100 Things to Know for the Living Environment Regents
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
homeostasis
the ability of an organism to maintain a stable internal balanced environment
metabolism
the sum of all the chemical reactions that occur within the cells of an organism
organic molecules
molecules that contain skeleton structures of carbon with hydrogen and oxygen
organelles
the small organ like parts that make up a cell
vacuoles
organelles that store waste and water
ribosome
very small organelles that are the site at which amino acids undergo protein synthesis
mitochondria
the site at which cellular respiration occurs making ATP
chloroplasts
organelles only found in plant cells that are the site for photosynthesis
nucleus
the control center of the cell with contains DNA
nucleolus
an organelle in the nucleus that makes ribosomes
cytoplasm
the liquid substance that fills a cell
cell membrane
separates the contents of the cell from the outside environment and controls the transport of materials in and out of the cell because it is selectively permeable
cellular communication
recognizes and responds to chemical signals by using receptor molecules
active transport
the moving of energy from an area of low concentration to high concentration using ATP
diffusion
the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration without using energy
digestive system
a system of the body that breaks down nutrients and puts them into the blood stream
circulatory system
a system of the body that transports materials throughout the body
respiratory system
a system of the body that exchanges carbon dioxide and oxygen
excretory system
a system of the body that removes metabolic wastes from blood and the body
nervous system
a system that quickly picks up and responds to stimuli
endocrine system
a system of the body that is slower to respond to changes by secreting hormones to the target tissues
control
hormones are produced in the endocrine glands and chemicals produced by nerve cells that are primary responsible for communication between cells
respiration
the process used by all organisms to produce energy by using oxygen to burn sugar in order to release energy in the form of ATP
hydrolysis / digestion
the breaking down of large molecules
transport
involves the movement of materials inside the cell as well as movement between parts of multicellular organisms
dehydration synthesis
the removal of water to make or build larger molecules from smaller molecules
photosynthesis
the process of storing the energy from the sun in the chemical bonds of glucose (sugar)
cellular respiration
the process of releasing the energy stored in the bonds of glucose as ATP
enzymes
special proteins that affect the rate of chemical reactions, they are catalysts used in digestion and synthesis
dynamic equilibrium
an ecosystem in homeostasis
negative feedback
a type of feedback mechanism that helps maintain hormone levels by secreting the opposite of whatever hormone level is too high or low
surface receptor protein
a molecule found on the cell membrane that the immune system recognizes as either part of the body or an outside invader
antibodies
special proteins produced by the white blood cells that fight diseases
immunity
the body's ability to fight diseases
vaccination
a substance inserted into the body containing a weakened or dead virus that trigger our white blood cells to produce antibodies to fight a specific pathogen
diseases
caused by pathogens (virus, bacterium, fungi)
cell division
the process by which a cell replicates and splits; mitosis and meiosis
mitosis
a type of asexual reproduction used by all cells except gametes in which a parent cell splits to form two identical offspring
gonads
sex glands (ovaries and testes)
gametes
the sex cells that unite in fertilization to form a zygote (egg and sperm)
zygote
a fertilized egg
fertilization
the process in which a male the male and female gametes unite to form a diploid cell (occurs in the fallopian tubes)
differentiation
the process that transforms developing cells into specialized cells with different structures and functions
vagina
opening for birth of child and urethra for urination
uterus
the place in which a baby develops
placenta
the organ through which nutrients diffuse from the mother to the baby
oviducts / fallopian tubes
the place where fertilization occurs
testes
the male gonads that produce sperm and male hormones like testosterone
artificial insemination
using sperm from a donor to get pregnant
amniocentesis
