Chapter 20 - Radiology and Nuclear Medicine
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Characteristics of X-Rays
-Expose photographic plates
-Penetrate substances
-Invisible
-Travel in straight lines
-Scatter
-Ionization
Diagnostic Techniques
-X ray studies -> digital radiography, CT, contrast studies
-Fluoroscopy
-Digital imaging techniques
-Interventional radiology
-Ultrasound
-MRI or MR
Digital Radiography
Uses digital x-ray detectors instead of photographic film
Contrast Studies
-Barium sulfate -> upper or lower GI
-Iodine compounds -> angiography, arthrography, cholangiography, digital subtraction angiography, hysterosalpingography, myelography, pyelography
Radionuclides/Radioisotopes
Alpha particles, beta particles, gamma rays
Nuclear Medicine Tests
In vitro: test tube
In vivo: in the body
Half-Life
Time required to lose half of its radioactivity (disintegration)
Analysis of Blood and Urine
Radioimmunoassay (RIA) uses radioactive chemicals and antibodies to detect hormones and drugs in the patient's blood
In vivo
Radiopharmaceutical
-Labeled compound concentrates in an organ
-Radioactive substance given directly to patient to evaluate organ function or image
-In vivo
Scintiscanner
-Gamma camera detection instrument produces picture (scintiscan)
-Radioactive substance given directly to patient to evaluate organ function or image
