Sound waves for physics unit 1 exam
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
how do you define sound? what type of wave is it? what is it produced by, for sound to exist it must travel through what?
Sound: is a mechanical, longitudinal wave produced by
a vibrating source. For sound to exist, it must travel
through a medium
Sound Waves
•Ultrasound:
Transducer produces what? and what does it travel through?
How is it reflected?
•Ultrasound
• Transducer produces sound pulses
• Sound pulses travel through tissue (a media)
• Is reflected from the boundaries between structures and then
returned to the transducer
what do sound waves consists of?
• Consist of energy
sound waves consist of energy, carried from.?
what are the different types of waves
Carried from one location to another
• Heat, sound, magnetic and light are types of waves
Wave classification electromagnetic VS mechanical
Let’s talk about Electromagnetic
Alternating what field
what’s the direction
can travel in what
what does this produce/what is this used for
Electromagnetic
• Alternating electric and magnetic field
• Perpendicular
• Can travel in a vacuum
• Light / X-Ray
Mechanical wave classification
what does it pass through and…
energy is passed between?
this is what wave?
Mechanical
• Passes through a medium and vibrates molecules
• Energy is passed between the molecules
• Sound!
(Molecules oscillate (vibrate back and forth)
This creates compressions and rarefactions)

what is this showing you?
Mechanical “Longitudinal”

what is this showing you
electromagnetic
Wave Classification. Longitudinal- define (sound waves in what)
Particles vibrate in a motion that is parallel to the direction of wave
propagation
• Sound waves in liquid
Wave Classification define transverse
Transverse
• Particle motion is perpendicular to the direction of wave
propagation
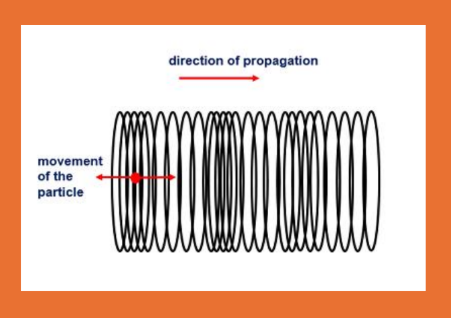
this is representing what wave
Longitudinal
wave anatomy:
mechanical waves can’t travel in what?
what is required for it travel?
what describe particle motion within a sound wave?
describe how the medium allows sound to travel, reflect, and attenuate?
IN what direction does it travel?
• Can’t travel in a vacuum
• Medium
• Required
• Molecules are compressed and rarefied
(What describes particle motion?” → Compression/rarefaction, This is how sound moves through the medium. These are acoustic variables
• Acoustic propagation properties (These describe the medium’s ability to transmit sound, not the wave motion itself.The main propagation properties are:
Density
Stiffness (elasticity)
Propagation speed
Attenuation
Acoustic impedance
These determine:
How fast sound travels
How much sound is reflected
How much is transmitted
How much is absorbed
Sound bounces back (reflects) when there is a change in acoustic impedance between tissues.
Impedance depends on:
Density
Propagation speed
• Travel in a straight line - longitudinal
Define compression
Compression: squeeze together
Define Rarefied
Rarefied: stretched apart
what are the acoustic variables we used this method for identifying what? It Distinguish between what? Sound waves =/
what are the variables?