removing some of the cells from the amniotic fluid that protects the fetus and analyzing their DNA
karyotype
a visual map of chromosomes that can be used to determine if the fetus has problems like Down's syndrome
Down's syndrome
a chromosomal problem in which a fetus has three copies of chromosome #21
cancer
occurs when certain mutations caused by an environment that can result in uncontrolled cell division
heredity
the passing of genetic information from one generation to the next through reproduction
asexual reproduction
a form of reproduction where one parent creates identical offspring
sexual reproduction
a type of reproduction where two parents' gametes unite to form a genetically similar offspring
clones
identical copies of genes
DNA
a double stranded helix polymer (large molecule) of nucleotides that contains the genetic code for an individual
nucleotide
the basic unit of DNA which is made of a phosphate, a sugar, and a nitrogenous base
RNA
a single stranded polymer that is produced by DNA that contains uracil instead of thymine
protein synthesis
the process in which proteins are made from amino acids
mutation
any alteration of the DNA sequence which changes the normal message carried by a gene (substitution, deletion, addition and inversion)
gene expression
an organism's environment can effect the way some genes are expressed
pointed gene
a gene in which the fur color of the Himalayan Rabbit changes due to temperature
genetic engineering
a technology that humans use to alter genetic instructions on organisms
gene splicing
cutting DNA and placing it into another organism (GFP Lab)
restriction enzyme
an enzyme that cuts DNA in specific places and is an essential tool in gene splicing as well as gel electrophoresis
DNA fingerprint
from gel electrophoresis that can be used to compare organisms; the more common bars, the more common the ancestry or heritage
species
a group of closely related organisms that share certain characteristics and can produce offspring capable of reproduction
evolution
the process by which organisms have changed over time from simple, single celled organisms to complex multicellular organisms
natural selection
the process by which organisms with better traits survive and reproduce, passing those traits on to their offspring
overproduction
producing more offspring than the environment can support; forces competition and natural selection to occur
competition
the fight for limited resources that results in the struggle for survival of organisms
variation
differences among organisms in a species (sexually reproducing organisms have more variation than asexually reproducing organisms)
adaptation
any trait that helps an organism survive and reproduce under a given set of environmental conditions
extinction
the disappearance of an entire species caused by a failure to adapt to a changing environment
ancestry
can be determined through cladograms or a family tree
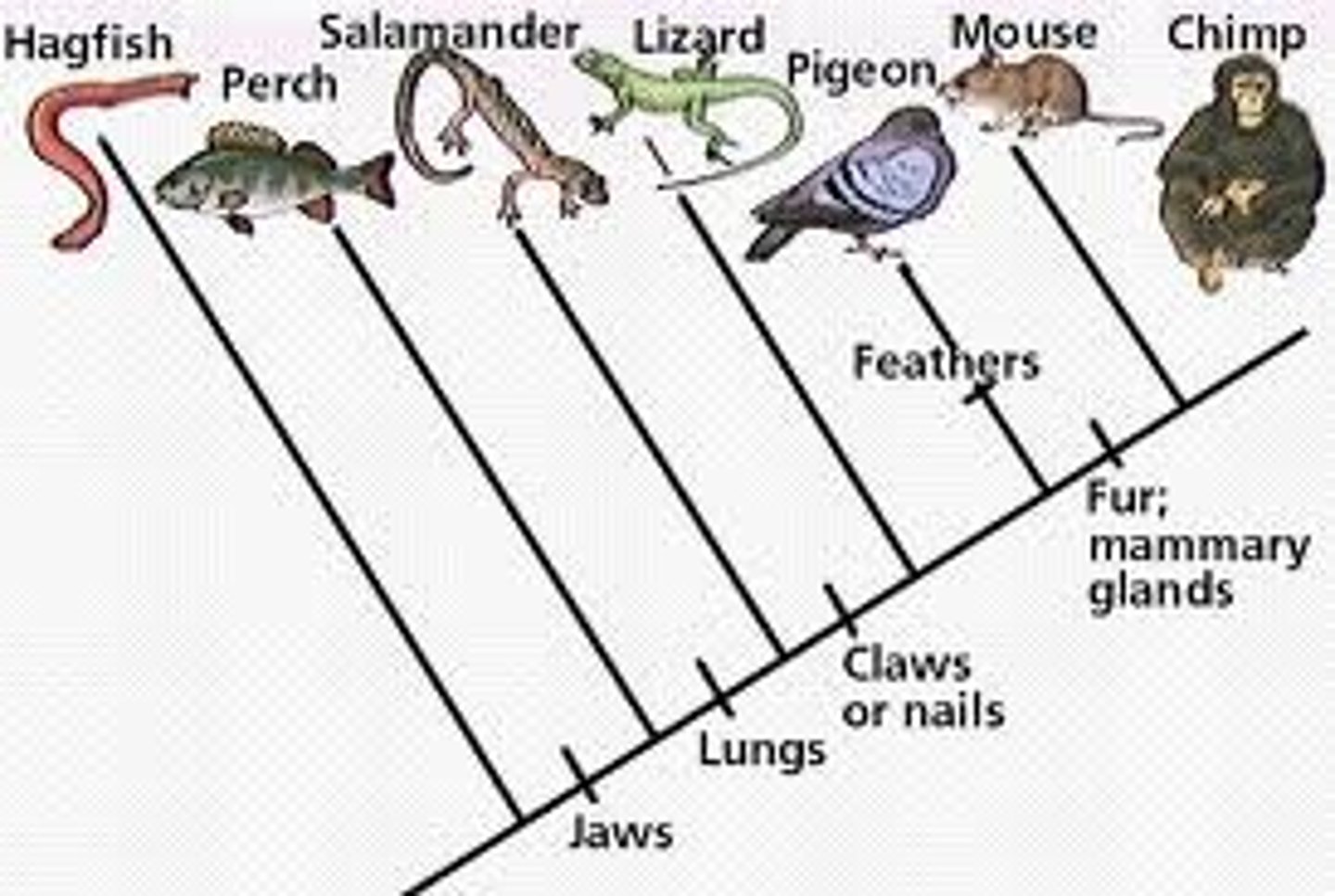
cladogram
a branching diagram that shows the ancestral relationship between organisms
ecology
the study of how organisms interact with each other and their physical environment
biotic factors
all the living factors in an environment
abiotic factors
all the nonliving factors in an environment
niche
an organism's role in an environment (ex. producer, consumer, etc.)
population
all the organisms of the same species that live in a particular environment
community
all the different populations in an area
biosphere
all the places on earth where life exists
limiting factors
the living and nonliving things in the environment that limit the size of populations
carrying capacity
the maximum population size that an environment can support
predators
kill and eat other organisms called prey
prey
organisms that are hunted and eaten by predators
autotrophs
producers make their own food through photosynthesis
heterotrophs
organisms that must eat something for food (consumers)
herbivores
can only eat plants
carnivores
can only eat other animals
omnivores
organisms that eat both plants and animals
consumers
same as heterotrophs
decomposers
break organisms down and return nutrients and return the nutrients to the environment
scavengers
eat dead organisms that they did not kill themselves
parasites
live off of another organism (host) and do not kill them usually (this organism benefits, while the host is harmed)
producers
the same as autotrophs
chemoautotrophs
organisms that make their own food through chemical reactions (usually live in areas with little sunlight)