13.3 Reactions of alkenes
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
why are alkenes more reactive than alkanes
1) alkenes have a pi bond 2) pi electron density is concentrated above and below the plane of the sigma bond 3) pi electrons are more exposed than the electrons in the sigma bond therefore the pi bond readily breaks
name 4 substances alkenes have addition reactions with
1) hydrogen in the presence of a nickel catalyst 2) halogens 3) hydrogen halides 4) steam in the presence of an acid catalyst
describe hydrogenation of alkenes
when an alkene is mixed with hydrogen and passed over a nickel catalyst at 423K an addition reaction takes place to form an alkane
describe halogenation of alkenes
alkenes react with the halogens chlorine or bromine at room temperature to form haloalkanes
describe a positive test for unsaturation
bromine water (orange) + alkene = haloalkane (colourless)
describe addition reactions of alkenes with hydrogen halides
alkenes react with gaseous hydrogen halides at room temperature to form multiple haloalkanes
how do addition reactions of alkenes with hydrogen halides occur when the alkene is a gas
reaction takes place when the two gases are mixed
how do addition reactions of alkenes with hydrogen halides take place when the alkene is a liquid
the hydrogen halide is bubbled through it
describe hydration reactions of alkenes
alkenes react with steam in the presence of a phosphoric acid catalyst H3PO4 to form alcohols
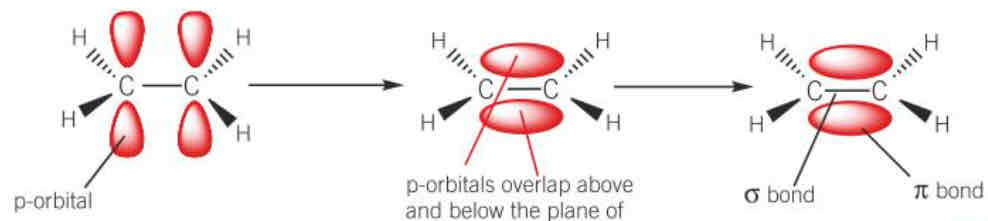
diagram of formation of a pi bond