• Acoustic variables
• Method for identifying waves
• Distinguish between sound and other types of waves
• Sound Waves = Acoustic Waves
Variables: Pressure, Density, Distance
Define the variable and tell me the unit, Pressure
Pressure: concentration of force in an area: pascals (Pa)
Define the variable and tell me the unit, Density
• Density: concentration of mass in a volume: kg/cm3
Define the variable and tell me the unit, Distance
Distance: measure of particle motion: cm, m
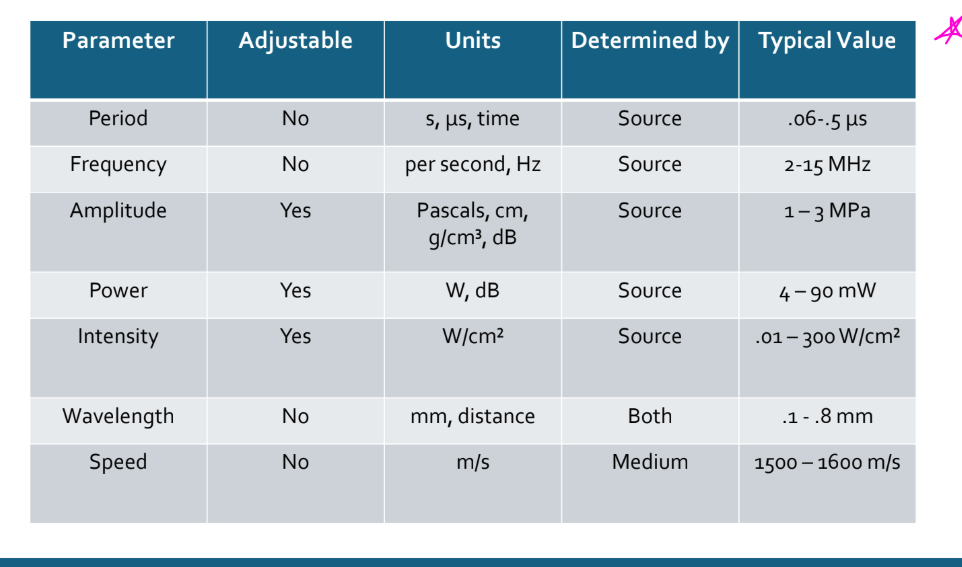
what are the & Acoustic parameters
Acoustic parameters
• Describes the features
• Period
• Frequency
• Amplitude
• Power
• Intensity
• Wavelength
• Propagation speed
Remember that sound waves are a ______cyclical event that travels in a _____line
One cycle =
this _____wave
Compression =
Rarefaction =
Remember
• Sound waves are a reoccurring cyclical event that travels in a
straight line
• One cycle = one peak + one trough
• Sine wave
• Compression: high pressure area, crests
• Rarefaction: low pressure, trough
Phase
• Comparing where the _____and ____-of two waves ____
• In-Phase: Peaks occur when
what type of interference
resulting wave is ?
• Phase
• Comparing where the peaks and troughs of two waves intersect
• In-Phase: peaks occur at the same time and location
• Constructive interference
• Resulting wave is larger than each individual wave
Out-of-Phase: _____and _____occur at ____time
what type of interference is this?
resulting wave is?
complete destructive of what
Out-of-Phase: peaks and troughs occur at different time
Destructive interference
• Resulting wave is smaller than each individual wave
• Complete destructive: wave amplitude match perfectly

• Phenomenon
• Waves with different?
one moment in time?
Phenomenon
• Waves with different frequencies
• One moment in time
• Constructive interference
• Destructive interference
what does frequency measure
complete cycle =
what are the units
Ultrasound imaging is in the range of ?
Doppler ultrasound is in the range of?
• Measurement
• Frequency = # of cycles
• Complete cycle = one crest + one trough
• Units
• Cycles / second = Hertz (Hz)
• Ultrasound imaging is in the range of MegaHertz (MHz)
• Doppler ultrasound is in the range of Hertz (Hz) to kiloHertz (kHz)
what is infrasound mean what is the frequency
• Infrasound
• Frequency < 20Hz
• Too low for humans to hear
what does Audible mean and what’s the frequency?
Audible
• Frequency 20Hz – 20kHz
what does Ultrasound mean and what’s the frequency?
