlarged, causing breathlessness.
bronchitis
inflammation of the bronchial tubes
Myocardial infarction
heart attack
False
T/F: Heart attacks look the same in men and women.
Traumatic brain injury
mild or severe trauma that can result from a violent impact to the head
Mild traumatic brain injury
- loss of consciousness for up to a few min
- headache, dizziness, loss of balance
- drowsiness, nausea, vomiting
moderate traumatic brain injury
- Characterized by LOC 30 min- 6 hrs and Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) 9-12
-Focal or diffuse brain injury may be seen with CT or MRI
-Post traumatic amnesia may last up to 24 hours
-Often requires hospitalization for close monitoring and prevention of secondary injury from brain edema, intracranial bleeding or inadequate cerebral perfusion
severe traumatic brain injury
- Loss of consciousness of more than 24 hours
- Posttraumatic amnesia of more than 7 days
- GCS score of 3-8
Postconcussion syndrome
A delayed condition characterized by persistent headaches, blurred vision, irritability, and an inability to concentrate.
closed brain injury
a head injury where the skull is not cracked.
penetrating brain injury
when an object penetrates the skull and enters the brain (example gunshot)
blast brain injury
damage to the brain caused by energy waves from an explosion, such as a bomb, that creates bulk acceleration of the head, vascular surge in the brain, and dynamic deformation of the skull
True
T/F: males are more likely to sustain a TBI
primary brain tumor
a tumor that originates in the brain
secondary brain tumor
These tumors are metastases. That is, they originate in another part of the body and spread to the brain. Thus, they are always cancerous.
nonmalignant brain tumor
a brain tumor that is benign, not cancerous; does not spread to body tissue; can become life threatening
malignant brain tumor
brain cancer
OPHI
Acronym
Occupational Performance History Interview
OPHI
Age
Not recommended for children under age 12
OPHI
Dx
Any
* Must be able to answer in-depth interview questions
OPHI
Setting
Any
OPHI
Data Collection
Semi-structured Interview
OPHI
What is assessed?
- Roles
- Activity/occupational choices
- Critical life events
- Occupation settings (environment)
- Routines
OPHI
3 rating scales
- Occupational identity
- Occupational competence
- Occupational settings
OPHI
Scoring
4 point rating scale:
(1) extreme occupational dysfunction - (4) exceptional competent occupational functioning
OPHI
What can we learn from it? (How can it be used for treatment planning and discharge recommendations?)
- Graphing of life events
- Develop an occupational profile
- Identify client's strengths and weaknesses
- Understand client's life hx to guide intervention
- Fosters communication and collaboration and a therapeutic relationship between client and OT
OCAIRS
Acronym
Occupational Circumstances Assessment Interview Rating Scale
OCAIRS
Age
Adults
OCAIRS
Dx
- Short-term psychiatric inpatient
* Must be able to participate in interview