A Level Biology, 3.8 - The Control of Gene Expression
1/98
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Cells are able to control their metabolic activities by regulating the transcription and translation of their genome. Although the cells within an organism carry the same coded genetic information, they translate only part of it. In multicellular organisms, this control of translation enables cells to have specialised functions, forming tissues and organs. There are many factors that control the expression of genes and, thus, the phenotype of organisms. Some are external, environmental factors, others are internal factors. The expression of genes is not as simple as once thought, with epigenetic regulation of transcription being increasingly recognised as important. Humans are learning how to control the expression of genes by altering the epigenome, and how to alter genomes and proteomes of organisms. This has many medical and technological applications. Consideration of cellular control mechanisms underpins the content of this section. Students who have studied it should develop an understanding of the ways in which organisms and cells control their activities. This should lead to an appreciation of common ailments resulting from a breakdown of these control mechanisms and the use of DNA technology in the diagnosis and treatment of human diseases.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
____________ mutation: one or more bases are swapped for another
substitution
____________ mutation: one or more bases are removed
deletion
____________ mutation: one or more bases are added
addition
____________ mutation: one or more bases are repeated
duplication
__________ mutation: sequence of bases is reversed
inversion
____________ mutation: sequence of bases moved from one location in the genome to another; this could be movement within the same chromosome or movement to a different chromosome
translocation
____________ mutations are passed on to the offspring through the gamete with this genetic disorder being fertilised
hereditary
____________ have huge affect on the ______________ of a gene through changing the number of bases in the DNA code which means it is read in a diferent way
frameshift mutations / base sequence
Which type of mutations cause frameshift mutations?
addition / duplication / deletion
What increases the rate of mutations?
mutagenic agents
Mutagenic Agents
Chemicals called ______________ can increase the rate of mutations through ______________ for a base during DNA replication, changing the base sequence in the new DNA
Chemicals can ___________ or _______ bases
Some types of ______________ can change the structure of DNA, which causes problems during replication
base analogs / substituting / delete / alter / radiation
What is an acquired mutation?
mutations that occur in individual cells after fertilisation
Mutations that occur in individual cells after fertilisation are called ________________. If these mutations occur in the genes that control the rate of cell division (by __________), it can cause uncontrolled cell division. If a cell divides uncontrollably, the result is a _________. Those that invade and destroy surrounding tissue are called cancers
acquired mutations / mitosis / tumour
What is the definition of a tumour?
abnormal cell mass
What are the two types of gene that control cell division?
tumour suppressor genes / proto-oncogenes
Normally, tumour suppressor genes __________ _____________ by producing ___________ that stop cells ___________ or cause _____________ to occur
slow cell division / proteins / dividing / apoptosis
______________ is a type of ________________. It’s where cells that are infected, damaged or have reached the end of their functional life are destroyed.
apoptosis / programmed cell death
Normally, proto-oncogenes _________ _____________ by producing certain proteins.
stimulate cell division
Cell Division and Cancer
If a mutation occurs in a _____________________, the gene will be _____________;
the protein it codes for isn’t produced and the cells divide uncontrollably (the rate of
division increases) resulting in a tumour
If a mutation occurs in a ________________, the gene can become ____________. This stimulates the cells to divide uncontrollably (the rate of division increases) resulting in a tumour. When mutatated, this is called an ___________.
tumour suppressor gene / inactivated / proto-oncogene / overactive / oncogene
Malignant vs Benign
Malignant tumours are cancers. They usually grow rapidly and invade and
destroy surrounding tissues. Cells can break off the tumours and spread to
other parts of the body in the ________________ or _______________ system.
Benign tumours are not cancerous. They usually grow slower than malignant
tumours and are often covered in _____________ that stops cells invading other
tissues. Benign tumours are often harmless, but they can cause blockages and
put pressure on organs. Some benign tumours can become malignant.
bloodstream / lymphatic / fibrous tissue
What do fibrous tissue do in ________ tumours?
benign / stops cells invading other tissues
Normal vs Tumour Cells
The nucleus is __________ and __________ than in normal cells. Sometimes the cells have more than one nucleus.
They have an _____________ shape.