•Ultrasound
• Frequency >20kHz
• Too high for humans to hear
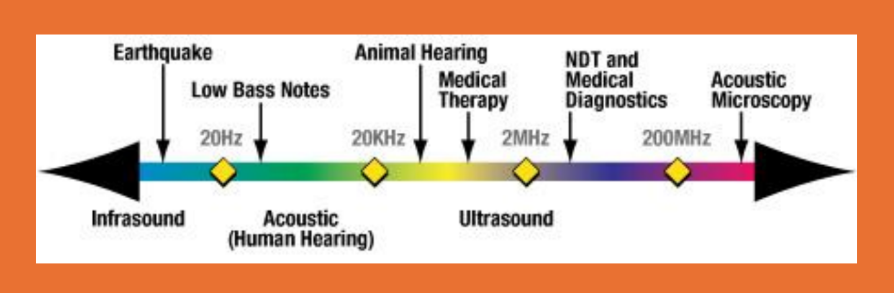
Diagnostic Sonography
• Frequency determined by? whats the Hz
• Frequency determined by the transducer
• 2MHz – 20 MHz
what does Frequency affects?
• Affects penetration and resolution
High frequency=
High frequency = better resolution
Low Frequency =
Low frequency = better penetration
•Ultrasound system / transducer
• “Source”
Control some of the what?
Can sonographer adjust this?
Control some of the parameters
• Sonographer can adjust
Medium- its an actual what
sound travels …..
can determine what
• Medium
• Actual tissue
• Sound travels through the tissue
• Can determine some parameters
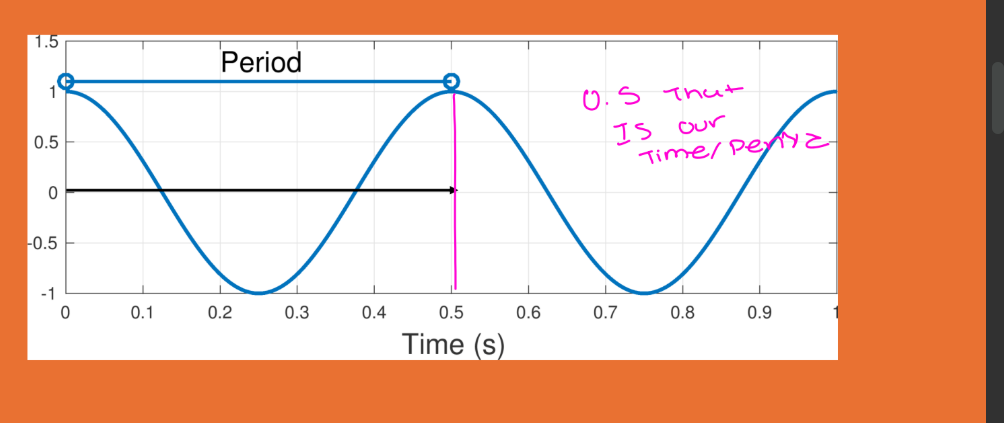
what is period and what are the units
what is it measuring and its determined by what? can sonographer change this? typical ultrasound wave=
p=
f=
Time it takes to complete one cycle
• Seconds, milliseconds, microseconds
• Measuring time from one point on the wave to a similar point on
consecutive waves
• Determined by the transducer
• Sonographer cannot change this
• Typical ultrasound wave
• .06 - .5 μs
P=1/f
f=frequency
Period and frequency have what type of relationship
High frequency= (what type of period)
Low Frequency= (what type of period)
• Period and frequency
• Inverse relationship
• High frequency = short period
• Low frequency = long period
Period and wavelength have what type of relationship?
measure how
• Period and wavelength
• Direct relationship
• Measure the same area, but with different units
Frequency
•Number of events that occur?
Ultrasound = # of….
units?
Determined by?
can or cannot be changed with the basic ultrasound system and transducer
whats the Typical ultrasound frequency range
Frequency
•Number of events that occur in a specific duration of time
• Ultrasound: # of cycles that occur in 1 second
• Units
• Hertz (Hz)
• Determined by the sound source (transducer)
• Can’t be changed with the basic ultrasound system and transducer
• 2MHz – 20MHz
Frequency
• Importance… its affects
Affects penetration and image quality (and resolution)
what type of relationship does frequency and period have
• Frequency and period
• Inversely related / reciprocal relationship (=1)
what does Amplitude describe?
