CH 22 - Heart (NOT COMPLETE)
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Arteries
carry blood away from heart
Capillaries
Network through tissues/organs.
Veins
carry blood to heart.
Right Atrium
Collect blood from systemic circuit
Right ventricle
Pump blood to pulmonary circuit
Left atrium
Collect blood from pulmonary circuit
Left ventricle
Pump blood to systemic circuit
Heart anatomy (upside down pyramid)
Great vessels at base, pointed tip is apex, in pericardial sac in mediastinum.
Superficial Anatomy of the heart
Atria: thin walled, expandable outer portion called the auricle. Coronary sulcus (groove) between the 2 atria and ventricles. Anterior and posterior interventricular sulci. KNOW ALL EXTERNAL HEART ANATOMY FROM SLIDES
Heart wall: Epicardium
superficial, Visceral pericardium
Heart wall: Myocardium
2nd layer. Thickest, cardiac muscle
Heart wall: Endocardium
deepest, simple squamous epithelium.
Internal Anatomy: Interatrial Septum
Foramen ovale–before birth, seals off at birth forming fossa ovalis. In the right atrium
Internal Anatomy: Atrioventricular (AV) Valves
Bicuspid–Between left atrium and left ventricle
Tricuspid–Between right atrium and right ventricle.
KNOW THE LOCATIONS
Internal Anatomy: Superior Vena Cava
Blood from head, neck, upper, limbs, and chest
Internal Anatomy: Inferior Vena Cava
Blood from trunk, viscera, and lower limbs
Internal Anatomy: Coronary Sinus
From cardiac veins
Tetanus in heart
Impossible since the heart muscles have a long refractory period unlike skeletal muscle.
muscle in Right Atrium
Pectinate muscles–Parallel muscular ridges
Right atrioventricular (AV) valve
tricuspid valve, chordae tendineae. Prevent valve from flopping backwards
muscle in Right Ventrical
Papillary muscles: trabeculae carneae, attach to chordae tendineae, control closing
Pulmonary Circuit: Conus arteriosus (Location)
Superior right ventricle
Pulmonary Circuit: Pulmonary semilunar valve
3 semilunar cusps
Pulmonary Circuit: Pulmonary trunk
right and left pulmonary arteries
Pulmonary Circuit: Left Atrium
Left and right pulmonary veins
Pulmonary Circuit: Left ventricle
Larger thicker, same volume as right. Aortic semilunar valve, ascending aorta, aortic arch: head, chest, upper limbs. Descending aorta: trunk and lower limbs.
Pulmonary Circuit: Left (AV) valve
bicuspid valve or mitral valve
Cardiac Skeleton
Fibrous collagen skeleton that supports and insulates the heart. The layer of nonconductive tissue isolates the atria from the ventricles. Exception of one small node that carries the signal across the skeleton. Atria contract before the ventricles, but this only takes one signal since it slows down between the atria and ventricles. “Lub-Dub”
Coronary Circulation: Arteries
Right and left coronary arteries travel within the coronary sulcus and supply the heart wall with oxygen and nutrients. Blood flows into heart wall when the heart relaxes and pressure falls.
Coronary Circulation: Veins
Return of blood from the heart wall occurs through 3 major veins: Great, Middle, and Small cardiac veins.
Heart Disease – Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Coronary ischemia: Area of partial or complete blockage of the coronary circulation.
Atherosclerosis: plaque on the wall of a coronary vessel.
Coronary thrombosis: Narrowed/blocked vessel
Myocardial Infarction (MI)
Heart attack. Cardiac cells die from lack of oxygen. Infarct: nonfunctional area of necrotic tissue. Block begins at beginning of coronary artery. 65% of MI deaths under age 50 within 1hr
Drugs that help with heart attacks
Nitroglycerine is a powerful vasodilator.
Balloon angioplasty
Catheter tip stuck into artery, balloon opens up to crush plaque. Stent hold vessel open.
Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG)
Vessel added to create detour around blockage.
Autorythmicity
The heart initiates its own heartbeat independent of the central nervous system. The CNS only speeds or slows down the rate.
Conducting System
Specialized cells that start and propagate electrical impulses to contractile cells.
Prepotential
This is how the heart beats without nervous signaling. Membrane gradually depolarizes and contains leak channels(ions leaked during resting state until threshold is met and another action potential fires).