They don’t produce all the ___________ needed to function correctly.
They have different ____________ on their surface.
They don’t respond to __________________________.
They divide (by mitosis) more frequently than normal cells.
larger / darker / irregular / proteins / antigens / growth regulating processes
What are 2 examples of factors that cause tumour growth?
abnormal methylation / increased oestrogen exposure
Methylation
Means adding a methyl (-______) group onto something.
Methylation of DNA is an important method of regulating gene expression - it can control whether or not a gene is ______________ (copied into mRNA) and _______________ (turned into a protein).
When methylation is happening normally, it plays a key role in many processes in the body.
It’s only when it happens too much (_________________) or too little (_________________) that it becomes a problem.
The growth of tumours can be caused by abnormal methylation of certain cancer-related genes.
CH3 / transcribed / translated / hypermethylation / hypomethylation
When ___________________ are __________________, the genes are not ______________ - so the proteins they produce to slow cell division aren’t made. This means that cells are able to divide uncontrollably by mitosis and tumours can develop.
tumour suppressor genes / hypermethylated / transcribed
What is a reason for cancer being caused by tumour suppressor genes?
hypermethylation
When ___________________ are __________________, they act as ______________ - increasing the production of the proteins that encourage cell division. This stimulates cells to divide uncontrollably, which causes the formation of tumours.
proto-oncogenes / hypomethylated / oncogenes
What is a reason for cancer being caused by proto-oncogenes?
hypomethylation
What do HRT drugs do? Why are they used for treating?
increase oestrogen (& usually also progesterone) / menopause symptoms
Theories why Oestrogen can Contribute to the Development of Breast Cancers
Oestrogen can stimulate certain _____________ to divide and replicate which increases the chance of mutations occurring.
Oestrogen’s ability to stimulate division could also mean that if cells do become cancerous, their rapid replication could be further assisted by oestrogen, helping tumours to form quickly.
Other research suggests that oestrogen is actually able to _______________ mutations directly into the _____ of certain breast cells.
breast cells / introduce / DNA
What is the term for when characteristics are affected by different genes?
polygenic
What are the 4 types of stem cell?
totipotent / pluripotent / multipotent / unipotent
Totipotent cells
Where are they found?
How do they remain unspecialised?
What can they develop into?
embryonic development / translate only DNA part / any body cell & supportive structures
Multipotent cells
Where are they found?
What can they develop into?
mature mammals / limited cell types
Pluripotent cells
Where are they found?
What do they develop into?
What have they lost in terms of the ability to become in comparison to totipotent cells?
What are they used for?
embryos / unlimited any body cell / cells that make placenta / treating human disorders
Unipotent cells
Where are they found?
What can they develop into?
mature mammals / 1 cell type
What is the name for the heart muscle cells that make up a lot of the tissue in our hearts? What has recent research shown? What has this come from?
cardiomyocytes / regenerative capability / replacement derived from small supply of cardiac unipotent stem cells
What are the main sources of stem cells?
adult / embryonic / induced pluripotent
What are induced pluripotent stem cells produced from?
specialised adult somatic cells
Production of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
Somatic cells are converted to iPS cells by _________________ using appropriate _________________________.
This makes somatic cells become __________________ so they can be used to treat disease.
activating genes / protein transcription factors / unspecialised
What are activators?
transcription factors that stimulate gene expression by interacting w RNA polymerase, allowing DNA binding
What are repressors?
transcription factors that inhibit gene expression by interacting w RNA polymerase, stopping DNA binding
How do peptide hormones regulate transcription?
bind to cell surface membrane to trigger secondary messenger response
How do lipid-soluble steroid hormones regulate hormones?
pass through phospholipid membrane to interact directly w DNA
Oestrogen
Enters cytoplasm of cell by passing through phospholipid bilayer.
Binds to receptors on _______________ which causes them to change shape and _________________________ forms - this can enter ___________.
Complex binds to ______________ of DNA which activates _____________ thus stimulating ________________.
transcription factors / oestrogen-oestrogen receptor complex / nucleus / promoter region / transcription / protein synthesis
RNA Interference
Small, _____________, ___________ RNA molecules that stop mRNA from target genes being translated into proteins through binding to the molecule and breaking it down.