Difference between?
what are the units?
•Describes wave magnitude (strength)
•Difference between max or minimum value and the baseline
•Units
• Variable
• Pressure – pascals
• Density – g/cm3
• Particle motion – any distance measurement
• Decibels
Amplitude
•Units
is it controlled by the sonographer?
•Units
• Ultrasound 1 MPa – 3 MPa (millions)
Yes Controlled by the sonographer its the Output power / power control
Amplitude will decrease when? this is called?
• Will decrease as wave travels in tissue
• Attenuation
How do you measure the wavelength of Amplitude (?)
Peak to Peak
• 2x the amplitude value or is the max and min amplitude value
Define Attenuation
Attenuation: weakening of the wave as it travels through tissue
Define Power
what’s the units?
• Rate of energy transfer or the rate at which work is performed
• Think of a light bulb
• 45 W bulb vs 100W bulb
• Rate of energy transmitted by the transducer into the body
•Units
• Watts (W)
• Ultrasound
• .004 - .09 W or 4 – 90 mW
is power controlled by the sonographer?
Yes, • Controlled by the sonographer
• Power output / power control button
• Power α Amplitude2
If one increases, what happens to the other
If one decreases, what happens to the other
If one increases, so does the other
• If one decreases, so does the other
what will happen to the power as it travels through the medium?
Will decrease as wave travels through the tissue • Attenuation
As sound goes deeper:
Some energy is absorbed (turned into heat)
Some is scattered
Some is reflected
📌 Because of this:
Power, amplitude, and intensity all decrease with depth
You send more energy into the body
The wave starts stronger
More energy survives attenuation
Deeper echoes can return
✅ This can help with deep structures
BUT why we DON’T just crank up power
Because:
Power increases patient exposure
Can increase tissue heating
Violates ALARA if overused
A sonographer increases the amplitude of a wave by a factor of 3. How has the
power changed?
Power α Amplitude2
Power = 3 x 3 = 9 (power has increased 9-fold)
When a sonographer decreases the amplitude of a wave to 1⁄2 of its original
value, how has the power changed?
Power α Amplitude2
Power = .5 x .5 = .25 (power is now 25% of its original value)
The sound wave now has only one-quarter of the energy it had before. (much weaker)
A sonographer will use full power for most exams they perform. Some exceptions when
the power would be decreased is:
Obstetrics (OB)
Infants and children
Transcranial Doppler (TCD)
and contrast
Intensity, its concentration of what
its describes what
and depends on
Intensity, Concentration of energy in sound beam
Describes how power in a wave is distributed in space
• Depends upon power and area
• Intensity =
If power doubles what happens to intensity? what’s the relationship
what’s the units?
• Intensity=power/area
If power doubles, intensity will double (directly related)
• Intensity α Amplitude2
•Units
• Watts/square (W/cm2)
when will intensity change
Intensity will change as wave travels into the tissue
Rate of change for intensity is dependent upon what
Rate of change is dependent upon wave characteristics and the
medium
(This is talking about how fast intensity decreases as the wave travels (attenuation).
Wave characteristics (things about the wave itself)
Frequency
Higher frequency → more attenuation
Intensity drops faster with depth
Amplitude / Power
Stronger waves start with higher intensity
🔹 The medium (tissue)
Different tissues weaken sound differently:
Fat → higher attenuation
Soft tissue → moderate
Fluid → very low attenuation
Bone → extremely high attenuation
📌 So:
The same ultrasound wave will lose intensity at different rates in different tissues.
• Intensity is dependent upon the ultrasound system (the ultrasound system determines how intense the beam is when it enters the body.)
Is intensity controlled by the sonographer?