-In vivo
Radioprocedures Using Radionuclides
-Bone scan
-Lymphoscintigraphy
-PET scan
-CT scan
-SPECT
-Technetium Tc-99m sestamibi (Cardiolite) scan
-Thallium scan
-Thyroid scan
PET Scan
-Positron emission tomography
-Radioisotopes (emission of positrons)
-IV injection
-High resolution images of body function and metabolism
-Concentrates radioisotopes in tissues where the radionuclide is/isn't being metabolized
-Useful in treating stroke, epilepsy, Alzheimer disease, brain tumors, abdominal and pulmonary malignancies
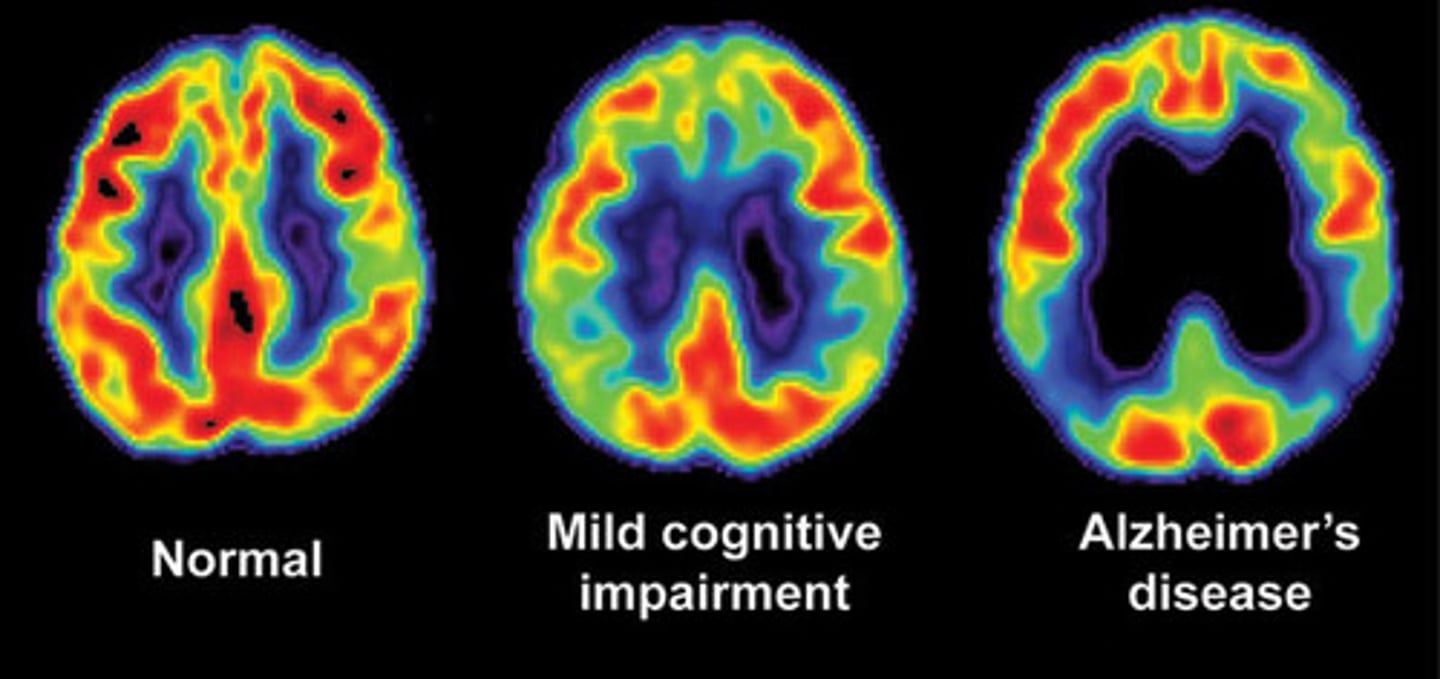
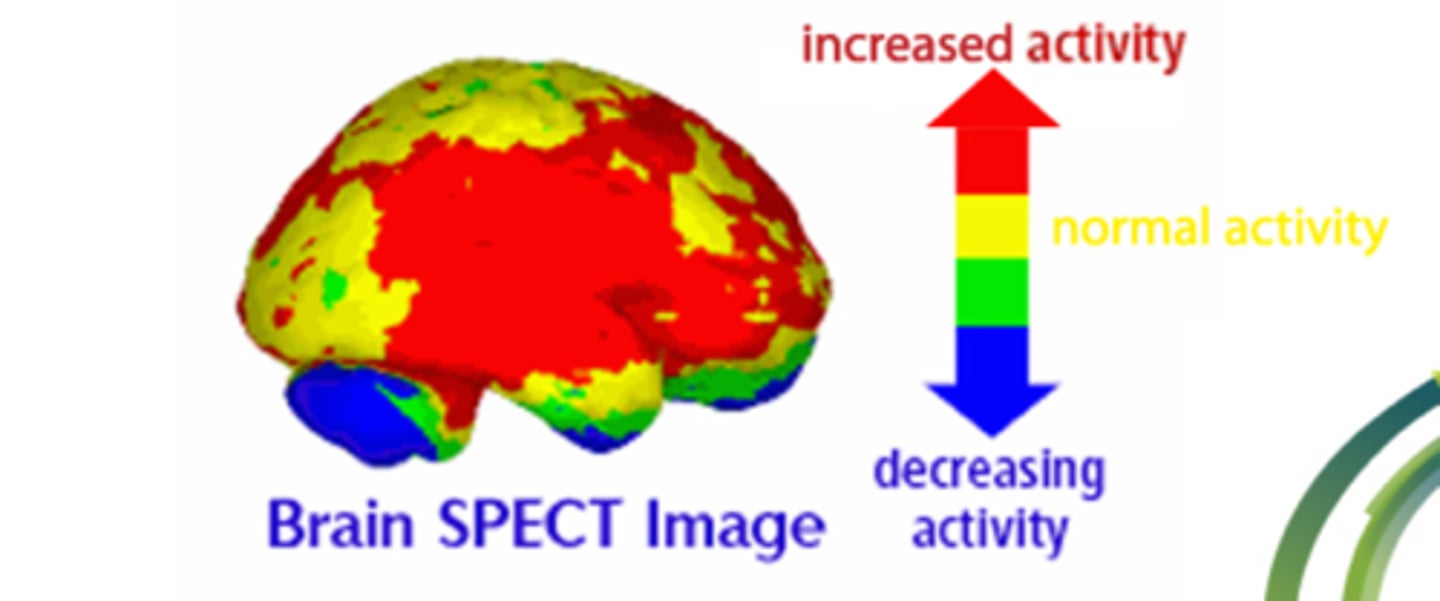
SPECT
-Single-photon emission computed tomography