What are the two types?
non coding / double stranded / siRNA + miRNA
siRNA
Once mRNA has been ____________, it leaves the nucleus for the cytoplasm.
In the cytoplasm, double-stranded siRNA associates with several proteins and unwinds.
One of the resulting single strands of siRNA is selected and the other strand is ________________.
Single strand of siRNA binds to ______________ target mRNA.
Proteins associated with siRNA cut mRNA into _____________________, which moves into a ______________ which degrades them.
transcribed / degraded / complementary / fragments / processing body
miRNA
When miRNA is first transcribed, it exists as a long, folded strand. It is processed into a double stand, and then into two single strands, by enzymes in the cytoplasm.
__________________ physically blocks the _____________ of the target mRNA. The mRNA is then moved into a _______________ where it can either be stored or degraded.
When it’s stored, it can be returned and translated at another time.
miRNA-protein complex / translation / processing body
What is the chemical layer that surrounds chromatin called?
epigenome
How does the epigenome making chromatin more condensed affect transcription?
prevents transcription factors binding to DNA so transcription inhibited
How does the epigenome making chromatin less condensed affect transcription?
allows easier access to transcription factors so transcription promoted
What are epigenetic markers?
groups that don’t alter base sequence but influence chromatin structure
What does increased acetylation cause? What does increased methylation cause?
chromatin less condensed / chromatin more condensed
Epigenetic Markers - Increased Methylation
Methyl groups bind to a ______ site on DNA (areas in DNA where __________________ are together in the base sequence).
Methyl groups cause the chromatin to __________.
______________________ can’t reach the DNA.
Methylation __________ transcription.
CpG / cytosine + guanine / condense / transcription factors / inhibits
What are CpG sites?
DNA areas where cytosine & guanine together in base sequence
Where and how does the methyl group attach as an epigenetic marker?
cytosine by DNA methyltransferases
Epigenetic Markers - Decreased Acetylation
Acetyl groups (___________) are removed from histone proteins.
Removal of acetyl groups increases the ______________ on histone proteins. This increases the attraction to ________________ on DNA.
Decreased acetylation causes the chromatin to _____________.
___________________ can’t reach the DNA.
COCH3 / positive charge / phosphate groups / condense / transcription factors
Which enzyme is responsible for removing the acetyl groups?
histone deacetylase
________________ - genes can be switched 'on' or switched 'off'; genes that are switched on will be expressed, and levels of gene expression can be measured.
microarrays
What are the important features of the genome?
exons / introns / reg genes
What have been the uses of genome projects?
medical advances / biotechnology / evolutionary relationships / further genome sequencing
_________________: faulty alleles in a person’s cells are replaced by working versions of those alleles.
gene therapy
What are the sections of DNA that are transferred called? What is the organism that receives these called? What is produced?
fragments / transgenic / recombinant DNA
Producing DNA Fragments - Reverse Transcriptase
mRNA isolated from cells.
Mixed with ________________________.
The enzyme uses the mRNA as a ___________ to synthesise new strands of __________.
free DNA nucleotides / template / cDNA
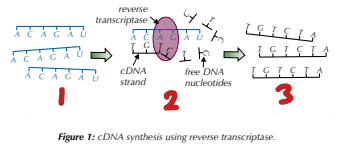
Label the Steps of Making DNA Fragments Using Reverse Transcriptase (1→3)
mRNA strands isolated / cDNA made from mRNA templates / many mRNA cDNA copies produced
Producing DNA Fragments - Restriction Endonuclease
DNA sample is incubated with the specific restriction endonuclease, which cuts the DNA fragment out via a ____________ reaction.
Sometimes the cut leaves ________________ - small tails of unpaired bases at each end of the fragment.