• Controlled by sonographer
• Power output / power control button
Determining Wave Strength
• Look at the relationship between
• Look at the relationship between amplitude, intensity and
power
Determining Wave Strength
• Look at the relationship between amplitude, intensity and
power
power=
if one increases, what happens to the other
if one decreases what happens to the other
• Power = Intensity
• If one increases, so does the other
• If one decreases, so does the other
Power/Intensity α Amplitude2
Amplitude doubles, then what happens with power/intensity
• Amplitude halves, then what happens to the power/intensity
Power/Intensity α Amplitude2
• Amplitude doubles, then power/intensity increase by 4
• Amplitude halves, then power/intensity decreases by a quarter
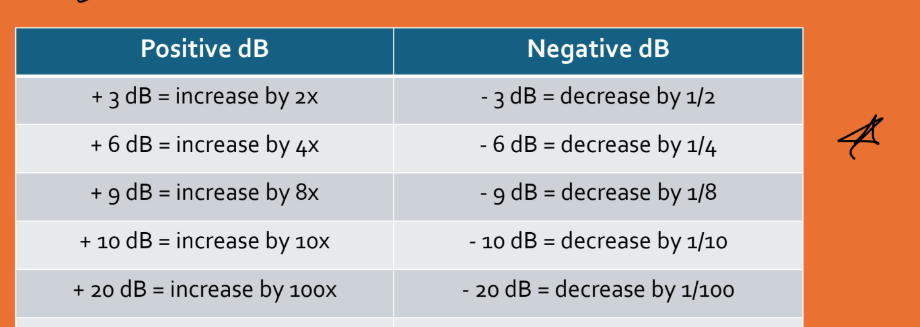
what does Decibels (dB) compares? Ratio units are expressed as?
Compares intensities or amplitudes of two waves or wave points
• Ratio units are expressed as decibels
Decibels (dB), Relate what? Express what values on a what scale?
Positive dB=
^this signal is what?
• Turning up ?– adding ?– stronger ?
• Will
• Relate two values to each other
• Express large range of values on a smaller scale
• Positive dB = increase in value
• Signal strength is increased
• Turning up gain – adding decibels – stronger echoes
dB tells you how much change occurred.
Decibels (dB)
• Will
• Negative dB =
what happens to the signal
sound wave is what
(what may the sonographer need to do)
Decibels (dB)
• Will
• Negative dB = decrease in value
• Signal is weakened
• Sound wave is attenuated or weakened as it travels through tissue
• Sonographer may need to adjust gain to strengthen signal!
what are the positive dB and negative dB values?
The power control, which determines the amount of _____that goes to the
transducer, can be expressed as a ______or in ____. How it is expressed is
dependent upon the _____. Power is controlled by the _______!
what is full power for db and %
The power control, which determines the amount of energy that goes to the
transducer, can be expressed as a percentage or in dB. How it is expressed is
dependent upon the vendor. Power is controlled by the sonographer!
100% is full power
0 dB is full power
The sound wave traveled through tissue and was attenuated by 6dB. The original intensity
of the wave was 16 mW/cm2. What is the ending intensity? Remember – attenuation is
weakening of the beam.
Look at the chart under negative dB (attenuation) and -6 dB equates to a decrease of 1⁄4 or
25%
16mW/cm2 x 1⁄4 = 4 mW/cm2
Ending intensity is 4mW/cm2
Define what we measure for the Wavelength (λ) and what are the unitts and ultrasound in soft tissue units…
determined by the? is it controlled by the sonographer?
•Distance / length of one complete cycle
• Units
• Millimeters, meters
• Ultrasound
• .1 - .8 mm in soft tissue
• Determined by the source and the medium
• Is not controlled by the sonographer
how is Wavelength (λ) related to frequency?
High f=
Low f=
• Inversely related to frequency (f)
• High f = short λ
• Low f = long λ
• Inversely related to frequency (f) - for Wavelength (λ)
what does the short wavelengths provide us with and what is the trade off?
