1-Electrolytes and Water Homeostasis
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Intracellular fluid
2/3 of total body water
-inside of cells of every kind
Extracellular fluid
1/3 total body water
-80%: interstitial and intravascular fluid
-20%:blood plasma
Blood colloidal osmotic pressure
helps keep water in blood vessels with the help of albumin
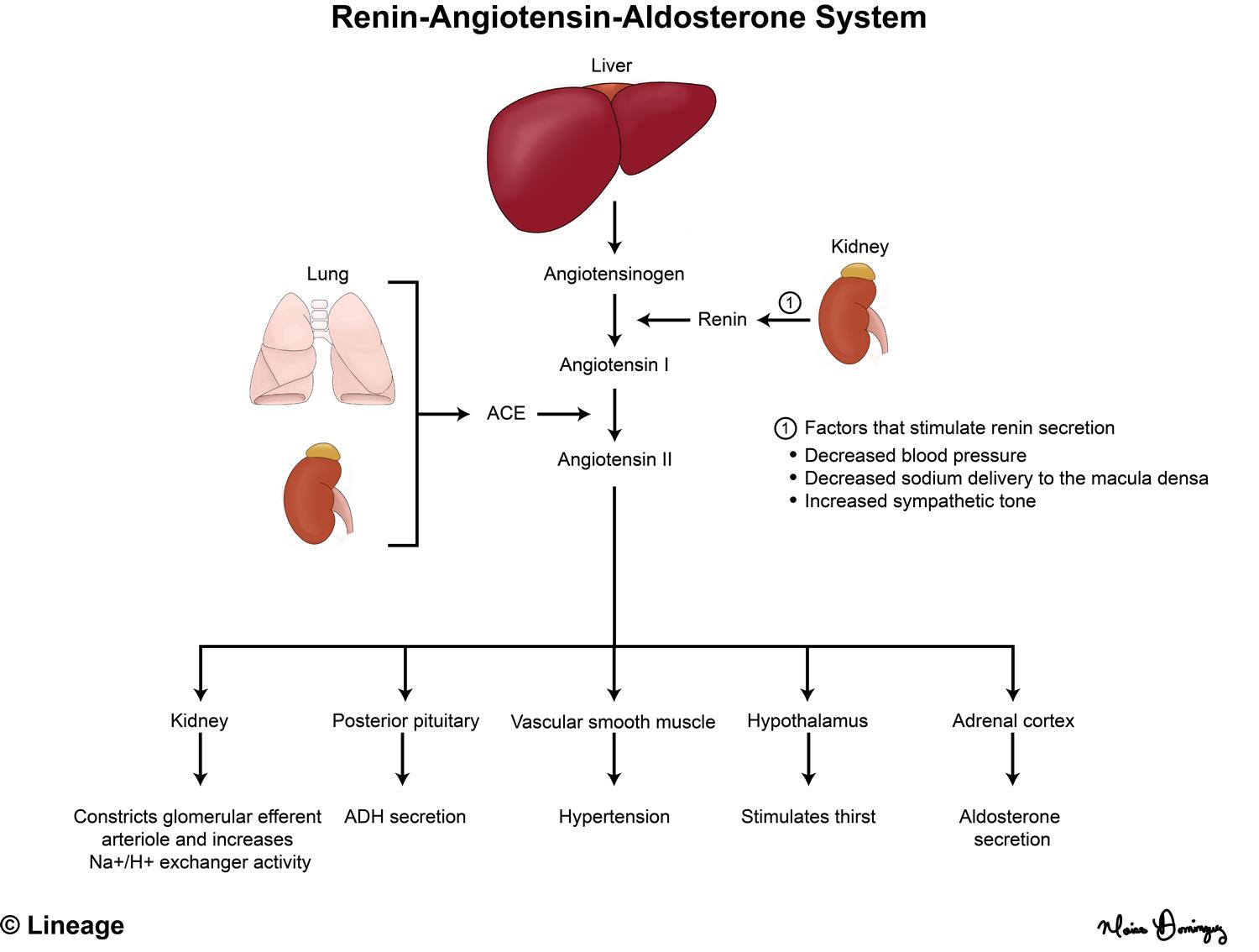
What initiates the RAAS
-incr sympathetic tone
-decr pressure
-decr sodium
Know RAAS steps
What is a colligative property?
property that depends on the # of particles in the solution
What are the 4 colligative properties?
osmotic pressure
boiling pt elevation
freezing pt depression
vapor pressure lowering
What colligative property does the osmometer use?
Freezing pt depression
Osmolality Formula
Posm =2Na + Glucose/18 + BUN/2.8
Osmolal Gap formula?
OG= measure -calculated osmolality
What can cause a high osmal gap?
-presence of other osmotically active substances
EX: Lactic acis, Keto acids, alcohols, ethylene glycol
Major electrolytes
sodium, potassium, chloride, and total CO2
What are electrolytes?
conduct an electrical current in solution
Normal range for Na+
135-145 mmol/L
What roles does Na+ have in the body?