These can be used to bind (_________) the DNA fragment to another piece of DNA that has sticky ends with complementary sequences
hydrolysis / sticky ends / anneal
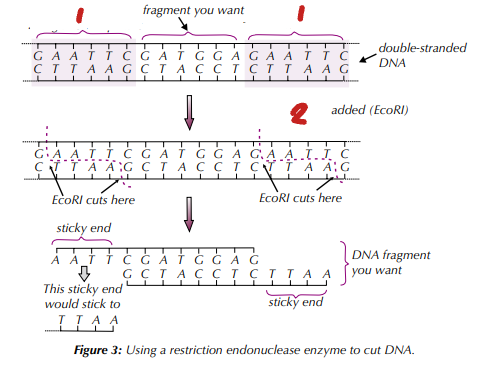
Label the Steps of Making DNA Fragments using Restriction Endonucleases (1→2)
recognition sequence / restriction endonuclease
Producing DNA Fragments - Using a Gene Machine
The sequence for the target gene is obtained from a ___________.
First nucleotide in sequence fixed to _____________.
____________________ are added throughout the synthesis to make sure the correct nucleotides are added (for the correct base sequence) and no _____________ are produced.
_____________________ (short sections of DNA) produced. Once these are complete, they are broken off from the support and all the protecting groups are removed. They can then be joined together to make longer DNA fragments.
database / support / protecting groups / side branches / oligonucleotides
What are palindromic base pairs?
antiparallel base pairs
What are recognition sequences?
specific palindromic sequences that restriction endonuclease recognises
How can DNA fragments be produced?
reverse transcriptase / restriction endonuclease / using gene machines
What are the different techniques of gene cloning?
in vivo / in vitro
What are the 3 stages of in vivo cloning?
making recombinant DNA / transforming cells / identifying transformed cells
In Vivo Cloning - Making Recombinant DNA (Stage 1)
_____________ cut open by __________________ which cut the DNA at specific _____________________. This leaves single-stranded ends of DNA called the ______________.
_______________ joins sticky ends on DNA fragment and vector DNA together.
vector DNA / restriction endonucleases / recognition sequences / sticky ends / DNA ligase
What is the process of joining sticky ends on DNA fragment and sticky ends on vector DNA called?
ligation
In Vivo Cloning - Transforming Cells (Stage 2)
The vector with the _______________ transfers gene into ___________ (these cells have been ‘transformed’).
If the vector is a plasmid , the host cells take up the recombinant DNA via ______________ (host bacterial cells placed in ice-cold caclcium chloride to make cell walls more permeable, plasmids added and mixture is heated to _____°C for ____________).
If the vector is a ______________ (virus), the recombinant DNA is injected into host cells.
recombinant DNA / host cells / heat-shock / 42 / 1 minute / bacteriophage
Other than heat-shock, how else can bacteria be encouraged to take up DNA in the process of in vivo cloning?
electroporation
In Vivo Cloning - Identifying Transforming Cells (Stage 3)
______________ inserted into vectors along with gene to be cloned.
Transformed cells will produce colonies where all the cells contain the cloned gene and the marker gene.
The marker gene can code for _________________ - host cells are grown on agar plates containing the specific antibiotic, so only transformed cells that have the marker gene will survive and grow.
Marker gene can code for ___________________ - when the agar plate is placed under a UV light only transformed cells will fluoresce.
Identified transformed cells are allowed to grow more, producing lots and lots of copies of the cloned gene.
marker genes / antibiotic resistance / fluorescence
If you want the transformed host cells to produce the protein coded for by the DNA fragment, what do you need to do?
ensure vector contains specific promoter & terminator regions
What are promoter/terminator regions?
DNA sequences that tell RNA polymerase where to start/stop producing mRNA
In Vitro Cloning - _________
Reaction mixture containing _________________________________ set up.
The DNA mixture is heated to _____°C to break the hydrogen bonds between the two strands of DNA.
The mixture is cooled to _______ °C so that the primers can bind (anneal) to the strands.
The reaction mixture is heated to ________°C, so DNA polymerase can work. The DNA polymerase lines up free DNA nucleotides alongside each template strand and joins the nucleotides together. Specific base pairing means new complementary strands are formed.
Two new copies of the fragment of DNA are formed and one cycle of PCR is complete. The cycle starts again - the mixture is heated to 95 °C and this time all four strands (two original and two new) are used as templates.