-IV injection of radioactive tracer (gamma rays)
-Computer reconstruction of 3D images
-Detects liver tumors, cardiac ischemia, diseases on bone and spine
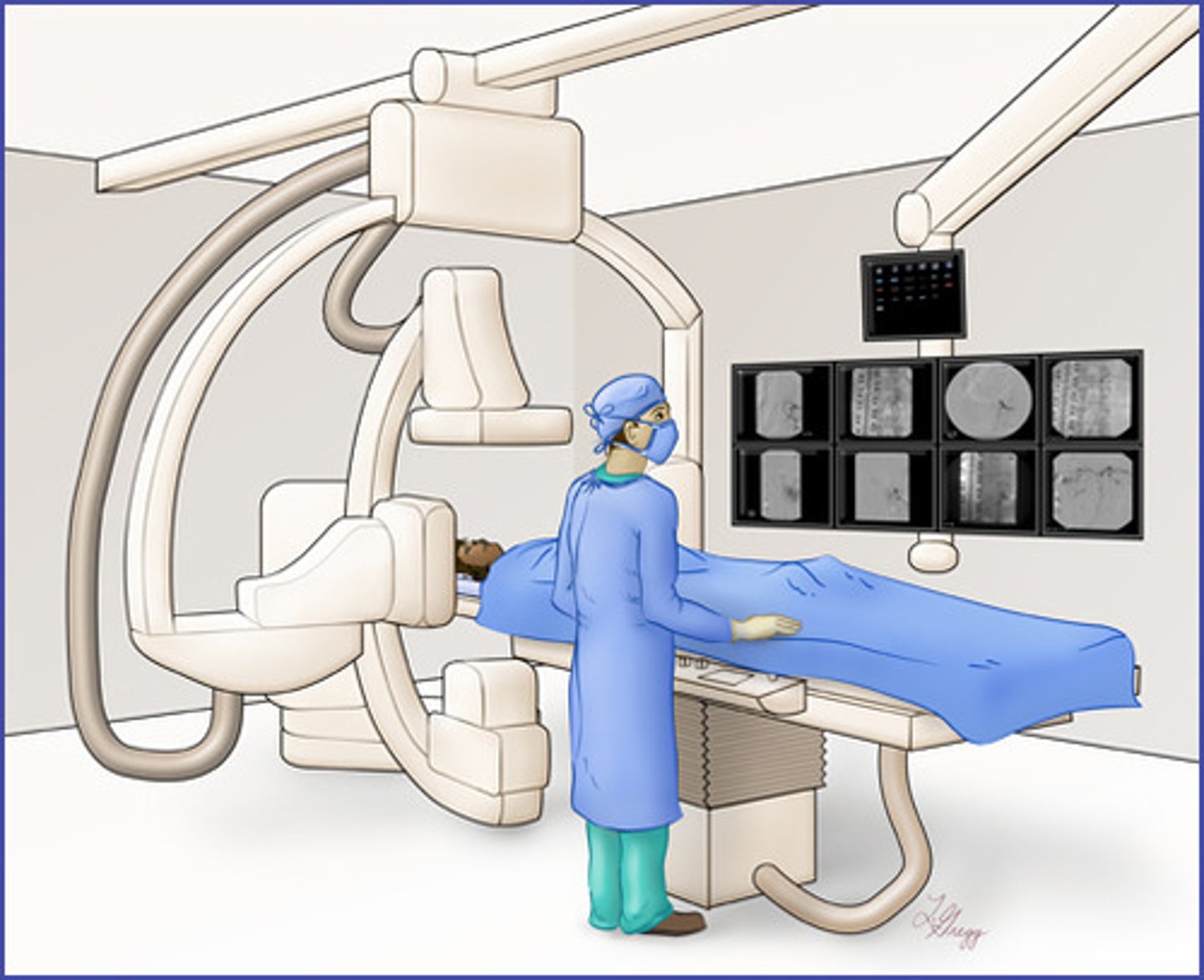
Interventional Radiology
-Treats patients using minimally invasive techniques as an alternative to surgery
-"Pinhole surgery"
Radioactive Decay
-Nucleus is unstable and will decay into a more stable atom
-Spontaneous
Radioactive Decay Types
Alpha particle, beta particle, gamma ray
Radionuclide (Radioisotope)
Substance that gives off high-energy particles or rays as it disintegrates
In Vitro
Test tube
In Vivo
In the body
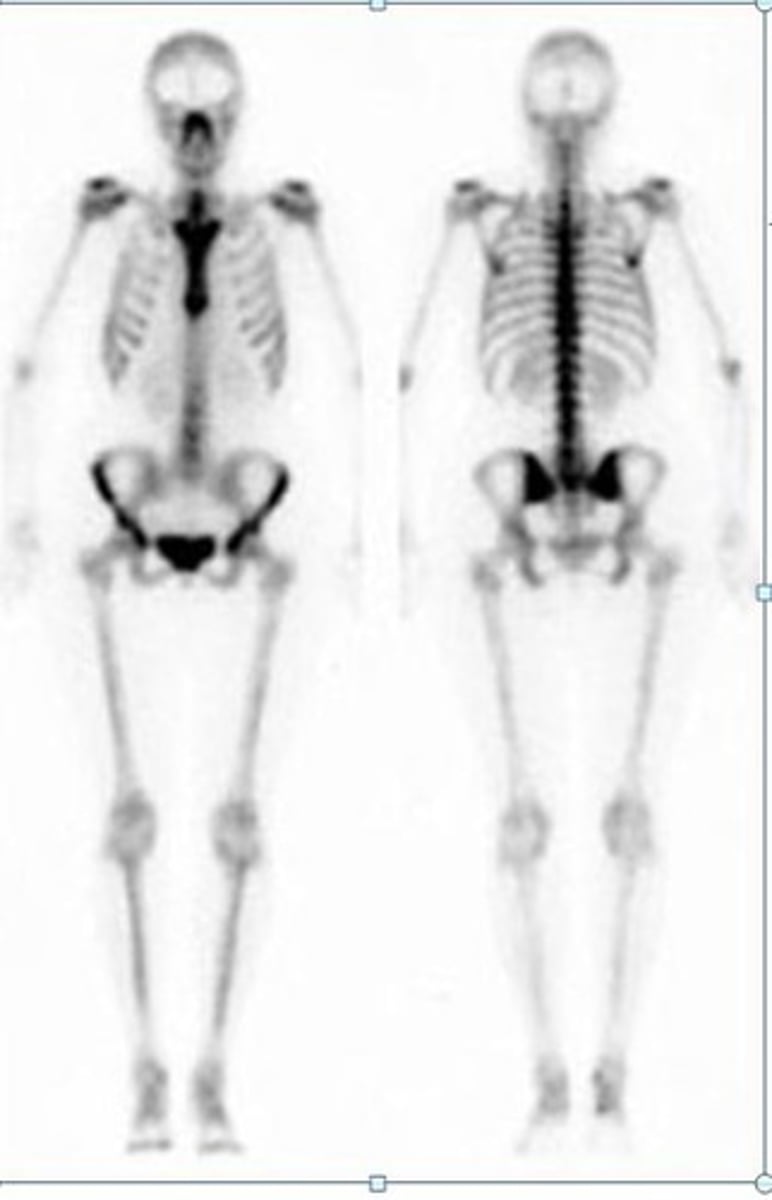