H2O homeostasis and osmotic pressure
Sodium is the major _____cation.
extracellular
What method measures Na+?
ISE
Normal range for K+
3.5-5.5 mmol/L
Potassium is the major ____cation
intracellular
Why is hemolysis unacceptable for K+?
ruptured RBC’s will falsely elevate K+
What method measures K+?
ISE with a valinomycin tip
Normal range for chloride (Cl-)
98-109 mmol/L
Chloride is the most abundant ___in the ___fluid.
most abundant anion in extracellular fluid
What method measures Cl-?
Coulometric-amperometric titration
Normal range for CO2
22-28 mmol/L
Total CO2 formula
Total CO2 = CO2 + HCO3-
-bicarb is majority
Normal range for Mg2+
1.5-2.4 mg/dL
What role does Mg play in the body?
-activates 300+ enzymes
-affects permeability and electric properties of membranes
What complex is made to measure Mg2+
Calmagite @ 532 nm
Can Mg assay handle hemolysis
No, Mg is higher inside cells
-hemolysis=false elevation
Anion Gap formula
AGap = (Na+ + K+) - (Cl- + HCO3-)
normal :8-16mmol/L
Where would you see an increased AGAP? (MUDPILES CAT)
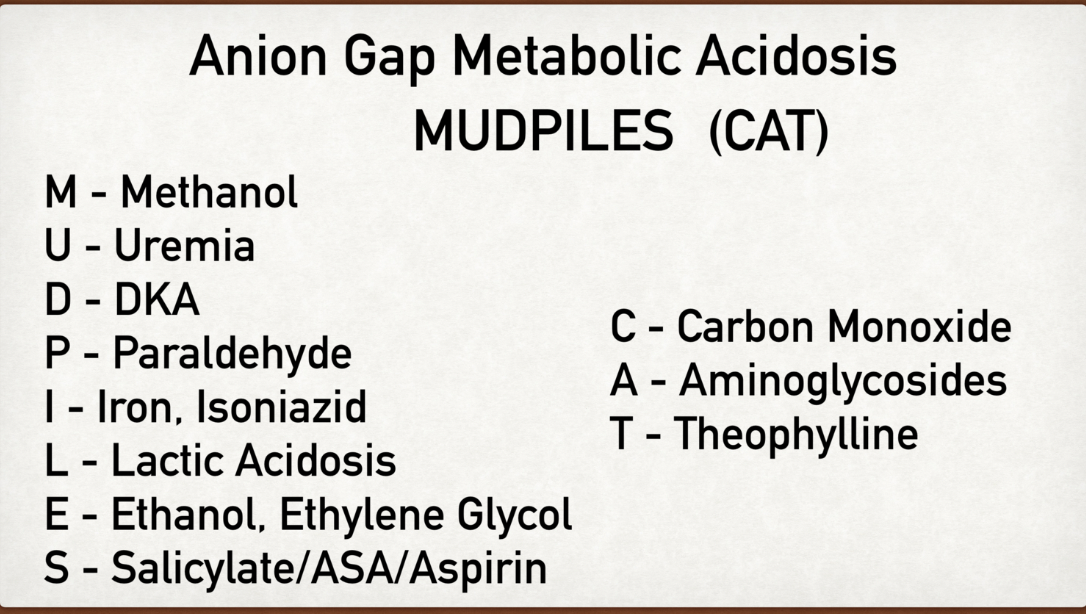
What analytes make the AGAP increase?
1 or more unmeasured anions
Where would you see a decreased AGAP?