PCR / DNA sample, free nucleotides, primers & DNA polymerase / 95 / 65 / 72
What are the key temperatures in the polymerase chain reaction of in vitro cloning?
95 / 65 / 72
In the polymerase chain reaction of in vitro cloning, why is the mixture heated to 95°C?
break hydrogen bonds between DNA strands
In the polymerase chain reaction of in vitro cloning, why is the mixture cooled to 65°C?
so primers can anneal to strand
In the polymerase chain reaction of in vitro cloning, why is the mixture heated to 72°C?
so DNA polymerase can work
What happens to the amount of DNA each PCR cycle?
doubles
How can recombinant DNA technology be used?
agriculture / industry / medicine
What are the types of gene therapy? Where do they alter alleles?
somatic - adult body cells / germ line - sex cells
Gene Therapy
Used to treat diseases that are caused by a ______________ in a gene.
The insertion used depends on the ____________________ of the gene that causes the disease.
If the mutation is in the recessive allele, a ____________ dominant allele is inserted into the genome. The dominant allele counteracts the mutant alleles.
If the mutation is in the dominant allele, an allele that '____________' the mutant allele is inserted in the genome.
mutation / allele interactions / wild-type / silences
What are the techniques used to diagnose disease using DNA probes?
electrophoresis / microarrays
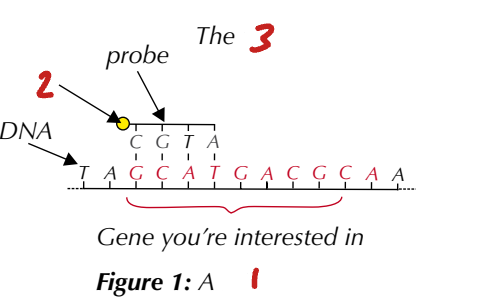
Label the Image (1→3)
DNA probe / label / probe hybridises to complementary gene part
DNA Probes
Section of __________________ that is complementary to DNA of the ______________. If present, it will bind to DNA probe through __________________.
DNA probes labelled with _____________ or _______________. If present, this label detected.
What are the techniques used to do this?
single-stranded DNA / target allele / hybridisation / radioactive phosphate / fluorescent tag / electrophoresis & microarrays
Using DNA Probes for Medical Diagnosis - ___________________
A sample of DNA is digested into ________________ using ___________________.
The separated DNA fragments are then transferred to a _____________________ and incubated (through ‘____________’) with a fluorescently labelled DNA probe. If the allele is present, the DNA probe will _________________.
The membrane is then exposed to UV light and if the gene is present there will be a ___________________.
electrophoresis / fragments / restriction enzymes / nylon membrane / washing over / hybridise / fluorescent band
Using DNA Probes for Medical Diagnosis - _____________
Use many DNA probes at once.
Slide with many indents - each indent contains the DNA probes for a specific gene.
The fluorescently labelled DNA sample is _____________.
Any DNA fragments that are complementary to the probes will ______________.
microarrays / washed over / hybridise
________________ can be used to identify….
if an individual is a __________ of a genetic disease.
if an individual is at greater risk of developing a disease.
how likely an individual is to respond to a particular ________.
genetic screening / carrier / drug
_________________ aims to determine…
if ____________ is advisable.
what the results of screening mean.
how to prevent or treat a _____________ identified through screening.
genetic counselling / screening / condition
What can genetic fingerprinting be used for?
genetic relationships / genetic variability / forensic science / medical diagnosis / breeding
What are the steps of producing genetic fingerprints?
PCR to make DNA fragments / gel electrophoresis to separate DNA fragment / genetic fingerprint analysis
Producing Genetic Fingerprints
DNA sample extacted from individual and _______________ using ______. ____________ are used that bind to either side of the VNTR repeats so the whole repeat is coped many times.
_____________ labelled using fluorescent labels and inserted into a well in a gel which is covered in _______________ that conducts electricity. Current passed through gel so _______________ DNA fragments move toward ________________.
_____________ analysed, the length (in nucleotides) of DNA fragments corresponds to the number of __________ the person has at each locus.
amplified / PCR / primers / DNA fragments / buffer solution / negative / positive electrode / DNA ladder / VNTRs