Bone Scan
-Nuclear scanning test that identifies new areas of bone growth or breakdown
-Evaluates bone damage, metastasized cancer, monitor infection and trauma
Lymphoscintigraphy
-Nuclear medicine test
-Locate lymph nodes and identify spread of caner
-Locate sentinel nodes for surgical removal
-Diagnose lymph system disease conditions
PET-CT Scan
-Combines PET and CT techniques to have a more accurate image
-Used with surgical planning, radiation therapy, and cancer staging
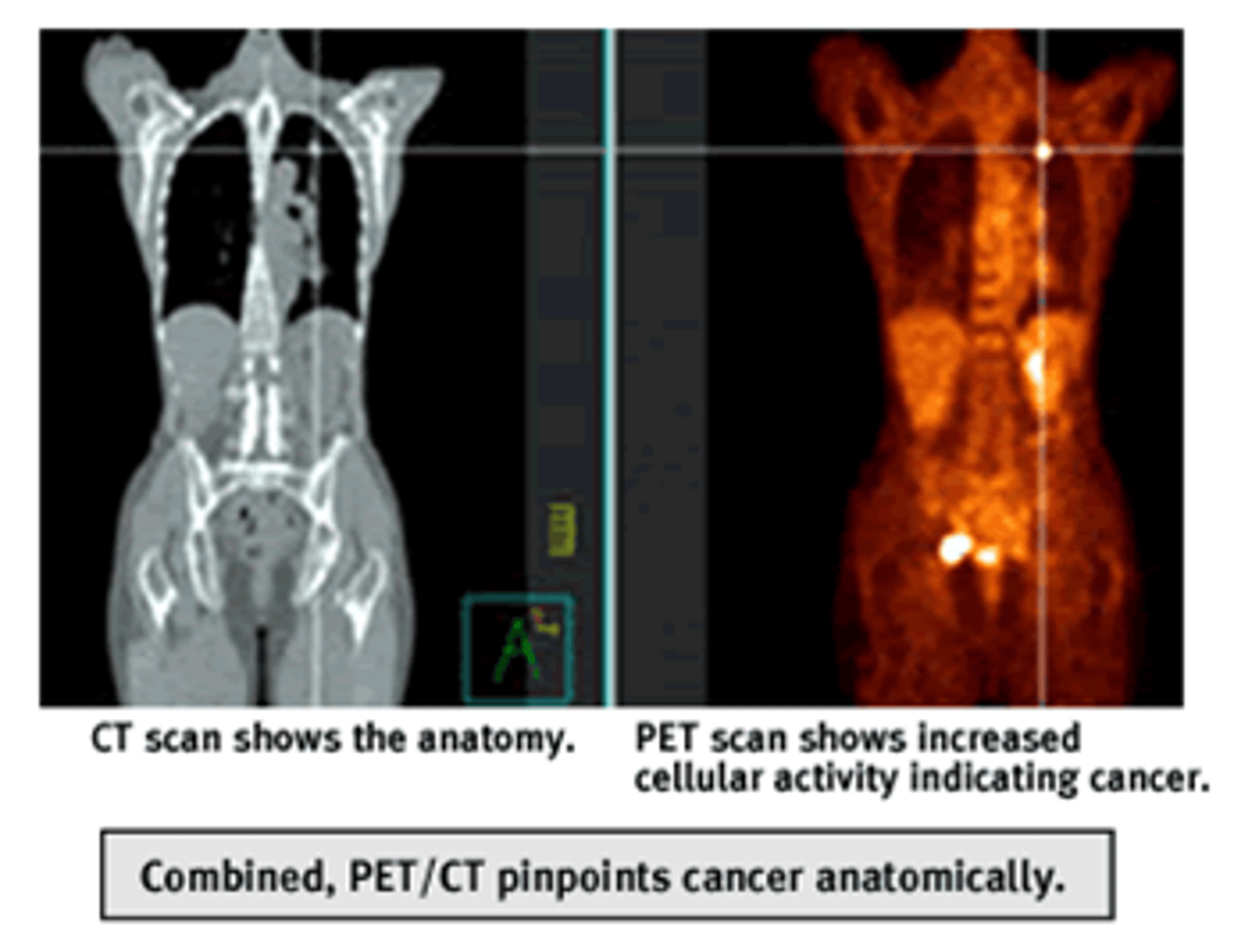
PET-MRI Scan
-MRI combined with PET scan
-MRI -> better for soft tissue
-PET -> evaluates function imaging
-Used in oncology, cardiology, and neurology mainly