-RARE
-instrument issue #1
-multiple myeloma
-hyponatremia
Iron metabolism
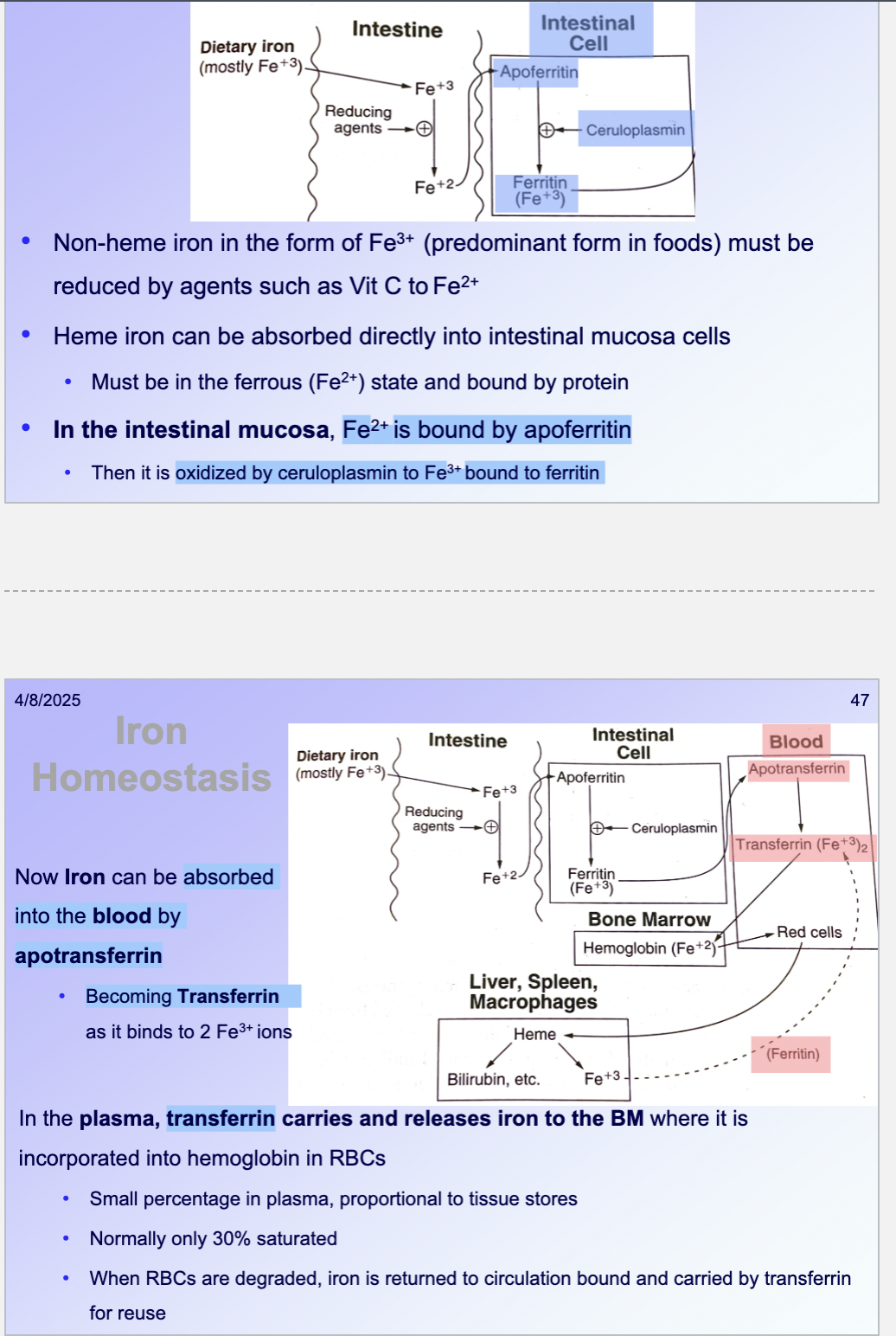
Total iron refers to Fe3+ bound to ___
transferrin
Total iron has diurnal variation, which sample is best?
morning
What preanalytical error should be avoided with total iron
hemolysis since colorimetric method is used
Ferritin
stores iron inside cells
Testing for ferritin helps asses___
iron storage
Transferrin
transports iron
Why do we test for transferrin
to monitor nutritional status
TIBC
measures body’s ability to bind iron
TIBC reflects ___levels
transferrin
A transferrin test ___measures its levels; TIBC ___measures transferrin.
Directly; Indirectly
IDA
-decr: serum iron, ferritin, %saturation
-incr: TIBC
Hemochromatosis
-incr: ser iron, %saturation, ferritin
-decr: TIBC
in the body, Zinc helps ____
enzymatically
Deficiency in Zinc will cause
-failure of growth
-impaired wound healing
-impair immunity
-mental
-parenteral nutiriotn
Copper is a cofactor for ___enzymes
oxidase
Menke’s syndrome
deficiency in copper
Wilson’s disease
copper toxicity
What key lab finding points to Wilsons disease?
decr ceruloplasmin
What will be incr in Wilsons
urine copper output
What role does Manganese Mn2+ have in the body
-metabolism in connective tissue
-physical growth
-reproductive function
Chromium binds to___
transferrin
List water soluble vitamins
-vit B
-vit C
List fat soluble vitamins
-vit A, D, E, K
B1 is also called___
thiamine
Def in B1 leads to
Beriberi syndrome-peripheral nerve damage
B3 is also called___
Niacin
Def in B3 leads to
Pellagra
B6 is also called___
pyridoxine
*Def in B6 leads to
def is rare and only happen in malabsorption syndromes
B7 is also called ____
Biotin
high levels of B7 can interfere with
immunoassays
B9 is also called
folate
B9 is important for
-RBC formation
-cell growth
B9 is crucial in ___
pregnany
Def in B9 leads to ___ and ___
-megaloblastic anemmia
-neural tube defects
(sometimes spina bifida)
B12 is also called____
cobalamin
Def in B12 leads to___and___
-pernicious anemia
-neurological defects
What is required for B12 absorption?
intrinstic factor
What role does vit C have in the body?
-forms blood vessels, cartilage, muscle, collagen in bones
-vital for wound healing
-antioxdant
Vit C ___in many assays since it is a ___substance
interferes; reducing
What role does Vit D play in the body
calcium absorption and bone metabolism
Def in Vit D
Rickets