Short wavelengths equate to higher quality images (detail)
• Trade off is poor penetration
Wavelength (λ) is directly related to what
•Directly related to propagation speed (c)
•Directly related to propagation speed (c) - Wavelength (λ)
C is dependent ?
• C changes so will the?
C is dependent upon the medium
• C changes so will the wavelength
why would the Sonographers will always use the highest frequency possible?
B/c it gives the most optimal penetration
Sonographers choose the highest frequency that still allows adequate penetration, in order to maximize image resolution.
Wavelength (λ)
•Defining
frequency, wavelength and propagation speed
what is the formula/ different formula for Wavelength (we can figure out different things)
• λ = c/f or c = f x λ or f = c/λ
Determine the wavelength produced by a 5.0 MHz
transducer traveling in soft tissue. c in soft tissue =
λ = c/f
soft tissue = 1.54 mm/μs
λ = 1.54 mm/μs / 5MHz = .3 mm
Relating Frequency, Period and
Wavelength, what are the relationships?

what is Propagation Speed
what are the units
what is it dependent upon
all sound travels at the….
no matter the?
Rate that a sound wave travels through a medium
•Units
• m/s or mm/μs
• Ultrasound
• 500 to 4000 m/s
• Is dependent upon the medium through which it travels
• All sound travels at the same speed in any given medium
• No matter the frequency of transducer
is Propagation Speed dependent on the frequency of transducer?
No matter the frequency of transducer
Propagation Speed
• Medium =
what are the different types?
Medium = Tissue
• Stiffness
• Density
• Elasticity
• Compressibility
for Propagation Speed ultrasound machine accounts for what?
can it be changed by the sonographer?
•Ultrasound machine
• Accounts for speed of sound
• Can’t be changed by sonographer
Soft Tissue (average) =
1540
how does sound travel in solids vs liquids vs gases
Sound travels fastest in solids, slower in liquids and slowest in gases
Characteristics of the Medium
Stiffness, is ability to what?
what happens if the material is squeezed? does it retains its shape, what happens with non-stiff material shape?
Stiffness
• Ability to resist compression
• What happens if the material is squeezed?
• Stiff material
• Retains its shape
• Non-Stiff material
• Changes its shape
Characteristics of the Medium
• Stiffness
• Directly related to?
Two ______materials
• Stiffer of the two will have the?
Stiffness
• Directly related to speed
• Two identical materials
• Stiffer of the two will have the higher speed of sound
what are the other terms for stiffness?
Other terms for stiffness
• Bulk modulus
• Elasticity
• Compressibility
Characteristics of the Medium
•Density
• Relative to what?
Equal volume of material, the dense material will
is steel or aluminum dense
density has a what relationship to speeds
speed is determined by?
•Density
• Relative weight of the material
• Equal volume of material, the dense material will weigh more
• Steel is dense, aluminum is not
• Inversely related to speed
• Dense material = slower speeds
• Speed is determined by density and stiffness of the medium
Characteristics of the Medium
• Materials stiff, but not dense =
fastest speed
Materials not very stiff, but dense =
slowest speed
Stiffness has the greatest influence on?
Speed
Air has ____ stiffness =
sound travels slowly in air
• Why does this matter? Pathological conditions can and will
affect the sound wave (disrupt ultrasound wave propagation./causes significant reflection and attenuation)
One of the reason why ultrasound gel is applied to the patient – conduit to get the sound wave into the patient
Air has low stiffness and is easily compressible, so sound energy is transferred inefficiently between molecules, resulting in a slow speed of sound.
Sound travels slowly in air because air is easy to compress (low stiffness).
Period and frequency
• Together because they are?
reciprocals =1
Amplitude, power and intensity=
Magnitude of the sound wave
• Sonographer can control
Wavelength
• Determined by
sound source and medium
• Speed
• Determined by
the medium

for period, frequency, amplitude, power, intensity, wavelength, speed