99M Technetium Sestamibi (Cardiolite) Scan
-Uses a tracer to produce images of heart muscle
-When combined with an exercise test it helps determine if areas of the heart are not receiving enough blood
-Diagnosis of coronary heart disease
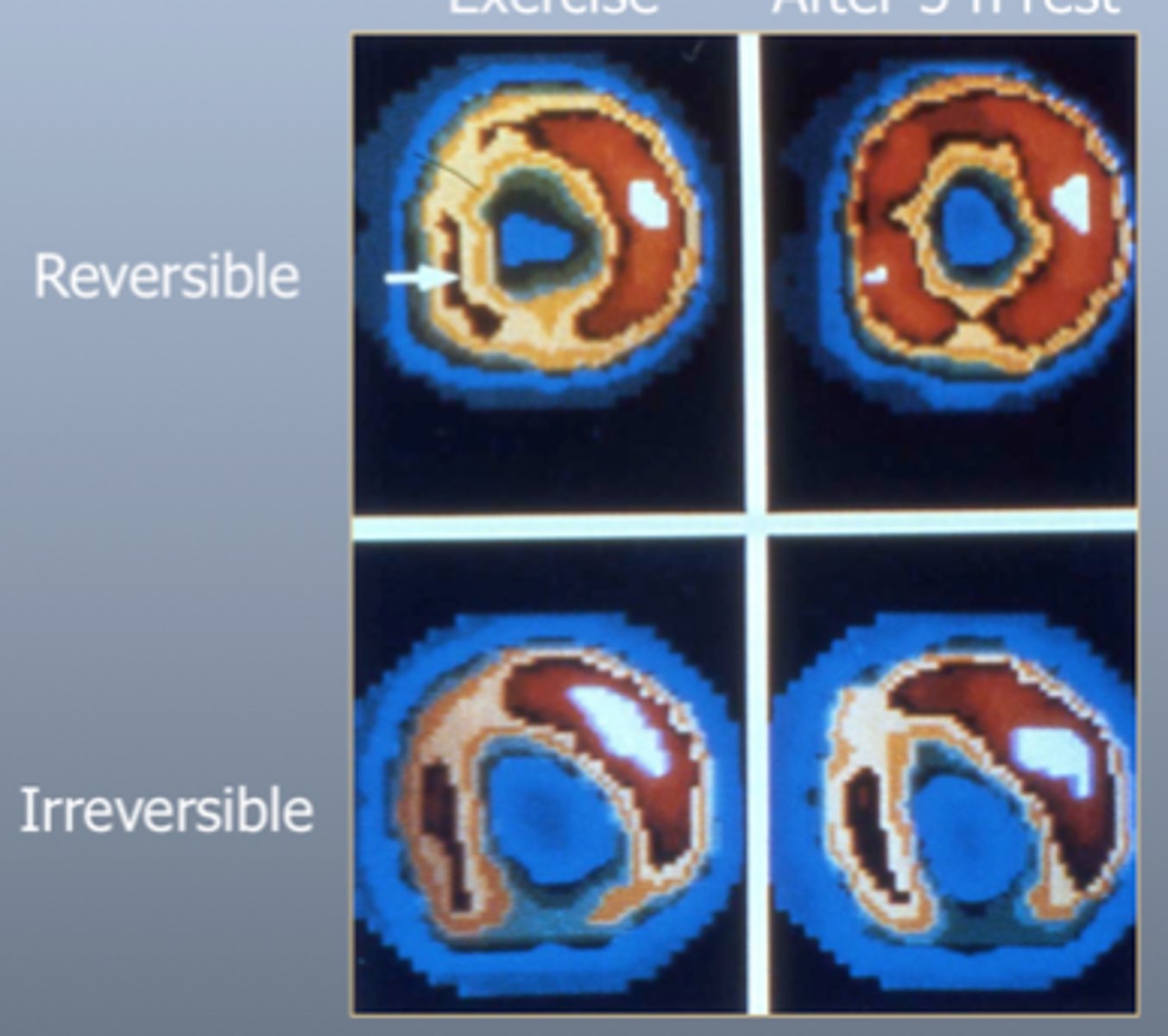
Thallium Scan
-Thallium-201 injected via IV to evaluate heart (myocardial) perfusion
-Lack of uptake of thallium-201 in areas of the heart with infarcted or scarred myocardium
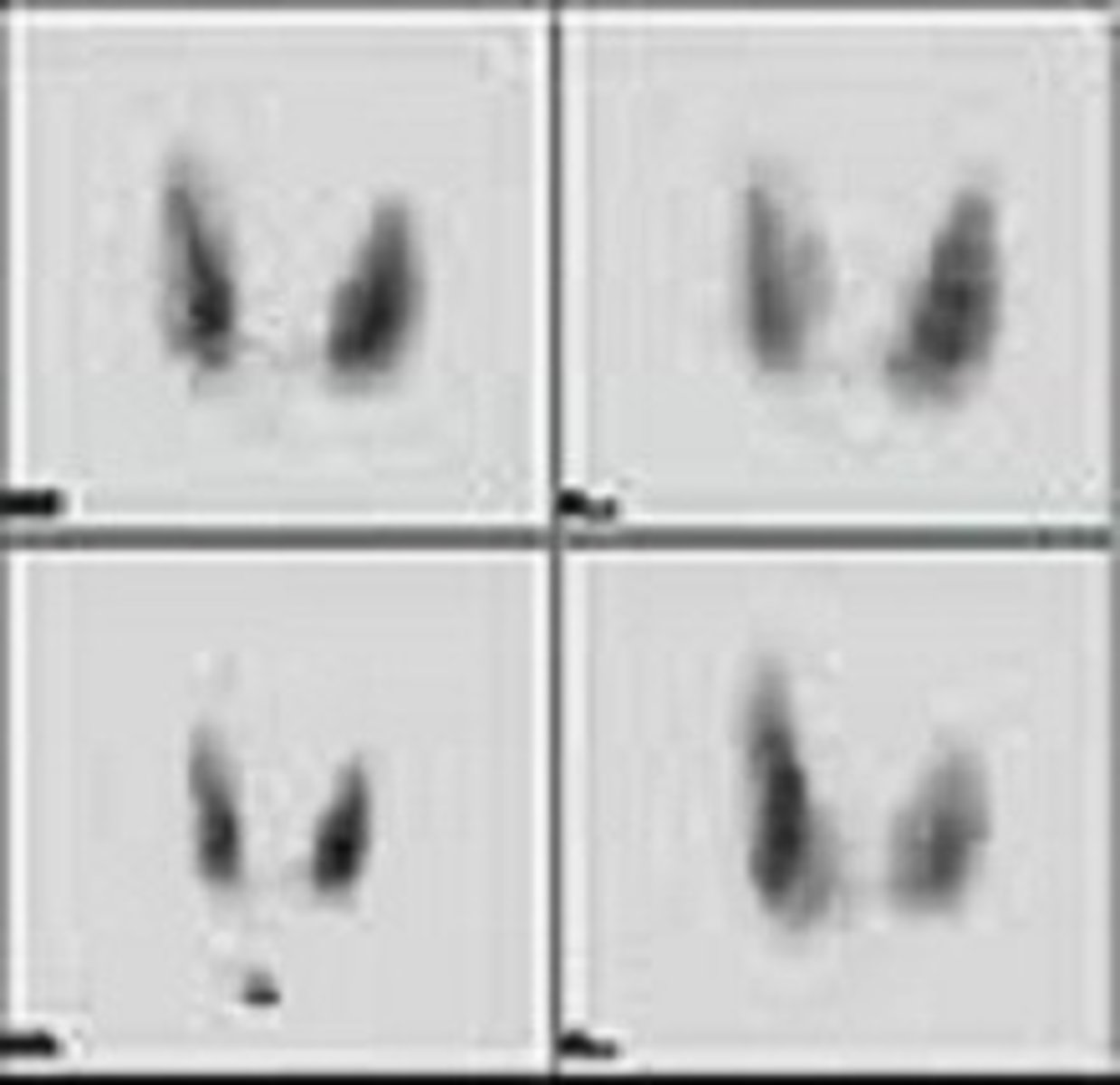
Thyroid Scan
-Radioactive iodine (iodine-123) is given orally
-Thyroid scanned to determine size and shape of glands
-Another test uses radioactive technetium IV to look for hyperfunctioning thyroid nodules accumulating more radioactivity (hot spots) and were there is no concentration (cold spots, thyroid cancer)
Obstructing the passage of x-rays:
A. Radiopaque
B. Radiolucent
C. Radioisotope
D. Radiopharmaceutical
A. Radiopaque
Which of the following is a handheld device that sends and receives ultrasound signals?
A. Gamma camera
B. Roentgenology
C. Radioisotope
D. Transducer
D. Transducer
Which term refers to movement away from the midline of the body?
A. Adduction
B. Abduction
C. PA
D. Inversion
B. Abduction
Which term refers to a patient lying on the back?
A. Prone
B. Supine
C. Flexion
D. Decubitus
B. Supine