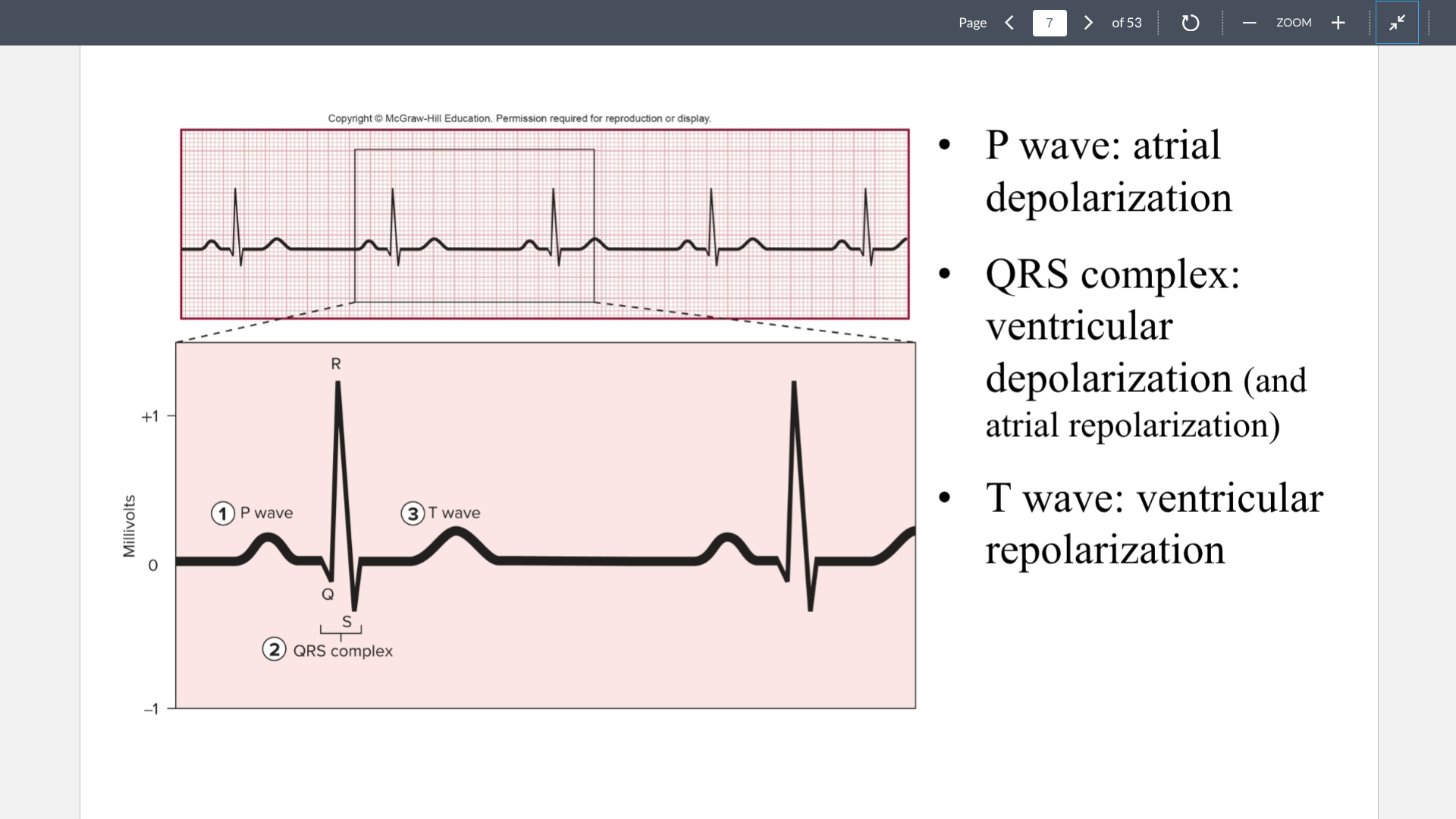
P wave
Atrial depolarization. Positive blip
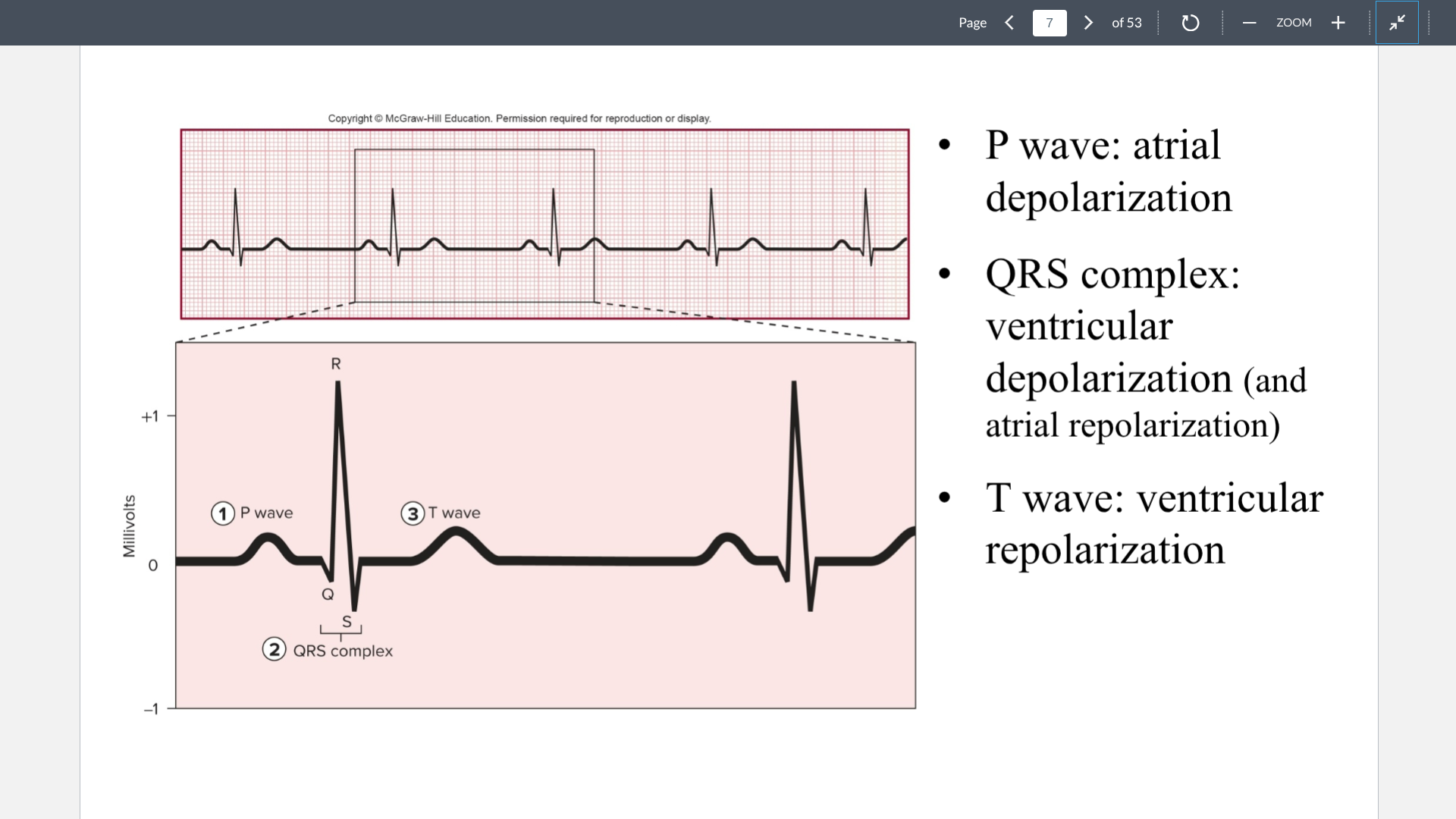
QRS complex
ventricular depolarization (Positive blip) and atrial repolarization (Negative blip)
T wave
Ventricular repolarization (Negative blip). This repolarization is negative since ventricles are the first to repolarize. So the wave shows an inverted negative blip which looks positive.
Bradycardia
abnormally slow heart rate
Tachycardia
abnormally Fast heart rate
Systole=
Contraction
Diastole=
Relaxation
Steps in the Cardiac Cycle
Atrial contraction and ventricular filling→Isovolumetric contraction→Ventricular ejection→Isovolumetric relaxation→Atrial relaxation and ventricular filling